Evaluation of the Release Kinetics of a Pharmacologically Active Substance from Model Intra-Articular Implants Replacing the Cruciate Ligaments of the Knee
Abstract
:1. Introduction
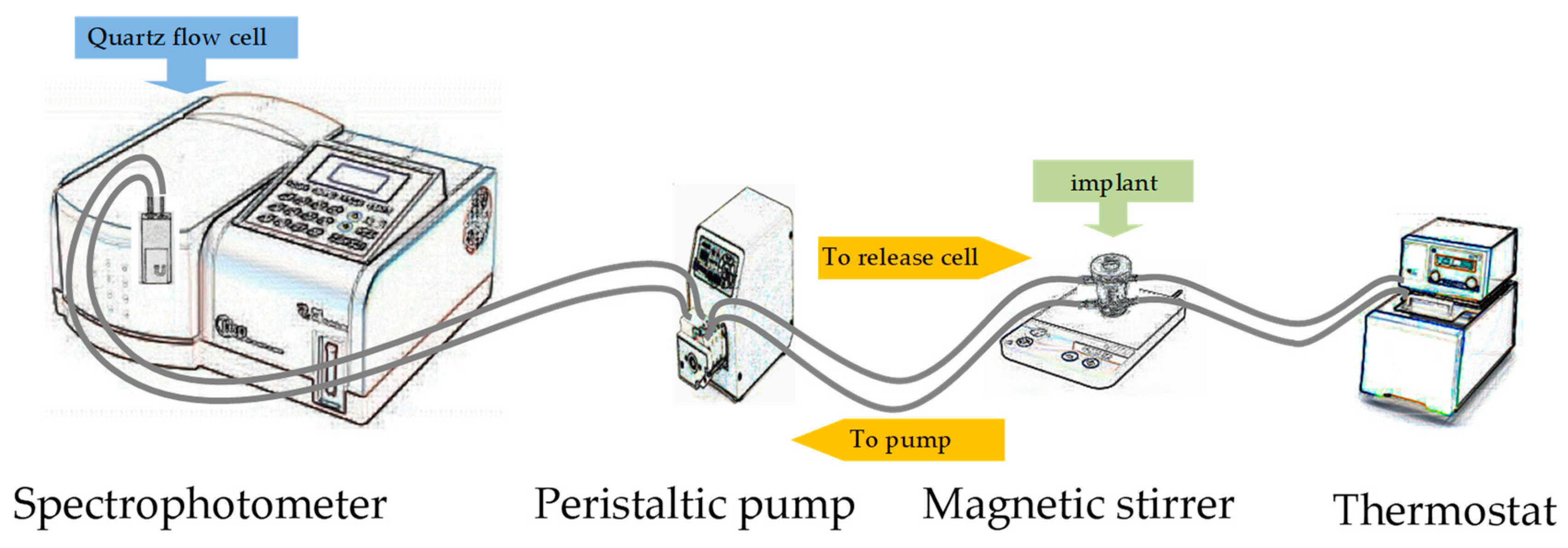
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
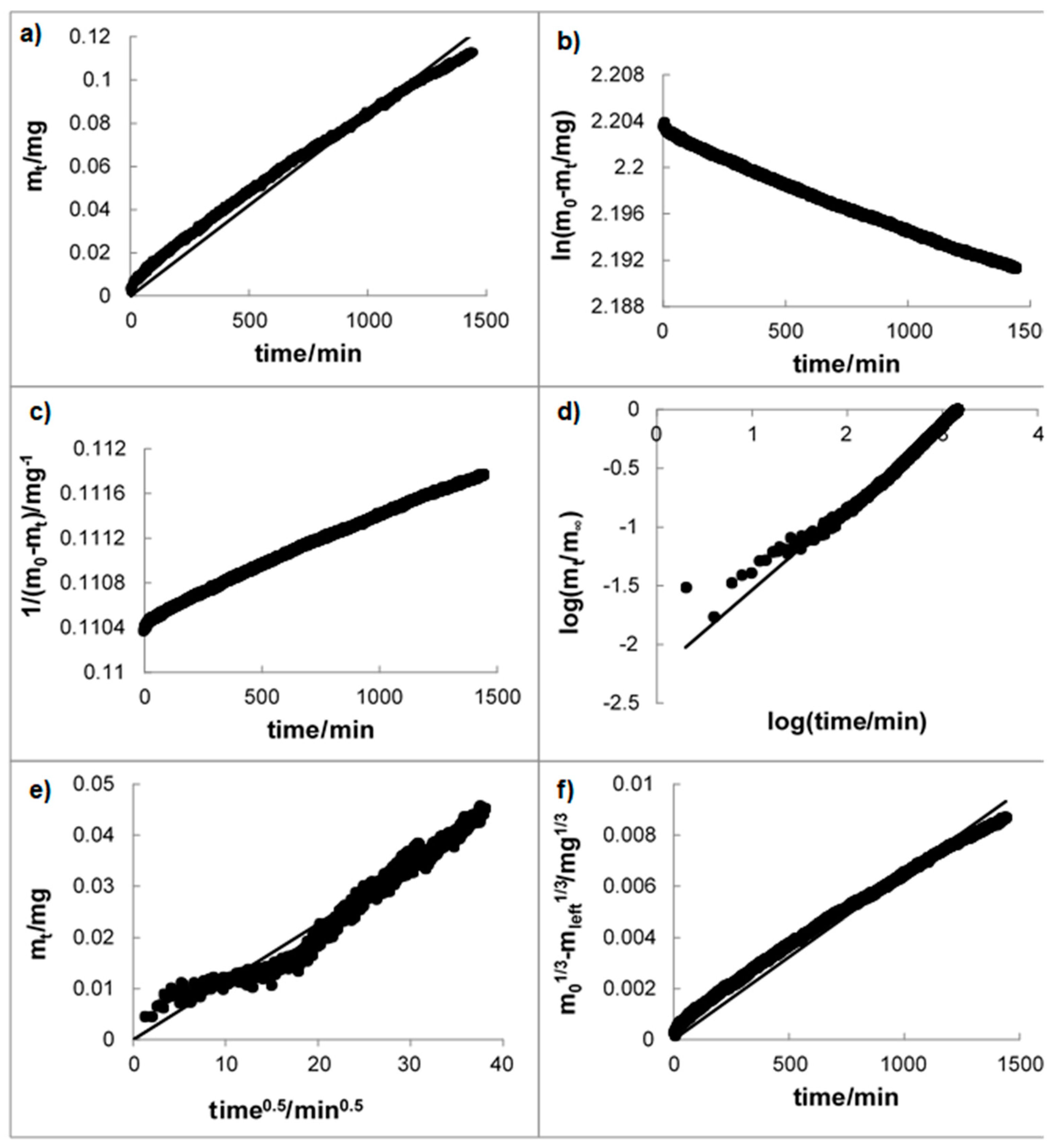
3.1. Mechanism of the Drug Release
3.2. Dissolution Study
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathiessen, A.; Conaghan, P.G. Synovitis in osteoarthritis: Current understanding with therapeutic implications. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanzello, C.R.; Steven, G.R. The Role of Synovitis in Osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone 2013, 51, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelka, K. A comparison of the therapeutic efficacy of diclofenac in osteoarthritis: A systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2012, 28, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjordal, J.M. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors, in osteoarthritic knee pain: Meta-analysis of randomised placebo controlled trials. BMJ 2004, 329, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychel, J.K. Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2010, 25, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, R. Management of Chronic Osteoarthritic Pain. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2000, 30, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbhen, D. Experimental osteoarthrosis for pharmacological anti-arthrotic compounds. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 1978, 302, 191. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, P. The pathobiology of osteoarthritis and the rationale for the use of pentosan polysulfate for its treatment. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 28, 211–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, R.; Cullis-Hill, D.; Jones, M. Systemic use of pentosan polysulphate in the treatment of osteoarthritis. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1996, 37, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, K.; Shirabe, S.; Miyata, N.; Murata, M.; Yamauchi, A.; Kataoka, Y.; Niwa, M. Sodium pentosan polysulfate resulted in cartilage improvement in knee osteoarthritis—An open clinical trial. BMC Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haan, J.; Goring, R.; Beale, B. Evaluation of Polysulfated Glycosaminoglycan for the Treatment of Hip Dysplasia in Dogs. Vet. Surg. 1994, 23, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotter, G.W.; Yovich, J.V.; McIlwraith, C.W.; Norrdin, R.W. Effects of intramuscular polysulfated glycosaminoglycan on chemical and physical defects in equine articular cartilage. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1989, 53, 224–230. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q. Therapeutic mechanisms of ibuprofen, prednisone and betamethasone in osteoarthritis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davalillo, T.C.; Vasavilbaso, T.C.; Alvarez, N.J.M.; Granado, C.M.P.; Jimenez, G.O.; del Sol, G.M.; Orbezo, G.F. Clinical efficacy of intra-articular injections in knee osteoarthritis: A prospective randomized study comparing hyaluronic acid and betamethasone. Open Access Rheumatol. Res. Rev. 2015, 2015, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribel-Madsen, S.; Bartels, E.M.; Stockmarr, A.; Borgwardt, A.; Cornett, C.; Danneskiold-Samsøe, B.; Bliddal, H. A Synoviocyte Model for Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Response to Ibuprofen, Betamethasone, and Ginger Extract—A Cross-Sectional In Vitro Study. Arthritis 2012, 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, T.M.D.; Kelsberg, G.M.D. Intra-articular Corticosteroid Injections for Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Am. Fam. Physician 2014, 90, 115–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Nuki, G.; Moskowitz, R.W.; Abramson, S.; Altman, R.D.; Arden, N.K.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.; Brandt, K.D.; Croft, P.; Doherty, M.; et al. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis. Part III: Changes in evidence following systematic cumulative update of research published through January 2009. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 476–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, S. Biomedical coatings on polyethylene terephthalate artificial ligaments. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 103, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.C.M.; Pippi, N.L.; Basso, P.C.; Schossler, J.E.W.; da Rosa, M.B.; Serafin, G.M.C. Implante sintético como estabilizador articular, após desmotomia dos ligamentos cruzados de cães: Proposição de técnica. Cienc. Rural 2010, 40, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benagiano, G.; Gabelnick, H.; Brosens, I. Long-acting hormonal contraception. Woman’s Heal. 2015, 11, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tolla, L.; Sanchez, R.; Khan, E.; Tyler, B.; Guarnieri, M. Subcutaneous Implants of Buprenorphine-Cholesterol-Triglyceride Powder in Mice. J. Vet. Med. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, N.; Cookson, M.S.; Gittelman, M.C. Long-term efficacy and tolerability of once-yearly histrelin acetate subcutaneous implant in patients with advanced prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2012, 109, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammerman, R.; Kim, S.; Adera, M.; Schwarz, A. Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Risperidone Subcutaneous Implants in Stable Patients with Schizophrenia. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2017, 7, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Ma, P.; Mu, H.; Wang, A.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Sun, K. Preparation and evaluation of a novel biodegradable long-acting intravitreal implant containing ligustrazine for the treatment of proliferative vitreoretinopathy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinagal, J.; Gupta, G.; Agarwal, A.; Aggarwal, K.; Akella, M.; Gupta, V.; Suril, D.; Gupta, A.; Singh, S.; Ram, J. Safety and efficacy of dexamethasone implant along with phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis associated uveitis. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 67, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, A.R.; Kim, S.; Squire, M.W.; Rose, W.E.; Ploeg, H.L. Vancomycin elution, activity and impact on mechanical properties when added to orthopedic bone cement. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 87, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieminska, L.; Ferguson, M.; Zerda, T.W.; Couch, E. Diffusion of Steroids in Porous Sol-Gel Glass: Application in Slow Drug Delivery. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 1997, 8, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Pharmacopoeia, 9th ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2017.
