Surface Nanostructuring of Parylene-C Coatings for Blood Contacting Implants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Preparation and Plasma Treatment
2.2. Surface Characterization
2.3. Diffusion Barrier Performance
2.4. Protein Adsorption
2.5. In Vivo Testing
3. Results
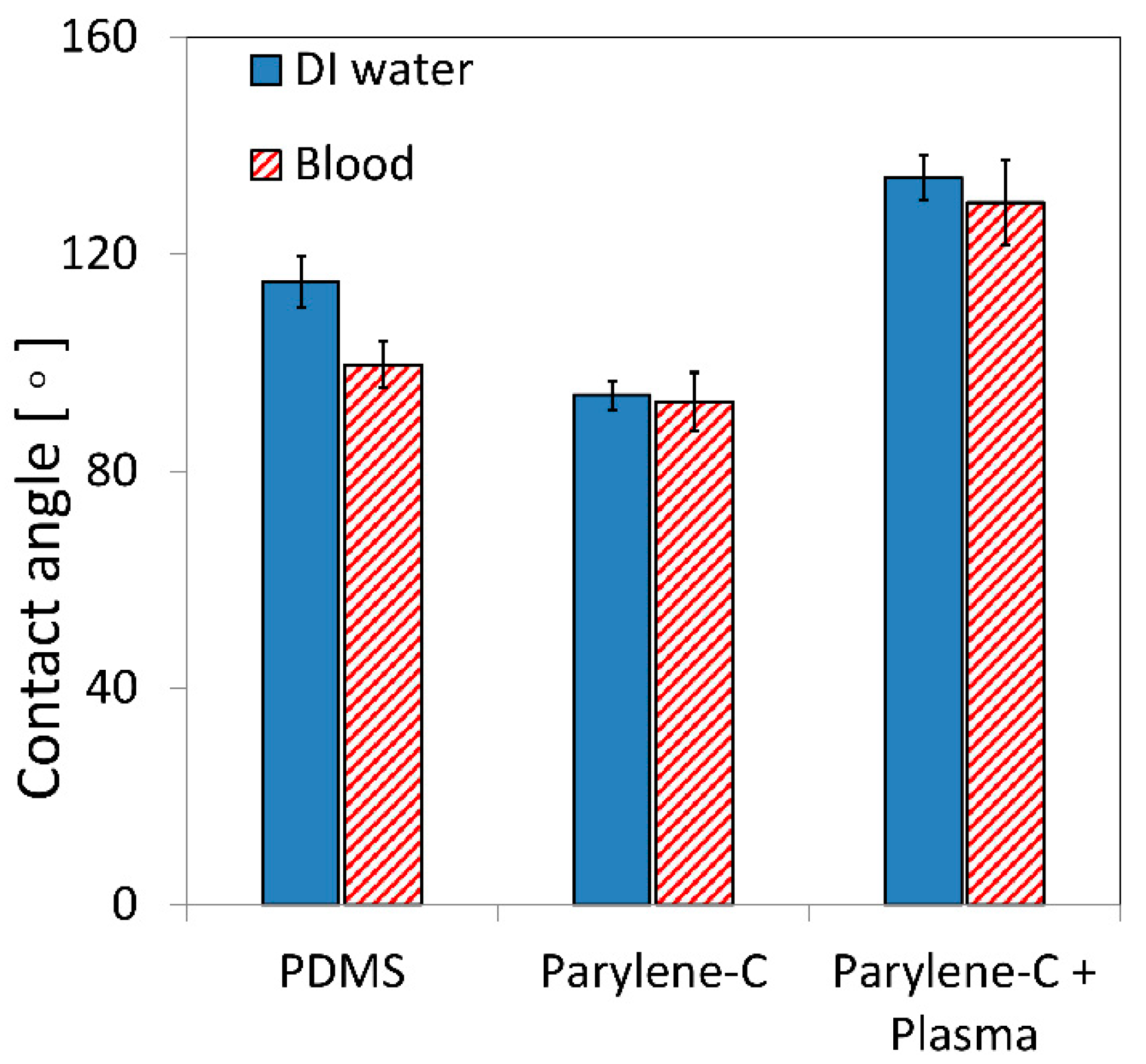
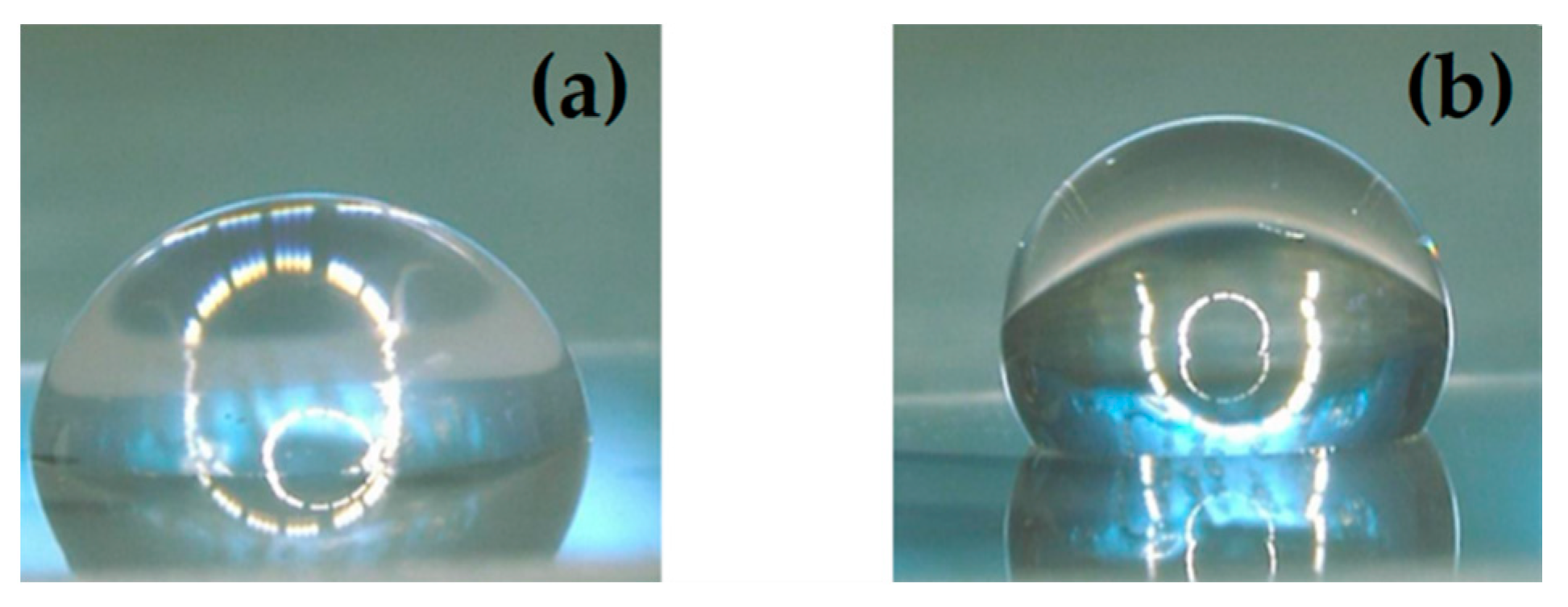
