Tuning Optical and Granulometric Properties of Gold Nanostructures Synthesized with the Aid of Different Types of Honeys for Microwave-Induced Hyperthermia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
2.2. Honey-mediated Green Synthesis of AuNPs
2.3. Characterization of AuNPs Produced under Optimal Conditions
2.4. Qualitative Analyses of Chemical Compounds in Honey Solutions
2.5. Quantitative Analyses of the Reducing Sugars and Phenolic Compounds Contained in Aqueous Honey Solutions
2.6. Thermal Behaviour of AuNPs in a Microwave Radiation Field
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Visual Observations of AuNPs Formation Followed by Determination of AuNPs Optical and Granulometric Properties
3.2. Morphology of AuNPs Synthesized under Selected Conditions
3.3. Qualitative Analyses of Chemical Compounds Present in Mixed Solutions
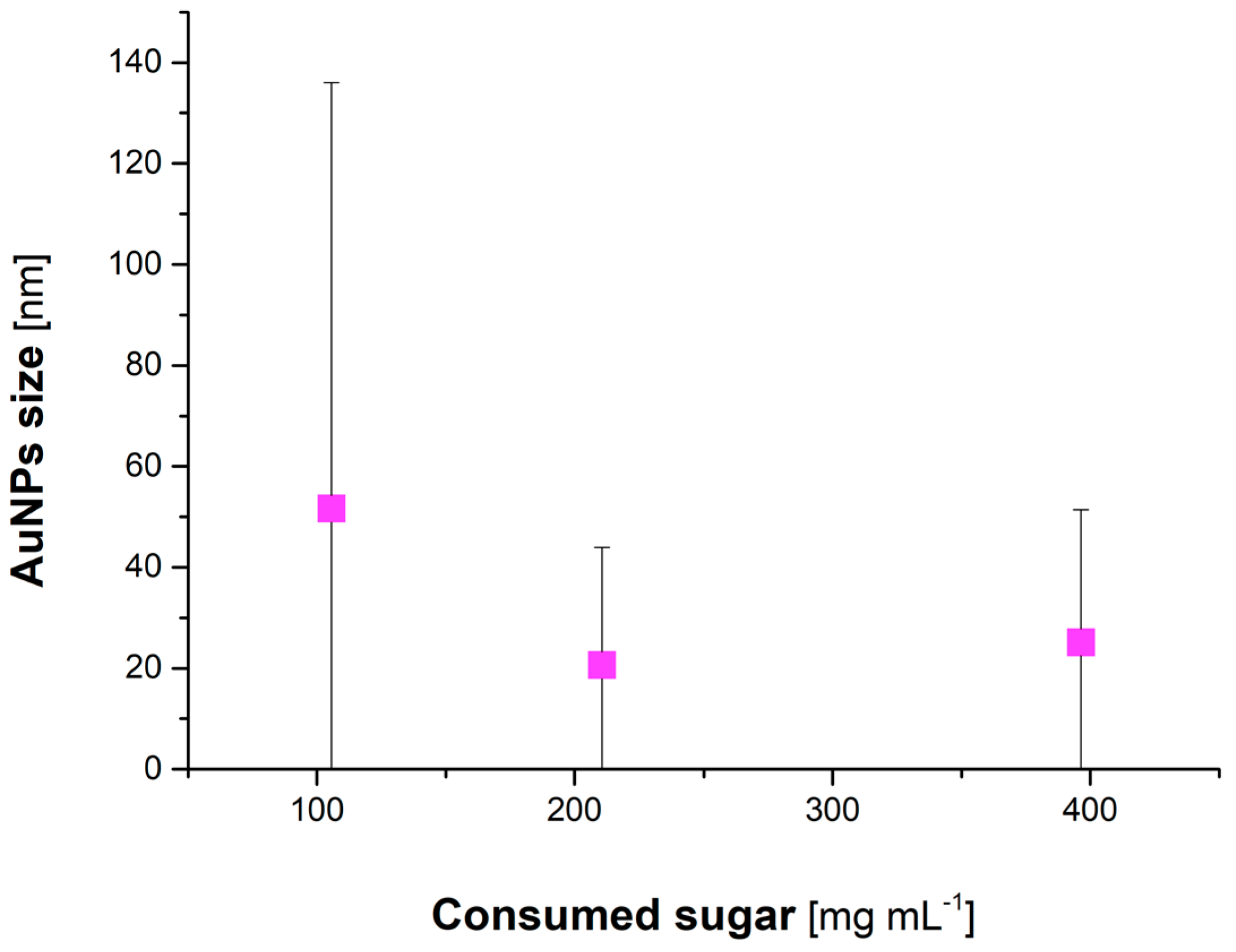
3.4. Quantitative Analyses of Reducing Sugars and Phenolic Compounds Contained in Honeys
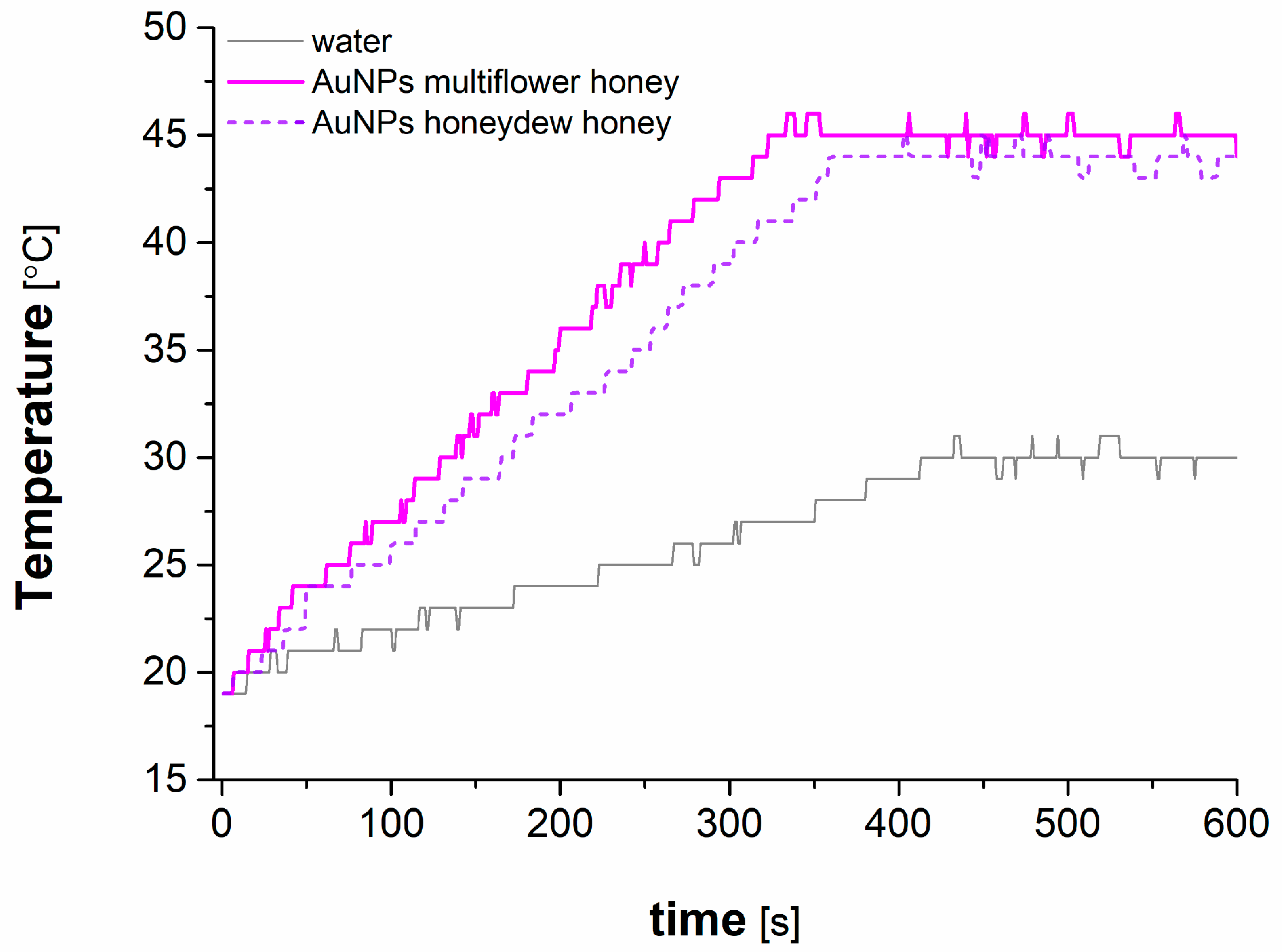
3.5. Application of AuNPs in Microwave-Induced Hyperthermia
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ray, P.C.; Yu, H.; Fu, P.P. Toxicity and environmental risks of nanomaterials challenges and future needs. J. Environ. Sci. Health C. Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2009, 27, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biener, J.; Wittstock, A.; Baumann, T.; Weissmuller, J.; Baumer, M.; Hamza, A. Surface chemistry in nanoscale materials. Materials 2009, 2, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsall, R.W.; Hamley, I.W.; Geoghegan, M. Nanoscale Science and Technology; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi, L.; Sancey, L.; Palermo, G.; Termine, R.; De Luca, A.; Szerb, E.I.; Aiello, I.; Ghedini, M.; Strangi, G.; La Deda, M. Plasmon-mediated cancer phototherapy: The combined effect of thermal and photodynamic processes. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 19279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzi, L.; Palermo, G.; Veltri, A.; Cataldi, U.; Burgi, T.; Ritacco, T.; De Luca, A. Photo-thermal study of a layer of randomly distributed gold nanoparticles: From nano-localization to macro-scale effects. J. Phys. D. 2017, 50, 435302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, G.; Ritacco, T.; Aceti, D.; Pezzi, L.; Giocondo, M.; De Luca, A. Photo-thermal effects in 1D gratings of gold nanoparticles. Crystals 