Age Hardening of Extruded AA 6005A Aluminium Alloy Powders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of as Received AA6005A Powder
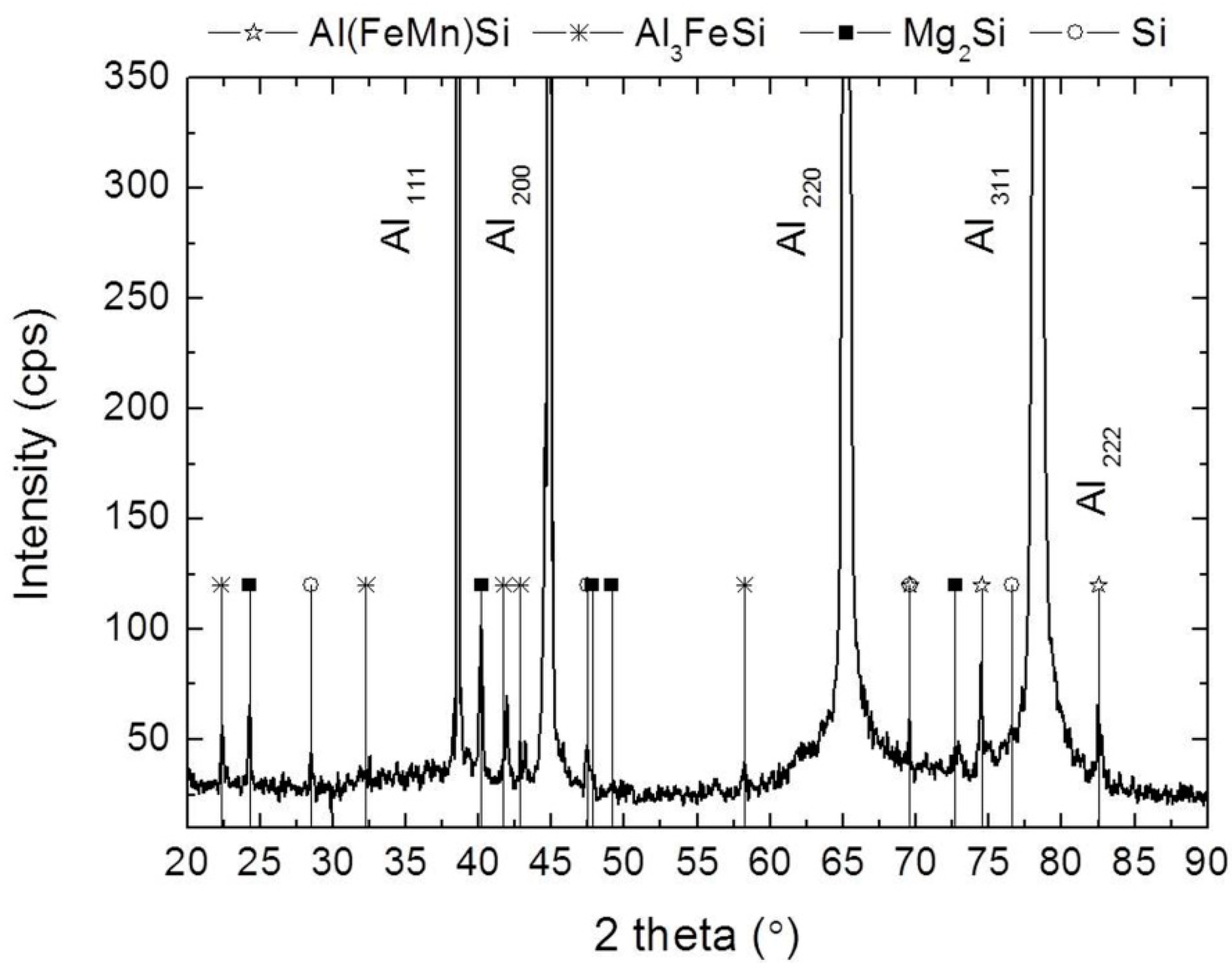
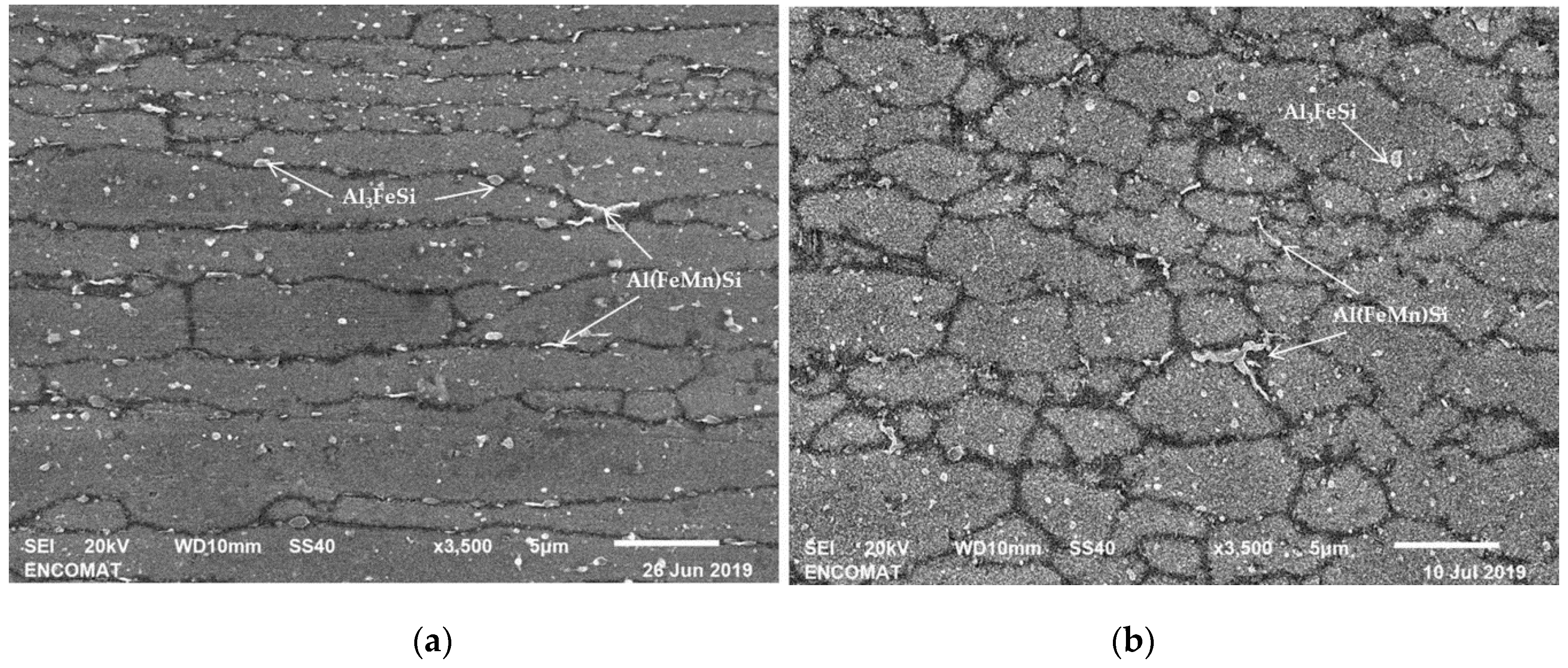
3.2. Characteristics of AA6005A P/M Extruded Alloys
