One-Pot Method for Preparation of Magnetic Multi-Core Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
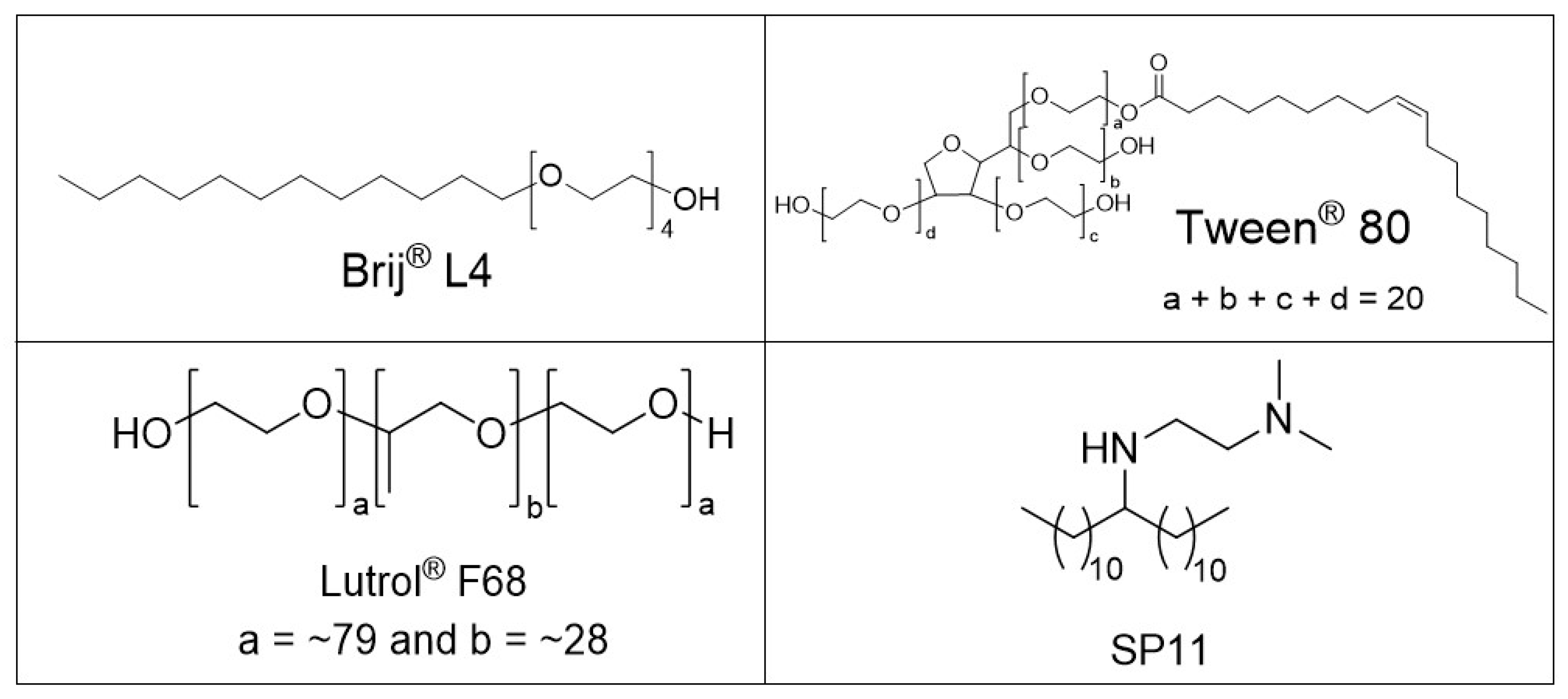
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Methods
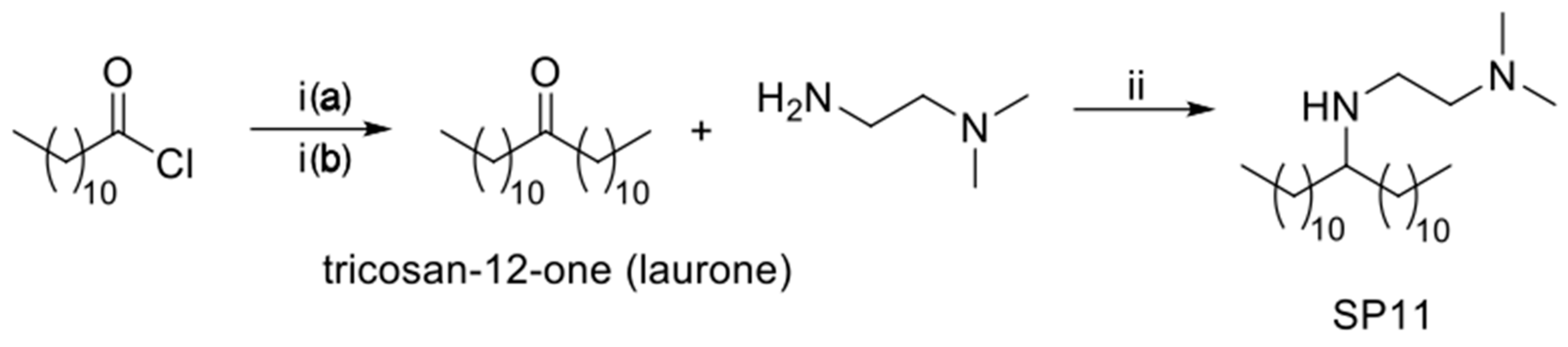
2.2.1. Synthesis of N1,N1-dimethyl-N2-(tricosan-12-yl)ethane-1,2-diamine (SP11)
Synthesis of Tricosan-12-one (Laurone)
Synthesis of N1,N1-dimethyl-N2-(tricosan-12-yl)ethane-1,2-diamine (SP11)
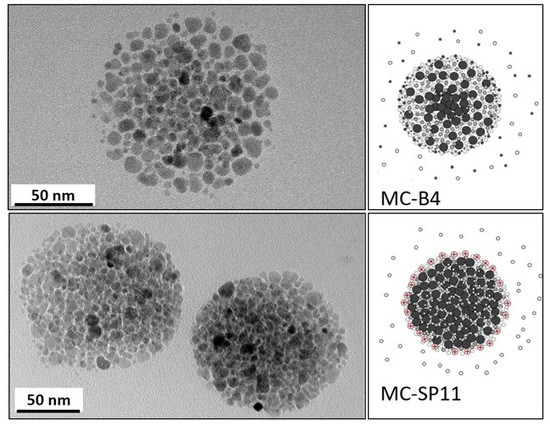
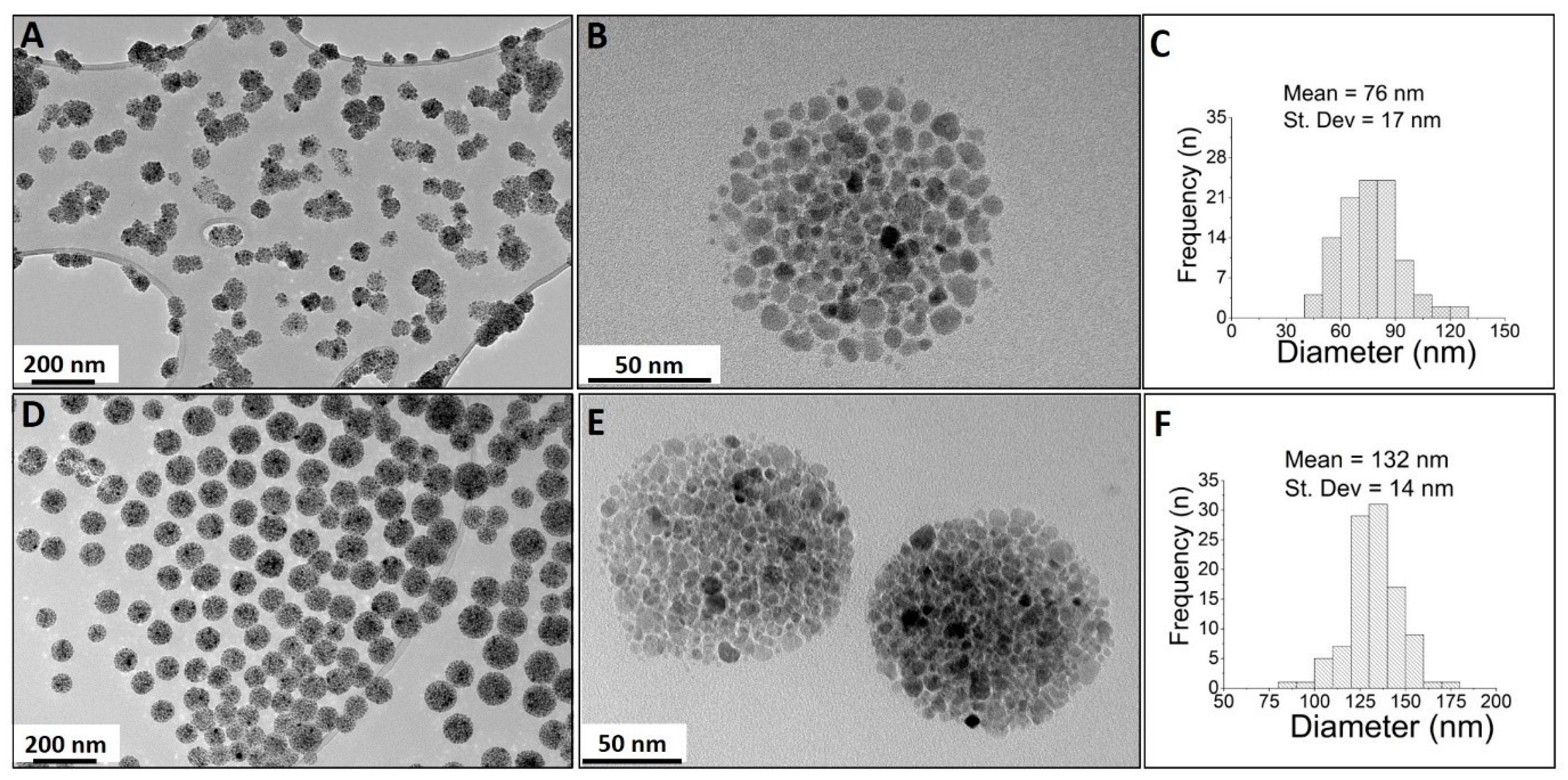
2.2.2. One-Pot Preparation of Magnetic Nanocarriers with Brij 4 (MC-B4)
2.2.3. One-Pot Preparation of Magnetic Nanocarriers with SP11 (MC-SP11)
2.2.4. Determination of Drug Loading
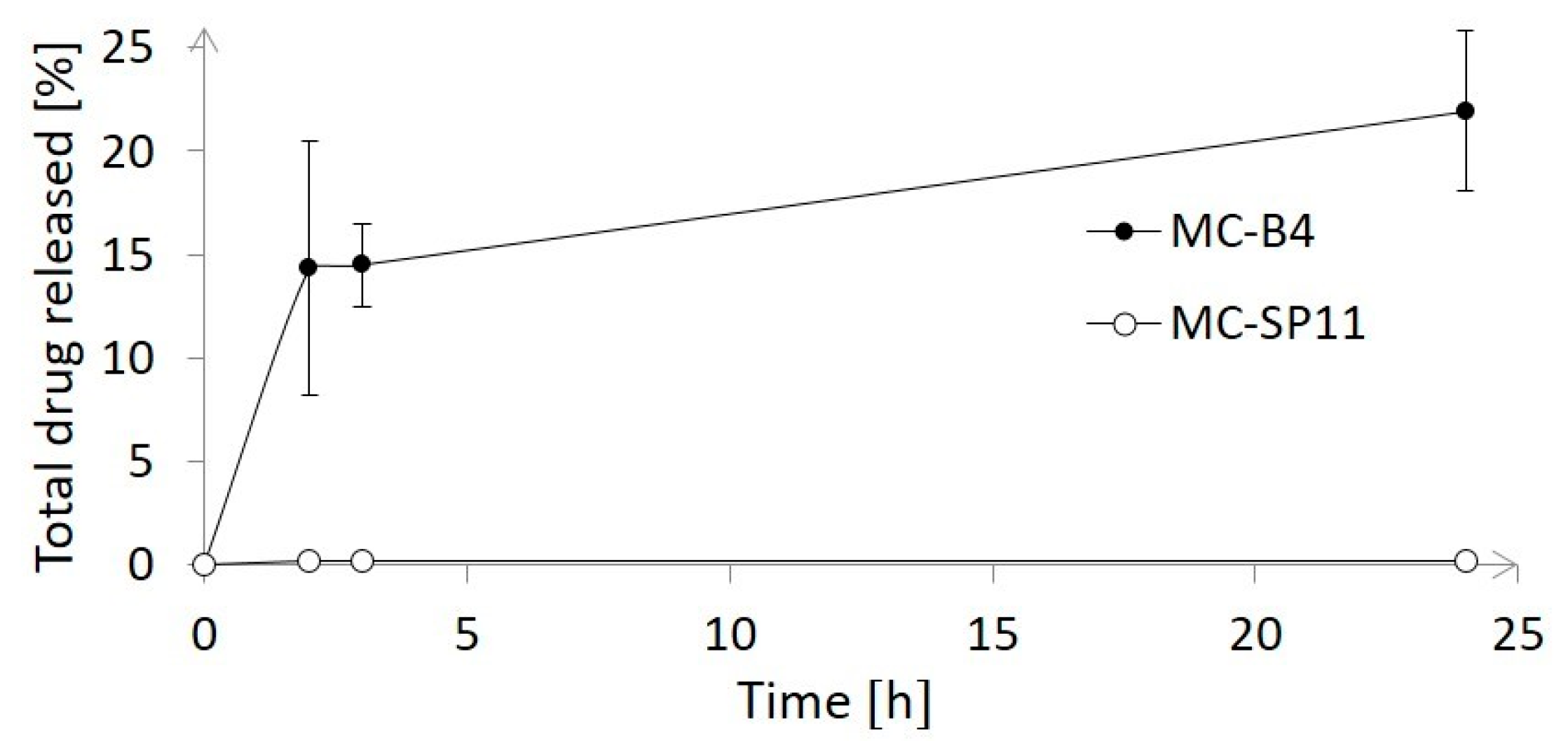
2.2.5. Drug-Release Studies
2.3. Characterization of Tricosan-12-One (Laurone) and SP11
2.4. HPLC Analysis of Orlistat
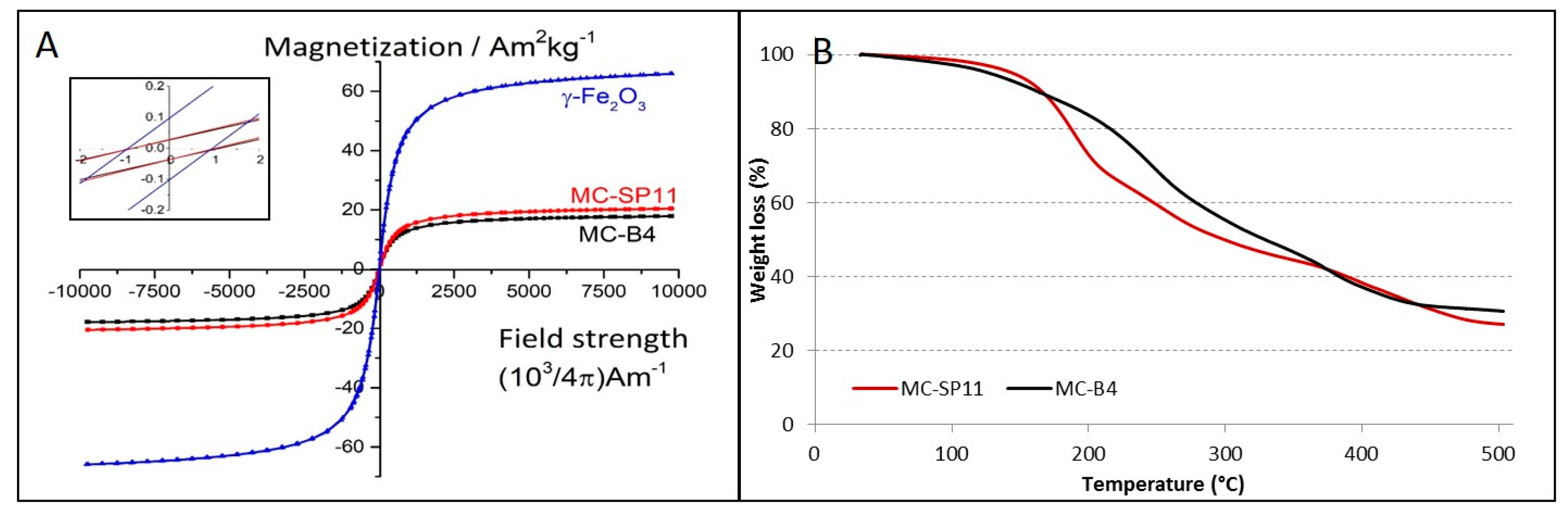
2.5. Characterization of the Magnetic Nanocarriers
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lisjak, D.; Mertelj, A. Anisotropic magnetic nanoparticles: A review of their properties, syntheses and potential applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 95, 286–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Wilhelm, C. Magnetic nanoparticles in cancer therapy: How can thermal approaches help? Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavre, I.; Kostevc, G.; Kralj, S.; Vilfan, A.; Babič, D. Fabrication of magneto-responsive microgears based on magnetic nanoparticle embedded PDMS. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 38316–38322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, C.; Vollin-Bringel, O.; Fiegel, V.; Harlepp, S.; Van der Schueren, B.; Bégin-Colin, S.; Bégin, D.; Mertz, D. Engineering of Mesoporous Silica Coated Carbon-Based Materials Optimized for an Ultrahigh Doxorubicin Payload and a Drug Release Activated by pH, T, and NIR-light. