Temperature Dependence of Anisotropy in Ti and Gd Doped NiMnGa-Based Multifunctional Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
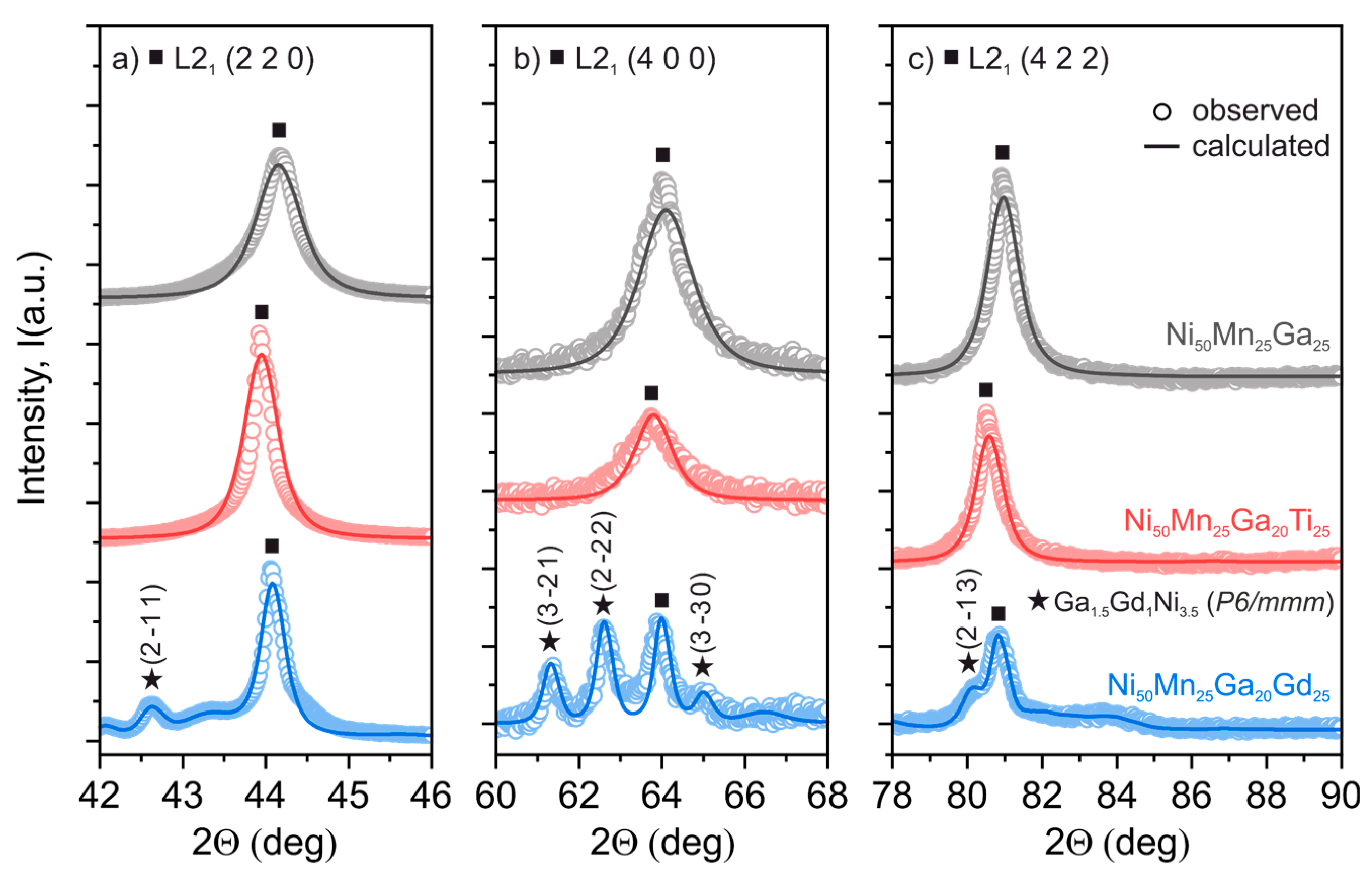
3.1. Microstructure Analysis
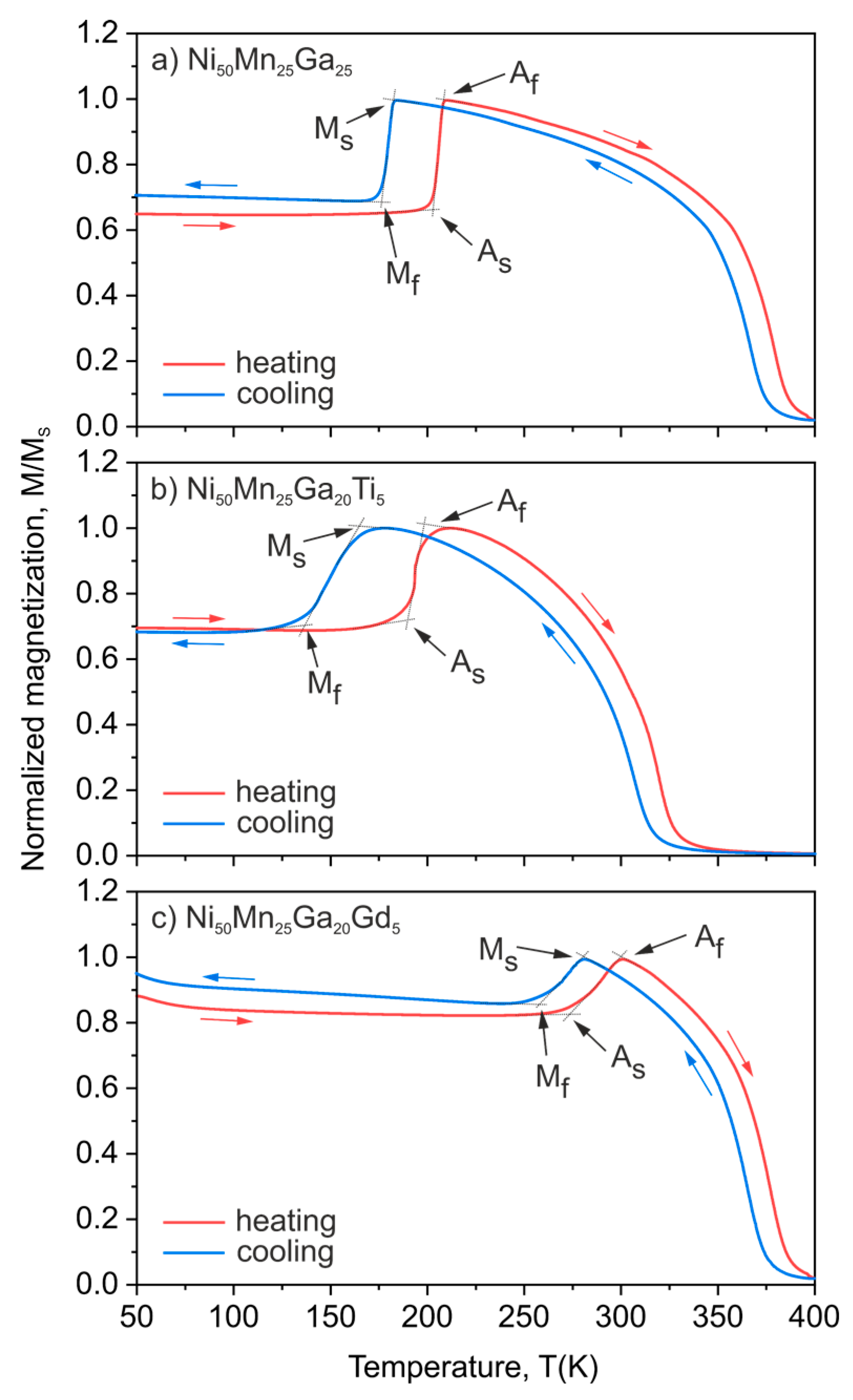
3.2. Temperature Dependence of Magnetization
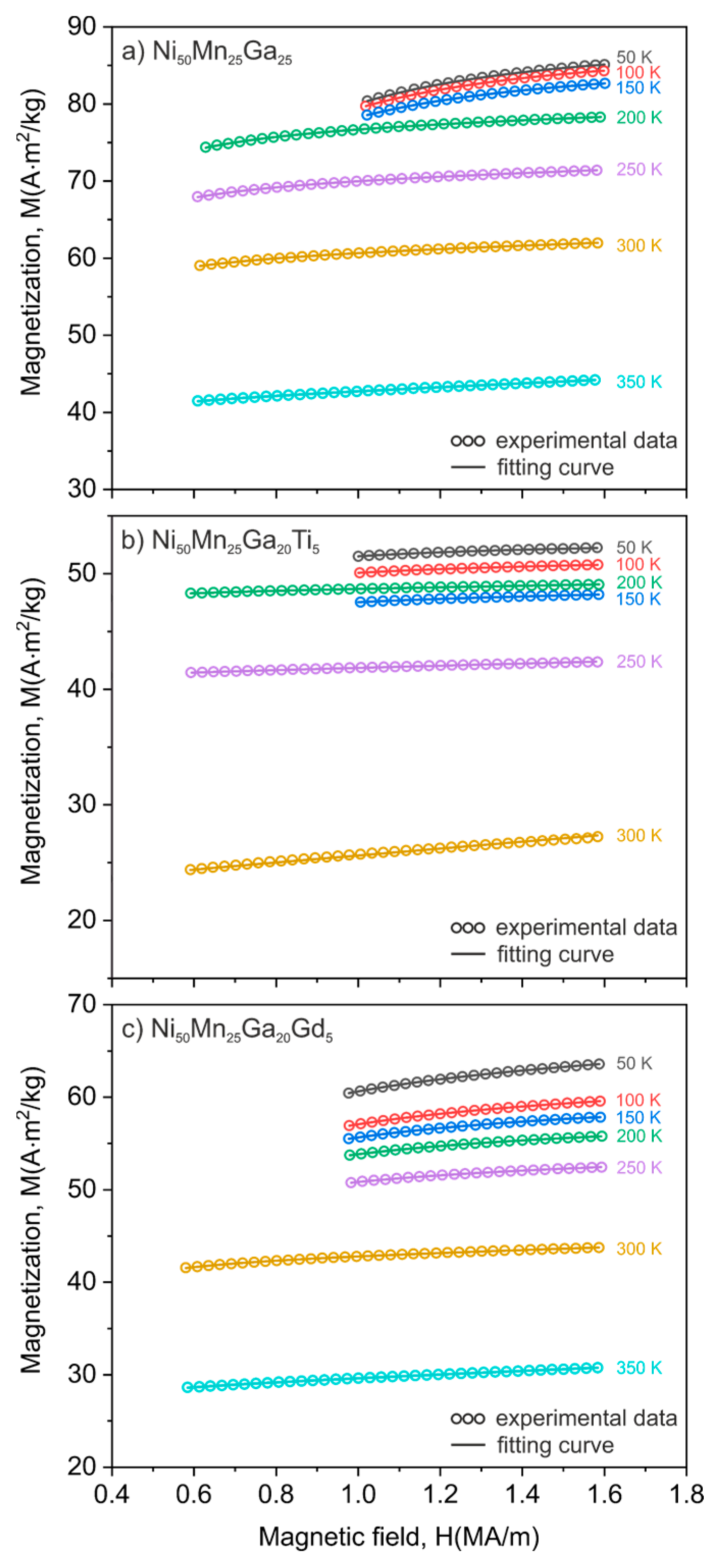
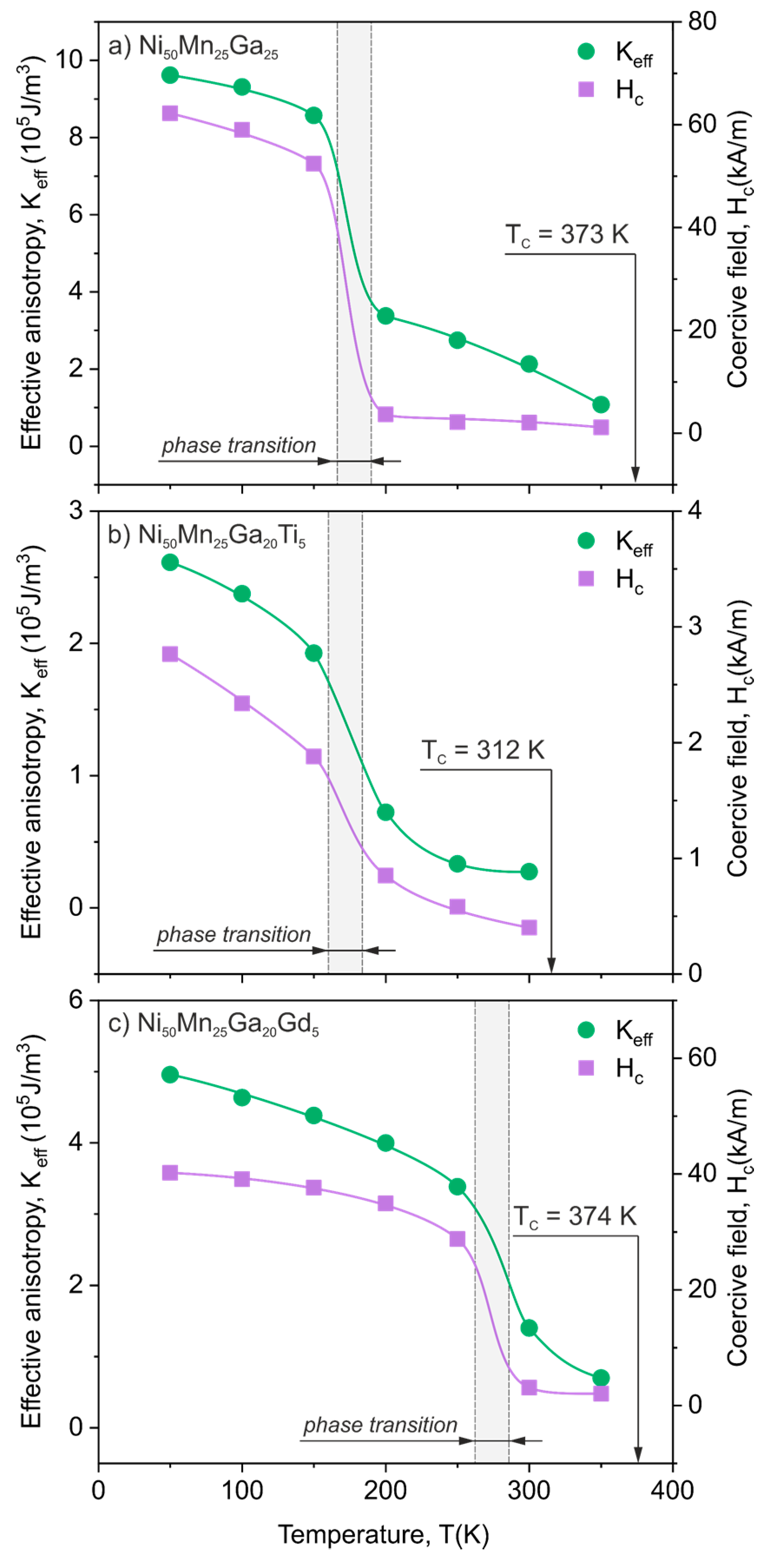
3.3. Law of Approach to Magnetic Saturation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faran, E.; Shilo, D. Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloys—Challenges, Applications, and Experimental Characterization. Exp. Tech. 2016, 40, 1005–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukov, A. Novel Functional Magnetic Materials; Zhukov, A., Ed.; Springer Series in Materials Science; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 231, ISBN 978-3-319-26104-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ahamed Khan, R.; Ghomashchi, R.; Xie, Z.; Chen, L. Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Heusler Materials: Synthesis, Microstructure Characterization and Magnetostructural Properties. Materials 2018, 11, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sozinov, A.; Lanska, N.; Soroka, A.; Zou, W. 12% magnetic field-induced strain in Ni-Mn-Ga-based non-modulated martensite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 21902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitzsch, U.; Pötschke, M.; Roth, S.; Rellinghaus, B.; Schultz, L. A 1% magnetostrain in polycrystalline 5M Ni–Mn–Ga. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullakko, K.; Huang, J.K.; Kantner, C.; O’Handley, R.C.; Kokorin, V.V. Large magnetic-field-induced strains in Ni2MnGa single crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 1966–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Kakeshita, T. Science and Technology of Shape-Memory Alloys: New Developments. MRS Bull. 2002, 27, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernenko, V.A.; L’vov, V.; Pons, J.; Cesari, E. Superelasticity