Phase Formation of Mg-Zn-Gd Alloys on the Mg-rich Corner
Abstract
1. Introduction
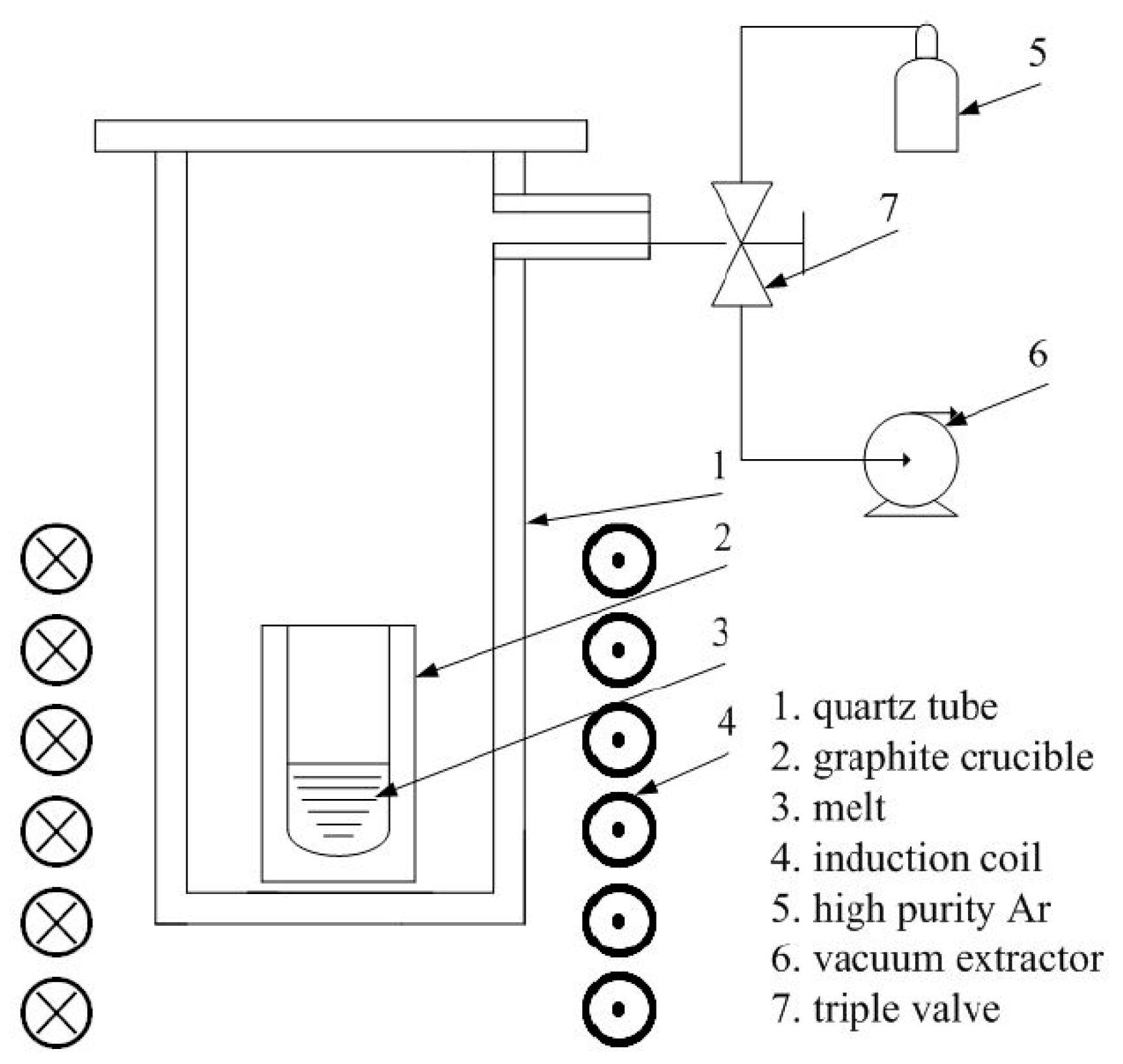
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
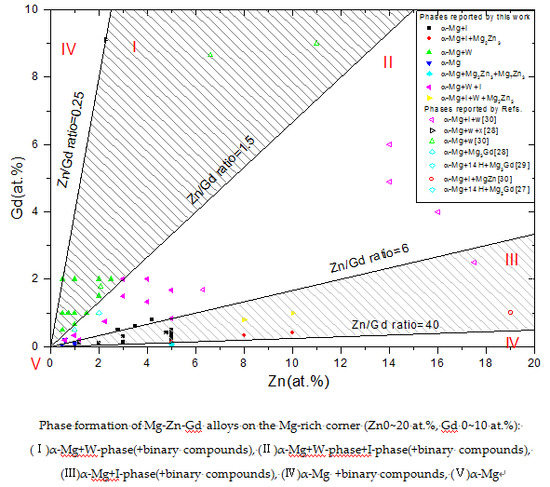
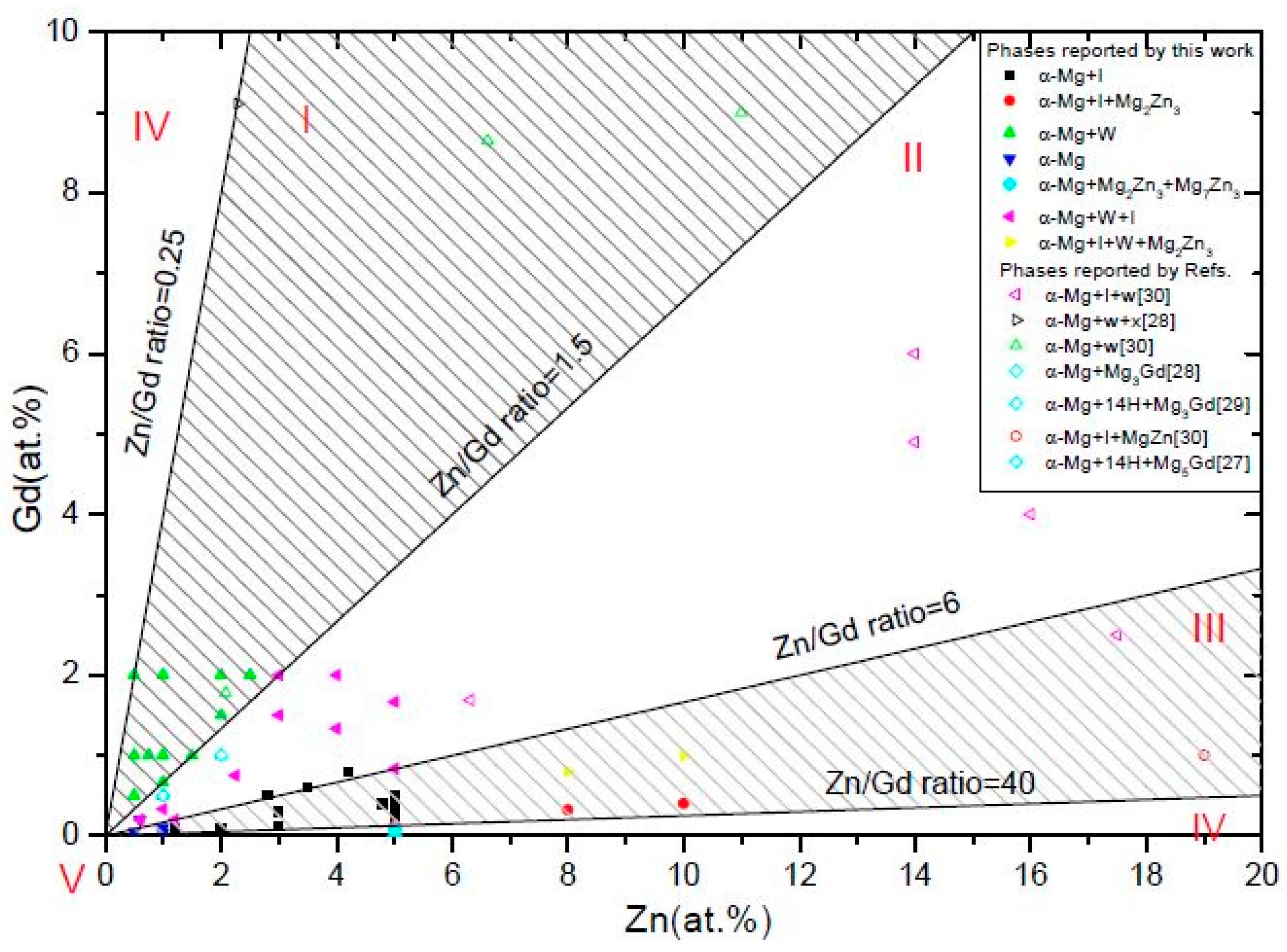
3.1. Phase Formation of Mg-Zn-Gd Alloy on the Mg-rich Corner
- (i)
- α-Mg+W-phase(+binary compounds),
- (ii)
- α-Mg+W-phase+I-phase(+binary compounds),
- (iii)
- α-Mg+I-phase(+binary compounds),
- (iv)
- α-Mg+binary compounds, and
- (v)
- α-Mg.