- Johnston, S.E.; Gil, N.L.; Wei, Y.-C.; Markovich, R.; Rustum, A.M. Development and Validation of a Stability-Indicating RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Assay of Betamethasone Dipropionate, Chlorocresol, and for the Estimation of Betamethasone Dipropionate related Compounds in a Pharmaceutical Cream and Ointment. J. Chromat. Sci. 2010, 48, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, H.W.; Elzanfaly, E.S.; Saad, A.S.; Abdelaleem, A.E.B. Full spectrum and selected spectrum based multivariate calibration methods for simultaneous determination of betamethasone dipropionate, clotrimazole and benzyl alcohol: Development, validation and application on commercial dosage form. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 169, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, D.J.; Crommelin, D.J.A.; Hussain, A.S.; Chen, M.-L. Assuring Quality and Performance of Sustained and Controlled Release Parenterals: EUFEPS Workshop Report. AAPS PharmSci. 2004, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewert, M.; Dressman, J.; Brown, C.; Shah, V.; Robinson, J.; Shah, V.; Uppoor, R.; Williams, R. FIP/AAPS Guidelines for Dissolution/In Vitro Release Testing of Novel/Special Dosage Forms. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2003, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, A.; Stippler, E.; Shah, V.P.; Burgess, D.J. Validation of USP apparatus 4 method for microsphere in vitro release testing. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, S.; Auel, T.; Kempin, W.; Bogdahn, M.; Weitschies, W.; Seidlitz, A. Influence of the test method on in vitro drug release from intravitreal model implants containing dexamethasone or fl uorescein sodium in poly (D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) or polycaprolactone. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A. Analysis of Fickian and non-Fickian drug release from polymers. Pharm. Acta Helv. 1985, 60, 110–111. [Google Scholar]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N.A. Higuchi equation: Derivation, applications, use and misuse. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 418, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hixon, A.W.; Crowell, J.H. Dependence of Reaction Velocity upon Surface and Agitation. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1931, 23, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N.A. Modeling of drug release from delivery systems based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.W.; Flanner, H.H. Mathematical Comparison of Dissolution Profiles. Pharm. Technol. 1996, 20, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- US Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Guidance for Industry. Dissolution Testing of Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms. Evaluation 1997, 4, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, P.; Lobo, J.M.S. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, R.; Baishya, H.; Qing, Z. Application of Mathematical Models in Drug Release Kinetics of Carbidopa and Levodopa ER Tablets. J. Dev. Drugs 2017, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramteke, K.H.; Dighe, P.A.; Kharat, A.R.; Patil, S.V. Kant’s biological conception of history. Sch. Acad. J. Pharm. 2014, 3, 388–396. [Google Scholar]