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiegel, V.; Harlepp, S.; Begin-Colin, S.; Begin, D.; Mertz, D. Design of Protein-Coated Carbon Nanotubes Loaded with Hydrophobic Drugs through Sacrificial Templating of Mesoporous Silica Shells. Chem. A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 4662–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostevšek, N.; Abramovič, I.; Hudoklin, S.; Kreft, M.E.; Serša, I.; Sepe, A.; Vidmar, J.; Šturm, S.; Spreitzer, M.; Ščančar, J.; et al. Hybrid FePt/SiO2/Au nanoparticles as a theranostic tool: In vitro photo-thermal treatment and MRI imaging. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 1308–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolosnjaj Tabi, J.; Lartigue, L.; Javed, Y.; Luciani, N.; Pellegrino, T.; Wilhelm, C.; Alloyeau, D.; Gazeau, F. Biotransformations of magnetic nanoparticles in the body. Nanotoday 2016, 11, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarjanli, Z.; Ghaedi, K.; Esmaeili, A.; Rahgozar, S.; Zarrabi, A. Iron oxide nanoparticles may damage to the neural tissue through iron accumulation, oxidative stress, and protein aggregation. BMC Neurosci. 2017, 18, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvindi, M.A.; De Matteis, V.; Galeone, A.; Brunetti, V.; Anyfantis, G.C.; Athanassiou, A.; Cingolani, R.; Pompa, P.P. Toxicity assessment of silica coated iron oxide nanoparticles and biocompatibility improvement by surface engineering. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier-Hauff, K.; Ulrich, F.; Nestler, D.; Niehoff, H.; Wust, P.; Thiesen, B.; Orawa, H.; Budach, V.; Jordan, A. Efficacy and safety of intratumoral thermotherapy using magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles combined with external beam radiotherapy on patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 103, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, A.; Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Abou-Hassan, A.; Plan Sangnier, A.; Curcio, A.; Silva, A.K.A.; Di Corato, R.; Neveu, S.; Pellegrino, T.