in high-temperature Ni–Mn–Ga alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 2394–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.F.; Zhang, X.X.; Wei, L.S.; Geng, L.; Peng, H.X. Effect of chemical ordering annealing on martensitic transformation and superelasticity in polycrystalline Ni–Mn–Ga microwires. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 645, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, X.K.; Xiao, J.Q.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Dai, X.F.; Liu, G.D.; Chen, J.L.; Wu, G.H. Large negative magnetoresistance in quaternary Heusler alloy Ni50Mn8Fe17Ga25 melt-spun ribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 182507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, D.; Mandal, K.; Gutfleisch, O. Large negative magnetoresistance in nickel-rich Ni–Mn–Ga Heusler alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 09B103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañosa, L.; Planes, A. Mechanocaloric effects in shape memory alloys. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2016, 374, 20150310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrici, S.; Kamarad, J.; Arnold, Z.; Casoli, F.; Paoluzi, A.; Bolzoni, F.; Cabassi, R.; Solzi, M.; Porcari, G.; Pernechele, C.; et al. From direct to inverse giant magnetocaloric effect in Co-doped NiMnGa multifunctional alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, J.; Mañosa, L.; Planes, A.; Casanova, F.; Batlle, X.; Labarta, A. Multiscale origin of the magnetocaloric effect in Ni-Mn-Ga shape-memory alloys. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2003, 68, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basso, V.; Sasso, C.P.; Skokov, K.P.; Gutfleisch, O.; Khovaylo, V.V. Hysteresis and magnetocaloric effect at the magnetostructural phase transition of Ni-Mn-Ga and Ni-Mn-Co-Sn Heusler alloys. