Experimental Investigation and Optimal Prediction of Maximum Forming Angle and Surface Roughness of an Al/SUS Bimetal Sheet in an Incremental Forming Process Using Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
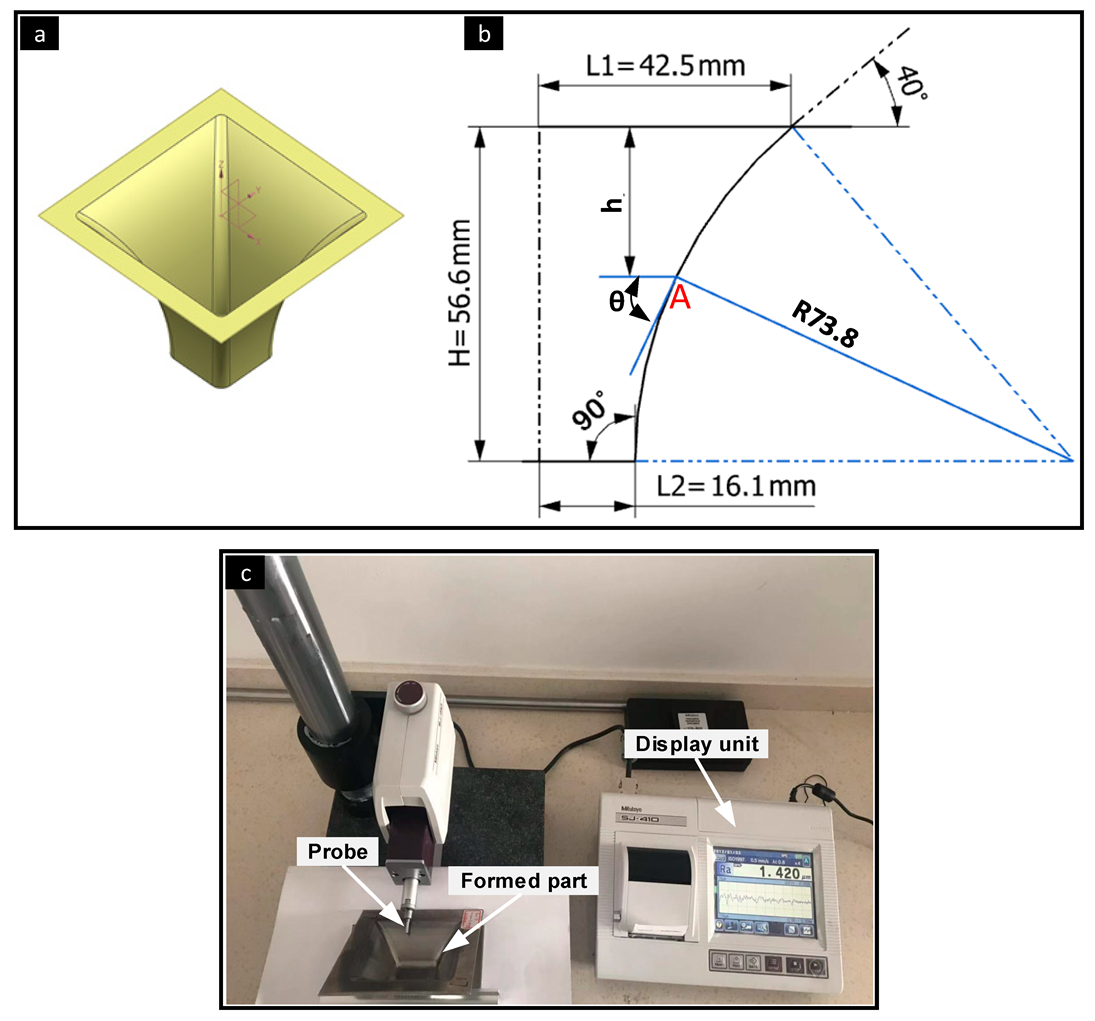
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Development of the Machine Learning Model
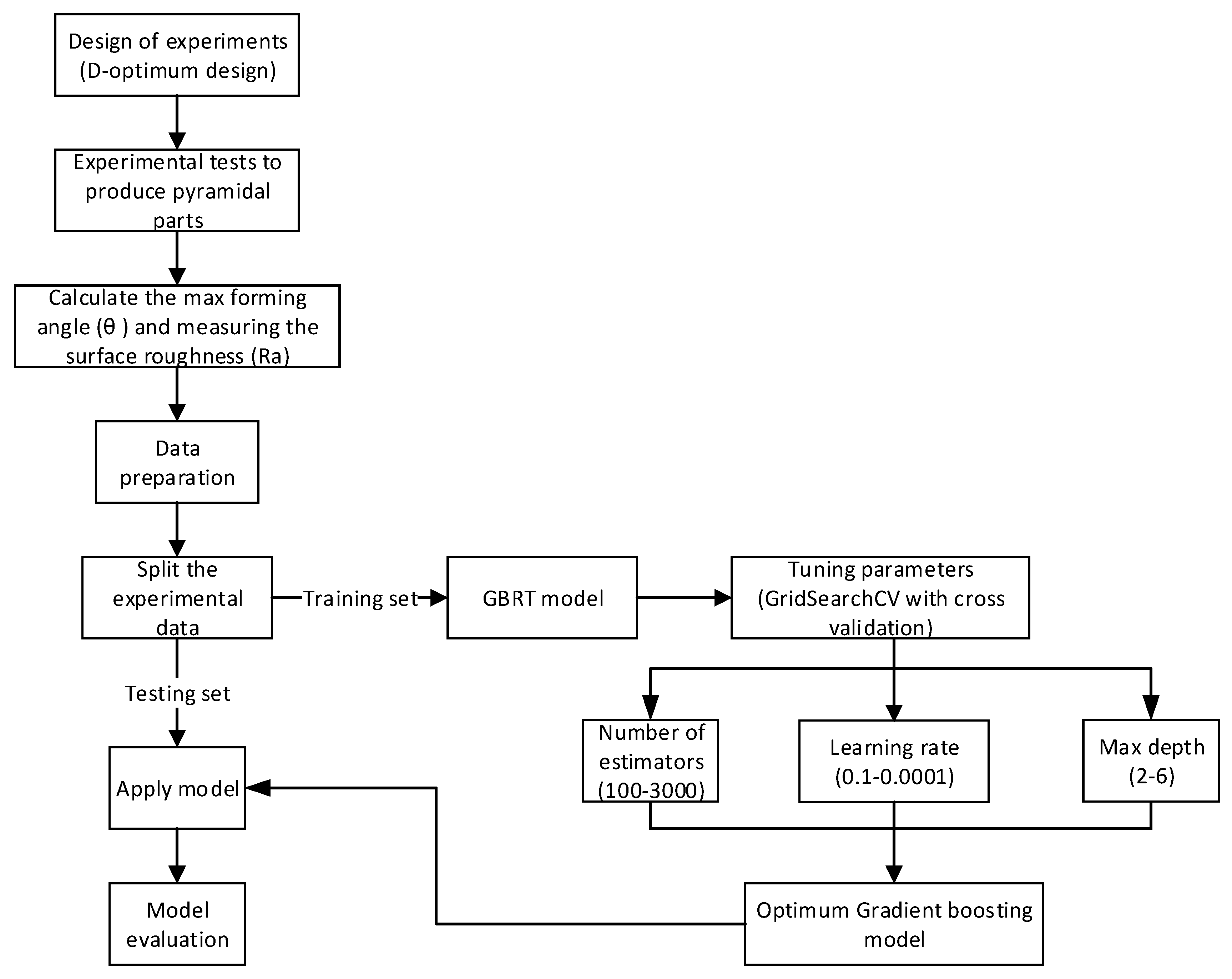
3.1. Proposed Methodology
3.2. Gradient Boosting Tree