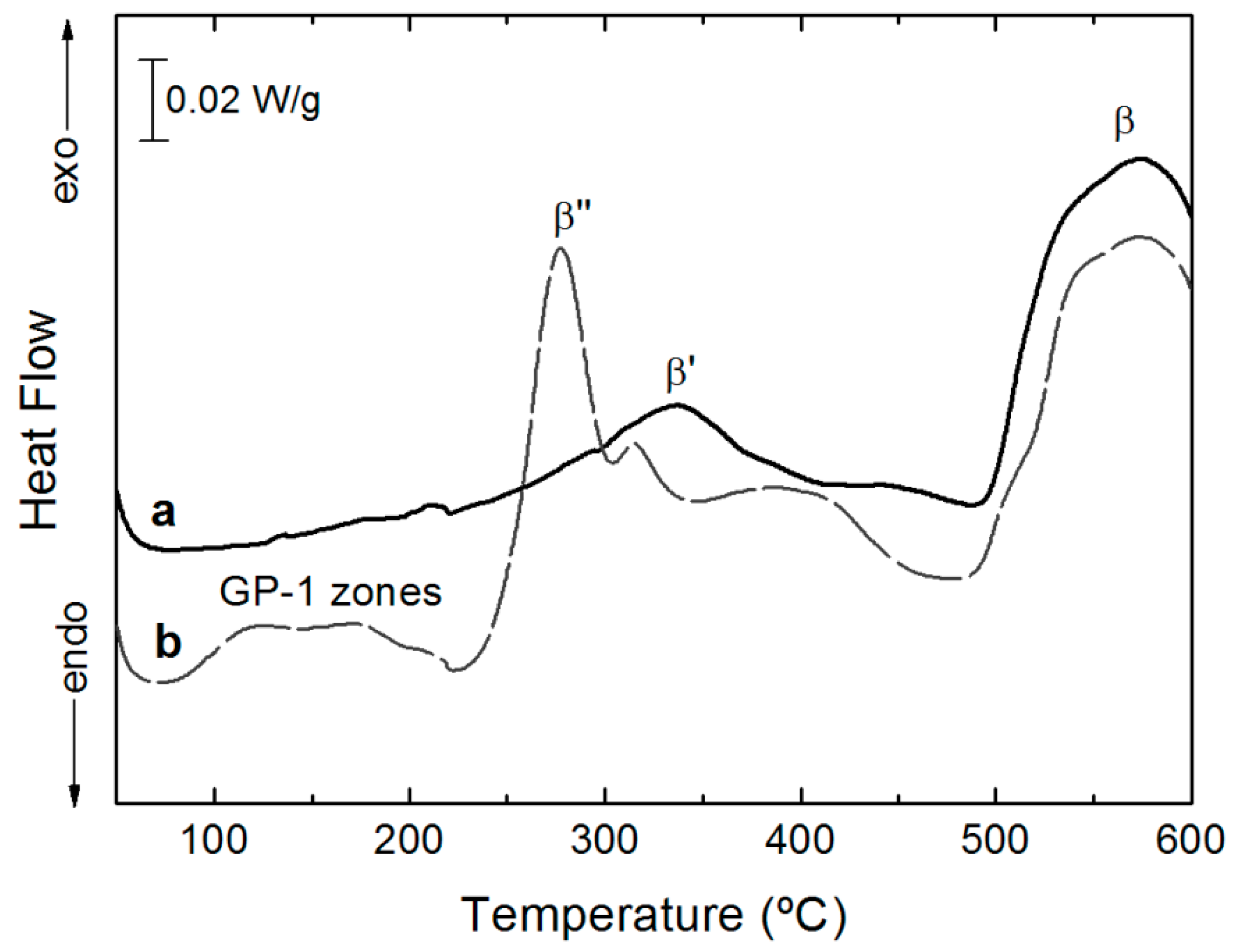
3.3. Age Hardening
3.4. Precipitation Hardening of the Extruded Profiles
4. Conclusions
- -
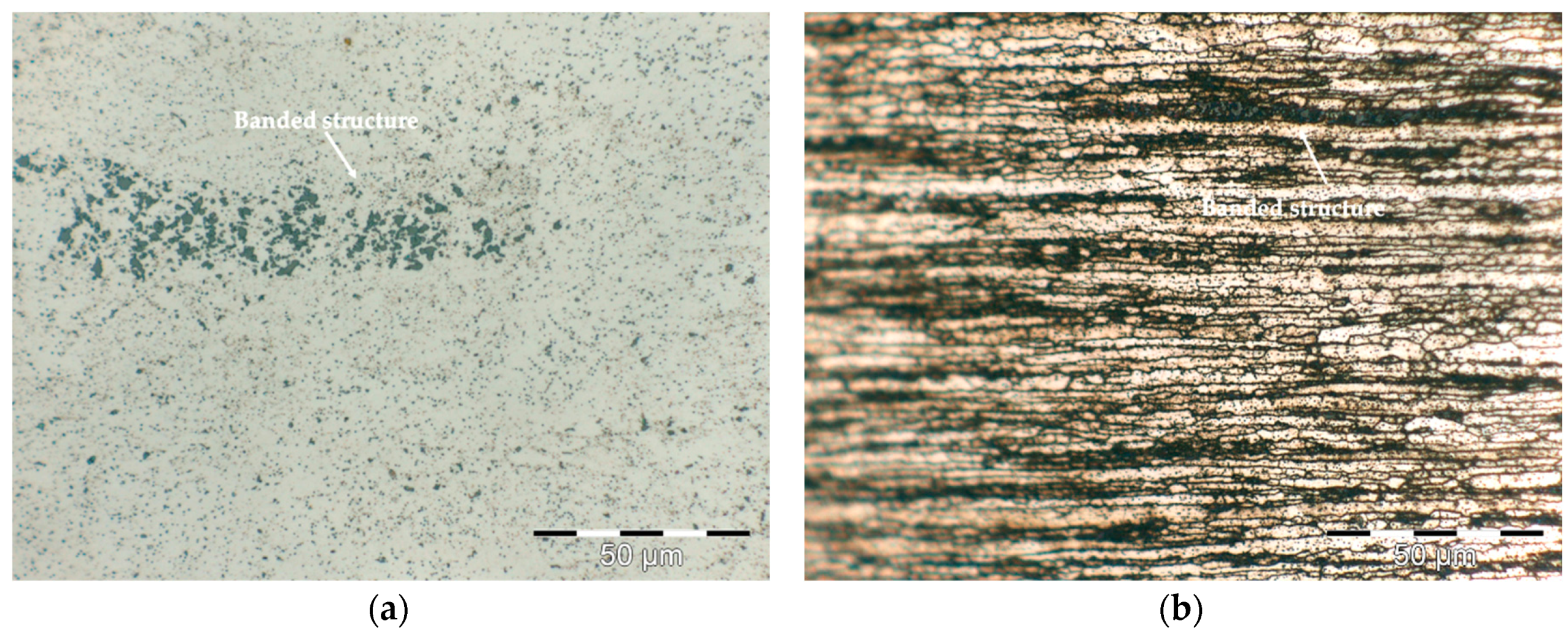
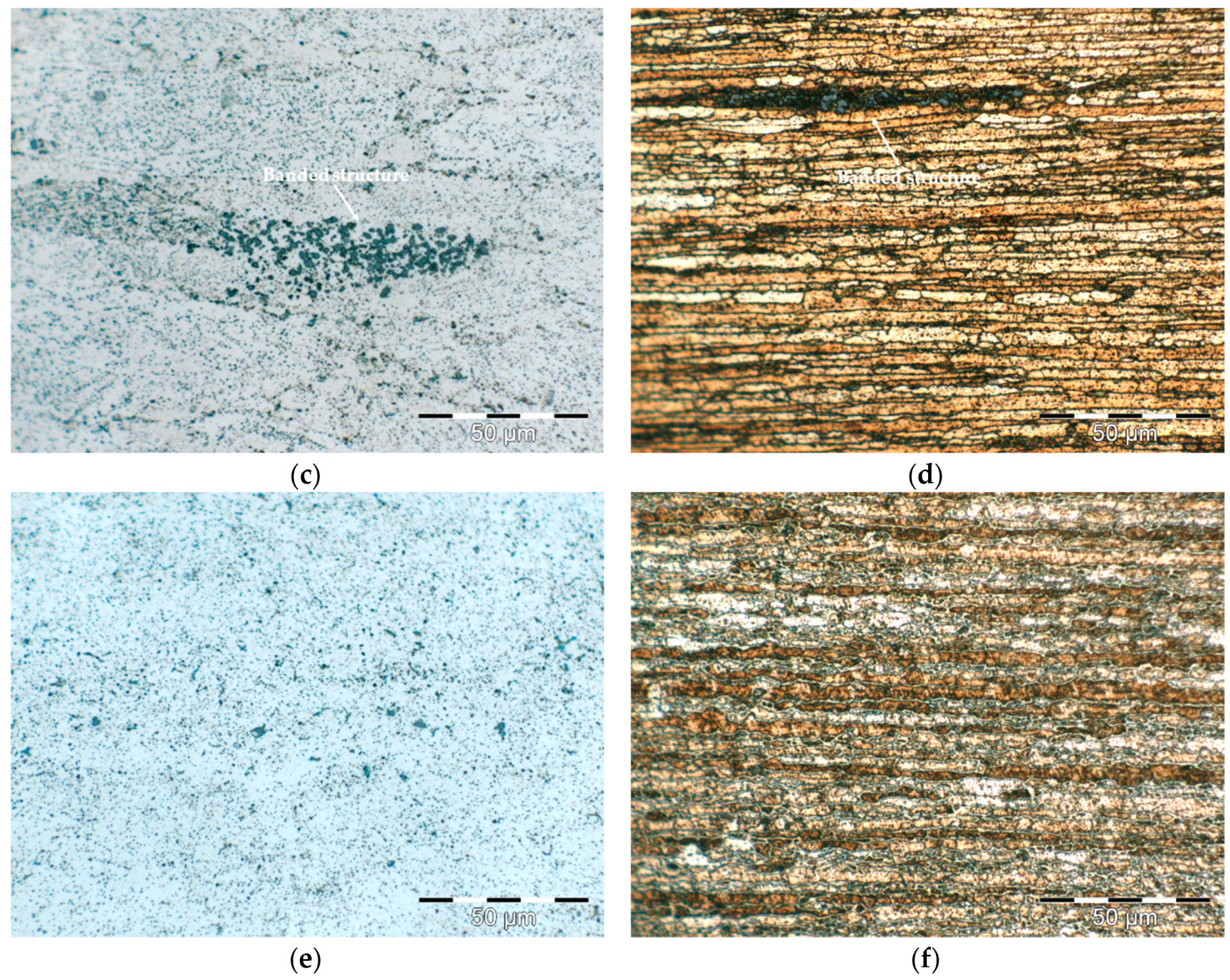
- The temperature selected temperature for hot extrusion was 500 °C, because the banded structure