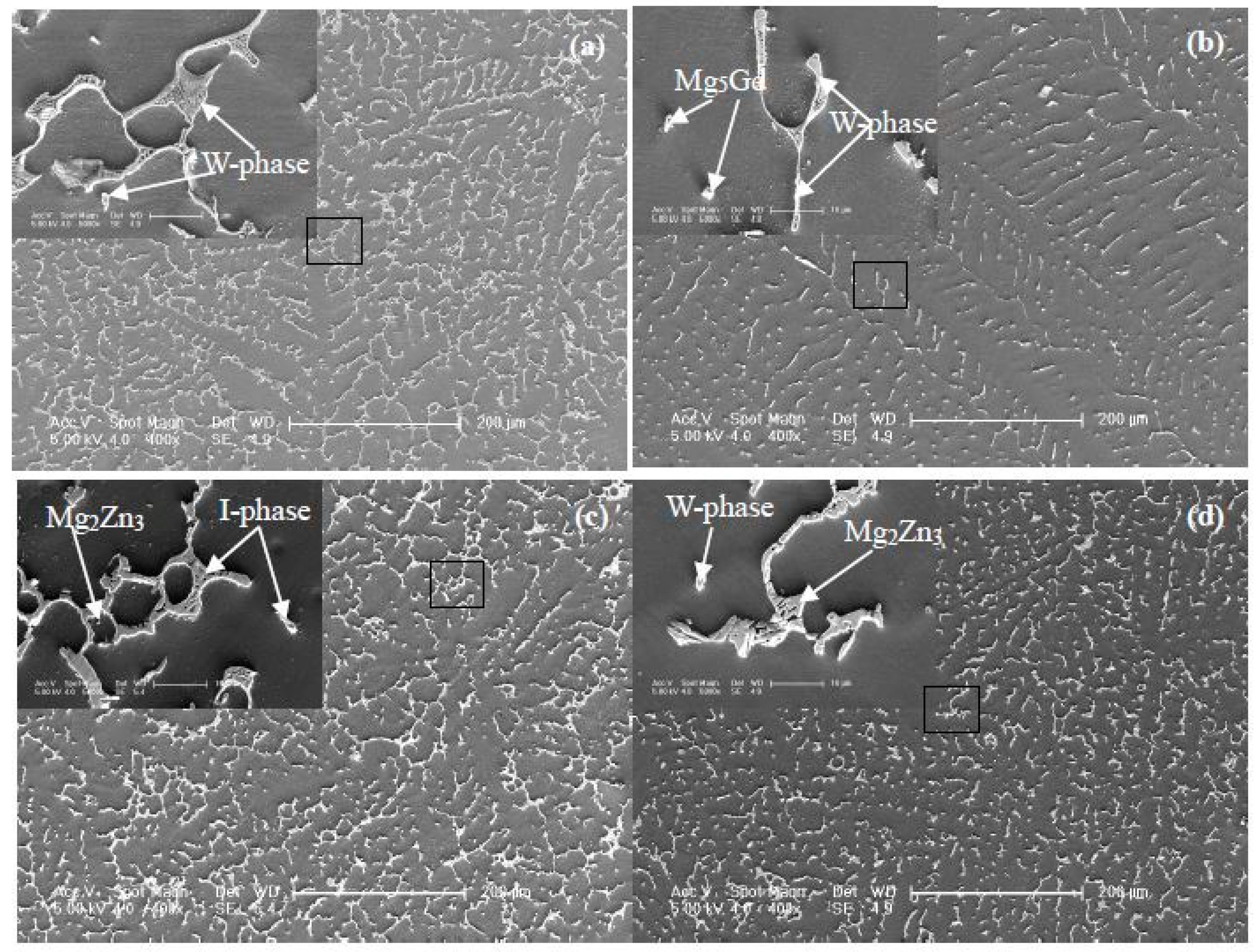
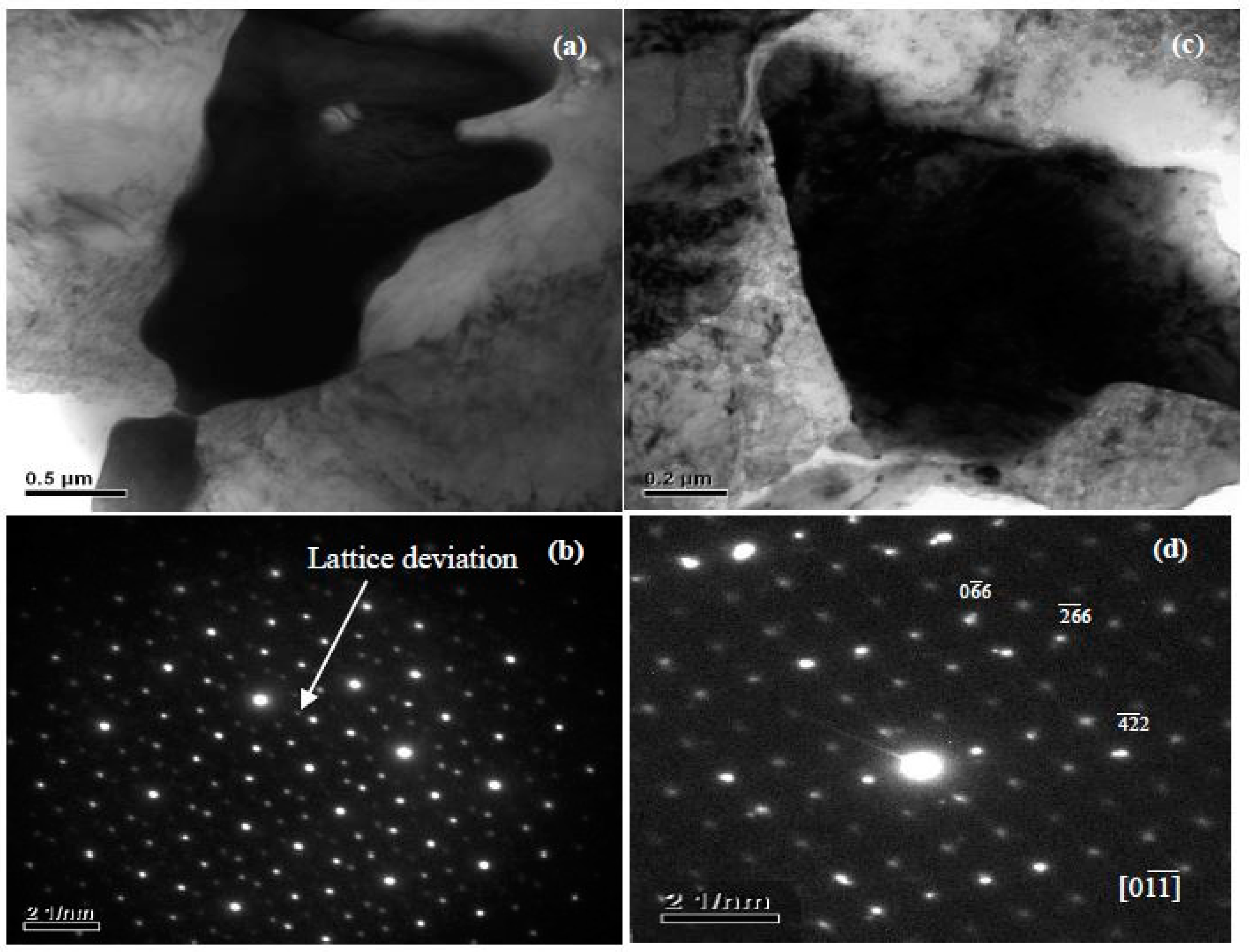
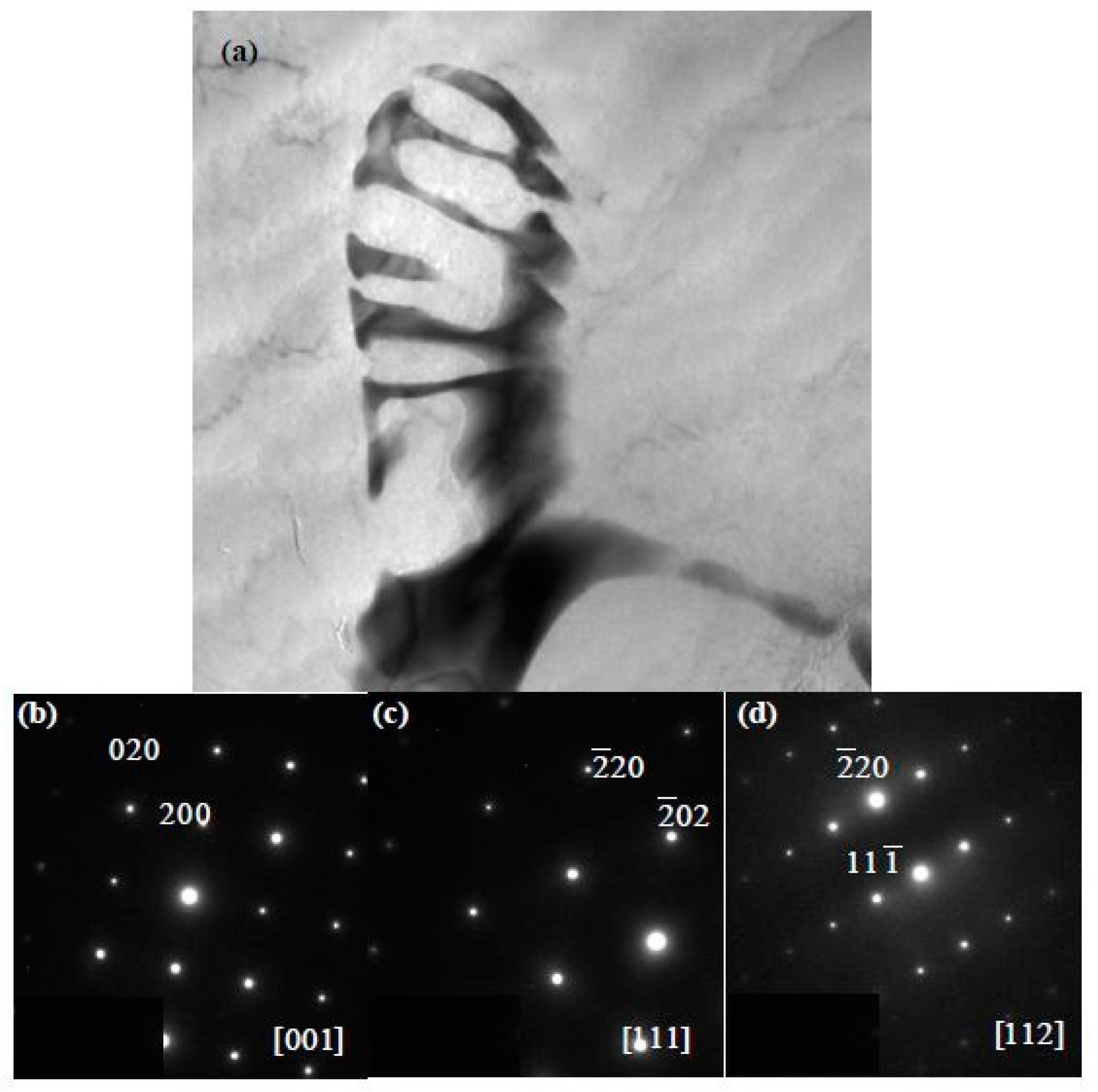
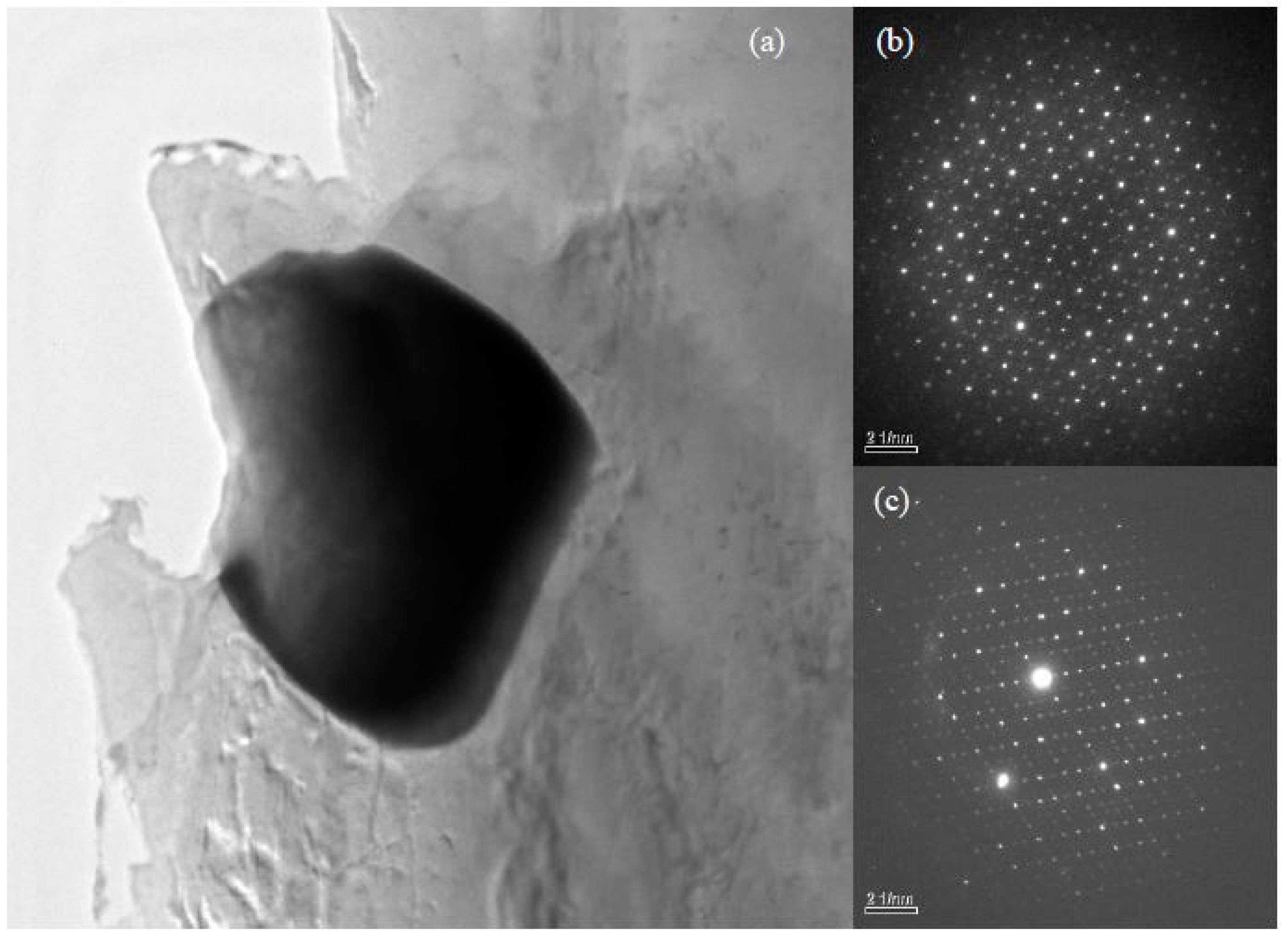
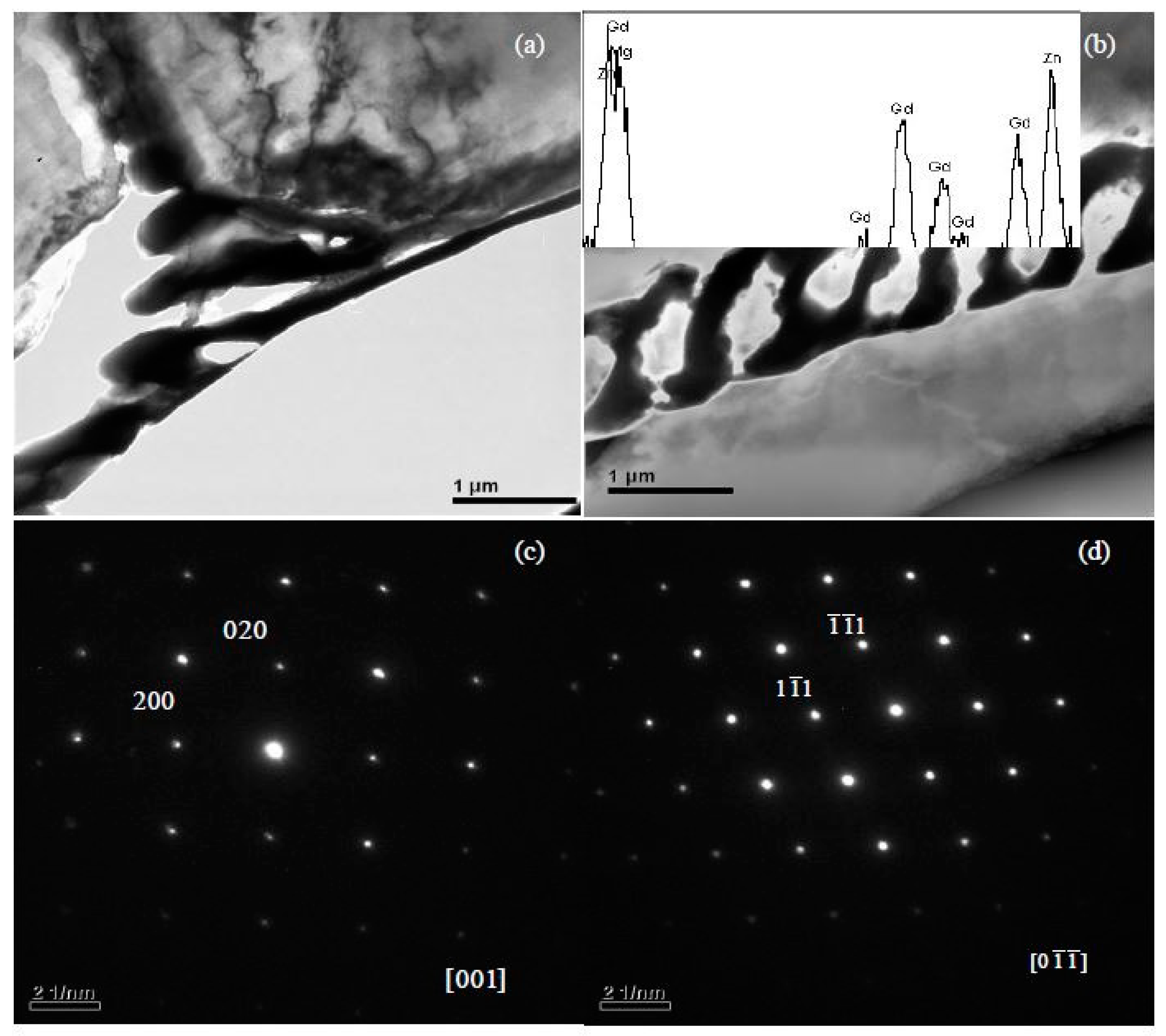
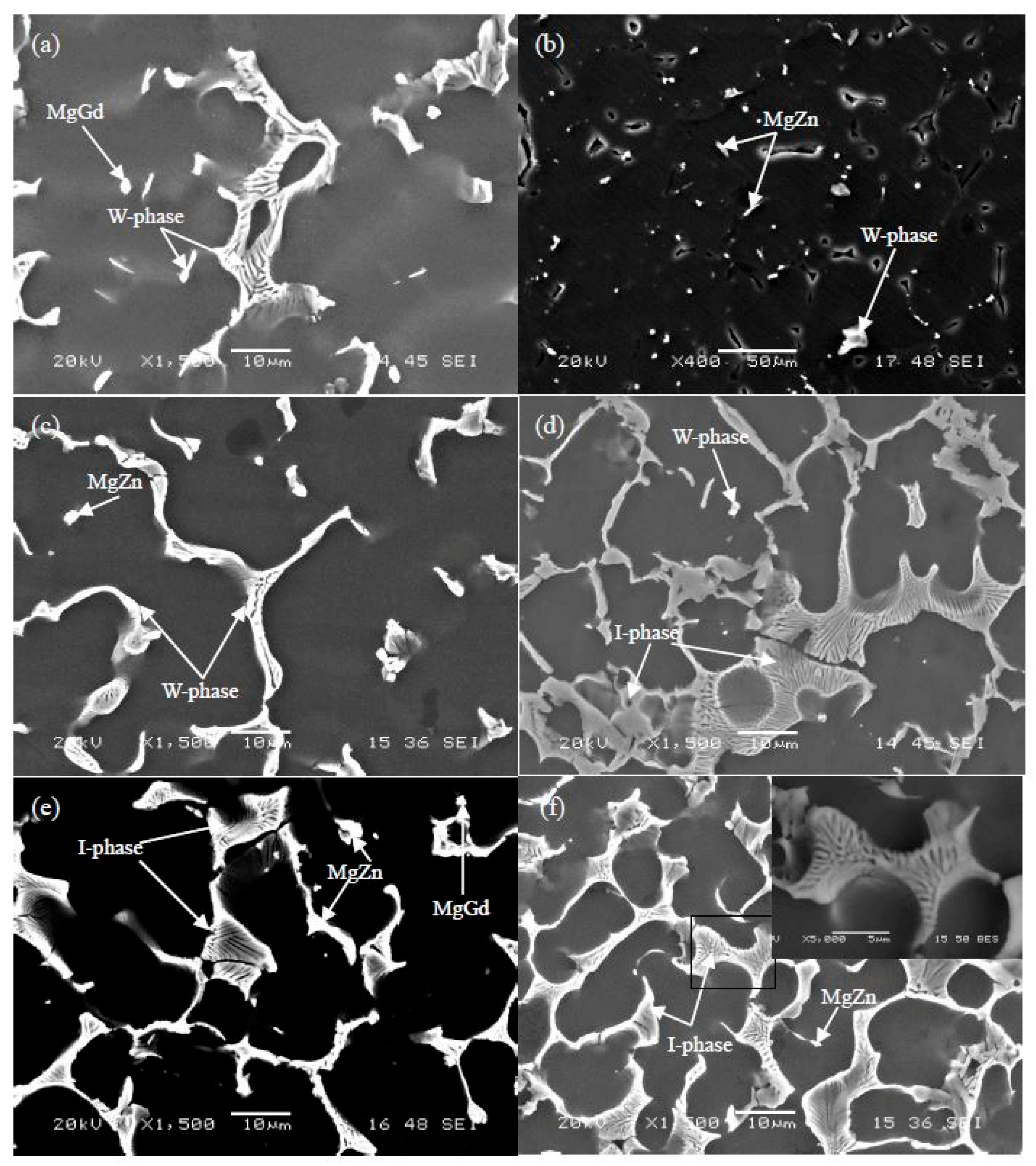
3.1.1. The Typical Microstructures and Phase Structures
3.1.2. The Effect of Zn/Gd Ratio on the Phase Formation
3.1.3. The Effect of Alloying Element Content on the Phase Formation
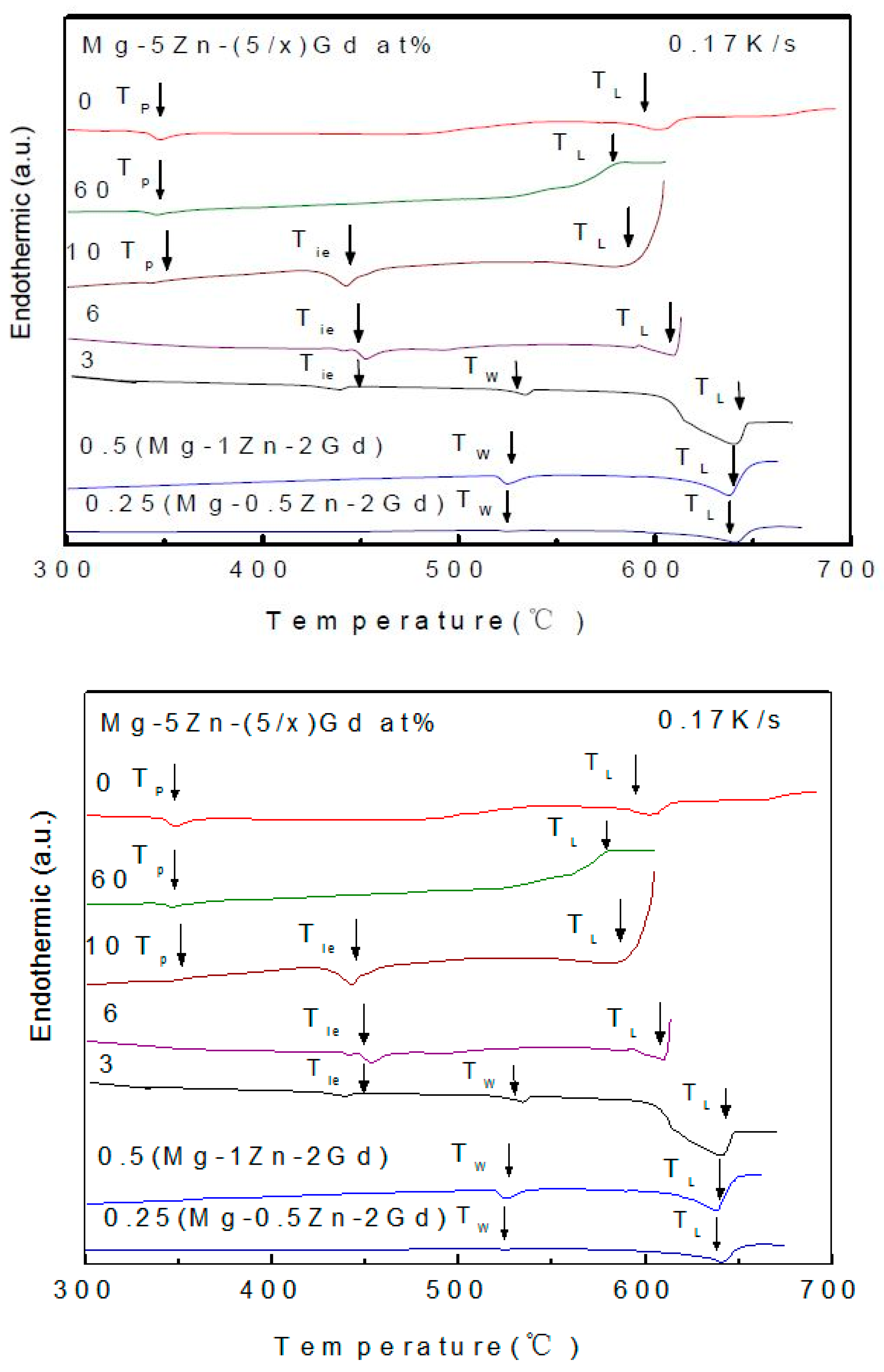
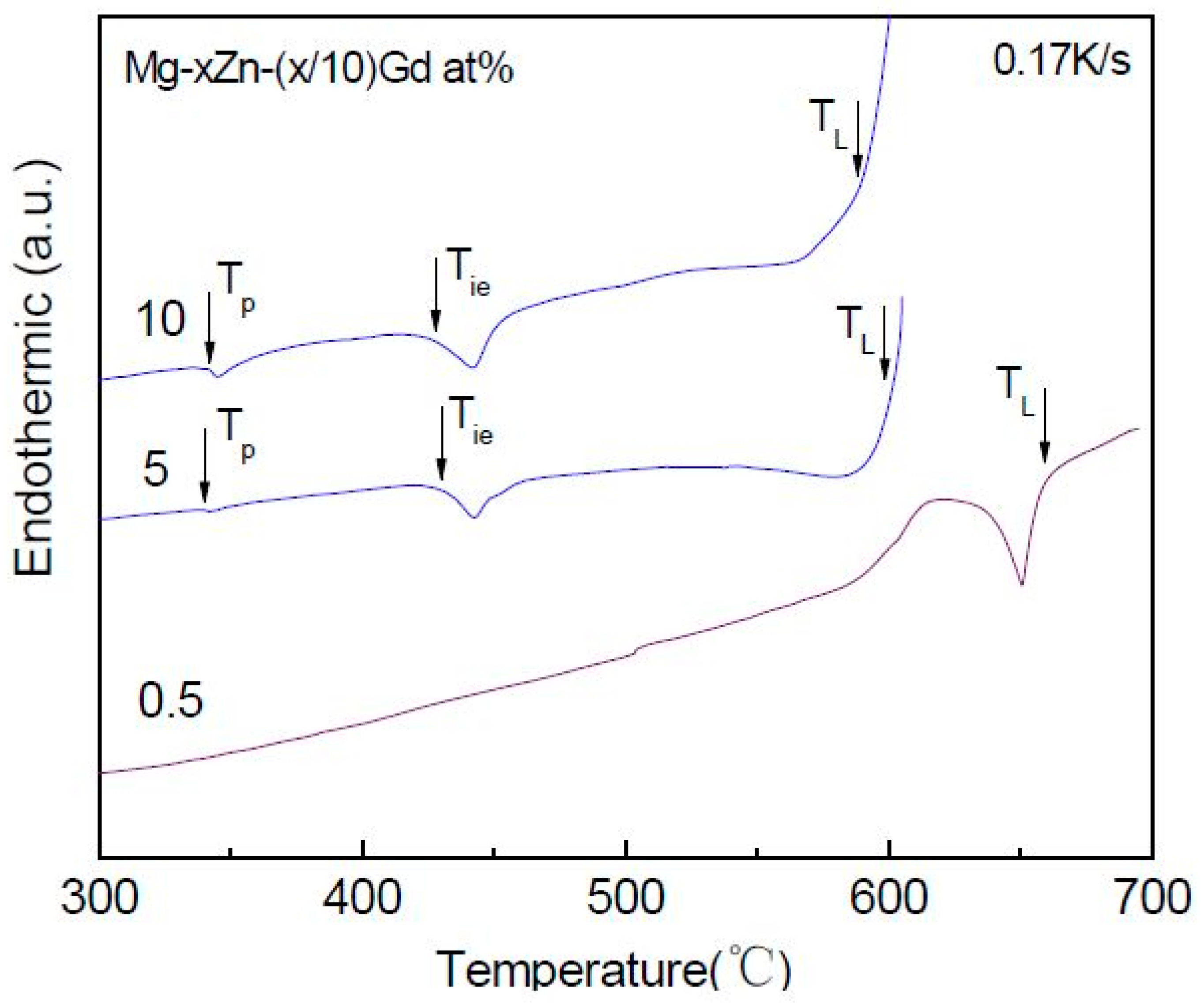
3.2. The DTA of Mg-Zn-Gd Alloys on the Mg-Rich Corner
4. Discussion
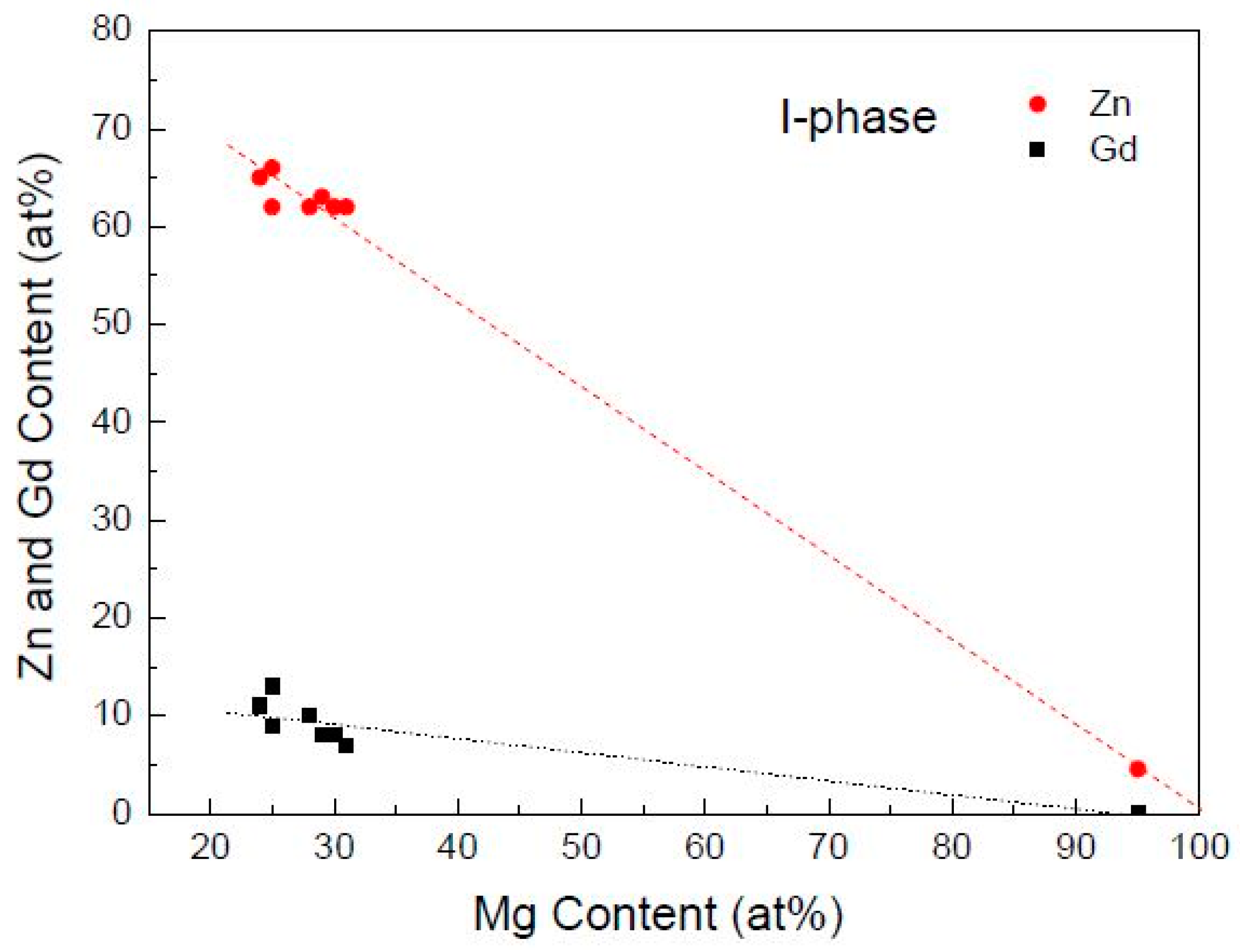
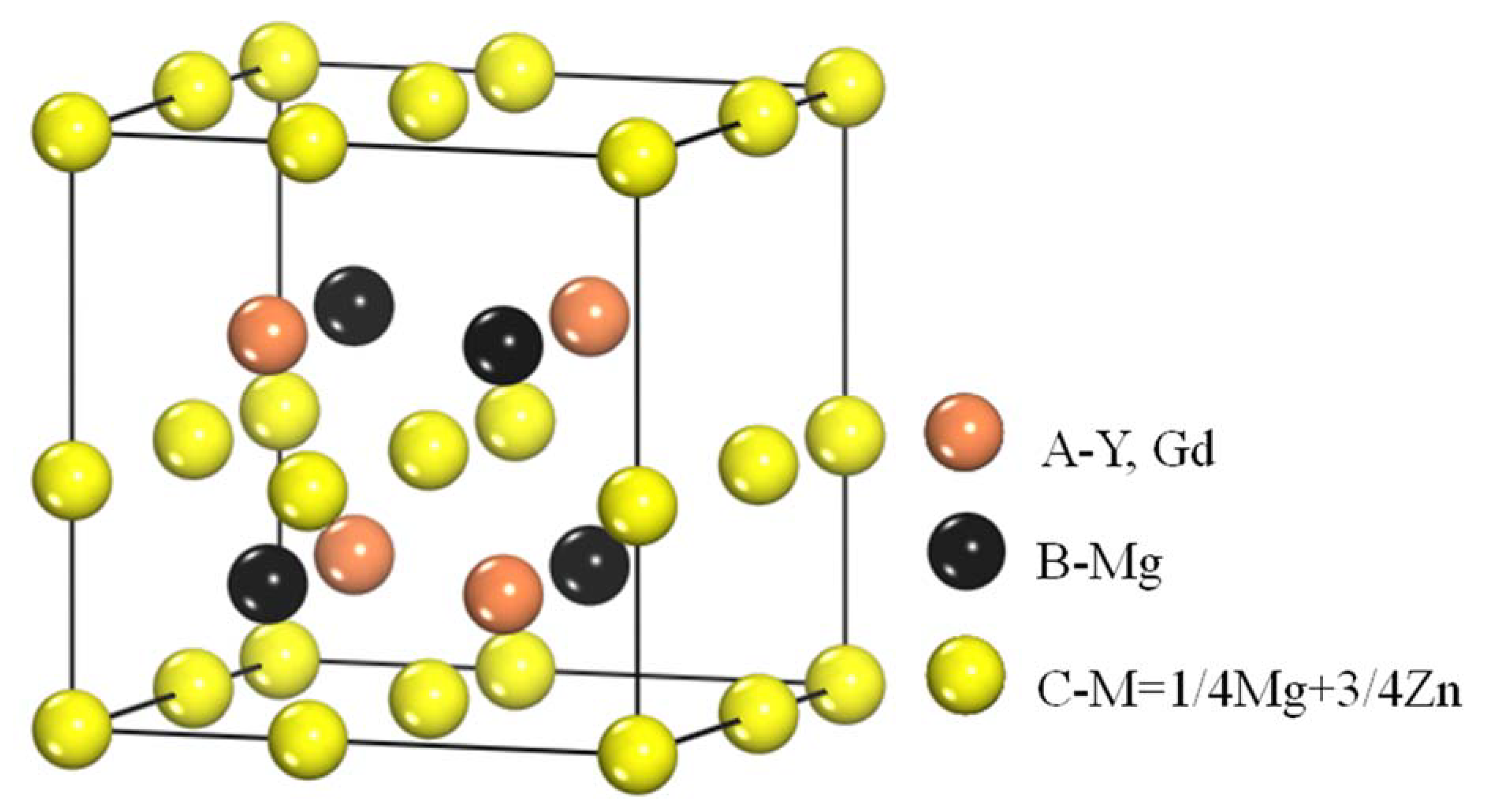
4.1. The Structure and Composition of I-Phase
4.2. The Structure and Composition of W-Phase
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Five regions can be classified in this Mg-rich section: (I)α-Mg+W-phase(+binary compounds), (II)α-Mg+W-phase+I-phase(+binary compounds), (III)α-Mg+I-phase (+binary compounds), (IV)α-Mg+binary compounds, and (V)α-Mg. This diagram of phase constitution would give a guideline for the design of Mg-Zn-Gd alloys to match the expecting properties by obtaining the desired phase components.
- (2)
- The I-phase in Mg-Zn-Gd alloys has a composition of Mg30±1Zn62Gd8±1 (at.%), belonging to FK-type quasicrystalline phase in terms of the Hume-Rothery rules. I-phase can be formed in Zn/Gd ratio range of 1.5~40. The equilibrium solidification range of ΔTLi is boarded when Zn/Gd ratio or alloying element content decrease, and it would largely influence the formability of the I-phase.
- (3)
- The W-phase in Mg-Zn-Gd alloy has fcc structure with the space group . It can be formed only in the Zn/Gd ratio range of 0.25~6. The composition of the W-phase is very sensitive to the composition of Mg-Zn-Gd alloys.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leontis, T.E. The Rare Earths; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.F. Precipitation and hardening in magnesium alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 3891–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saal, J.E.; Orlov, D. Overview: Age-Hardenable Microalloying in Magnesium. JOM 2015, 67, 2425–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.H.; Peng, Z.Z.; Jin, Q.Q.; Ma, X.L. Atomic-scale segregations at the deformation-induced symmetrical boundary in an Mg-Zn-Y alloy. Acta Mater. 2016, 118, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Tsai, A.P.; Nakamura, M.; Watanabe, M.; Kato, A. Nanoprecipitates of icosahedral phase in quasicrystal-strengthened Mg-Zn-Y alloys. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2003, 83, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Watanabe, M.; Kato, A.; Tsai, A.P. Twinning and the orientation relationships of icosahedral phase with the magnesium matrix. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 4733–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, D.