Fabrication of Micro-Patterned Surface for Pool-boiling Enhancement by Using Powder Injection Molding Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Materials
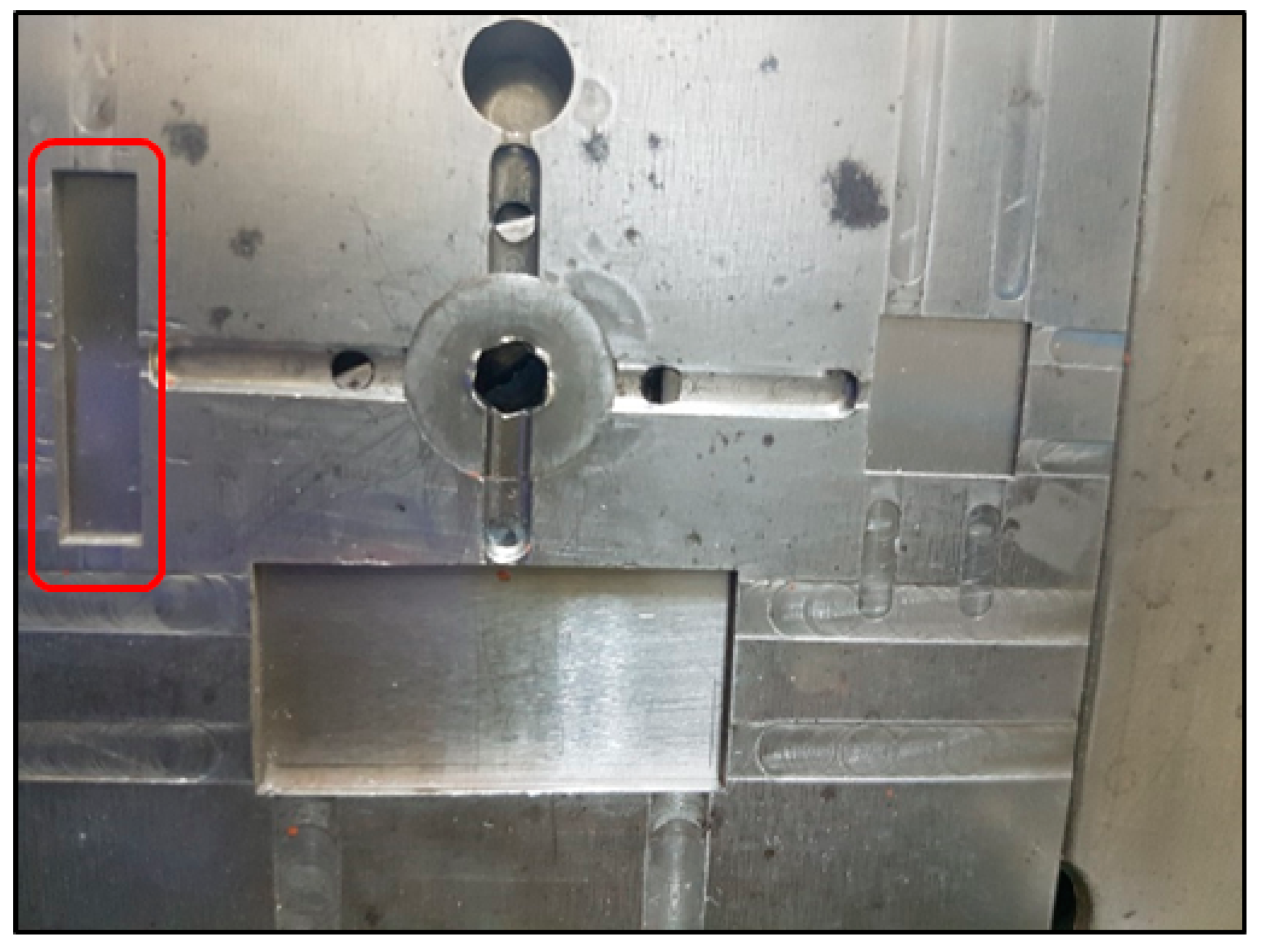
2.2. PIM Process
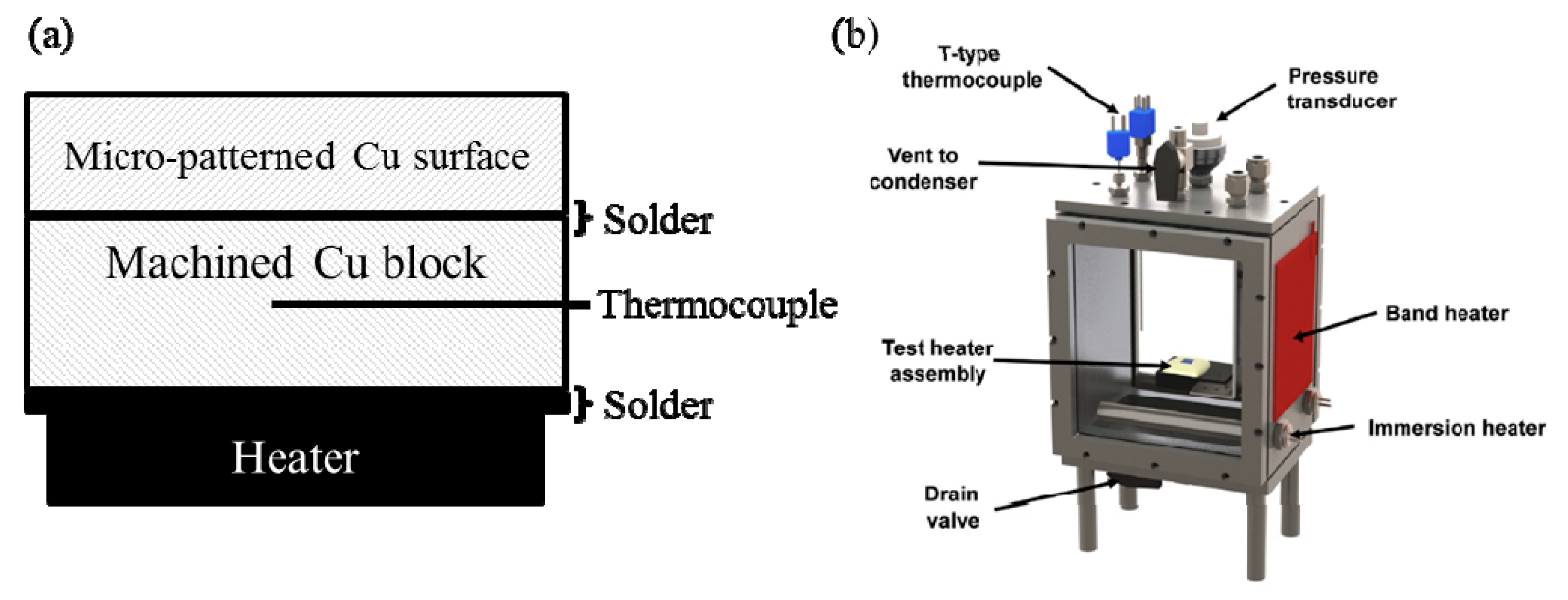
2.3. Pool-Boiling Experiment
2.4. Experimental Uncertainties
3. Results and Discussion
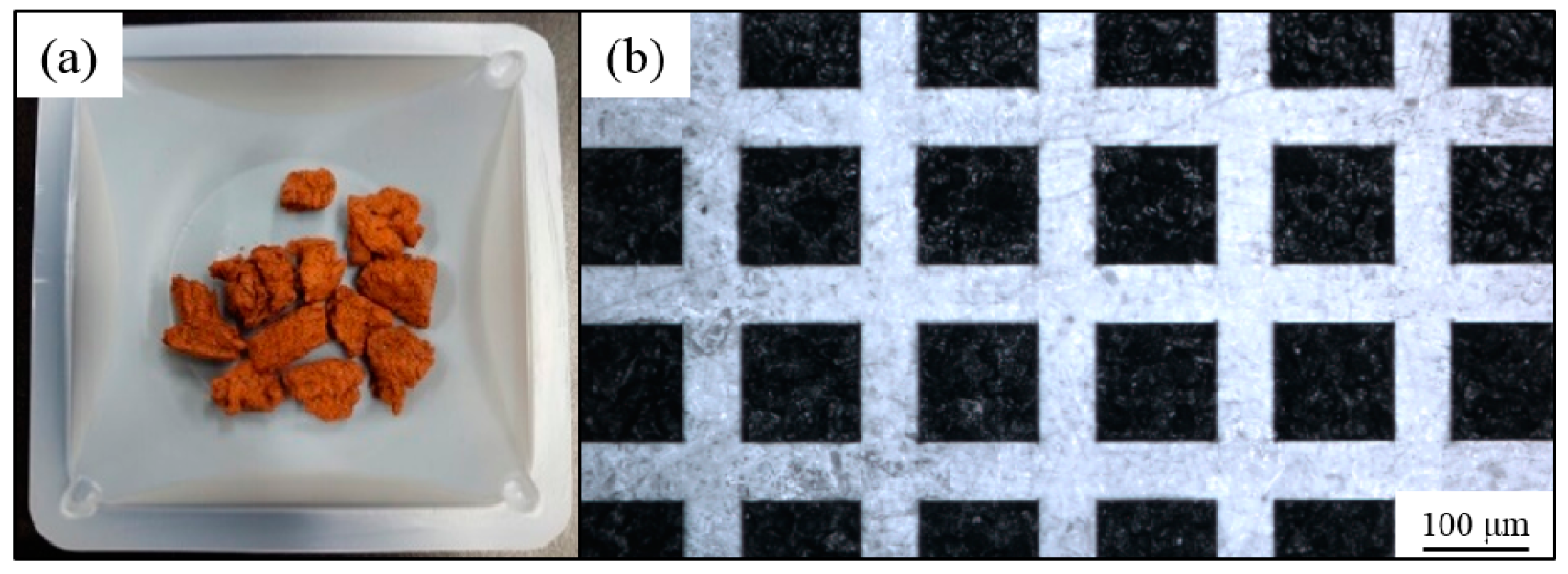
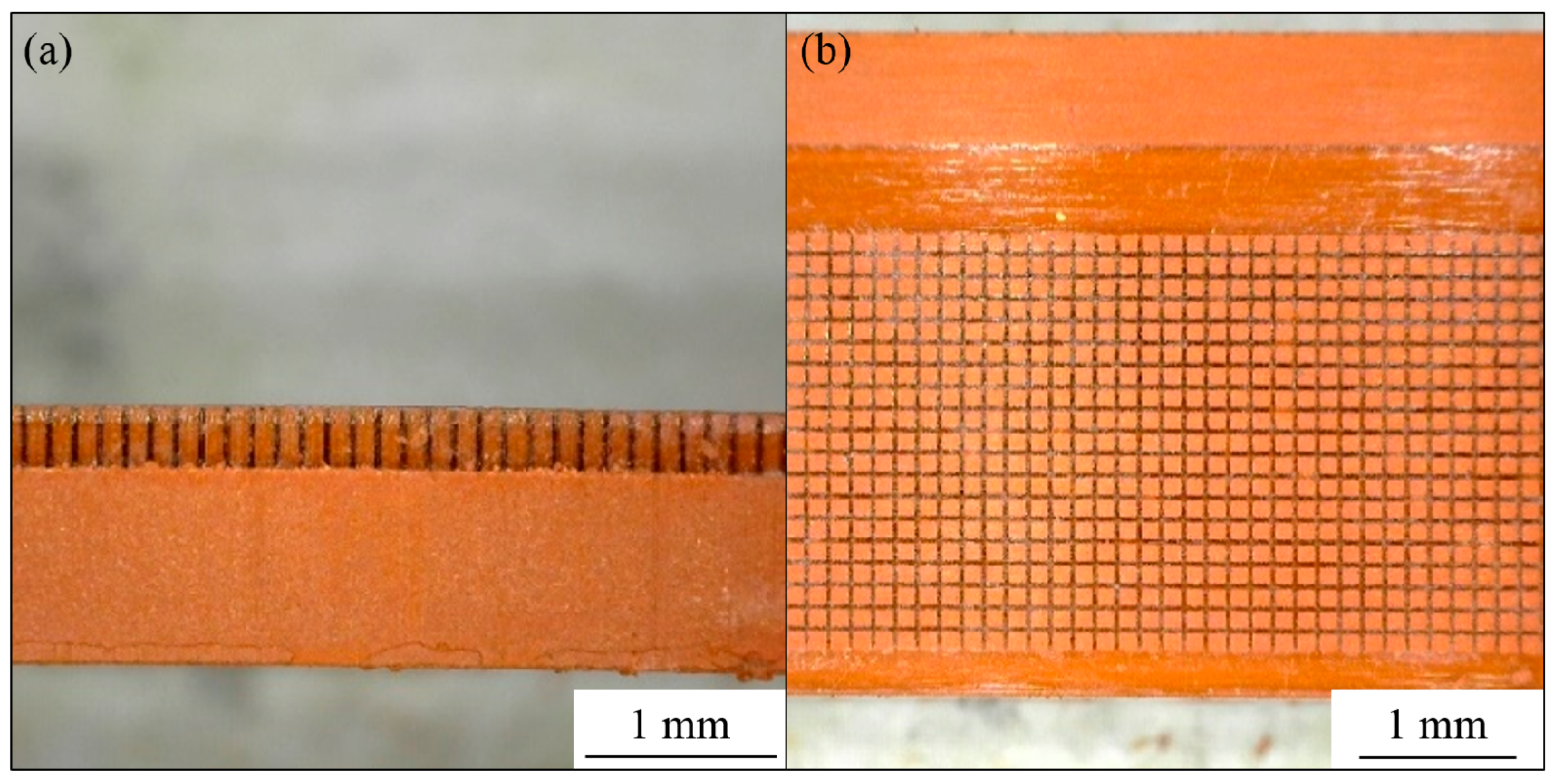
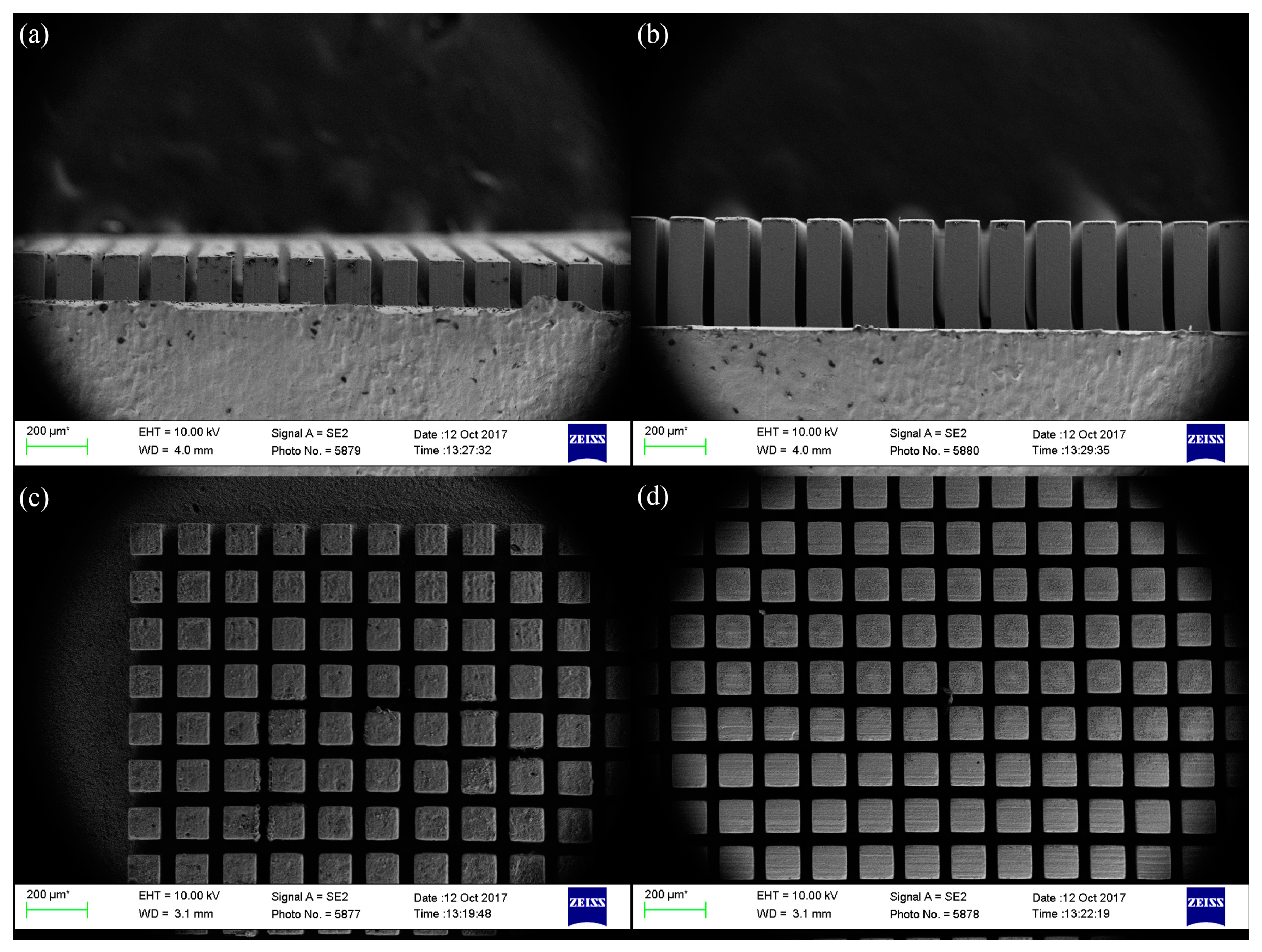
3.1. Fabrication of the Micro-Patterned Surface
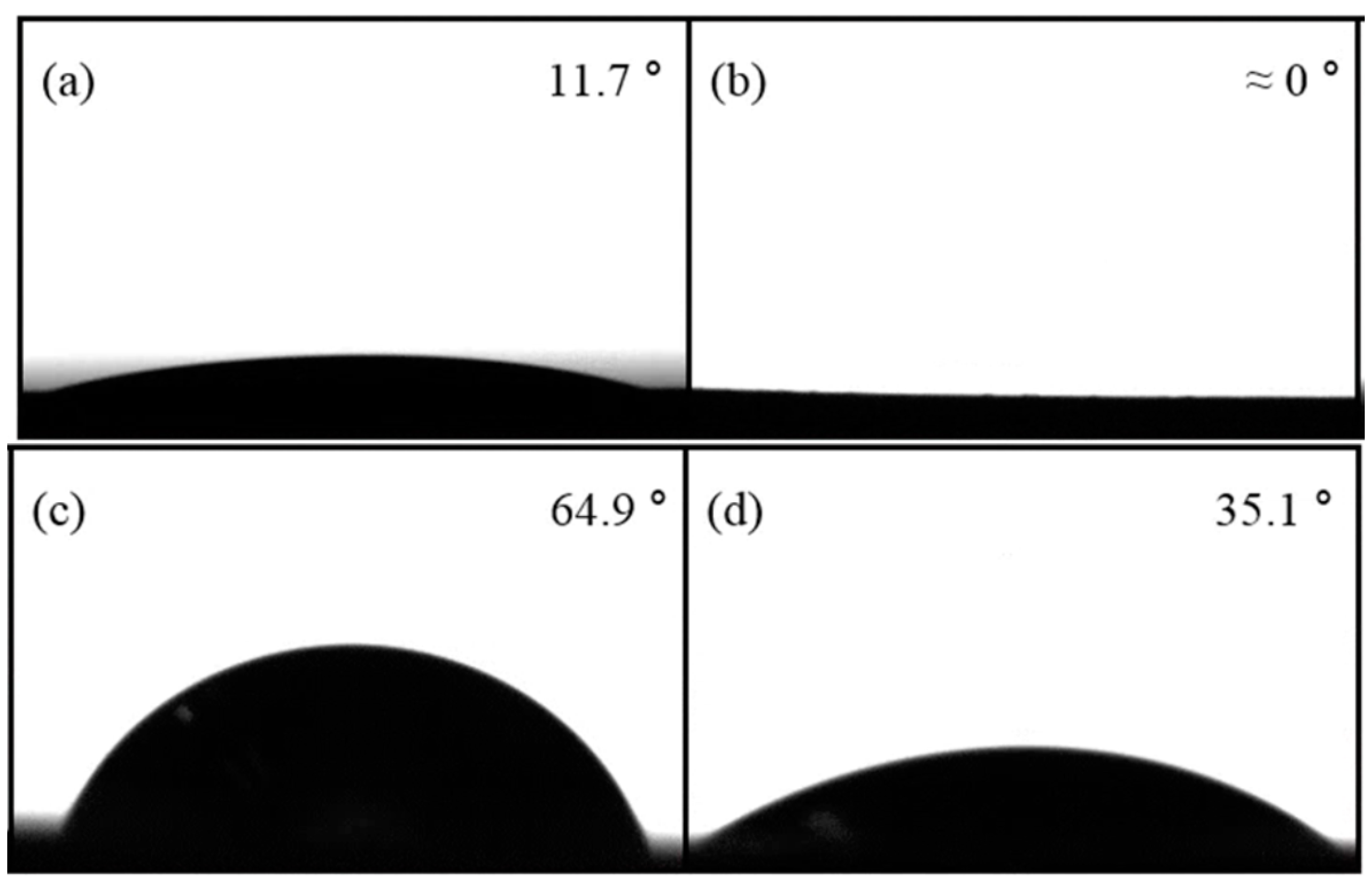
3.2. Contact Angle of the Micro-Patterned Surface
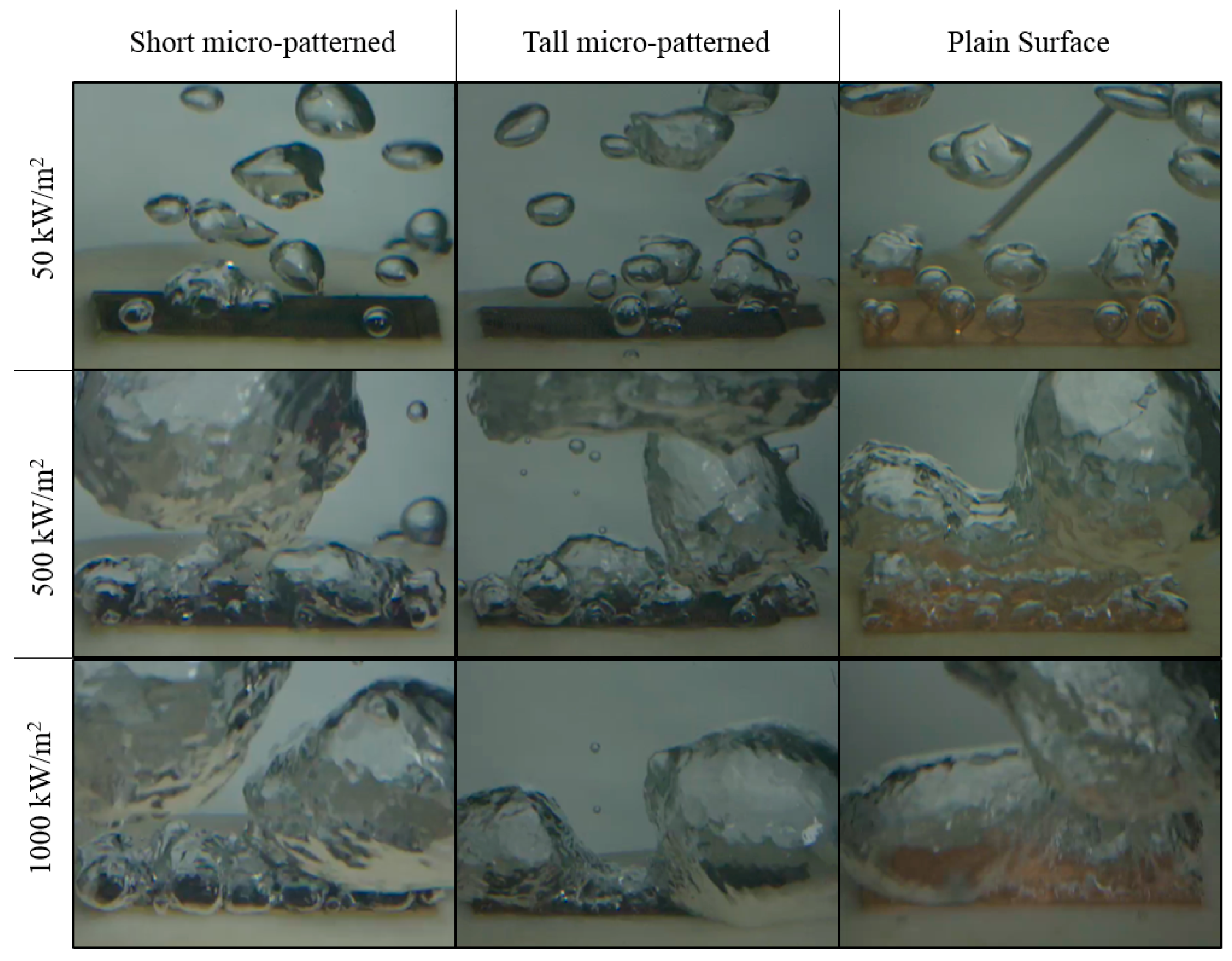
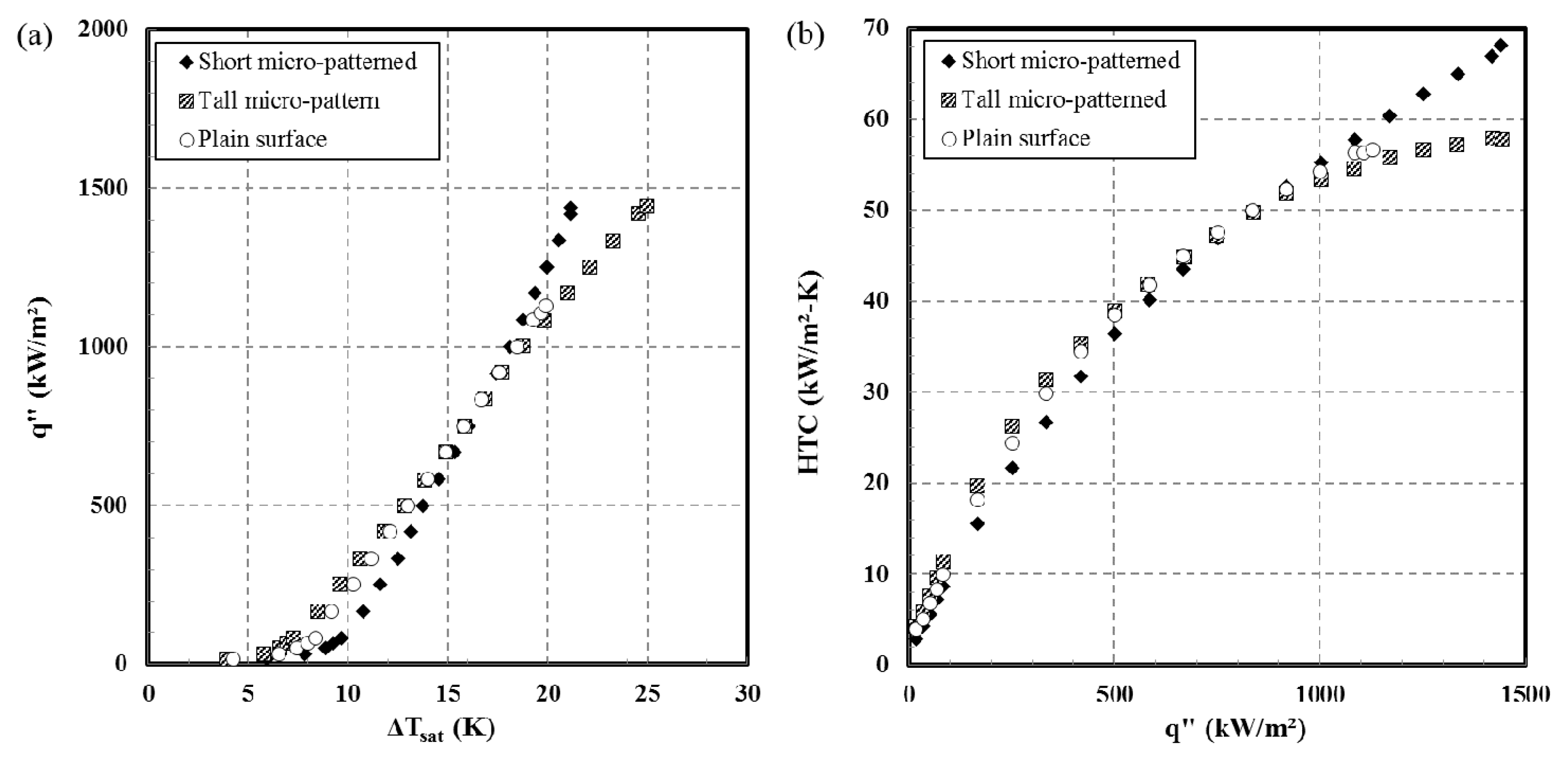
3.3. Results of the Pool-Boiling Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jun, S.; Kim, J.; Son, D.; Kim, H.Y.; You, S.M. Enhancement of pool boiling heat transfer in water using sintered copper microporous coatings. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2016, 48, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incropera, F.P.; Dewitt, D.P.; Bergman, T.L.; Lavine, A.S. Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 6th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 619–635. ISBN 0-471-45728-2. [Google Scholar]