2017, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, G.; Pagnotto, D.; Ricciardi, L.; Pezzi, L.; La Deda, M.; De Luca, A. Thermoplasmonic Effects in Gain-Assisted Nanoparticle Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 24185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Liao, F.; Molesa, S.; Redinger, D.; Subramanian, V. Plastic-compatible low resistance printable gold nanoparticle conductors for flexible electronics. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, G412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.L.V.; Stoeva, S.I.; Sorensen, C.M.; Zaikovski, V.; Klabunde, K.J. Gold nanoparticles as catalysts for polymerization of alkylsilanes to siloxane nanowires, filaments, and tubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 10488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, M.S.; Shafieem, H. Applications of gold nanoparticles in virus detection. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.E.; Ross, R.D.; Tilley, J.M.; Vargo-Gogola, T.; Roeder, R.K. Gold nanoparticles as contrast agents in x-ray imaging and computed tomography. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparkling, R.A.; Gil, P.R.; Zhang, F.; Zanella, M.; Parak, W.J. Biological applications of gold nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Jain, P.; El-Sayed, I.; El-Sayed, M. Plasmonic photothermal therapy (PPTT) using gold nanoparticles. Lasers. Med. Sci. 2008, 23, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heijden, A.G.; Kiemeney, L.A.; Gofrit, O.N.; Nativ, O.; Sidi, A.; Leib, Z.; Colombo, R.; Naspro, R.; Pavone, M.; Baniel, J.; et al. Preliminary european results of local microwave hyperthermia and chemotherapy treatment in intermediate or high risk superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Eur. Urol. 2004, 46, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burfeindt, M.J.; Zastrow, E.; Hagness, S.C.; Van Veen, B.D.; Medow, J.E. Microwave beamforming for non-invasive patient-specific hyperthermia treatment of pediatric brain cancer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumine, A.; Takegami, K.; Asanuma, K.; Matsubara, T.; Nakamura, T.; Uchida, A.; Sudo, A. A novel hyperthermia treatment for bone metastases using magnetic materials. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 16, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zastrow, E.; Hagness, S.C.; Van Veen, B.D. 3d computational study of non-invasive patient-specific microwave hyperthermia treatment of breast cancer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Converse, M.; Bond, E.J.; Veen, B.; Hagness, C. A computational study of ultra-wideband versus narrowband microwave hyperthermia for breast cancer treatment. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 2006, 54, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Abbosh, A.M.; Crozier, S. 3-d focused microwave hyperthermia for breast cancer treatment with experimental validation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.T.; Haddad, M.G.; Cravalho, E.G.; Bowman, H.F. Thermal model for the local microwave hyperthermia treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1992, 39, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Wakabayashi, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Imamura, M.; Tamai, T.; Nishimura, A.; Yamashiki, N.; Okamura, A.; Inoue, K. Percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy for patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison with percutaneous ethanol injection therapy. Cancer Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 1999, 85, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svaasand, L.O.; Gomer, C.J.; Morinelli, E. On the physical rationale of laser induced hyperthermia. Lasers Med. Sci. 1990, 5, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyganowski, P.; Dzimitrowicz, A.; Jamroz, P.; Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D.; Pohl, P. Polymerization-driven immobilization of dc-apgd synthesized gold nanoparticles into a quaternary ammonium-based hydrogel resulting in a polymeric nanocomposite with heat-transfer applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzimitrowicz, A.; Cyganowski, P.; Pohl, P.; Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D.; Terefinko, D.; Jamroz, P. Atmospheric pressure plasma-mediated synthesis of platinum nanoparticles stabilized by poly(vinylpyrrolidone) with application in heat management systems for internal combustion chambers. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarov, V.V.; Love, A.J.; Sinitsyna, O.V.; Makarova, S.S.; Yaminsky, I.V.; Taliansky, M.E.; Kalinina, N.O. “Green” nanotechnologies: Synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Nat. 2014, 6, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Celentano, M.; Jakhmola, A.; Profeta, M.; Battista, E.; Guarnieri, D.; Gentile, F.; Netti, P.A.; Vecchione, R. Diffusion limited green synthesis of ultra-small gold nanoparticles at room temperature. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 558, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakhmola, A.; Celentano, M.; Vecchione, R.; Manikas, A.; Battista, E.; Calcagno, V.; Netti, P.A. Self-assembly of gold nanowire networks into gold foams: Production, ultrastructure and applications. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzimitrowicz, A.; Jamroz, P.; diCenzo, G.; Sergiel, I.; Kozlecki, T.; Pohl, P. Preparation and characterization of gold nanoparticles prepared with aqueous extracts of Lamiaceae plants and the effect of follow-up treatment with atmospheric pressure glow microdischarge. Arab. J. Chem. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankamwar, B. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles (green-gold) using leaves extract of Terminalia catappa. E-J. Chem. 2010, 7, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.P.; Lahtinen, M.; Sillanpaa, M. Green synthesis and characterizations of silver and gold nanoparticles using leaf extract of Rosa rugosa. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 364, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, D. Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using Hibiscus rosa sinensis. Physica E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2010, 42, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, D.; Lu, Y.; Su, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Shao, W.; He, N.; Hong, J.; Chen, C. Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by novel sundried Cinnamomum camphora leaf. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 105104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzimitrowicz, A.; Berent, S.; Motyka, A.; Jamroz, P.; Kurcbach, K.; Sledz, W.; Pohl, P. Comparison of the characteristics of gold nanoparticles synthesized using aqueous plant extract and natural plant essential oil of Eucalyptus globulus and Rosmarinus officinalis. Arab. J. Chem. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljabali, A.A.; Akkam, Y.; Al Zoubi, M.S.; Al-Batayneh, K.M.; Al-Trad, B.; Abo Alrob, O.; Alkilany, A.M.; Benamara, M.; Evans, D.J. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using leaf extract of Ziziphus zizyphus and their antimicrobial activity. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankamwar, B.; Pansare, S.; Sur, U.K. Centrifuge controlled shape tuning of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles obtained from Plumbago zeylanica leaf extract. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadagouda, M.N.; Iyanna, N.; Lalley, J.; Han, C.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Varma, R.S. Synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using antioxidants from blackberry, blueberry, pomegranate, and turmeric extracts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheny, D.S.; Mathew, J.; Philip, D. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic action of hexagonal gold nanoparticles using essential oils extracted from Anacardium occidentale. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 97, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniyappan, N.; Nagarajan, N.S. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Curcuma pseudomontana essential oil, its biological activity and cytotoxicity against human ductal breast carcinoma cells T47D. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.S.; Bag, B.G. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using renewable Punica granatum juice and study of its catalytic activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2014, 4, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogireddy, N.K.R.; Gomez, L.M.; Osorio-Roman, I.; Agarwal, V. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Coffea Arabica fruit extract. Adv. Nano. Res. 2017, 5, 253. [Google Scholar]
- Roy Chowdhury, N.; Cowin, A.; Zilm, P.; Vasilev, K. “Chocolate” gold nanoparticles—One pot synthesis and biocompatibility. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, D. Honey-mediated green synthesis of gold nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 73, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snitka, V.; Naumenko, D.O.; Ramanauskaite, L.; Kravchenko, S.A.; Snopok, B.A. Generation of diversiform gold nanostructures by honey’s components: Growth mechanism, characterization, and shape separation by centrifugation-assisted sedimentation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 386, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreelakshmi, C.; Datta, K.K.R.; Yadav, J.S.; Reddy, B.V. Honey derivatized Au and Ag nanoparticles and evaluation of its antimicrobial activity. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, D.W. The chemical composition of honey. J. Chem. Edu. 2007, 84, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukraa, L. Honey in Traditional and Modern Medicine; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum, S. Honey: From Flower to Table; Chronicle Books: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, P.; Stecka, H.; Sergiel, I.; Jamroz, P. Different aspects of the elemental analysis of honey by flame atomic absorption and emission spectrometry: A review. Food Anal. Methods 2012, 5, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kliks, M.M.; Jun, S.; Jackson, M.; Li, Q.X. Rapid analysis of glucose, fructose, sucrose, and maltose in honeys from different geographic regions using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. J. Food. Sci. 2010, 75, C208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato, I.; Huidobro, J.F.; Simal-Lozano, J.; Sancho, M.T. Rapid determination of nonaromatic organic acids in honey by capillary zone electrophoresis with direct ultraviolet detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesaga, M.; Pyrzynska, K. Stability of bioactive polyphenols from honey during different extraction methods. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerkovic, I.; Kus, P.M. Terpenes in honey: Occurrence, origin and their role as chemical biomarkers. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 31710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Vazquez, L.; Perez-Coello, M.S.; Cabezudo, M.D. Analysis of volatile compounds of rosemary honey. Comparison of different extraction techniques. Chromatographia 2003, 57, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidan Kumar, C.S.; Mythily, R.; Venkatachalapathy, R.; Chandraju, S. Bio-mimic conversion of Maida (polysaccharides) to reducing sugars by acid hydrolysis and its estimation using standard methods. Int. Food Res. J. 2014, 21, 523. [Google Scholar]
- Dzimitrowicz, A.; Jamroz, P.; Gil, W.; Bojszczak, W.; Motyka, A.; Pogoda, D.; Pohl, P. Fermented juices as reducing and capping agents for the biosynthesis of size-defined spherical gold nanoparticles. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2018, 22, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmeister, L.C. Convective Heat Transfer: Solutions Manual; John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Haes, A.J.; Zou, S.; Schatz, G.C.; van Duyne, R.P. A nanoscale optical biosensor: The long range distance dependence of the Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance of noble metals nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.B.; Kryschi, C. A