Amphiphilic Copolymer of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS) Methacrylate for Solid Dispersion of Paclitaxel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
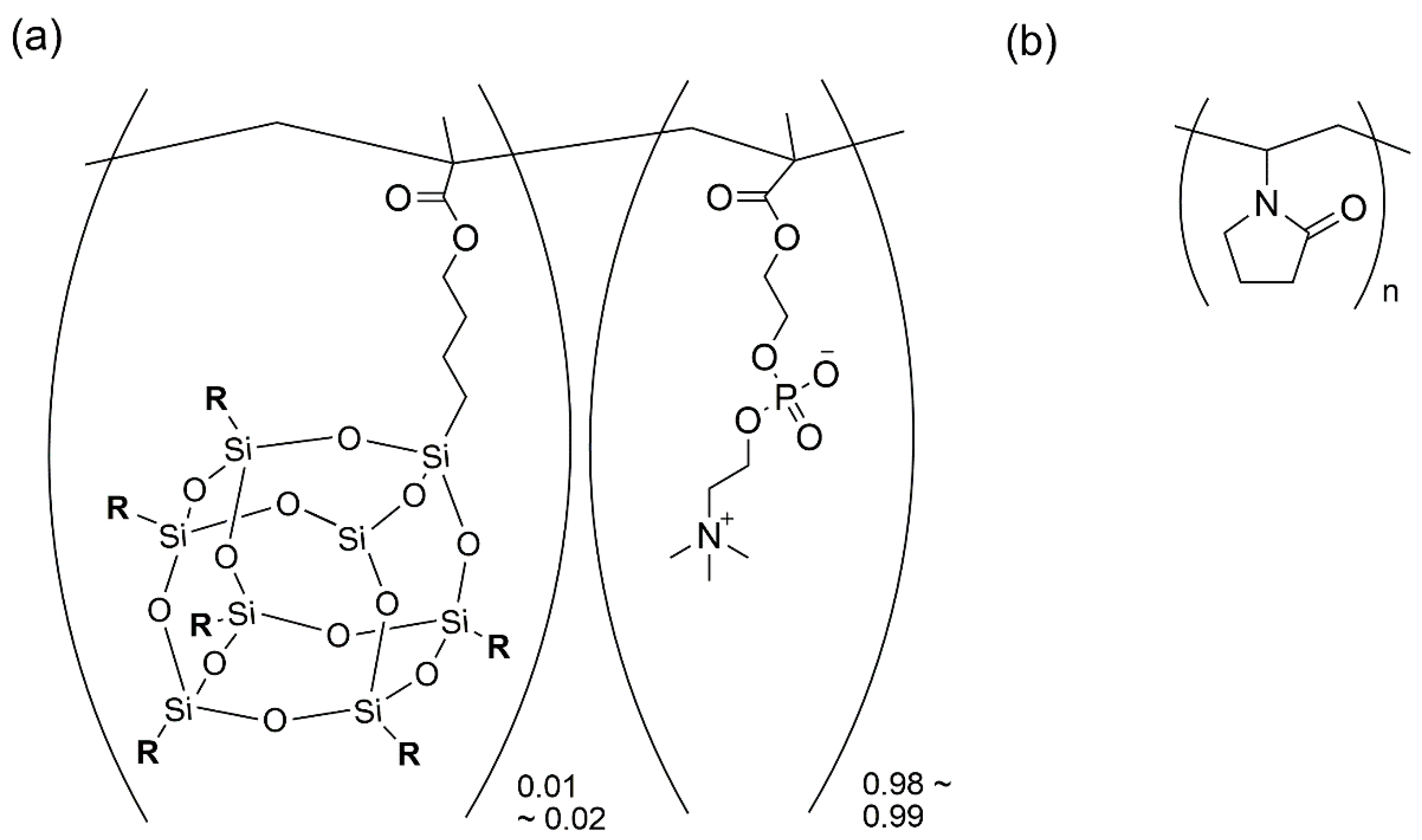
2.2. PTX Solid Formulation Using MPC-ran-C2H5-POSS and PVP
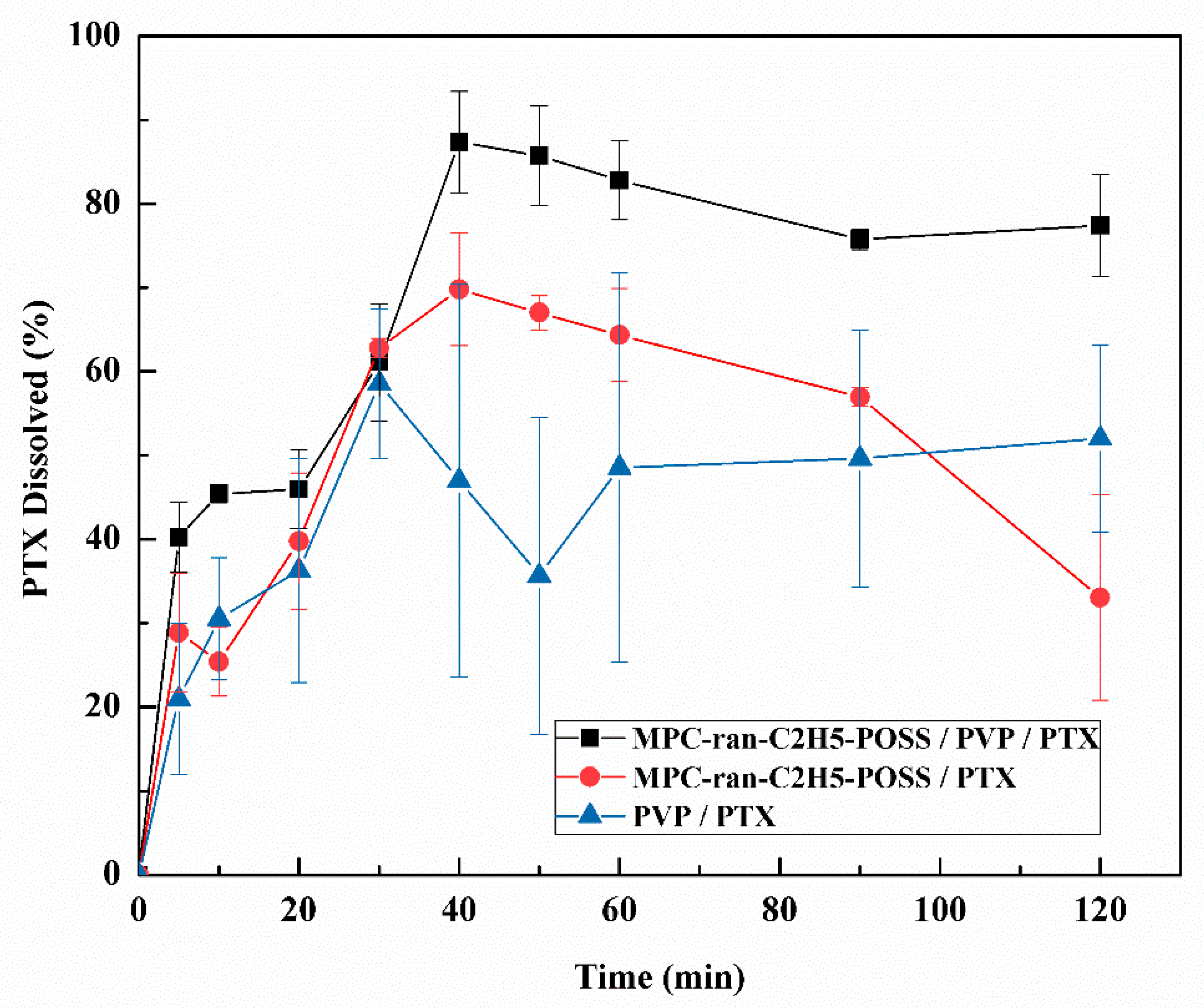
2.3. Dissolution Test
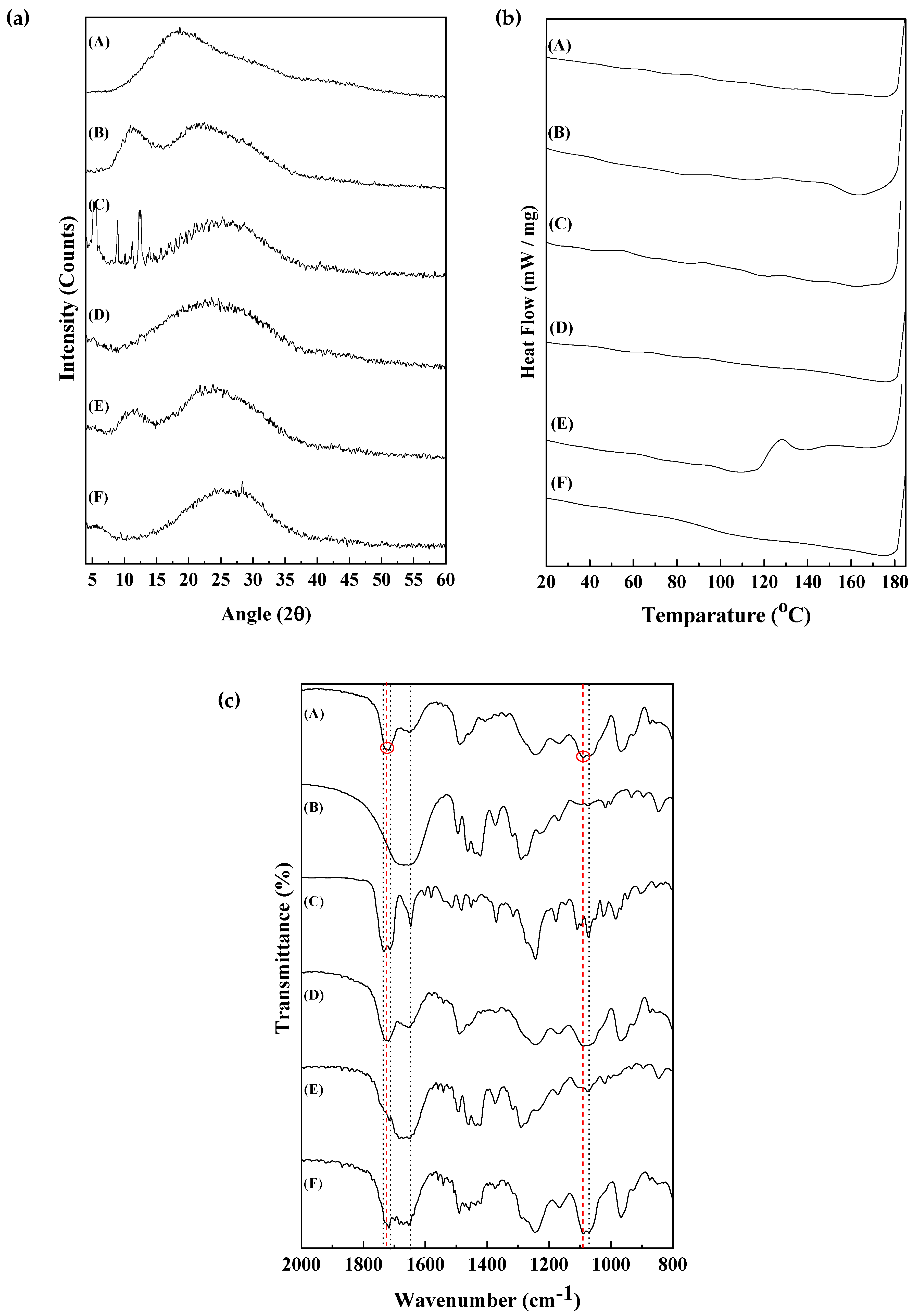
2.4. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the PTX Solid Formulation
3.2. Dissolution Behavior of PTX from the Formulation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gelderblom, H.; Verweij, J.; Nooter, K.; Sparreboom, A. Cremophor EL: The drawbacks and advantages of vehicle selection for drug formulation. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37, 1590–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Ali, R.; Al-Jenoobi, F.I.; Al-Mohizea, A.M. Solid dispersions: A strategy for poorly aqueous soluble drugs and technology updates. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 1419–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikiaris, D.N. Solid dispersions, Part I: Recent evolutions and future opportunities in manufacturing methods for dissolution rate enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 1501–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.Q.; Lu, F.; Hou, J.W.; Shen, Y.Y.; Guo, S.R. Incorporation of paclitaxel solid dispersions with poloxamer188 or polyethylene glycol to tune drug release from poly(epsilon-caprolactone) films. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Cui, F.D.; Choi, M.K.; Lin, H.X.; Chung, S.J.; Shim, C.K.; Kim, D.D. Liposome formulation of paclitaxel with enhanced solubility and stability. Drug Deliv. 2007, 14, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.S.; Lin, L.; Xing, P.Y.; Zhang, C.G.; Wang, L.; Liz, Y.Q. The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Paclitaxel Liposome on the Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, S902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabeu, E.; Cagel, M.; Lagomarsino, E.; Moretton, M.; Chiappetta, D.A. Paclitaxel: What has been done and the challenges remain ahead. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 474–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louage, B.; De Wever, O.; Hennink, W.E.; De Geest, B.G. Developments and future clinical outlook of taxane nanomedicines. J. Control. Release 2017, 253, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouquet, W.; Ceelen, W.; Fritzinger, B.; Pattyn, P.; Peeters, M.; Remon, J.P.; Vervaet, C. Paclitaxel/beta-cyclodextrin complexes for hyperthermic peritoneal perfusion—Formulation and stability. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 66, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, H.; Ishihara, K.; Masuoka, N.; Mikuni, K.; Nakajima, N. Enhancement of water-solubility and bioactivity of paclitaxel using modified cyclodextrins. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 102, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moes, J.; Koolen, S.; Huitema, A.; Schellens, J.; Beijnen, J.; Nuijen, B. Development of an oral solid dispersion formulation for use in low-dose metronomic chemotherapy of paclitaxel. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 83, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.H.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, Q.Y.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhao, B.X.; Wang, Y.T.; Cai, Y.; Li, G.F. Bioavailability Enhancement of Paclitaxel via a Novel Oral Drug Delivery System: Paclitaxel-Loaded Glycyrrhizic Acid Micelles. Molecules 2015, 20, 4337–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusa, S.I.; Fukuda, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Ishihara, K.; Morishima, Y. Synthesis of well-defined amphiphilic block copolymers having phospholipid polymer sequences as a novel blocompatible polymer micelle reagent. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, T.; Watanabe, J.; Ishihara, K. Enhanced solubility of paclitaxel using water-soluble and biocompatible 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine polymers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2003, 65, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoue, S.; Kojo, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Yuminoki, K.; Kou, K.; Kawabata, Y.; Yamauchi, Y.; Hashimoto, N.; Yamada, S. Development of novel solid dispersion of tranilast using amphiphilic block copolymer for improved oral bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 452, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, L.S.; Zografi, G. Spectroscopic characterization of interactions between PVP and indomethacin in amorphous molecular dispersions. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, C.L.N.; Park, C.; Lee, B.J. Current trends and future perspectives of solid dispersions containing poorly water-soluble drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Nishino, T.; Ooya, T. Tuned Surface and Mechanical Properties of Polymeric Film Prepared by Random Copolymers Consisting of Methacrylate-POSS and 2-(Methacryloyloxy)ethyl Phosphorylcholine. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2018, 219, 1700572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Ooya, T. Hydrophobic Nature of Methacrylate-POSS in Combination with 2-(Methacryloyloxy)ethyl Phosphorylcholine for Enhanced Solubility and Controlled Release of Paclitaxel. Langmuir 2018, 35, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Lei, L.; Hou, J.W.; Tang, M.F.; Guo, S.R.; Wang, Z.M.; Chen, K.M. Evaluation of two polymeric blends (EVA/PLA and EVA/PEG) as coating film materials for paclitaxel-eluting stent application. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.K.; Lee, B.J.; Lee, H.K. Enhanced dissolution and bioavailability of biochanin A via the preparation of solid dispersion: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.Y.; Chung, Y.Y.; Cheah, X.Z.; Tan, E.Y.L.; Quah, J. The characterization and dissolution performances of spray dried solid dispersion of ketoprofen in hydrophilic carriers. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, C.H. Characteristics of polymers enabling nano-comminution of water-insoluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 355, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, R.E.; Schwarz, M.; Ranade, S.; Chan, A.K.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Sumerlin, B. Evaluation of acrylate-based block copolymers prepared by atom transfer radical polymerization as matrices for paclitaxel delivery from coronary stents. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3410–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogeras, I.M.; Haag Lobland, H.E. The Nature of the Glassy State: Structure and Glass Transitions. J. Mater. Educ. 2012, 34, 69–94. [Google Scholar]
- Brostow, W.; Chiu, R.; Kalogeras, I.M.; Vassilikou-Dova, A. Prediction of glass transition temperatures: Binary blends and copolymers. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3152–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, R.J.; Brostow, W.; Fasina, O.; Kalogeras, I.M.; Sathigari, S.; Vassilikou-Dova, A. Encapsulation of Hydrophobic Drugs in a Copolymer: Glass Transition Behavior and Miscibility Evaluation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, T.; Kyomoto, M.; Kakinoki, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Ishihara, K. Reduced platelets and bacteria adhesion on poly(ether ether ketone) by photoinduced and self-initiated graft polymerization of 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, C.L.; Gao, Y.; Raina, S.A.