Effect of a Synthetic Nano-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O Gel on the Early-Stage Shrinkage Performance of Alkali-Activated Slag Mortars
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Synthesis of C-A-S-H gel and Its Characteristics
2.2. Materials, Mixing Proportion and Preparation of Alkali-Activated Slag Mortars
2.3. Measurements of Length Changes
2.4. Miscrostructure
2.4.1. Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP)
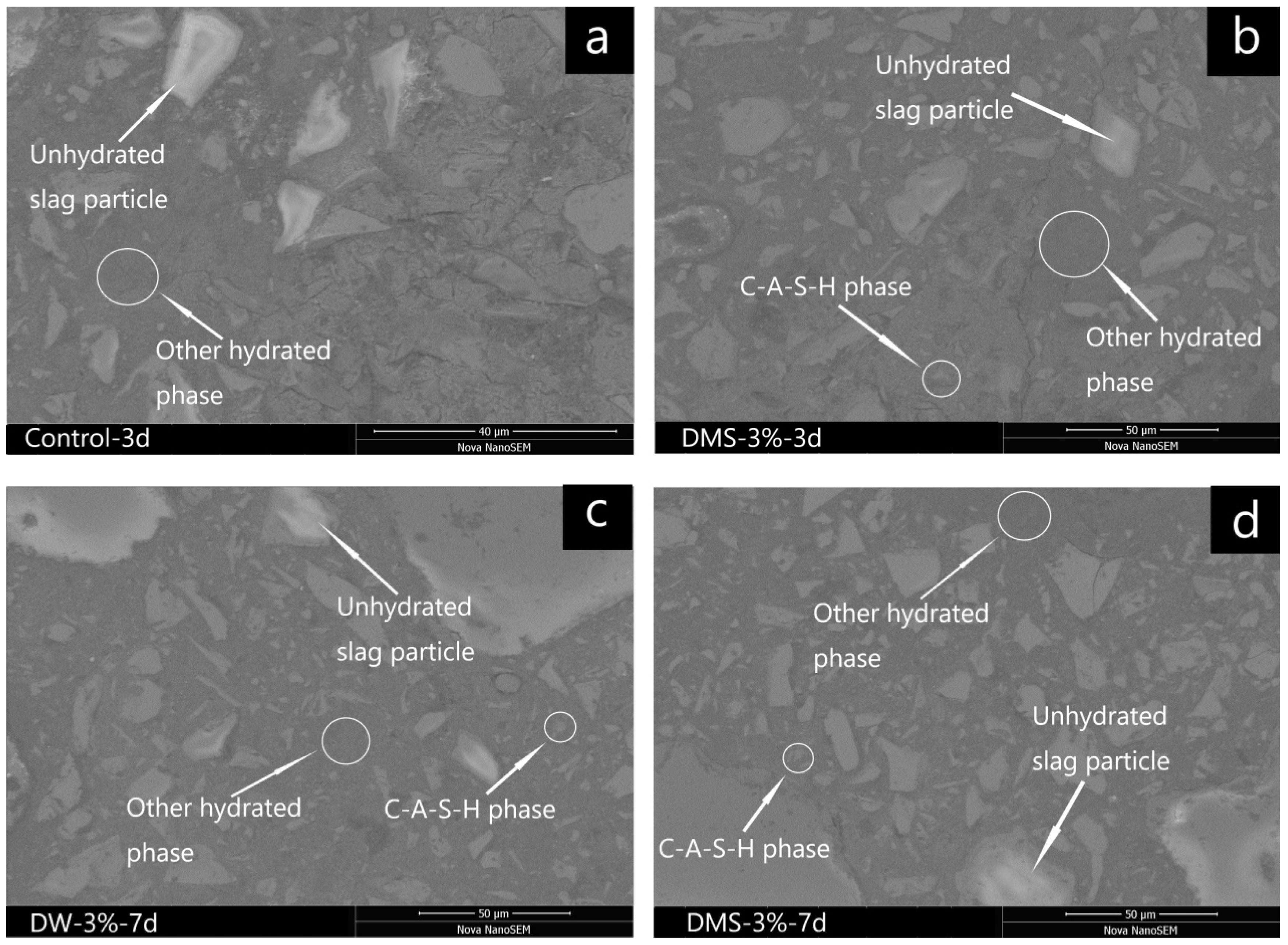
2.4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS)
3. Results and Discussion
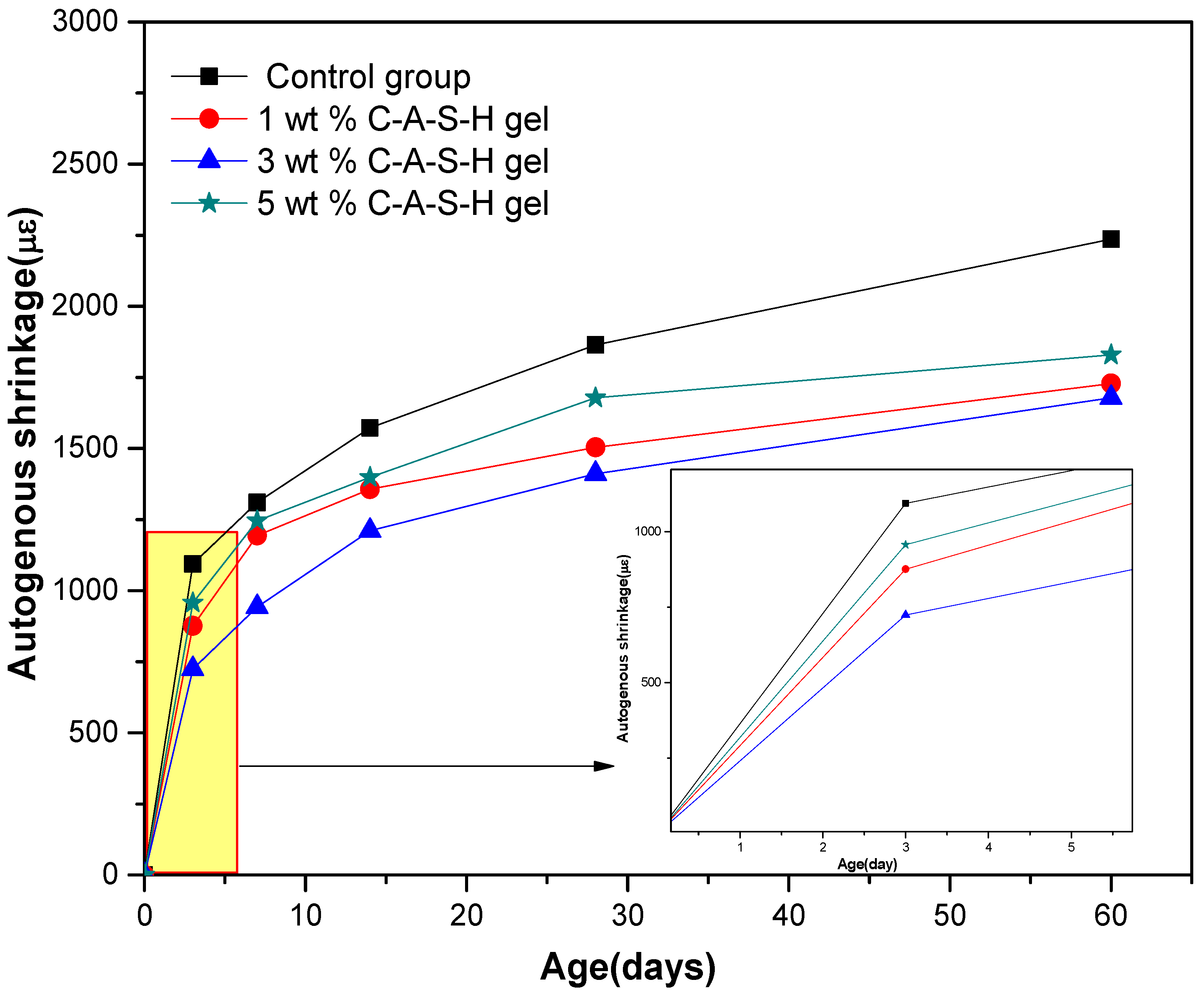
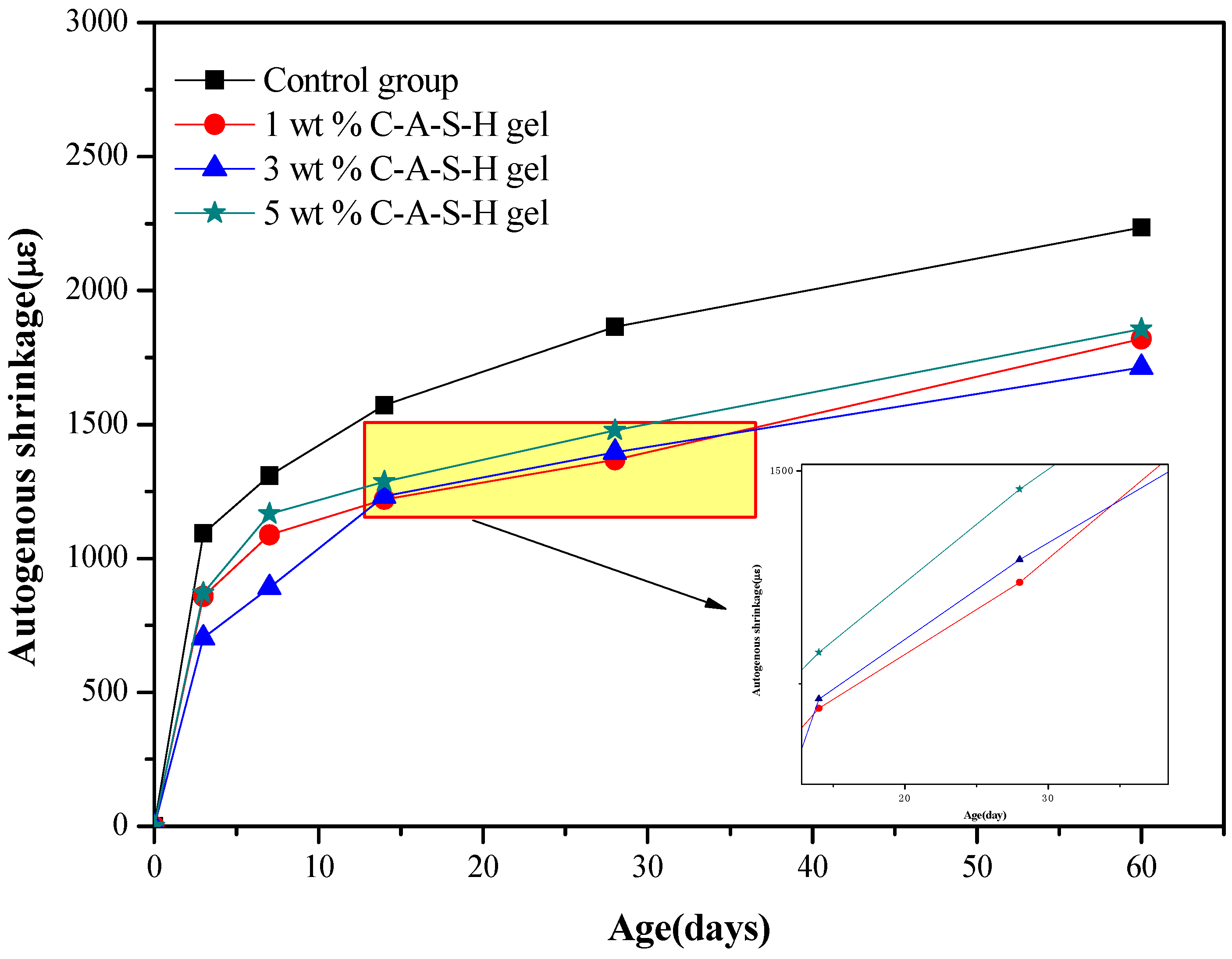
3.1. Effects of Synthetic C-A-S-H on the Shrinkage of AAS Mortars
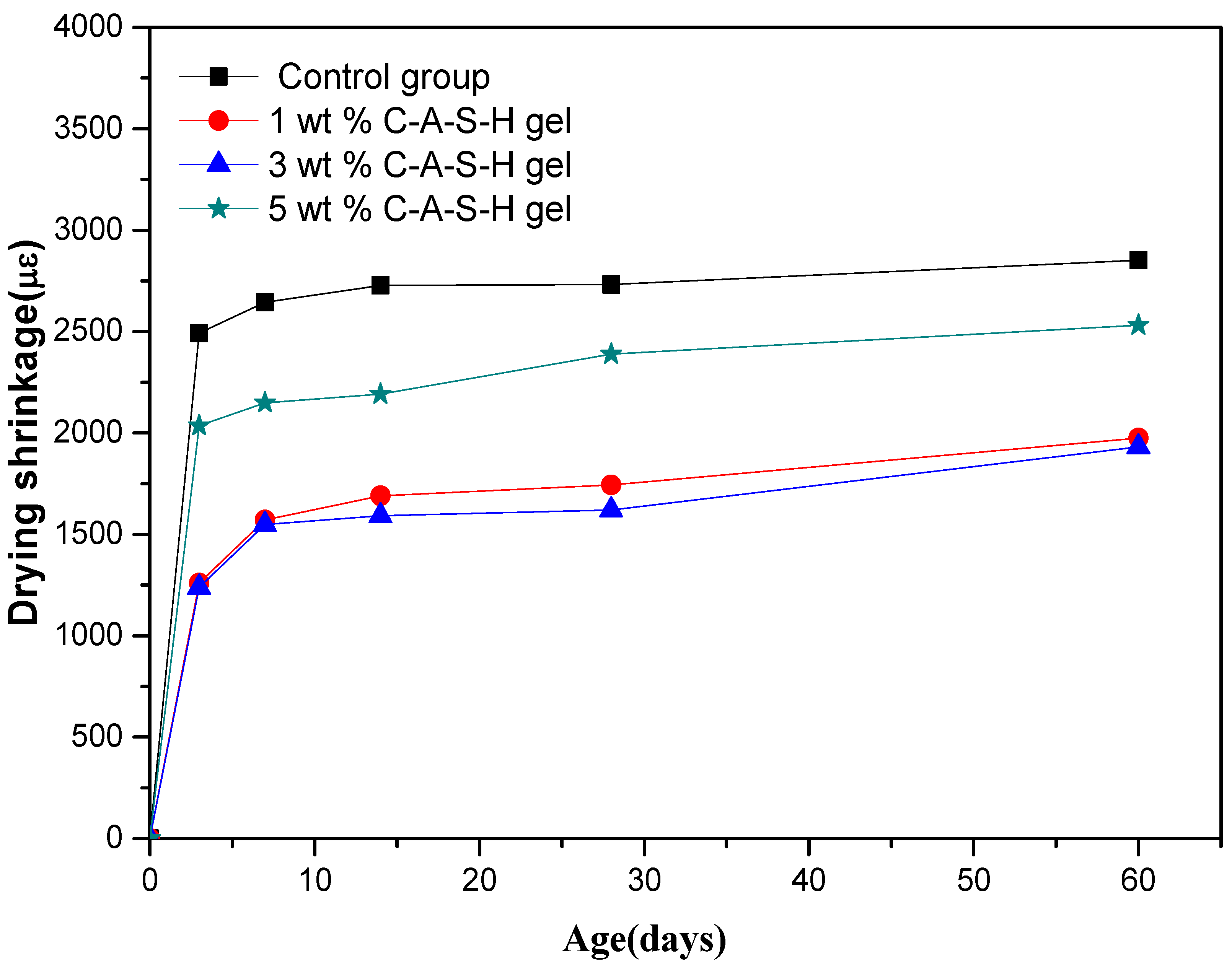
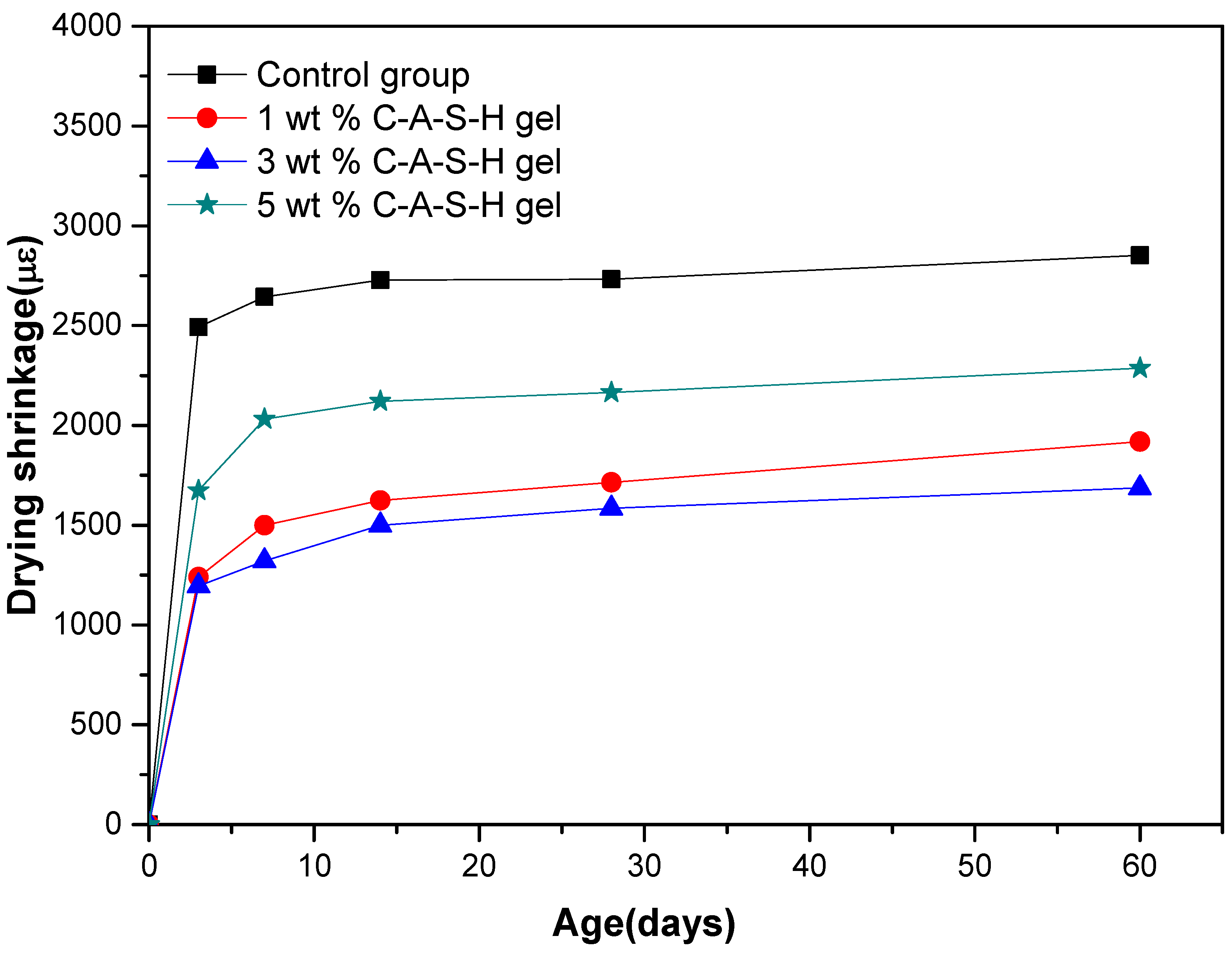
3.1.1. Drying Shrinkage and Autogenous Shrinkage of AAS Mortars
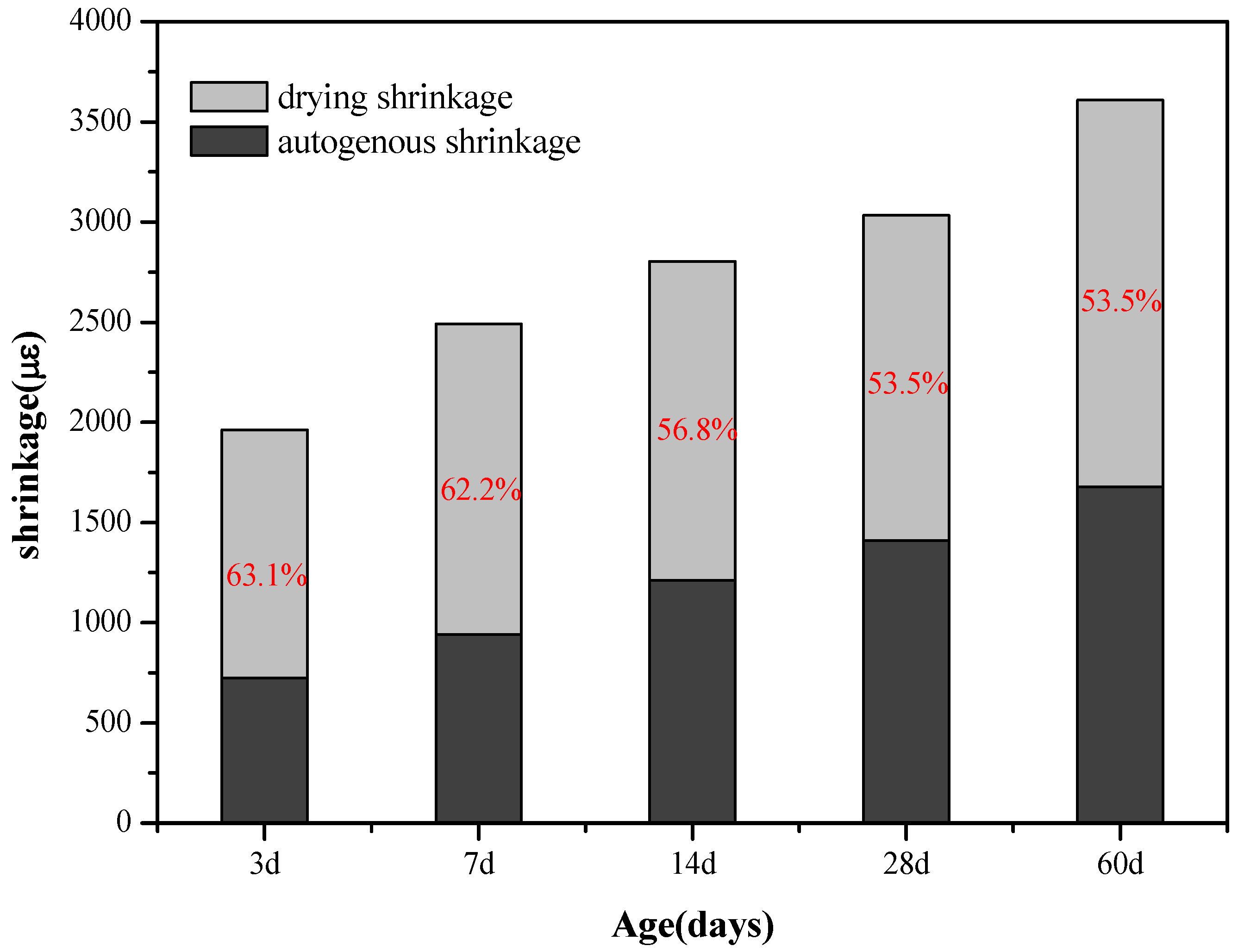
3.1.2. Relationship between Drying and Autogenous Shrinkage of AAS Mortars
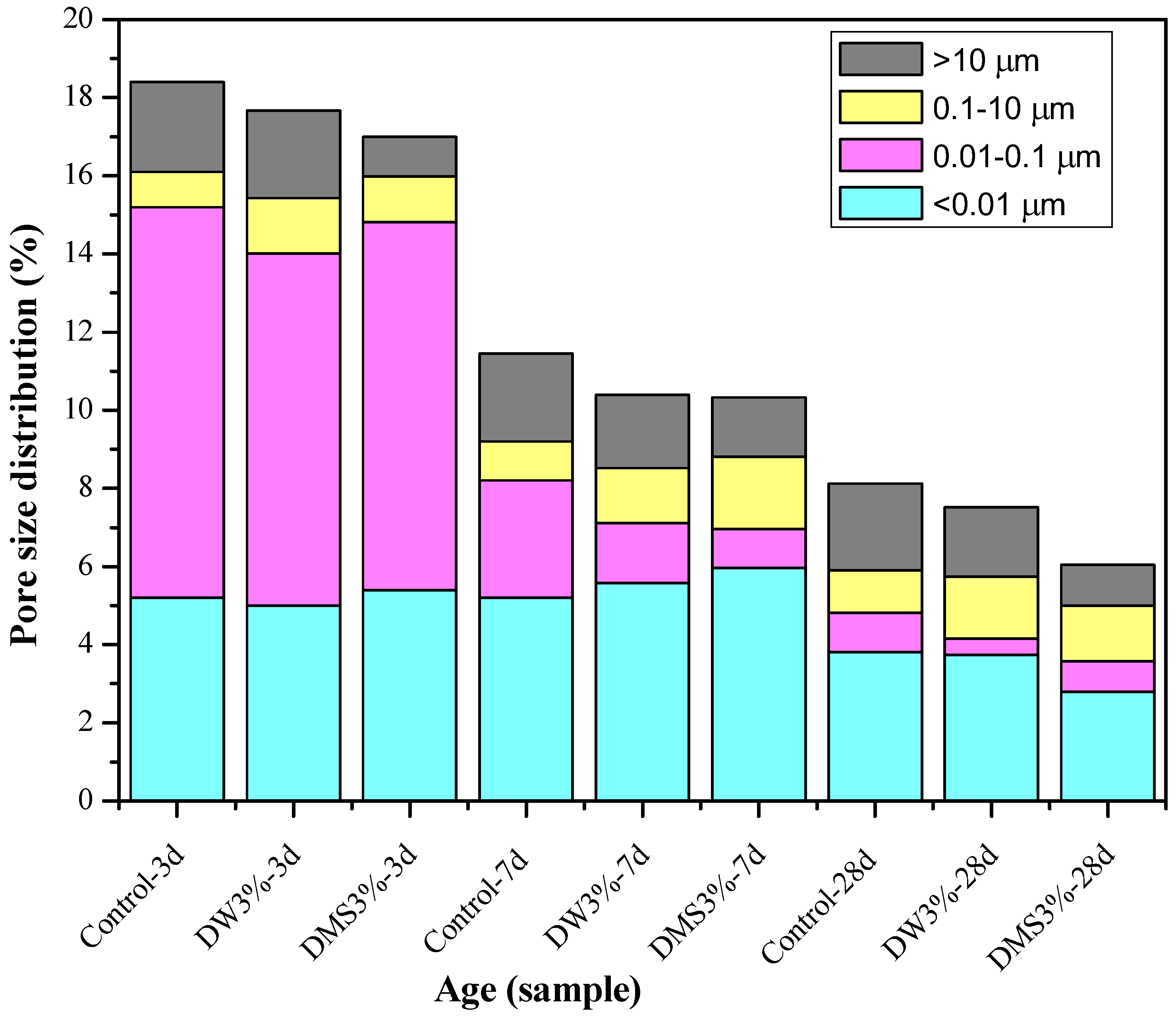
3.2. Effect of Synthetic C-A-S-H on the Pore Structure of AAS Mortars
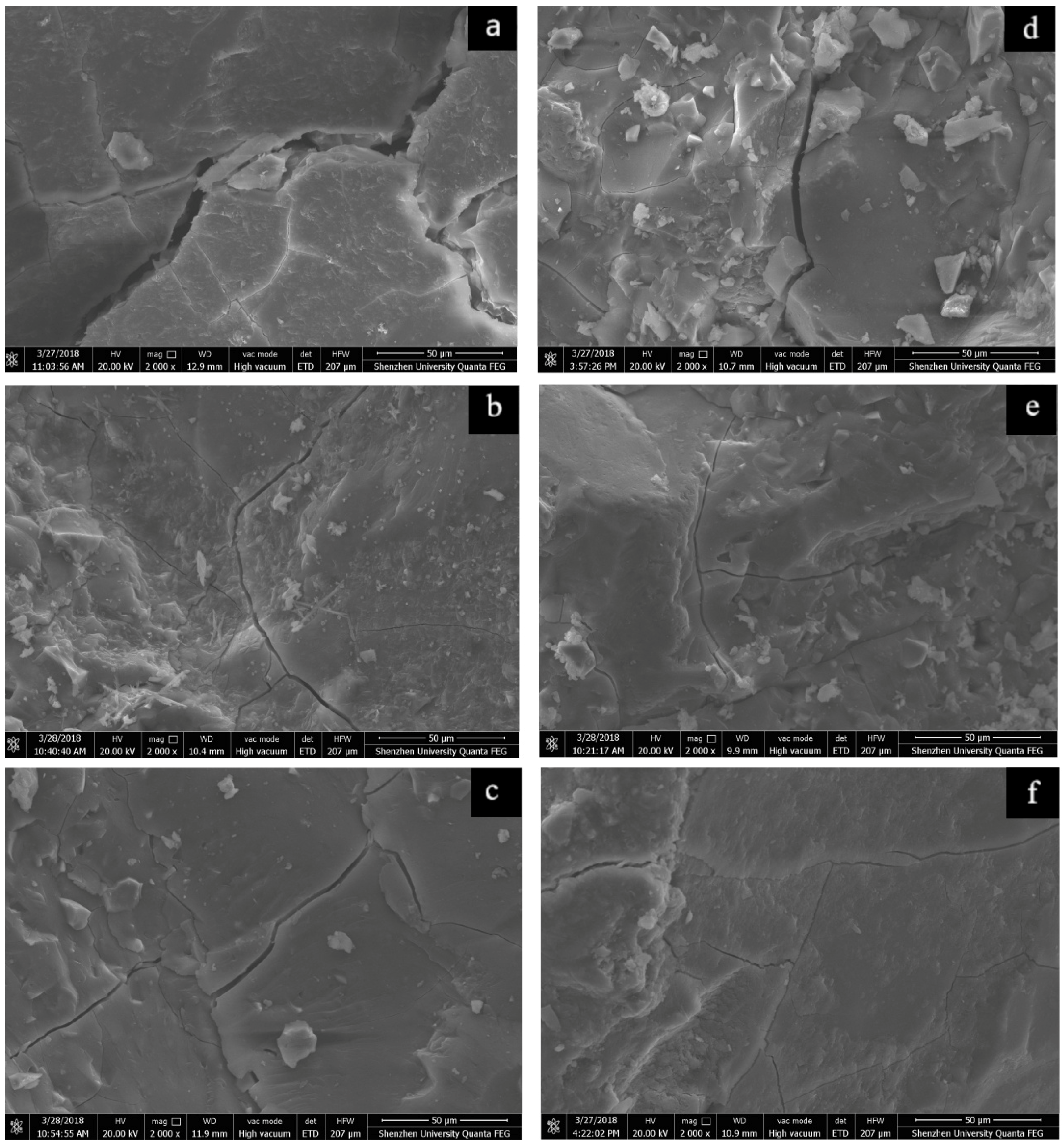
3.3. Effect of Synthetic C-A-S-H on the Microstructure of AAS Mortars
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rashad, A.M. A synopsis about the effect of metakaolin on the durability of Portland cement—An overview. Sci. Iran. 2015, 22, 579–603. [Google Scholar]
- Juenger, M.C.G.; Winnefeld, F.; Provis, J.L.; Ideker, J.H. Advances in alternative cementitious binders. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, C.; Rajabipour, F.; Radlinska, A. Shrinkage Characteristics of Alkali-Activated Slag Cements. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2015, 27, B4014007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hou, D.; Han, Y. Micromechanical modeling on autogenous and drying shrinkages of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovler, K.; Zhutovsky, S. Overview and Future Trends of Shrinkage Research. Mater. Struct. 2006, 39, 827–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Radlińska, A. Shrinkage mechanisms of alkali-activated slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 88, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran Atiş, C.; Bilim, C.; Çelik, Ö.; Karahan, O. Influence of activator on the strength and drying shrinkage of alkali-activated slag mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, F.; Sanjayan, J.G. Effect of pore size distribution on drying shrinkage of alkali-activated slag concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1401–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo Neto, A.A.; Cincotto, M.A.; Repette, W. Drying and autogenous shrinkage of pastes and mortars with activated slag cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collepardi, M.; Borsoi, A.; Collepardi, S.; Ogoumah Olagot, J.J.; Troli, R. Effects of shrinkage reducing admixture in shrinkage compensating concrete under non-wet curing conditions. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Ruacho, J.; Gettu, R.; Aguado, A. Influence of shrinkage-reducing admixtures on the reduction of plastic shrinkage cracking in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakulich, A.R.; Bentz, D.P. Mitigation of autogenous shrinkage in alkali activated slag mortars by internal curing. Mater. Struct. 2013, 46, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.H.; Chen, W.; Lu, Z.A.; Chen, H.G. Shrinkage compensation of alkali-activated slag concrete and microstructural analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.H.; Liu, J.F.; Chen, Y.Q. Effect of magnesia on properties and microstructureof alkali-activated slag cement. Water Sci. Eng. 2011, 4, 463–469. [Google Scholar]
- Kalina, L.; Bílek, V.; Bartoníčková, E.; Krouská, J. Polypropylene Glycols as Effective Shrinkage-Reducing Admixtures in Alkali-Activated Materials. ACI Mater. J. 2018, 115, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bílek, V.; Kalina, L.; Novotný, R.; Tkacz, J.; Pařízek, L. Some Issues of Shrinkage-Reducing Admixtures Application in Alkali-Activated Slag Systems. Materials 2016, 9, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.G.; Lee, N.K.; Lee, H.K. Fresh and hardened properties of alkali-activated fly ash/slag pastes with superplasticizers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, R.; Mehrotra, S.P. Influence of granulated blast furnace slag on the reaction, structure and properties of fly ash based geopolymer. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.K.; Kim, H.K.; Park, I.S.; Lee, H.K. Alkali-activated, cementless, controlled low-strength materials (CLSM) utilizing industrial by-products. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, S. Influence of slag as additive on compressive strength of fly ash-based geopolymer. J. Mater. Civil Eng. 2007, 19, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, R.R.; Provis, J.L.; Deventer, J.S.J.V. Microscopy and microanalysis of inorganic polymer cements. 1: Remnant fly ash particles. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, R.R.; Provis, J.L.; Deventer, J.S.J.V. Microscopy and microanalysis of inorganic polymer cements. 2: The gel binder. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.J.; Jennings, H.M.; Chen, J.J. Influence of Nucleation Seeding on the Hydration Mechanisms of Tricalcium Silicate and Cement. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2009, 113, 4327–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, R.; Raki, L.; Makar, J.M.; Beaudoin, J.J.; Moudrakovski, I. Hydration of tricalcium silicate in the presence of synthetic calcium-silicate-hydrate. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 7937–7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.B.; Li, D.X.; Fang, Y. Synthesis of Nanoscale CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O and Na2O-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O Using the Hydrothermal Method and Their Characterization. Materials 2017, 10, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.B.; Li, D.X.; Fang, Y. Effect of Synthetic CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O on the Early-Stage Performance of Alkali-Activated Slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 167, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.D.; Scrivener, K.L. hydration products of alkali-activated slag cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.K.; Jang, J.G.; Lee, H.K. Shrinkage characteristics of alkali-activated fly ash/slag paste and mortar at early ages. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 53, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, T.; Sanjayan, J.G. Mechanism of early age shrinkage of concretes. Mater. Struct. 2009, 42, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecomte, I.; Henrist, C.; Liégeois, M.; Maseri, F.; Rulmont, A.; Cloots, R. (Micro)-structural comparison between geopolymers, alkali-activated slag cement and Portland cement. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 3789–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennis, P.D.; Jennings, H.M. A model for two types of calcium silicate hydrate in the microstructure of Portland cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.H.; Wu, X.Q.; Xu, Z.Z.; Tang, M.H. Kinetic-Study on hydration of alkali-activated slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 1993, 23, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Wang, P. Autogenous relative humidity change an autogenous shrinkage of high-performance cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Lodeiro, I.; Palomo, A.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Macphee, D.E. Compatibility studies between N-A-S-H and C-A-S-H gels. Study in the ternary diagram Na2O-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas, F.; Palacios, M.; Manzano, H.; Dolado, J.S.; Rico, A.; Rodríguez, J. A model for the C-A-S-H gel formed in alkali-activated slag cements. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 2043–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Krivenko, P.; Roy, D. Alkali-Activated Cements and Concretes; Taylor & Francis: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, I.; Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L.; San Nicolas, R.; Hamdan, S.; van Deventer, J.S. Modification of phase evolution in alkali-activated blast furnace slag by the incorporation of fly ash. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 45, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebregziabiher, B.S.; Thomas, R.; Peethamparan, S. Very early-age reaction kinetics and microstructural development in alkali-activated slag. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 55, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakulich, A.R.; Miller, S.; Barsoum, M.W. Chemical and Microstructural Characterization of 20-Month-Old Alkali-Activated Slag Cements. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, G.; Stephan, D. The effect of synthesis conditions on the efficiency of C-S-H seeds to accelerate cement hydration. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 87, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
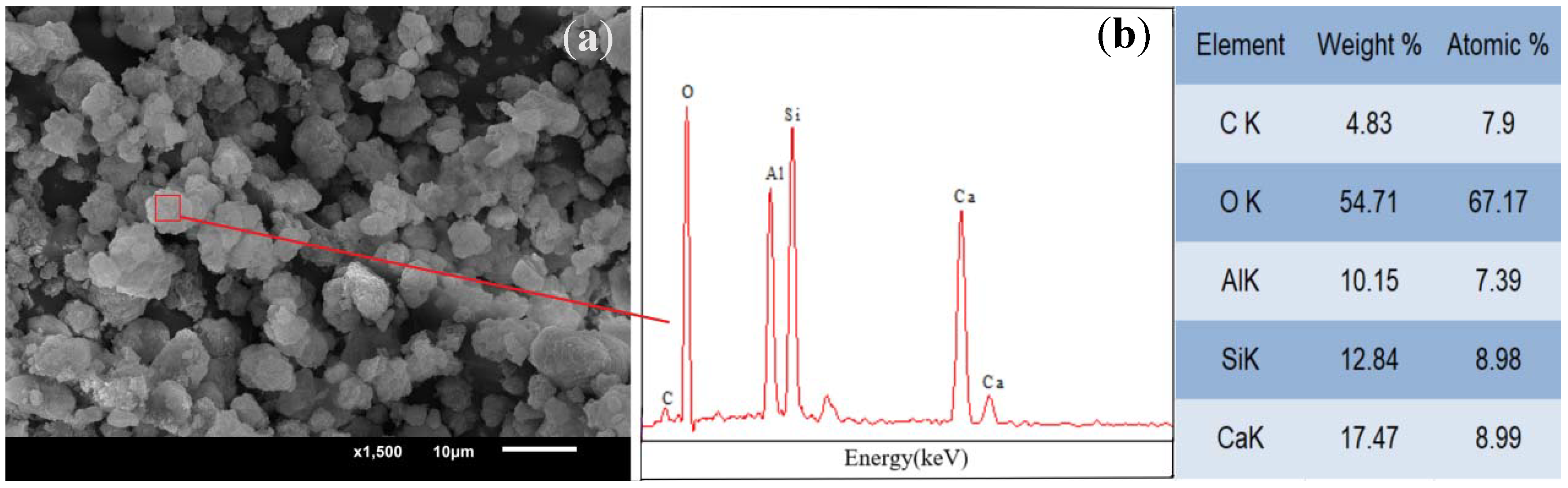
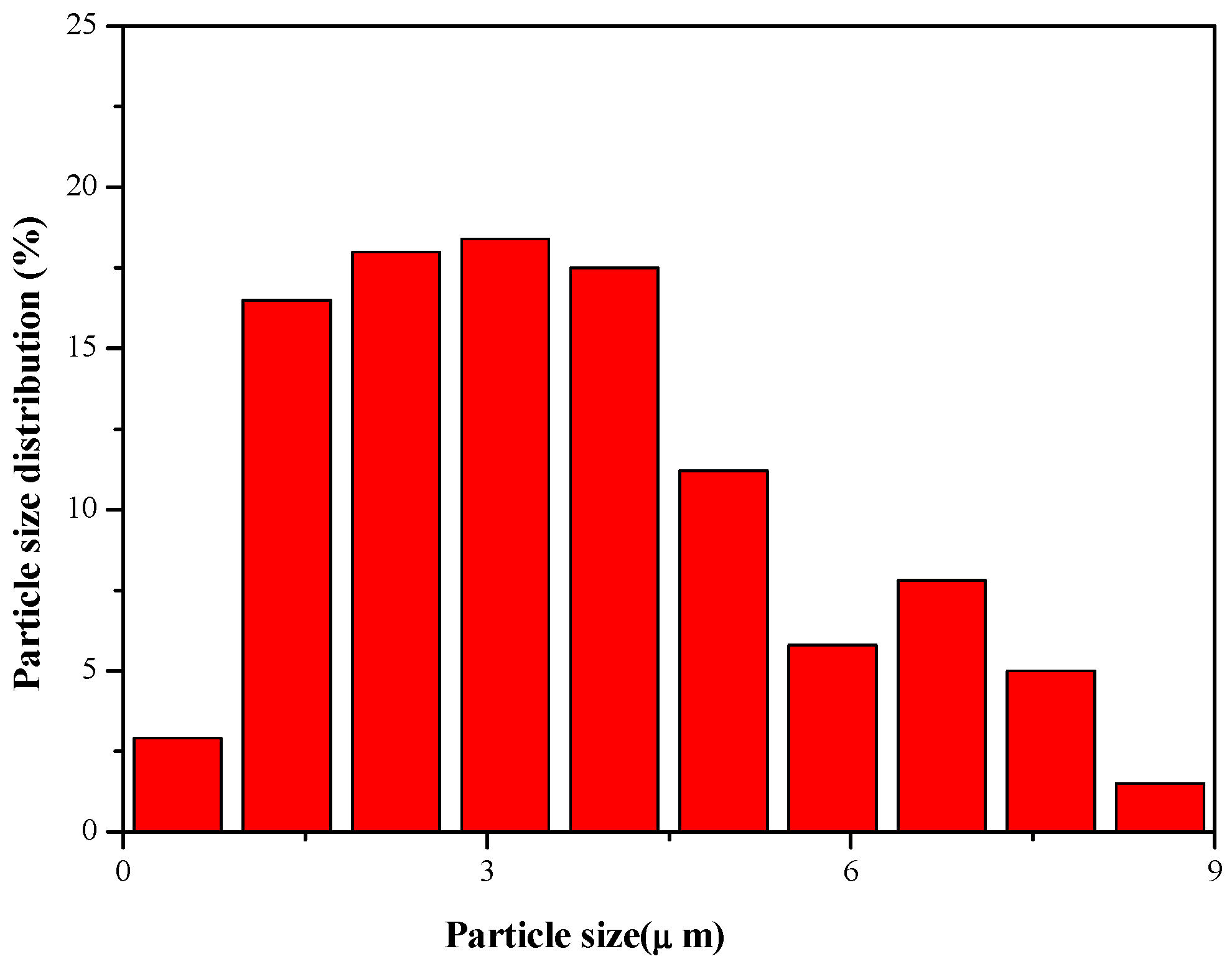
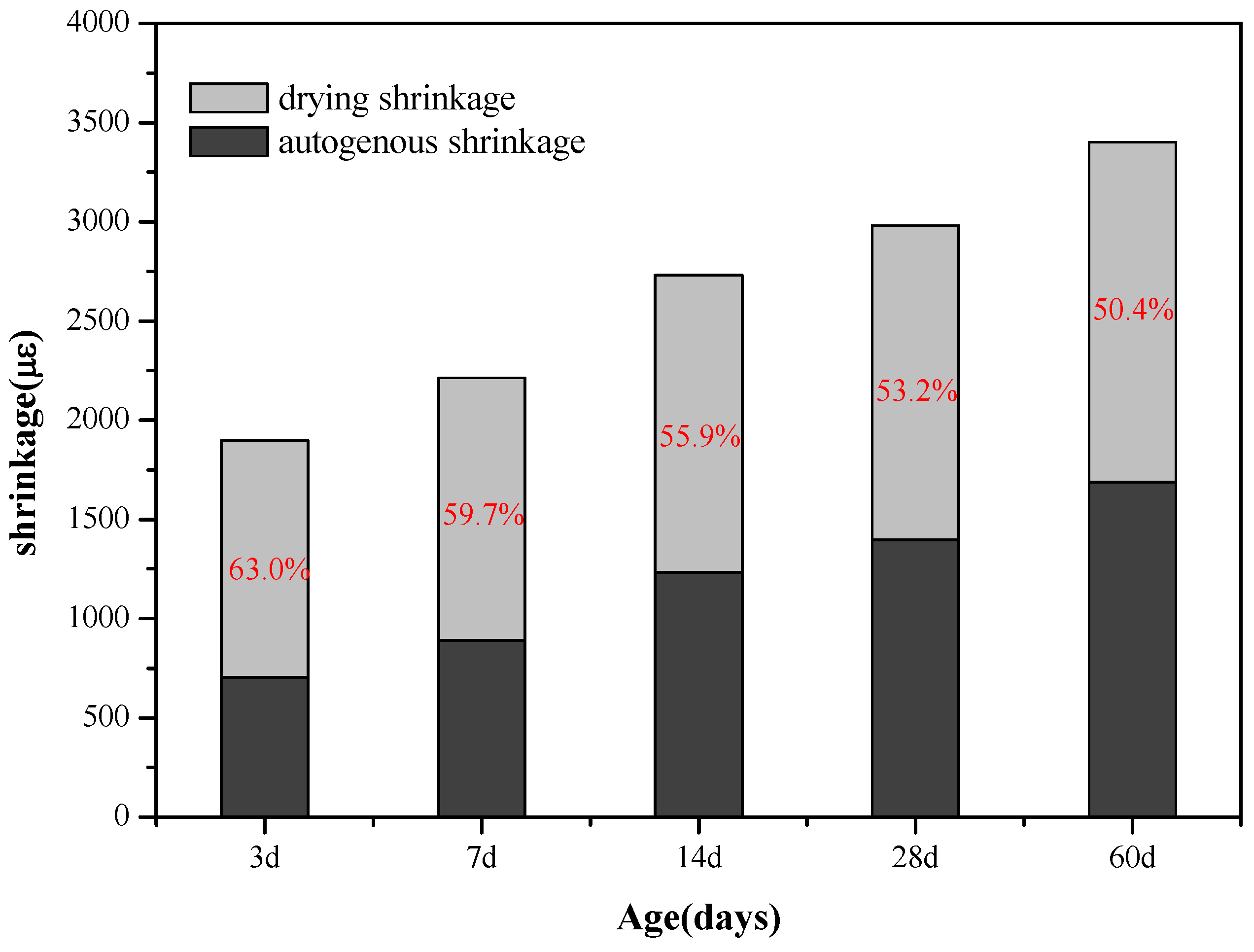

| CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | SO3 | TiO2 | K2O | Fe2O3 | MnO | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 39.83 | 31.13 | 17.24 | 8.47 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.364 | 0.234 | 0.255 | 0.364 |
| No. | Standard Sand (g) | Slag (g) | C-A-S-H Gel (%) (by Slag Mass) | Alkali Equivalent a (W(Na2O)/W(slag)) (%) | Water/Slag Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1350 | 450 | 0 | 5 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 1350 | 450 | 1 | 5 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 1350 | 450 | 3 | 5 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 1350 | 450 | 5 | 5 | 0.5 |
| Age | C-A-S-H Gels Dosage (wt %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 5 | |