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, W.T. Deformation behavior of Mg–Zn–Y alloys reinforced by icosahedral quasicrystalline particles. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 2343–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, D.H.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, K.T.; Kim, W.T.; Kim, D.H. Application of quasicrystalline particles as a strengthening phase in Mg-Zn-Y alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 342, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.B.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.P.; Cheng, L.R.; Meng, J.; Zhang, H.J. Dynamic recrystallization and texture evolution of Mg-Y-Zn alloy during hot extrusion process. Mater. Charact. 2014, 92, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, T.Y.; Lim, H.K.; Kim, W.J. Hot compression characteristics and processing maps of a cast Mg-9.5Zn-2.0Y alloy with icosahedral quasicrystalline phase. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 644, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.Y.; Kato, H.; Amiya, K.; Inoue, A. Excellent creep properties of Mg-Zn-Cu-Gd-based alloy strengthened by quasicrystals and Laves phases. J. Mater. Res. 2005, 20, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, G.Y.; Lu, C.; Ding, W.J. Deformation behavior of Mg-Zn-Gd-based alloys reinforced with quasicrystal and Laves phases at elevated temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 427, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, G.Y.; Lu, C.; Ding, W.J. Stable icosahedral phase in Mg-Zn-Gd alloy. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, G.Y.; Lu, C.; Ding, W.J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of extruded Mg-Zn-Gd-based alloy reinforced by quasicrystals and laves phase. Mater. Sci. Forum 2007, 546–549, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, G.Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.P.; Ding, W.J.; Lu, C. Effects of Zn/Gd ratio and content of Zn, Gd on phase constitutions of Mg alloys. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.F.; Liu, K.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, S.B.; Du, W.B. Microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of as-extruded Mg-Zn-Er alloys containing W-phase. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 602, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Sun, C.C.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, S.B.; Wang, Q.F.; Du, W.B. Microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Er alloys containing I-phase and W-phase simultaneously. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 665, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H.; Qi, W.J.; Xu, J. Effect of microstructure on impact toughness of magnesium alloys. Trans. Nonferr. Metals Soc. China 2012, 22, 2334–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Somekawa, H.; Mukai, T. Compressive strength and yield asymmetry in extruded Mg-Zn-Ho alloys containing quasicrystal phase. Scr. Mater. 