due to the presence of segregated phases in the pre-alloyed powders is less visible and a more uniform grain size distribution was obtained.
- -
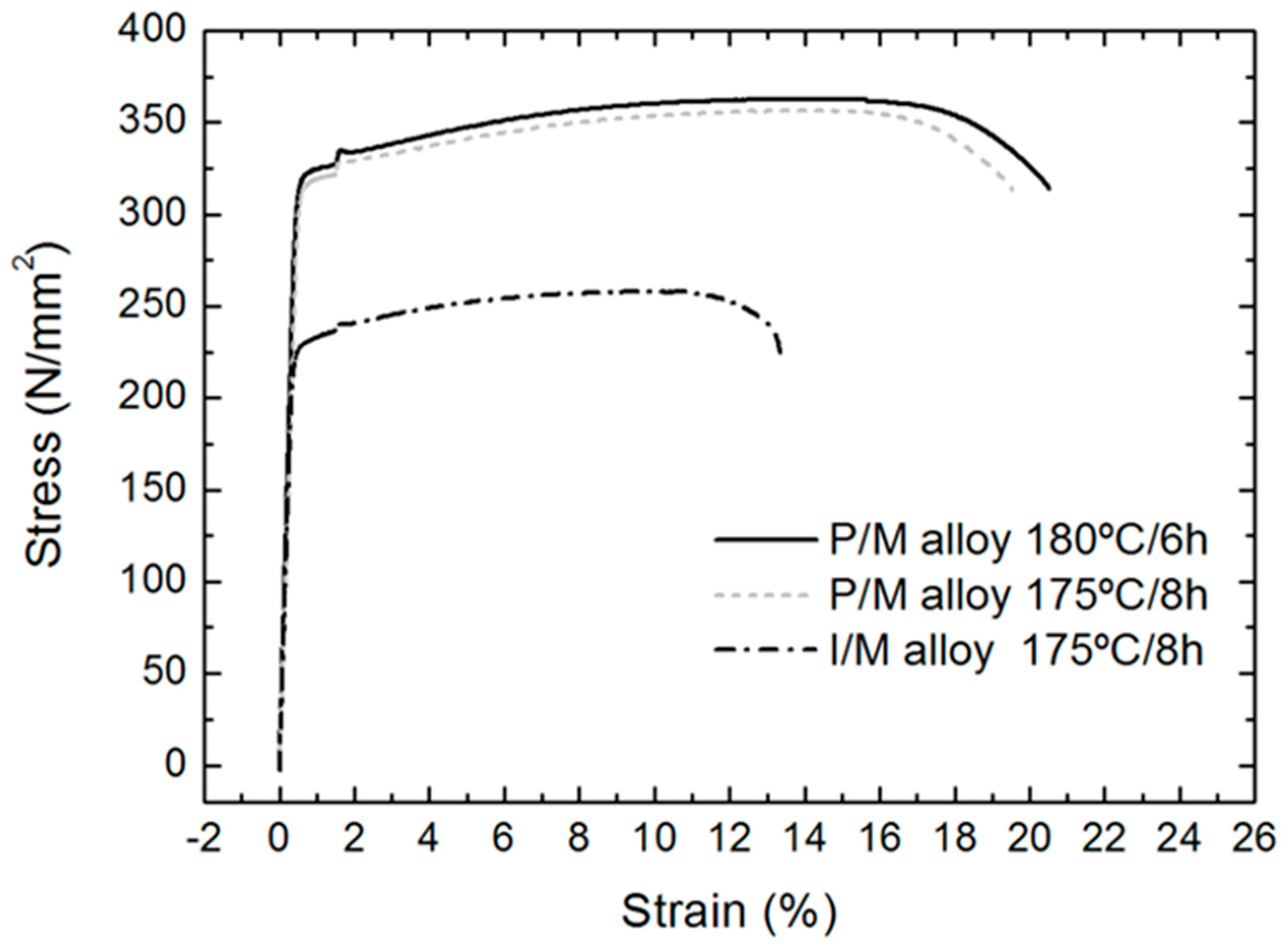
- Peak hardening conditions (T6) for the precipitation hardening of the P/M alloy were: 180 °C and 6 h. Temperature was slightly higher and the time was shorter than those normally used in the conventional route, in good agreement with the published results indicating that high-temperature and short-time aging are more efficient to produce a simultaneous enhancement of strength and ductility.