| Shrinkage Reduction (%) Brought by C-A-S-H Gel Dry-Mixed with Slag | |||
| 3 day | 49.48 | 50.32 | 18.30 |
| 7 day | 40.47 | 41.41 | 18.76 |
| 14 day | 38.05 | 41.68 | 19.65 |
| 28 day | 36.16 | 40.67 | 12.55 |
| 60 day | 30.79 | 32.30 | 11.22 |
| Shrinkage Reduction (%) Brought by C-A-S-H gel Dispersed in Water | |||
| 3 day | 50.24 | 52.00 | 32.83 |
| 7 day | 43.27 | 50.04 | 23.18 |
| 14 day | 40.47 | 45.01 | 22.25 |
| 28 day | 37.26 | 41.98 | 20.75 |
| 60 day | 32.71 | 40.85 | 19.81 |
| Age | C-A-S-H Gels Dosage (wt %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 5 | |
| Shrinkage Reduction (%) Brought by C-A-S-H Gel Dry-Mixed with Slag | |||
| 3 day | 19.01 | 33.82 | 12.52 |
| 7 day | 8.85 | 28.02 | 4.89 |
| 14 day | 15.84 | 22.96 | 11.07 |
| 28 day | 19.31 | 24.30 | 9.98 |
| 60 day | 22.72 | 24.96 | 18.20 |
| Shrinkage Reduction (%) Brought by C-A-S-H Gel Dispersed in Water | |||
| 3 day | 21.48 | 35.74 | 20.48 |
| 7 day | 16.87 | 31.91 | 10.92 |
| 14 day | 22.33 | 21.63 | 18.13 |
| 28 day | 26.56 | 25.11 | 20.65 |
| 60 day | 18.60 | 23.35 | 16.99 |
| C-A-S-H Mixing Method | Mortar | Curing Age | Total Porosity (%) | Mesopore Volume (<0.05 µm)/Total Pore Volume (%) | Average Pore Diameter (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | AAS | 3 | 18.40 | 80.43 | 0.0226 |
| 7 | 11.4 | 70.62 | 0.0172 | ||
| 28 | 8.03 | 57.84 | 0.0165 | ||
| DW | AAS + 3 wt % C-A-S-H | 3 | 17.67 | 69.23 | 0.0180 |
| 7 | 10.4 | 58.27 | 0.0163 | ||
| 28 | 7.52 | 45.19 | 0.0148 | ||
| DMS | AAS + 3 wt % C-A-S-H | 3 | 16.99 | 67.57 | 0.0178 |
| 7 | 10.33 | 57.38 | 0.0161 | ||
| 28 | 6.04 | 47.95 | 0.0152 |
