Properties of Undoped Few-Layer Graphene-Based Transparent Heaters
Abstract
1. Introduction
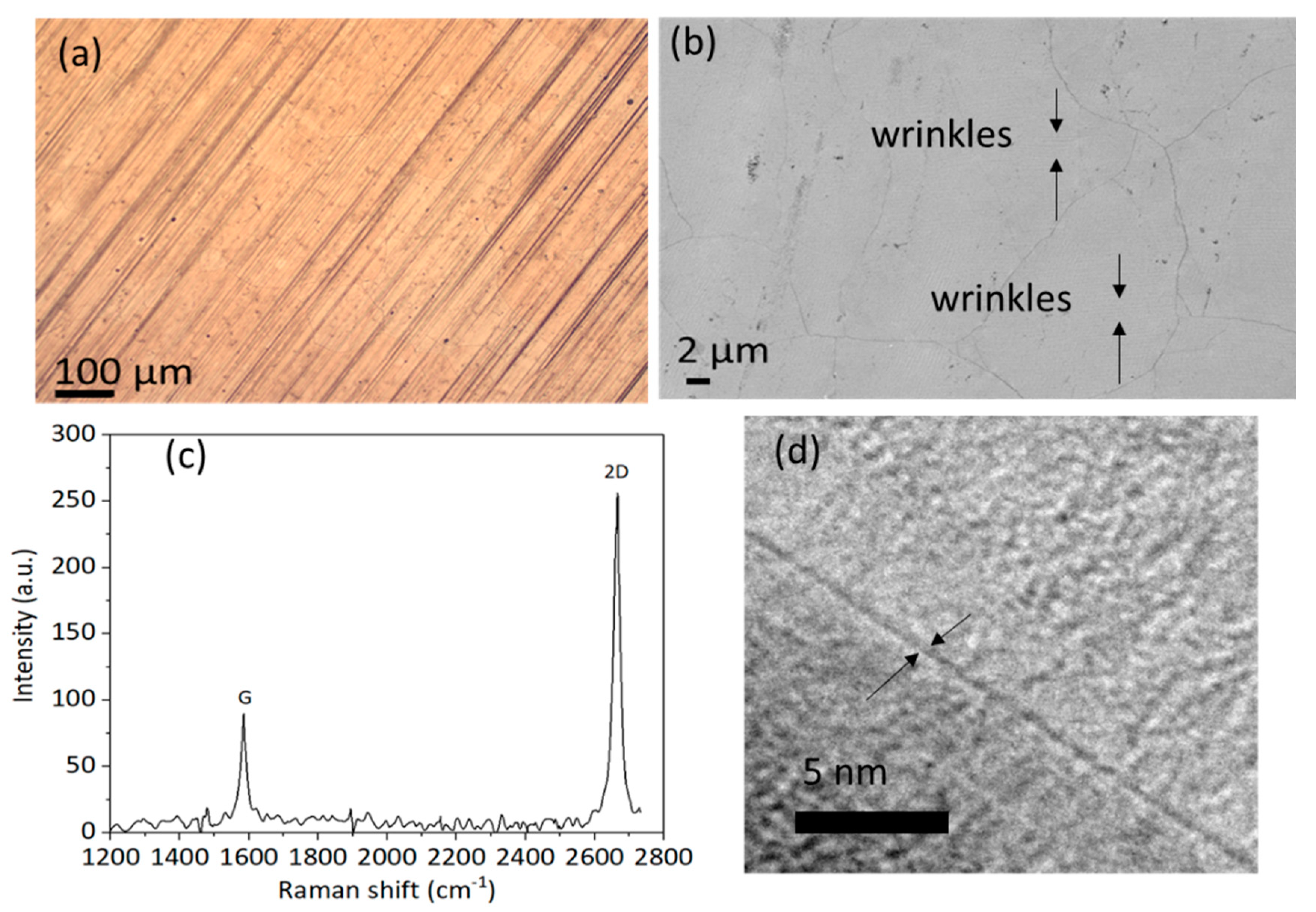
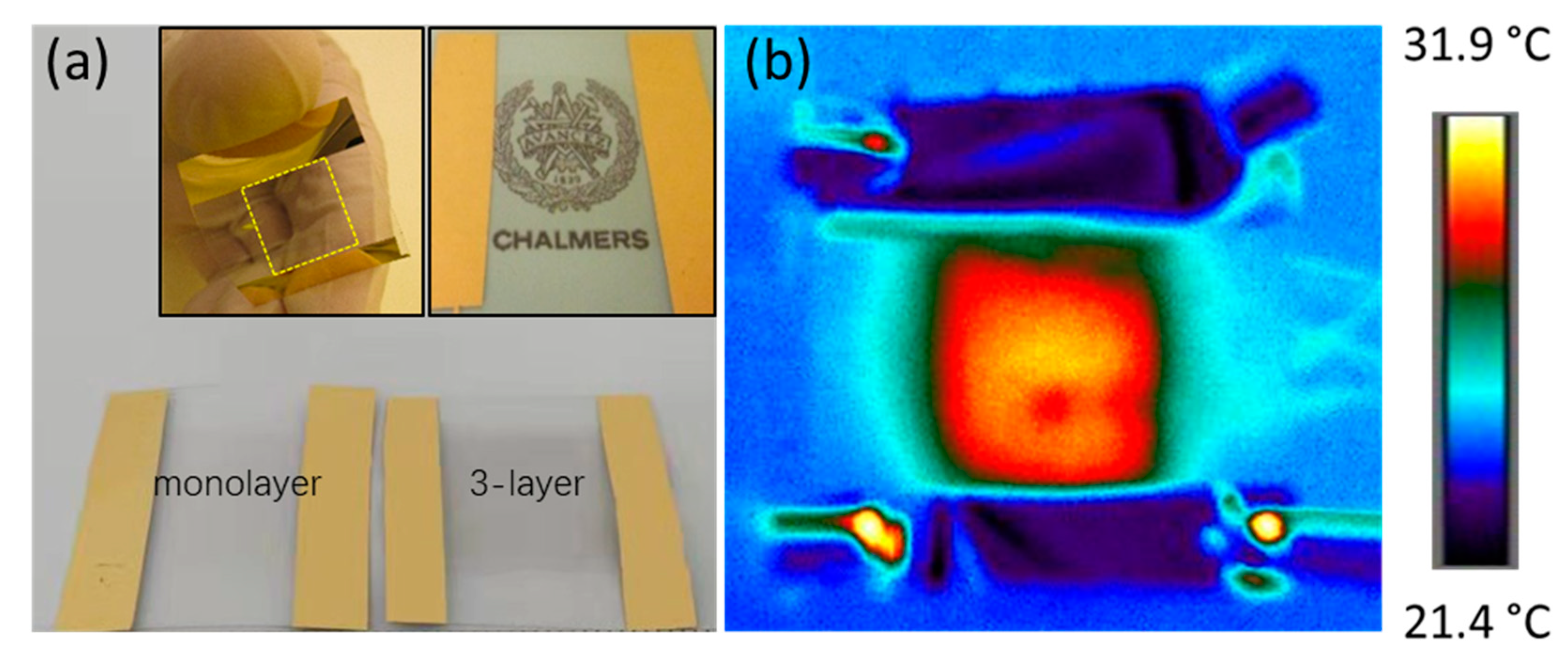
2. Fabrication and Evaluation of Graphene-Based Heater Samples
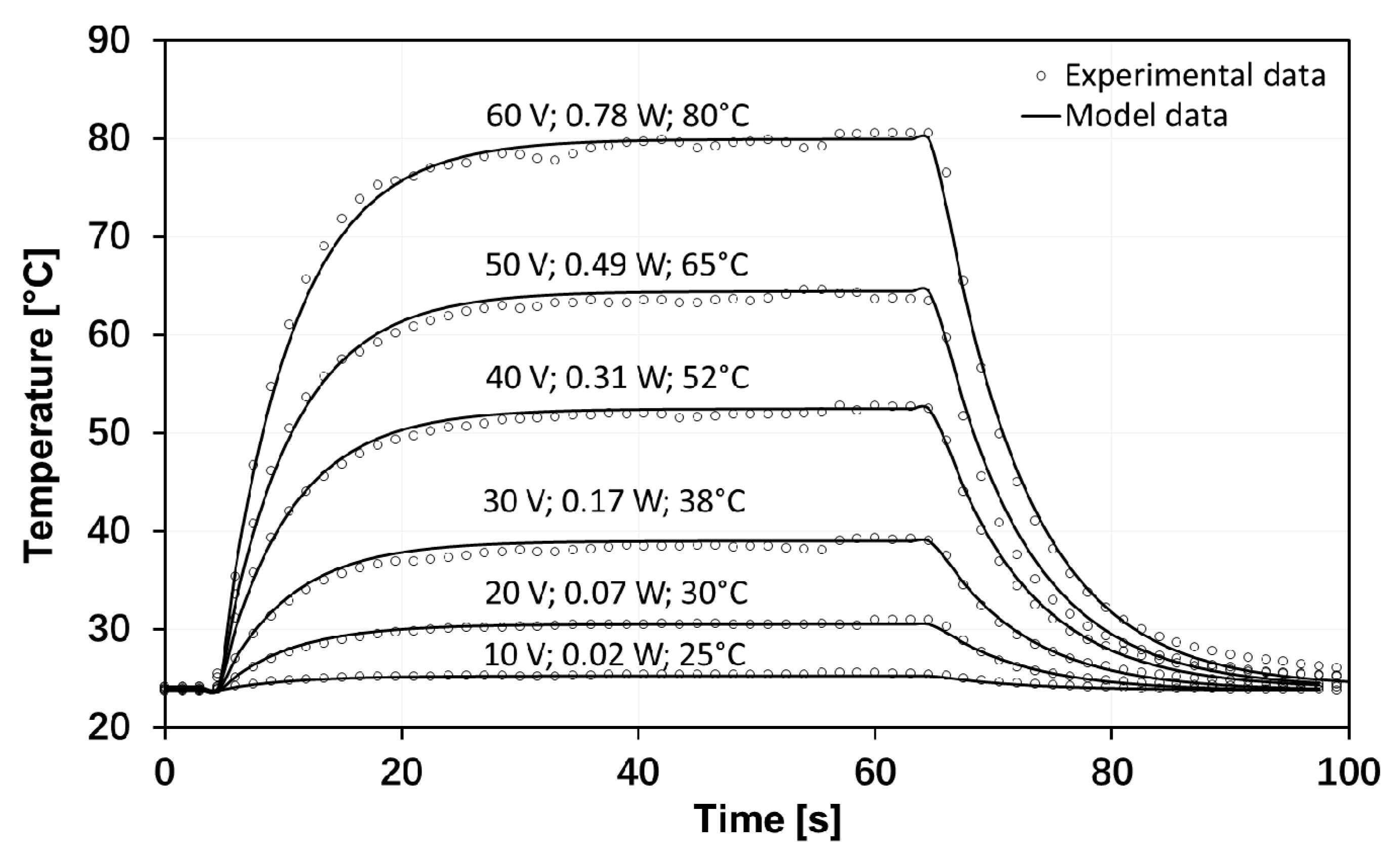
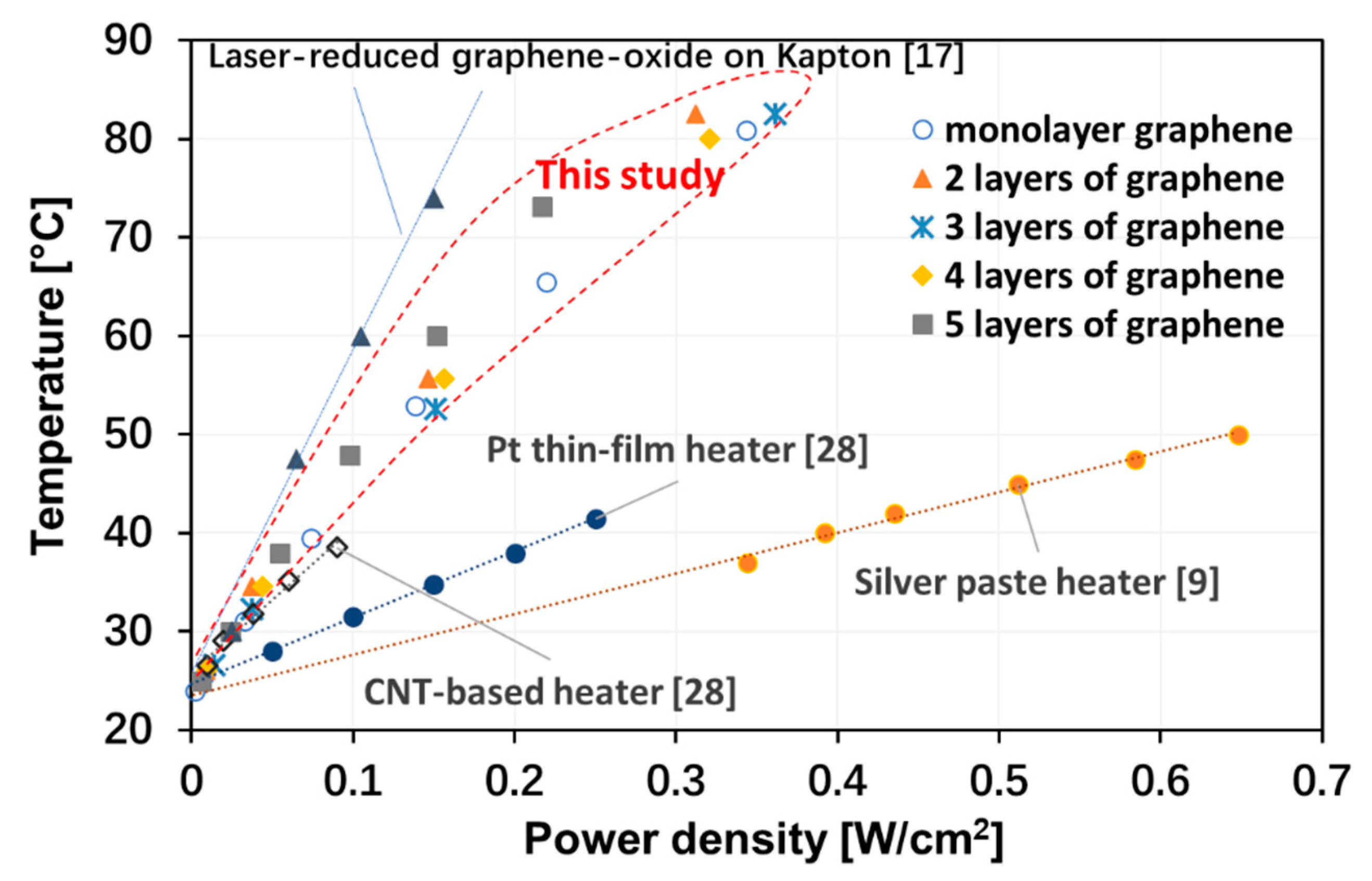
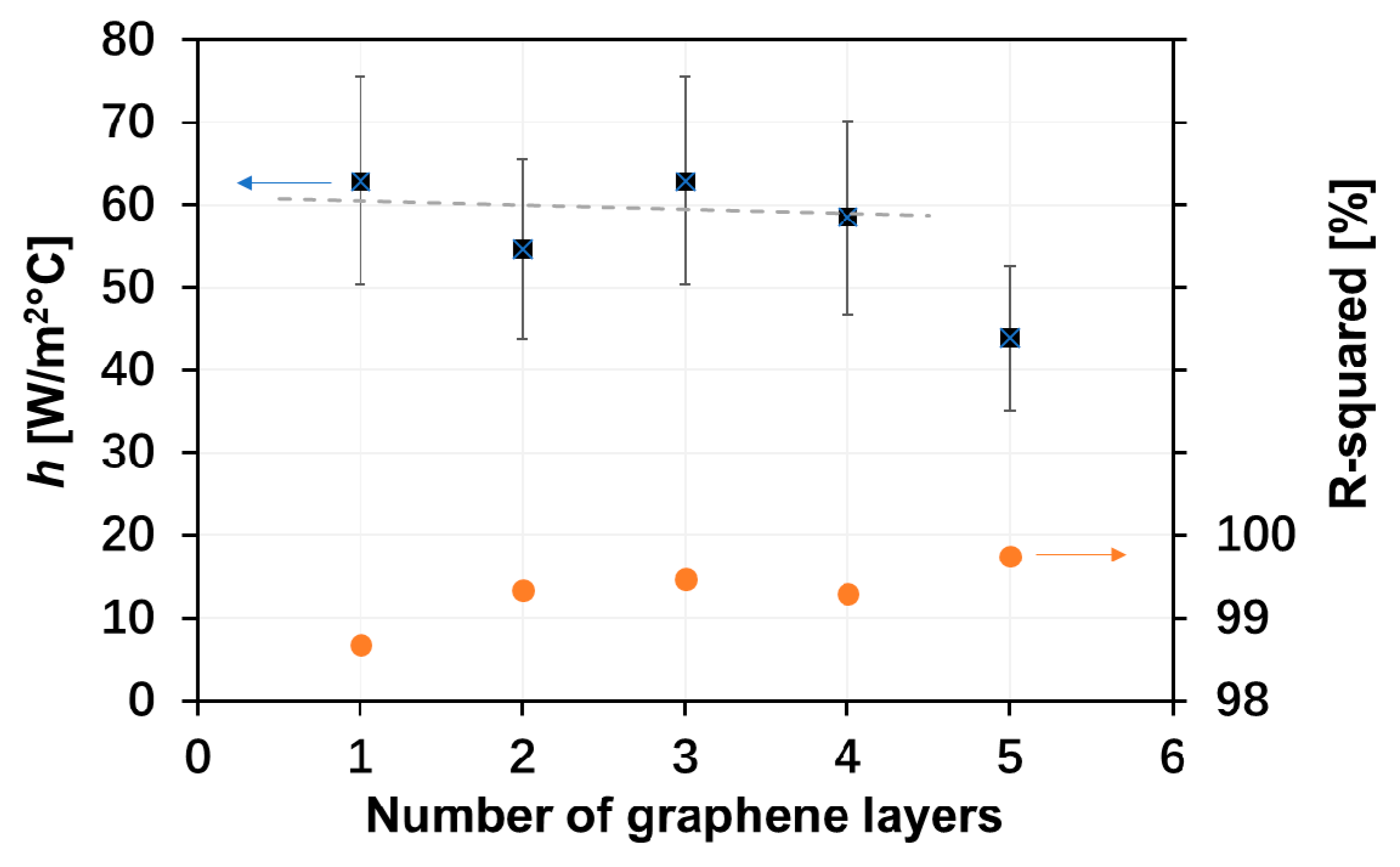
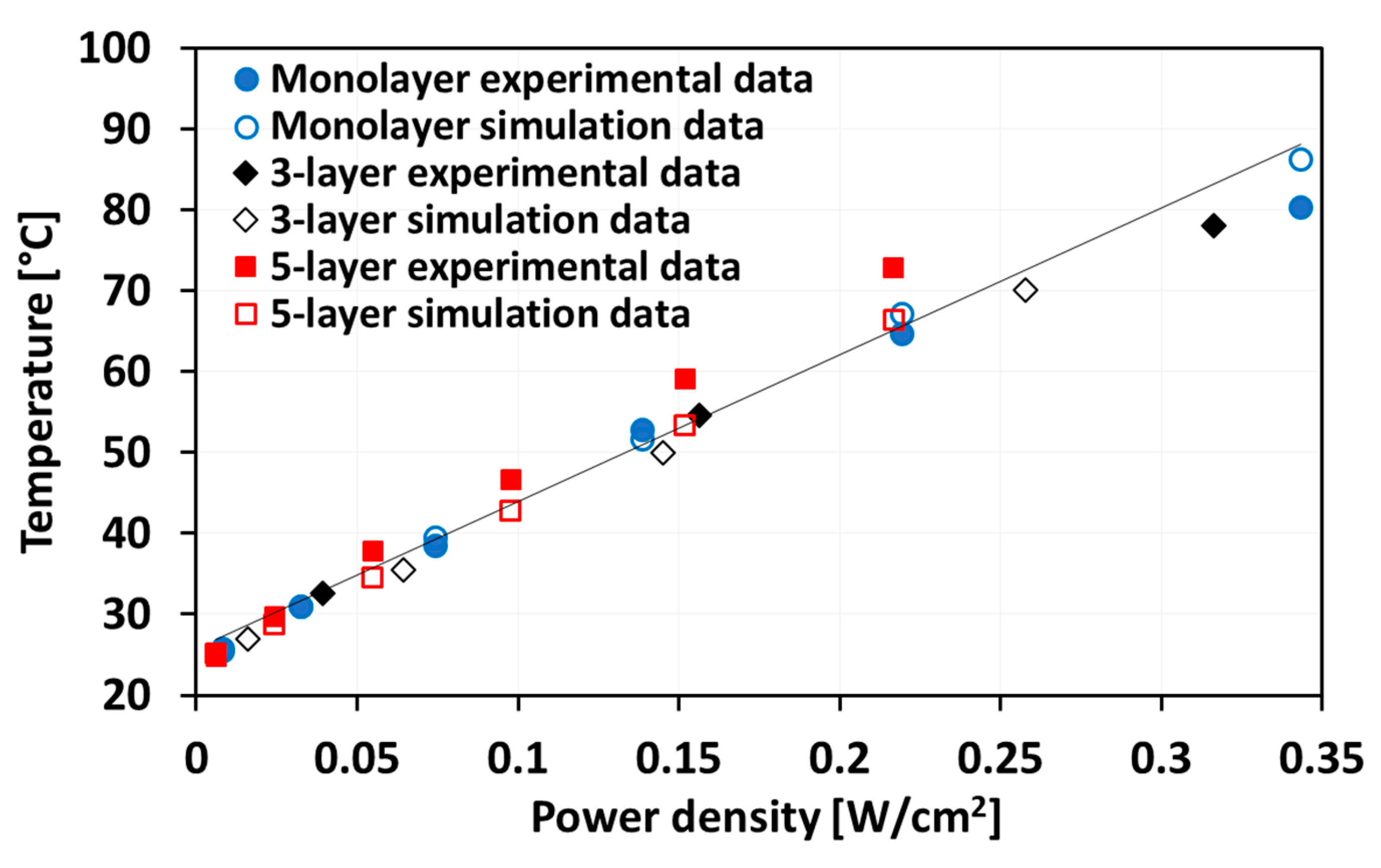
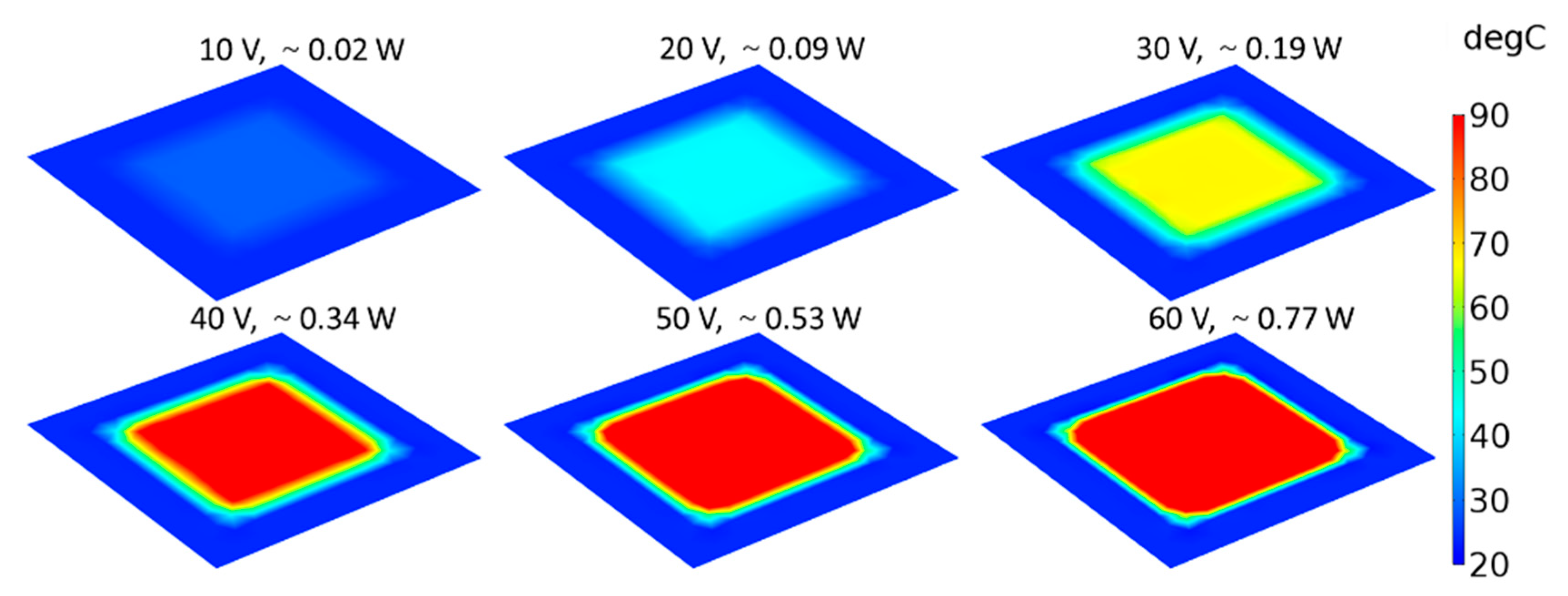
3. Electrothermal Performance of Graphene-Based Heaters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mo, Y.W.; Okawa, Y.; Tajima, M.; Nakai, T.; Yoshiike, N.; Natukawa, K. Micro-machined gas sensor array based on metal film micro-heater. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2001, 79, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, L.A.; Jiang, K.L.; Fan, S.S. Carbon-Nanotube-film microheater on a polyethylene terephthalate substrate and its application in thermochromic displays. Small 2011, 7, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.J.; Lim, S.C.; Han, G.H.; Jo, Y.W.; Doung, D.L.; Kim, E.S.; Chae, S.J.; Huy, T.Q.; Luan, N.V.; Lee, Y.H. Heat