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Experimental Results
4.1.1. Feature Importance Based on GBRT
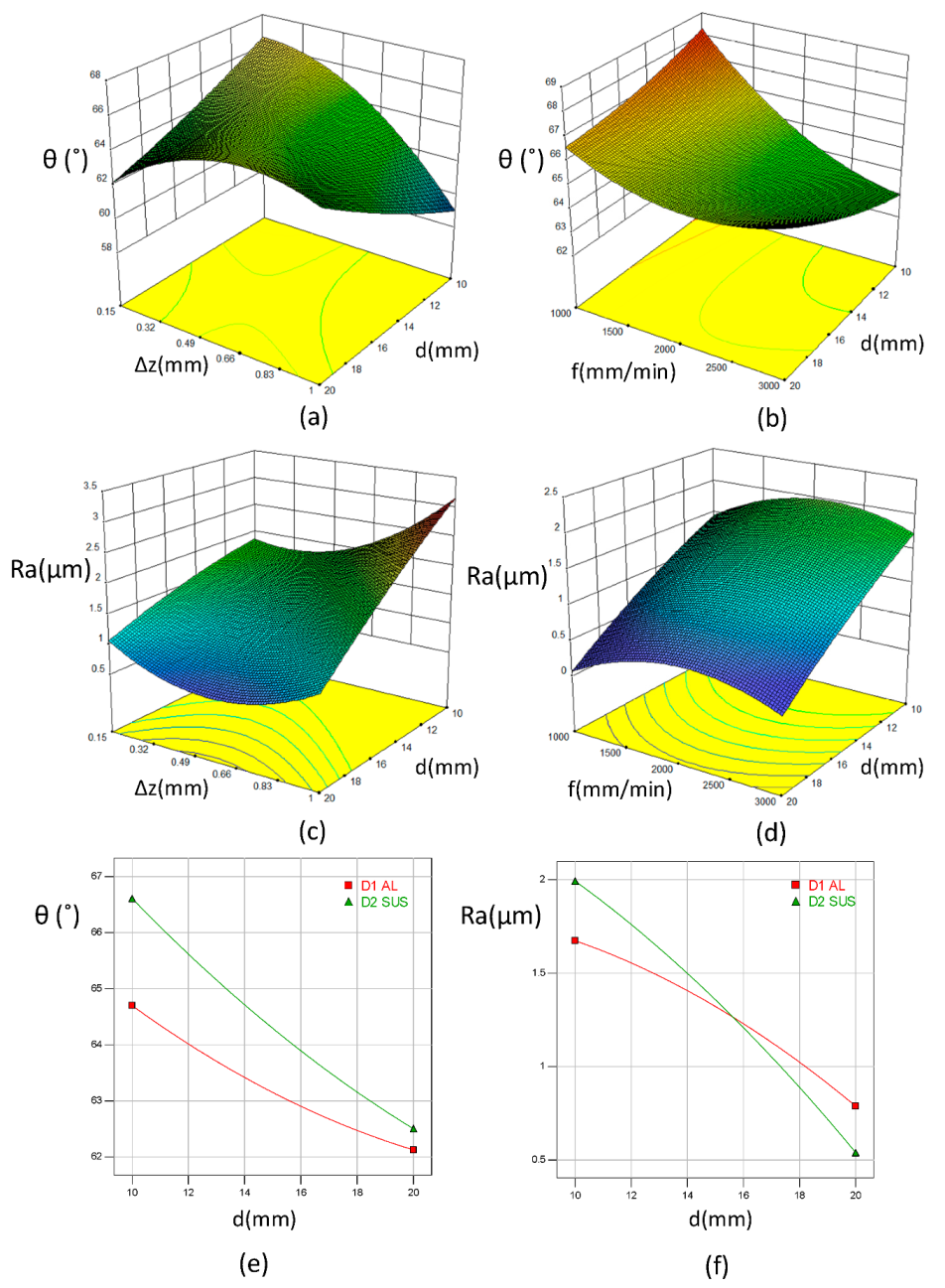
4.1.2. Experimental Parameters Effect
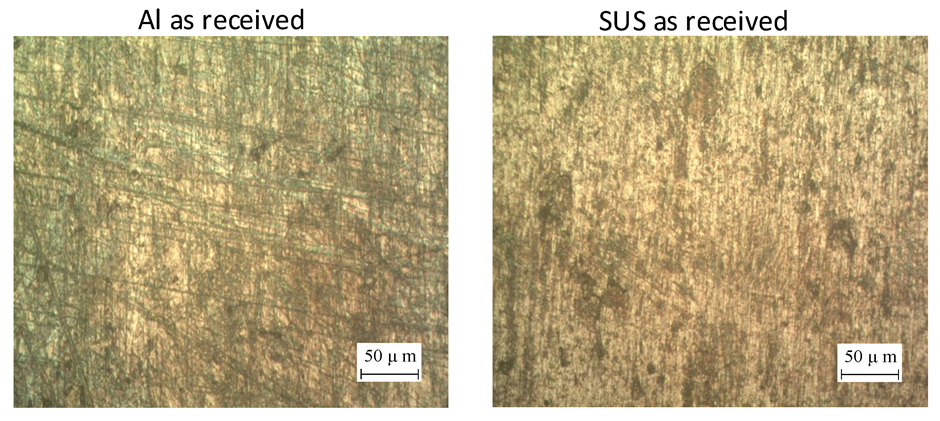
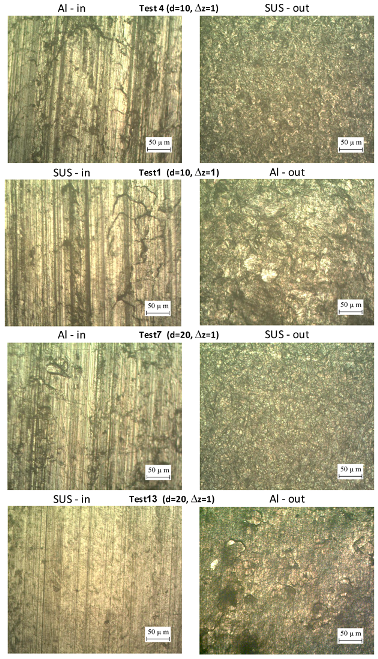
4.1.3. Microstructure Analysis of the Bimetal Surfaces
4.2. Analysis of Modeling Results
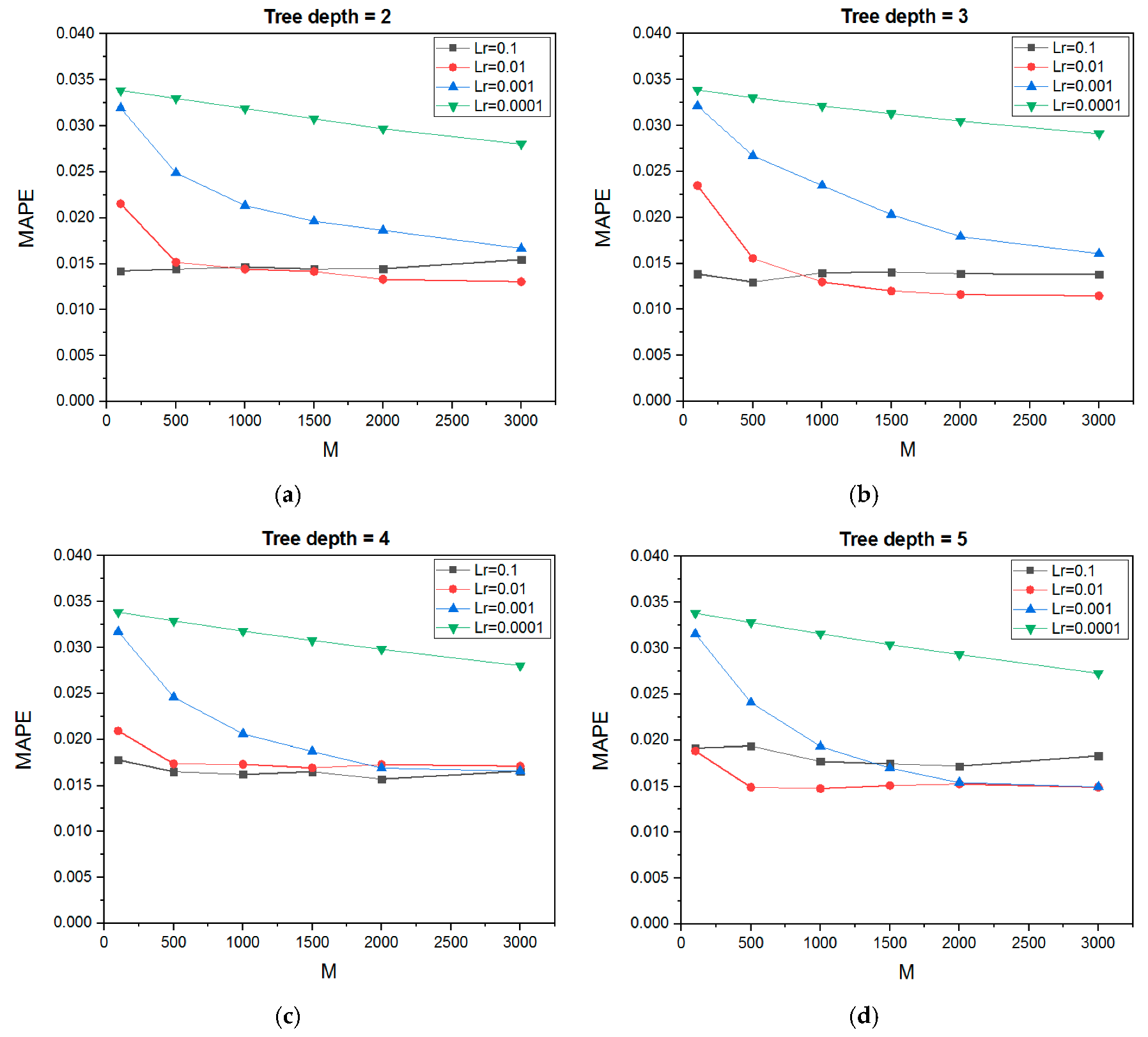
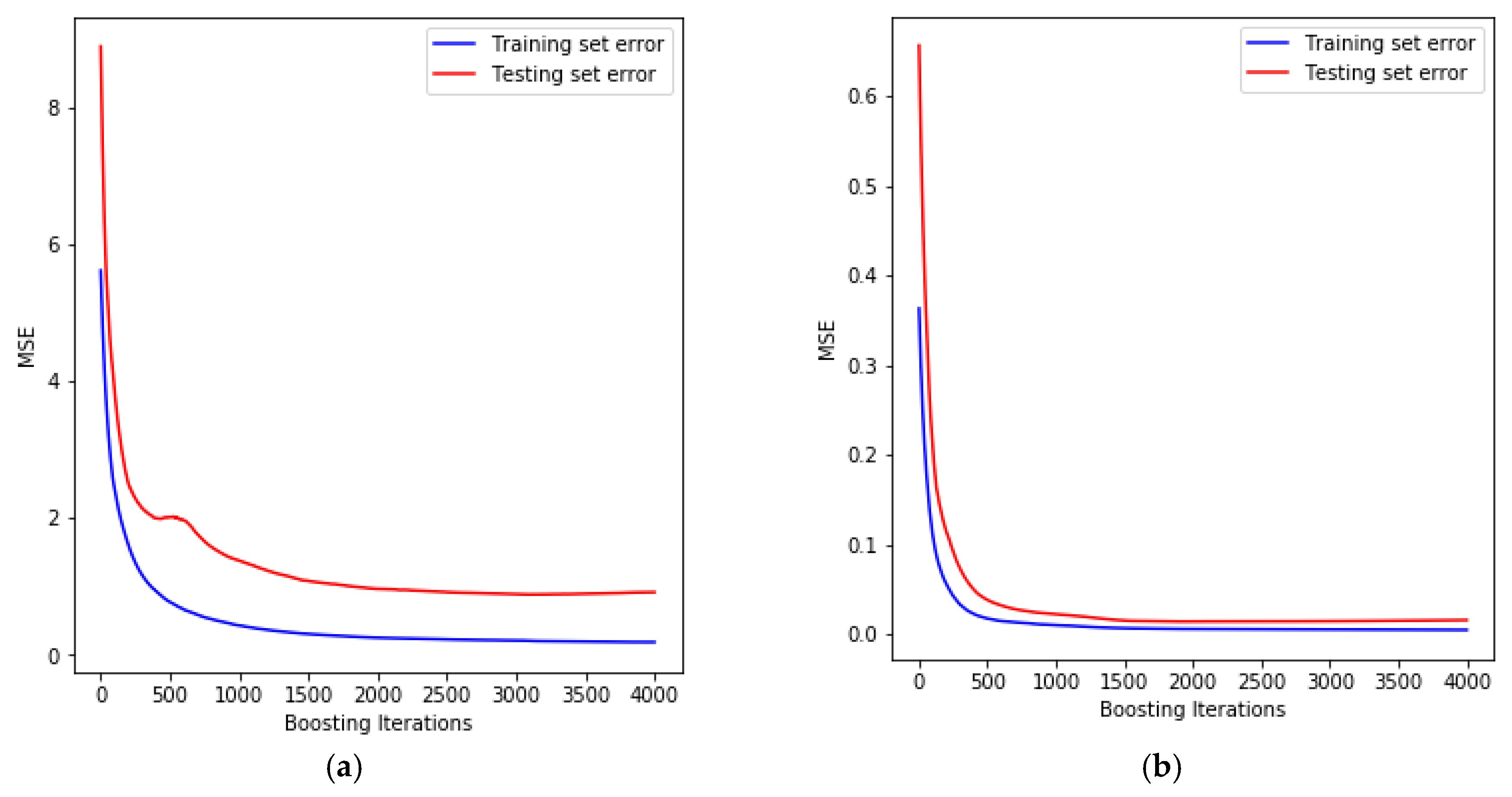
