In Vitro Simulation of Dental Implant Bridges Removal: Influence of Luting Agent and Abutments Geometry on Retrievability
Abstract
1. Introduction
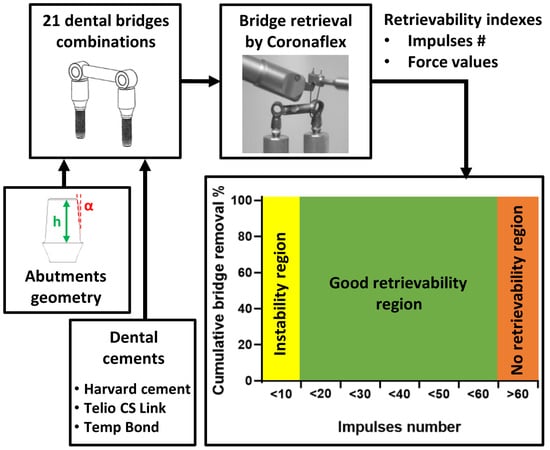
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Preparation
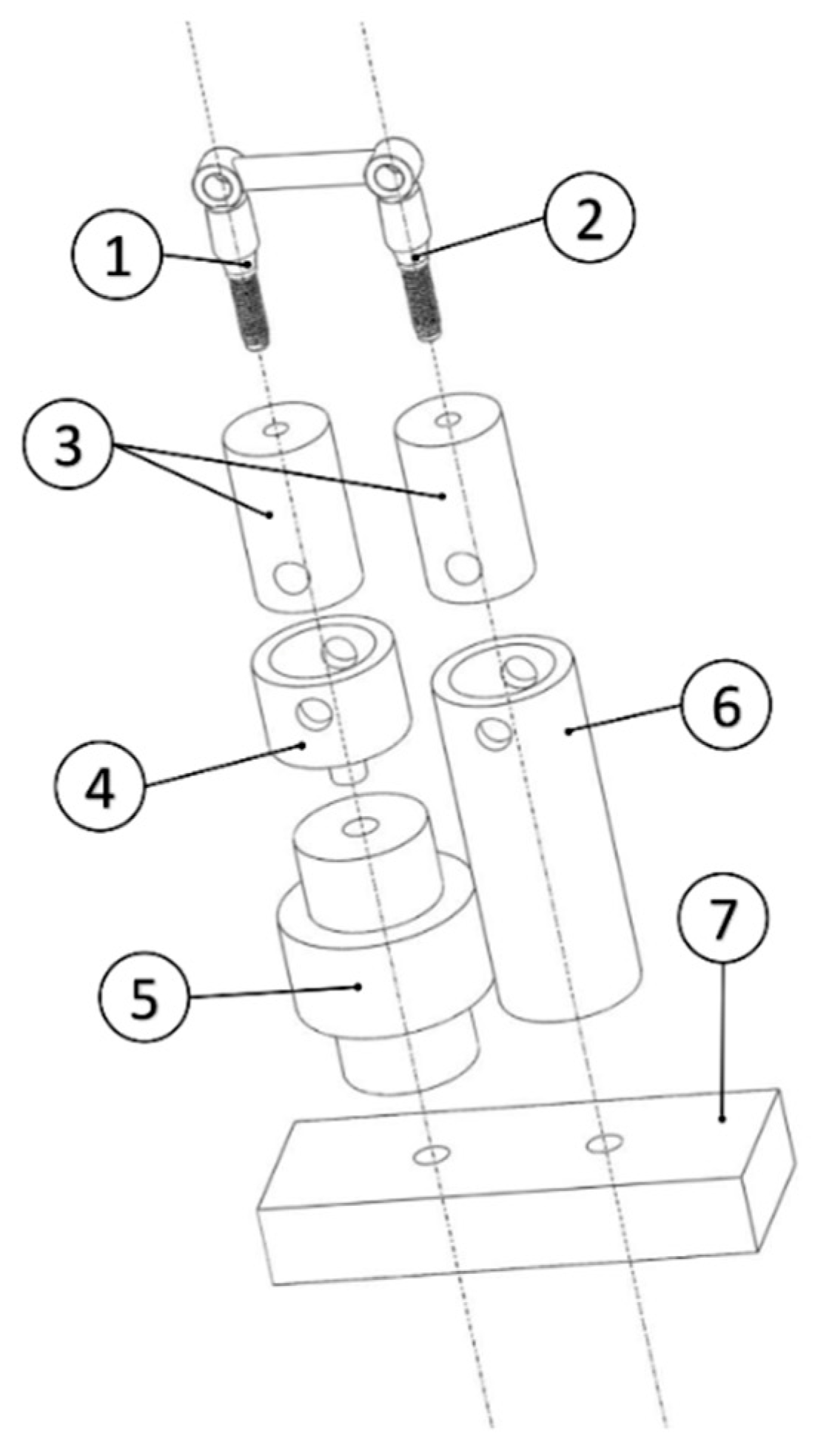
