Influence of Scanning Speed on Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladded Fe-Based Amorphous Coatings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
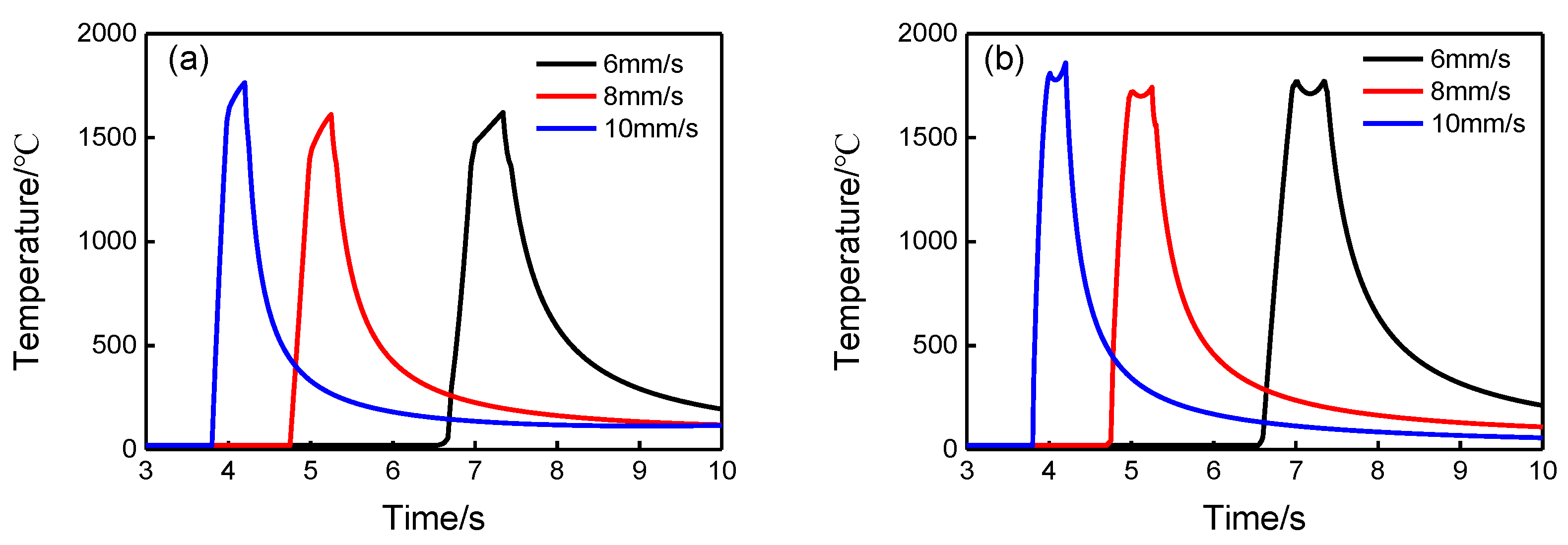
2.2. Laser Cladding