dissipation of transparent graphene defoggers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4819–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiruthika, S.; Gupta, R.; Kulkarni, G.U. Large area defrosting windows based on electrothermal heating of highly conducting and transmitting Ag wire mesh. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 49745–49751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.J. ITO films prepared by long-throw magnetron sputtering without oxygen partial pressure. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Higgins, T.M.; Lyons, P.E.; Doherty, E.M.; Nirmalraj, P.N.; Blau, W.J.; Boland, J.J.; Coleman, J.N. Silver nanowire networks as flexible, transparent, conducting films: Extremely high DC to optical conductivity ratios. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celle, C.; Mayousse, C.; Moreau, E.; Basti, H.; Carella, A.; Simonato, J.P. Highly flexible transparent film heaters based on random networks of silver nanowires. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.L.; He, W.W.; Wang, K.; Ran, Y.X.; Ye, C.H. Thermal response of transparent silver nanowire/PEDOT:PSS film heaters. Small 2014, 10, 4951–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.H.; Song, J.W.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Park, J.K.; Oh, S.K.; Han, C.S. Transparent film heater using single-walled carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 4284–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.S.; Jeon, S.K.; Nahm, S.H. The manufacture of a transparent film heater by spinning multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2011, 49, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Zhu, L.J.; Jeong, D.J.; Chun, K.; Bang, Y.Y.; Kim, S.R.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, S.K. Transparent flexible heater based on hybrid of carbon nanotubes and silver nanowires. Carbon 2013, 63, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotin, K.I.; Sikes, K.J.; Jiang, Z.; Klima, M.; Fudenberg, G.; Hone, J.; Kim, P.; Stormer, H.L. Ultrahigh electron mobility in suspended graphene. Solid State Commun. 