- Liter, S.G.; Kaviany, M. Pool-boiling CHF enhancement by modulated porous-layer coating: Theory and experiment. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2001, 44, 4287–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupančič, M.; Može, M.; Gregorčič, P.; Sitar, A.; Golobič, I. Evaluation of enhanced nucleate boiling performance through walltemperature distributions on PDMS-silica coated and non-coated laser textured stainless steel surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 111, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheitaghy, A.M.; Saffari, H.; Ghasimi, D.; Ghasemi, A. Effect of electrolyte temperature on porous electrodeposited copper for pool boiling enhancement. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 113, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheitaghy, A.M.; Saffari, H.; Mohebbi, M. Investigation pool boiling heat transfer in U-shaped mesochannel with electrodeposited porous coating. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2016, 76, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ji, X.; Xu, J. Pool boiling heat transfer on copper foam covers with water as working fluid. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 49, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Peterson, G.P. Parametric study of pool boiling on horizontal highly conductive microporous coated surfaces. J. Heat Transf. 2007, 129, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Okuyama, K. Enhancement of the critical heat flux in saturated pool boiling using honeycomb porous media. Int. J. Multiphase Flow 2009, 35, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, C.M.; Santhanam, K.S.V.; Kandlikar, S.G. Development of a two-step electrodeposition process for enhancing pool boiling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 79, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jun, S.; Lee, J.; Godinez, J.; You, S.M. Effect of surface roughness on pool boiling heat transfer of water on a superhydrophilic aluminum surface. J. Heat Transf. 2017, 139, 101501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Ölçeroğlu, E.; McCarthy, M. Scalable nanomanufacturing of virus-templated coatings for enhanced boiling. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 1, 1300107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, C.M.; Anderson, T.; Wilson, C.; Zuhlke, C.; Alexander, D.; Gogos, G.; Ndao, S. Enhanced pool-boiling heat transfer and critical heat flux on femtosecond laser processed stainless steel surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 82, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Jun, S.; Laksnarain, R.; You, S.M. Effect of surface roughness on pool boiling heat transfer at a heated surface having moderate wettability. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 101, 992–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, H.; Takamastu, H.; Wei, J.J. Enhanced boiling of FC-72 on silicon chips with nicro-pin-fins and submicron-scale roughness. J. Heat Transf. 2002, 124, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandlikar, S.G. Controlling bubble motion over heated surface through evaporation momentum force to enhance pool boiling heat transfer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 051611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudawar, I.; Anderson, T.M. Optimization of enhanced surfaces for high flux chip cooling by pool boiling. J. Electron. Packag. 1993, 115, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, W.; Qi, B.; Wei, J. CHF correlation of boiling in FC-72 with micro-pin-fins for electronics cooling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 138, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Antao, D.S.; Lu, Z.; Somasundaram, S.; Zhang, T.; Wang, E.N. Prediction and characterization of dry-out heat flux in micropillar wick structures. Langmuir 2016, 32, 1920–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.J.; Guo, L.J.; Honda, H. Experimental study of boiling phenomena and heat transfer performances of FC-72 over micro-pin-finned silicon chips. Heat Mass Transf. 2005, 41, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaikumar, A.; Kandlikar, S.G. Enhanced pool boiling heat transfer mechanisms for selectively sintered open microchannels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 88, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, C.M.; Kandlikar, S.G. Pool boiling enhancement through microporous coatings selectively electrodeposited on fin tops of open microchannels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 79, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, R.M.; Bose, A. Injection Molding of Metals and Ceramics; Metal Powder Industries Federation: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1997; pp. 11–24. ISBN 1-878-954-61-X. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.W.; Kim, Y.D.; Suk, M.J. Micropatterns of W-Cu composites fabricated by metal powder injection molding. Met. Mater. Int. 2007, 13, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoodi, R.; Pillai, K.M. Wicking in Porous Materials; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 3–4. ISBN 978-1-4398-7433-2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.G.; Fu, G.; Reading, I.; Tor, S.B.; Loh, N.H.; Chaturvedi, P.; Yoon, S.F.; Youcef-Toumi, K. Dimensional variation in production of high-aspect-ratio