2007, 56, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Inoue, A.; Masumoto, T. Platform Science and Technology for Advanced Magnesium Alloys. Rapidly Solidified Powder Metallurgy Mg97Zn1Y2 Alloys with Excellent Tensile Yield Strength above 600 MPa. Mater. Trans. 2001, 42, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, L.; Lu, C.; Lin, D. Recrystallization and microstructural evolution during hot extrusion of Mg97Y2Zn1 alloy. Metals Mater. Int. 2014, 20, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Sandlöbes, S.; Raabe, D. On the room temperature deformation mechanisms of a Mg-Y-Zn alloy with long-period-stacking-ordered structures. Acta Mater. 2015, 82, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoi, T.; Seimiya, T.; Kawamura, Y.; Hirohashi, M. Long period stacking structures observed in Mg97Zn1Y2 alloy. Scr. Mater. 2004, 51, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoi, T.; Inazawa, T.; Kuroda, Y.; Yamasaki, M.; Kawamura, Y.; Hirohash, M. Tensile property and cold formability of a Mg96Zn2Y2 alloy sheet with a long-period ordered phase. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 2277–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.B.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, H.J. Effect of long period stacking ordered phase on the microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of extruded Mg-Y-Zn alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 563, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Anan, T.; Yoshimoto, S.; Kawamura, Y. Mechanical properties of warm-extruded Mg-Zn-Gd alloy with coherent 14H long periodic stacking ordered structure precipitate. Scr. Mater. 2005, 53, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Sasaki, M.; Nishijima, M.; Hiraga, K.; Kawamura, Y. Formation of 14H long period stacking ordered structure and profuse stacking faults in Mg-Zn-Gd alloys during isothermal aging at high temperature. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 6798–6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padezhnova, E.M.; Melnik, E.V.; Miliyevskiy, R.A.; Dobatkina, T.V.; Kinzhibalo, V.V. Investigation of the Mg-Zn-Y System. Russ. Metall. 1982, 4, 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.K.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.B.; Han, E.H. Effect of microstructure and texture on the mechanical properties of the as-extruded Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 443, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Liu, L.; Lu, C.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Y. Effects of yttrium on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-extruded Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 373, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.K.; Tang, W.N.