2008, 146, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasher, R. Graphene spreads the heat. Science 2010, 328, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, S.P.; Hernandez, Y.; Feng, X.L.; Mullen, K. Graphene as transparent electrode material for organic electronics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2779–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Fatemi, V.; Fang, S.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Kaxiras, E.; Jarillo-Herrero, P. Unconventional superconductivity in magic-angle graphene superlattices. Nature 2018, 556, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, D.; Huang, Y.; Huang, L.; Liang, J.J.; Ma, Y.F.; Chen, Y.S. Flexible and transparent electrothermal film heaters based on graphene materials. Small 2011, 7, 3186–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, F.J.; Rivadeneyra, A.; Ortiz-Gomez, I.; Salinas, A.; Godoy, A.; Morales, D.P.; Rodriguez, N. Inexpensive graphene oxide heaters lithographed by laser. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobinger, M.R.; Romero, F.J.; Salinas-Castillo, A.; Becherer, M.; Lugli, P.; Morales, D.P.; Rodriguez, N.; Rivadeneyra, A. Flexible and robust laser-induced graphene heaters photothermally scribed on bare polyimide substrates. Carbon 2019, 144, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, R.; Barg, S.; Miranda, M.; Anthony, D.B.; Bawaked, S.M.; Mokhtar, M.; Al-Thabaiti, S.A.; Basahel, S.N.; Saiz, E.; Shaffer, M.S.P. Joule heating characteristics of emulsion-templated graphene aerogels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.; Xu, X.; Park, J.S.; Zheng, Y.; Balakrishnan, J.; Lei, T.; Kim, H.R.; Song, Y.I.; et al. Roll-to-roll production of 30-inch graphene films for transparent electrodes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, S.K.; Bae, S.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, J.B.; Hong, B.H. High-performance graphene-based transparent flexible heaters. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5154–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Yuen, M.M.F.; Liu, J. Thermal chemical vapor deposition grown graphene heat spreader for thermal management of hot spots. Carbon 2013, 61, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Edwards, M.; Jeppson, K.; Ye, L.; Liu, J. Chemical