Design and Fabrication of Random Metal Foam Structures for Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
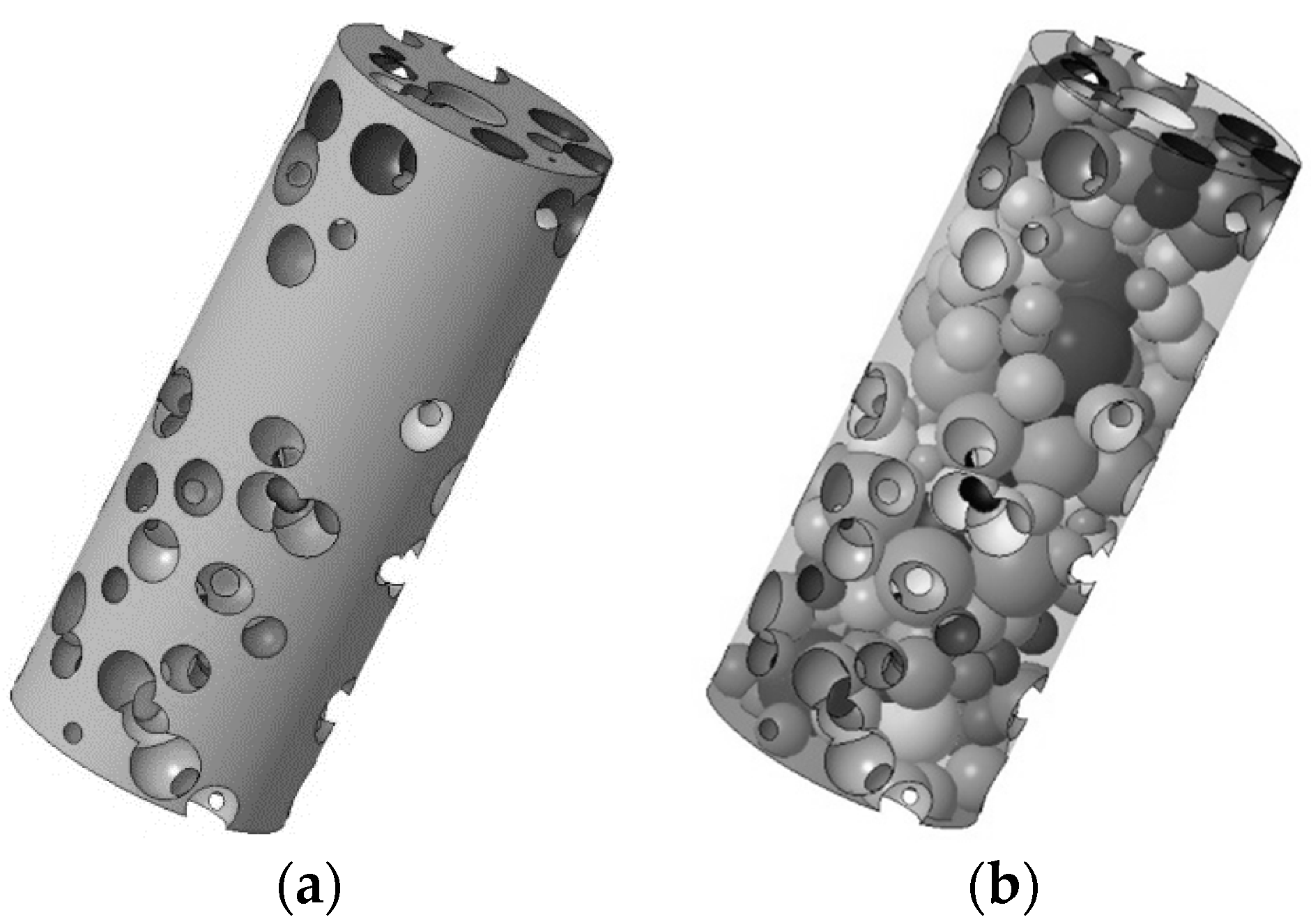
2.1. Design of a Random Foam
- Interconnection of inner pores is mandatory.
- A minimum solid fraction preventing the collapse of the structure must be offered at any layer.
- The wall thickness must be larger with respect to the effective melting diameter.