2.2. Test Setup
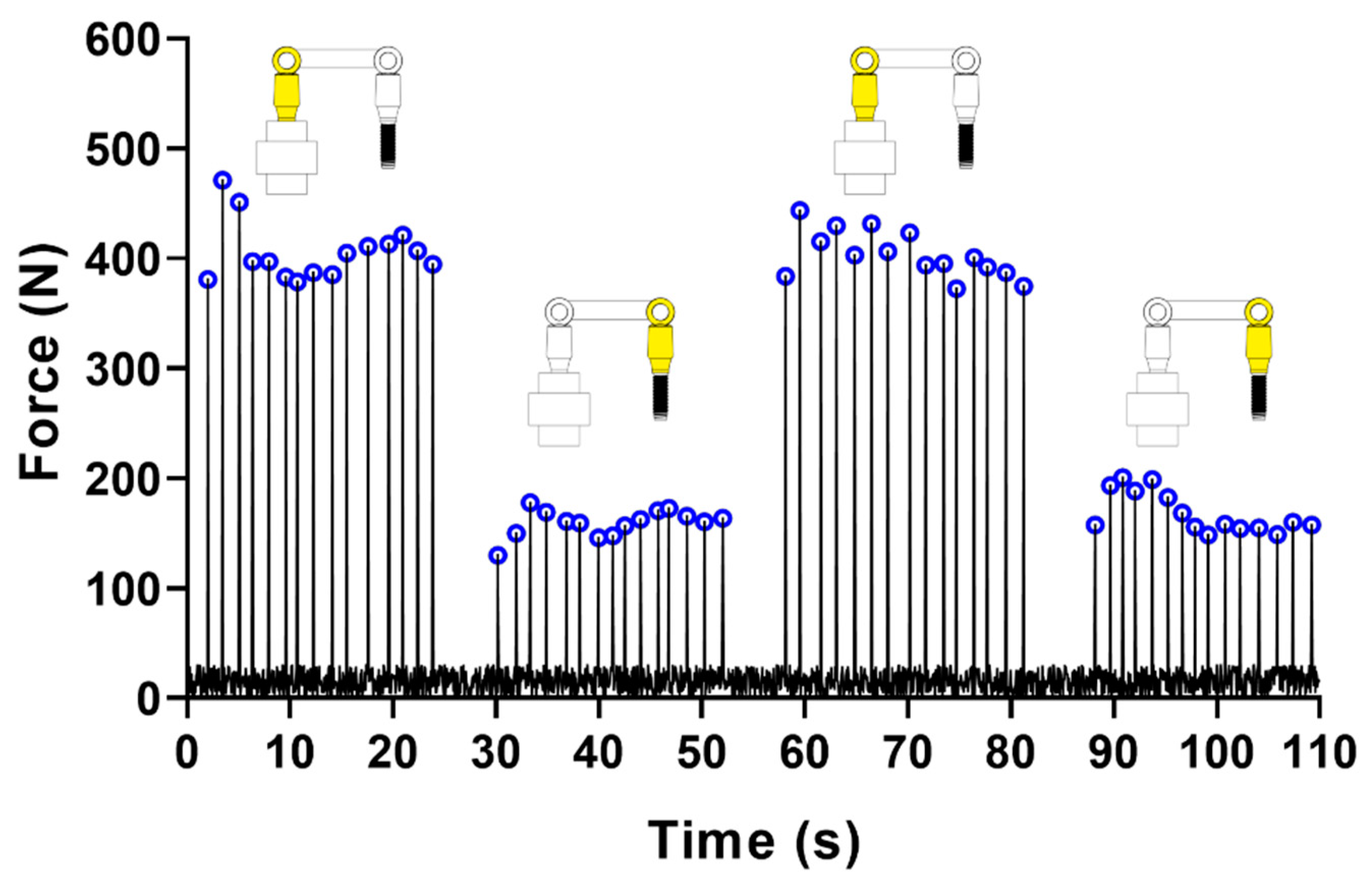
2.3. Test Protocol
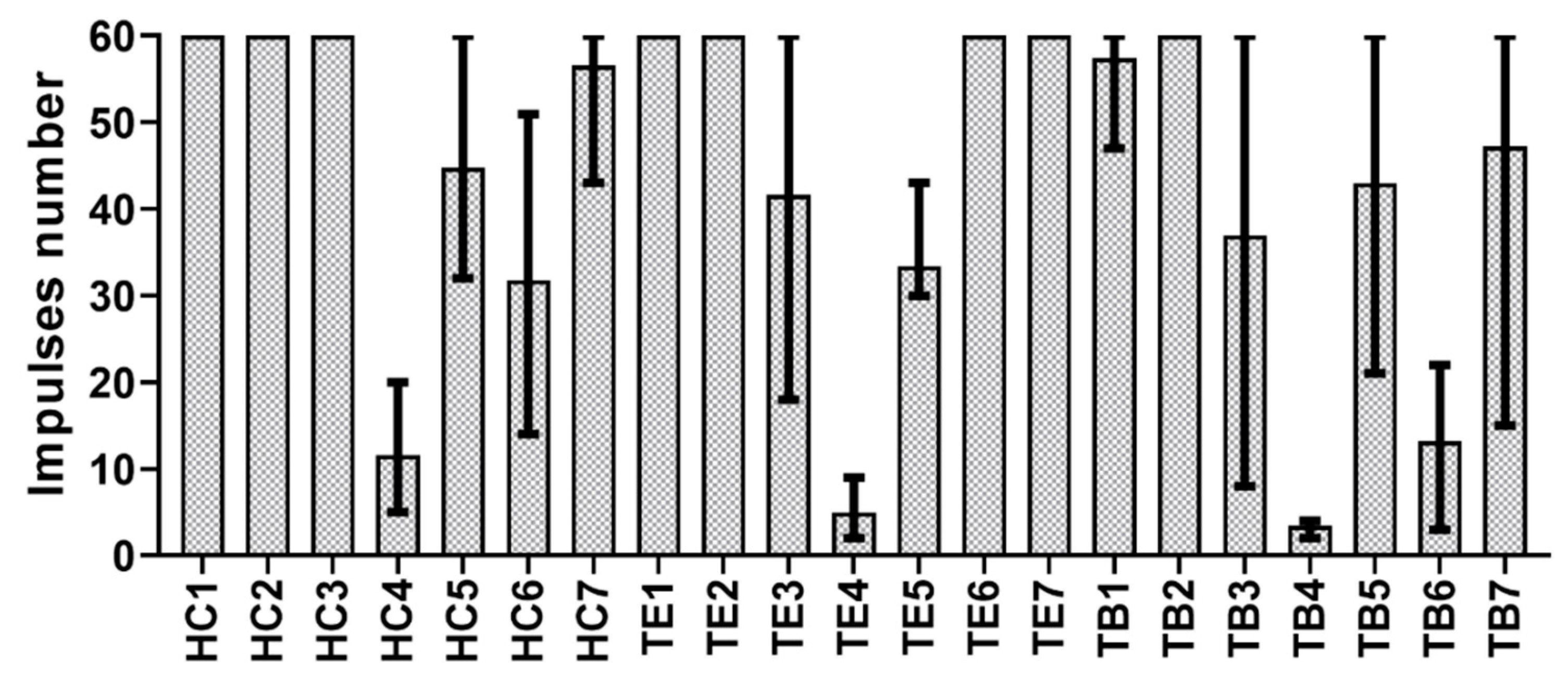
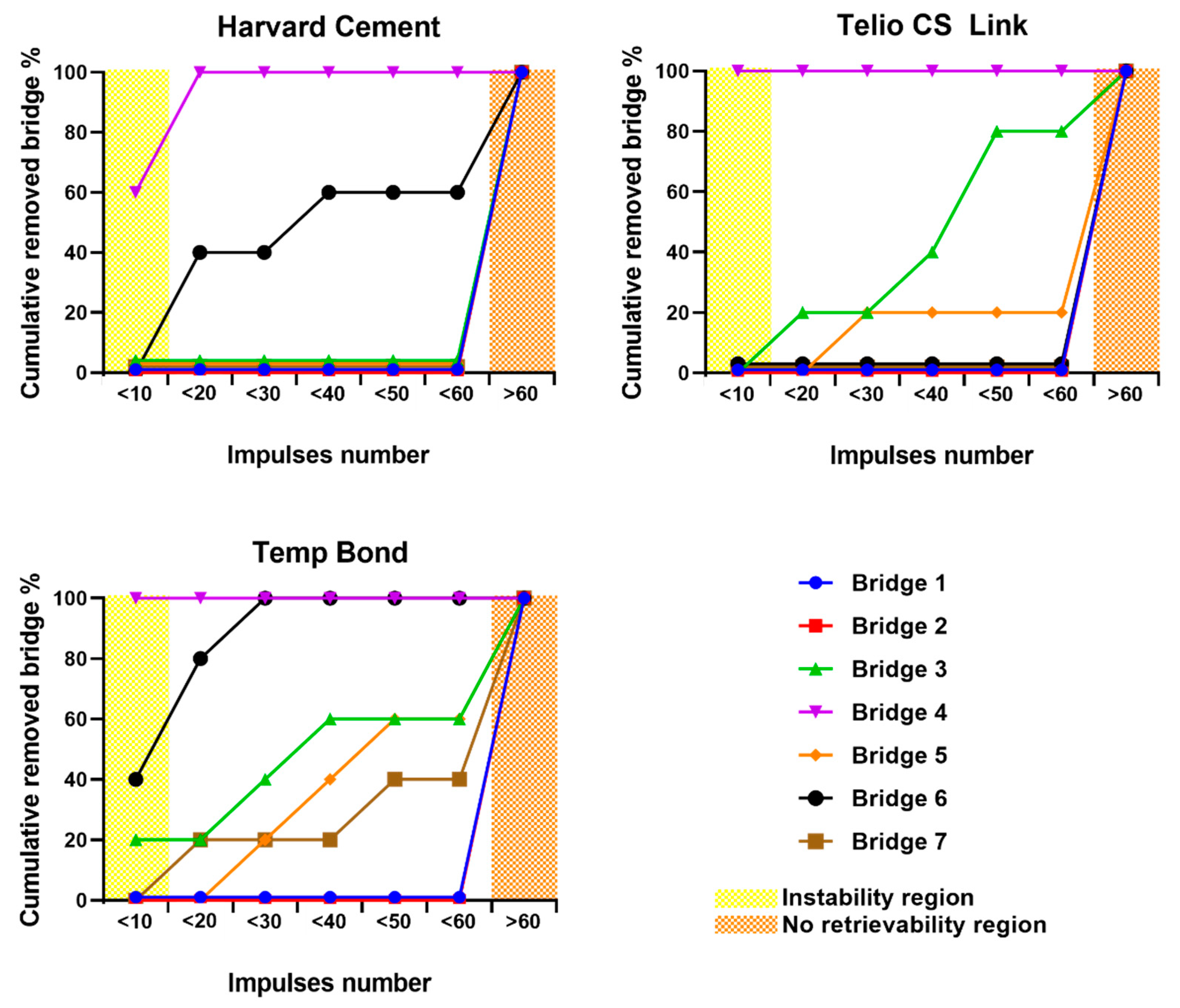