- Vummaneni, V.; Nagpal, D.; Surapaneni, S. Formulation and optimization of famotidine floating tablets using 23 factorial design. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 5, 5280–5284. [Google Scholar]
- Antesh, J.K.; Bhattacharya, A.; Verma, P. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of sustained release matrix tablets of metoprolol succinate using hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. Tech. Res. 2009, 1, 972–977. [Google Scholar]
| Implant Type | SAP Activation Procedure | Temperature and Time of Coating Stabilization | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer Substrate | Coating | Implementation of SAP during Synthesis of the Coating | Implementation of SAP to Final Material | ||
| A | Polyester | - | - | SAP | 35 °C; 10 h |
| B | Polyester | - | - | SAP | 125 °C; 5 h |
| C | Polyester | SiO2 | - | SAP | 125 °C;5 h |
| D | Polyester | SiO2 | SAP | - | 35 °C; 10 h |
| E | Polyester | SiO2 | SAP | - | 125 °C; 5 h |
| F | Polyester | SiO2 | SAP | SAP | 35 °C; 10 h |
| G | Polyester | SiO2 | SAP | SAP | 125 °C; 5 h |
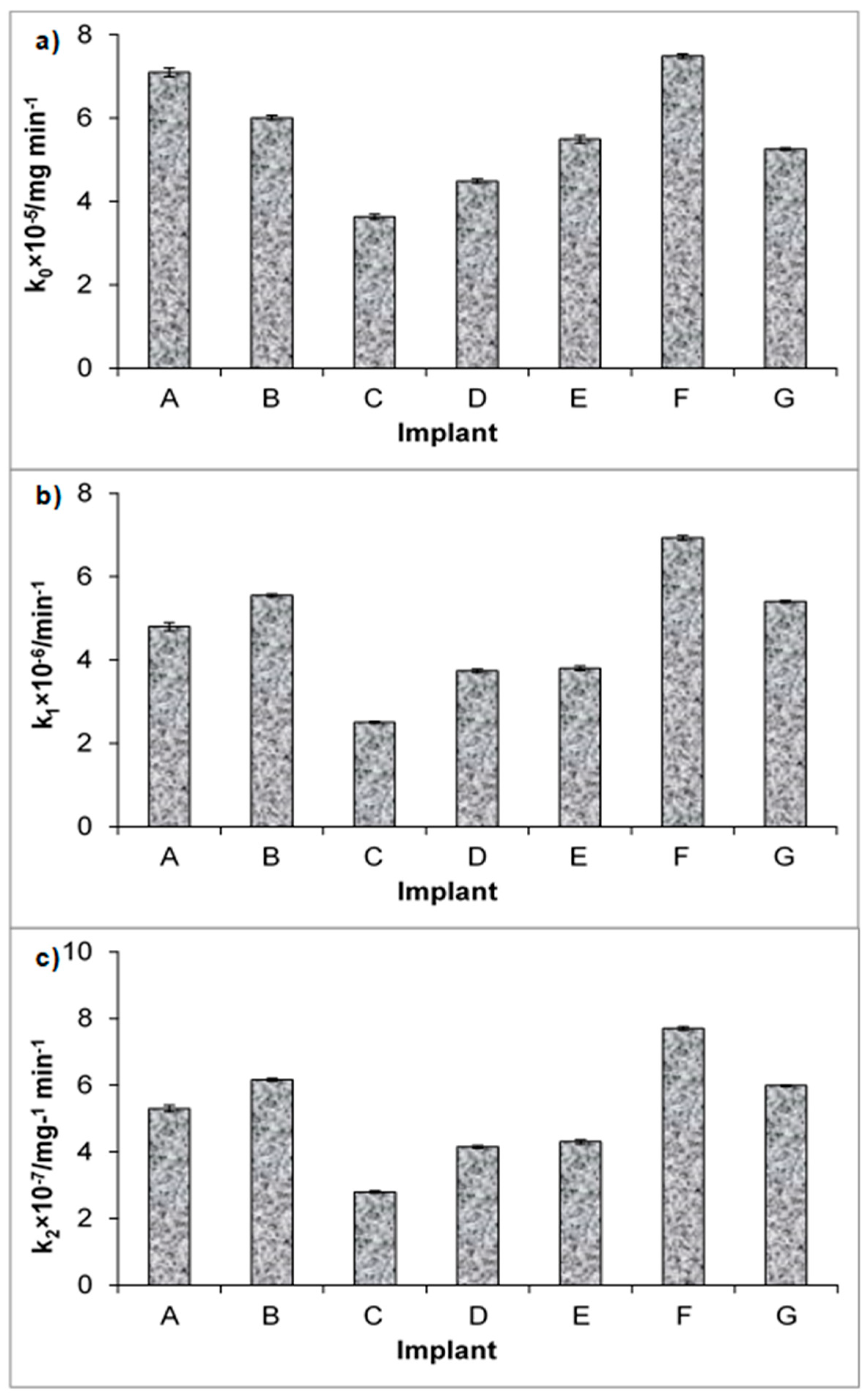
| Kinetic Model | Kinetic Parameters | A | B | C | D | E | F | G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z–O | k0 × 105/mg min−1 | 7.1 ± 0.1 | 6.01 ± 0.05 | 3.63 ± 0.06 | 4.49 ± 0.05 | 5.49 ± 0.09 | 7.49 ± 0.05 | 5.26 ± 0.03 |
| R2 | 0.9451 | 0.9830 | 0.9568 | 0.9771 | 0.9614 | 0.9880 | 0.9978 | |
| t0.5/min | 69,088 ± 1136 | 89,563 ± 949 | 133,064 ± 1881 | 101,189 ± 1142 | 91,966 ± 1571 | 61,461 ± 433 | 92,293 ± 438 | |
| F–O | k1 × 106/min−1 | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 5.55 ± 0.04 | 2.5 ± 0.03 | 3.74 ± 0.04 | 3.8 ± 0.05 | 6.93 ± 0.05 | 5.4 ± 0.02 |
| R2 | 0.9216 | 0.9841 | 0.9802 | 0.9799 | 0.9419 | 0.9896 | 0.9986 | |
| t0.5/min | 154,398 ± 2836 | 161,737 ± 1708 | 275,687 ± 2926 | 185,248 ± 1920 | 184,738 ± 3086 | 102,166 ± 763 | 135,310 ± 456 | |
| S–O | k2 × 107/mg−1 min−1 | 5.3 ± 0.1 | 6.16 ± 0.04 | 2.8 ± 0.03 | 4.15 ± 0.04 | 4.3 ± 0.06 | 7.70 ± 0.05 | 5.99 ± 0.02 |
| R2 | 0.9218 | 0.9842 | 0.9802 | 0.9801 | 0.9420 | 0.9895 | 0.9981 | |
| t0.5/min | 221,412 ± 4063 | 232,403 ± 2445 | 396,449 ± 4212 | 266,269 ± 2746 | 265,355 ± 4425 | 146,461 ± 1099 | 194,543 ± 654 | |
| H | kH × 103/mg × min−1/2 | 2.27 ± 0.02 | 1.87 ± 0.02 | 1.15 ± 0.009 | 1.406 ± 0.006 | - | - | —— |
| R2 | 0.9872 | 0.9898 | 0.9878 | 0.9962 | - | - | —— | |
| t0.5/min | 334 ± 3 | 438 ± 3 | 648.3 ± 5.5 | 495 ± 2 | - | - | —— | |
| K–P | kK–P × 103/min−n | 68.7 ± 3.7 | 18.2 ± 1.2 | 71.0 ± 4.0 | 16.6 ± 0.7 | 56.2 ± 4.5 | - | 4.6 ± 0.3 |