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; et al. Magnetic (Hyper)Thermia or Photothermia? Progressive Comparison of Iron Oxide and Gold Nanoparticles Heating in Water, in Cells, and In Vivo. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Andujar, C.; Walter, A.; Cotin, G.; Bordeianu, C.; Mertz, D.; Felder-Flesch, D.; Begin-Colin, S. Design of iron oxide-based nanoparticles for MRI and magnetic hyperthermia. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 1889–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemsley, B.; Rollo, M.; Georgiou, A.; Balandin, S.; Hill, S. The health literacy demands of electronic personal health records (e-PHRs): An integrative review to inform future inclusive research. Patient Educ. Couns. 2018, 101, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, A.; Di Corato, R.; Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Flaud, P.; Pellegrino, T.; Wilhelm, C. Duality of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy: Amplification of Heating Efficiency by Magnetic Hyperthermia and Photothermal Bimodal Treatment. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2436–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Di Corato, R.; Lartigue, L.; Marangon, I.; Guardia, P.; Silva, A.K.A.; Luciani, N.; Clément, O.; Flaud, P.; Singh, J.V.; et al. Heat-generating iron oxide nanocubes: Subtle “destructurators” of the tumoral microenvironment. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4268–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ménard, M.; Meyer, F.; Parkhomenko, K.; Leuvrey, C.; Francius, G.; Bégin-Colin, S.; Mertz, D. Mesoporous silica templated-albumin nanoparticles with high doxorubicin payload for drug delivery assessed with a 3-D tumor cell