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2012, 85, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquale, M.; Sasso, C.P.; Lewis, L.H.; Giudici, L.; Lograsso, T.; Schlagel, D. Magnetostructural transition and magnetocaloric effect in Ni55Mn20Ga25 single crystals. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 094435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaufmann, S.; Niemann, R.; Thersleff, T.; Rößler, U.K.; Heczko, O.; Buschbeck, J.; Holzapfel, B.; Schultz, L.; Fähler, S. Modulated martensite: Why it forms and why it deforms easily. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 053029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullakko, K.; Huang, J.K.; Kokorin, V.V.; O’Handley, R.C. Magnetically controlled shape memory effect in Ni2MnGa intermetallics. Scr. Mater. 1997, 36, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Feng, G.; Gong, S.; Xu, H. Effect of Ni excess on phase transformation temperatures of NiMnGa alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 342, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.K.; Yang, S.T. Effect of composition on transformation temperatures of Ni-Mn-Ga shape memory alloys. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 4291–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khovaylo, V.V.; Buchelnikov, V.D.; Kainuma, R.; Koledov, V.V.; Ohtsuka, M.; Shavrov, V.G.; Takagi, T.; Taskaev, S.V.; Vasiliev, A.N. Phase transitions in Ni2+xMn1-xGa with a high Ni excess. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2005, 72, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banik, S.; Mukhopadhyay, P.K.; Awasthi, A.M.; Barman, S.R. Structural studies on Mn excess and Ga deficient Ni-Mn-Ga. Adv. Mater. Res. 2008, 52, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázpita, P.; Barandiarán, J.M.; Gutiérrez, J.; Feuchtwanger, J.; Chernenko, V.A.; Richard, M.L. Magnetic moment and chemical order in off-stoichiometric Ni–Mn–Ga ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 033039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, V.O.; Vovk, A.Y.; O’Connor, C.J.; Kotov, V.V.; Yakovenko, P.G.; Ullakko, K. Magnetic and structural properties of nonstoichiometric Ni2MnGa alloys with Ni and Ga excess. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 8504–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Rawat, R.; Barman, S.R. Existence of modulated structure and negative magnetoresistance in Ga excess Ni-Mn-Ga. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrici, S.; Porcari, G.; Cugini, F.; Solzi, M.; Kamarad, J.; Arnold, Z.; Cabassi, R.; Albertini, F. Co and In Doped Ni-Mn-Ga Magnetic Shape Memory Alloys: A Thorough Structural, Magnetic and Magnetocaloric Study. Entropy 2014, 16, 2204–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarkar, S.K.; Babu, P.D.; Biswas, A.; Siruguri, V.; Krishnan, M. Giant magnetocaloric effect from reverse martensitic transformation in Ni–Mn–Ga–Cu ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 670, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Łaszcz, A.; Hasiak, M.; Kaleta, J. Effects of Ti and Gd for Ga substitution on microstructure, magnetic and mechanical properties of polycrystalline Ni-Mn-Ga magnetic shape memory alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 476, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Giri, S.; Majumdar, S.; De, S.K.; Koledov, V. V Effect of Sn doping on the martensitic and premartensitic transitions in Ni2MnGa. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 1891–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łaszcz, A.; Hasiak, M.; Kaleta, J. Microstructure, magnetism and nanomechanical properties of Ni50Mn25Ga20Gd5 magnetic shape memory alloy before and after heat treatment. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 1224–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Jiang, Y.L.; Chen, F.; Tong, Y.X.