Thermoplastic Disks Used for Commercial Orthodontic Aligners: Complete Physicochemical and Mechanical Characterization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicophysical Characterization of the As-Received Disks
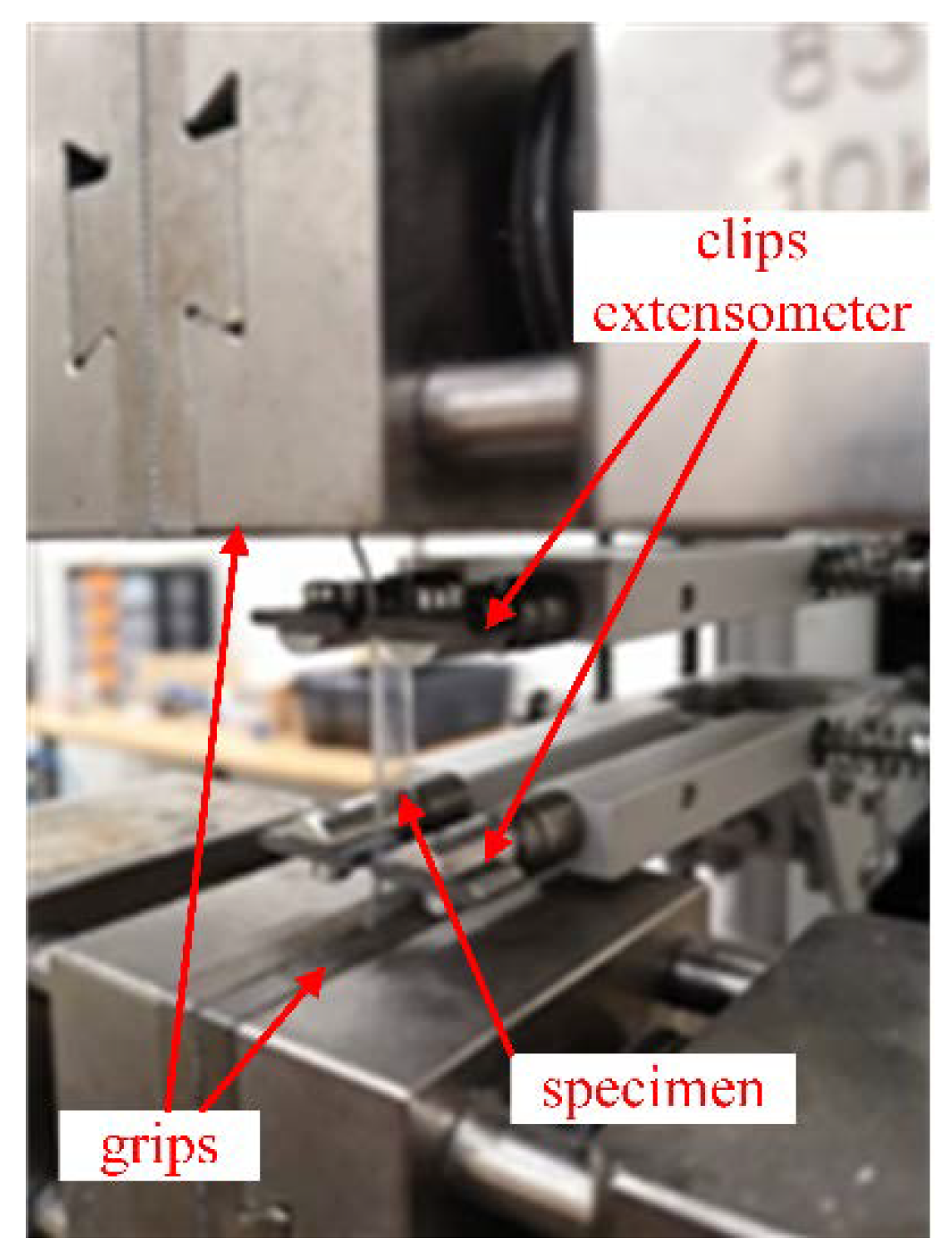
2.2. Mechanical Characterization of the As-Received Disks
2.3. Immersion into Staining Beverages: Colour Change Evaluations.
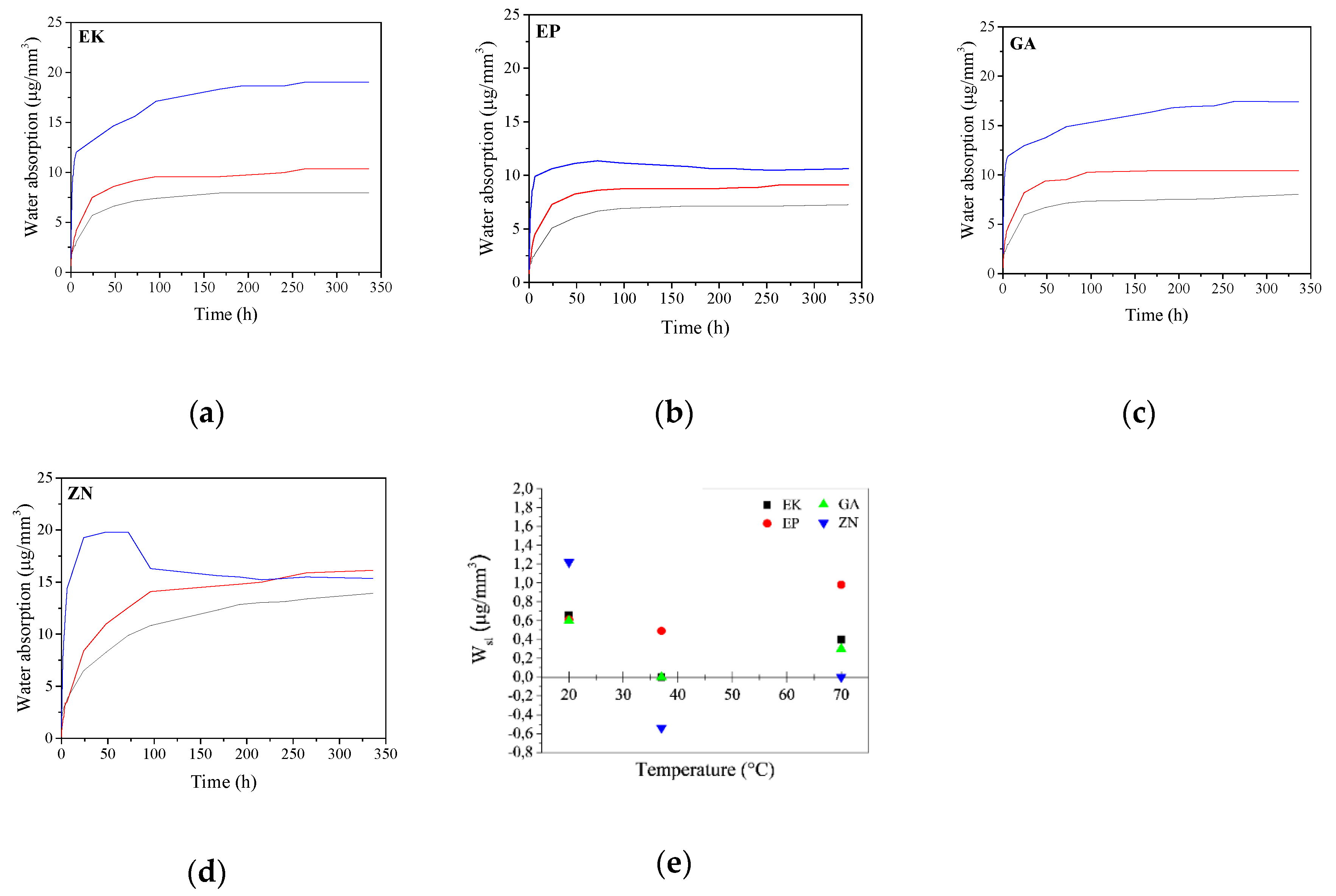
2.4. Water Absorption Test at Different Temperatures
3. Results and Discussion
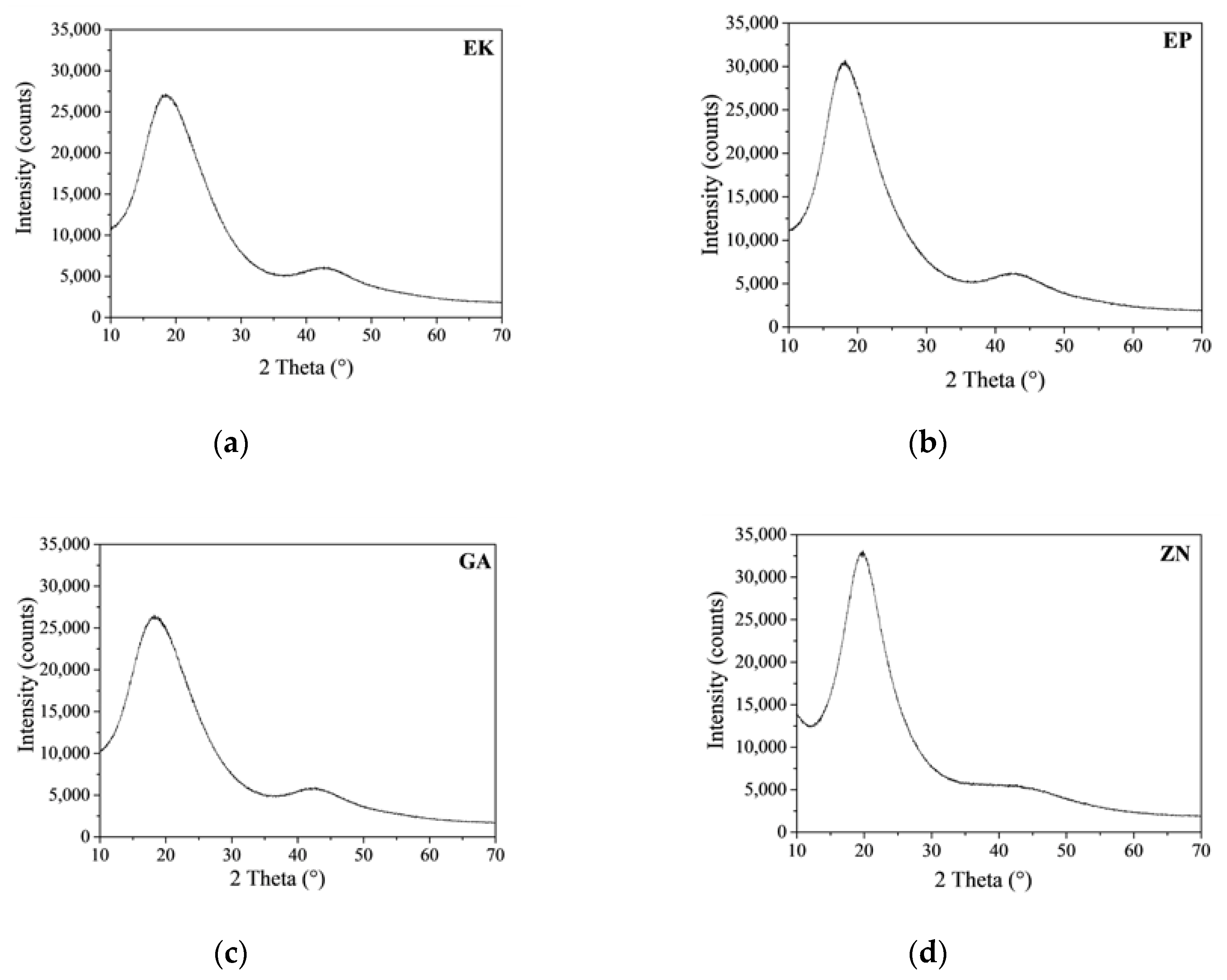
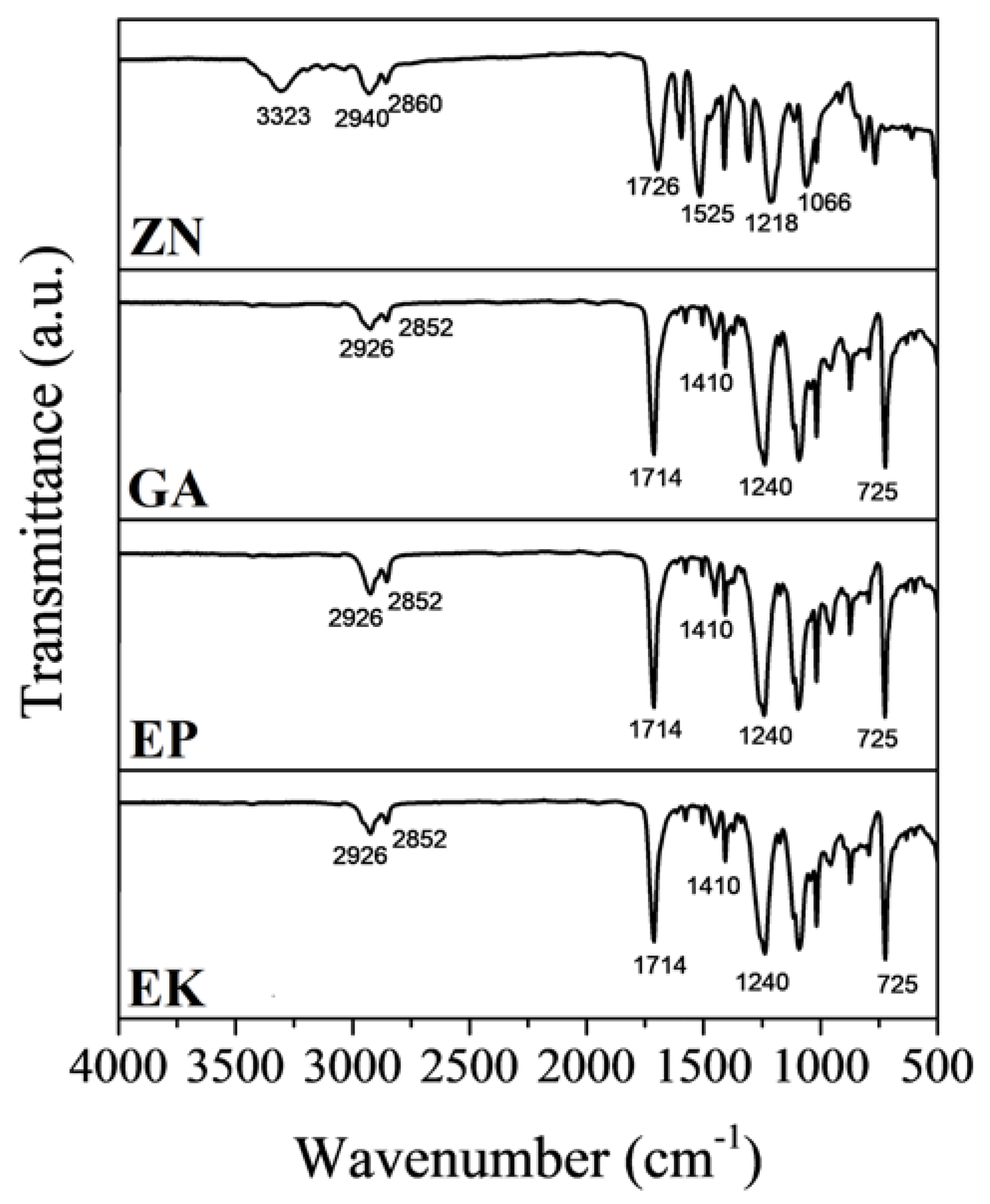
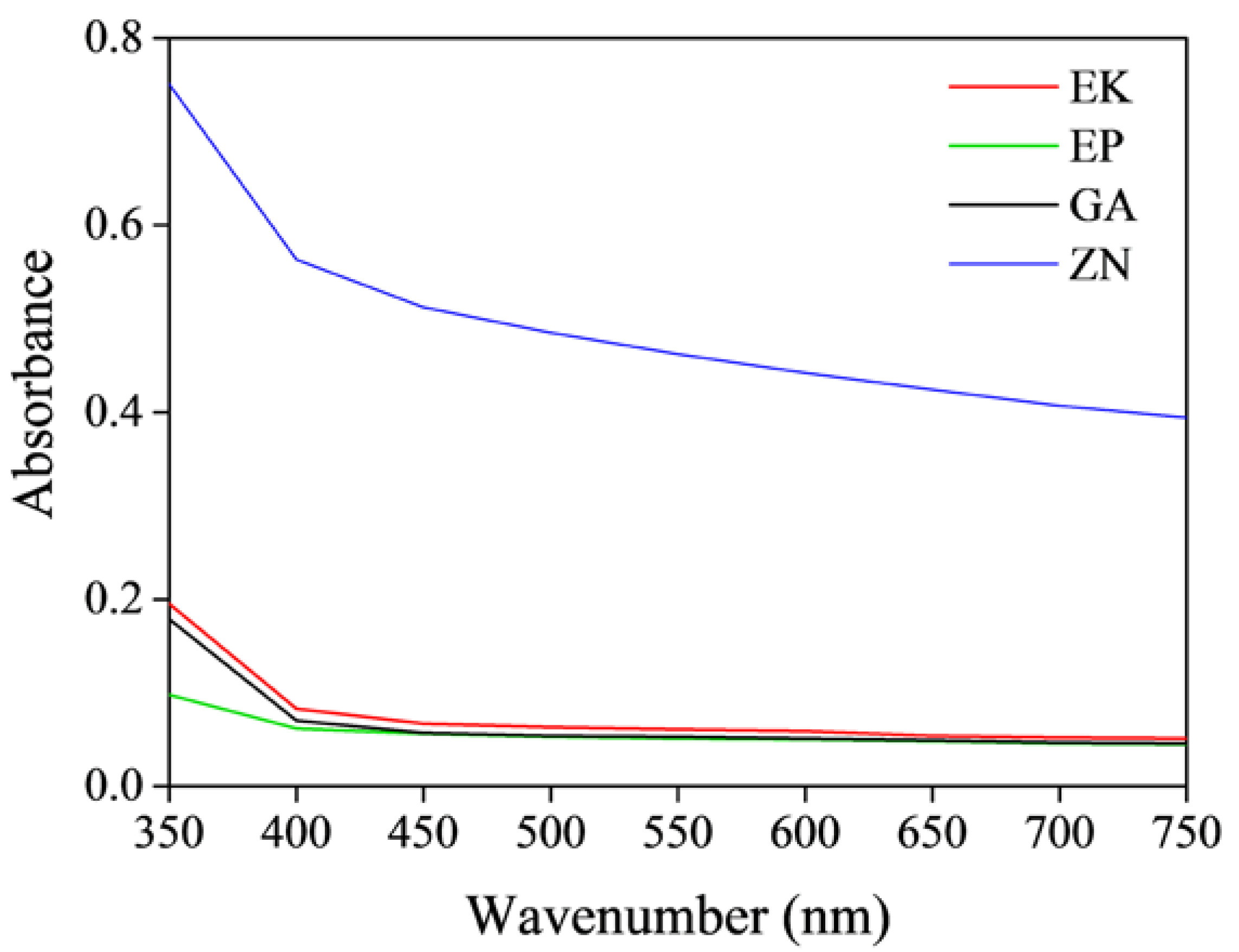
3.1. Chemicophysical and Mechanical Characterization of the Disks
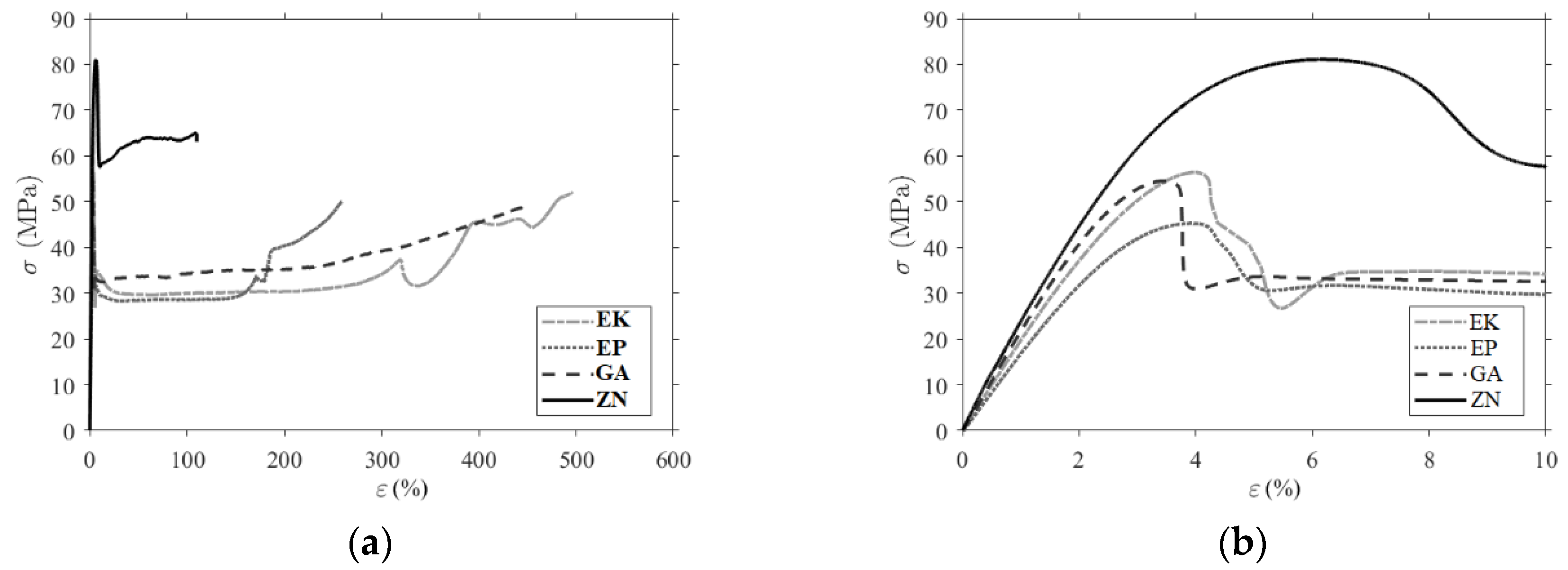
3.2. Mechanical Characterization
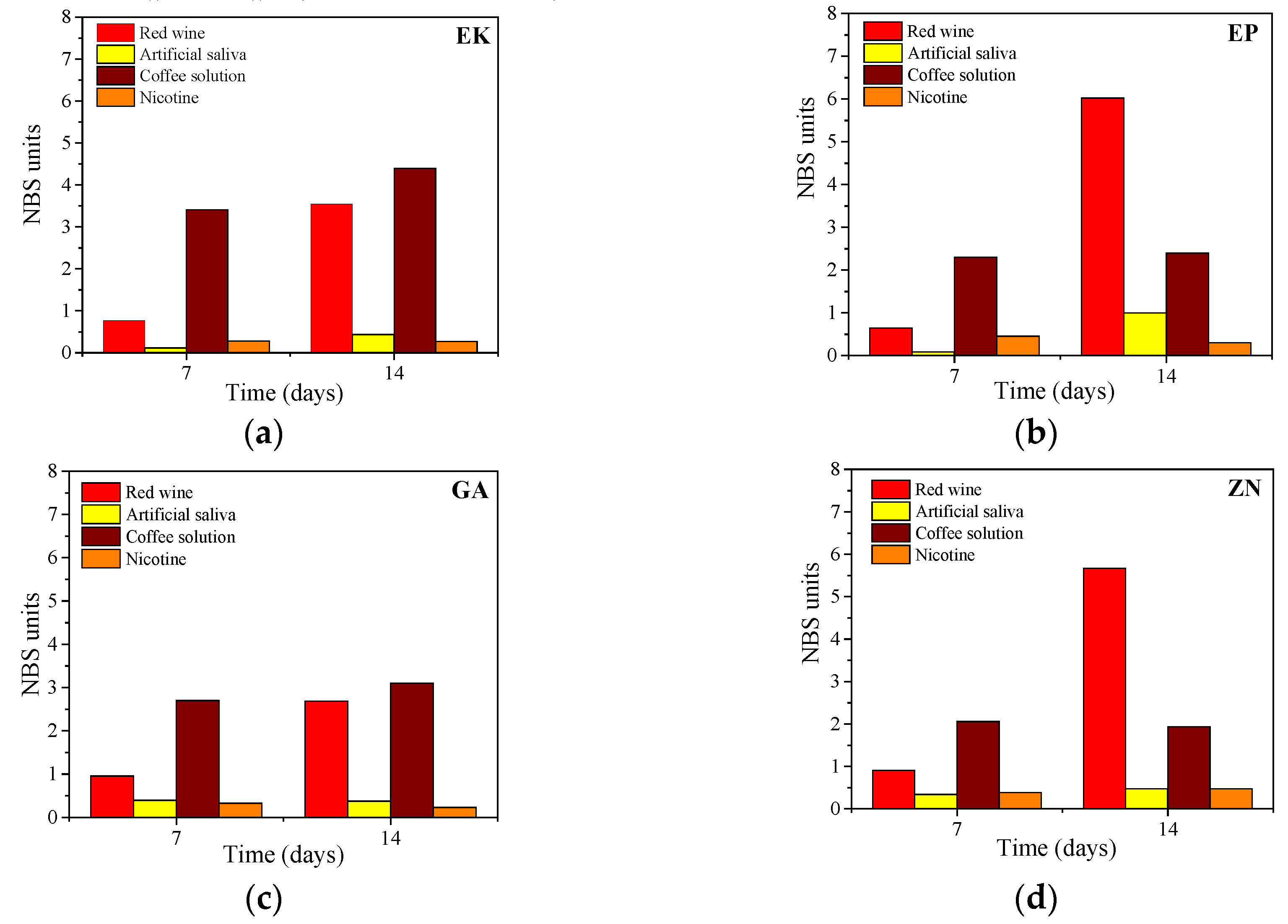
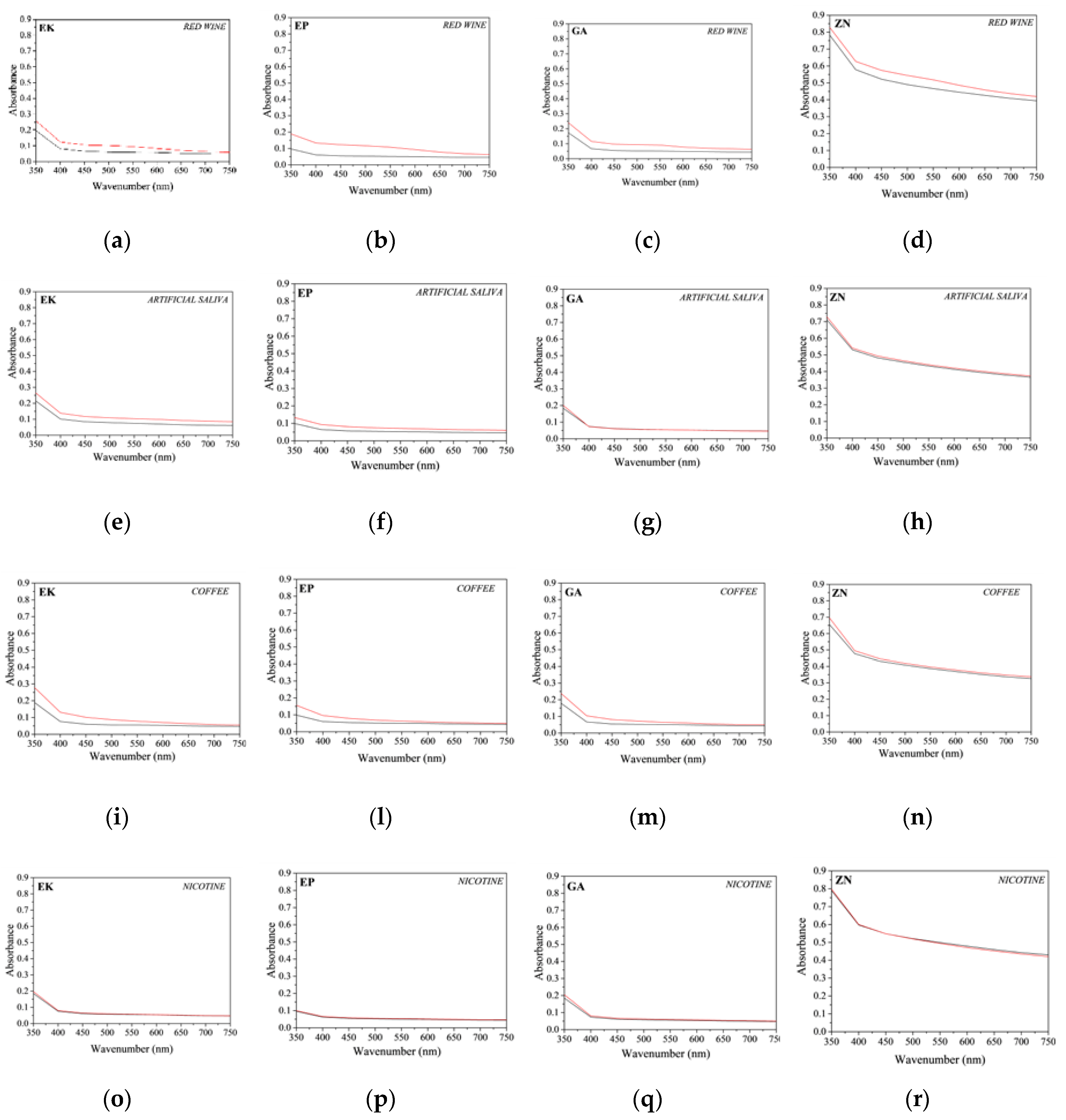
3.3. Colour Change Evaluations
3.4. Water Absorption Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martorelli, M.; Gerbino, S.; Giudice, M.; Ausiello, P. A comparison between customized clear and removable orthodontic appliances manufactured using RP and CNC techniques. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, e1–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogaard, B.; Rølla, G.; Arends, J. Orthodontic appliances and enamel demineralization. Part 1. Lesion development. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1988, 94, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Featherstone, J. Dental caries: A dynamic disease process. Aust. Dent. J. 2008, 53, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joffe, L. Invisalign: Early experiences. J. Orthod. 2003, 30, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesling, H.D. The philosophy of the tooth positioning appliance. Am. J. Orthod. Oral Surg. 1945, 31, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, J.J. The Readers’ Corner. 2. What percentage of your patients are being treated with Invisalign appliances? J. Clin. Orthod. 2004, 38, 544–545. [Google Scholar]