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.B.; Han, E.H. Effect of W-phase on the mechanical properties of as-cast Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 461, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, A.; Huang, Y.; Mendis, C.L.; Blawert, C.; Kainer, K.U.; Hort, N. Investigations on microstructures, mechanical and corrosion properties of Mg-Gd-Zn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 595, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, S.; Garces, G.; Perez, P.; Adeva, P. Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of Powder Metallurgy Mg 98.5 Gd 1 Zn 0.5 Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 3222–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobner, J.; Kozlov, A.; Fang, X.Y.; Zhu, S.M.; Nie, J.F.; Gibson, M.A.R. Phase equilibria and transformations in ternary Mg-Gd-Zn alloys. Acta Mater. 2015, 90, 400–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.Y.; Huang, G.X.; Bo, H.; Xu, G.L.; Liu, L.B.; Jin, Z.P. Experimental investigation and thermodynamic assessment of the Mg-Zn-Gd system focused on Mg-rich corner. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boissieu, M. Stability of quasicrystals: Energy, entropy and phason modes. Philos. Mag. A 2006, 86, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.P.; Hashimoto, H. High-resolution electron microscopy observation of a new crystalline approximant W’ of Mg-Zn-Y icosahedral quasicrystal. Micron 2000, 31, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorimer, G.W.; Cliff, G.; Champness, P.E.; Dickinson, C.; Hasan, F.; Kenway, P.B. Analytical Electron Microscopy. San Francisco Press: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Elaser, V. Indexing problems in quasicrystal diffraction. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 32, 4892–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancel, P.A.; Heiney, P.A.; Stephens, P.W.; Goldman, A.I.; Horn, P.M. Structure of rapidly quenched Al-Mn. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1985, 54, 2422–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, I.M. The Principles and Practice of Electron Microscopy; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.Y.; Lim, H.K.; Kim, D.H. Effects of Zn/Y ratio on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Y alloys. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 3801–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Lim, H.K.; Kim, D.H. Effect of volume fraction of qusicrystal on the mechanical properties of quasicrystal-reinforced Mg-Zn-Y alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 449–451, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, C.; Ding, W.J. Effect of quasicrystal and Laves phases on strength and ductility of