The Characterization of Stress Corrosion Cracking in the AE44 Magnesium Casting Alloy Using Quantitative Fractography Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- continuous crack propagation caused by anodic dissolution of the alloy at the top of cracks,
- -
- discontinuous crack propagation caused by a series of cracks occurring at the crack tip.
- -
- local decohesion of the crystal lattice caused by hydrogen (hydrogen enhanced decohesion—HEDE),
- -
- local hydrogen-induced plasticization (hydrogen enhanced localized plasticity—HELP),
- -
- dislocation emission caused by adsorption (adsorption-induced dislocation-emission—AIDE),
- -
- delayed hydride cracking (DHC).
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- placing the cut samples in a conductive resin using a press;
- -
- grinding of sample surfaces on abrasive papers with SiC particles with gradation of grains: 120, 320, 600, and 1200;
- -
- rinsing of the ground surface of the samples under running water and polishing with the use of diamond suspensions with the following particle sizes: 6 μm, 3 μm, and 1 μm;
- -
- the last stage of sample preparation was polishing in a Al2O3 suspension with a grain size of 0.05 μm.
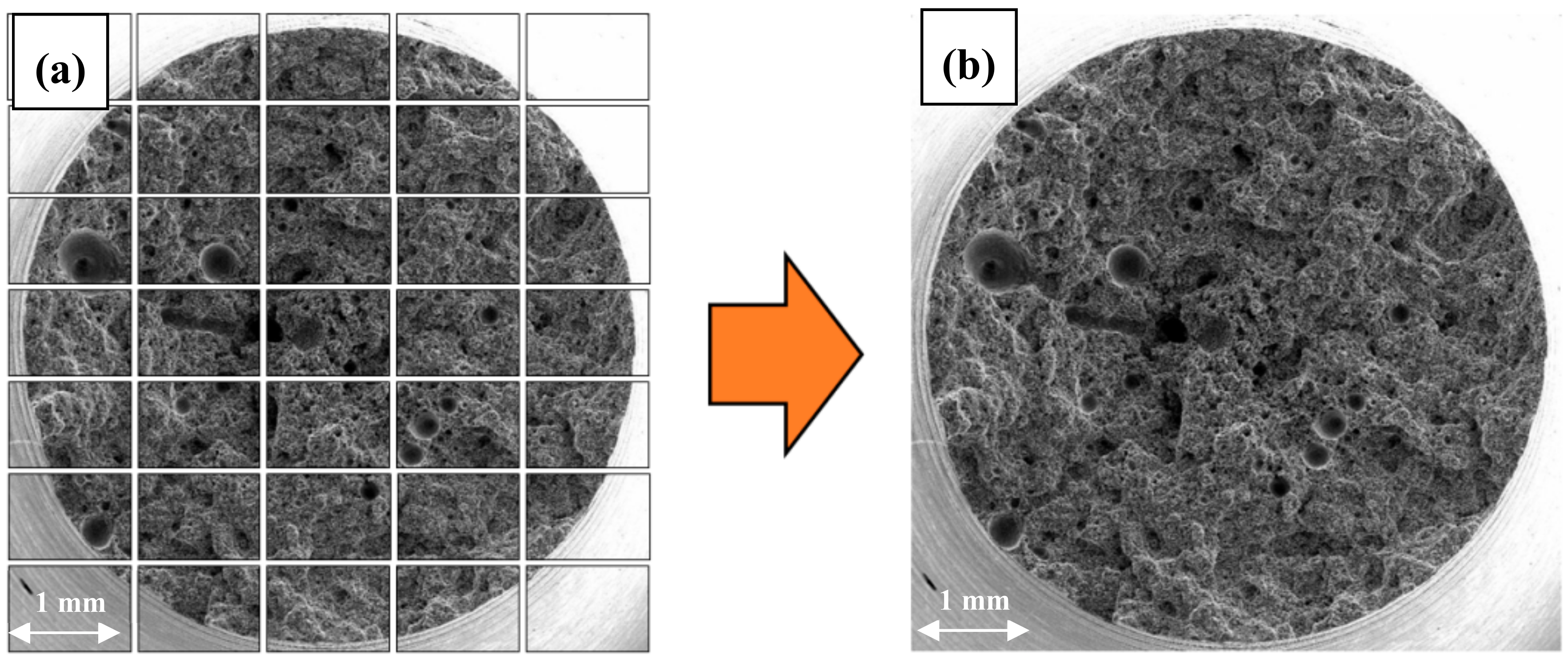
- Stage 1—the preparation of a high-resolution image of the entire fracture surface, made up of a series of images with marked cracks (cracks had to be marked manually in the GIMP image manipulation program as the greyness differences between cracks and some elements of the structure were insufficient for automatic detection),
- Stage 2—the use of image analysis methods (the correction of brightness and contrast and the creation of a binary image of cracks) to determine the quantitative crack parameters.