- Nahoum, H. The vacuum formed dental contour appliance. N. Y. State Dent. J. 1964, 9, 385–390. [Google Scholar]
- Ponitz, R.J. Invisible retainers. Am. J. Orthod. 1971, 59, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melko, A.B. Advances in digital technology and orthodontics: A reference to the Invisalign method. Med. Sci. Monit. 2005, 11, PI39–PI42. [Google Scholar]
- Dupaix, R.B.; Boyce, M.C. Finite strain behavior of poly (ethylene terephthalate)(PET) and poly (ethylene terephthalate)-glycol (PETG). Polymer 2005, 46, 4827–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Zhang, N.; Chen, H.; Bai, Y. Dynamic stress relaxation of orthodontic thermoplastic materials in a simulated oral environment. Dent. Mater. J. 2013, 32, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, L.; Martines, E.; Mazzanti, V.; Arreghini, A.; Mollica, F.; Siciliani, G. Stress relaxation properties of four orthodontic aligner materials: A 24-hour in vitro study. Angle Orthod. 2017, 87, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Sun, W.T.; Liao, W.; Lu, W.X.; Li, Q.W.; Jeong, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.H. Colour stabilities of three types of orthodontic clear aligners exposed to staining agents. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2016, 8, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, C.M.; Ruyter, I.E. Staining of resin-based veneering materials with coffee and tea. Quintessence Int. 1991, 22, 377–386. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, Y.K. Measurement of discolouration of orthodontic elastomeric modules with a digital camera. Eur. J. Orthod. 2009, 31, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.B.; Ribeiro, A.A.; Araujo, M.V.; Ruellas, A.C.O. Influence of exogenous pigmentation on the optical properties of orthodontic elastic ligatures. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2012, 20, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdemir, U.; Yildiz, E.; Eren, M.M. Effects of sports drinks on color stability of nanofilled and microhybrid composites after long-term immersion. J. Dent. 2012, 40, e55–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and characterization of thermoplastic materials for invisible orthodontics. Dent. Mater. J. 2011, 30, 954–959. [Google Scholar]
- Boubakri, A.; Haddar, N.; Elleuch, K.; Bienvenu, Y. Impact of aging conditions on mechanical properties of thermoplastic polyurethane. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4194–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nève, B.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Water absorption by an epoxy resin and its effect on the mechanical properties and infra-red spectra. Polymer 1993, 34, 5099–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, A.; Elleuch, K.; Guermazi, N.; Ayedi, H.F. Investigations of hygrothermal aging of thermoplastic polyurethane material. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 3958–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.; Fan, C.H.; Hung, C.Y.; Tsai, F.J. Amorphous Copolyesters Based on 1,3/1,4-Cyclohexanedimethanol: Synthesis, Characterization and Properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 2598–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkodent Erich Kopp GmbH. Available online: https://www.erkodent.de/wp-content/documents/products/Erkodur_EN.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Thermoplastic Sheets. Available online: https://www.bartmedical.com/site/en/products/thermoplastic_sheets/ghost_aligner.html (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Zendura Dental. Available online: https://www.zenduradental.com/pages/properties (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Ryu, J.H.; Kwon, J.S.; Jiang, H.B.; Cha, J.Y.; Kim, K.M. Effects of thermoforming on the physical and mechanical properties of thermoplastic materials for transparent orthodontic aligners. Korean J. Orthod. 