The Interactions of Quantum Dot-Labeled Silk Fibroin Micro/Nanoparticles with Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Silk Fibroin Solution
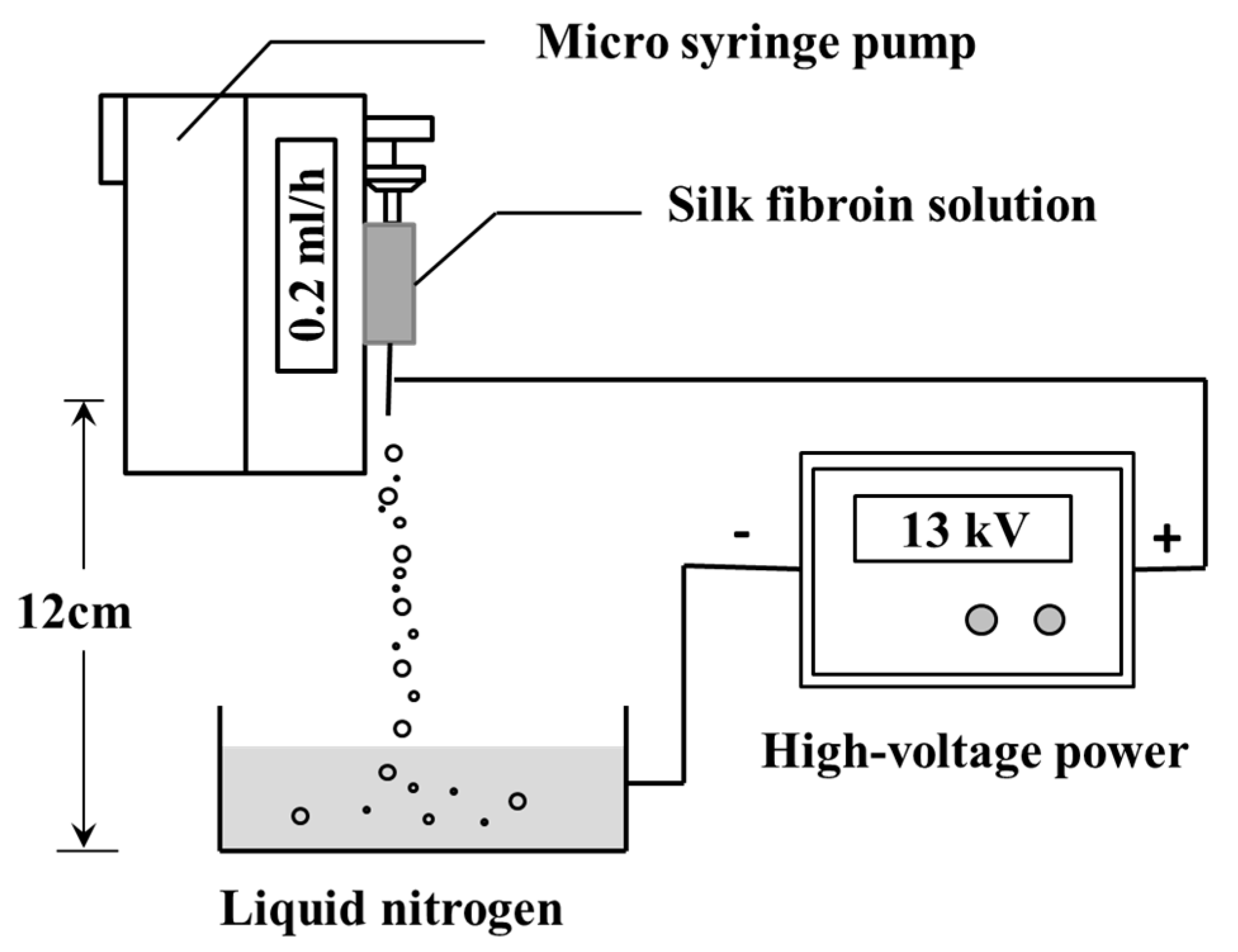
2.2. Preparation of Silk Fibroin Micro/nanoparticles
2.3. Preparation of Fluorescence Labeled Silk Fibroin Micro/Nanoparticles
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.5. Dynamic Light Scattering
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.7. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.8. Photostability of Fluorescence Labeled Silk Fibroin Microparticles
2.9. Cell Culture
2.9.1. Cell Proliferation In Vitro
2.9.2. Particles Cultured with Cells
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of QD-SFMPs and QD-SFNPs
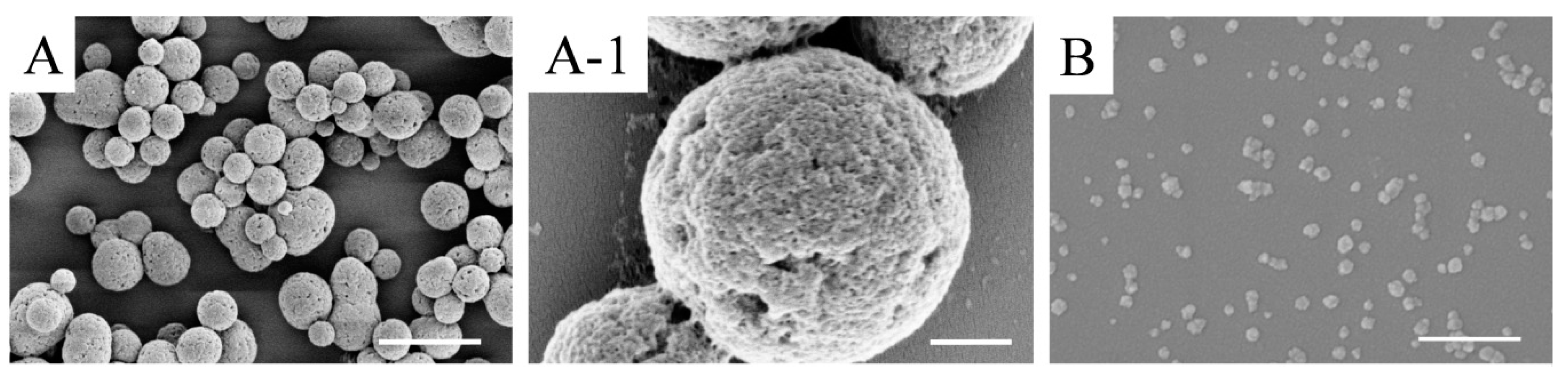
3.1.1. Morphology
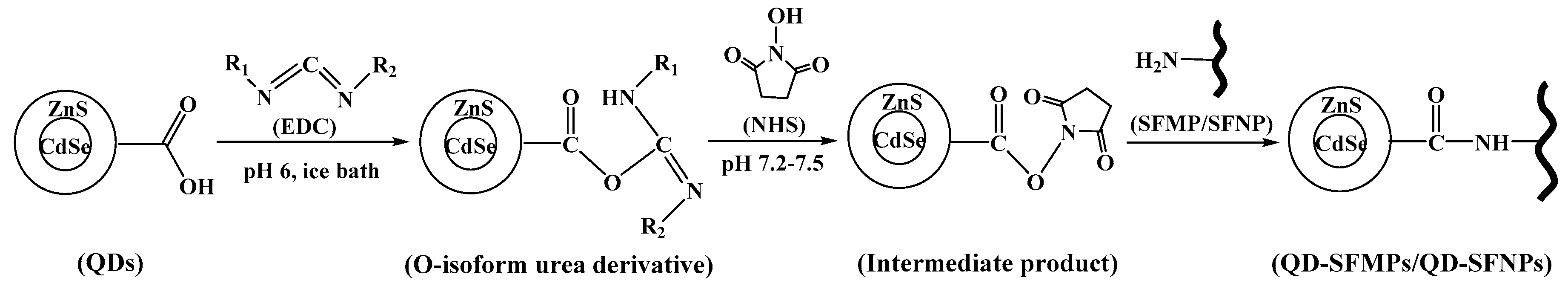
3.1.2. Principle of Labeling
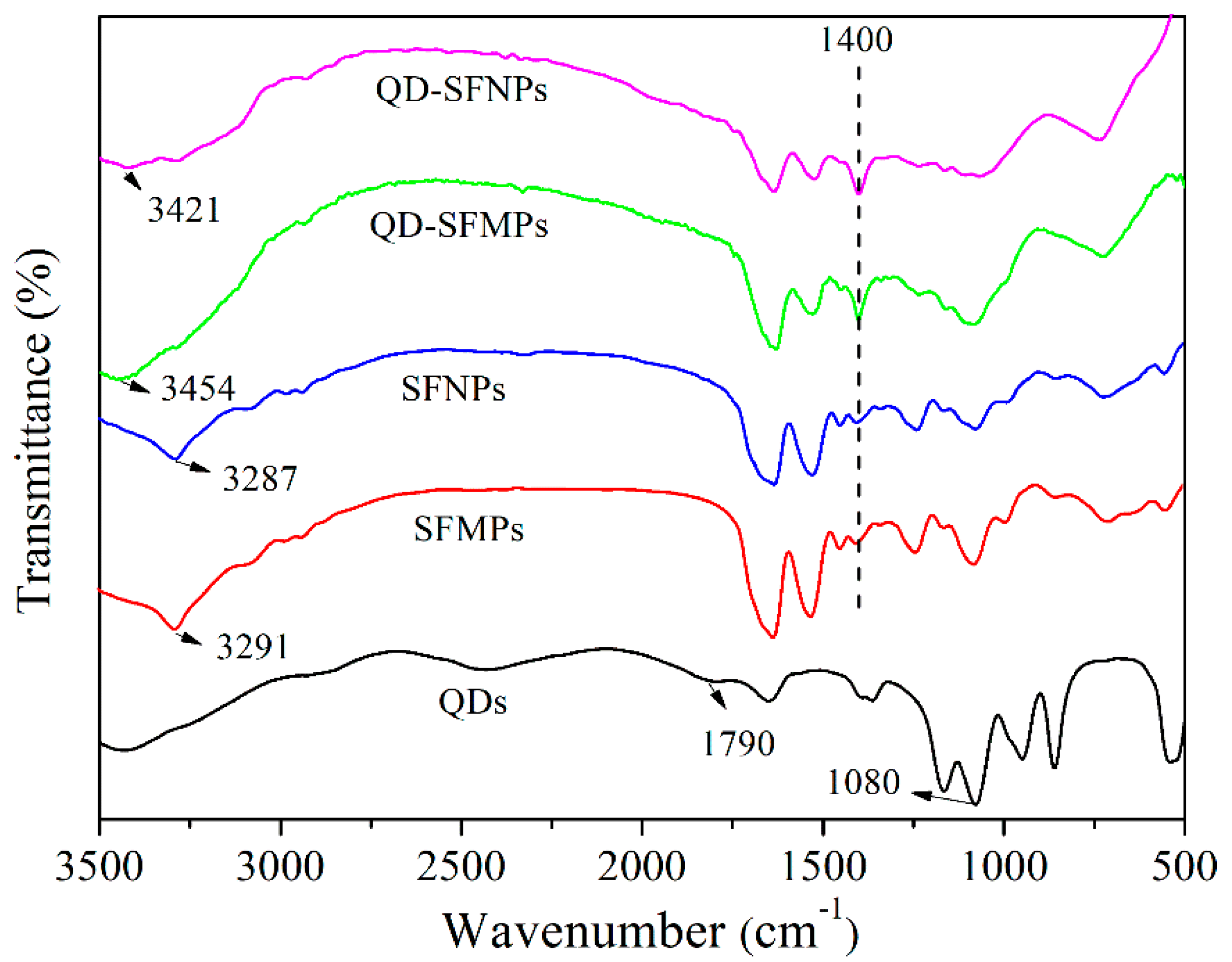
3.1.3. FTIR
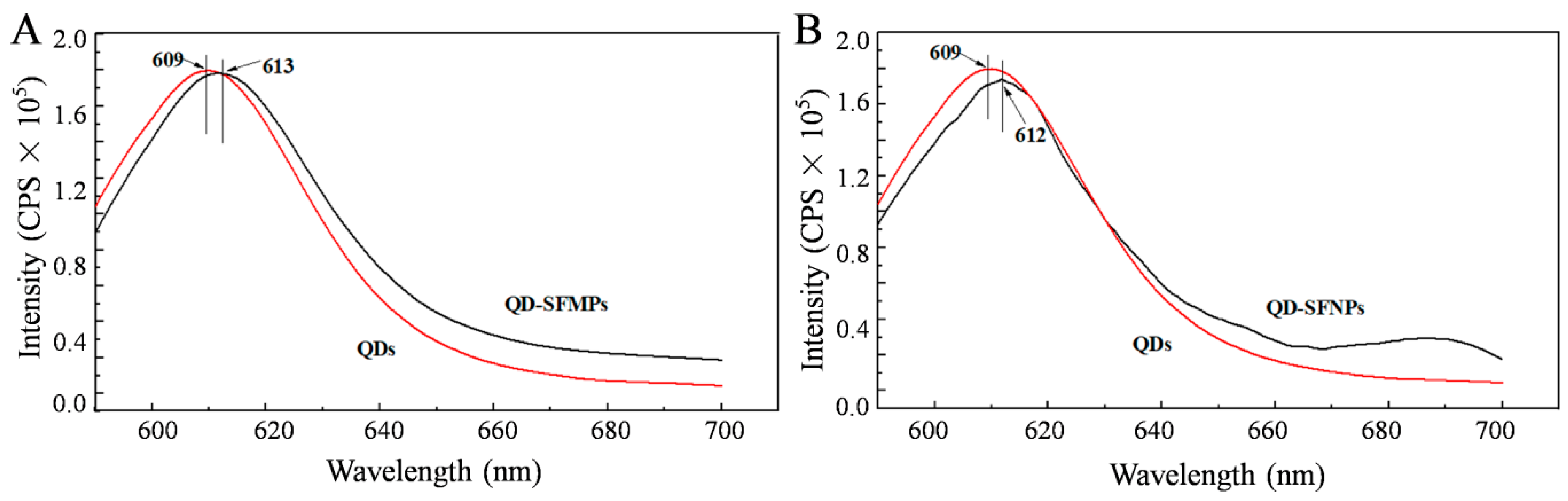
3.1.4. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
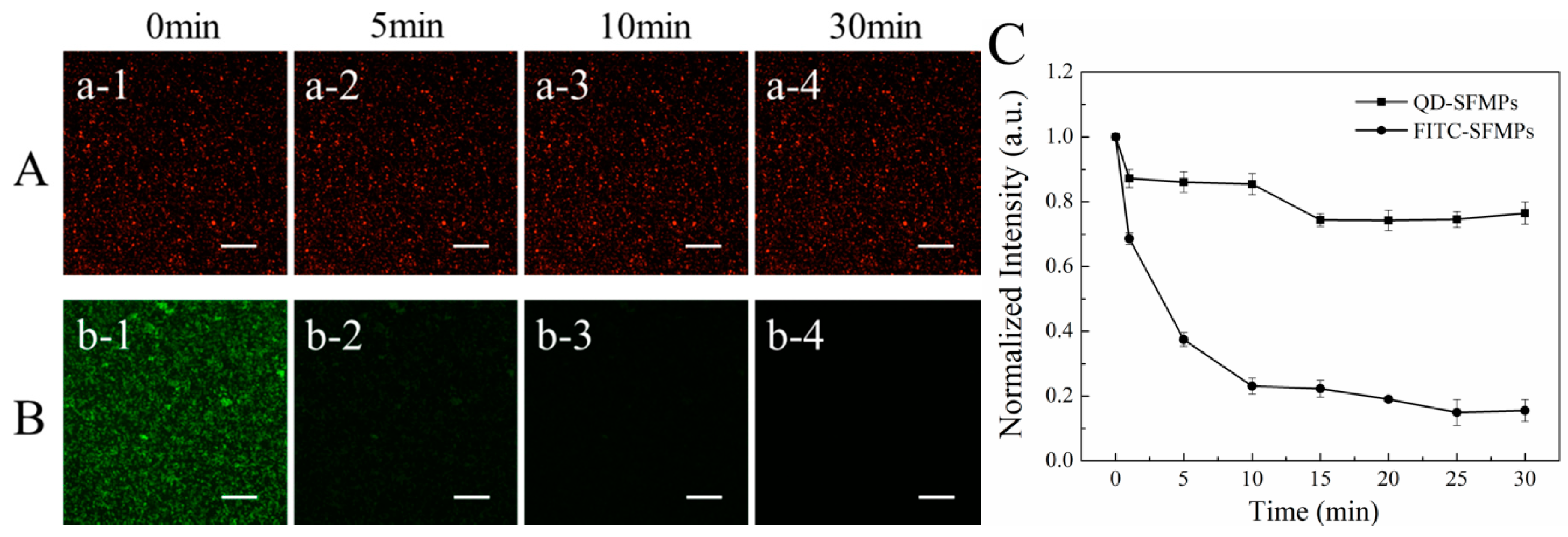
3.1.5. Fluorescence Stability
3.2. Cell Proliferation
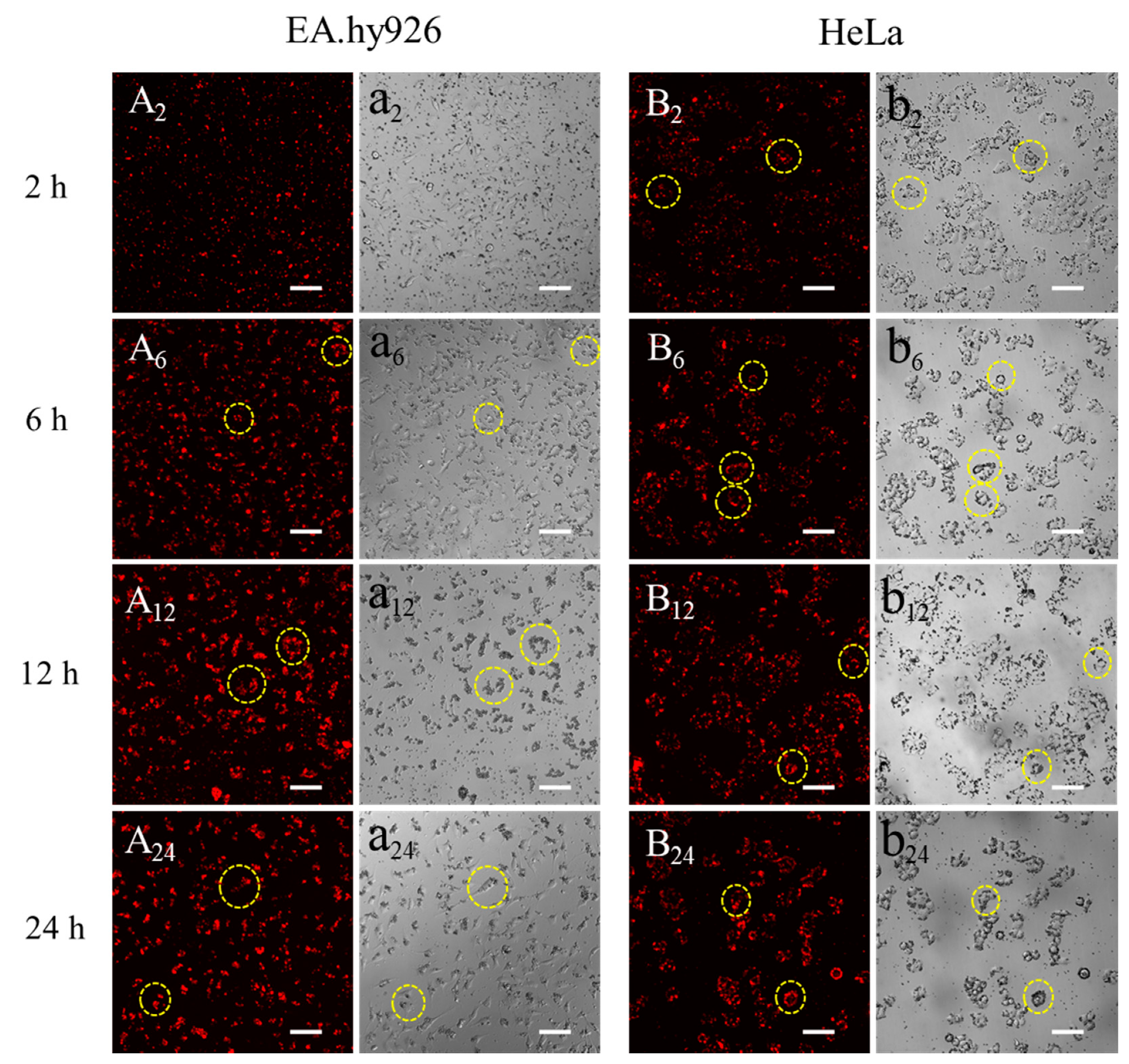
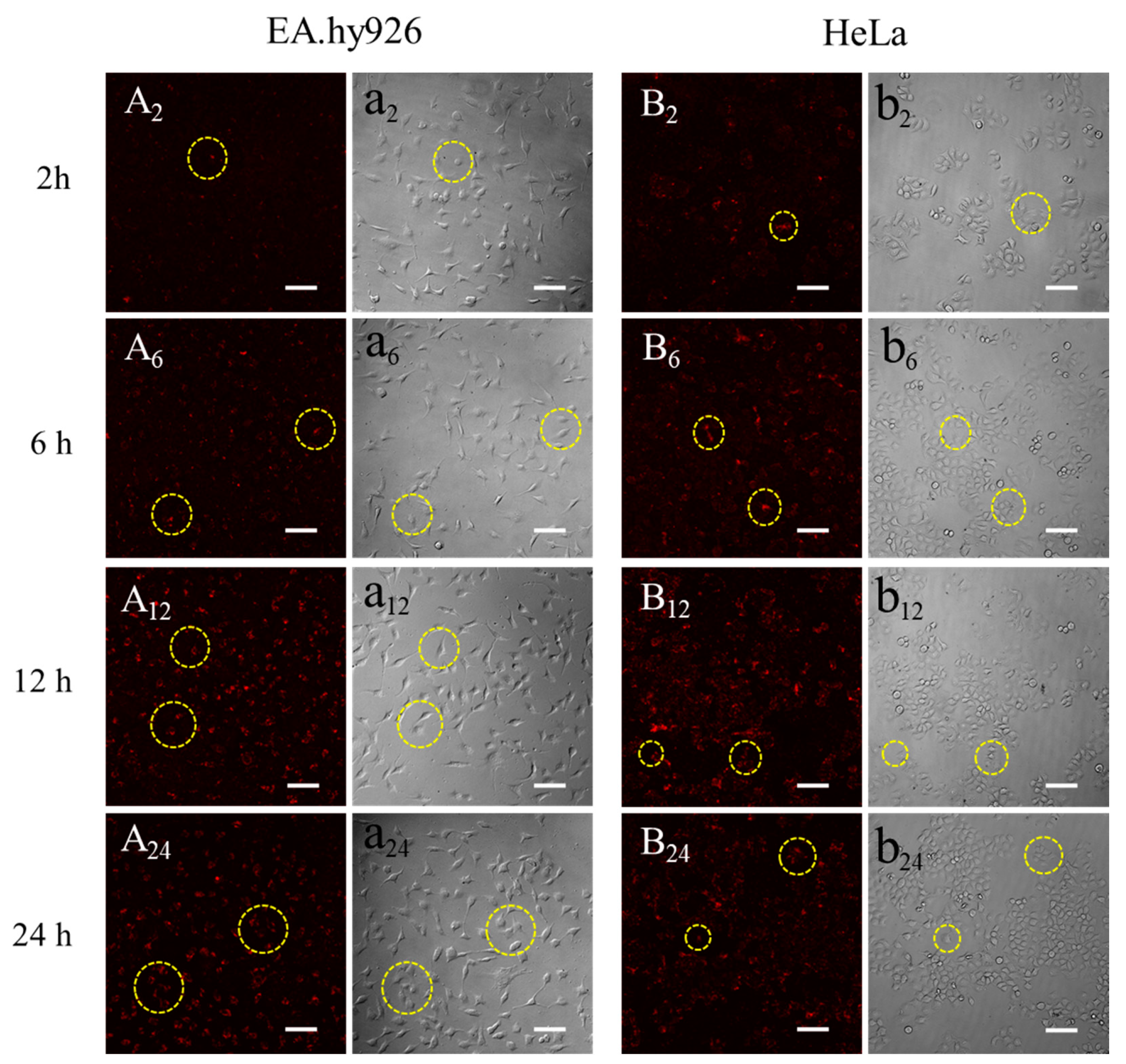
3.3. Observation of Silk Fibroin Particles Cultured with Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Xie, M.B. Silk fibroin-based nanoparticles for drug delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 4880–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengyel, M.; Kállai-Szabó, N.; Antal, V.; Laki, A.J.; Antal, I. Microparticles, microspheres, and microcapsules for advanced drug delivery. Sci. Pharm. 2019, 87, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.R.; Su, T.; Cao, J.; Luo, X.L.; Li, L.; Pu, Y.; He, B. Environment-stimulated nanocarriers enabling multi-active sites for high drug encapsulation as an "on demand" drug release system. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2018, 6, 2258–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.A.A.; Saleh, A.M. Applications of nanoparticle systems in drug delivery technology. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langiu, M.; Dadparvar, M.; Kreuter, J.; Ruonala, M.O. Human serum albumin-based nanoparticle-mediated in vitro gene delivery. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesniak, A.; Salvati, A.; Santos-Martinez, M.J.; Radomski, M.W.; Dawson, K.A.; Aberg, C. Nanoparticle adhesion to the cell membrane and its effect on nanoparticle uptake efficiency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Lane, L.A. Probing the biological obstacles of nanomedicine with gold nanoparticles. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfinger, L.E.; Michael, J.V. Regulation of Ras signaling and function by plasma membrane microdomains. Biosci. Trends 2017, 11, 01220–01237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, J.; Jin, X.; Sun, S.; Mei, L.; Huang, L. Intracellular trafficking network and autophagy of PHBHHx nanoparticles and their implications for drug delivery. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9585–9594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Matsui, M.; Corey, D.R. Activating frataxin expression by repeat-targeted nucleic acids. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10606–10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canton, I.B.G. Endocytosis at the nanoscale. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2718–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totten, J.D.; Wongpinyochit, T.; Seib, F.P. Silk nanoparticles: Proof of lysosomotropic anticancer drug delivery at single-cell resolution. J. Drug Target. 2017, 25, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; He, Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J. Nuclear-targeted drug delivery of TAT peptide-conjugated monodisperse mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5722–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Guo, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Xie, L. Size-dependent cellular uptake and localization profiles of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4247–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobashi, M.; Kuze, K.; Kanetake, N. Cell structure control of porous titanium composite synthesized by combustion reaction. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2006, 8, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; You, R.; Li, M. Preparation of silk fibroin microspheres and its cytocompatibility. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 4, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Ishii, T.; Kanehira, K.; Sato, T.; Taniguchi, A. Uniform TiO2 nanoparticles induce apoptosis in epithelial cell lines in a size-dependent manner. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; MonteiroRiviere, N.A. Mechanisms of cell uptake, inflammatory potential and protein corona effects with gold nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 3185–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalos-Padilla, Y.; Knorr, R.L.; Javier-Reyna, R.; Garcia-Rivera, G.; Lipowsky, R.; Dimova, R.; Orozco, E. The conserved ESCRT-III machinery participates in the phagocytosis of entamoeba histolytica. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol 2018, 8, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, E.S.C.; Roblegg, E.; Kueznik, T.; Zimmer, A.; Absenger, M.; Pieber, T.R. Cytotoxicity of nanoparticles independent from oxidative stress. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 34, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tammam, S.N.; Azzazy, H.M.E.; Lamprecht, A. The effect of nanoparticle size and NLS density on nuclear targeting in cancer and normal cells; impaired nuclear import and aberrant nanoparticle intracellular trafficking in glioma. J. Control. Release 2017, 253, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Kim, J.Y.; Smith, M.A.; Haura, E.B.; Anderson, A.R.A. Cell signaling heterogeneity is modulated by both cell-intrinsic and -extrinsic mechanisms: An integrated approach to understanding targeted therapy. Plos Biol. 2018, 16, e2002930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, K.; Guo, Q.; Huang, J.; Li, W. Aptamer-mediated indirect quantum dot labeling and fluorescent imaging of target proteins in living cells. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 505502–505512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.W.; Lin, Y.F.; Li, Y.X.; Hu, C.C.; Chiu, T.C. Synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots as selective and sensitive probes for cupric ions and cell imaging. Molecules 2019, 24, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Tsuruda, Y.; Furukawa, T.; Negishi, L.; Imura, Y.; Sakuda, S.; Yoshimura, E.; Suzuki, M. Synthesis of CdSe quantum dots using fusarium oxysporum. Materials 2016, 9, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Zhao, H.; Peng, K.; Lv, F.; Liu, L.; Bao, J.; Wang, S. Quantum dots for monitoring choline consumption process of living cells via an electrostatic force-mediated energy transfer. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2019, 2, 5528–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Zheng, Z.; Guo, S.; Wang, C.; Kaplan, D.L.; Wang, X. Binding quantum dots to silk biomaterials for optical sensing. J. Sens. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoti, A.S.; Shukla, R.; Shanker, R.; Singh, S. Surface functionalization of quantum dots for biological applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 215, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Gonzalez, M.; de la Escosura-Muniz, A.; Fernandez-Arguelles, M.T.; Garcia Alonso, F.J.; Costa-Fernandez, J.M. Quantum dot bioconjugates for diagnostic applications. Top. Curr. Chem. 2020, 378, 35–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, T.K.; Bowles, R.D.; Tainter, D.M.; Bell, R.D.; Kaplan, D.L.; Setton, L.A. Synthesis and characterization of silk fibroin microparticles for intra-articular drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 485, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomeh, M.A.; Hadianamrei, R.; Zhao, X. Silk Fibroin as a functional biomaterial for drug and gene delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessonov, I.V.; Rochev, Y.A.; Arkhipova capital, A.C.; Kopitsyna, M.N.; Bagrov, D.V.; Karpushkin, E.A.; Bibikova, T.N.; Moysenovich, A.M.; Soldatenko, A.S.; Nikishin, I.I.; et al. Fabrication of hydrogel scaffolds via photocrosslinking of methacrylated silk fibroin. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 14, 034102–034128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Bao, H.; Liang, J.; Xu, S.; Cheng, G.; Zhu, Y. Fabrication and characterization of silk fibroin/curcumin sustained-release film. Materials 2019, 12, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenk, E.; Merkle, H.P.; Meinel, L. Silk fibroin as a vehicle for drug delivery applications. J. Control. Release 2011, 150, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivelli, B.; Perteghella, S.; Bari, E.; Sorrenti, M.; Tripodo, G.; Chlapanidas, T.; Torre, M.L. Silk nanoparticles: From inert supports to bioactive natural carriers for drug delivery. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.; Haider, T.; Jain, P.; Gupta, P.N.; Soni, V. Silk as a leading-edge biological macromolecule for improved drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101294–101313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Wang, L.; Niu, L.; Lin, J.; Huang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Li, M. Porous Silk fibroin microspheres sustainably releasing bioactive basic fibroblast growth factor. Materials 2018, 11, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Ye, D.; Zhang, Q.; You, R.; Xu, W. Facile Preparation of biocompatible silk fibroin/cellulose nanocomposite films with high mechanical performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 6227–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, M.; Guan, G.; Wang, L.; King, M. Influence of layer-by-layer polyelectrolyte deposition and EDC/NHS activated heparin immobilization onto silk fibroin fabric. Materials 2014, 7, 2956–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ke, R.; Zhang, S. Breaking the sporoderm of Ganoderma lucidum spores by combining Chemical reaction with physical actuation. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 2428–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhu, Z. Study on the blends of silk fibroin and sodium alginate: Hydrogen bond formation, structure and properties. Polymer 2019, 163, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutipakdeevong, J.; Ruktanonchai, U.; Supaphol, P. Hybrid