2.1.1. Generating the Solid Model
2.1.2. Generating the STL File
2.1.3. Slicing the Model
2.2. Manufacturing of the Foams
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Modelling of a Cylindrical Random Pore Foam
3.2. Building of a Cylindrical Random Pore Foam
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khoda, A.K.; Ozbolat, I.T.; Koc, B. Designing heterogeneous porous tissue scaffolds for additive manufacturing processes. Comput. Aided Des. 2013, 45, 1507–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmelmann, C.; Sander, P.; Kranz, J.; Wycisk, E. Laser additive manufacturing and bionics: Redefining lightweight design. Phys. Procedia 2011, 12, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Lee, K.; Shim, D. Effects of process parameters on properties of porous foams formed by laser-assisted melting of steel powder (AISI P21)/foaming agent (ZrH2) mixture. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 98, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiazzo, F.; Campanelli, S.; Cardaropoli, F.; Contuzzi, N.; Sergi, V.; Ludovico, A. Manufacturing and characterization of similar to foam steel components processed through selective laser melting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, D. Computer-aided design for Additive Manufacturing of cellular structures. Comput. Aided Des. Appl. 2007, 4, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usera, D.; Alfieri, V.; Caiazzo, F.; Argenio, P.; Corrado, G.; Ares, E. Redesign and manufacturing of a metal towing hook via laser additive manufacturing with powder bed. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 13, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syam, W.; Jianwei, W.; Zhao, B.; Maskery, I.; Elmadih, W.; Leach, R. Design and analysis of strut-based lattice structures for vibration isolation. Precis. Eng. 2018, 52, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiazzo, F.; Cardaropoli, F.; Alfieri, V.; Sergi, V.; Cuccaro, L. Experimental analysis of Selective Laser Melting process for Ti-6Al-4V turbine blade manufacturing. In Proceedings of the XIX International Symposium on High-Power Laser Systems and Applications 2012, Istanbul, Turkey, 10–14 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Shen, J.; Zhou, S.; Huang, X.; Xie, Y. Design of lattice structures with controlled anisotropy. Mater. Des. 2016, 93, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Tong, L.; Steven, G.P. Behaviour of 3D orthogonal woven CFRP composites, part II: FEA and analytical modeling approaches. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2000, 31, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, C. Benefits of metal foams and developments in modelling techniques to assess their materials behaviour: A review. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2012, 28, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chougrani, L.; Pernot, J.; Véron, P.; Abed, S. Lattice structure lightweight triangulation for Additive Manufacturing. Comput. Aided Des. 2017, 90, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, P.; West, T.B.; Coward, S.; Notarberardino, B.; Walker, B.; Abdul-Aziz, A. An efficient approach to converting three-dimensional image data into highly accurate computational models. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2008, 366, 3155–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, L. Constrained Delaunay Triangulations. Algorithmica 1989, 4, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Eifert, H.; Banhart, J.; Baumeister, J. Metal foaming by a powder metallurgy method: Production, properties and applications. Mater. Res. Innov. 1998, 2, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; Byun, J. Production processes of porous metals and their applications. Korean J. Mater. Res. 2015, 25, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T.; Aoki, T.; Nakajima, H. Fabrication of lotus-type porous stainless steel by continuous zone melting technique and mechanical property. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2005, 36, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiazzo, F.; Alfieri, V. Laser-aided Directed Energy Deposition of steel powder over flat surfaces and edges. Materials 2018, 11, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calignano, F. Design optimization of supports for overhanging structures in aluminum and titanium alloys by selective laser melting. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szilvśi-Nagy, M.; Mátyási, G. Analysis of STL files. Math. Comput. Model. 2003, 38, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, M.; Gross, M.; Kobbelt, L. Efficient simplification of point-sampled surfaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE Visualization 2002, Boston, MA, USA, 28–29 October 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Koc, B.; Ma, Y.; Lee, Y. Smoothing STL files by Max-Fit biarc curves for Rapid Prototyping. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2000, 6, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiazzo, F.; Alfieri, V.; Corrado, G.; Argenio, P. Laser powder-bed fusion of Inconel 718 to manufacture turbine blades. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 4023–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, H.; Ashrafizadeh, F.; Hosseini, S.; Ghomashchi, R.; Liu, R. Characterization of simultaneous aged and plasma nitrided 17-4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2017, 133, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Factor | Value |
|---|---|
| Laser power | 195 W |
| Scanning speed | 0.75 m/s |
| Hatch spacing | 100 μm |
| Scan length | 20 mm |
| Layer thickness | 20 μm |
| Nominal (mm) | Actual (mm) | Mismatch (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.46 | 0.51 | 8.9 |
| 1.81 | 1.97 | 8.8 |
| 2.62 | 2.71 | 3.2 |
| 2.87 | 2.91 | 1.4 |
| 2.88 | 2.98 | 3.6 |
| 2.91 | 3.07 | 5.3 |
| 3.51 | 3.79 | 8.1 |
| 4.13 | 4.12 | 0.0 |
| 4.37 | 4.45 | 1.8 |
| 4.38 | 4.32 | 1.4 |
| 4.81 | 4.92 | 2.2 |
| 6.00 | 6.17 | 2.8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Contuzzi, N.; Campanelli, S.L.; Caiazzo, F.; Alfieri, V. Design and Fabrication of Random Metal Foam Structures for Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Materials 2019, 12, 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081301
Contuzzi N, Campanelli SL, Caiazzo F, Alfieri V. Design and Fabrication of Random Metal Foam Structures for Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Materials. 2019; 12(8):1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081301
Chicago/Turabian StyleContuzzi, Nicola, Sabina Luisa Campanelli, Fabrizia Caiazzo, and Vittorio Alfieri. 2019. "Design and Fabrication of Random Metal Foam Structures for Laser Powder Bed Fusion" Materials 12, no. 8: 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081301
APA StyleContuzzi, N., Campanelli, S. L., Caiazzo, F., & Alfieri, V. (2019). Design and Fabrication of Random Metal Foam Structures for Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Materials, 12(8), 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081301