4.2.1. Optimum GBRT Parameters for Maximum Forming Angle and Surface Roughness Models
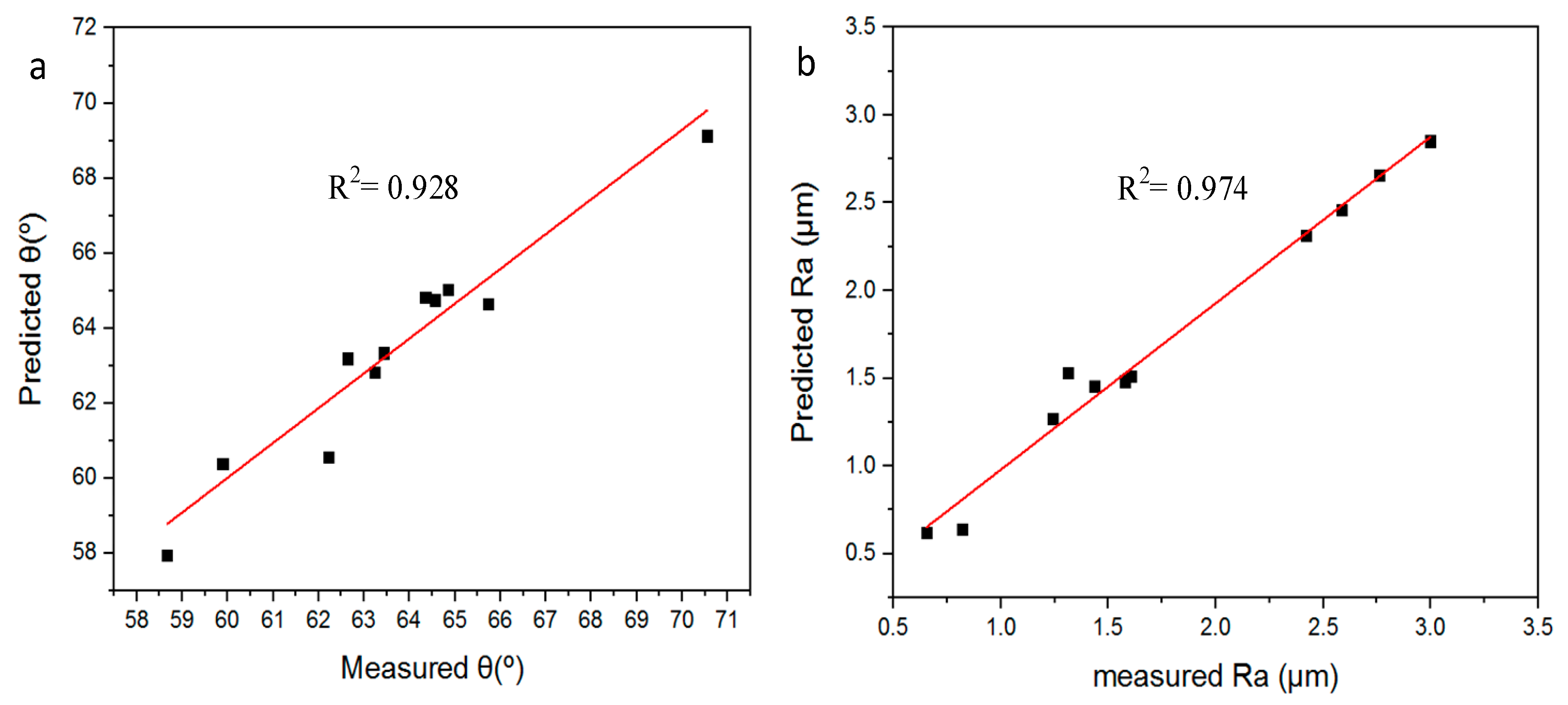
4.2.2. Prediction of Maximum Forming Angle and Surface Roughness
5. Conclusions
- The tool diameter has the highest effect on the maximum forming angle of the Al/SUS bimetal sheet, while the layer arrangement feature has the smallest effect, but this effect cannot be neglected. The GBRT model with a maximum tree depth of 3, trees numbering 3000, and a learning rate of 0.01 is suitable for the maximum forming angle prediction.
- The tool diameter has the highest effect on the surface roughness of the Al/SUS bimetal sheet, while the feed rate feature has the smallest effect, but this effect cannot be neglected. The GBRT model with a maximum tree depth of 3, trees numbering 2000, and a learning rate of 0.01 is suitable for the surface roughness prediction.
- The high value of tool diameter has a negative effect on the maximum forming angle of the SUS/Al bimetal sheet but a positive effect on the surface roughness and microstructure observations. Moreover, the small value of the step size has a positive effect on both the maximum forming angle and the surface quality for Al/SUS and SUS/Al bimetal sheets.
- The best structure is observed in the case of the SUS layer forming the internal surface in the SUS/Al bimetal sheet using a large tool diameter and small step size. Furthermore, the roughening in the case of the Al layer forms the external surface is higher than that in the case of the SUS layer, especially with a small tool diameter.
- The microstructure observations demonstrated that the contact surfaces experience micro cracks and striations while the non-contact surfaces experience orange peel and micro voids which are responsible for the roughening of the Al/SUS bimetal sheets.