biomimetic electrospun fibrous mats derived from poly(ε-caprolactone) and silk fibroin protein for wound dressing application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41653–41663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Xu, J.; Fan, Z.; Du, Y.; Pan, Y.; Xiao, H.; Eić, M.; Qin, G.; Guo, Y.; Hu, Y. Preparation and characterization of cysteine-formaldehyde cross-linked complex for CO2 capture. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 3012–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshrat Harush-Frenkel, Y.A. Simon Benita1, Nanoparticle–cell interactions: Drug delivery implications. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2008, 25, 485–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammel, A.S.; Hu, X.; Park, S.H.; Kaplan, D.L.; Scheibel, T.R. Controlling silk fibroin particle features for drug delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4583–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.Z.; Yang, Y.M.; Wang, S.B.; Wang, G.Y.; Liu, Y.G.; Sun, Q.Q. Preparation of methotrexate-loaded, large, highly-porous PLLA microspheres by a high-voltage electrostatic antisolvent process. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Kuang, D.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Z.; Yadavalli, V.K.; Lu, S. Swellable silk fibroin microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yin, H.; Liu, X.; Shi, Y.; Jin, M.; Ding, D. An experimental and theoretical study of solvent hydrogen-bond-donating capacity effects on ultrafast intramolecular charge transfer of LD 490. Spectrochim Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 184, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fothergill, S.M.; Joyce, C.; Xie, F. Metal enhanced fluorescence biosensing: From ultra-violet towards second near-infrared window. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 20914–20929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, G.M.; Contento, A.M.; Rios, A. Use of Cdse/ZnS quantum dots for sensitive detection and quantification of paraquat in water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 801, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlcek, J.; Lapcik, L.; Havrdova, M.; Polakova, K.; Lapcikova, B.; Opletal, T.; Froning, J.P.; Otyepka, M. Flow induced HeLa cell detachment kinetics show that oxygen-containing functional groups in graphene oxide are potent cell adhesion enhancers. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3222–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, J.; Chung, Y.I.; Kim, Y.H.; Tae, G.; Kundu, S.C. Silk fibroin nanoparticles for cellular uptake and control release. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 388, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Yang, A.; Piao, L.; Hao, S.; Du, L.; Meng, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, H. Comparative study of in vitro effects of different nanoparticles at non-cytotoxic concentration on the adherens junction of human vascular endothelial cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4475–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foresta, V.; Cottier, M.; Pourchez, J. Electrostatic interactions favor the binding of positive nanoparticles on cells: A reductive theory. Nano Today 2015, 10, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, R.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Lu, S.; Li, M. Response of filopodia and lamellipodia to surface topography on micropatterned silk fibroin films. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 4206–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Rajkhowa, R.; Wang, X.; Devi, D. Milled non-mulberry silk fibroin microparticles as biomaterial for biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Wu, S.H.; Hung, Y.; Mou, C.Y. Size effect on cell uptake in well-suspended, uniform mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Small 2009, 5, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Peng, C.; Ravi, S.; Siddiki, A.K.M.N.A.; Zheng, J.; Balkus, K.J. Biphenyl wrinkled mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-responsive doxorubicin drug delivery. Materials 2020, 13, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, W.; Wang, H.; Han, J.; Zhao, S.; Dumbleton, J.; Agarwal, P.