| Sample | Phase | Ca/Si | Al/Si | Na/Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic | Atomic | Atomic | ||
| Control | Other hydrated | 0.82 | 0.35 | 0.59 |
| Unhydrated slag | 1.27 | 0.43 | 0.07 | |
| DW-3%-7d | Other hydrated | 0.88 | 0.36 | 0.47 |
| C–A–S–H | 1.00 | 0.83 | – | |
| Unhydrated slag | 1.23 | 0.41 | 0.04 | |
| DMS-3%-7d | Other hydrated | 0.89 | 0.37 | 0.48 |
| C–A–S–H | 1.02 | 0.87 | – | |
| Unhydrated slag | 1.25 | 0.40 | 0.05 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Li, D.; Xing, F.; Fang, Y. Effect of a Synthetic Nano-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O Gel on the Early-Stage Shrinkage Performance of Alkali-Activated Slag Mortars. Materials 2018, 11, 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071128
Liu B, Yang J, Li D, Xing F, Fang Y. Effect of a Synthetic Nano-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O Gel on the Early-Stage Shrinkage Performance of Alkali-Activated Slag Mortars. Materials. 2018; 11(7):1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071128
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bao, Jingbin Yang, Dongxu Li, Feng Xing, and Yuan Fang. 2018. "Effect of a Synthetic Nano-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O Gel on the Early-Stage Shrinkage Performance of Alkali-Activated Slag Mortars" Materials 11, no. 7: 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071128
APA StyleLiu, B., Yang, J., Li, D., Xing, F., & Fang, Y. (2018). Effect of a Synthetic Nano-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O Gel on the Early-Stage Shrinkage Performance of Alkali-Activated Slag Mortars. Materials, 11(7), 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071128





