Research and Optimization of Surface Roughness in Milling of SLM Semi-Finished Parts Manufactured by Using the Different Laser Scanning Speed
Abstract
1. Introduction
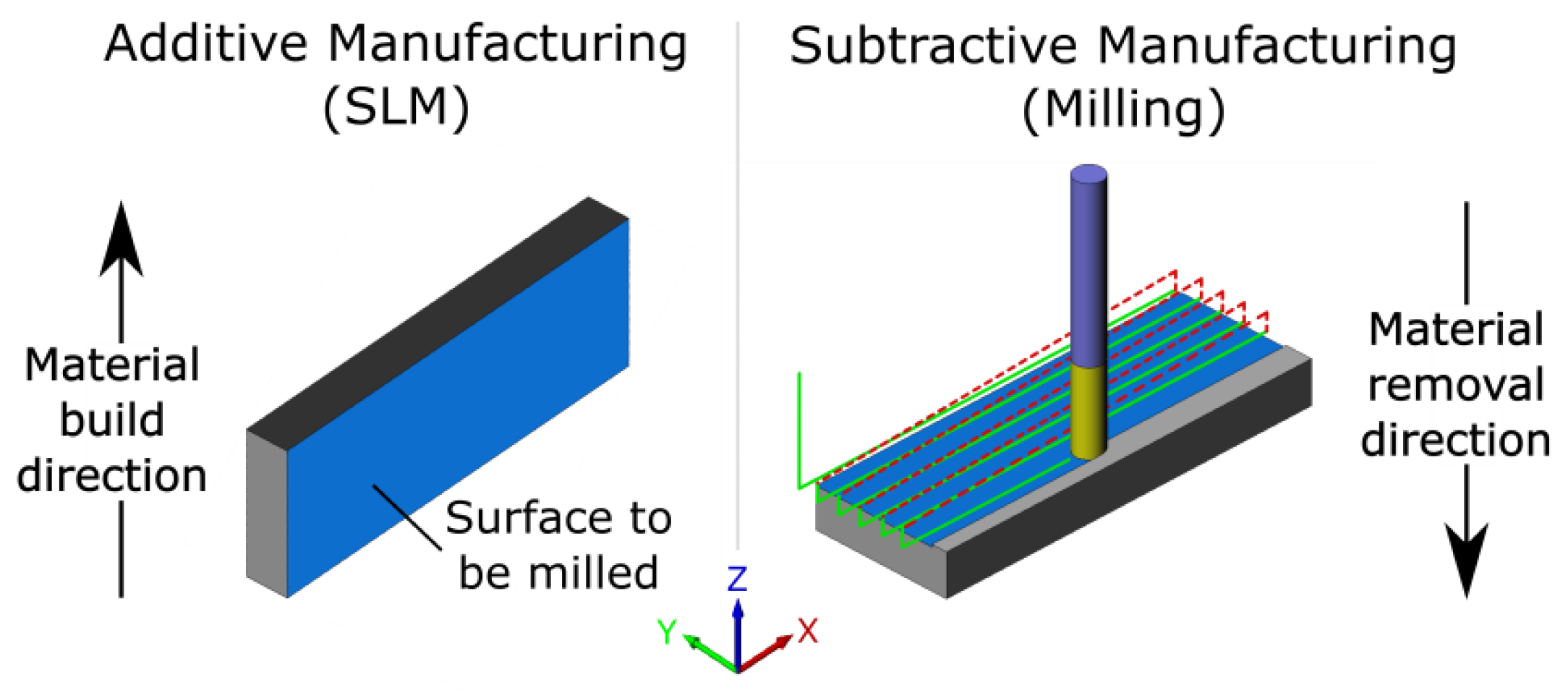
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
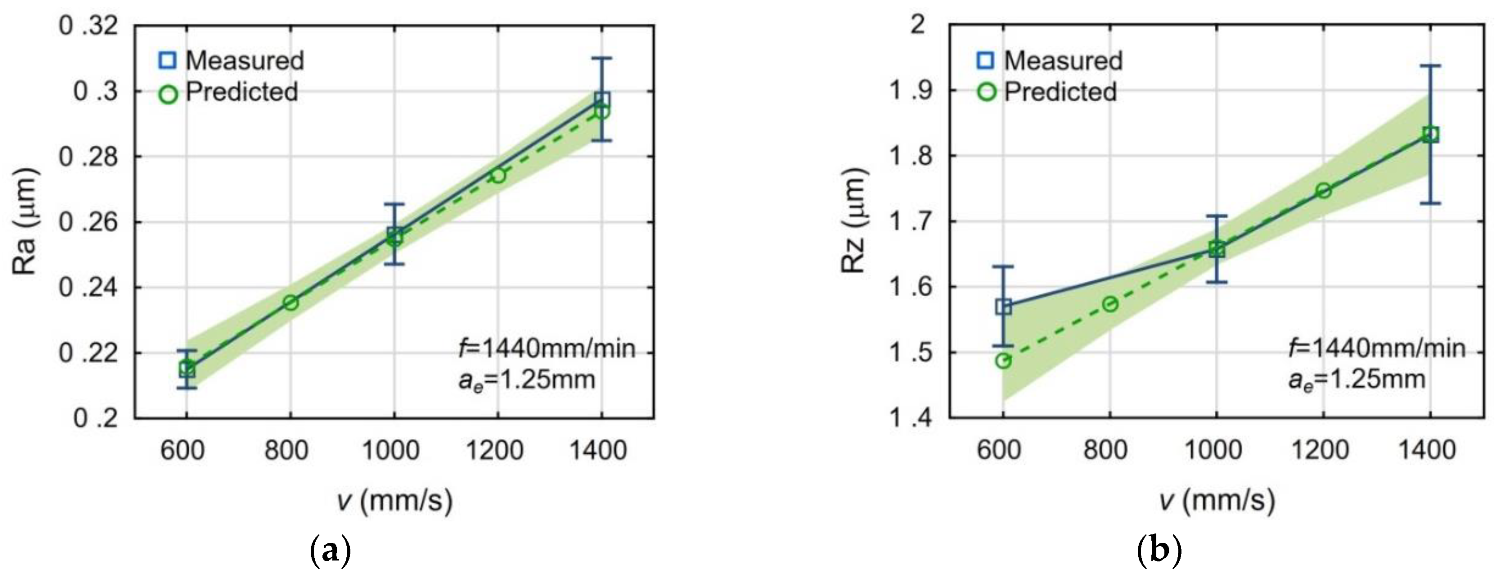
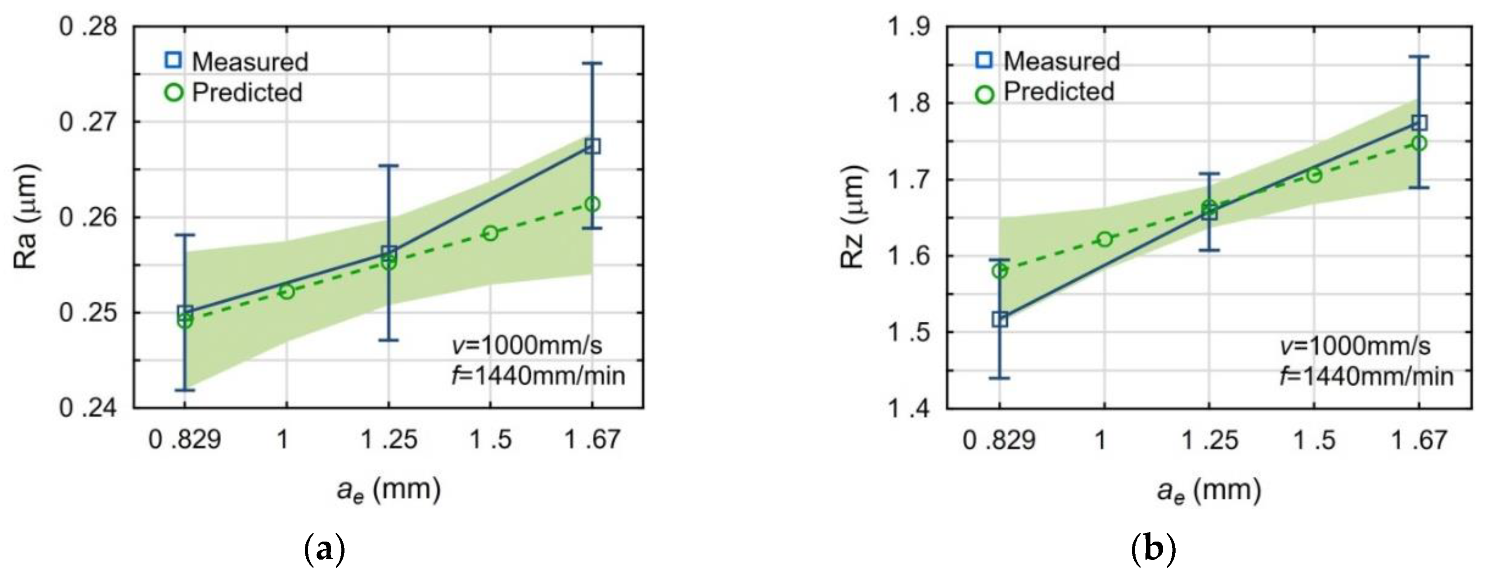
3.1. Impact of the Laser Scanning Speed and Machining Parameters on the Surface Roughness
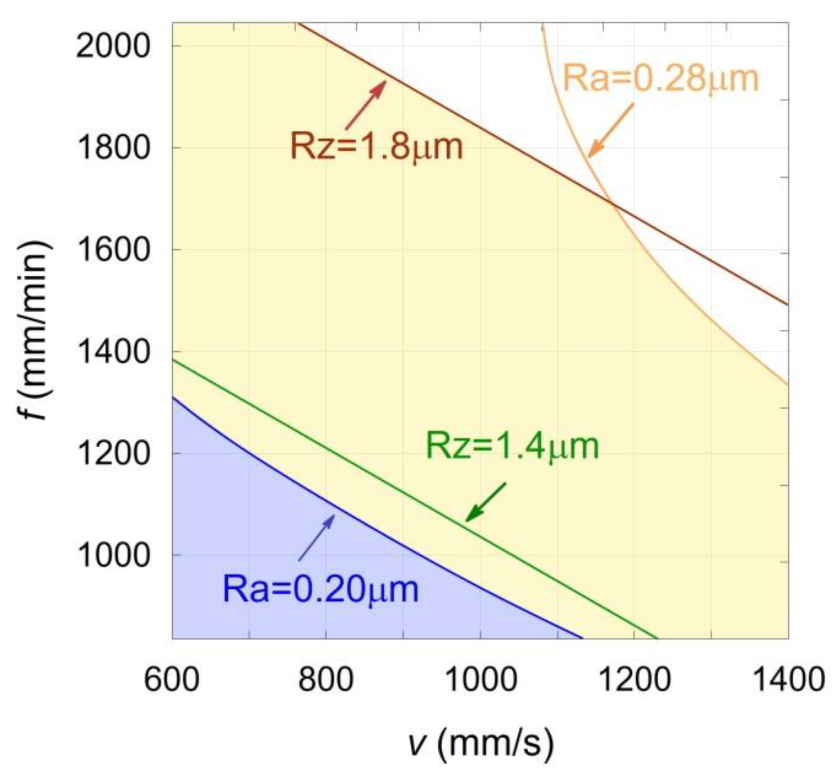
3.2. Application of the Response Surface Methodology for the Optimization of the Analysed Process Parameters
4. Conclusions
- The milling allows the surface roughness of the SLM-manufactured semi-finish parts to be reduced more than 20-fold.
- The impact of the laser scanning speed on the surface roughness of the SLM-manufactured semi-finish parts was observed. The increase of the laser scanning speed in the analyzed range causes a deterioration of the surface roughness of SLM-manufactured semi-finished parts.
- Defects in the internal microstructure of the SLM semi-finished parts manufactured by using high laser scanning speed were observed.
- The impact of the laser scanning speed used in the SLM process on the obtained by milling surface was observed. The milled SLM semi-finish parts made at higher laser scanning speeds have higher surface roughness. It was also observed that the chip adjoining to the rake face of back cutting tooth causes the milled surface damages. This phenomenon intensifies as the laser scanning speed used in the SLM process increases.
- The impact of the studied milling parameters on the milled surface roughness was observed. The surface roughness increases as the feed rate grows. The increase of cutting width also increases the surface roughness, but to a lesser degree than the feed rate increases.