model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralj, S.; Potrc, T.; Kocbek, P.; Makovec, S.M. Design and Fabrication of Magnetically Responsive Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 454–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kralj, S.; Makovec, D. The chemically directed assembly of nanoparticle clusters from superparamagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 13167–13171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippova, O.; Barabanova, A.; Molchanov, V.; Khokhlov, A. Magnetic polymer beads: Recent trends and developments in synthetic design and applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 542–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralj, S.; Makovec, D. Magnetic Assembly of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Clusters into Nanochains and Nanobundles. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9700–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, S.; Yang, P.; Ma, P.; Wang, D.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Niu, N.; Lin, J. Fibrous-structured magnetic and mesoporous Fe3O4/silica microspheres: Synthesis and intracellular doxorubicin delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 16420–16426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadic, M.; Kralj, S.; Jagodic, M.; Hanzel, D.; Makovec, D. Magnetic properties of novel superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoclusters and their peculiarity under annealing treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 322, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Bi, J.; Tang, Y.; Qiao, S.Z. Magnetic Core-Shell Silica Nanoparticles with Large Radial Mesopores for siRNA Delivery. Small 2016, 12, 4735–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.R.O.; Ramos, J.M.F.; Gomes, I.T.; Almeida, B.G.; Araújo, J.P.; Queiroz, M.J.R.P.; Coutinho, P.J.G.; Castanheira, E.M.S. Magnetoliposomes based on manganese ferrite nanoparticles as nanocarriers for antitumor drugs. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 17302–17313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobuto, H.; Sugita, T.; Kubo, T.; Shimose, S.; Yasunaga, Y.; Murakami, T.; Ochi, M. Evaluation of systemic chemotherapy with magnetic liposomal doxorubicin and a dipole external electromagnet. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhaylov, G.; Mikac, U.; Magaeva, A.A.; Itin, V.I.; Naiden, E.P.; Psakhye, I.; Babes, L.; Reinheckel, T.; Peters, C.; Zeiser, R.; et al. Ferri-liposomes as an MRI-visible drug-delivery system for targeting tumours and their microenvironment. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardiansyah, A.; Yang, M.C.; Liu, T.Y.; Kuo, C.Y.; Huang, L.Y.; Chan, T.Y. Hydrophobic Drug-Loaded PEGylated Magnetic Liposomes for Drug-Controlled Release. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro-Cordova, A.; Flores-Cruz, M.; Santoyo-Salazar, J.; Carrillo-Nava, E.; Jurado, R.; Figueroa-Rodriguez, P.A.; Lopez-Sanchez, P.; Medina, L.A.; Garcia-Lopez, P. Liposomes loaded with cisplatin and magnetic nanoparticles: Physicochemical characterization, pharmacokinetics, and in-vitro efficacy. Molecules 2018, 23, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocbek, P.; Kralj, S.; Kreft, M.E.; Kristl, J. Targeting intracellular compartments by magnetic polymeric nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.R.O.; Almeida, B.G.; Rodrigues, J.M.; Queiroz, M.J.R.P.; Calhelha, R.C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Pires, A.; Pereira, A.M.; Araújo, J.P.; Coutinho, P.J.G.; et al. Magnetoliposomes as carriers for promising antitumor thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-arylamines: photophysical and biological studies. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15352–15361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plassat, V.; Wilhelm, C.; Marsaud, V.; Menager, C.; Gazeau, F.; Renoir, J.