3. Results and Discussion
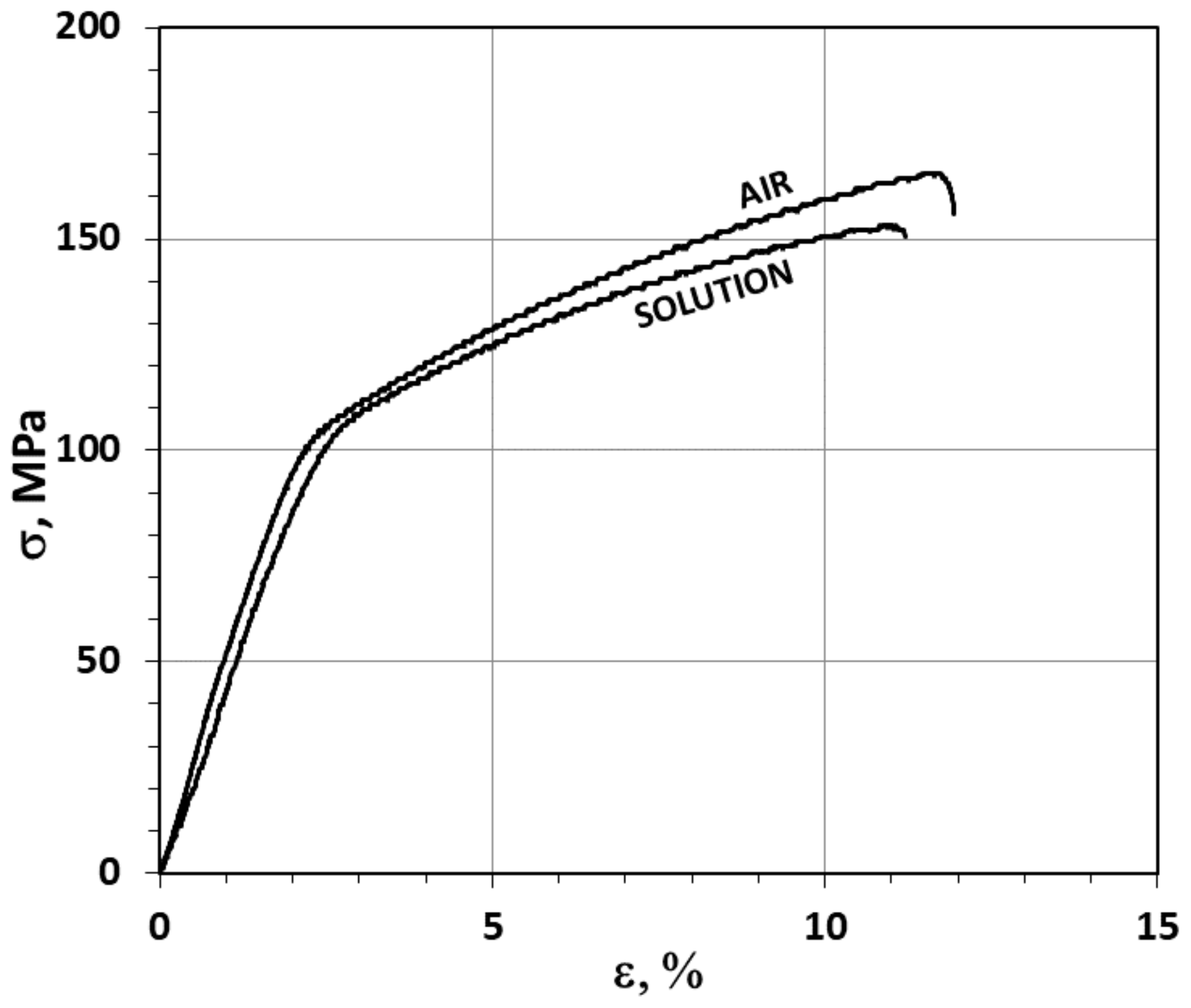
3.1. The Slow Strain Rate (SSR) Test Results
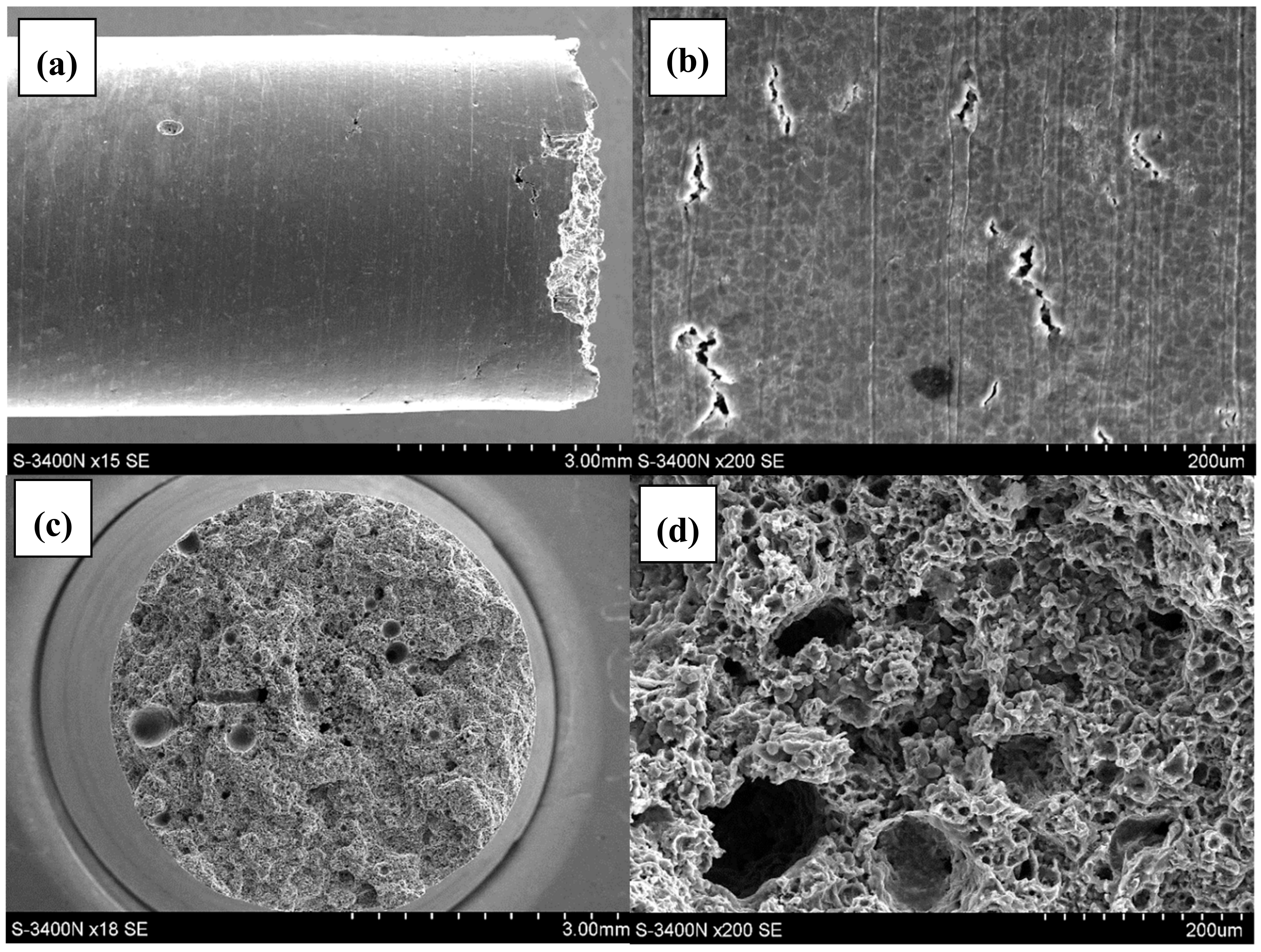
