Construction and Swelling Properties of Thermosensitive N-isopropyl Acrylamide Microspheres With Controllable Size
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of Microspheres
2.3. Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FT-IR and TEM
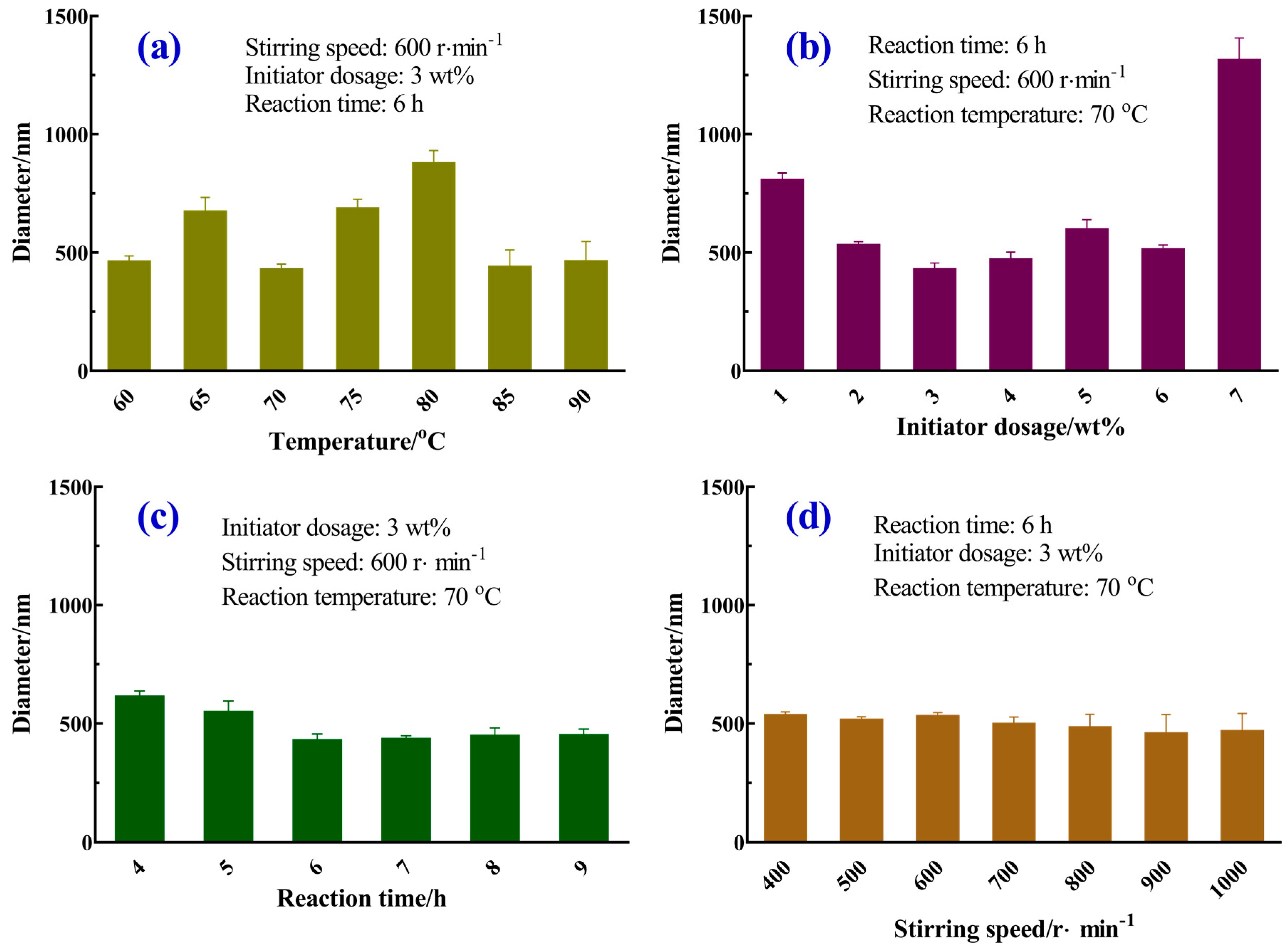
3.2. Effects of Main Reaction Parameters on the Size of Homogeneous Microspheres
3.2.1. Reaction Temperature
3.2.2. Initiator Dosage
3.2.3. Reaction Time
3.2.4. Stirring Speed
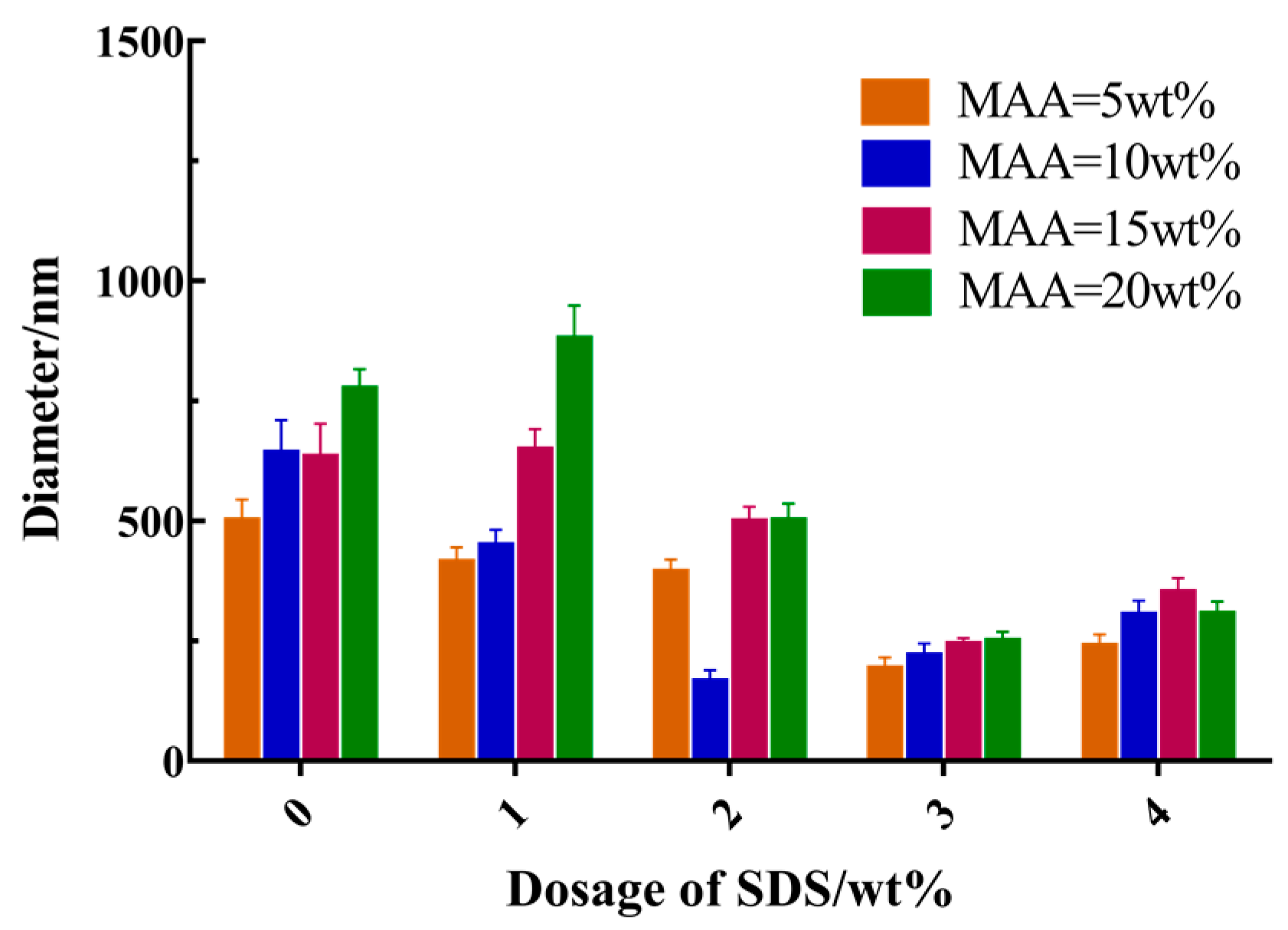
3.3. Effects of Main Reaction Parameters on the Size of Hollow Microspheres
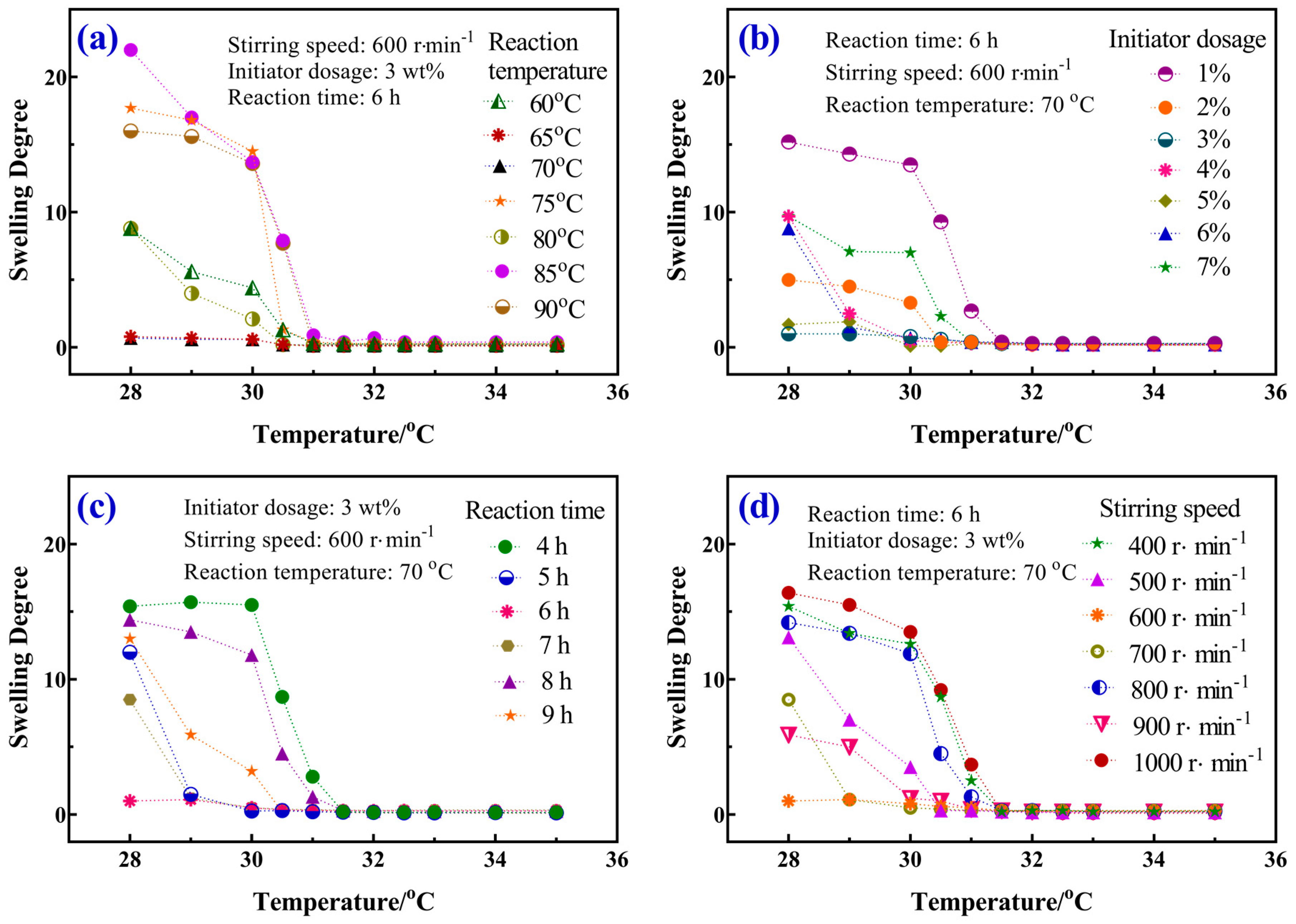
3.4. Swelling Behavior
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, M.; Ju, X.; Xie, R.; Wang, W.; Chu, L. Micromechanical Properties of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogel Microspheres Determined Using a Simple Method. Particuology 2015, 19, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, S.; Cesur, B.; Zhang, Z.; Geest, B.; Hoogenboom, R. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Coated Gold Nanoparticles as Colourimetric Temperature and Salt Sensors. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 1705–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, H. Micro hydrogels: Preparation, properties, and applications. Polym. Int. 2014, 63, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Gao, Y.; Serpe, M.J. Reductant-Responsive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Microgels and Microgel-Based Optical Materials. Can. J. Chem. 2015, 93, 685–689. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, G.; Bai, Y.; Li, W.; Gao, Z.; Chen, S.; Qiu, N.; Satoh, T.; Kakuchi, T.; Duan, Q. Synthesis and Characterization of Eu(III) Complexes of Modified D-glucosamine and Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Meng, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J. Formation of Thermo-Sensitive Polyelectrolyte Complex Micelles From Two Biocompatible Graft Copolymers for Drug Delivery. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2014, 102, 2163–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caykara, T.; Kiper, S.; Demirel, G. Thermosensitive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylamide) Hydrogels: Synthesis, Swelling and Interaction with Ionic Surfactants. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Yang, B.; Zhu, S.; Yao, M. Thermal-Responsive Poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)/Sodium Alginate Hydrogels: Preparation, Swelling Behaviors, and Mechanical Properties. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2016, 294, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Ge, Z.; Liu, S. Fabrication of Thermoresponsive Cross-Linked Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Nanocapsules and Silver Nanoparticle-embedded Hybrid Capsules with Controlled Shell Thickness. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 2370–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, K.; Wu, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, P. Synthesis of Temperature-responsive Hybrid Capsules and Their Controlled Release Property. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 385, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Deng, Y. In Situ Synthesis of Temperature-Sensitive Hollow Microspheres Via Interfacial Polymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8274–8275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, C.M.W.S.; Paula, H.C.B.; Seabra, V.; Feitosa, J.P.A.; Sarmento, B.; De Paula, R.C.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Non-toxic and Thermo-Sensitive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Grafted Cashew Gum Nanoparticles as a Potential Epirubicin Delivery Matrix. Carbohyd. Polym. 2016, 154, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, A.; Zhang, Q. One-Pot Synthesis of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/Chitosan Composite Microspheres Via Microemulsion. Carbohyd. Polym. 