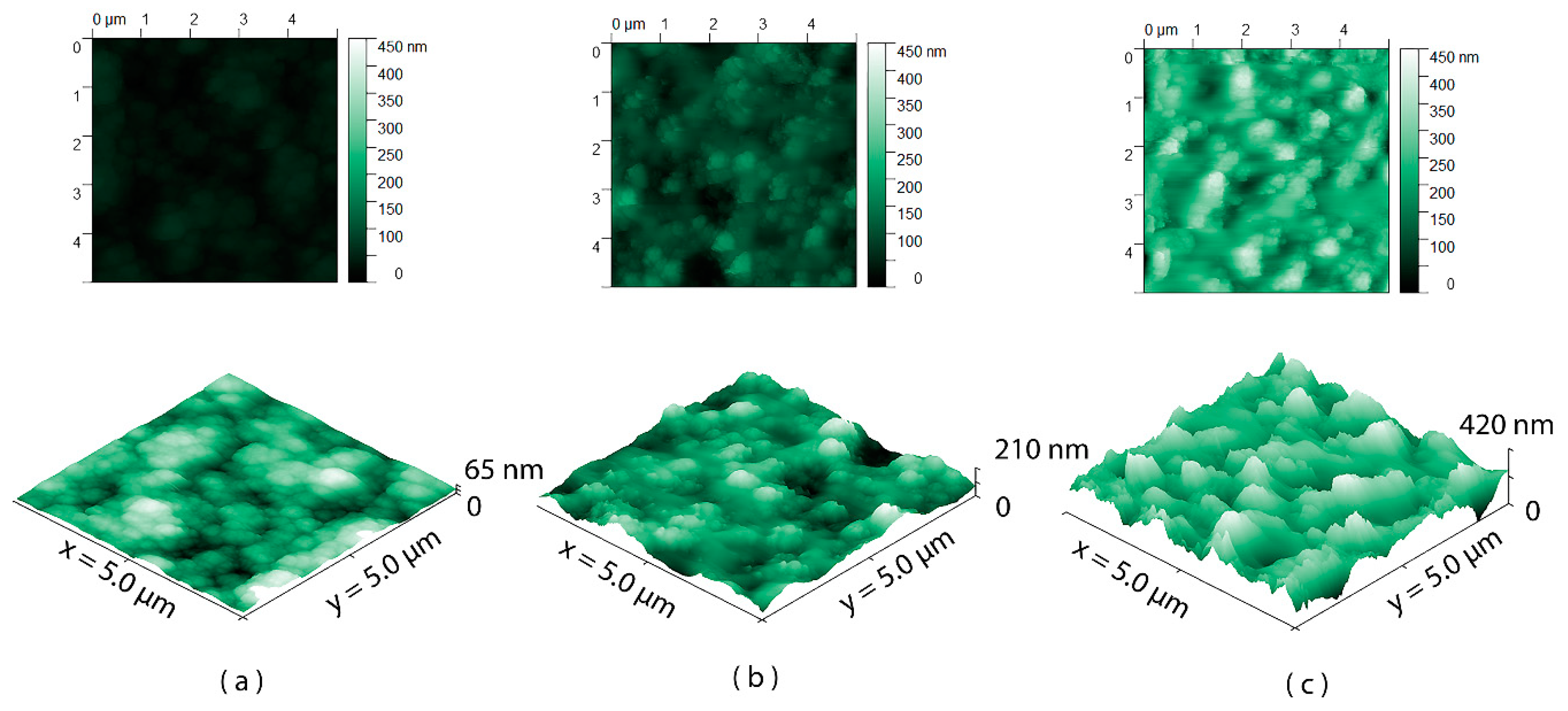
3.1. Surface Wettability and Topography
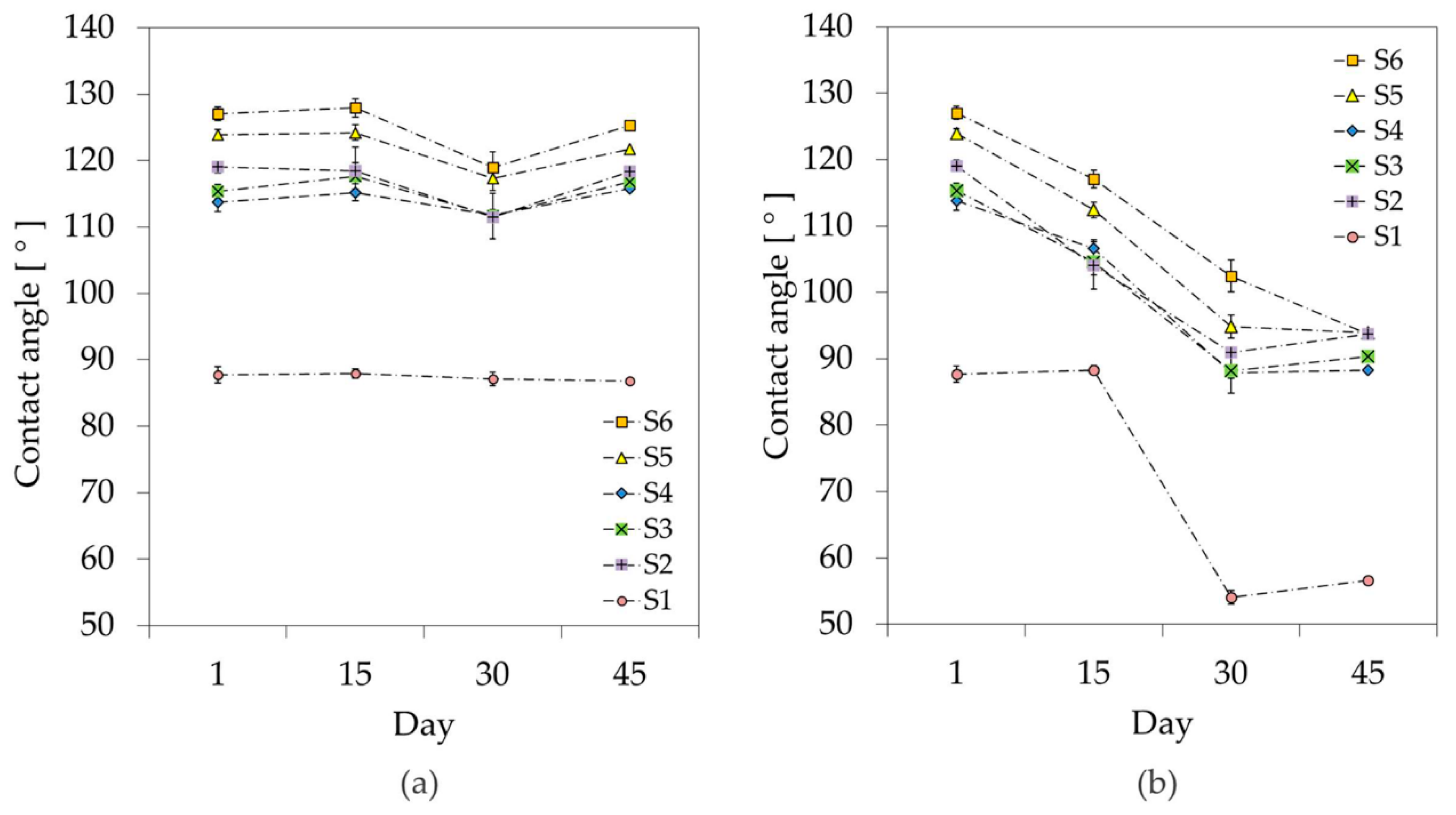