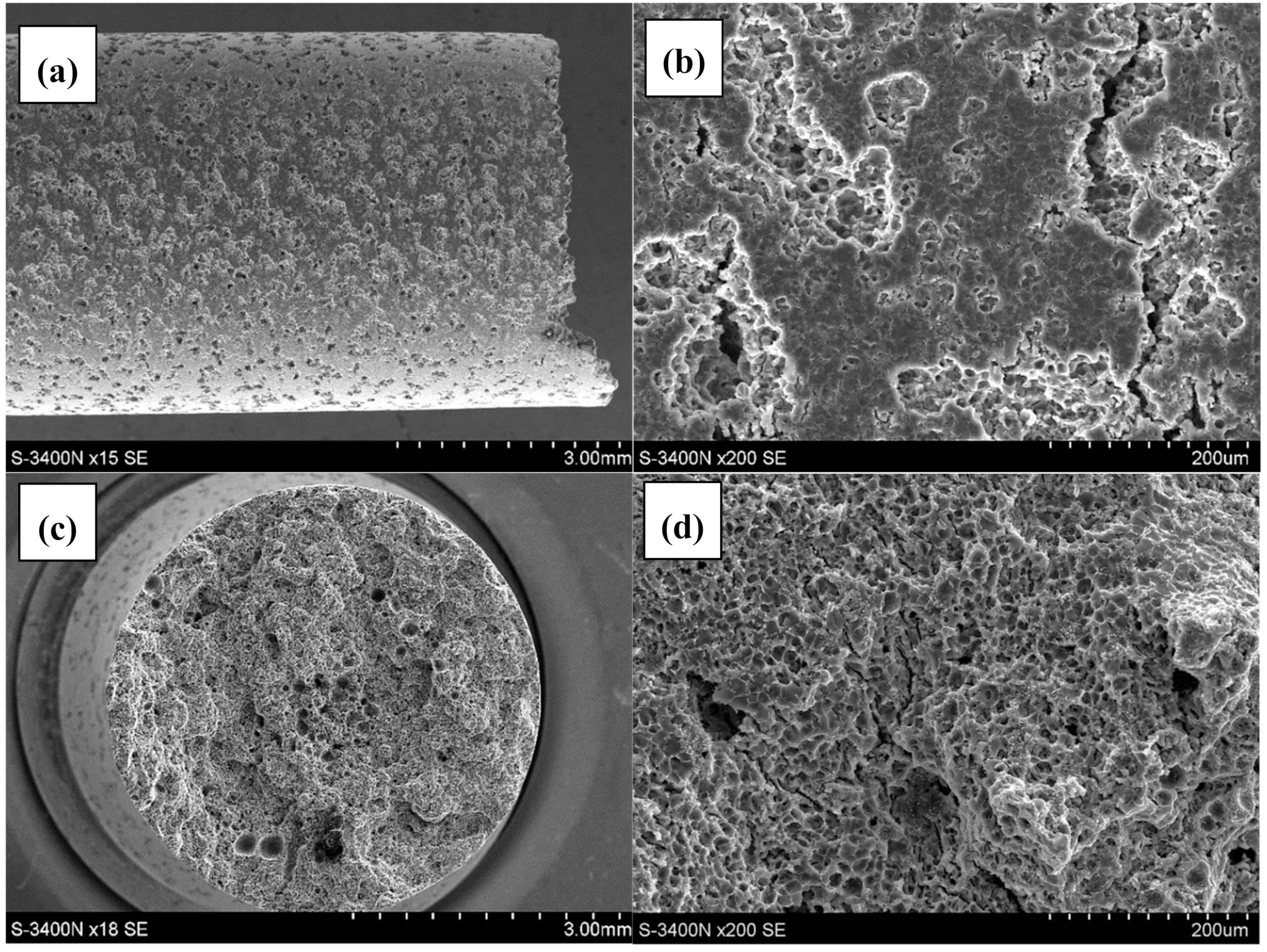
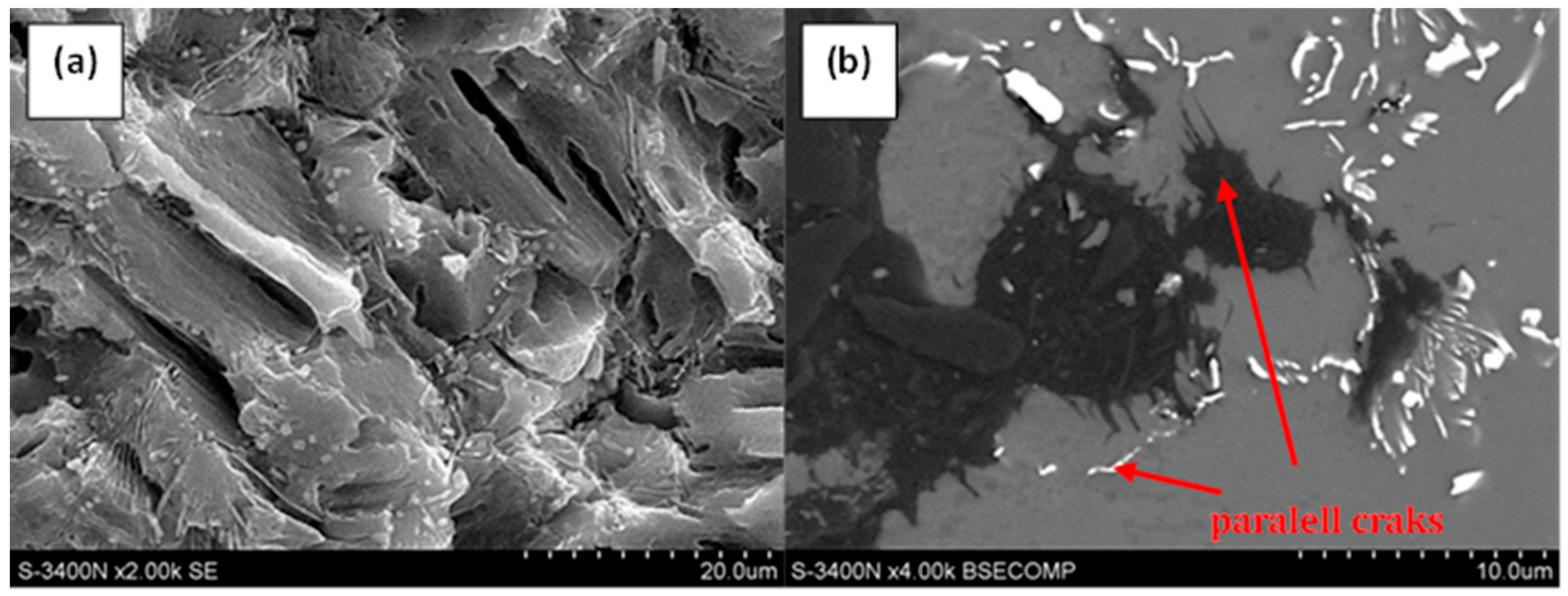
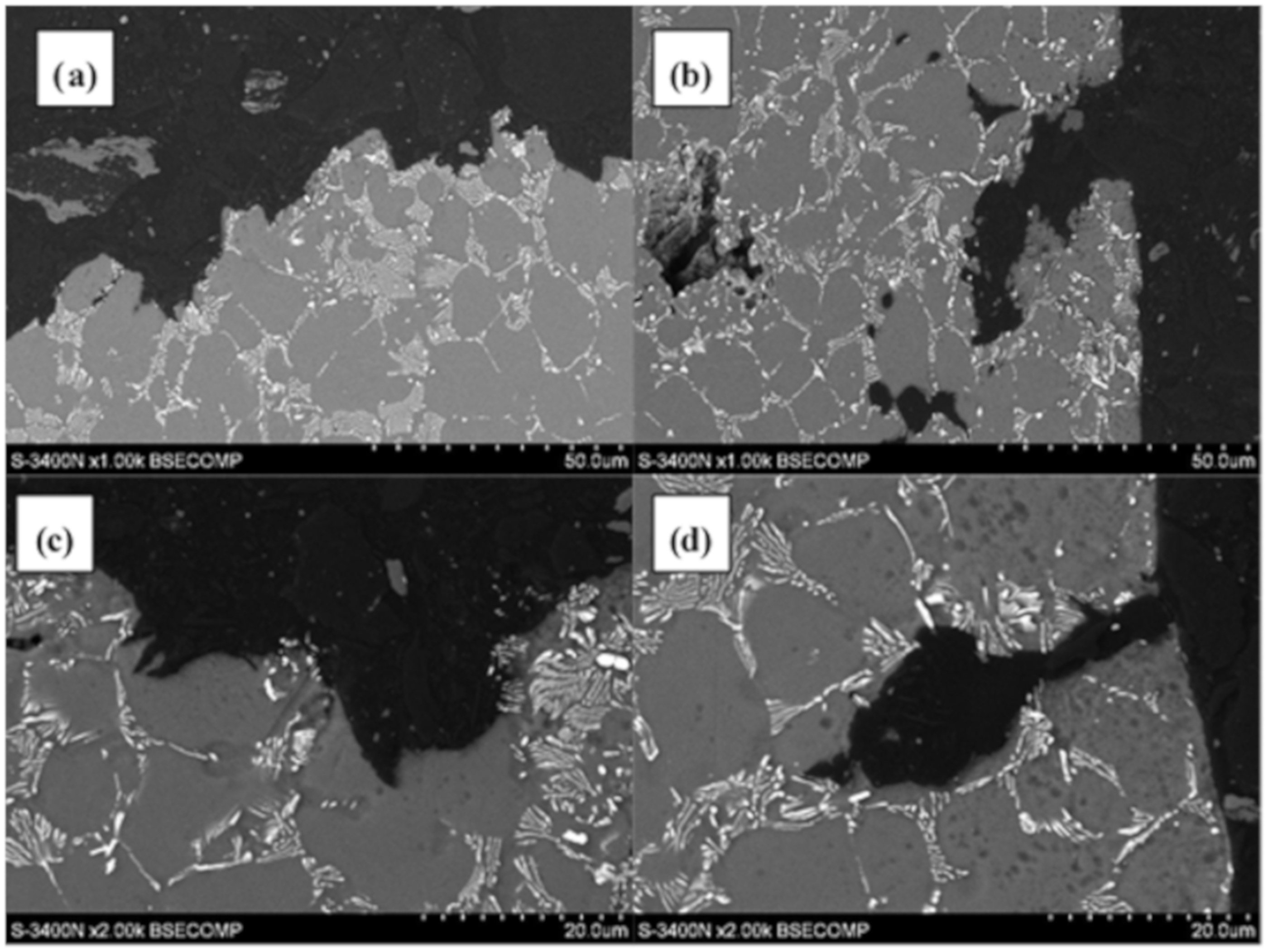
3.2. Qualitative and Quantitative Evaluation of the Fracture Surface after the SSR Tests Using The Oryginaly Developed Quantitative Fractography Method
- -
- methods based on metallographic cross-sections of the fracture surface, i.e., profilometric analysis,
- -
- methods based on images of the fracture surface, i.e., quantitative description of the fracture surface.