as-extruded and heat treated Mg-Zn-Gd-based alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 472, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, A.P.; Niikura, A.; Inoue, A.; Masumoto, T.; Nishida, Y.; Tsuda, K.; Tanaka, M. Highly ordered structure of icosahedral quasicrystals in Zn-Mg-RE (RE= rare earth metals) systems. Philos. Mag. Lett. 1994, 70, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebalard, S.; Spaepen, F. The body-centered-cubic-type icosahedral reciprocal lattice of the Al-Cu-Fe quasi-periodic crystal. J. Mater. Res. 1989, 4, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.P.; Zhang, S.Q. High-resolution electron microscopy on the X-Mg12ZnY phase in a high strength Mg-Zn-Zr-Y magnesium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2000, 19, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.K.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.B.; Han, E.H. The influence of element Y on the mechanical properties of the as-extruded Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys. J. Alloys Comp. 2006, 426, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.W.; Teng, X.Y.; Zhou, G.R.; Zhao, D.G. Microstructure transformations in the heat-treated Mg-Zn-Y alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 577, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Yang, Y.; Chang, H.X. Influence of W-phase on mechanical properties and damping capacity of Mg-Zn-Y-Nd-Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 609, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.F.; Yang, Z.Q.; Ye, H.Q. Solid-state formation of icosahedral quasicrystals at Zn3Mg3Y2/Mg interfaces in a Mg-Zn-Y alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 650, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Composition (at.%) | Zn/Gd Ratio | Experimentally Detected Phases (Other than α-Mg) by XRD | Analysis Beside XRD | Regions | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-19Zn-1Gd | 19.00 | I+MgZn | III | [34] | ||
| Mg-17.5Zn-2.5Gd | 7.00 | I+W | II | [34] | ||
| Mg-16Zn-4Gd | 4.00 | I+W | II | [34] | ||
| Mg-14Zn-6Gd | 2.33 | I+W | II | [34] | ||
| Mg-14Zn-4.9Gd | 2.86 | I+W | II | [34] | ||
| Mg-11Zn-9Gd | 1.22 | W | I | [34] | ||
| 1 | Mg-10Zn-1Gd | 10.00 | I+W+MgZn2 | DTA/SEM | II | |
| 2 | Mg-10Zn-0.4Gd | 25.00 | I+Mg2Zn3 | EDS/SEM | III | |
| 3 | Mg-8Zn-0.8Gd | 10.00 | I+W+Mg2Zn3 | II | ||
| 4 | Mg-8Zn-0.32Gd | 25.00 | I+MgZn2 | III | ||
| Mg-5Zn-15Gd | 0.33 | Mg3Gd | IV | [34] | ||
| 5 | Mg-5Zn-1.667Gd | 3.00 | I+W | DTA | II | |
| 6 | Mg-5Zn-0.833Gd | 6.00 | I+W | DTA | II | |
| 7 | Mg-5Zn-0.5Gd | 10.00 | I | EDS/DTA/SEM | III | |
| 8 | Mg-5Zn-0.417Gd | 11.99 | I | III | ||
| 9 | Mg-5Zn-0.333Gd | 15.02 | I | III | ||
| 10 | Mg-5Zn-0.278Gd | 17.99 | I | EDS/SEM /TEM/SAED | III | |
| 11 | Mg-5Zn-0.2Gd | 25.00 | I | EDS | III | |
| 12 | Mg-5Zn-0.125Gd | 40.00 | I | III | ||