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.F. Effect of Zr addition on the microstructure, phase transformation and mechanical property of Ni50Mn25Ga17Cu8 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 617, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, D.; Hernández, F.A.; Flores-Zúñiga, H.; Moya, X.; Mañosa, L.; Planes, A.; Aksoy, S.; Acet, M.; Krenke, T. Phase diagram of Fe-doped Ni-Mn-Ga ferromagnetic shape-memory alloys. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2008, 77, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.Q.; Lu, X.; Wang, D.Y.; Qin, Z.X. The effect of Co-doping on martensitic transformation temperatures in Ni–Mn–Ga Heusler alloys. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 065030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, B.; Li, J.; Qi, Y.; Wang, X. The effect of doped elements on the martensitic transformation in Ni–Mn–Ga magnetic shape memory alloy. Smart Mater. Struct. 2005, 14, S236–S238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikazumi, S. Physics of Ferromagnetism, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Kök, M.; Aydoǧdu, Y. Effect of composition on the thermal behavior of NiMnGa alloys. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 113, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Physical metallurgy of Ti-Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 511–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janovec, J.; Straka, L.; Sozinov, A.; Heczko, O.; Zelený, M. First-principles study of Zn-doping effects on phase stability and magnetic anisotropy of Ni-Mn-Ga alloys. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 026101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreev, S.V.; Bartashevich, M.I.; Pushkarskya, V.I.; Maltsev, V.N.; Pamyatnykh, L.A.; Tarasov, E.N.; Kudrevatykh, N.V.; Goto, T. Law of approach to saturation in highly anisotropic ferromagnets application to Nd-Fe-B melt-spun ribbons. J. Alloys Compd. 1997, 260, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; He, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, K.; Jing, C. Evolution of phase transformation and magnetic properties with Fe content in Ni55− xFexMn20Ga25 Heusler alloys. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 075004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Muhammad, Y.; Deng, L.; Wu, W.; Xu, H. Composition dependence on the martensitic structures of the Mn-rich NiMnGa alloys. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 2779–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Polo, C.; Pérez-Landazabal, J.I.; Recarte, V.; Sánchez-Alarcos, V.; Chernenko, V.A. Temperature and time dependent magnetic phenomena in a nearly stoichiometric Ni2MnGa alloy. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 026020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, N.; Fukuda, T.; Kakeshita, T.; Takeuchi, T. Magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant and twinning stress in martensite phase of Ni–Mn–Ga. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 438–440, 948–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Łaszcz, A.; Hasiak, M.; Kaleta, J. Temperature Dependence of Anisotropy in Ti and Gd Doped NiMnGa-Based Multifunctional Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloys. Materials 2020, 13, 2906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132906
Łaszcz A, Hasiak M, Kaleta J. Temperature Dependence of Anisotropy in Ti and Gd Doped NiMnGa-Based Multifunctional Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloys. Materials. 2020; 13(13):2906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132906
Chicago/Turabian StyleŁaszcz, Amadeusz, Mariusz Hasiak, and Jerzy Kaleta. 2020. "Temperature Dependence of Anisotropy in Ti and Gd Doped NiMnGa-Based Multifunctional Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloys" Materials 13, no. 13: 2906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132906
APA StyleŁaszcz, A., Hasiak, M., & Kaleta, J. (2020). Temperature Dependence of Anisotropy in Ti and Gd Doped NiMnGa-Based Multifunctional Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloys. Materials, 13(13), 2906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132906