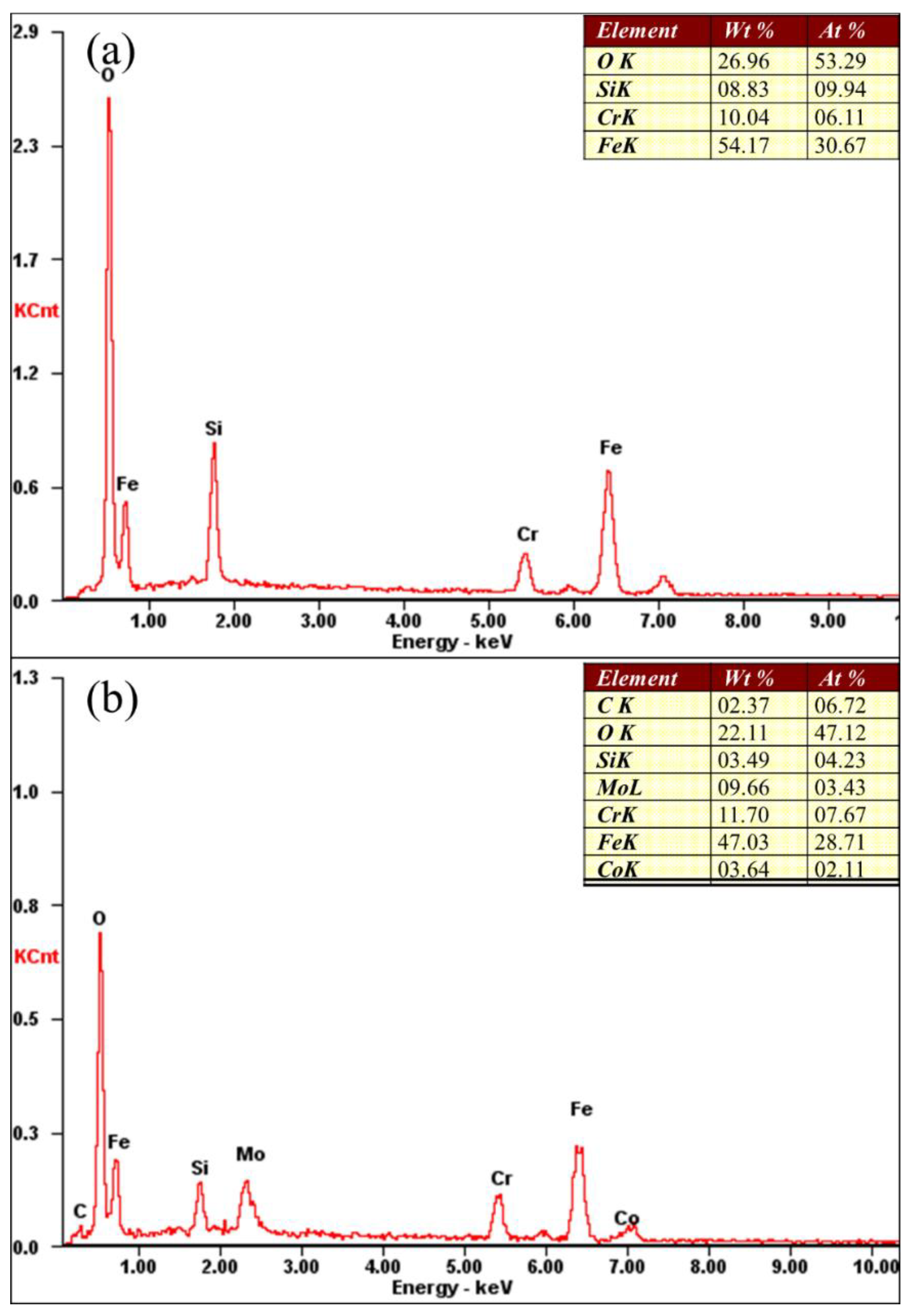
2.3. Microanalysis
2.4. Microhardness and Tribological Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phases
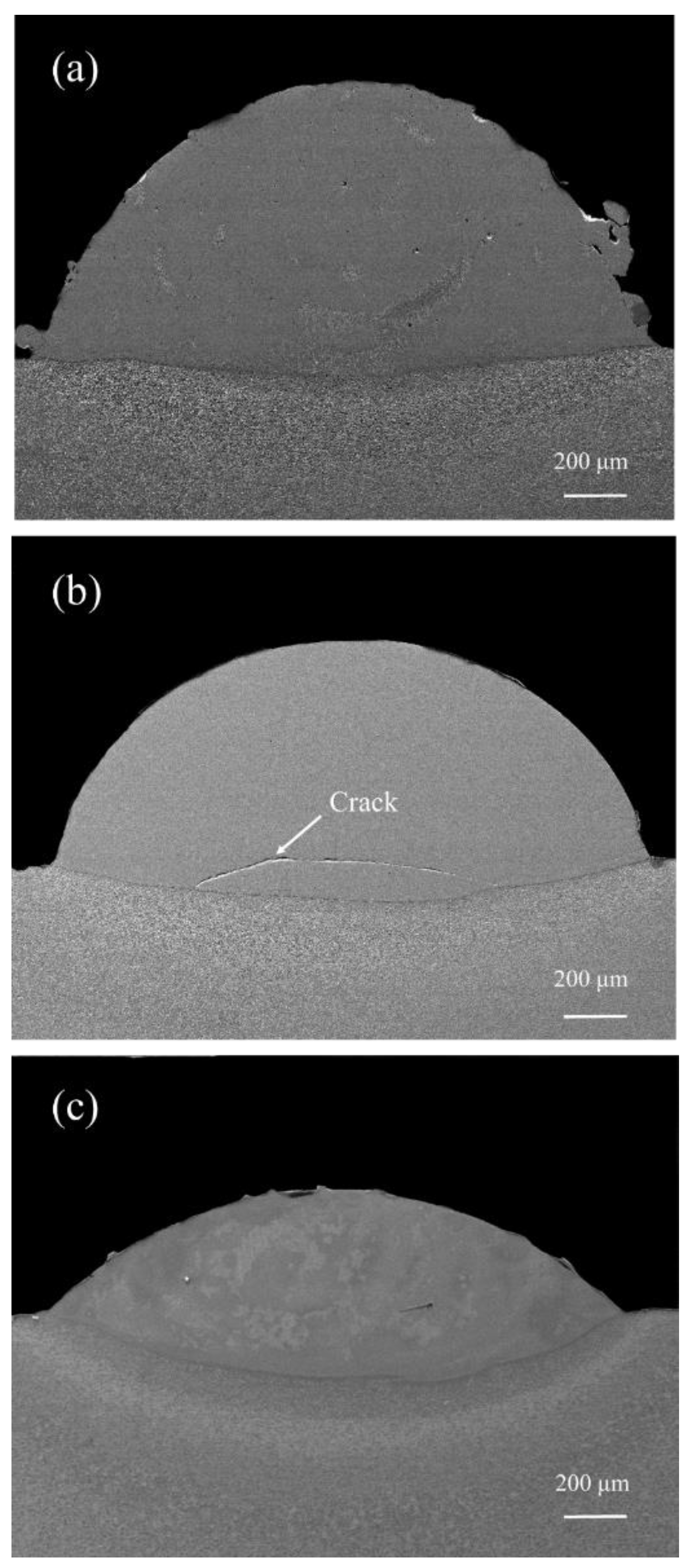
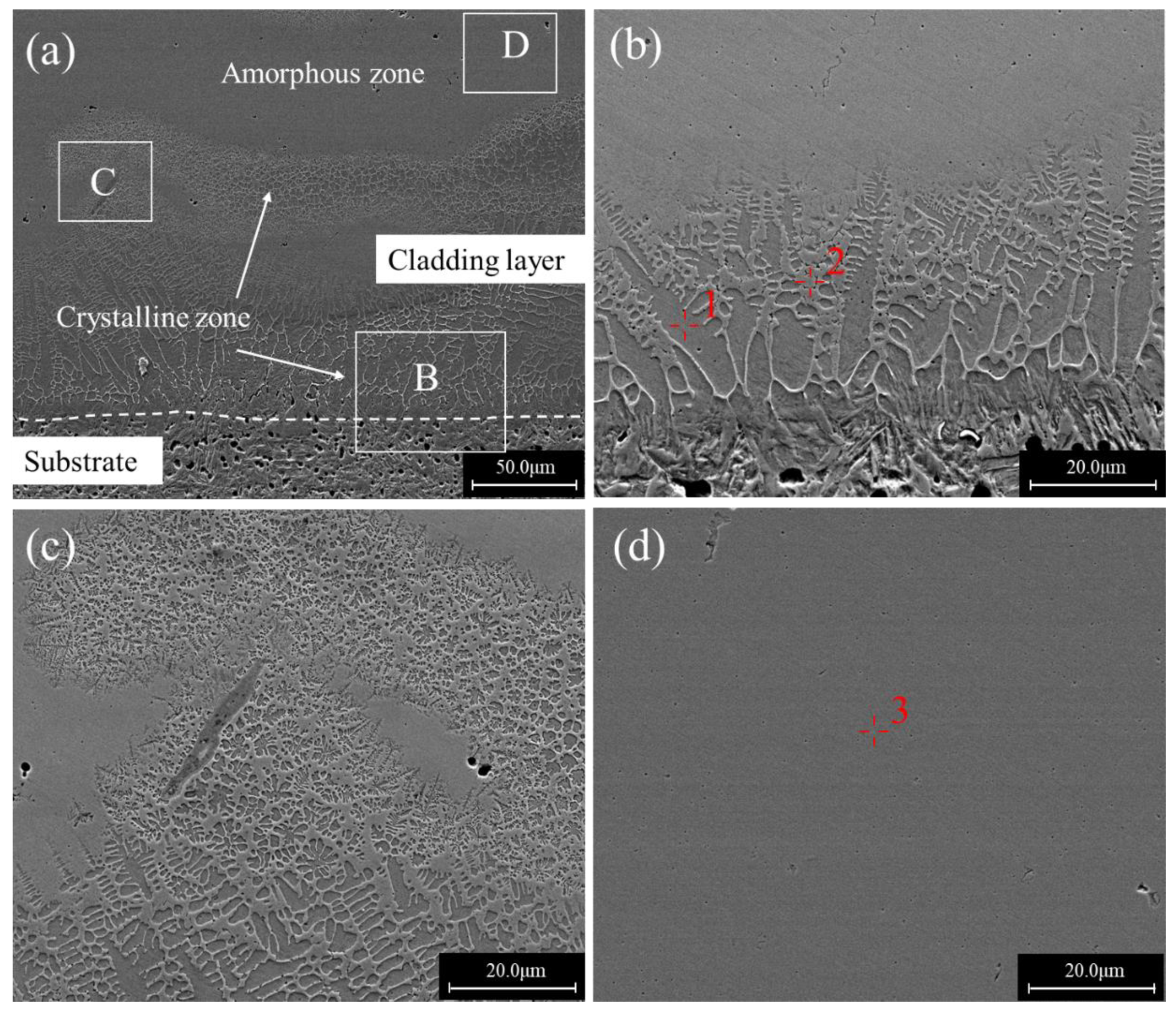
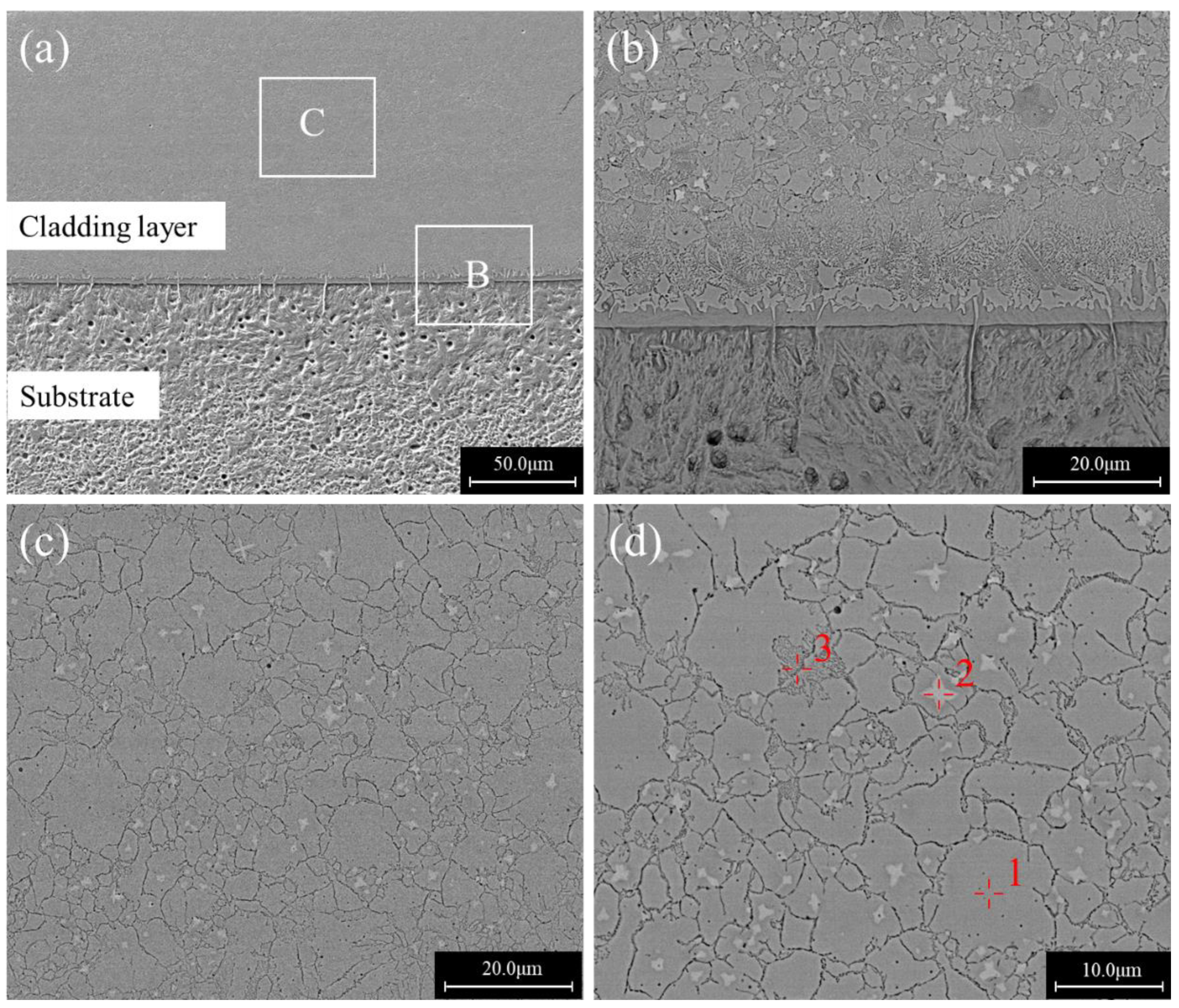