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Tse, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W. Optimization of processing parameters and establishment of a relationship between microstructure and mechanical properties of SLM titanium alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 112, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhao, C.; Escano, L.I.; Young, Z.; Xiong, L.; Fezzaa, K.; Everhart, W.; Brown, B.; Sun, T.; Chen, L. Transient dynamics of powder spattering in laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process revealed by in-situ high-speed high-energy x-ray imaging. Acta Mater. 2018, 151, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairallah, S.A.; Anderson, A.T.; Rubenchik, A.; King, W.E. Laser powder-bed fusion additive manufacturing: Physics of complex melt flow and formation mechanisms of pores, spatter, and denudation zones. Acta Mater. 2016, 108, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.; Pal, D.; Gong, H.; Zeng, K.; Briggs, K.; Patil, N.; Stucker, B. A review of defect modeling in laser material processing. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 14, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Rafi, K.; Gu, H.; Starr, T.; Stucker, B. Analysis of defect generation in Ti-6Al-4V parts made using powder bed fusion additive manufacturing processes. Addit. Manuf. 2014, 1–4, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitz, S.; Uerlich, R.; Bokelmann, T.; Diener, A.; Vietor, T.; Kwade, A. Influence of Powder Deposition on Powder Bed and Specimen Properties. Materials 2019, 12, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Perevoshchikova, N.; Sha, Y.; Wu, X. The Effects of Selective Laser Melting Process Parameters on Relative Density of the AlSi10Mg Parts and Suitable Procedures of the Archimedes Method. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, X. Experimental investigation on selective laser melting of 17-4PH stainless steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 87, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Ke, L.; Zhu, H.; Liao, H.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, X. Influence of processing parameters on selective laser melted SiCp/AlSi10Mg composites: Densification, microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 764, 138155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkovsky, I.; Morozov, Y.; Smurov, I. Nanostructural self-organization under selective laser sintering of exothermic powder mixtures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 5565–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.R.; Richter, H. Modeling of Processing-Induced Pore Morphology in an Additively-Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials 2017, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wu, J. Experimental investigation on densification behavior and surface roughness of AlSi10Mg powders produced by selective laser melting. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 96, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Wei, Z.; Chen, Z.; Du, J.; He, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y. The AlSi10Mg samples produced by selective laser melting: single track, densification, microstructure and mechanical behavior. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 408, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamoun, A.H.; Xue, Y.F.; Elbestawi, M.A.; Veldhuis, S.C. The Effect of Selective Laser Melting Process Parameters on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al6061 and AlSi10Mg Alloys. Materials 2019, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, H.; Gao, M. Effect of processing parameters on solidification defects behavior of laser deposited AlSi10Mg alloy. Vacuum 2019, 167, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, F.; Calignano, F.; Lorusso, M.; Pakkanen, J.; Aversa, A.; Ambrosio, E.P.; Lombardi, M.; Fino, P.; Manfredi, D. On the Selective Laser Melting (SLM) of the AlSi10Mg Alloy: Process, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties. Materials 2017, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struzikiewicz, G.; Zȩbala, W.; Matras, A.; Machno, M.; Ślusarczyk, Ł.; Hichert, S.; Laufer, F. Turning research of additive laser molten stainless steel 316L obtained by 3D printing. Materials 2019, 12, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, A.; Ueda, T.; Furumoto, T.; Hosokawa, A.; Tanaka, R.; Abe, S. Experimental investigation on cutting mechanism of laser sintered material using small ball end mill. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 5680–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaynak, Y.; Kitay, O. The effect of post-processing operations on surface characteristics of 316L stainless steel produced by selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 26, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaynak, Y.; Tascioglu, E. Finish machining-induced surface roughness, microhardness and XRD analysis of selective laser melted Inconel 718 alloy. Procedia CIRP 2018, 71, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, S.; Morandeau, A.; Chalon, F.; Leroy, R. Influence of Finish Machining on the Surface Integrity of Ti6Al4V Produced by Selective Laser Melting. Procedia CIRP 2016, 45, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struzikiewicz, G.; Zębala, W.; Słodki, B. Cutting parameters selection for sintered alloy AlSi10Mg longitudinal turning. Measurement 2019, 138, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, M.; Cabanettes, F.; Kaminski, R.; Valiorgue, F.; Picot, E.; Lefebvre, F.; Grosjean, C.; Rech, J. Influence of the finish cutting operations on the fatigue performance of Ti-6Al-4V parts produced by Selective Laser Melting. Procedia CIRP 2018, 71, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DebRoy, T.; Wei, H.L.; Zuback, J.S.; Mukherjee, T.; Elmer, J.W.; Milewski, J.O.; Beese, A.M.; Wilson-Heid, A.; De, A.; Zhang, W. Additive manufacturing of metallic components—Process, structure and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 92, 112–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| D10 | D50 | D90 |
|---|---|---|
| 21.4 µm | 33.7 µm | 54.0 µm |
| Element | Fe | Si | Mg | Mn | Zn | Cu | Other | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition, (wt.%) | 0.14 | 10.4 | 0.33 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.03 | <0.04 | Balance |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Laser power (W) | 175 |
| Hatching space (μm) | 200 |
| Powder layer thickness (μm) | 20 |
| Scan Strategy | Chessboard |
| Shielding gas | Ar |
| Diameter of laser beam (μm) | 30 |
| Laser wavelength (nm) | 1.070 |
| Chamber temperature (°C) | 26.8 (27% RF) |
| Oxygen level (%) | 0.11 |
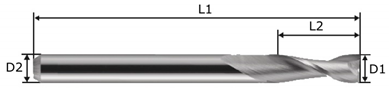 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | D2 | L1 | L2 | Helix Angle |
| 3 mm | 3 mm | 40 mm | 10 mm | 30° |
| Source | Adj SS | DF | Adj MS | F-Value | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v | 0.025450 | 1 | 0.025450 | 144.7667 | 0.000000 |
| v2 | 0.000180 | 1 | 0.000180 | 1.0251 | 0.315513 |
| f | 0.038103 | 1 | 0.038103 | 216.7457 | 0.000000 |
| f2 | 0.002637 | 1 | 0.002637 | 14.9982 | 0.000276 |
| ae | 0.000779 | 1 | 0.000779 | 4.4314 | 0.039625 |
| ae2 | 0.000238 | 1 | 0.000238 | 1.3515 | 0.249785 |
| v·f | 0.000132 | 1 | 0.000132 | 0.7519 | 0.389443 |
| v· ae | 0.000004 | 1 | 0.000004 | 0.0217 | 0.883412 |
| f· ae | 0.000135 | 1 | 0.000135 | 0.7687 | 0.384241 |
| Residual Error | 0.010196 | 58 | 0.000176 | ||
| Total | 0.077778 | 67 |
| Source | Adj SS | DF | Adj MS | F-Value | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v | 0.493185 | 1 | 0.493185 | 37.6595 | 0.000000 |
| v2 | 0.000093 | 1 | 0.000093 | 0.0071 | 0.933264 |
| f | 1.924128 | 1 | 1.924128 | 146.9261 | 0.000000 |
| f2 | 0.020342 | 1 | 0.020342 | 1.5533 | 0.217653 |
| ae | 0.145135 | 1 | 0.145135 | 11.0825 | 0.001519 |
| ae2 | 0.030916 | 1 | 0.030916 | 2.3607 | 0.129860 |
| v·f | 0.011284 | 1 | 0.011284 | 0.8617 | 0.357123 |
| v·ae | 0.020938 | 1 | 0.020938 | 1.5988 | 0.211132 |
| f·ae | 0.004389 | 1 | 0.004389 | 0.3352 | 0.564870 |
| Residual Error | 0.759561 | 58 | 0.013096 | ||
| Total | 3.462712 | 67 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matras, A. Research and Optimization of Surface Roughness in Milling of SLM Semi-Finished Parts Manufactured by Using the Different Laser Scanning Speed. Materials 2020, 13, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010009
Matras A. Research and Optimization of Surface Roughness in Milling of SLM Semi-Finished Parts Manufactured by Using the Different Laser Scanning Speed. Materials. 2020; 13(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatras, Andrzej. 2020. "Research and Optimization of Surface Roughness in Milling of SLM Semi-Finished Parts Manufactured by Using the Different Laser Scanning Speed" Materials 13, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010009
APA StyleMatras, A. (2020). Research and Optimization of Surface Roughness in Milling of SLM Semi-Finished Parts Manufactured by Using the Different Laser Scanning Speed. Materials, 13(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010009