- -
- Stage one: as a result of exposure of the alloy to the environment containing hydrogen, due to the difference in its concentration in both media, it diffuses from the environment to the surface layer of the alloy. Hydrogen diffusion is gradually weakened by the Mg(OH)2 layer formed on the surface of the alloy, which arises as a result of its exposure to the corrosive environment,
- -
- Stage two: as a result of the synergic interaction of the external mechanical loads to which the alloy is subjected, and internal stresses induced by the presence of hydrogen in the material microstructure, cracking occurs in the hydrogen-saturated surface layer of the alloy,
- -
- Stage three: the cracks created in the microstructure of the alloy reveal previously covered with Mg(OH)2 layer, a metal substrate enabling easier and faster diffusion of hydrogen to the inside of the alloy through the surfaces of freshly formed cracks,
- -
- Stage four: the cracks in the material propagate into the material, followed by decohesion of the alloy in the areas of the microstructure located in front of the crack tip, where there is a high concentration of stress caused by external mechanical loads and internal stresses induced by the diffusion of hydrogen. In addition, secondary cracks also develop in these areas.
4. Conclusions
- The impact of mechanical loads and the corrosive environment (OCP) under SSC conditions on the properties of AE44 took the form of deterioration in mechanical properties.
- The influence of hydrogen on the mechanical properties of AE44 was difficult to evaluate as the measured content of hydrogen in AE44 was the sum of hydrogen that penetrated into the alloy from the solution during the SSR test and hydrogen contained in pores that formed in the alloy during the manufacture process.
- The qualitative analysis of the fracture surfaces of the AE44 specimens after the SSR tests in air and in the corrosive solution under OCP conditions revealed a significantly greater presence of cracks in the case of the specimens tested in the corrosive environment.
- The quantitative analysis of the cracks (number, length, and size distribution) in the AE44 specimens after the SSR tests indicated a significant difference between the alloy’s susceptibility to SCC in a corrosive environment and in air. Such clear differences could not be observed when the adopted criterion of the alloy’s susceptibility was the changes in its mechanical properties in SSR tests.
- The analysis of the results concerning the susceptibility of the AE44 magnesium-based alloy to the action of a corrosive environment under SSC conditions can lead to the conclusion that the results obtained from the quantitative fractography methods are an important complement to the SSR tests (changes in mechanical properties) being the basic criterion for the assessment of an alloy’s susceptibility to the combined action of stresses and a corrosive environment, but also that the developed quantitative fractography method is more unambiguous and more sensitive to changes in the corrosive environment and the mechanical load than the change in mechanical properties during SSR tests.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raja, V.S.; Shoji, T. Stress Corrosion Cracking: Theory and Practice; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 1–89. [Google Scholar]
- Song, R.G.; Blawert, C.; Dietzel, W.; Atrens, A. A study on stress corrosion cracking and hydrogen embrittlement of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 399, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzer, N.; Atrens, A.; Dietzel, W.; Song, G.; Kainer, K.U. Comparison of the linearly increasing stress test and the constant extension rate test in the evaluation of transgranular stress corrosion cracking of magnesium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 472, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Han, E.; Dong, J.; Ke, W. States and transport of hydrogen in the corrosion process of an AZ91 magnesium alloy in aqueous solution. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1292–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G129. In Standard Practice for Slow Strain Rate Testing to Evaluate the Susceptibility of Metallic Materials to Environmentally Assisted Cracking; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- ISO 7539-7. In Corrosion of metals and alloys—Stress corrosion testing—Part 7: Method for slow strain rate testing; ISO: Genewa, Switzerland, 1987.