2018, 48, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.; Eliades, G.; Zinelis, S.; Eliades, T.; Bradley, T.G. Structural conformation and leaching from in vitro aged and retrieved Invisalign appliances. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2004, 126, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryokawa, H.; Miyazaki, Y.; Fujishima, A.; Miyazaki, T.; Maki, K. The mechanical properties of dental thermoplastic materials in a simulated intraoral environment. Orthod. Waves 2006, 65, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.S.; Fang, D.Y.; Zhang, N.; Ding, X.J.; Zhang, K.Y.; Bai, Y.K. Mechanical properties of orthodontic thermoplastics PETG/PC2858 after blending. Chin. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 19, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bárány, T.; Földes, E.; Czigány, T. Effect of thermal and hygrothermal aging on the plane stress fracture toughness of poly(ethylene terephthalate) sheets. Express Polym. Lett. 2007, 3, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 527-2:2012 Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 2: Test Conditions for Moulding and Extrusion Plastics. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/56046.html (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Donnini, J.; Chiappini, G.; Lancioni, G.; Corinaldesi, V. Tensile behaviour of glass FRCM systems with fabrics’ overlap: Experimental results and numerical modeling. Compos. Struct. 2019, 212, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Chiappini, G.; Sasso, M. Characterization of aluminum alloys using a 3D full field measurement. In Application of Imaging Techniques to Mechanics of Materials and Structures; Proulx, T., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, W.M. Color measurement in dentistry. J. Dent. 