- -
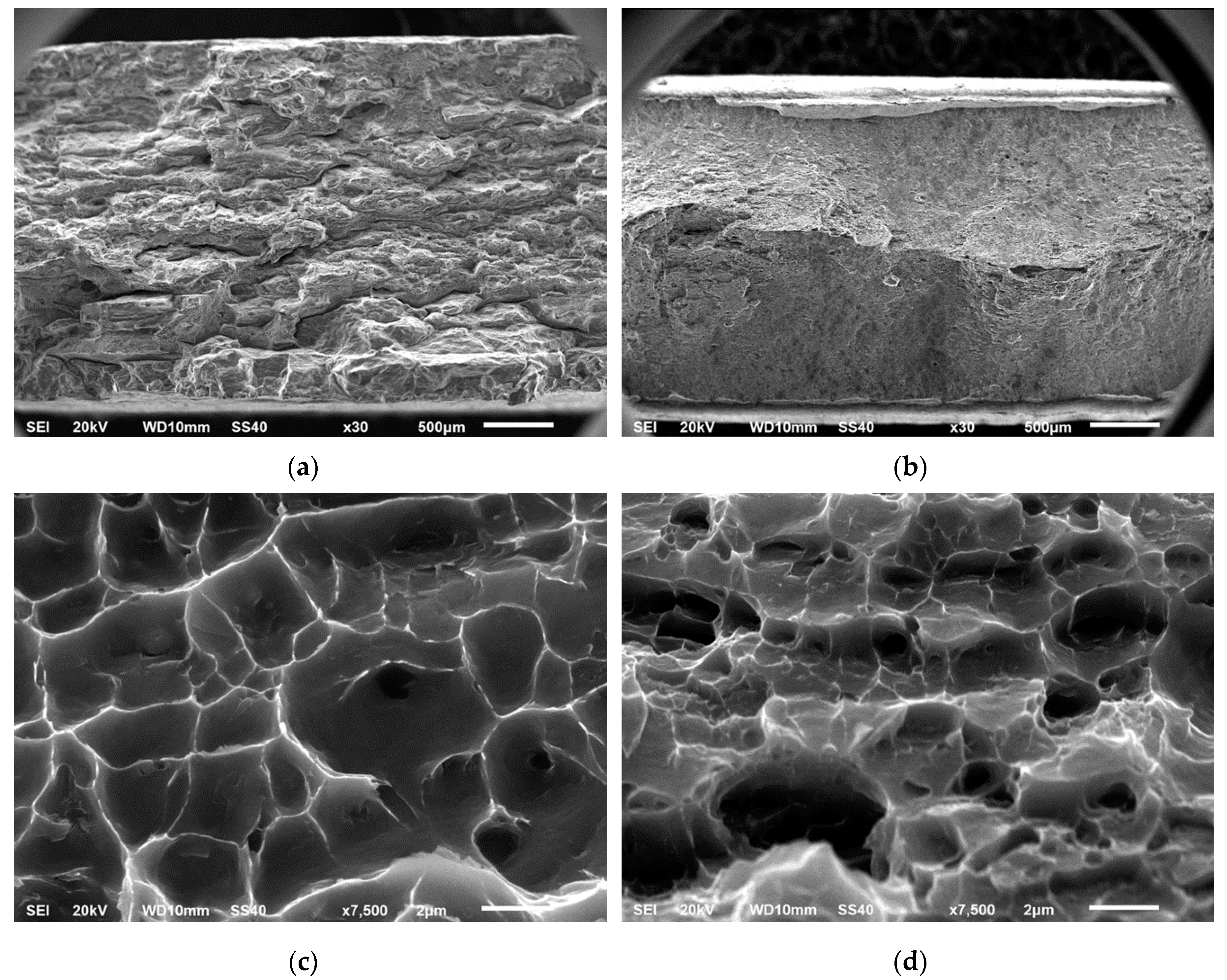
- The extruded profiles produced by powder metallurgy, hot extruded and aged at peak hardness conditions presented superior mechanical properties than the extruded profiles from conventional ingot metallurgy, achieving a simultaneous improvement of ~40% in strength and ~47% in ductility.