-M.; Lesieur, S. Anti-estrogen-loaded superparamagnetic liposomes for intracellular magnetic targeting and treatment of breast cancer tumors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 21, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grit, M.; Crommelin, D.J.A. Chemical stability of liposomes: implications for their physical stability. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1993, 64, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, U.S. Liposomes in drug delivery: progress and limitations. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 154, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kadasala, N.R.; Abouelmagd, S.A.; Castanares, M.A.; Collins, D.S.; Wei, A.; Yeo, Y. Polymer-iron oxide composite nanoparticles for EPR-independent drug delivery. Biomaterials 2016, 101, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, S.; Hosseinzadeh, H.; Pashaei, S.; Khodaparast, Z. Synthesis of stimuli-responsive chitosan nanocomposites via RAFT copolymerization for doxorubicin delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.R.; Carrião, M.S.; Pacheco, M.T.; Branquinho, L.C.; de Souza, A.L.R.; Bakuzis, A.F.; Lima, E.M. Triggered release of paclitaxel from magnetic solid lipid nanoparticles by magnetic hyperthermia. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, G.E.; Yet, L. Progress in the development of fatty acid synthase inhibitors as anticancer targets. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 4363–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, J.C. Laurone. In Organic Syntheses; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2003; p. 68. ISBN 9780471264224. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Fan, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Kong, D.; Yang, P.; Quan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Lin, J. Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Spheres for Drug Targeting and Controlled Release. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estefany Delgado-Rosales, E.; Quintanar, D.; Piñón-Segundo, E.; Magaña, N.; Leyva-Gómez, G.; Martínez-Martínez, F.; Mendoza Muñoz, N. Novel drug delivery systems based on the encapsulation of superparamagnetic nanoparticles into lipid nanocomposites. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezaniova, I.; Hruby, M.; Kralova, J.; Kral, V.; Cernochova, Z.; Cernoch, P.; Slouf, M.; Kredatusova, J.; Stepanek, P. Temoporfin-loaded 1-tetradecanol-based thermoresponsive solid lipid nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy. J. Control. Release 2016, 241, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dragar, Č.; Potrč, T.; Nemec, S.; Roškar, R.; Pajk, S.; Kocbek, P.; Kralj, S. One-Pot Method for Preparation of Magnetic Multi-Core Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery. Materials 2019, 12, 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030540
Dragar Č, Potrč T, Nemec S, Roškar R, Pajk S, Kocbek P, Kralj S. One-Pot Method for Preparation of Magnetic Multi-Core Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery. Materials. 2019; 12(3):540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030540
Chicago/Turabian StyleDragar, Črt, Tanja Potrč, Sebastjan Nemec, Robert Roškar, Stane Pajk, Petra Kocbek, and Slavko Kralj. 2019. "One-Pot Method for Preparation of Magnetic Multi-Core Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery" Materials 12, no. 3: 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030540
APA StyleDragar, Č., Potrč, T., Nemec, S., Roškar, R., Pajk, S., Kocbek, P., & Kralj, S. (2019). One-Pot Method for Preparation of Magnetic Multi-Core Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery. Materials, 12(3), 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030540