2012, 90, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Fillmore, D.J. Kinetics of Swelling of Gels. J. Chem. Phys. 1979, 70, 1214–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, C.; He, X.; Ju, X.; Xie, R.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chu, L. Change in Size and Structure of Monodisperse Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Microcapsules in Response to Varying Temperature and Ethyl Gallate Concentration. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 210, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, H. Alternative Procedure for the Incorporation of Quantum Dots into Poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) Microgels Based on Multiple Interactions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Smitha, J.; Cinu, T.A.; Chacko, A.J.; Premaletha, K. Cross-Linked Chitosan Microspheres for Oral Delivery of Insulin: Taguchi Design and in Vivo Testing. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 92, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeso Vera, C.; Cornejo Bravo, J.M.; Serrano Medina, A.; Licea Claverie, A. Effect of Crosslinkers on Size and Temperature Sensitivity of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Microgels. Polym. Bull. 2013, 70, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gola, A.; Knysak, T.; Musial, W. The Influence of Anionic Initiator on the Selected Properties of Poly-N-isopropyl Acrylamide Evaluated for Controlled Drug Delivery. Molecules 2016, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, S.; Kawaguchi, H. Colored Thin Films Prepared from Hydrogel Microspheres. Langmuir 2005, 21, 8439–8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, C.C. Preparation of P(NIPAM-co-AA) Microcontainers Surface-Anchored with Magnetic Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2009, 25, 8255–8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.R. Polymer Chemistry, 5th ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 