Effect of Tilt Angle and Pin Depth on Dissimilar Friction Stir Lap Welded Joints of Aluminum and Steel Alloys
Abstract
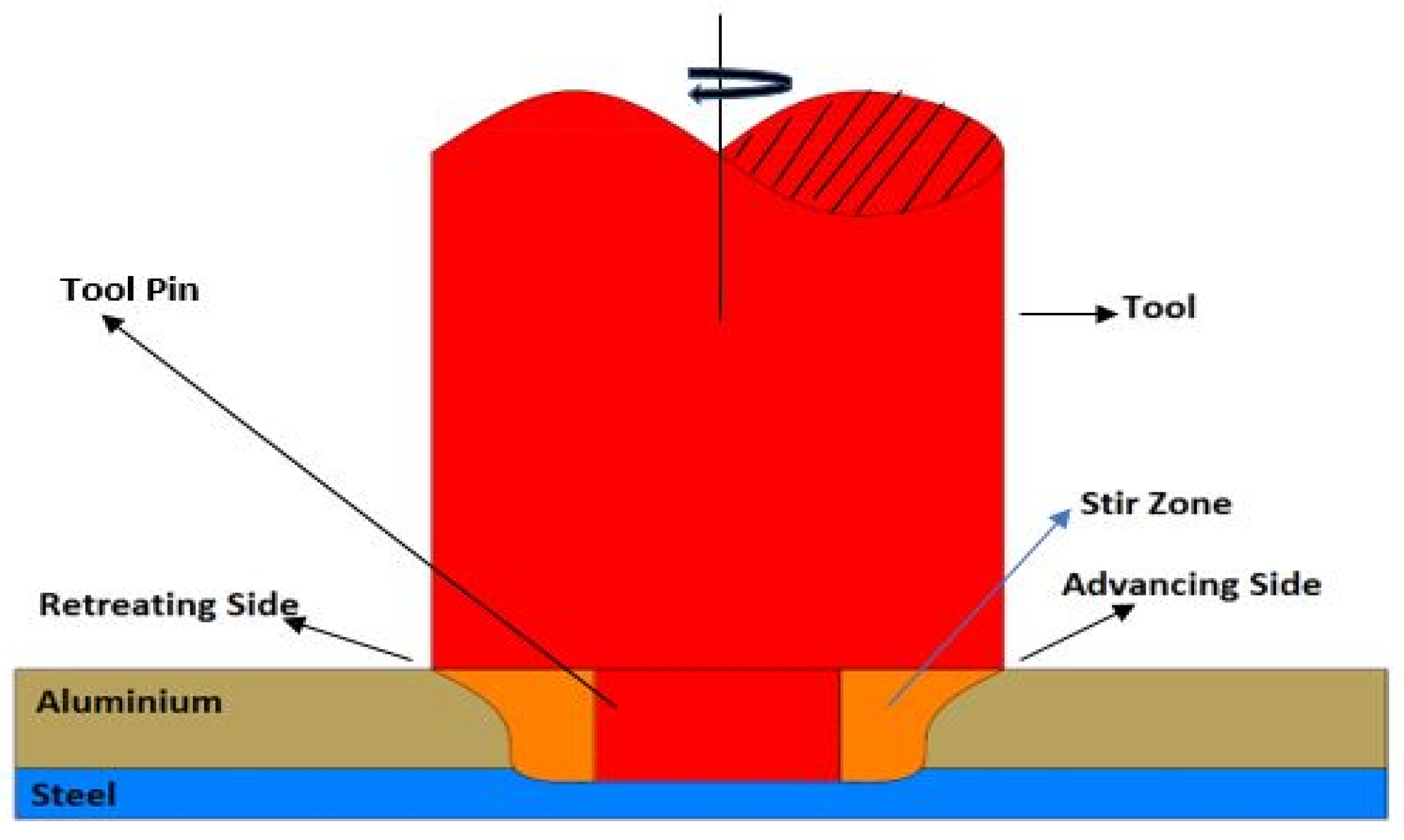
:1. Introduction
