Grain Size and Phase Transformation Behavior of TiNi Shape-Memory-Alloy Thin Film under Different Deposition Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Growth of the Thin Film
2.2. Characterization of Thin Films
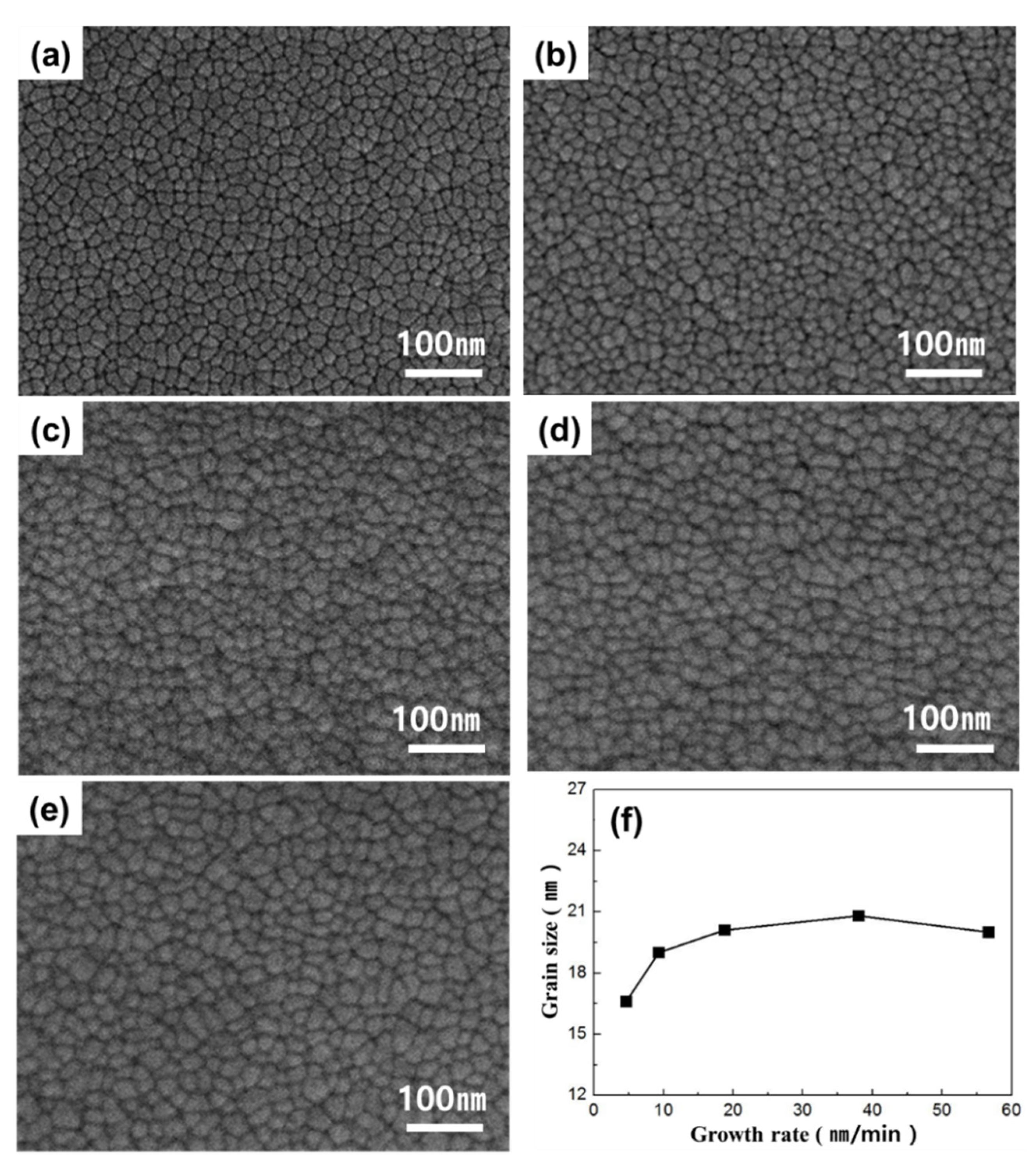
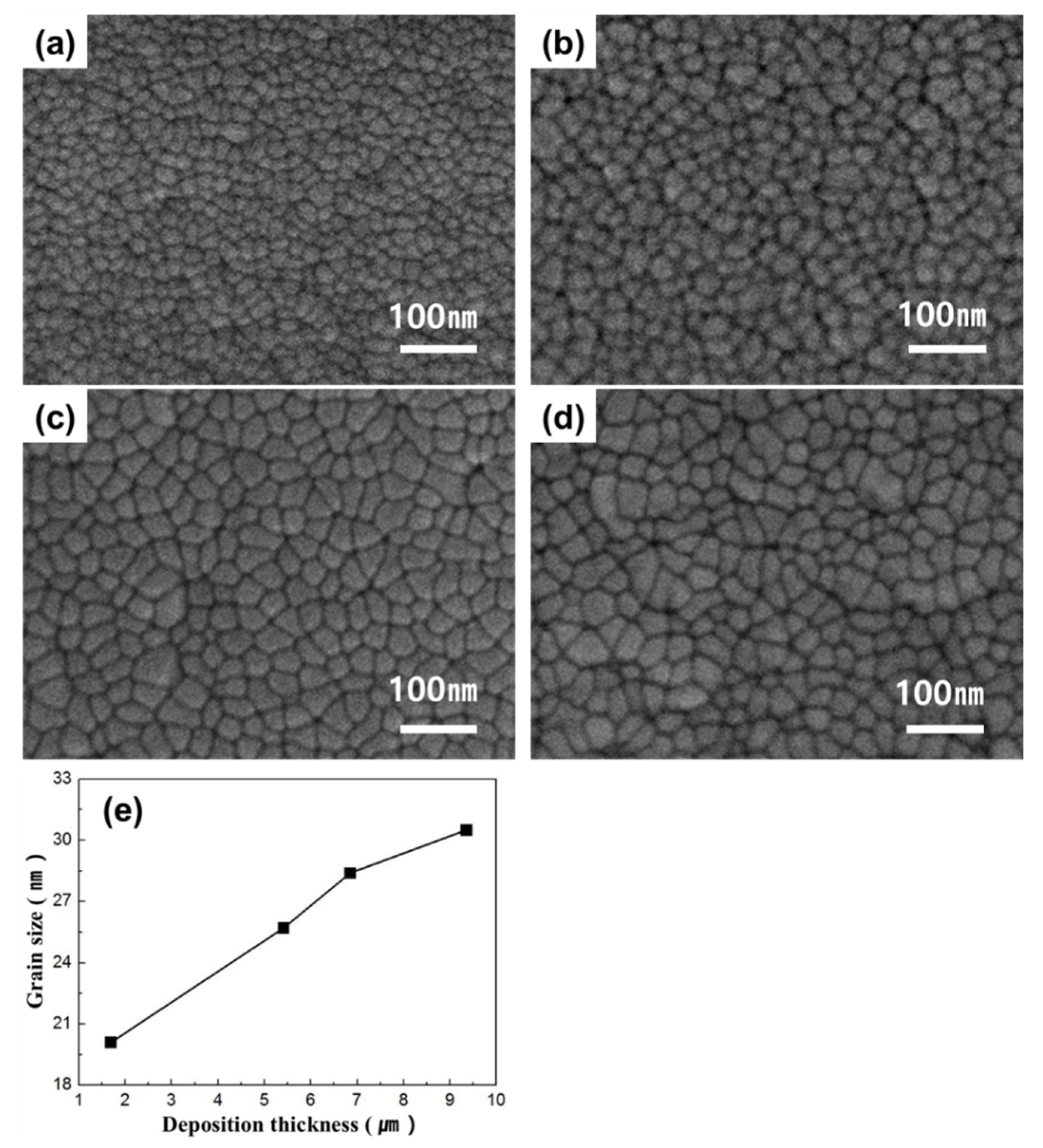
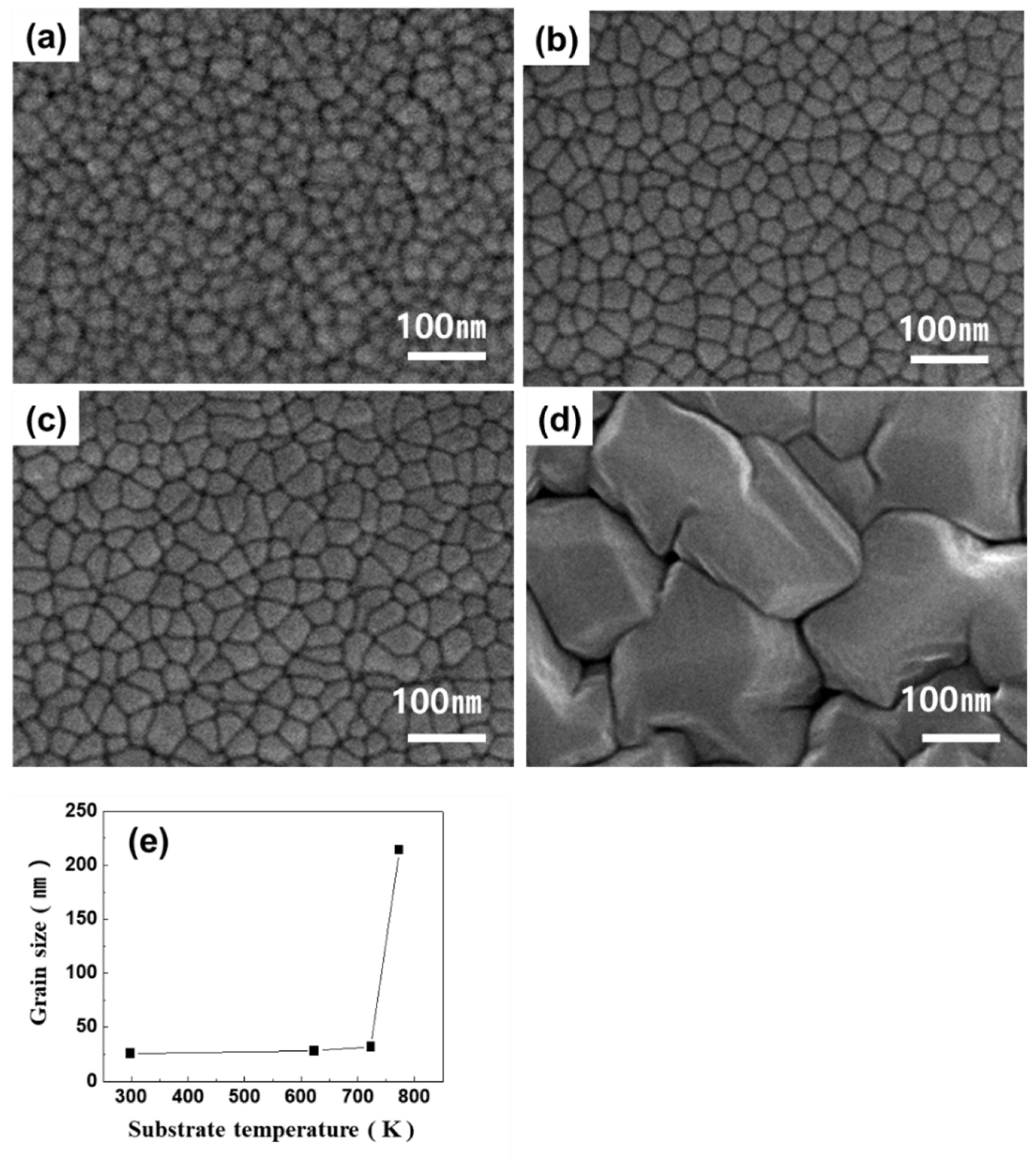
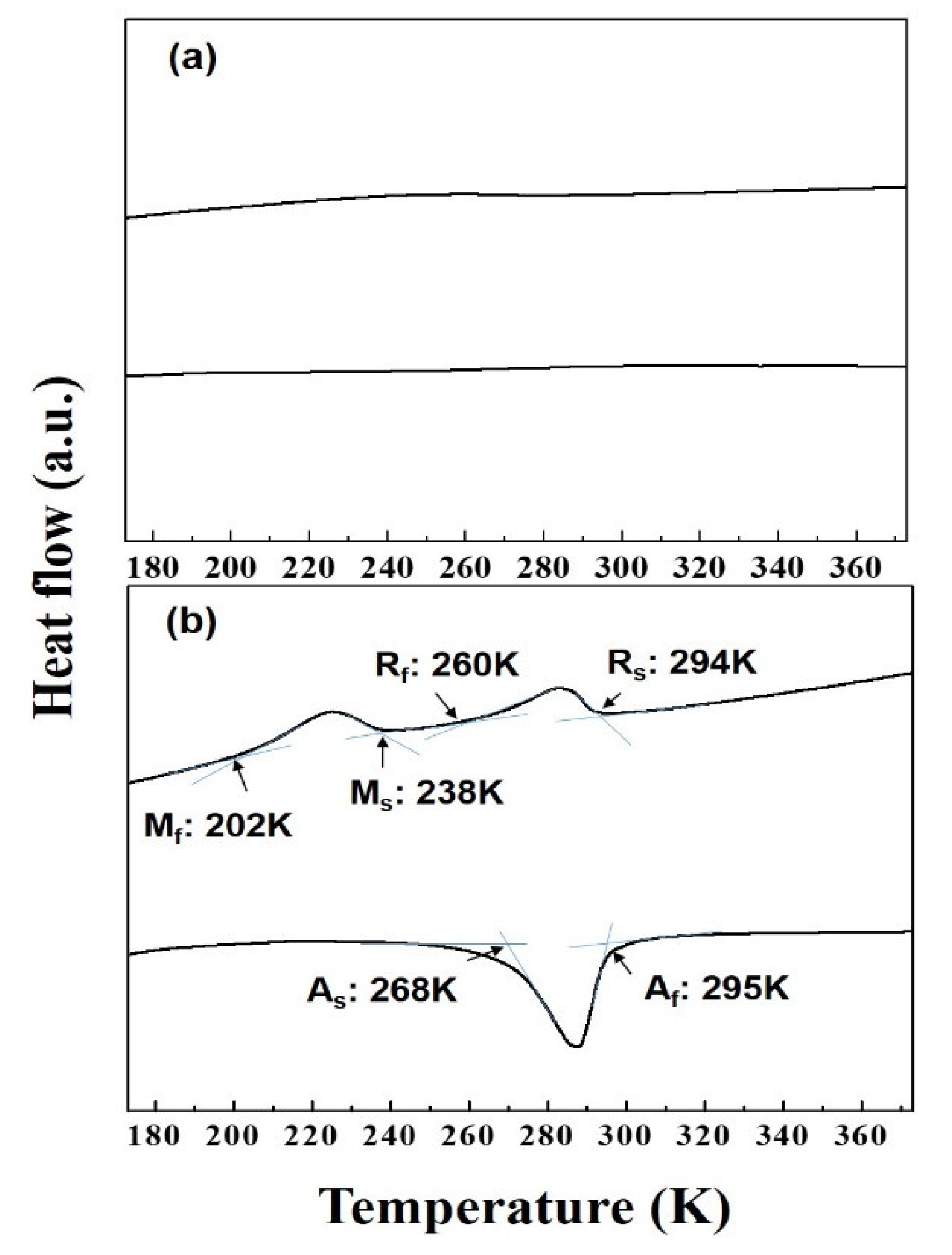
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otsuka, K.; Shimizu, K. Memory effect and thermoelastic martensite transformation in CuAlNi alloy. Scr. Met. 1970, 4, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Wayman, C.M. Mechanism of Shape Memory Effect and Superelasticity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Lagoudas, D.C. Shape Memory Alloys Modeling and Engineering Application; Springer Science & Business: Berlin, Germany, 2010; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, N.; Kaur, D. Shape memory alloy thin films and heterostructures for MEMS applications: A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 242, 162–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Do, D. Shape memory characterisitics of highly porous Ti-rich TiNi alloys. Mater. Lett. 2016, 162, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhou, W.T.; Wang, C.; Ii, S.; Hsueh, C.H. Nanoscaled superelastic behavior of shape memory alloy/metallic glass multilayered films. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 142, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wang, L.; Ding, G.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, A.; Cai, B. Characteristics and fabrication of NiTi/Si diaphragm micropump. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 93, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Otsuka, K. Development of shape memory alloys. ISIJ Int. 1989, 29, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Humbeeck, J. Non-medical applications of shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 273, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, R.; Hane, K. Martensitic transformations and shape-memory materials. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 197–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Physical metallurgy of Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 511–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krulevitch, P.; Ramsey, P.; Makowiecki, D.; Lee, A.; Northrup, M.; Johnson, G. Mixed-sputter deposition of Ni-Ti-Cu shape memory films. Thin Solid. Films 1996, 274, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miyazaki, S.; Ishida, A. Martensitic transformation and shape memory behavior in sputter-deposied TiNi-base thin films. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1999, 273, 106–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, R.H.; Heuer, A.H. TiNi (shape memory) films silicon for MEMS applications. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 1995, 4, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, H.; Huff, M.A.; Heuer, A.H. The TiNi shape-memory alloy and its applications for MEMS. J. Micromech. Microeng. 1998, 8, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, T.M.; Kirkpatrick, S.; Wang, Z.; Siahmakoun, A. NiTi shape memory alloy thin films deposited by co-evaporation. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 1161–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciabattari, F.; Fuso, F.; Arimondo, E. Plused laser deposition and characterization of NiTi-based MEMS prototypes. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Proc. 2004, 79, 623–626. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.-G.; Chun, S.-Y. Growing Behavior of Nanocrystalline TiN Films by Asymmetric Pulsed DC Reactive Magnetron Sputtering. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2011, 48, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yoon, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, K.H. A comparative study on tribological behavior of TiN and TiAlN coatings prepared by arc ion plating technique. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 161, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, J.; Vlček, J. A perspective of magnetron sputtering in surface engineering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 112, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzydłowski, K. A model for the flow stress dependence on the distribution of grain size in polycrystals. Scr. Met. Mater. 1990, 24, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.-H.; Huh, S.; Choi, B.-K.; Jeong, H.; Noh, J.-P. Phase transformation behavior of TiNi shape-memory-alloy thin films deposited using DC magnetron sputtering. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Eng. 2018, 42, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waitz, T.; Antretter, T.; Fischer, F.D.; Karnthaler, H. Size effects on martensitic phase transformations in nanocrystalline NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2008, 24, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Chung, C.W. Effect of deposition parameters on the properties of TiN thin films deposited by rf magnetron sputtering, Korean. J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 46, 676–680. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, C.V.; Smith, H.I. Surface-energy-driven secondary grain in ultrathin (<100 nm) films of silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1984, 44, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, K.; Mott, N.F. The conductivity of thin metallic films according to the electron theory of metals. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1938, 34, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, W.; Momeni, S. Influence of in-situ and postannealing technique on tribological performance of NiTi SMA thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 276, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Otsuka, K. Mechanical behaviour associated with the premartensitic rhombohedral-phase transition in a Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy. Philos. Mag. A 1985, 50, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, T.-H.; Chung, D.W.; Noh, J.-P.; Lee, H.W. Phase transformation behavior and wire drawing properties of Ti-Ni-Mo shape memory alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 4181–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, T.-H.; Noh, J.-P.; Jung, D.-W.; Kim, Y.-W.; Im, H.-J.; Ahn, J.-S.; Mitani, T. The R phase transformation in Ti-49Ni (at.%) shape memory alloy ribbons fabricated by melt spinning. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2002, 21, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-H.; Wu, S.-K. Textures in cold-rolled and annealed Ti50Ni50 shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, J.; Lee, H.; Seo, D.; Yun, S.; Yang, J.; Huh, S.; Jeong, H.; Noh, J. Grain Size and Phase Transformation Behavior of TiNi Shape-Memory-Alloy Thin Film under Different Deposition Conditions. Materials 2020, 13, 3229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143229
Bae J, Lee H, Seo D, Yun S, Yang J, Huh S, Jeong H, Noh J. Grain Size and Phase Transformation Behavior of TiNi Shape-Memory-Alloy Thin Film under Different Deposition Conditions. Materials. 2020; 13(14):3229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143229
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Joohyeon, Hyunsuk Lee, Duckhyeon Seo, Sangdu Yun, Jeonghyeon Yang, Sunchul Huh, Hyomin Jeong, and Jungpil Noh. 2020. "Grain Size and Phase Transformation Behavior of TiNi Shape-Memory-Alloy Thin Film under Different Deposition Conditions" Materials 13, no. 14: 3229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143229
APA StyleBae, J., Lee, H., Seo, D., Yun, S., Yang, J., Huh, S., Jeong, H., & Noh, J. (2020). Grain Size and Phase Transformation Behavior of TiNi Shape-Memory-Alloy Thin Film under Different Deposition Conditions. Materials, 13(14), 3229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143229