| n | 0.368 ± 0.006 | 0.582 ± 0.004 | 0.351 ± 0.007 | 0.579 ± 0.005 | 0.46 ± 0.01 | - | 0.75 ± 0.01 | |
| R2 | 0.8967 | 0.9508 | 0.8744 | 0.9667 | 0.8113 | - | 0.9722 | |
| t0.5/min | 332.0 ± 58.6 | 493 ± 47 | 394 ± 77 | 461 ± 41 | 399 ± 57 | - | 564 ± 49 | |
| H–C | kH–C × 106/mg1/3min−1 | - | 4.63 ± 0.04 | - | 3.58 ± 0.04 | 3.8 ± 0.05 | 6.07 ± 0.04 | 3.25 ± 0.01 |
| R2 | - | 0.9831 | - | 0.9743 | 0.9615 | 0.9922 | 0.9989 | |
| t0.5/min | - | 110,648 ± 1170 | - | 120,126 ± 1448 | 54,503 ± 720 | 71,870 ± 460 | 132,865 ± 372 | |
| Best fit | H | H | H | H | H–C, Z–O | F–O | F–O | |
| Implant | A | B | C | D | E | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| B | 27 | - | - | - | - | - |
| C | 50 | 37 | - | - | - | - |
| D | 40 | 23 | 22.5 | - | - | - |
| E | 32 | 17 | 37 | 13 | - | - |
| F | 14 | 24 | 49 | 38.5 | 31 | - |
| G | 31 | 12 | 47 | 22 | 18 | 29 |
| Implant | A | B | C | D | E | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| B | 0.139 | - | - | - | - | - |
| C | 0.325 | 0.186 | - | - | - | - |
| D | 0.259 | 0.120 | 0.066 | - | - | - |
| E | 0.207 | 0.068 | 0.118 | 0.052 | - | - |
| F | 0.017 | 0.122 | 0.308 | 0.242 | 0.190 | - |
| G | 0.199 | 0.061 | 0.125 | 0.059 | 0.007 | 0.183 |
| Implant | A | B | C | D | E | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| B | 12.21 | - | - | - | - | - |
| C | 37.95 | 19.36 | - | - | - | - |
| D | 27.22 | 11.42 | 9.23 | - | - | - |
| E | 21.51 | 6.35 | 16.26 | 6.25 | - | - |
| F | 1.19 | 8.98 | 26.81 | 19.83 | 15.47 | - |
| G | 16.75 | 4.71 | 12.44 | 5.45 | 0.65 | 12.93 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wojcik-Pastuszka, D.; Krzak, J.; Macikowski, B.; Berkowski, R.; Osiński, B.; Musiał, W. Evaluation of the Release Kinetics of a Pharmacologically Active Substance from Model Intra-Articular Implants Replacing the Cruciate Ligaments of the Knee. Materials 2019, 12, 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081202
Wojcik-Pastuszka D, Krzak J, Macikowski B, Berkowski R, Osiński B, Musiał W. Evaluation of the Release Kinetics of a Pharmacologically Active Substance from Model Intra-Articular Implants Replacing the Cruciate Ligaments of the Knee. Materials. 2019; 12(8):1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081202
Chicago/Turabian StyleWojcik-Pastuszka, Dorota, Justyna Krzak, Bartosz Macikowski, Ryszard Berkowski, Bogdan Osiński, and Witold Musiał. 2019. "Evaluation of the Release Kinetics of a Pharmacologically Active Substance from Model Intra-Articular Implants Replacing the Cruciate Ligaments of the Knee" Materials 12, no. 8: 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081202
APA StyleWojcik-Pastuszka, D., Krzak, J., Macikowski, B., Berkowski, R., Osiński, B., & Musiał, W. (2019). Evaluation of the Release Kinetics of a Pharmacologically Active Substance from Model Intra-Articular Implants Replacing the Cruciate Ligaments of the Knee. Materials, 12(8), 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12081202