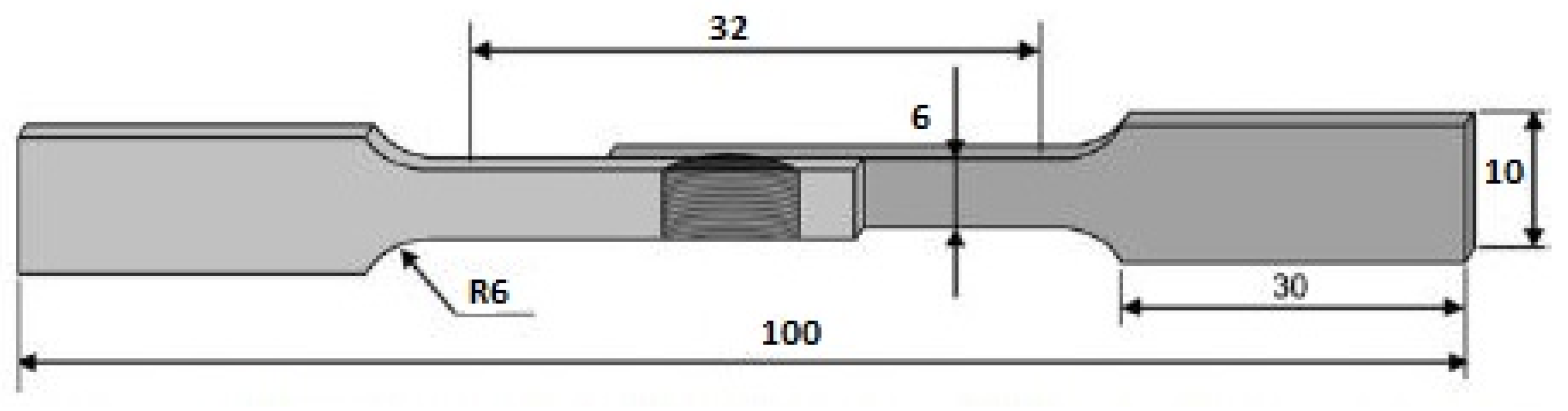
2. Experimental Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
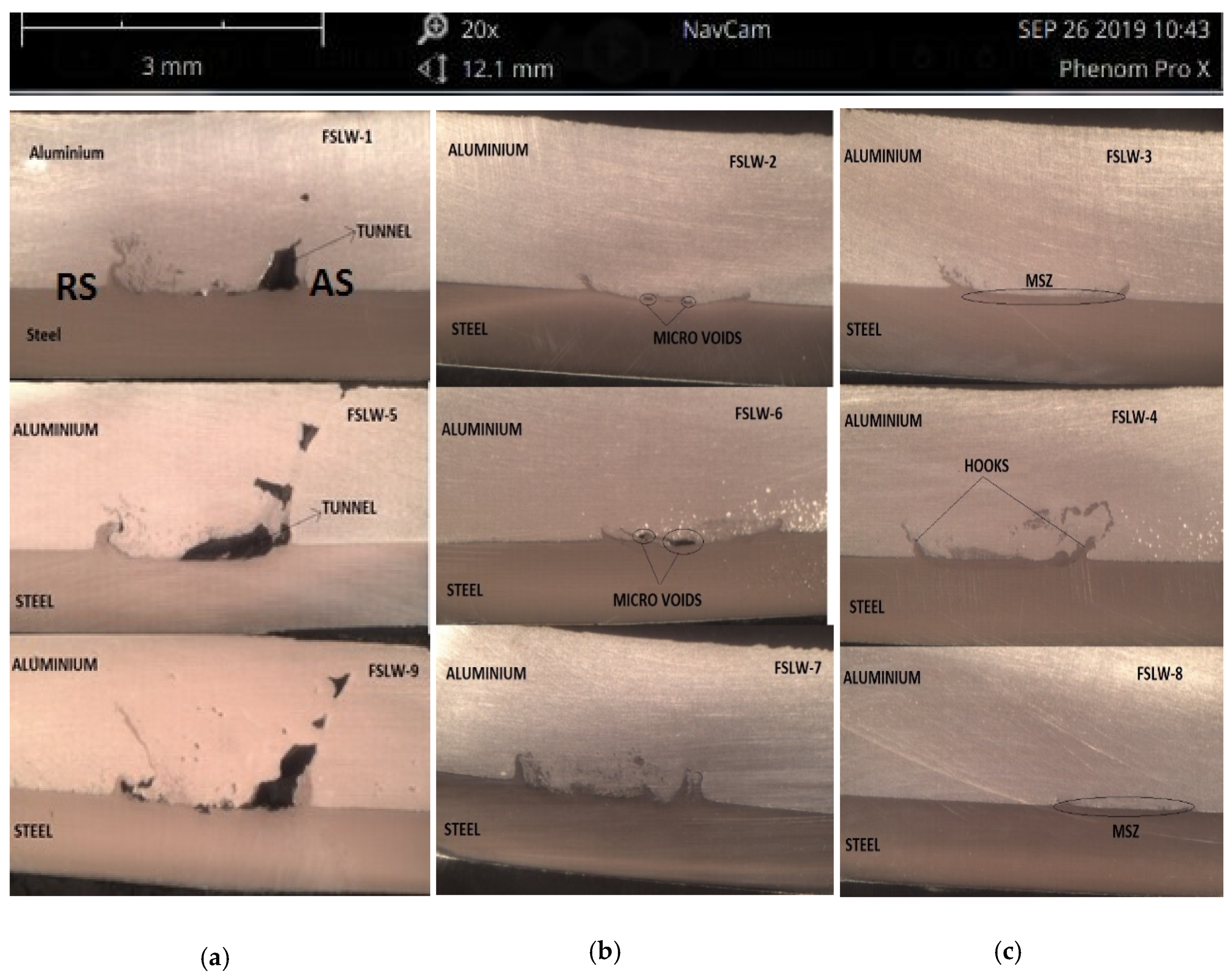
3.1. Macrostructure of the Lap Joints
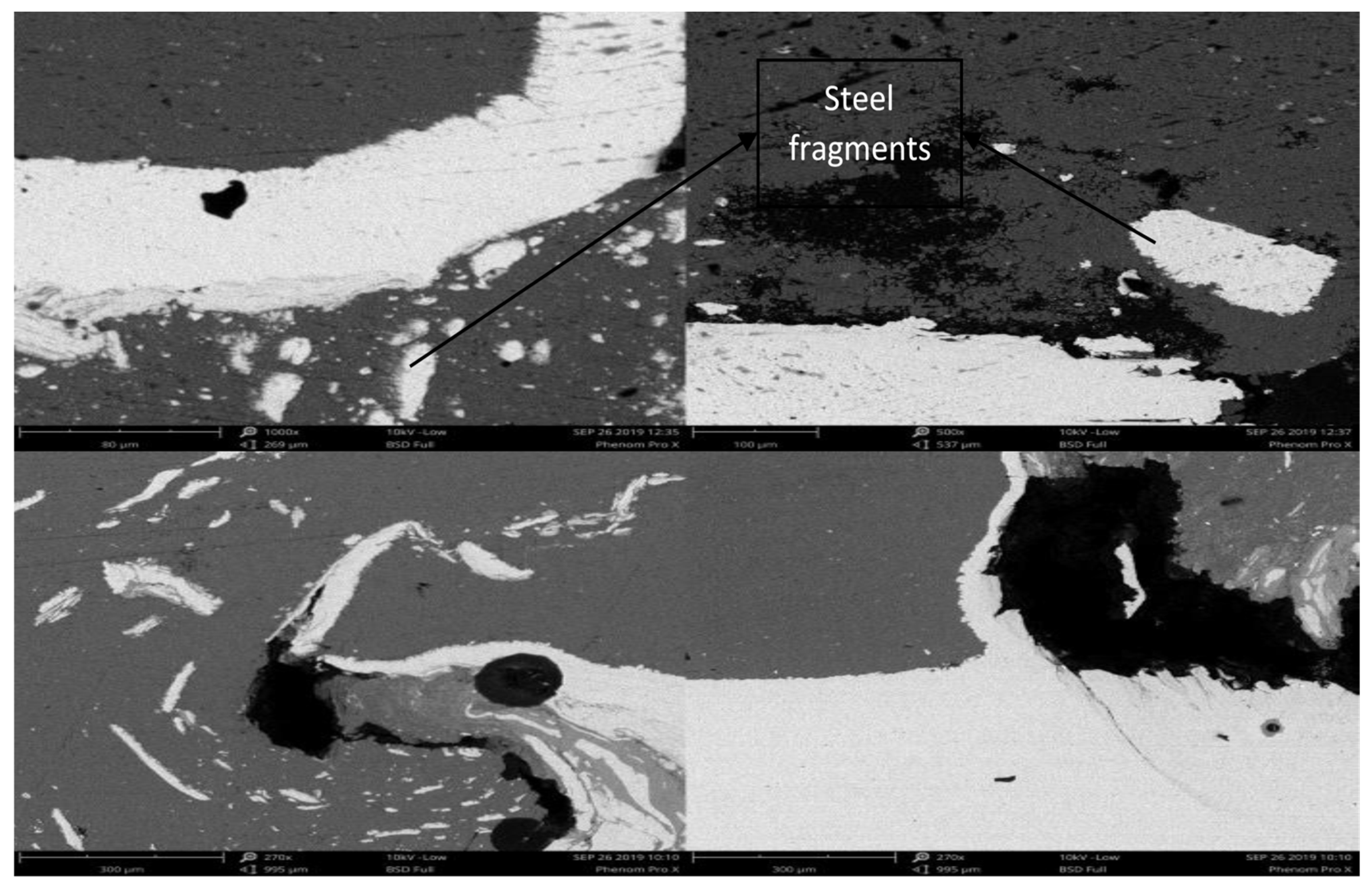