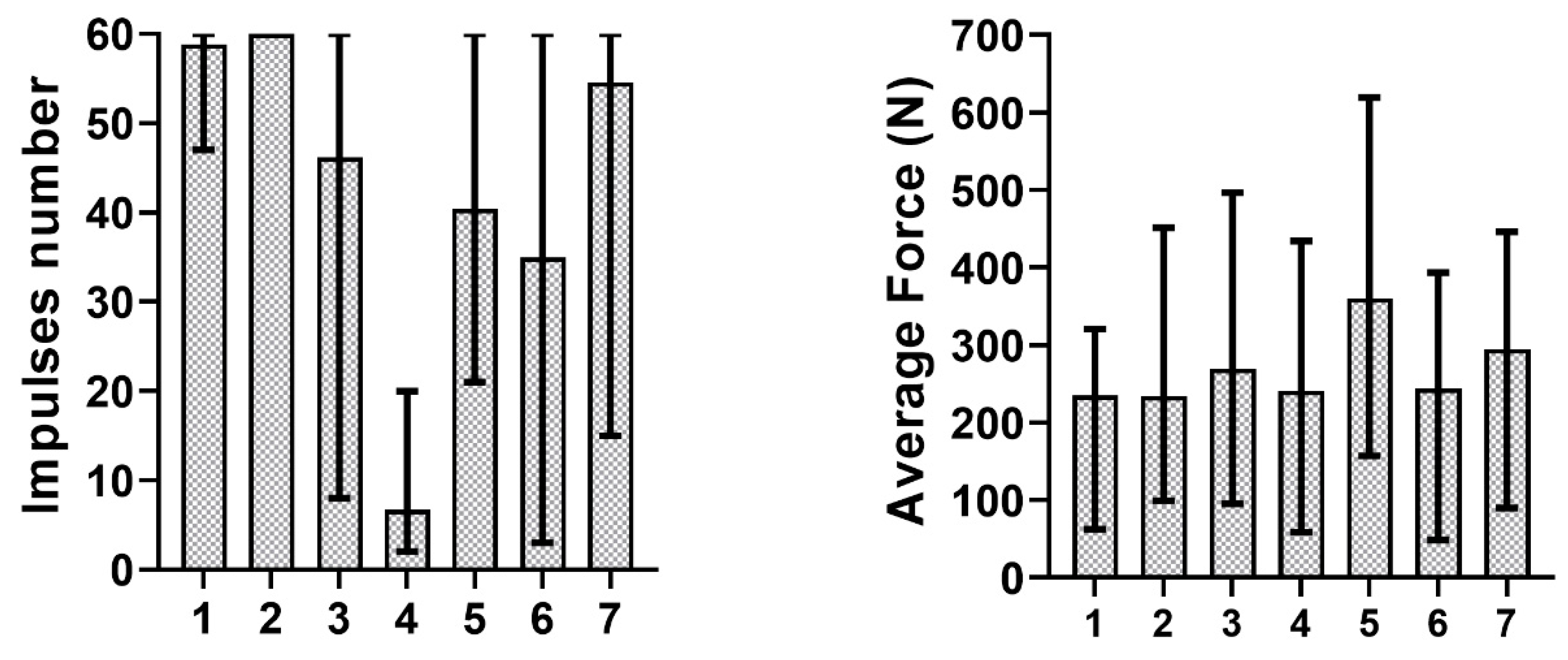
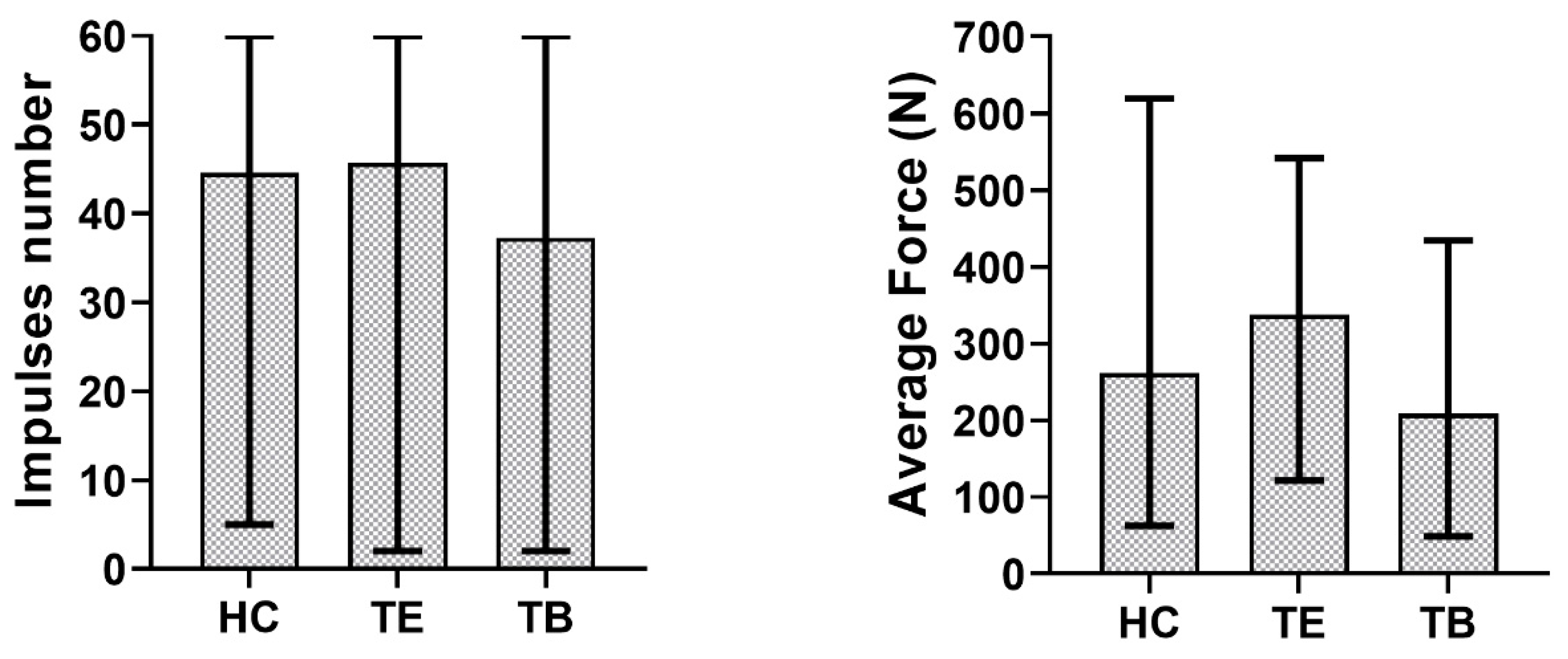
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The number of impulses, performed on the bridge with a clinical removal tool, is a more reliable index of retrievability, compared to the measured force.