| 13 | Mg-5Zn-0.125Gd | 40.00 | I+Mg2Zn5 | III | ||
| 14 | Mg-5Zn-0.083Gd | 60.24 | Mg2Zn3+Mg7Zn3 | EDS/DTA/SEM | IV | |
| 15 | Mg-5Zn | Mg2Zn3+Mg7Zn3 | DTA | IV | ||
| 16 | Mg-4.8Zn-0.4Gd | 12.00 | I | III | ||
| 17 | Mg-4.2Zn-0.8Gd | 5.25 | I | III | ||
| 18 | Mg-4Zn-2Gd | 2.00 | I+W | II | ||
| 19 | Mg-4Zn-1.333Gd | 3.00 | I+W | II | ||
| 20 | Mg-3.5Zn-0.6Gd | 5.83 | I | III | ||
| 21 | Mg-3Zn-2Gd | 1.50 | I+W | II | ||
| 22 | Mg-3Zn-1.5Gd | 2.00 | I+W | II | ||
| 23 | Mg-3Zn-0.3Gd | 10.00 | I | EDS/SEM | III | |
| 24 | Mg-3Zn-0.12Gd | 25.00 | I | EDS | III | |
| 25 | Mg-2.8Zn-0.5Gd | 5.60 | I | III | ||
| 26 | Mg-2.5Zn-2Gd | 1.25 | W | I | ||
| 27 | Mg-2.25Zn-0.75Gd | 3.00 | I+W | II | ||
| 28 | Mg-2Zn-2Gd | 1.00 | W | I | ||
| 29 | Mg-2Zn-1.5Gd | 1.33 | W | I | ||
| 30 | Mg-2Zn-1Gd | 2.00 | W | I | ||
| Mg-2Zn-1Gd | 2.00 | 14H+Mg5Gd | IV | [27] | ||
| 31 | Mg-2Zn-0.1Gd | 20.00 | I | III | ||
| Mg-1.55Zn-0.937Gd | 1.65 | W+X(LPSO)+Mg3Gd | I | [32] | ||
| Mg-1.51Zn-2.78Gd | 0.54 | W+Mg3Gd | I | [32] | ||
| 32 | Mg-1.5Zn-1Gd | 1.50 | W | I | ||
| 33 | Mg-1.2Zn-0.2Gd | 6.00 | I+W | II | ||
| 34 | Mg-1.2Zn-0.1Gd | 12.00 | I | III | ||
| 35 | Mg-1Zn-2Gd | 0.50 | W | EDS/DTA/SEM | I | |
| 36 | Mg-1Zn-1Gd | 1.00 | W | TEM/SAED | I | |
| 37 | Mg-1Zn-0.667Gd | 1.50 | W | I | ||
| 38 | Mg-1Zn-0.5Gd | 2.00 | W | I | ||
| Mg-1Zn-0.5Gd | 2.00 | 14H+Mg3Gd | IV | [33] | ||
| 39 | Mg-1Zn-0.333Gd | 3.00 | I+W+Mg5Gd | EDS/SEM /TEM/SAED | II | |
| 40 | Mg-1Zn-0.1Gd | 10.00 | SEM | V | ||
| 41 | Mg-1Zn-0.04Gd | 25.00 | V | |||
| 42 | Mg-0.75Zn-1Gd | 0.75 | W | I | ||
| 43 | Mg-0.6Zn-0.2Gd | 3.00 | V | |||
| 44 | Mg-0.6Zn-0.2Gd | 3.00 | I+W | II | ||
| 45 | Mg-0.5Zn-2Gd | 0.25 | W+Mg3Gd | DTA/SEM | I | |
| 46 | Mg-0.5Zn-1Gd | 0.50 | W | I | ||
| 47 | Mg-0.5Zn-0.5Gd | 1.00 | W | I | ||
| 48 | Mg-0.5Zn-0.05Gd | 10.00 | DTA | V | ||
| Mg-0.283Zn-0.796Gd | 0.36 | W+Mg3Gd | I | [32] | ||
| Mg-0.276Zn-2.48Gd | 0.11 | I+W+Mg3Gd | II | [32] |
| Alloys (Zn/Gd Ratio) | Location | Mg at.% | Zn at.% | Gd at.% | Zn/Gd Ratio | Compound Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-1Zn-2Gd (0.5) | D | 90.87 | 3.95 | 5.19 | 0.76 | MgZnGd | Sample 35 |
| P | 93.47 | 2.78 | 3.75 | 0.74 | MgZnGd | ||
| M | 99.29 | 0.20 | 0.51 | 0.39 | Gd-rich | ||
| Mg-1Zn-0.333Gd (3) | D | 79.10 | 13.88 | 7.03 | 1.97 | MgZnGd | Sample 39 |
| P | 83.09 | 0.62 | 16.3 | Mg5Gd | |||
| M | 99.34 | 0.66 | Zn-rich | ||||
| Mg-5Zn-0.278Gd (18) | D | 56.02 | 40.03 | 3.94 | 10.2 | I-phase | Sample 10 |
| P | 91.93 | 8.07 | Mg2Zn3 | ||||
| M | 96.43 | 3.34 | 0.23 | Zn-rich | |||
| Mg-5Zn-0.083Gd (60) | D | 82.88 | 16.35 | 0.77 | 21.2 | Mg2Zn3 with Gd | Sample 14 |
| P | 73.91 | 18.17 | 7.92 | 2.29 | MgZnGd | ||
| M | 98.21 | 1.79 | Zn-rich |
| Alloys (Zn/Gd Ratio) | Crystal Plane (hkl) | Mean a Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (111) | (200) | (220) | (311) | (400) | (422) | (Å) | ||