112–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hana, M.; Daniel, H. Effects of the Reaction Parameters on the Properties of Thermosensitive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Microspheres Prepared by Precipitation and Dispersion Polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 968–982. [Google Scholar]
- Sanson, N.; Rieger, J. Synthesis of Nanogels/Microgels by Conventional and Controlled Radical Crosslinking Copolymerization. Polym. Chem. 2010, 1, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Q. The Synthesis of PNIPAM Microgels. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J.; Chi, W.H.; Hyeon, S.M.; Canlier, A.; Hwang, T.S. Synthesis of Polyketone-g-vinylbenzyl Chloride Anion Exchange Membrane Via Irradiation and Its Properties. Macromol. Res. 2017, 25, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Lu, S.-x.; Wang, L.; Hui, Y.; Lu, Y.-r.; Chen, W.-j. Construction and Swelling Properties of Thermosensitive N-isopropyl Acrylamide Microspheres With Controllable Size. Materials 2019, 12, 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12152428
Wang C, Lu S-x, Wang L, Hui Y, Lu Y-r, Chen W-j. Construction and Swelling Properties of Thermosensitive N-isopropyl Acrylamide Microspheres With Controllable Size. Materials. 2019; 12(15):2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12152428
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chen, Si-xian Lu, Liang Wang, Yao Hui, Yan-ru Lu, and Wei-jia Chen. 2019. "Construction and Swelling Properties of Thermosensitive N-isopropyl Acrylamide Microspheres With Controllable Size" Materials 12, no. 15: 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12152428
APA StyleWang, C., Lu, S.-x., Wang, L., Hui, Y., Lu, Y.-r., & Chen, W.-j. (2019). Construction and Swelling Properties of Thermosensitive N-isopropyl Acrylamide Microspheres With Controllable Size. Materials, 12(15), 2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12152428