2009, 37, e2–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colorimetry. Available online: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/Legacy/MONO/nbsmonograph104.pdf (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Cörekçi, B.; Irgin, C.; Malkoҫ, S.; Oztürk, B. Effects of staining solutions on the discoloration of orthodontic adhesives: An in-vitro study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2010, 138, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inami, T.; Tanimoto, Y.; Minami, N.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kasai, K. Color stability of laboratory glass-fiber-reinforced plastics for esthetic orthodontic wires. Korean J. Orthod. 2015, 45, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koksal, T.; Dikbas, I. Color stability of different denture teeth materials against various staining agents. Dent. Mater. J. 2008, 27, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentistry-Base Polymers-Part 2: Orthodontic Base Polymers. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/62279.html (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Hamanaka, I.; Iwamoto, M.; Lassila, L.; Vallittu, P.; Shimizu, H.; Takahashi, Y. Influence of water sorption on mechanical properties of injection-molded thermoplastic denture base resins. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2014, 72, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Influence of Annealing Temperature on the Morphology of a Copolyester (Petg). Available online: http://livrozilla.com/doc/1125147/petg---ipen (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Greco, A.; Timo, A.; Maffezzoli, A. Development and Characterization of Amorphous Thermoplastic Matrix Graphene Nanocomposites. Materials 2012, 5, 1972–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovati, G.; Sanches, E.A.; Neto, S.C.; Mascarenhas, Y.P.; Chierice, G.O. Characterization of Polyurethane Resins by FTIR, TGA, and XRD. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Enhai, S.; Akihiko, F.; Hongcai, W.; Koichi, N.; Katsumi, Y. Synthesis and Characterization of Photoconducting Polyaniline-TiO2 Nanocomposite. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2000, 73, 2627–2633. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, S.R. Development of Amorphous Copolyesters Basedon 1,4-Cyclohexanedimethanol. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 5847–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, A.; Rochman, A. Characterization of TPU-elastomers by thermal analysis (DSC). Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Jeong, K.S.; Jung, J.C. Thermal and mechanical properties of amorphous copolyester (PETG)/LCP blends. Eur. Polym. J. 1999, 35, 1439–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszkiewicz, S.; Szymczyk, A.; Pawlikowska, D.; Irska, I.; Taraghi, I.; Pilawka, R.; Gu, J.; Li, X.; Tu, Y.; Piesowicz, E. Synthesis and characterization of poly (ethylene terephthalate-co-1,4-cyclohexanedimethylene terephtlatate)-block-poly (tetramethylene oxide) copolymers. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 41745–41754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, J. Surface hydrophilic modification of acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene terpolymer by poly(ethylene glycol-co-1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol terephthalate): Preparation, characterization, and properties studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 388, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Jiang, G.; Li, G.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J. Poly(ethylene glycol-co-1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol terephthalate) random copolymers: Effect of copolymer composition and microstructure on the thermal properties and crystallization behavior. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 60570–60580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. Alkali resistance of poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) and poly(ethylene glycol-co-1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol terephthalate) (PETG) copolyesteres: The role of composition. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 120, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, R.B.; Carraher, C.E. Structure-Property Relationships in Polymers; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984; p. 28. [Google Scholar]


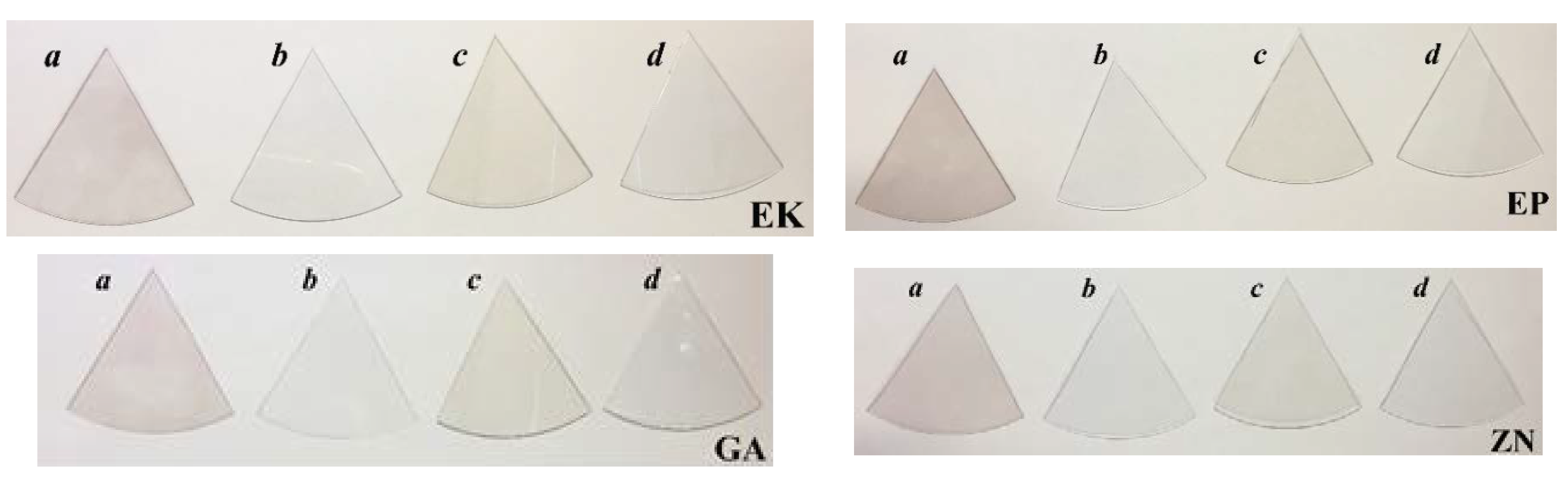

| Sample Name | Brand (Manufacturer) * | Chemical Composition |
|---|---|---|
| EK | Erkodur (Erkodent Erich Kopp GmbH, Pfalzgrafenweiler, Deutschland) | polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) |
| EP | Essix Plastic (Dentsply Sirona, York, PA USA) | polyethylene terephthalate (PET) |
| GA | Ghost Aligner (BART MEDICAL S.r.l., Mezzano, Italy) | polyethylene terephthalate (PET) |
| ZN | Zendura (Zendura, Bay Materials LLC, Fremont, CA, USA) | polyurethane (PU) |
| National Bureau of Standards Units | Descriptions of Colour Changes | NBS = 0.92 × ΔE* |
| 0.0–0.5 | Trace: extremely slight change | |
| 0.5–1.5 | Slight: slight change | |
| 1.5–3.0 | Noticeable: perceivable | |
| 3.0–6.0 | Appreciable: marked change | |
| 6.0–12.0 | Much: extremely marked change | |
| 12.0 or more | Very much: change to another colour |
| Sample | EK | EP | GA | ZN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWHM (° 2θ) | 9.643 | 8.148 | 9.695 | 6.313 |
| Sample | σm (MPa) | εm (%) | εtb (%) | E (MPa) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μ | σ | cv | μ | σ | cv | μ | σ | cv | μ | σ | cv | |
| EK | 55.93 | 0.42 | 0.8% | 3.99% | 0.13% | 3.3% | 507% | 59% | 11.6% | 1933.03 | 130 | 6.7% |
| EP | 45.37 | 0.54 | 1.2% | 3.91% | 0.02% | 0.4% | 261% | 5% | 1.8% | 1742.03 | 46 | 2.6% |
| GA | 53.65 | 0.85 | 1.6% | 3.32% | 0.15% | 4.5% | 396% | 58% | 14.7% | 2102.83 | 24 | 1.1% |