- (2)
- The abutment height and taper angle have a higher influence on copings retentiveness than the luting agent.
- (3)
- The best compromise for stability and retrievability consists of a long, slightly tapered abutment, cemented with a temporary cement.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zanetti, E.M.; Pascoletti, G.; Cali, M.; Bignardi, C.; Franceschini, G. Clinical assessment of dental implant stability during follow-up: What is actually measured, and perspectives. Biosensors 2018, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittneben, J.G.; Joda, T.; Weber, H.P.; Brägger, U. Screw retained vs. cement retained implant-supported fixed dental prosthesis. Periodontol. 2000 2017, 73, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigolo, P.; Givani, A.; Majzoub, Z.; Cordioli, G. Cemented versus screw-retained implant-supported single-tooth crowns: A 4-year prospective clinical study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2004, 19, 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Manzella, C.; Bignardi, C.; Burello, V.; Carossa, S.; Schierano, G. Method to improve passive fit of frameworks on implant-supported prostheses: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 116, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assenza, B.; Scarano, A.; Leghissa, G.; Carusi, G.; Thams, U.; Roman, F.S.; Piattelli, A. Screw- vs cement-implant-retained restorations: An experimental study in the beagle. Part 1. screw and abutment loosening. J. Oral Implantol. 2005, 31, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzella, C.; Burello, V.; Bignardi, C.; Carossa, S.; Schierano, G. A method to improve passive fit of frameworks on implant-supported prostheses: An in vivo study. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2013, 26, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadid, R.; Sadaqa, N. A comparison between screw-and cement-retained implant prostheses. A literature review. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 38, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menini, M.; Piccardo, P.; Baldi, D.; Dellepiane, E.; Pera, P. Morphological and chemical characteristics of different titanium surfaces treated by bicarbonate and glycine powder air abrasive systems. Implant Dent. 2015, 24, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breeding, L.C.; Dixon, D.L.; Bogacki, M.T.; Tietge, J.D. Use of luting agents with an implant system: Part I. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1992, 68, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addy, L.; Bartley, A.; Hayes, S. Crown and bridge disassembly—When, why and how. Dent. Update 2007, 34, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.; Ercoli, C.; Graser, G.; Tallents, R.; Moss, M. Comparative evaluation of casting retention using the ITI solid abutment with six cements. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2002, 13, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Hamad, K.Q.; Al Rashdan, B.A.; Abu-Sitta, E.H. The effects of height and surface roughness of abutments and the type of cement on bond strength of cement-retained implant restorations. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehl, C.; Harder, S.; Schwarz, D.; Steiner, M.; Vollrath, O.; Kern, M. In vitro influence of ultrasonic stress, removal force preload and thermocycling on the retrievability of implant-retained crowns. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, C.; Harder, S.; Wolfart, M.; Kern, M.; Wolfart, S. Retrievability of implant-retained crowns following cementation. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008, 19, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akça, K.; Iplikçioğlu, H.; Cehreli, M.C. Comparison of uniaxial resistance forces of cements used with implant-supported crowns. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2002, 17, 536–542. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, S.; Schröder, C.; Corcodel, N.; Hassel, A.J.; Rammelsberg, P. Retrospective comparison of semipermanent and permanent cementation of implant-supported single crowns and FDPs with regard to the incidence of survival and complications. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2012, 14, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.; Tredwin, C.J.; Nesbit, M.; Setchell, D.J.; Moles, D.R. The effect of engaging the screw access channel of an implant abutment with a cement-retained restoration. J. Prosthodont. 2009, 18, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, M.F.; Johnston, W.M.; Rosenstiel, S.F. Influence of tooth preparation taper and cement type on recementation strength of complete metal crowns. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2009, 102, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciano, M.; Schierano, G.; Manzella, C.; Screti, A.; Bignardi, C.; Preti, G. Retention of luting agents on implant abutments of different height and taper. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2005, 16, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultekin, P.; Gultekin, B.A.; Aydin, M.; Yalcin, S. Cement selection for implant-supported crowns fabricated with different luting space settings. J. Prosthodont. 2013, 22, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, J.E.; Richards, L.C.; Abbottf, J.R. Retention of cast crown copings cemented to implant abutments. Aust. Dent. J. 2008, 53, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugas, A.T.; Terzini, M.; Zanetti, E.M.; Schierano, G.; Manzella, C.; Baldi, D.; Bignardi, C.; Audenino, A.L. In vitro impact testing to simulate implant-supported prosthesis retrievability in clinical practice: Influence of cement and abutment geometry. Materials 2020, 13, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiessl, C.; Schaefer, L.; Winter, C.; Fuerst, J.; Rosentritt, M.; Zeman, F.; Behr, M. Factors determining the retentiveness of luting agents used with metal- and ceramic-based implant components. Clin. Oral Investig. 2013, 17, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierano, G.; Manzella, C.; Menicucci, G.; Parrotta, A.; Zanetti, E.M.; Audenino, A.L. In vitro standardization of two different removal devices in cemented implant prosthesis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignardi, C.; Terzini, M.; Ciccola, A.R.; Audenino, A.L.; Zanetti, E.M.; Schierano, G. Reliability, learnability and efficiency of two tools for cement crowns retrieval in dentistry. Open Biomed. Eng. J. 2018, 12, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bernal, G.; Okamura, M.; Muñoz, C.A. The effects of abutment taper, length and cement type on resistance to dislodgement of cement-retained, implant-supported restorations. J. Prosthodont. 2003, 12, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, F.; Mundt, T.; Biffar, R. Retrospective evaluation of temporary cemented, tooth and implant supported fixed partial dentures. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 34, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, C.; Harder, S.; Steiner, M.; Vollrath, O.; Kern, M. Influence of cement film thickness on the retention of implant-retained crowns. J. Prosthodont. 2013, 22, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worni, A.; Gholami, H.; Marchand, L.; Katsoulis, J.; Mericske-Stern, R.; Enkling, N. Retrievability of implant-supported crowns when using three different cements: A controlled clinical trial. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 28, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Choi, K.H.; Da Son, K.B.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, K.B. Influence of abutment height and convergence angle on the retrievability of cement-retained implant prostheses with a lingual slot. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2018, 10, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Faruk, S.T. Enhancing retrievability of cement retained implant supported restorations. EC Dent. Sci. 2019, 3, 508–512. [Google Scholar]