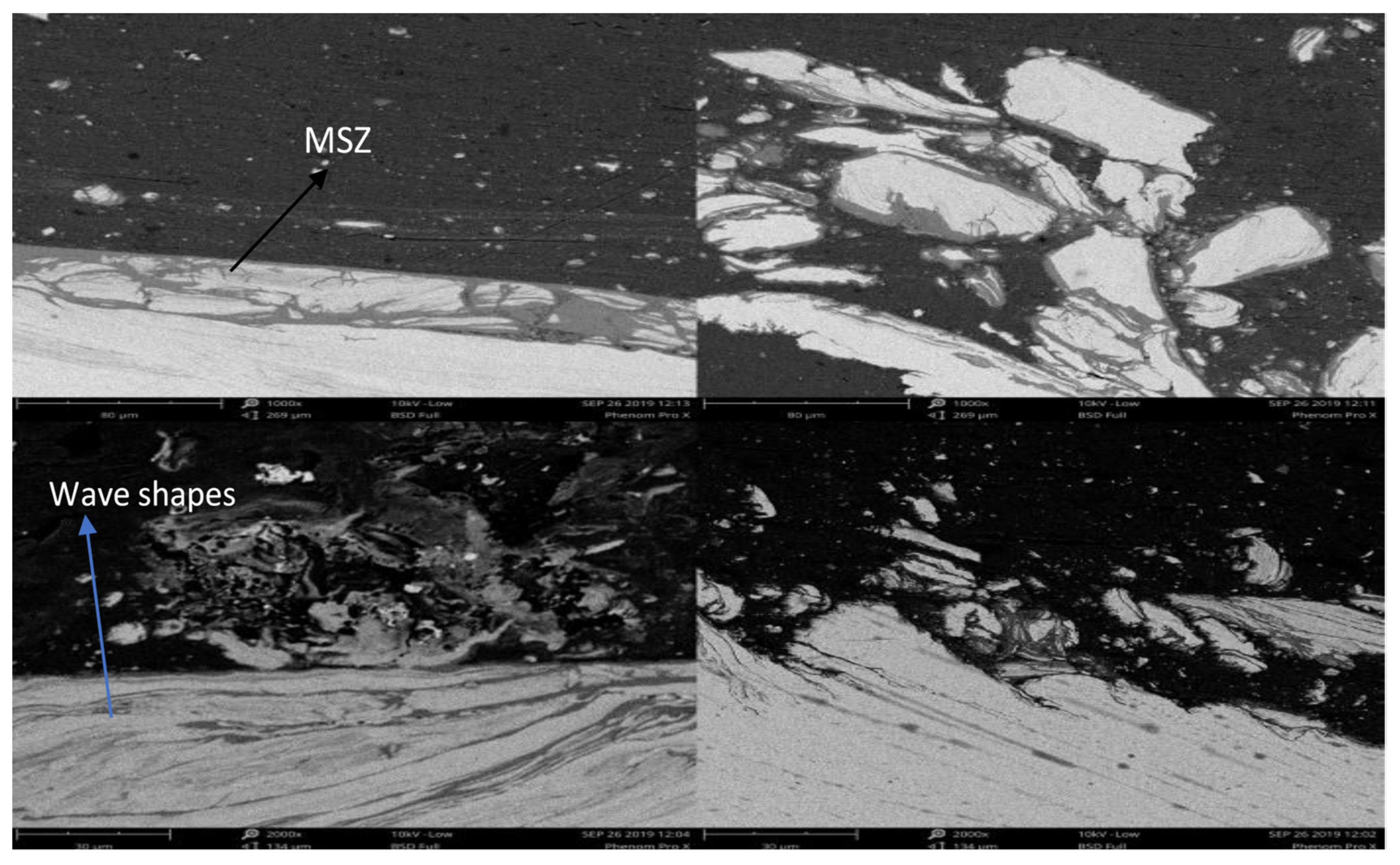
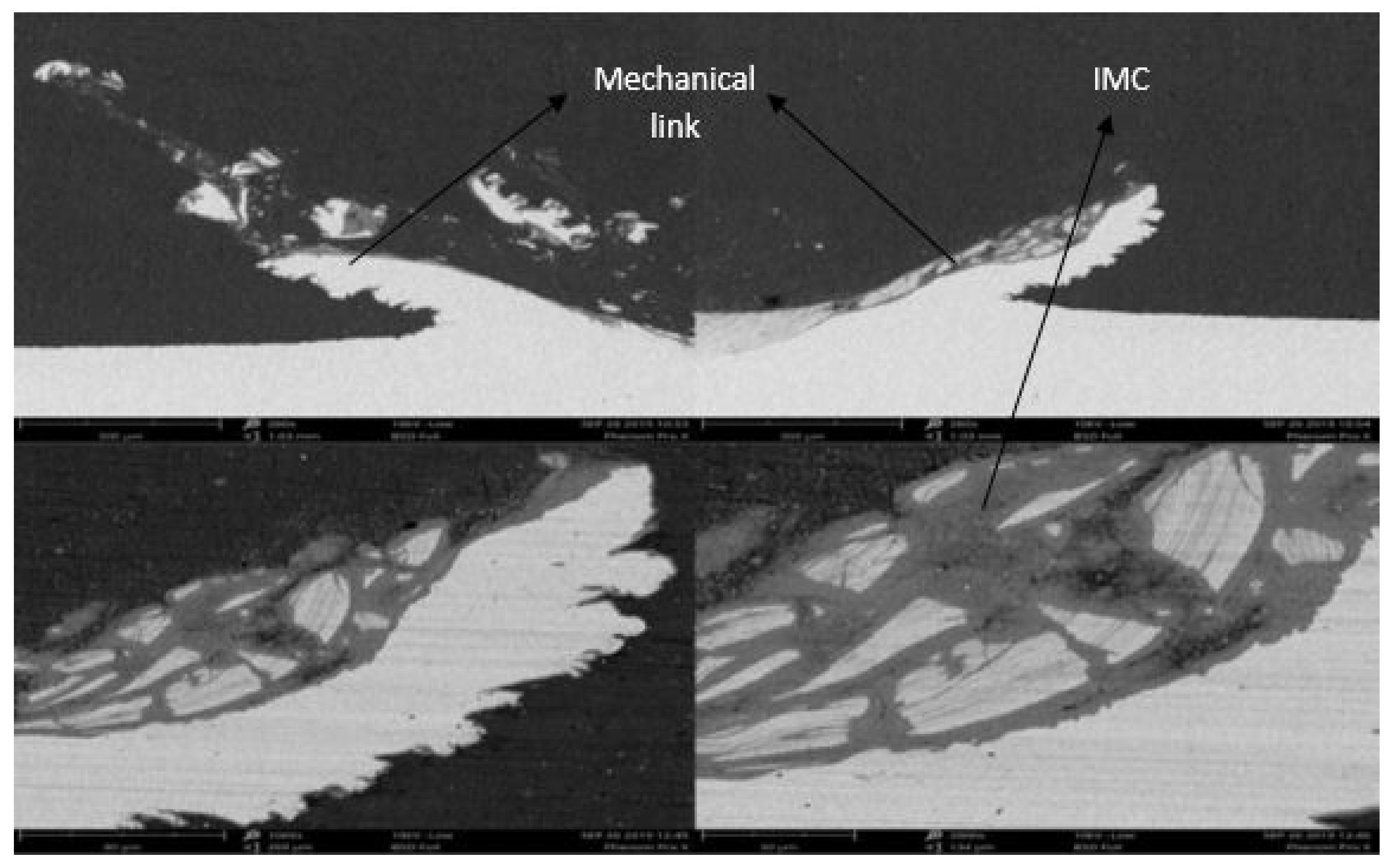
3.2. Microstructure of the Lap Joints
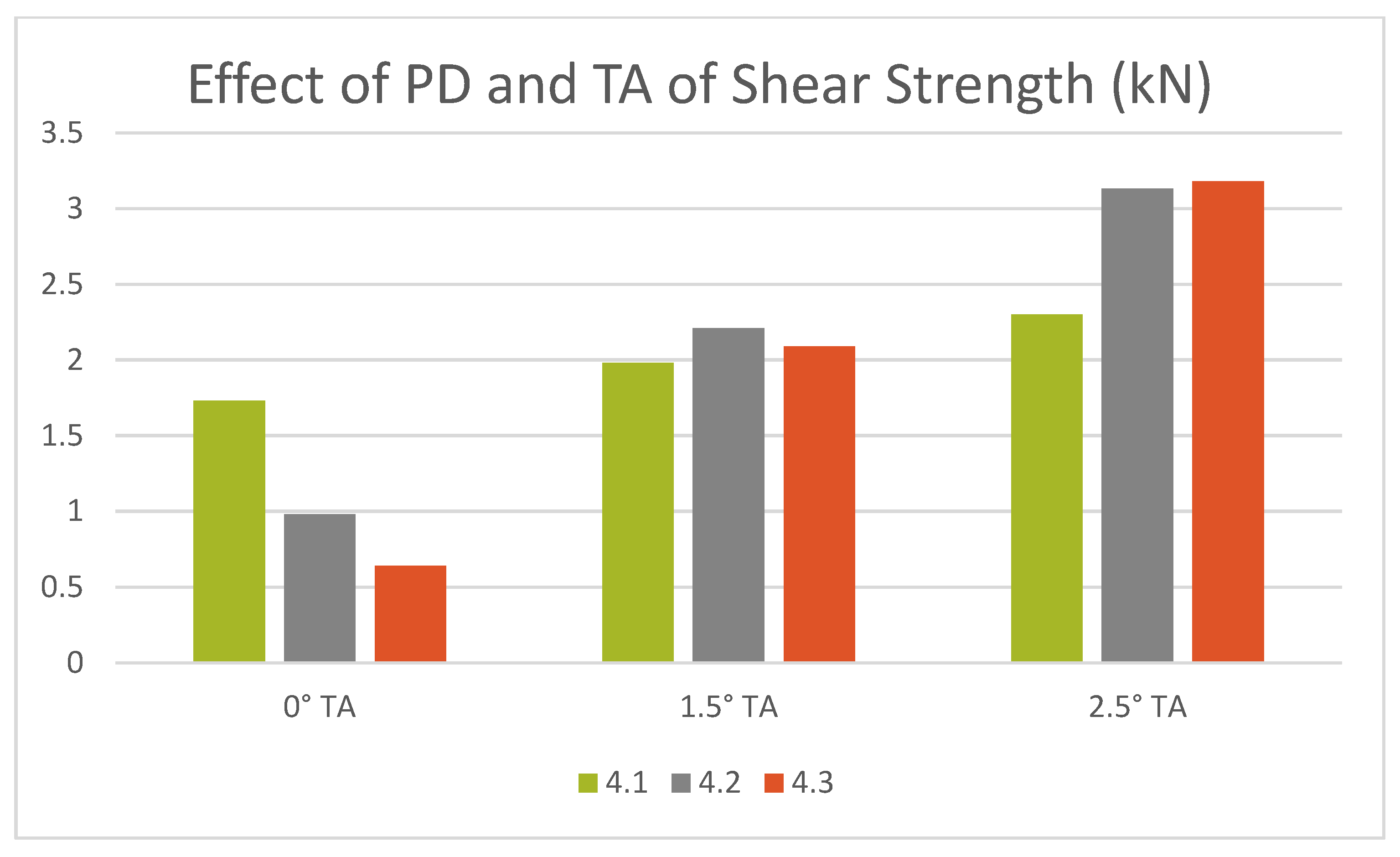