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, G.; Yu, J.; Zynger, D.L.; et al. Chitosan-Decorated Doxorubicin-Encapsulated Nanoparticle Targets and Eliminates Tumor Reinitiating Cancer Stem-like Cells. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5725–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; You, R.; Qu, J.; Li, M. Functionalized silk fibroin dressing with topical bioactive insulin release for accelerated chronic wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 72, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, S.; Murundi, S.; Crawford, L.; Putnam, D. Enabling P-glycoprotein inhibition in multidrug resistant cancer through the reverse targeting of a quinidine-PEG conjugate. J. Control. Release 2020, 317, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, B.; Yuan, S.; Wang, X.; Li, K. Quercetin reversed MDR in breast cancer cells through down-regulating P-gp expression and eliminating cancer stem cells mediated by YB-1 nuclear translocation. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, L.; Shi, M.; Feng, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Li, M. The Interactions of Quantum Dot-Labeled Silk Fibroin Micro/Nanoparticles with Cells. Materials 2020, 13, 3372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153372
Niu L, Shi M, Feng Y, Sun X, Wang Y, Cheng Z, Li M. The Interactions of Quantum Dot-Labeled Silk Fibroin Micro/Nanoparticles with Cells. Materials. 2020; 13(15):3372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153372
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Longxing, Meijing Shi, Yanfei Feng, Xiaoxiao Sun, Ying Wang, Zhiling Cheng, and Mingzhong Li. 2020. "The Interactions of Quantum Dot-Labeled Silk Fibroin Micro/Nanoparticles with Cells" Materials 13, no. 15: 3372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153372
APA StyleNiu, L., Shi, M., Feng, Y., Sun, X., Wang, Y., Cheng, Z., & Li, M. (2020). The Interactions of Quantum Dot-Labeled Silk Fibroin Micro/Nanoparticles with Cells. Materials, 13(15), 3372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153372