- Emms, M.; Tredwin, C.J.; Setchell, D.J.; Moles, D.R. The effects of abutment wall height, platform size, and screw access channel filling method on resistance to dislodgement of cement-retained, implant-supported restorations. J. Prosthodont. 2007, 16, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, E.E.; Lott, J. A Clinically focused discussion of luting materials. Aust. Dent. J. 2011, 56, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, T.E.; Cho, G.C. Contemporary evaluation of dental cements. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 1999, 20, 197–199. [Google Scholar]
- Burbano, M.; Wilson, T.; Valderrama, P.; Blansett, J.; Wadhwani, C.; Choudhary, P.; Rodriguez, L.; Rodrigues, D. Characterization of cement particles found in peri-implantitis–affected human biopsy specimens. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2015, 30, 1168–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, C.; Ali, S.; El Bahra, S.; Harder, S.; Vollrath, O.; Kern, M. Is there a correlation between tensile strength and retrievability of cemented implant-retained crowns using artificial aging? Int. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 29, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennartz, A.; Dohmen, A.; Bishti, S.; Fischer, H.; Wolfart, S. Retrievability of implant-supported zirconia restorations cemented on zirconia abutments. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 120, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
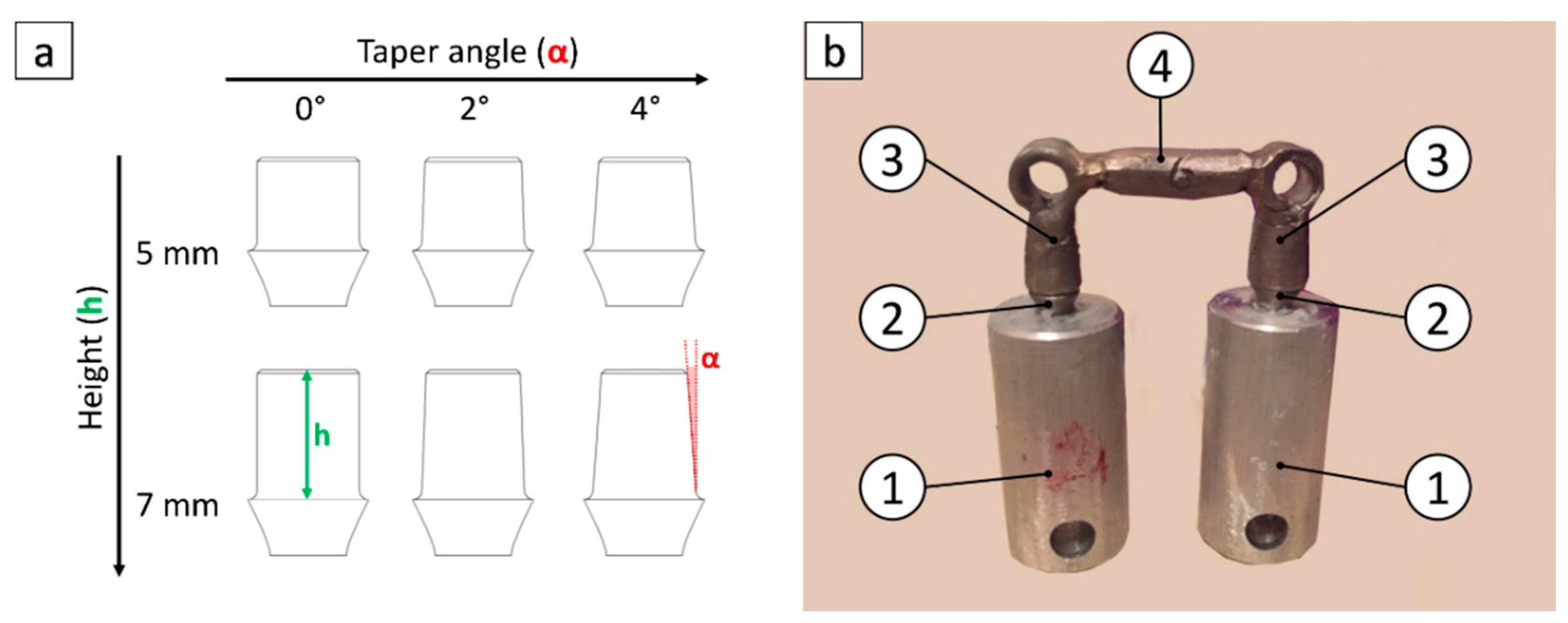

| Bridge | Abutment 1 Geometry | Abutment 2 Geometry |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 mm-0° | 5 mm-0° |
| 2 | 7 mm-0° | 7 mm-0° |
| 3 | 7 mm-2° | 7 mm-2° |
| 4 | 5 mm-2° | 5 mm-4° |
| 5 | 5 mm-0° | 5 mm-4° |
| 6 | 7 mm-2° | 7 mm-4° |
| 7 | 7 mm-0° | 7 mm-4° |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lugas, A.T.; Terzini, M.; Zanetti, E.M.; Schierano, G.; Manzella, C.; Baldi, D.; Bignardi, C.; Audenino, A.L. In Vitro Simulation of Dental Implant Bridges Removal: Influence of Luting Agent and Abutments Geometry on Retrievability. Materials 2020, 13, 2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13122797
Lugas AT, Terzini M, Zanetti EM, Schierano G, Manzella C, Baldi D, Bignardi C, Audenino AL. In Vitro Simulation of Dental Implant Bridges Removal: Influence of Luting Agent and Abutments Geometry on Retrievability. Materials. 2020; 13(12):2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13122797
Chicago/Turabian StyleLugas, Andrea T., Mara Terzini, Elisabetta M. Zanetti, Gianmario Schierano, Carlo Manzella, Domenico Baldi, Cristina Bignardi, and Alberto L. Audenino. 2020. "In Vitro Simulation of Dental Implant Bridges Removal: Influence of Luting Agent and Abutments Geometry on Retrievability" Materials 13, no. 12: 2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13122797
APA StyleLugas, A. T., Terzini, M., Zanetti, E. M., Schierano, G., Manzella, C., Baldi, D., Bignardi, C., & Audenino, A. L. (2020). In Vitro Simulation of Dental Implant Bridges Removal: Influence of Luting Agent and Abutments Geometry on Retrievability. Materials, 13(12), 2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13122797