facile one-pot synthesis of blue and red luminescent thiol stabilized gold nanoclusters. A through optical and microscopy study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 21423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mie, G. A contribution to the optics of turbid media, especially colloidal metallic suspensions. Ann. Phys. 1908, 25, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchert, H.; Shevchenko, E.V.; Robert, A.; Mekis, I.; Kornowski, A.; Grubel, G.; Weller, H. Determination of nanocrystal sizes: A comparison of tem, saxs, and xrd studies of highly monodisperse copt3 particles. Langmuir 2005, 21, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedzierska-Matysek, M.; Matwijczuk, A.; Florek, M.; Barlowska, J.; Wolanciuk, A.; Matwijczuk, A.; Chrusciel, E.; Walkowiak, R.; Karcz, D.; Gladyszewska, B. Application of FTIR spectroscopy for analysis of the quality of honey. In Proceedings of the BIO Web of Conferences, Krakow, Poland, 25–27 September 2017; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
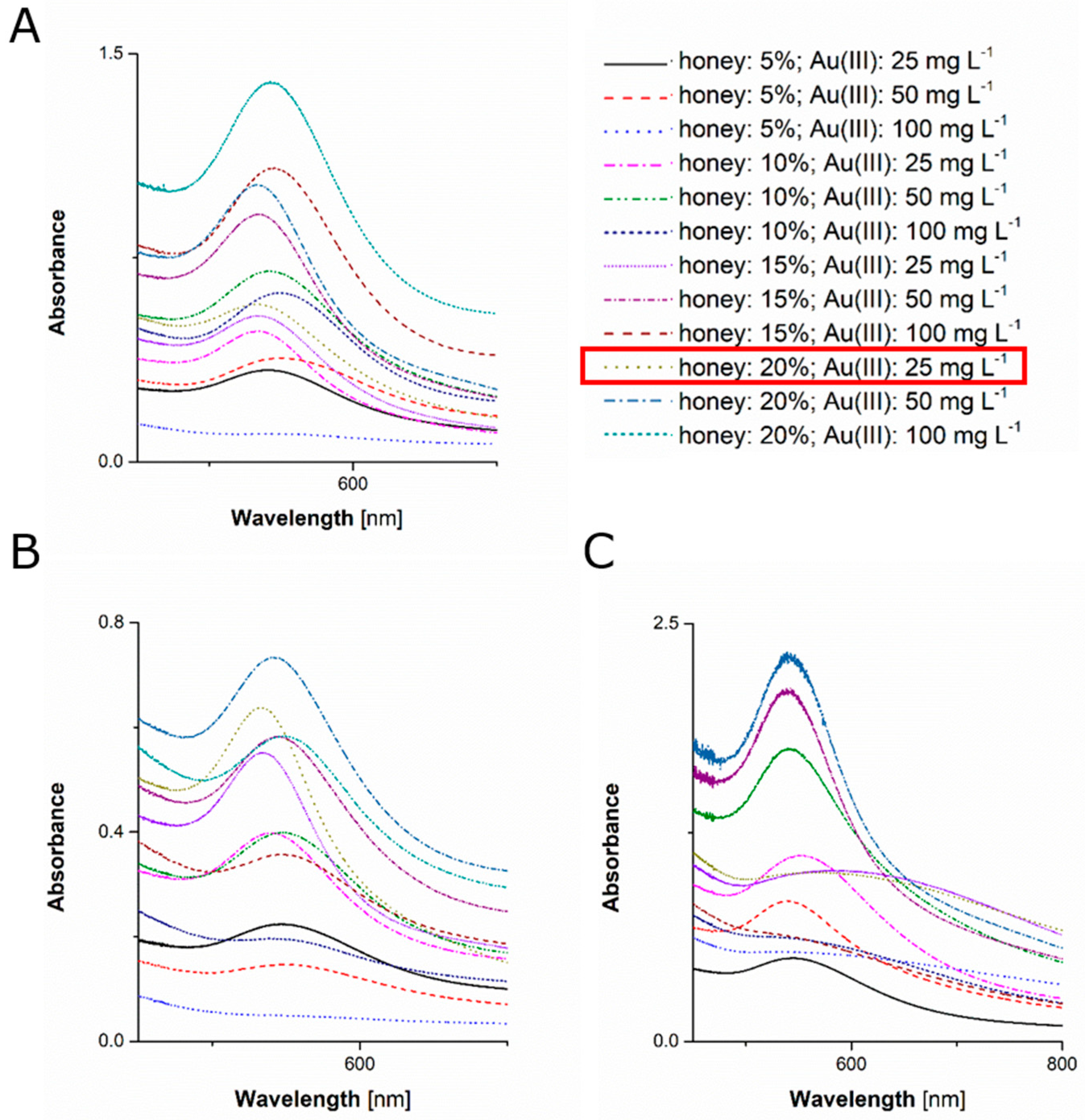


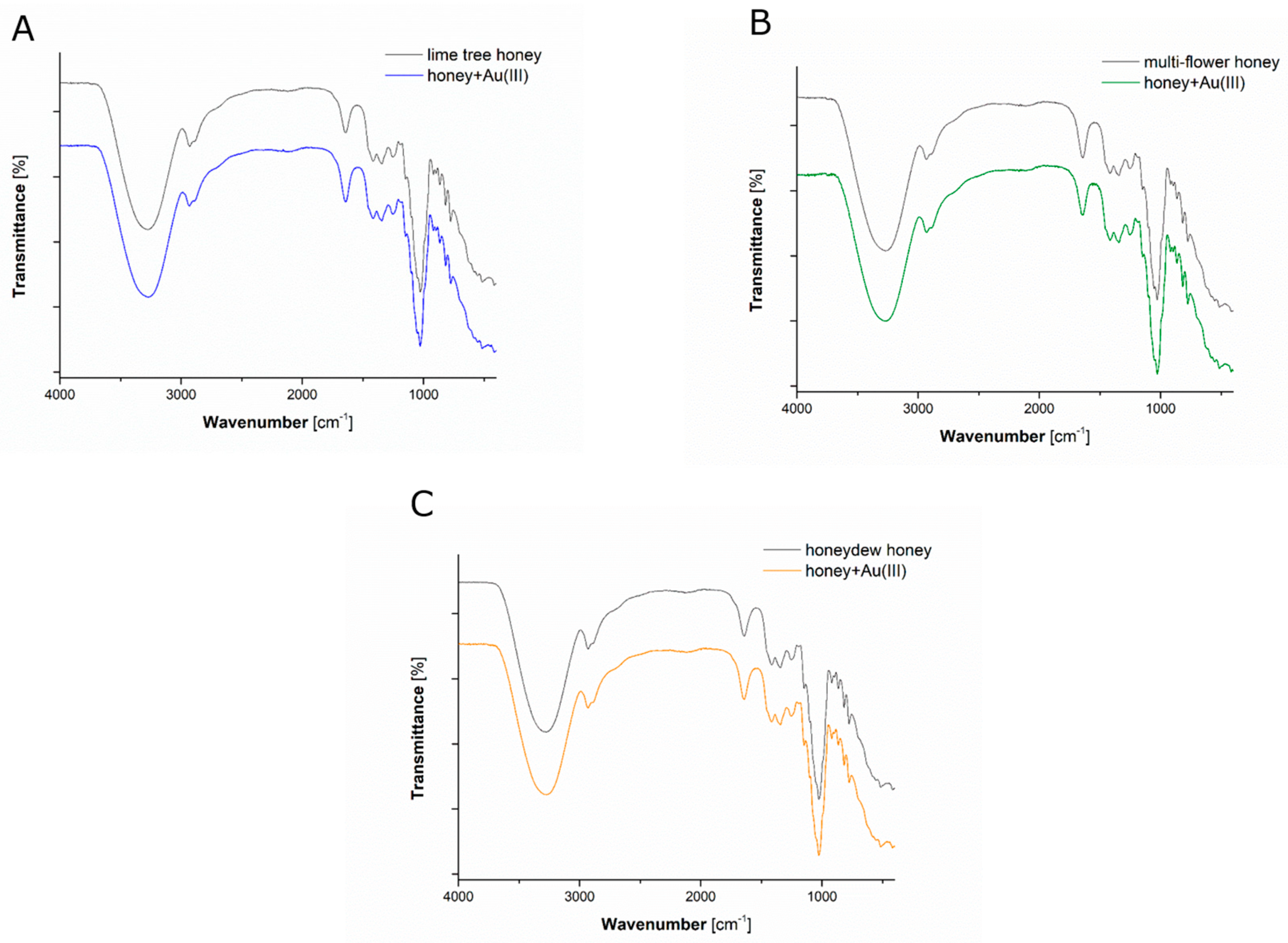
| No. | Type of Honey | Honey Concentration (%) | Au(III) Concentration (mg·L−1) | λmax (nm) | A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lime tree | 20 | 100 | 563.4 | 0.17 |
| 2 | Lime tree | 20 | 50 | 550.4 | 0.55 |
| 3 | Lime tree | 20 | 25 | 538.5 | 0.43 |
| 4 | Lime tree | 15 | 100 | 552.5 | 0.45 |
| 5 | Lime tree | 15 | 50 | 543.2 | 0.38 |
| 6 | Lime tree | 15 | 25 | 540.2 | 0.21 |
| 7 | Lime tree | 10 | 100 | 558.1 | 0.27 |
| 8 | Lime tree | 10 | 50 | 551.4 | 0.26 |
| 9 | Lime tree | 10 | 25 | 539.5 | 0.20 |
| 10 | Lime tree | 5 | 100 | 565.2 | 0.02 |
| 11 | Lime tree | 5 | 50 | 561.9 | 0.13 |
| 12 | Lime tree | 5 | 25 | 550.5 | 0.12 |
| 13 | Multiflower | 20 | 100 | 558.3 | 0.15 |
| 14 | Multiflower | 20 | 50 | 550.3 | 0.23 |
| 15 | Multiflower | 20 | 25 | 538.3 | 0.25 |
| 16 | Multiflower | 15 | 100 | 559.1 | 0.08 |
| 17 | Multiflower | 15 | 50 | 553.1 | 0.20 |
| 18 | Multiflower | 15 | 25 | 538.5 | 0.21 |
| 19 | Multiflower | 10 | 100 | 538.4 | 0.25 |
| 20 | Multiflower | 10 | 50 | 559.1 | 0.08 |
| 21 | Multiflower | 10 | 25 | 553.4 | 0.19 |
| 22 | Multiflower | 5 | 100 | 561.4 | 0.02 |
| 23 | Multiflower | 5 | 50 | 557.2 | 0.13 |
| 24 | Multiflower | 5 | 25 | 547.9 | 0.14 |
| 25 | Honeydew | 20 | 100 | 569.6 | 0.01 |
| 26 | Honeydew | 20 | 50 | 558.2 | 0.07 |