| ZN | 78.20 | 5.25 | 6.7% | 6.22% | 0.05% | 0.8% | 95% | 30% | 31.7% | 2489.43 | 74 | 3.0% |
| Sample | EK | EP | GA | ZN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E’RT (MPa) | 2430 | 2160 | 2280 | 2840 |
| Tgonset (°C) | 77.2 | 79.5 | 71.9 | 88.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daniele, V.; Macera, L.; Taglieri, G.; Di Giambattista, A.; Spagnoli, G.; Massaria, A.; Messori, M.; Quagliarini, E.; Chiappini, G.; Campanella, V.; et al. Thermoplastic Disks Used for Commercial Orthodontic Aligners: Complete Physicochemical and Mechanical Characterization. Materials 2020, 13, 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13102386
Daniele V, Macera L, Taglieri G, Di Giambattista A, Spagnoli G, Massaria A, Messori M, Quagliarini E, Chiappini G, Campanella V, et al. Thermoplastic Disks Used for Commercial Orthodontic Aligners: Complete Physicochemical and Mechanical Characterization. Materials. 2020; 13(10):2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13102386
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaniele, Valeria, Ludovico Macera, Giuliana Taglieri, Alessandra Di Giambattista, Giuseppe Spagnoli, Alessandra Massaria, Massimo Messori, Enrico Quagliarini, Gianluca Chiappini, Vincenzo Campanella, and et al. 2020. "Thermoplastic Disks Used for Commercial Orthodontic Aligners: Complete Physicochemical and Mechanical Characterization" Materials 13, no. 10: 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13102386
APA StyleDaniele, V., Macera, L., Taglieri, G., Di Giambattista, A., Spagnoli, G., Massaria, A., Messori, M., Quagliarini, E., Chiappini, G., Campanella, V., Mummolo, S., Marchetti, E., Marzo, G., & Quinzi, V. (2020). Thermoplastic Disks Used for Commercial Orthodontic Aligners: Complete Physicochemical and Mechanical Characterization. Materials, 13(10), 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13102386