vapor deposition grown graphene on Cu-Pt alloys. Mater. Lett. 2017, 193, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, W.; An, J.; Kim, S.; Nah, J.; Yang, D.; Piner, R.; Velamakanni, A.; Jung, I.; Tutuc, E.; et al. Large-area synthesis of high-quality and uniform graphene films on copper foils. Science 2009, 324, 1312–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Meyer, J.C.; Scardaci, V.; Casiraghi, C.; Lazzeri, M.; Mauri, F.; Piscanec, S.; Jiang, D.; Novoselov, K.S.; Roth, S.; et al. Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 187401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.R.; Blake, P.; Grigorenko, A.N.; Novoselov, K.S.; Booth, T.J.; Stauber, T.; Peres, N.M.R.; Geim, A.K. Fine structure constant defines visual transparency of graphene. Science 2008, 320, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.Y.; Yu, X.X.; Zheng, H.M.; Jin, H.B.; Wang, L.; Cao, M.S. Temperature- and thickness-dependent electrical conductivity of few-layer graphene and graphene nanosheets. Phys. Lett. A 2015, 379, 2245–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.J.; Kim, T.; Seo, S.M.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, Y.H. Thickness-dependent thermal resistance of a transparent glass heater with a single-walled carbon nanotube coating. Carbon 2011, 49, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrina, S.; Kotchetkov, D.; Balandin, A.A. Heat removal in silicon-on-insulator integrated circuits with graphene lateral heat spreaders. IEEE Electr. Device Lett. 2009, 30, 1281–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.F.; Zeng, M.Q.; Wu, Q.; Chen, L.F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Eckert, J.; Rummeli, M.H.; Fu, L. Direct growth of ultrafast transparent single-layer graphene defoggers. Small 2015, 11, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Kim, M.; Campbell, D.; Alsalman, H.A.; Kwak, J.Y.; Shivaraman, S.; Woll, A.R.; Singh, A.K.; Hennig, R.G.; Gorantla, S.; et al. van der Waals epitaxial growth of graphene on sapphire by chemical vapor deposition without a metal catalyst. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, W.; Park, J.; Yoon, T.; Kim, T.S.; Kim, S.; Han, C.S. Prevention of water permeation by strong adhesion between graphene and SiO2 substrate. Small 2014, 10, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Tan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jeppson, K.; Wei, B.; Liu, J. Properties of Undoped Few-Layer Graphene-Based Transparent Heaters. Materials 2020, 13, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010104
Zhang Y, Liu H, Tan L, Zhang Y, Jeppson K, Wei B, Liu J. Properties of Undoped Few-Layer Graphene-Based Transparent Heaters. Materials. 2020; 13(1):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010104
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yong, Hao Liu, Longwang Tan, Yan Zhang, Kjell Jeppson, Bin Wei, and Johan Liu. 2020. "Properties of Undoped Few-Layer Graphene-Based Transparent Heaters" Materials 13, no. 1: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010104
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liu, H., Tan, L., Zhang, Y., Jeppson, K., Wei, B., & Liu, J. (2020). Properties of Undoped Few-Layer Graphene-Based Transparent Heaters. Materials, 13(1), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010104