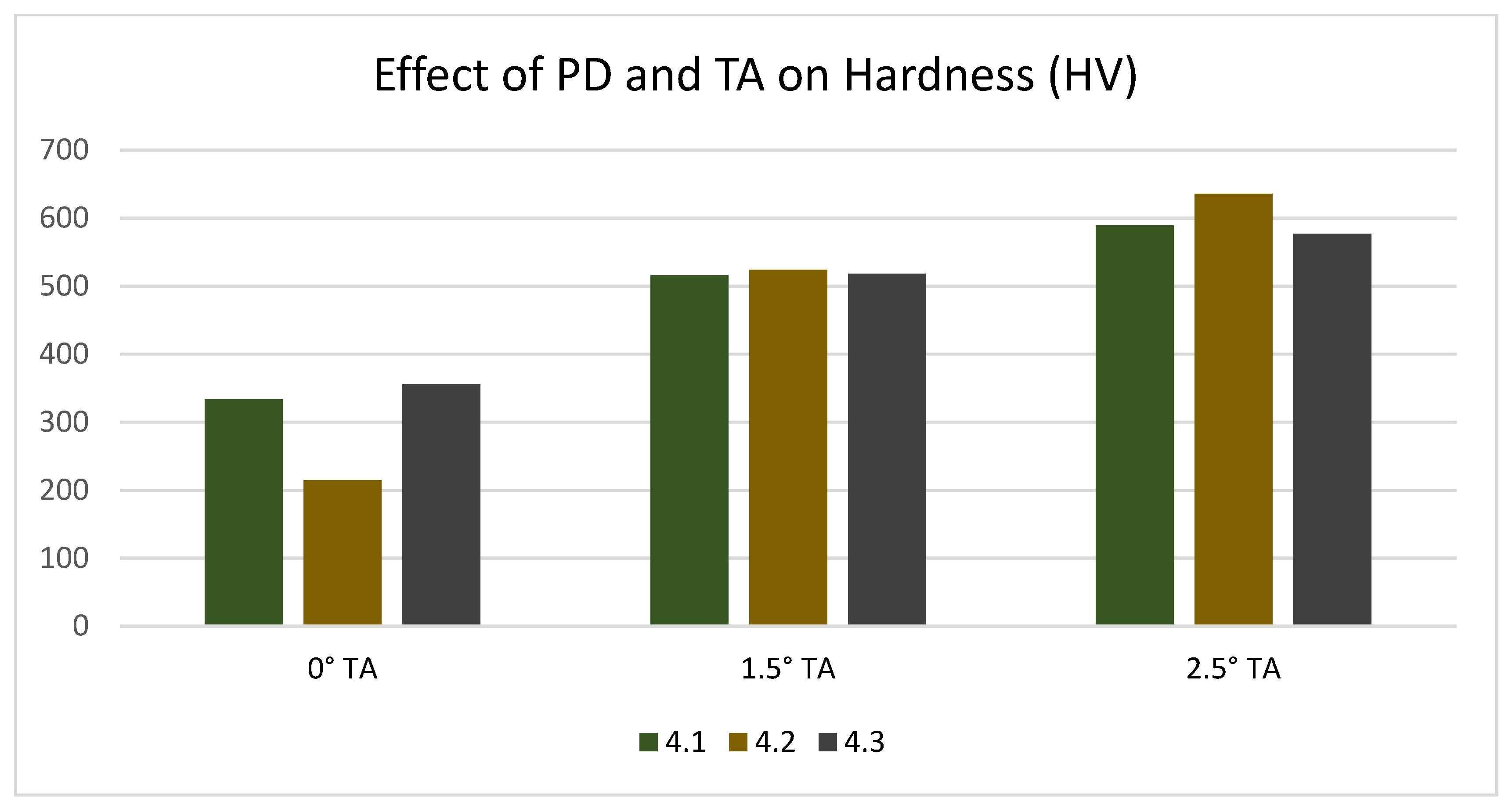
3.3. Mechanical Properties of the Lap Joint
3.4. Signal-to-Noise Ratio Analysis
4. Conclusions
- Microstructural analysis revealed that a defect-free joint can be achieved with a tilt angle of 2.5° if the mixed stir zone is visible with respect to pin depth. Micro voids are formed if the tilt angle is reduced to 1.5° with steel fragments scattering in the mixed stir zone, and tunnel defects are clearly visible on the advancing side of the stir zone and uneven distribution of steel particles on the retreating side when the tilt angle is further reduced to 0°.