micro-pillars array by micro powder injection molding. Appl. Phys. A 2007, 89, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Loh, N.H.; Tay, B.Y.; Tor, S.B. Microstructure evolution of 316L stainless steel micro components prepared by micro powder injection molding. Powder Technol. 2011, 206, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Tor, S.B.; Loh, N.H.; Tay, B.Y.; Hardt, D.E. A micro powder injection molding apparatus for high aspect ratio metal micro-structure production. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Jeon, J.H.; Lim, G.; Chang, S.S. Manufacture of a micro-sized piezoelectric ceramic structure using a sacrificial polymer mold insert. Microsyst. Technol. 2013, 19, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.S.; Gal, C.W.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J. Fabrication of high-aspect-ratio micro piezoelectric array by powder injection molding. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 9475–9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.S.; Jo, H.J.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, M.H. Effect of liquid spreading due to nano/microstructures on the critical heat flux during pool boiling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 071908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Chung, S.T.; Kwon, Y.S.; Park, S.J. Preparation of Ti-6Al-4V feedstock for titanium powder injection molding. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 1859–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, S. Development rate of PMMA exposed to synchrotron x-ray radiation for LIGA applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 21, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Li, Y.M.; Yue, J.L.; Luo, F.H. Deformation behavior and strength evolution of MIM compacts during thermal debinding. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2008, 18, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, S.J.; McClintock, F.A. Describing uncertainties in single-sample experiments. Mech. Eng. 1993, 75, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kandlikar, S.G. A theoretical model to predict pool boiling CHF incorporating effects of contact angle and orientation. J. Heat Transf. 2001, 123, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| D10 (μm) | D50 (μm) | D90 (μm) | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.01 | 4.73 | 15.23 | 8.638 |
| Component | Contents (wt. %) | Melting Point (°C) | Decomposition Range (°C) | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paraffin wax (PW) | 57.5 | 51 | 242–280 | 0.92 |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 25.0 | 78 | 464–481 | 0.92 |