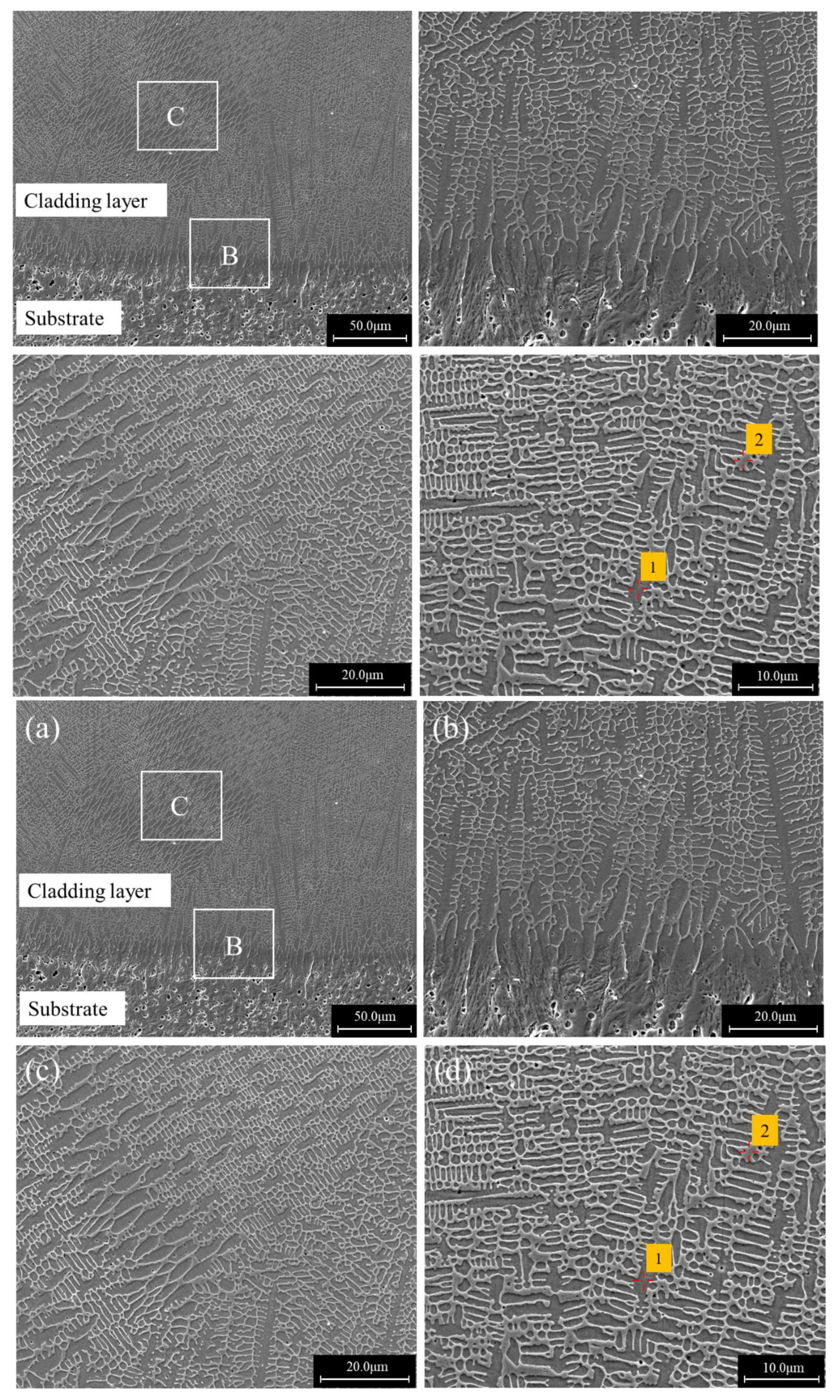
3.2. Geometrical Morphologies and Microstructures
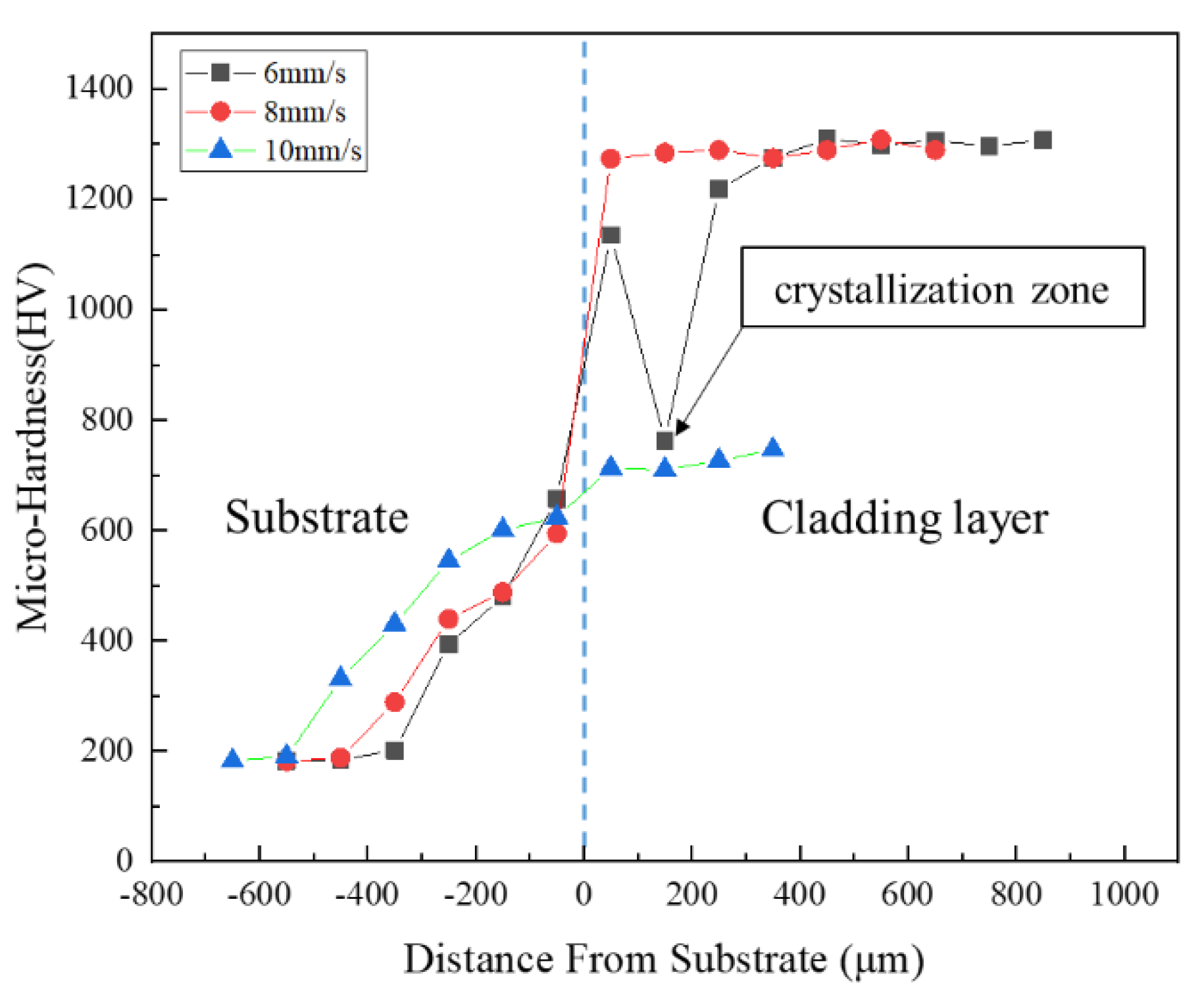
3.3. Microhardness
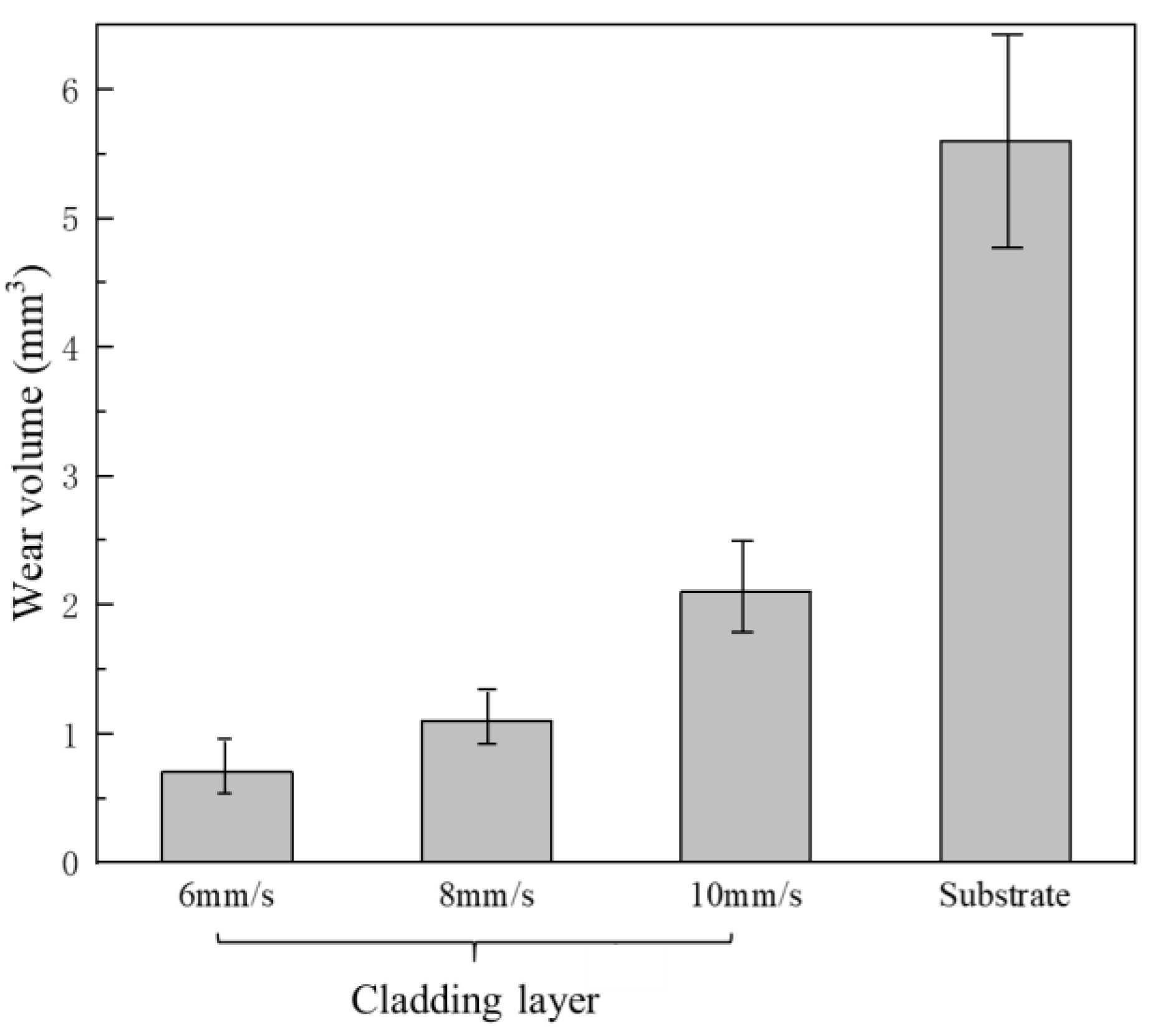
3.4. Wear Resistance
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The laser cladding layers exhibited three distinct microstructures at various scanning speeds. At the scanning speed of 6 mm/s, the cladding layer was a mixture of amorphous and crystalline regions. For a scanning speed of 8 mm/s, the cladding layer was mainly composed of a block grain structure. For a scanning speed of 10 mm/s, the cladding layer was composed entirely of dendrites. The dilution ratios were more dominant than the scanning speed in determining the resultant microstructures.
- (2)
- Compared with the hardness of the substrate of 200 , the cladding layers had an extremely high hardness of about 1300 at scanning speeds of 6 mm/s and 8 mm/s, and a lower high hardness of 700 at the scanning speed of 10mm/s.