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Taylor, L.S. Paclitaxel Crystal Seeds with Different Intrinsic Properties and Their Impact on Dissolution of Paclitaxel-HPMCAS Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, A.K.; Singh, S. Physicochemical characterization and dissolution study of solid dispersions of diacerein with polyethylene glycol 6000. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2011, 37, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Beig, A.; Carr, R.A.; Spence, J.K.; Dahan, A. A Win-Win Solution in Oral Delivery of Lipophilic Drugs: Supersaturation via Amorphous Solid Dispersions Increases Apparent Solubility without Sacrifice of Intestinal Membrane Permeability. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample Codes | (K) | (K) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MPC-ran-C2H5-POSS | 343 | - | - |
| PVP | 429 | - | - |
| PTX | 379 | - | - |
| MPC-ran-C2H5-POSS/PTX | 333 | 347 | −14 |
| PVP/PTX | 377 | 422 | −45 |
| MPC-ran-C2H5-POSS/PVP/PTX | 364 | 381 | −17 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chatterjee, S.; Ooya, T. Amphiphilic Copolymer of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS) Methacrylate for Solid Dispersion of Paclitaxel. Materials 2019, 12, 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071058
Chatterjee S, Ooya T. Amphiphilic Copolymer of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS) Methacrylate for Solid Dispersion of Paclitaxel. Materials. 2019; 12(7):1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071058
Chicago/Turabian StyleChatterjee, Suchismita, and Tooru Ooya. 2019. "Amphiphilic Copolymer of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS) Methacrylate for Solid Dispersion of Paclitaxel" Materials 12, no. 7: 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071058
APA StyleChatterjee, S., & Ooya, T. (2019). Amphiphilic Copolymer of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS) Methacrylate for Solid Dispersion of Paclitaxel. Materials, 12(7), 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071058