- Kłyk-Spyra, K.; Sozańska, M. Quantitative fractography of 2205 duplex stainless steel after a sulfide stress cracking test. Mater. Charact. 2006, 56, 384–388. [Google Scholar]
- Michalska, J.; Sozańska, M.; Hetmańczyk, M. Application of quantitative fractography in the assessment of hydrogen damage of duplex stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozańska, M.; Sojka, J.; Beťáková, P.; Dagbert, C.; Hyspecká, L.; Galland, J.; Tvrdý, M. Examination of hydrogen interaction in carbon steel by means of quantitative microstructure and fracture description. Mater. Charact. 2001, 46, 239–243. [Google Scholar]
- Sozańska, M.; Sojka, J. Quantitative description of the “fish eyes” type hydrogen embrittlement in steels for power industry. Inż. Mater. 2008, 4, 247–249. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Han, E.; Ke, W. Investigation of Stress Corrosion Cracking Behaviors of an AZ91 Magnesium Alloy in 0.1kmol/m3 Na2SO4 Solution Using Slow Strain Rate Test. Mater. Trans. 2008, 5, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Han, E.; Ke, W. Electrochemical corrosion and mechanical behaviors of the charged magnesium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 494, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.F.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wu, W.; Li, X.G.; Du, C.W.; Jiang, B. Stress corrosion cracking behavior of ZK60 magnesium alloy under different conditions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 26162–26174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, M.B.; Dietzel, W.; Raman, R.K.S.; Lyon, P. Hydrogen-induced-cracking in magnesium alloy under cathodic polarization. Scripta Mater. 2007, 57, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, T.S.; Park, I.S.; Lee, M.H. Volume 1: Biological interactions, mechanical properties and testing. In Surface Modification of Magnesium and Its Alloys for Biomedical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.L. Corrosion of Magnesium Alloys; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 1–656. [Google Scholar]
- Zieliński, A. Niszczenie Wodorowe Metali Nieżelaznych i Ich Stopów; Gdańskie Towarzystwo Naukowe: Gdańsk, Poland, 1999; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Antolovich, S.; Gokhale, A.; Bathias, C. Applications of Quantitative Fractography and Computed Tomography to Fracture Processes in Materials. In Quantitative Methods in Fractography; Strauss, B.M., Putatunda, S.K., Eds.; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1990; pp. 3–25. [Google Scholar]
- Undervood, E.E. Quantitative Stereology; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1970; pp. 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Met-Ilo®; Version 15.03; Computer program; Instytut Inżynierii Materiałowej: Katowice, Poland, 2015.
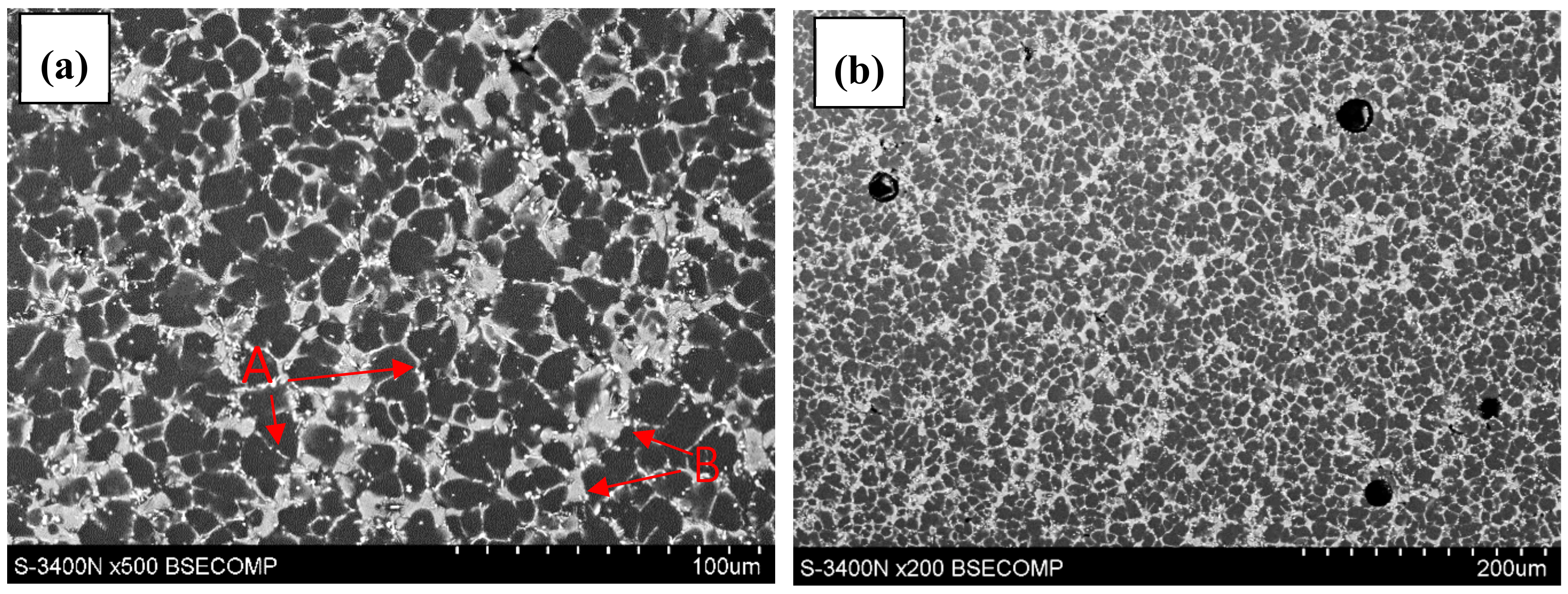
- Rzychoń, T.; Kiełbus, A.; Dercz, G. Structural and quantitative analysis of die cast AE44 magnesium alloy, JAMME. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2007, 22, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Revie, R.W.; Uhlig, H.H. Corrosion and Corrosion Control; John Wiley & Sons, Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Rzychoń, T.; Kiełbus, A. Microstructure and tensile properties of sand cast and die cast AE44 magnesium alloy. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2008, 58, 901–907. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, R.C.; Yin, Z.Z.; Chen, X.B.; Xu, D.K. Corrosion Types of Magnesium Alloys. In Magnesium Alloys: Selected Issue; Tański, T., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 29–52. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, L.; Raman, R.K.S.; Hofstetter, J.; Uggowitzer, P.J. In-vitro characterization of stress corrosion cracking of aluminium-free magnesium alloys for temporary bio-implant applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 42, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.D.; Xu, D.K.; Wang, B.J.; Sheng, L.Y.; Han, E.H.; Dong, C. Effect of solution treatment on stress corrosion cracking behavior of an as-forged Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, L.; Raman, R.K.S. Magnesium alloys as body implants: Fracture mechanism under dynamic and static loadings in a physiological environment. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.L. Corrosion behavior and prevention strategies for magnesium (Mg) alloys. Woodhead Publ. Ser. Met. Surf. Eng. 2013, 1, 3–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.G.; Patel, G.R.; Gokhale, A.M.; Sreeranganathan, A.; Horstemeyer, M.F. Quantitative fractographic analysis of variability in the tensile ductility of high-pressure die-cast AE44 Mg-alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 427, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, E.F.; Morozova, G.I. Role of hydrogen in deformed magnesium alloys of the Mg-Zn-Zr-REM system. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2008, 50, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrens, A.; Dietzel, W.; Bala, S.P.; Bobby Kannan, M. Stress corrosion cracking (SSC) of magnesium alloy. In Stress Corrosion Cracking: Theory and Practice; Raja, V.S., Shoji, T., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd: Cambridge, UK, 2011; Chapter 9; pp. 341–380. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, R.C.; Dietzel, W.; Zettler, R.; Gan, W.M.; Sun, X.X. Microstructural evolution and delayed hydride cracking of FSW-AZ31 magnesium alloy during SSRT. Trans. Nonferr. Mrtal. Soc. 2014, 24, 3060–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrigth, K.; Karlsson, B. Topograpic Quantification of Nonplanar Localized Surfaces. In Proceedings of the Third European Symposium for Stereology, Ljubljana, Yugoslavia, 22–27 June 1981; pp. 247–253. [Google Scholar]
- Coster, M.; Chermant, J.L. Précis d’Analyse d’Images; Editions du CNRS: Paris, France, 1985; pp. 13–60. [Google Scholar]
- Undervood, E.E.; Banerji, K. Quantitative Fractography. In ASM Handbook Volume 12: Fractography, 9th ed.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1987; pp. 193–210. [Google Scholar]
- Sozańska, M.; Mościcki, A.; Chmiela, B. Investigation of stress corrosion cracking in magnesium alloys by quantitative fractography methods. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2017, 62, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]




| Test Environment | Elongation ε [%] | Necking Z [%] | Ultimate Tensile Strength UTS [MPa] | Fracture Time [h] | Hydrogen Concentration CH [ppm] | Hydrogen Embrittlement Index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EIε [%] | EIZ [%] | ||||||
| Strained in air | 11.9 | 7.8 | 166 | 39.5 | 99.7 | - | - |
| Strained in solution | 11.2 | 4.0 | 153 | 37.7 | 98.7 | 5.9 | 49 |
| SSRT Environment | Number of Cracks | Length of Cracks [µm] | Width of Cracks [µm] | Distance between Adjacent Cracks [µm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| strained in air | 141 | 34.5 ± 43.8% | 1.02 ± 14.1% | 118 ± 99% |
| strained in solution | 900 | 21.3 ± 48.7% | 1.04 ± 18.9% | 58 ± 76% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sozańska, M.; Mościcki, A.; Czujko, T. The Characterization of Stress Corrosion Cracking in the AE44 Magnesium Casting Alloy Using Quantitative Fractography Methods. Materials 2019, 12, 4125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12244125
Sozańska M, Mościcki A, Czujko T. The Characterization of Stress Corrosion Cracking in the AE44 Magnesium Casting Alloy Using Quantitative Fractography Methods. Materials. 2019; 12(24):4125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12244125
Chicago/Turabian StyleSozańska, Maria, Adrian Mościcki, and Tomasz Czujko. 2019. "The Characterization of Stress Corrosion Cracking in the AE44 Magnesium Casting Alloy Using Quantitative Fractography Methods" Materials 12, no. 24: 4125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12244125
APA StyleSozańska, M., Mościcki, A., & Czujko, T. (2019). The Characterization of Stress Corrosion Cracking in the AE44 Magnesium Casting Alloy Using Quantitative Fractography Methods. Materials, 12(24), 4125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12244125