| 27 | Honeydew | 20 | 25 | 550.2 | 0.90 |
| 28 | Honeydew | 15 | 100 | 654.1 | 0.16 |
| 29 | Honeydew | 15 | 50 | 576.9 | 0.04 |
| 30 | Honeydew | 15 | 25 | 657.2 | 0.25 |
| 31 | Honeydew | 10 | 100 | 595.1 | 0.06 |
| 32 | Honeydew | 10 | 50 | 553.5 | 0.59 |
| 33 | Honeydew | 10 | 25 | 551.3 | 0.39 |
| 34 | Honeydew | 5 | 100 | 631.8 | 0.04 |
| 35 | Honeydew | 5 | 50 | 540.7 | 0.83 |
| 36 | Honeydew | 5 | 25 | 552.3 | 0.28 |
| Honey | Before Addition of Au(III) | After Addition of Au(III) | AuNPs Mean Size (nm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reducing Sugars | Polyphenols | Reducing Sugars | Polyphenols | ||
| Lime tree | 620.7 | 65.97 | 515.0 | 56.29 | 51.6 ± 84.4 |
| Multiflower | 780.2 | 41.61 | 569.6 | 35.46 | 20.6 ± 23.3 |
| Honeydew | 889.5 | 145.4 | 493.1 | 104.7 | 25.1 ± 26.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dzimitrowicz, A.; Cyganowski, P.; Jamroz, P.; Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D.; Rzegocka, M.; Cwiklinska, A.; Pohl, P. Tuning Optical and Granulometric Properties of Gold Nanostructures Synthesized with the Aid of Different Types of Honeys for Microwave-Induced Hyperthermia. Materials 2019, 12, 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060898
Dzimitrowicz A, Cyganowski P, Jamroz P, Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak D, Rzegocka M, Cwiklinska A, Pohl P. Tuning Optical and Granulometric Properties of Gold Nanostructures Synthesized with the Aid of Different Types of Honeys for Microwave-Induced Hyperthermia. Materials. 2019; 12(6):898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060898
Chicago/Turabian StyleDzimitrowicz, Anna, Piotr Cyganowski, Piotr Jamroz, Dorota Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, Malgorzata Rzegocka, Agnieszka Cwiklinska, and Pawel Pohl. 2019. "Tuning Optical and Granulometric Properties of Gold Nanostructures Synthesized with the Aid of Different Types of Honeys for Microwave-Induced Hyperthermia" Materials 12, no. 6: 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060898
APA StyleDzimitrowicz, A., Cyganowski, P., Jamroz, P., Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D., Rzegocka, M., Cwiklinska, A., & Pohl, P. (2019). Tuning Optical and Granulometric Properties of Gold Nanostructures Synthesized with the Aid of Different Types of Honeys for Microwave-Induced Hyperthermia. Materials, 12(6), 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060898