- Tensile shear test results showed that a maximum strength of 3.18 N was achieved with 800 rpm, 40 mm/min, and a pin depth of 4.3 mm when the angle was tilted to 2.5° due to the fact of a good mixed stir zone with intermetallic compounds.
- Eliminating the micro voids and tunnel defects achieved a maximum hardness of HV 635.36 with 1000 rpm, 20 mm/min, and a pin depth of 4.2 mm when the angle was tilted to 2.5° and when a defect-free weld was obtained.
- From the microstructural analysis and tensile shear strength result, it is evident that a better joint strength is achieved with a tilt angle of 2.5° and a pin depth of 4.3 mm.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wan, L.; Huang, Y. Friction stir welding of dissimilar aluminium alloys and steels: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 99, 1781–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, K. A review on friction-based joining of dissimilar aluminum–steel joints. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 34, 78–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrefaey, A.; Gouda, M.; Takahashi, M.; Ikeuchi, K. Characterization of aluminium/steel lap joint by friction stir welding. J. Materi. Eng. Perform. 2005, 14, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimapong, K.; Watanabe, T. Lap joint of A5083 aluminum alloy and SS400 steel by friction stir welding. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Nakata, K. Effect of the Surface State of Steel on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Metal Lap Joints of Aluminum and Steel by Friction Stir Welding. Metall. Mat. Trans. A 2008, 39, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, R.S.; Kostka, A.; Sheikhi, S.; Dos Santos, J.; Pyzalla, A.R. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of an AA6181-T4 Aluminium Alloy to HC340LA High Strength Steel Friction Stir Overlap Weld. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, M.; Kokabi, A.H.; Reihani, S.S.; Najafi, H. Mechanical and Microstructural characterization of Al-5083/St-12 lap joints made by friction stir welding. Procedia Eng. 2011, 10, 3297–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, H.; Basak, S.; Das, G.; Pal, T.K. Influence of energy induced from process parameters on the mechanical properties of friction stir welded lap joint of aluminium to coated steel sheet. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 64, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, F. Effect of tool pin insertion depth on friction stir lap welding of aluminium to stainless steel. J. Materi. Eng. Perform. 2013, 22, 3005–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Huang, Y. Microstructure and Mechanical properties of Al/Steel Friction Stir Lap Weld. Metals 2017, 7, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.N.; Nguyen, Q.M.; Thi HT, D.; Huang, S.C. Investigation on lap joint friction stir welding between AA6351 alloys and Dp800 steels. Sādhanā 2018, 43, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.T.; Li, J.L.; Qian, J.W.; Zhang, F.S.; Huang, W.D. High strength lap joint of aluminium and stainless steels fabricated by friction stir welding with cutting pin. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2012, 17, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsujjoha, M.; Jasthi, B.K.; West, M.; Widener, C. Friction Stir Lap Welding of Aluminum to Steel Using Refractory Metal Pin Tools. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2015, 137, 021009–021017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, H.; Jana, S.S.; Pal, T.K.; De, A. Numerical and experimental investigation on friction stir lap welding of aluminium to steel. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2014, 19, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, H.; Ghosh, R.N.; Pal, T.K. Study on the formation and characterization of the Intermetallics in Friction stir welding of Aluminium alloy to coated steel sheet lap joint. Metall. Mat. Trans. A 2014, 45, 5098–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumerzoug, Z.; Helal, Y. Friction stir welding of dissimilar materials aluminum AL6061-T6 to low carbon steel. Metals 2017, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, M.; Kokabi, A.H.; Reihani, S.S.; Cheng, W.J.; Wang, C.J. Effect of annealing treatment on joint strength of aluminum/steel friction stir lap weld. Mater. Design 2013, 44, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas, M.; Abdel-Gwad, A.; Omran, A.M.; Gökçe, B.; Sahraeinejad, S.; Gerlich, A.P. Friction stir weld assisted diffusion bonding of 5754 aluminum alloy to coated high strength steels. Mater. Design 2014, 55, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, H.; Ogura, T.; Hatano, R.; Kurashima, H.; Fujimoto, M.; Hirose, A. Fracture toughness and fatigue crack behaviour of A3003/SUS304 lap friction stir welded joints. Weld. Int. 2017, 31, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wan, L.; Meng, X.; Liu, H.; Li, H. Self-riveting friction stir lap welding of aluminium alloy to steel. Mater. Lett. 2016, 185, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basariya, M.I.R.; Mukhopadhyay, N.K. Chapter 5, Structural and mechanical behaviour of Al-Fe intermetallics. In Intermetallics Compounds; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]

| SS 304 Elements | Fe | Cr | Ni | Mn | N | S | C | Si | P |
| Percentage (wt.%) | Bal | 18 | 8 | 2 | 0.1 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.75 | 0.045 |
| AA 5052 Elements | Al | Cr | Mg | Mn | Fe | Cu | Zn | Si | Others |
| Percentage (wt.%) | Bal | 0.15–0.35 | 2.2–2.8 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.15 |
| Parameter | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tool Rotational Speed (rpm) | 800 | 1000 | 1200 |
| Welding Speed (mm/min) | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| Pin Depth (mm) | 4.1 | 4.2 | 4.3 |
| Tilt Angle (Degree) | 0 | 1.5 | 2.5 |
| Run | TRS (rpm) | WS (mm/min) | PD (mm) | TA (degree) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSLW-1 | 800 | 20 | 4.1 | 0 |
| FSLW-2 | 800 | 30 | 4.2 | 1.5 |
| FSLW-3 | 800 | 40 | 4.3 | 2.5 |
| FSLW-4 | 1000 | 20 | 4.2 | 2.5 |
| FSLW-5 | 1000 | 30 | 4.3 | 0 |
| FSLW-6 | 1000 | 40 | 4.1 | 1.5 |
| FSLW-7 | 1200 | 20 | 4.3 | 1.5 |
| FSLW-8 | 1200 | 30 | 4.1 | 2.5 |
| FSLW-9 | 1200 | 40 | 4.2 | 0 |
| Run | TRS (rpm) | WS (mm/min) | PD (mm) | Tilt Angle (degree) | Hardness (HV) | Shear Strength (kN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSLW-1 | 800 | 20 | 4.1 | 0 | 333.32 | 1.73 |
| FSLW-2 | 800 | 30 | 4.2 | 1.5 | 524.02 | 2.21 |
| FSLW-3 | 800 | 40 | 4.3 | 2.5 | 576.9 | 3.18 |
| FSLW-4 | 1000 | 20 | 4.2 | 2.5 | 635.46 | 3.13 |
| FSLW-5 | 1000 | 30 | 4.3 | 0 | 355.42 | 0.64 |
| FSLW-6 | 1000 | 40 | 4.1 | 1.5 | 516.42 | 1.98 |
| FSLW-7 | 1200 | 20 | 4.3 | 1.5 | 517.9 | 2.09 |
| FSLW-8 | 1200 | 30 | 4.1 | 2.5 | 588.86 | 2.30 |
| FSLW-9 | 1200 | 40 | 4.2 | 0 | 214.84 | 0.98 |
| Level | Tool Rotational Speed | Welding Speed | Pin Depth | Tilt Angle |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 67.25 | 67.04 | 65.99 | 60.25 |
| 2 | 63.99 | 63.43 | 65.57 | 66.43 |
| 3 | 64.52 | 65.29 | 64.21 | 69.08 |
| Delta | 3.25 | 3.61 | 1.78 | 8.83 |
| Rank | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chitturi, V.; Pedapati, S.R.; Awang, M. Effect of Tilt Angle and Pin Depth on Dissimilar Friction Stir Lap Welded Joints of Aluminum and Steel Alloys. Materials 2019, 12, 3901. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233901
Chitturi V, Pedapati SR, Awang M. Effect of Tilt Angle and Pin Depth on Dissimilar Friction Stir Lap Welded Joints of Aluminum and Steel Alloys. Materials. 2019; 12(23):3901. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233901
Chicago/Turabian StyleChitturi, Veerendra, Srinivasa Rao Pedapati, and Mokhtar Awang. 2019. "Effect of Tilt Angle and Pin Depth on Dissimilar Friction Stir Lap Welded Joints of Aluminum and Steel Alloys" Materials 12, no. 23: 3901. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233901
APA StyleChitturi, V., Pedapati, S. R., & Awang, M. (2019). Effect of Tilt Angle and Pin Depth on Dissimilar Friction Stir Lap Welded Joints of Aluminum and Steel Alloys. Materials, 12(23), 3901. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233901