- (3)
- The wear resistance of the cladding layers was much higher than that of the substrate, and the wear resistance of the cladding layers could be improved by using a lower scanning speed due to the formation of high hardness wear resistant phases.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amiya, K.; Nishiyama, N.; Inoue, A.; Masumoto, T. Mechanical strength and thermal stability of Ti-based amorphous alloys with large glass-forming ability. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1994, 179–180, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, C.A.; Hufnagel, T.C.; Ramamurty, U. Mechanical behavior of amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 4067–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.T.; Heatherly, L.; Horton, J.A.; Easton, D.S.; Carmichael, C.A.; Wright, J.L.; Schneibel, J.H.; Yoo, M.H.; Chen, C.H.; Inoue, A. Test environments and mechanical properties of Zr-base bulk amorphous alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1998, 29, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, N.; Liu, L. Study of structure and corrosion resistance of Fe-based amorphous coatings prepared by HVAF and HVOF. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 2351–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishitake, K.; Era, H.; Otsubo, F. Thermal-sprayed Fe-10Cr-13P-7C amorphous coatings possessing excellent corrosion resistance. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 1996, 5, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadney, S.; Brochu, M. Formation of amorphous Zr41.2Ti13.8Ni10Cu12.5Be22.5 coatings via the ElectroSpark Deposition process. Intermetallics 2008, 16, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, H.W.; Mordike, B.L. Laser and electron-beam melted amorphous layers. J. Mater. Sci. 1981, 16, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.Y.; Su, J.Y. The microstructure and tribological characteristics of laser-clad Ni-Cr-Al coatings on aluminium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 290, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Han, L.; Dong, C. Influence of laser power on microstructure and properties of laser clad Co-based amorphous composite coatings. Surf. Interfaces 2017, 6, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahasrabudhe, H.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Laser processing of Fe based bulk amorphous alloy coating on zirconium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 240, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, H.; Asami, K.; Kawashima, A.; Hashimoto, K. Laser-processed corrosion-resistant amorphous Ni Cr P B surface alloys on a mild steel. Corros. Sci. 1987, 27, 981–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.M.; Su, Y.P.; Yang, H.O. Laser cladding of Zr65Al7.5Ni10Cu17.5 amorphous alloy on magnesium. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xu, B.; Hong, Y. Synthesis of thick Ni66Cr5Mo4Zr6P15B4 amorphous alloy coating and large glass-forming ability by laser cladding. Mater. Lett. 2002, 56, 838–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Gao, Y. Laser Cladding Amorphous Composite Coating of Cu-Zr-Al on Magnesium Alloy Surface. Chin. J. Lasers 2006, 33, 709–713. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.; Zhu, H.; Kuang, T.; Shi, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z. Laser cladding Al-based amorphous-nanocrystalline composite coatings on AZ80 magnesium alloy under water cooling condition. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 690, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, F.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; He, W.; Sui, S.; Liu, B. Synthesis of amorphous coating by laser cladding multi-layer Co-based self-fluxed alloy powder. Mater. Lett. 2016, 176, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Qu, S.; Wang, X.; Zou, Z. Synthesis of Fe-based amorphous composite coatings with low purity materials by laser cladding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 7060–7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, M.; Li, R.; Wu, Y. Amorphous structure evolution of high power diode laser cladded Fe-Co-B-Si-Nb coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 261, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hong, Y. Fe-based thick amorphous-alloy coating by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 141, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhu, Y. Dilution effect on the formation of amorphous phase in the laser cladded Ni-Fe-B-Si-Nb coatings after laser remelting process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 7956–7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Yao, J.H.; Hu, X.X.; Chai, G.Z. Effect of laser power on the cladding temperature field and the heat affected zone. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2011, 18, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Du, D.; Chang, B. Studies of the Influence of Beam Profile and Cooling Conditions on the Laser Deposition of a Directionally-Solidified Superalloy. Materials 2018, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisig, J.; Schädlich, N.; Giebeler, L.; Sander, J.; Eckert, J.; Kühn, U.; Hufenbach, J. Microstructure and abrasive wear behavior of a novel FeCrMoVC laser cladding alloy for high-performance tool steels. Wear 2017, 382–383, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Samant, A.N.; Harimkar, S.P.; Majumdar, J.D.; Manna, I.; Dahotre, N.B. Laser surface coating of Fe-Cr-Mo-Y-B-C bulk metallic glass composition on AISI 4140 steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 2623–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, C.; Xia, Y.; Sandip, B.; Dong, C. Microstructure and properties of laser clad Zr-based alloy coatings on Ti substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 176, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Zhou, Y.; Smugeresky, J.E.; Lavernia, E.J. Processing and behavior of fe-based metallic glass components via laser-engineered net shaping. Int. J. Powder Metall. 2009, 45, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, W.M.; Mazumder, J. Basic Laser Optics. In Laser Material Processing; Springer: London, UK, 2010; pp. 79–130. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, Y.; Murakawa, H.; Ma, N. Mechanical Simulation of Welding. In Welding Deformation & Residual Stress Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 55–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Li, L.; Huang, H.; Chang, S.; Murakawa, H. Residual stresses in laser-arc hybrid welded butt-joint with different energy ratios. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 220, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.J.; Li, R.F.; Zheng, Q.C.; Li, H.; Wu, M.F. Structure and properties of laser-cladded Ni-based amorphous composite coatings. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casellas, D.; Caro, J.; Molas, S.; Prado, J.M.; Valls, I. Fracture toughness of carbides in tool steels evaluated by nanoindentation. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 4277–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

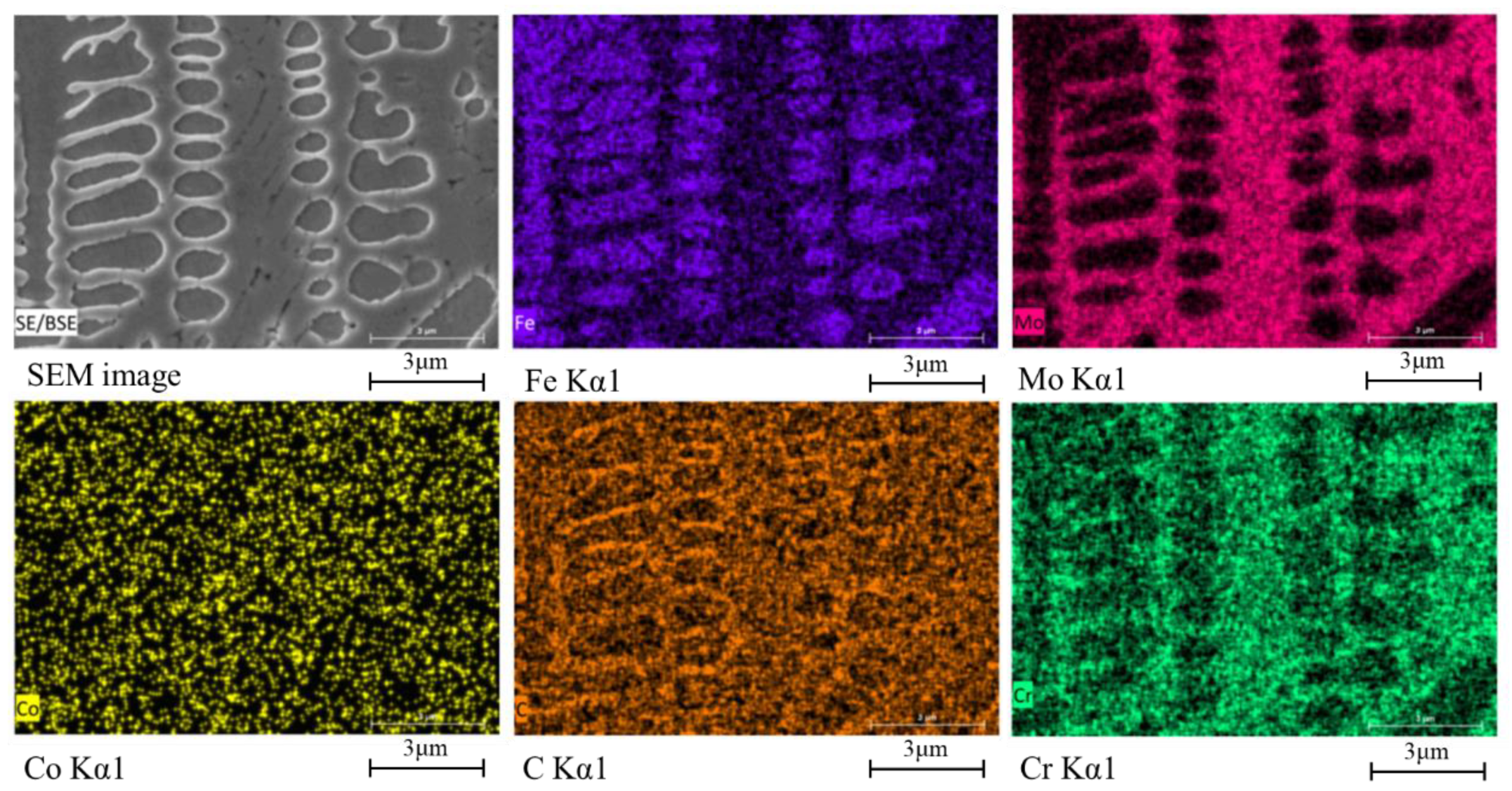

| Element | C | Mn | Ni | Si | P | S | Cr | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 0.26–0.35 | ≤1.00 | ≤0.60 | ≤1.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | 12.00–14.00 | Balance |
| Laser Power (W) | Scanning Speed (mm/s) | Powder Feeding Rate (g/min) | Heat Input (J/mm) | Overlapping Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 6 | 20 | 166.7 | 30 |
| 1000 | 8 | 20 | 125.0 | 30 |
| 1000 | 10 | 20 | 100.0 | 30 |
| Scanning Speed (mm/s) | Width of the Cladding Layer (μm) | Height of the Cladding Layer (μm) | Depth of the Molten Substrate (μm) | Dilution Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 2139.2 | 906.9 | 68.3 | 7.0% |
| 8 | 2070.7 | 749.6 | 120.6 | 13.9% |
| 10 | 1965.8 | 409.2 | 230.6 | 36.0% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, X.; Du, D.; Chang, B.; Ma, N. Influence of Scanning Speed on Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladded Fe-Based Amorphous Coatings. Materials 2019, 12, 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081279
Hou X, Du D, Chang B, Ma N. Influence of Scanning Speed on Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladded Fe-Based Amorphous Coatings. Materials. 2019; 12(8):1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081279
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Xiangchun, Dong Du, Baohua Chang, and Ninshu Ma. 2019. "Influence of Scanning Speed on Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladded Fe-Based Amorphous Coatings" Materials 12, no. 8: 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081279
APA StyleHou, X., Du, D., Chang, B., & Ma, N. (2019). Influence of Scanning Speed on Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladded Fe-Based Amorphous Coatings. Materials, 12(8), 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081279