- The effect of layer arrangement on the surface roughness is higher than that on the maximum forming angle. The higher maximum forming angle with better surface quality is found to be for the SUS/Al layer arrangement rather than the Al/SUS layer arrangement.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Ghamdi, K.A.; Hussain, G. On the comparison of formability of roll-bonded steel-Cu composite sheet metal in incremental forming and stamping processes. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghamdi, K.A.; Hussain, G. Parameter-formability relationship in ISF of tri-layered Cu-Steel-Cu composite sheet metal: Response surface and microscopic analyses. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2016, 17, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheysarian, A.; Honarpisheh, M. An experimental study on the process parameters of incremental forming of Al-Cu Bimetal. J. Comput. Appl. Res. Mech. Eng. 2017, 7, 73–83. [Google Scholar]
- Honarpisheh, M.; Mohammadi Jobedar, M.; Alinaghian, I. Multi-response optimization on single-point incremental forming of hyperbolic shape Al-1050/Cu bimetal using response surface methodology. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 3069–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, G. Single point incremental forming of Cu-Al composite sheets: A comprehensive study on deformation behaviors. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2019, 19, 484–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghamdi, K.A.; Hussain, G. On the free-surface roughness in incremental forming of a sheet metal: A study from the perspective of isf strain, surface morphology, post-forming properties, and process conditions. Metals 2019, 9, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echrif, S.B.M.; Hrairi, M. Significant parameters for the surface roughness in incremental forming process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2014, 29, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, K.; Jeswiet, J. Single point incremental forming at high feed rates and rotational speeds: Surface and structural consequences. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 59, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, M.C.; Cristea, I. Processing metal sheets by SPIF and analysis of parts quality. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2013, 28, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Gulati, V.; Kumar, P.; Singh, V.; Kumar, B.; Singh, H. Parametric effects on formability of AA2024-Oaluminum alloy sheets in single point incrementalforming. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 8, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, K.; Kumar, G. Inverse analysis and multi-objective optimization of single-point incremental forming of AA5083 aluminum alloy sheet. Soft Comput. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, N.G.; Farias, J.S.; Bastos, R.P.; Teixeira, P.; Davim, J.P.; Alves de Sousa, R.J. Lubrication aspects during Single Point Incremental Forming for steel and aluminum materials. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 16, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Hussain, G.; Iqbal, A.; Zhang, Z.P. Surface roughness as the function of friction indicator and an important parameters-combination having controlling influence on the roughness: Recent results in incremental forming. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 101, 2533–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurra, S.; Hifzur Rahman, N.; Regalla, S.P.; Gupta, A.K. Modeling and optimization of surface roughness in single point incremental forming process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulay, A.; Ben, B.S.; Ismail, S.; Kocanda, A. Prediction of average surface roughness and formability in single point incremental forming using artificial neural network. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2019, 19, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Prasad, K.S.; Mehto, A.; Bagchi, J.; Ganesh, Y.S.; Mohanty, S.; Sidpara, A.M.; Panda, S.K. Parameter optimization and texture evolution in single point incremental sheet forming process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Yuan, Q.; Shi, P. Parameter optimization for deformation energy and forming quality in single point incremental forming process using response surface methodology. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, A.; Pandivelan, C.; Jeevanantham, A.K. Optimization of AA5052 in incremental sheet forming using grey relational analysis. Measurement 2017, 106, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, S.; Lu, B.; Chen, J.; Long, H.; Ou, H. Evaluation of deformation stability and fracture mechanism in incremental sheet forming. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 124–125, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, M.; Formisano, A.; Langella, A. Comparison between analytical and experimental roughness values of components created by incremental forming. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 1934–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Chen, J. Analytical model and experimental validation of surface roughness for incremental sheet metal forming parts. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2019, 146, 103453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C. Experrimenta Design, 4th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kleijnen, J.P.C. Design and analysis of simulation experiments. In Proceedings of the Springer Proceedings in Mathematics and Statistics, New Delhi, India, 23–25 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, G.; Gao, L. A novel method to test the thinning limits of sheet metals in negative incremental forming. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.H.; Lee, D.N. Tensile deformation behavior of stainless steel clad aluminum bilayer sheet. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1997, 222, 158–165. [Google Scholar]