- -
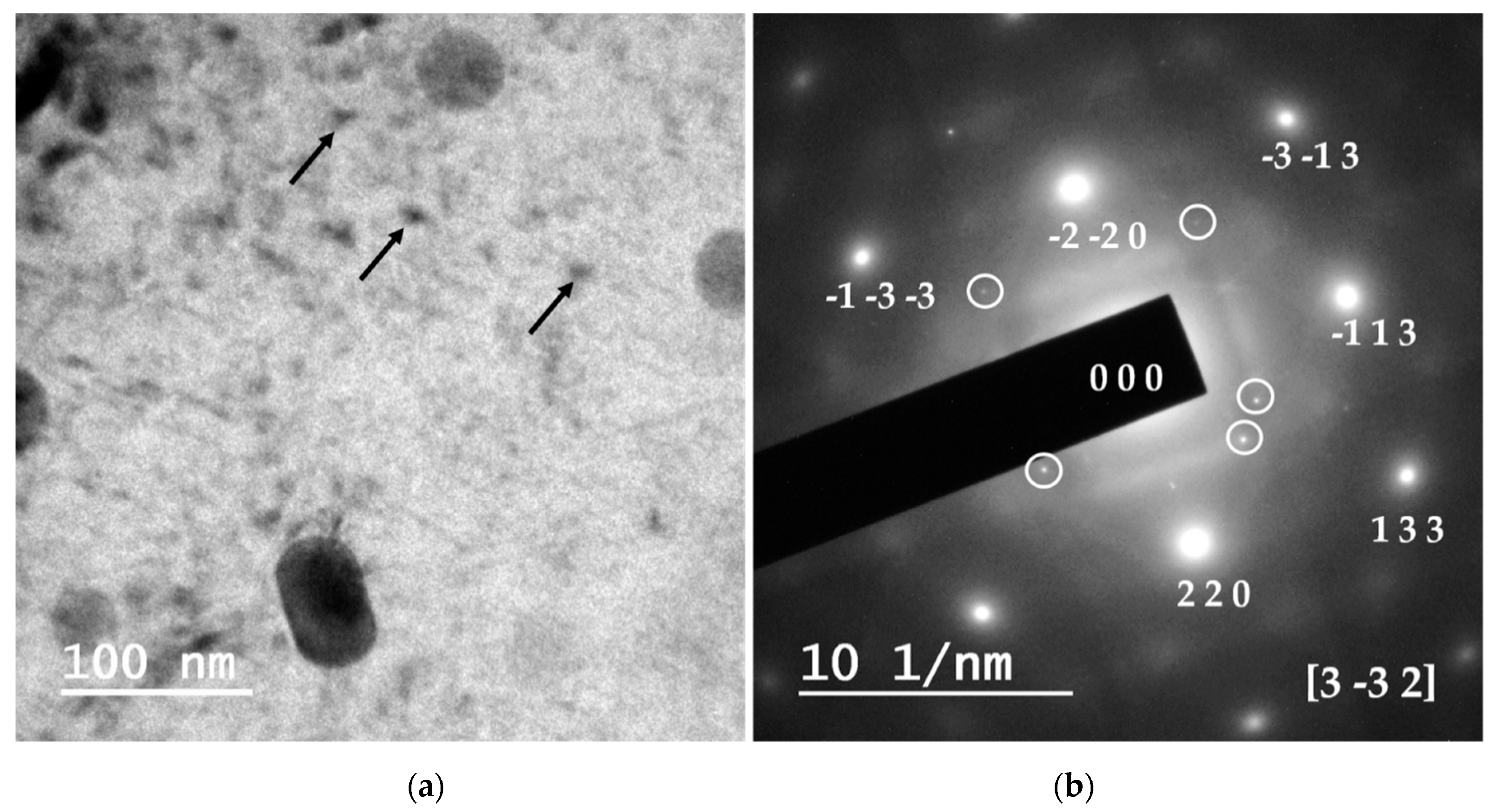
- The increase in both properties can be explained by combined effect of a UFG structure and a high density of nano-sized β″ precipitates.
- -
- This enhancement in properties can open the doors for the use of components extruded from AA 6005A P/M aerospace or military industries where the cost of manufacturing powders can be compensated with best performance of the alloy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, J.R. ASM Specialty Handbook: Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Polmear, I.J. Light Alloys: Metallurgy of the Light Metals, 3rd ed.; J. Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Soboyejo, W.O.; Srivatsan, T.S. Advanced Structural Materials: Properties, Design Optimization, and Applications; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Froyen, L.; Verlinden, B. TALAT Lecture 1401: Aluminum Powder Metallurgy; European Aluminium Association: Brussels, Belgium, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Pickens, J.R. High-Strength Aluminum Powder Metallurgy Alloys. In Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Material, 10th ed.; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 1990; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Gökçe, A.; Fehim, F.; Kurt, A.O. Microstructural examination and properties of premixed Al-Cu-Mg powder metallurgy alloy. Mater. Charact. 2011, 62, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D.P.; Cahoon, J.R.; Chaturvedi, M.C.; Kipouros, G.J.; Caley, W.F. On enhancing the mechanical properties of aluminum P/M alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 290, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capus, J. PM light alloys gaining applications in automotive sector. Met. Powder Rep. 2013, 68, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishan, P. Automotive applications of powder metallurgy. Adv. Powder Metall. Prop. Process. Appl. 2013, 493–519. [Google Scholar]
- Loberto, A.; Lopes, H.; Iervolino, F.; Salgado, L. PM Trends for the Automotive Industry. In Proceedings of the SAE 2010 World Congress & Exhibition, Detroit, MI, USA, 13–15 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Erdem, O. The Development and Applications of Powder Metallurgy Manufacturing Methods in Automotive Industry. Int. J. Eng. Res. Dev. 2017, 9, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schubert, T.; Weißgärber, T.; Kieback, B.; Balzer, H.; Neubing, H.-C.; Baum, U.; Braun, R. Aluminium PM ‘is a challenge that industry can overcome’. Met. Powder Rep. 2005, 60, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, G.; Sercombe, T.; Lumley, R. Liquid phase sintering of aluminium alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2001, 67, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, G.; Chen, L. Influence of extrusion parameters on microstructure, texture, and second-phase particles in an Al-Mg-Si alloy. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2019, 270, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiso, O. Extrusion of AlMgSi Alloys. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys (ICAA9), Brisbane, Australia, 2–5 August 2004; pp. 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Berndt, N.; Frint, P.; Wagner, M.F.-X. Influence of Extrusion Temperature on the Aging Behavior and Mechanical Properties of an AA6060 Aluminum Alloy. Metals 2018, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Sano, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Yukawa, N.; Sakamoto, J.; Tozawa, Y. Effect of Extrusion Conditions on Metal Flow and Microstructures of Aluminum Alloys. CIRP Ann. 2006, 55, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zheng, R.; Hanada, S.; Xiao, W.; Ma, C. Effect of hot extrusion and subsequent T6 treatment on the microstructure evolution and tensile properties of an Al-6Si-2Cu-0.5Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 710, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.J.; Zandbergen, H.W.; Jansen, J.; TrÆholt, C.; Tundal, U.; Reiso, O. The crystal structure of the β″ phase in Al-Mg-Si alloys. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 3283–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.K.; Matsumura, S.; Fukui, K.; Takeda, M. The compositions of metastable phase precipitates observed at peak hardness condition in an Al-Mg-Si alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, R.A.; Abdullah, H.A.; Al-Belushi, K.R. Influence of aging parameters on the mechanical properties of 6063 aluminium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2000, 102, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuniberti, A.; Tolley, A.; Riglos, M.V.C.; Giovachini, R. Influence of natural aging on the precipitation hardening of an AlMgSi alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 5307–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Cheng, G.J. Microstructure-properties relationship in two Al-Mg-Si alloys through a combination of extrusion and aging. JOM 2007, 59, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Lloyd, D.J.; Court, S.A. Precipitation hardening in Al-Mg-Si alloys with and without excess Si. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 316, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Sanders, R.E.; Liu, Q.; Yang, G. The natural aging and precipitation hardening behaviour of Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloys with different Mg/Si ratios and Cu additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 627, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.C.; Shin, C.S.; Chan, S.L.I. Effect of temper, specimen orientation and test temperature on tensile and fatigue properties of wrought and PM AA6061-alloys. Int. J. Fatigue 2004, 26, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmuş, H.K.; Meric, C. Age-hardening behavior of powder metallurgy AA2014 alloy. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Matsuki, K.; Takatsuji, N.; Yokote, T.; Kusui, J.; Yokoe, K. An investigation of the age hardening behavior of PM 2024Al-Fe-Ni alloys and the effect of consolidation conditions. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, A.; Fehim, F.; Kurt, A.O. Effects of Mg content on aging behavior of Al4CuXMg PM Alloy. Mater. Des. 2013, 46, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.; Özyürek, D.; Gürü, M. The Effects of Precipitate Size on the Hardness and Wear Behaviors of Aged 7075 Aluminum Alloys Produced by Powder Metallurgy Route. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 4273–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, M.; Feijoo, I.; Merino, P.; Pena, G.; Pérez, M.C.; Cruz, S.; Rey, P. Effect of high energy ball milling on the morphology, microstructure and properties of nano-sized TiC particle-reinforced 6005A aluminium alloy matrix composite. Powder Technol. 2017, 321, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Yu, M.; Du, Y. Preparation of bimodal grain size 7075 aviation aluminum alloys and their corrosion properties. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2017, 30, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari Taleghani, M.A.; Ruiz Navas, E.M.; Torralba, J.M. Microstructural and mechanical characterisation of 7075 aluminium alloy consolidated from a premixed powder by cold compaction and hot extrusion. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubizarreta, C.; Giménez, S.; Martín, J.M.; Iturriza, I. Effect of the heat treatment prior to extrusion on the direct hot-extrusion of aluminium powder compacts. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 467, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharzadeh, H.; Simchi, A.; Kim, H.S. Dynamic restoration and microstructural evolution during hot deformation of a P/M Al6063 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 542, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnárová, O.; Málek, P.; Lukáč, F.; Chráska, T. Spark Plasma Sintering of a Gas Atomized Al7075 Alloy: Microstructure and Properties. Materials 2016, 9, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, W.; Zhu, Q.; Merkel, R.; McQueen, H.J. Geometric dynamic recrystallization in hot torsion of Al-5Mg-0.6Mn (AA5083). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 205, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Logé, R.E. A review of dynamic recrystallization phenomena in metallic materials. Mater. Des. 2016, 111, 548–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, R.D.; Hughes, D.A.; Humphreys, F.J.; Jonas, J.J.; Juul Jensen, D.; Kassner, M.E.; King, W.E.; McNelley, T.R.; McQueen, H.J.; Rollett, A.D. Current issues in recrystallization: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1997, 238, 219–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourdet, S.; Montheillet, F. An experimental study of the recrystallization mechanism during hot deformation of aluminium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 283, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, I.; Allen, S.M. A calorimetric study of precipitation in aluminum alloy 6061. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1991, 10, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, G.A.; Stiller, K.; Dunlop, G.L.; Couper, M.J. The precipitation sequence in Al-Mg-Si alloys. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 3893–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.C.; Wang, M.P.; Zhang, R.R.; Zhang, Q.; Sheng, X.F. The diffraction patterns from β″ precipitates in 12 orientations in Al-Mg-Si alloy. Scr. Mater. 2010, 62, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E.; Zhu, T. Towards strength–ductility synergy through the design of heterogeneous nanostructures in metals. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovid’ko, I.A.; Valiev, R.Z.; Zhu, Y.T. Review on superior strength and enhanced ductility of metallic nanomaterials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 94, 462–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zhao, Y.H.; Zhu, Y.T.; Ma, E. Optimizing the strength and ductility of fine structured 2024 Al alloy by nano-precipitation. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 5822–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawancy, H.M.; Ul-Hamid, A.; Abbas, N.M. Practical Engineering Failure Analysis; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
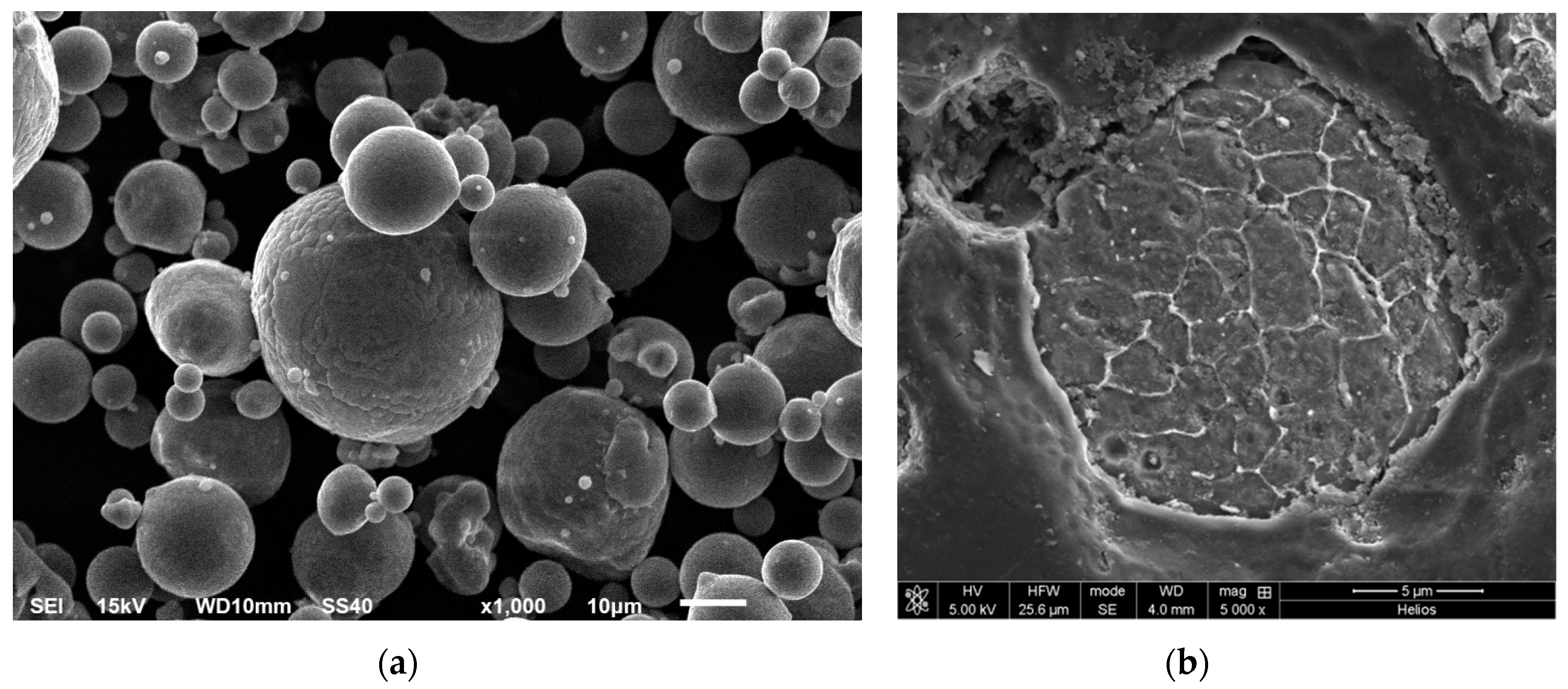


| Spectrum | Element at (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Mg | Si | Fe | |
| A | 58.30 | 0.40 | 41.09 | 0.21 |
| B | 78.81 | 0.57 | 17.84 | 2.78 |
| C | 77.26 | 15.54 | 7.20 | - |
| D | 98.84 | 0.68 | 0.46 | 0.03 |
| Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Cr | Zn | Ti | Mn + Cr | Al | Oxygen (ISO 4491/4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.845 | 0.087 | 0.047 | 0.064 | 0.635 | 0.005 | 0.045 | 0.056 | 0.069 | Bal. | 0.118 |
| Time (h) | Temperature (°C) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 170 | 175 | 180 | 185 | 190 | |
| 6 | 104 ± 2 | 103 ± 1 | 109 ± 1 | 95 ± 1 | 96 ± 1 |
| 7 | 105 ± 1 | 106 ± 3 | 106 ± 7 | 99 ± 3 | 86 ± 5 |
| 8 | 102 ± 1 | 106 ± 2 | 101 ± 1 | 99 ± 4 | 71 ± 5 |
| Alloy | Aging Treatment | Mechanical Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (h) | Temperature (°C) | 0, 2%YS (MPa) | UTS (MPa) | Elongation (%) | |
| AA 6005A P/M alloy | 6 | 180 | 318 ± 2 | 359 ± 3 | 21.33 ± 0.76 |
| AA 6005A P/M alloy | 8 | 175 | 313 ± 3 | 354 ± 4 | 19.33 ± 1.75 |
| AA 6005A I/M alloy | 8 | 175 | 228 ± 2 | 257 ± 1 | 14.50 ± 1.00 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feijoo, I.; Cabeza, M.; Merino, P.; Pena, G.; Rey, P. Age Hardening of Extruded AA 6005A Aluminium Alloy Powders. Materials 2019, 12, 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142316
Feijoo I, Cabeza M, Merino P, Pena G, Rey P. Age Hardening of Extruded AA 6005A Aluminium Alloy Powders. Materials. 2019; 12(14):2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142316
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeijoo, Iria, Marta Cabeza, Pedro Merino, Gloria Pena, and Pilar Rey. 2019. "Age Hardening of Extruded AA 6005A Aluminium Alloy Powders" Materials 12, no. 14: 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142316
APA StyleFeijoo, I., Cabeza, M., Merino, P., Pena, G., & Rey, P. (2019). Age Hardening of Extruded AA 6005A Aluminium Alloy Powders. Materials, 12(14), 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142316