| Mg-0.5Zn-2Gd (0.25) | 7.217 | 7.230 | 7.217 | 7.215 | 7.221 | — | 7.220 ± 0.015 | Sample 45 |
| Mg-1Zn-2Gd (0.5) | 7.144 | 7.155 | 7.146 | 7.145 | 7.158 | 7.142 | 7.148 ± 0.016 | Sample 35 |
| Mg-2Zn-2Gd (1) | 7.066 | 7.088 | 7.065 | 7.068 | 7.065 | 7.067 | 7.070 ± 0.023 | Sample 28 |
| Mg-3Zn-2Gd (1.5) | 6.909 | 6.904 | — | 6.892 | 6.894 | 6.890 | 6.898 ± 0.019 | Sample 21 |
| Mg-4Zn-2Gd (2) | 6.909 | 6.904 | — | 6.901 | 6.894 | 6.906 | 6.903 ± 0.015 | Sample 18 |
| Mg-5Zn-1.67Gd (3) | 6.909 | 6.909 | — | 6.907 | 6.903 | 6.910 | 6.908 ± 0.007 | Sample 5 |
| Mg-5Zn-0.83Gd (6) | 6.909 | 6.904 | — | — | 6.897 | — | 6.903 ± 0.013 | Sample 6 |
| Alloys (Zn/Gd Ratio) | I-Phase (at.%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | Gd | Zn | Zn/Gd Ratio | ||
| Mg-3Zn-0.3Gd (10) | 75.28 | 3.47 | 21.24 | 6.12 | Sample 23 |
| Mg-5Zn-0.5Gd (10) | 67.78 | 3.61 | 28.61 | 7.93 | Sample 7 |
| Mg-10Zn-1Gd (10) | 65.69 | 3.71 | 30.60 | 8.25 | Sample 1 |
| Mg-3Zn-0.12Gd (25) | 70.63 | 2.46 | 26.92 | 10.94 | Sample 24 |
| Mg-5Zn-0.2Gd (25) | 62.87 | 3.86 | 33.28 | 8.62 | Sample 11 |
| Mg-10Zn-0.4Gd (25) | 55.11 | 2.79 | 42.10 | 15.09 | Sample 2 |
| Alloys (Zn/Gd Ratio) | Characteristic Temperatures (°C ± 0.2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | Tie | TW | TL | TL-Ti | ||
| Mg-0.5Zn-2Gd (0.25) | 519 | 635 | Sample 45 | |||
| Mg-1Zn-2Gd (0.5) | 519 | 635 | Sample 35 | |||
| Mg-5Zn-1.667Gd (3) | 431 | 519 | 635 | 204 | Sample 5 | |
| Mg-5Zn-0.833Gd (6) | 431 | 611 | 180 | Sample 6 | ||
| Mg-5Zn-0.5Gd (10) | 341 | 431 | 595 | 164 | Sample 7 | |
| Mg-5Zn-0.083Gd (60) | 336 | 588 | Sample 14 | |||
| Mg-5Zn | 336 | 613 | Sample 15 | |||
| Mg-0.5Zn-0.05Gd (10) | 655 | Sample 48 | ||||
| Mg-10Zn-1Gd (10) | 340 | 428 | 567 | 139 | Sample 1 | |
| Elements | Valence Electron Concentration (e/a) | Atomic Radii (nm) | Electro Negativity | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | 2 | 0.160 | 1.31 | |
| Zn | 2 | 0.137 | 1.65 | |
| RE (Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er) | 3 | [45] | ||
| Gd | 3 | 0.181 | 1.1 | [44,45,46] |
| Y | 3 | 0.178 | 1.2 | [42,43] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, L.; Liu, Y.; Duan, M. Phase Formation of Mg-Zn-Gd Alloys on the Mg-rich Corner. Materials 2018, 11, 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081351
Luo L, Liu Y, Duan M. Phase Formation of Mg-Zn-Gd Alloys on the Mg-rich Corner. Materials. 2018; 11(8):1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081351
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Lan, Yong Liu, and Meng Duan. 2018. "Phase Formation of Mg-Zn-Gd Alloys on the Mg-rich Corner" Materials 11, no. 8: 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081351
APA StyleLuo, L., Liu, Y., & Duan, M. (2018). Phase Formation of Mg-Zn-Gd Alloys on the Mg-rich Corner. Materials, 11(8), 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081351