| Polyethylene (PE) | 15.0 | 120 | 464–471 | 0.93 |
| Stearic acid (SA) | 2.5 | 53 | 246–275 | 0.95 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, H.; Godinez, J.; Han, J.S.; Fadda, D.; You, S.M.; Lee, J.; Park, S.J. Fabrication of Micro-Patterned Surface for Pool-boiling Enhancement by Using Powder Injection Molding Process. Materials 2019, 12, 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030507
Cho H, Godinez J, Han JS, Fadda D, You SM, Lee J, Park SJ. Fabrication of Micro-Patterned Surface for Pool-boiling Enhancement by Using Powder Injection Molding Process. Materials. 2019; 12(3):507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030507
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Hanlyun, Juan Godinez, Jun Sae Han, Dani Fadda, Seung Mun You, Jungho Lee, and Seong Jin Park. 2019. "Fabrication of Micro-Patterned Surface for Pool-boiling Enhancement by Using Powder Injection Molding Process" Materials 12, no. 3: 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030507
APA StyleCho, H., Godinez, J., Han, J. S., Fadda, D., You, S. M., Lee, J., & Park, S. J. (2019). Fabrication of Micro-Patterned Surface for Pool-boiling Enhancement by Using Powder Injection Molding Process. Materials, 12(3), 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030507