- Parsa, M.H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takakura, N. Redrawing analysis of aluminum-stainless-steel laminated sheet using FEM simulations and experiments. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2001, 43, 2331–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.A. Formability and failure analyses of Al/SUS bilayer sheet in single point incremental forming. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 2785–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Zhang, S.; Szeto, W.Y.; Chen, X. (Michael) Multi-step-ahead traffic speed forecasting using multi-output gradient boosting regression tree. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 2450, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, K.; Jeswiet, J. Visual categorization and quantification of the orange peel effect in single point incremental forming at high forming speeds. In Proceedings of the Transactions of the North American Manufacturing Research Institution of SME, Kingston, ON, Canada, 26–28 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mirnia, M.J.; Vahdani, M.; Shamsari, M. Ductile damage and deformation mechanics in multistage single point incremental forming. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 136, 396–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.-W.; Khaki, B.; Li, T.; Chu, C.; Gadh, R. Ensemble machine learning-based algorithm for electric vehicle user behavior prediction. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Unit | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Tool diameter | mm | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| Feed rate | mm/min | 1000 | 2000 | 3000 |
| Step size | mm | 0.15 | 0.57 | 1 |
| Layer arrangement | - | Al/SUS | SUS/Al | - |
| Test | Numeric Factors | Categorical Factor | Responses | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d (mm) | f (mm/min) | ∆z (mm) | (LA) | (°) | Ra (μm) | |
| 1 | 10 | 3000 | 1 | SUS/Al | 57.59 | 2.947 |
| 2 | 15 | 1000 | 0.15 | Al/SUS | 63.22 | 0.783 |
| 3 | 20 | 2000 | 0.57 | Al/SUS | 66.38 | 0.694 |
| 4 | 10 | 1000 | 1 | Al/SUS | 60.85 | 2.552 |
| 5 | 20 | 2000 | 0.57 | SUS/Al | 64.93 | 0.682 |
| 6 | 15 | 1000 | 1 | SUS/Al | 63.77 | 1.678 |
| 7 | 20 | 1000 | 1 | Al/SUS | 65.88 | 1.091 |
| 8 | 10 | 3000 | 0.15 | Al/SUS | 64.94 | 0.986 |
| 9 | 10 | 1000 | 0.57 | SUS/Al | 68.75 | 1.443 |
| 10 | 10 | 2000 | 0.15 | SUS/Al | 66.95 | 1.934 |
| 11 | 20 | 1000 | 1 | Al/SUS | 65.35 | 1.045 |
| 12 | 15 | 3000 | 0.15 | SUS/Al | 63.48 | 1.244 |
| 13 | 20 | 3000 | 1 | SUS/Al | 65.54 | 0.735 |
| 14 | 10 | 2000 | 0.15 | SUS/Al | 66.13 | 1.825 |
| 15 | 10 | 3000 | 0.15 | Al/SUS | 65.12 | 1.173 |
| 16 | 15 | 2000 | 1 | SUS/Al | 61.66 | 2.167 |
| 17 | 15 | 1000 | 0.15 | SUS/Al | 67.16 | 1.134 |
| 18 | 20 | 3000 | 0.15 | Al/SUS | 64.39 | 0.845 |
| 19 | 15 | 3000 | 1 | Al/SUS | 64.68 | 2.187 |
| 20 | 10 | 2000 | 0.57 | Al/SUS | 64.10 | 1.648 |
| 21 | 10 | 1000 | 0.57 | SUS/Al | 67.81 | 1.484 |
| 22 | 20 | 1000 | 0.15 | SUS/Al | 63.83 | 0.512 |
| Response | M | H | Lr | MAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3000 | 3 | 0.01 | 1.161 | |
| Ra | 2000 | 3 | 0.01 | 6.865 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abd Ali, R.; Chen, W.; Al-Furjan, M.S.H.; Jin, X.; Wang, Z. Experimental Investigation and Optimal Prediction of Maximum Forming Angle and Surface Roughness of an Al/SUS Bimetal Sheet in an Incremental Forming Process Using Machine Learning. Materials 2019, 12, 4150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12244150
Abd Ali R, Chen W, Al-Furjan MSH, Jin X, Wang Z. Experimental Investigation and Optimal Prediction of Maximum Forming Angle and Surface Roughness of an Al/SUS Bimetal Sheet in an Incremental Forming Process Using Machine Learning. Materials. 2019; 12(24):4150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12244150
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbd Ali, Raneen, Wenliang Chen, M.S.H. Al-Furjan, Xia Jin, and Ziyu Wang. 2019. "Experimental Investigation and Optimal Prediction of Maximum Forming Angle and Surface Roughness of an Al/SUS Bimetal Sheet in an Incremental Forming Process Using Machine Learning" Materials 12, no. 24: 4150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12244150
APA StyleAbd Ali, R., Chen, W., Al-Furjan, M. S. H., Jin, X., & Wang, Z. (2019). Experimental Investigation and Optimal Prediction of Maximum Forming Angle and Surface Roughness of an Al/SUS Bimetal Sheet in an Incremental Forming Process Using Machine Learning. Materials, 12(24), 4150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12244150