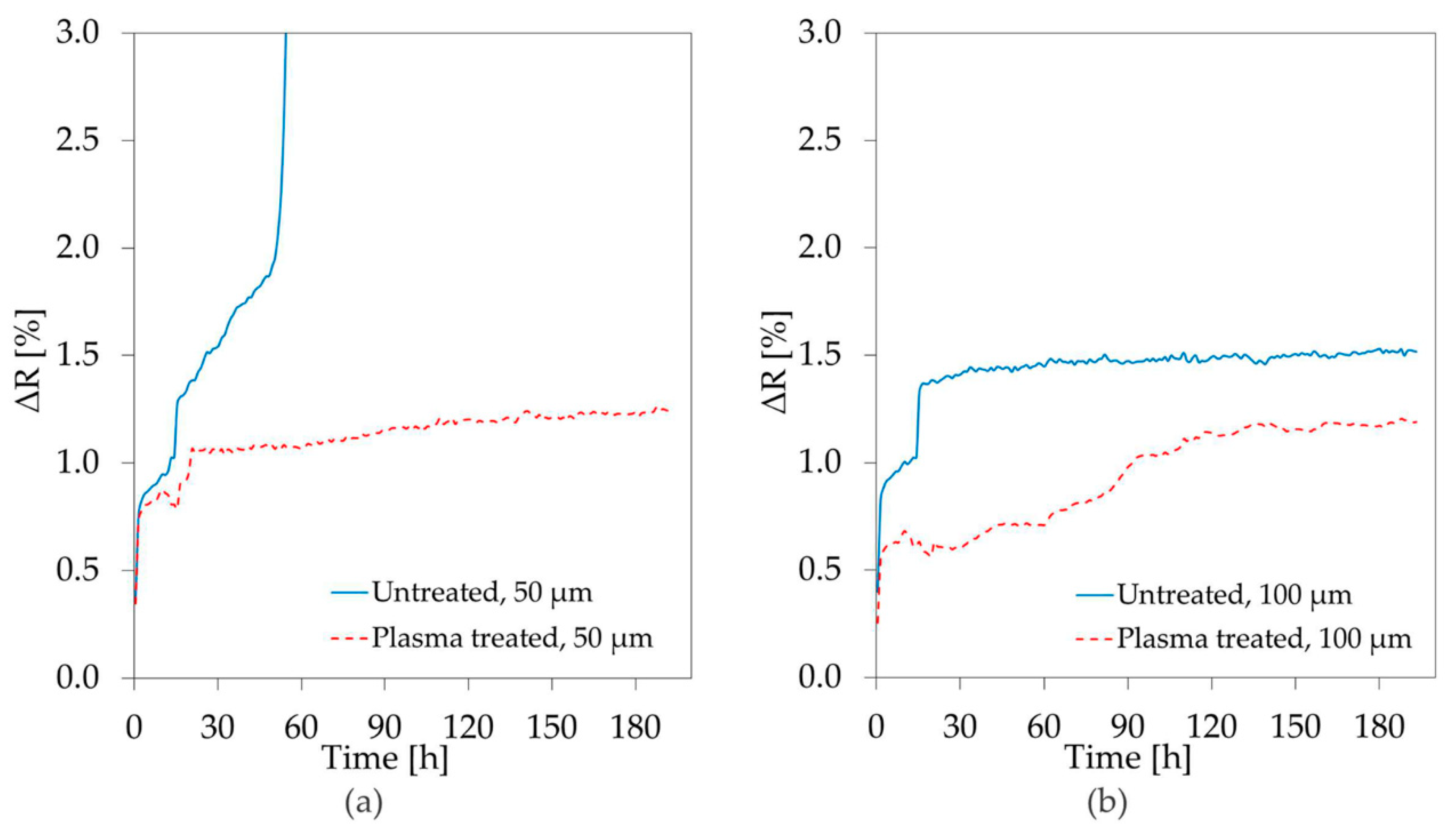
3.2. Stability Study
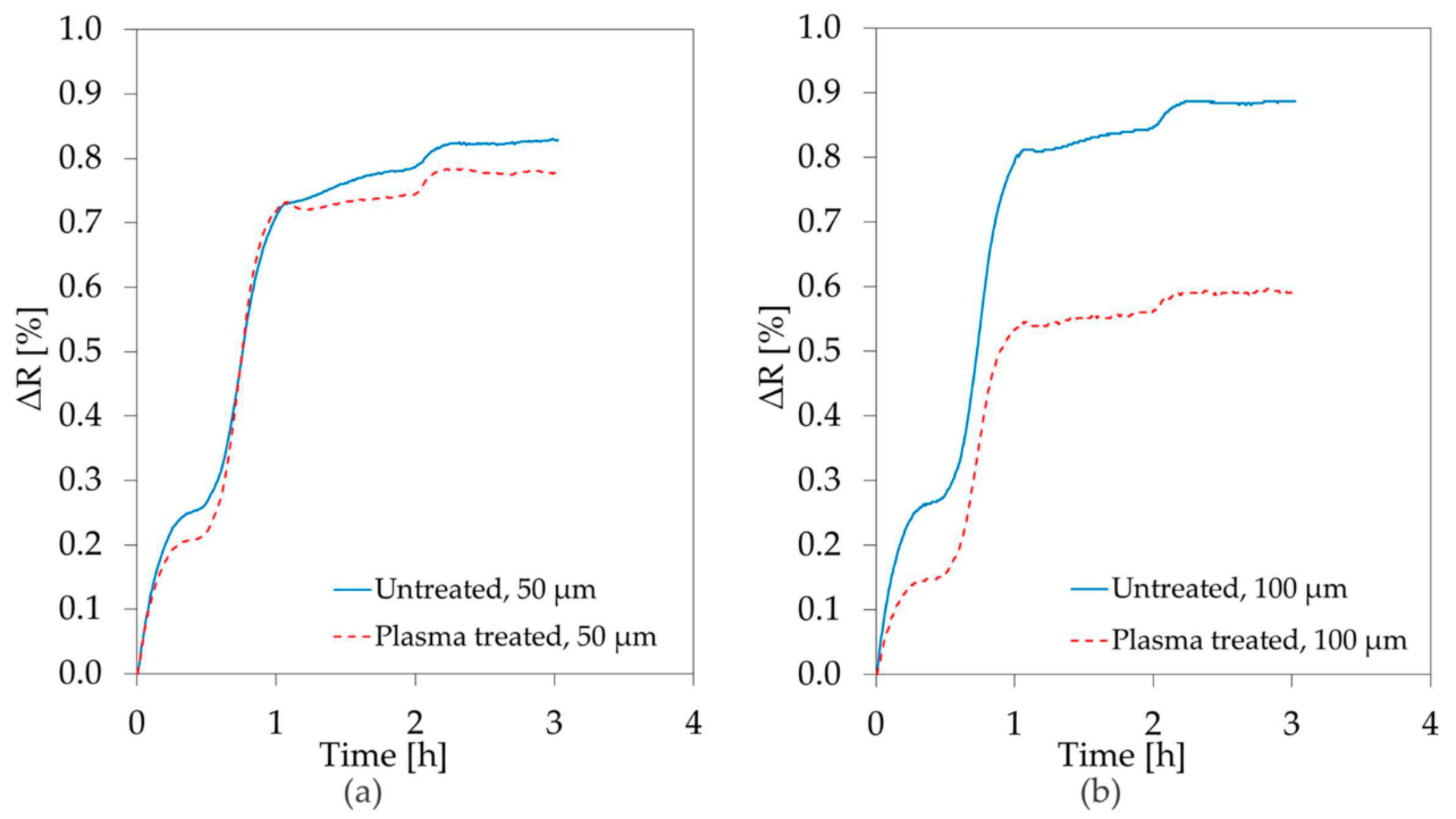
3.3. Diffusion Barrier Properties
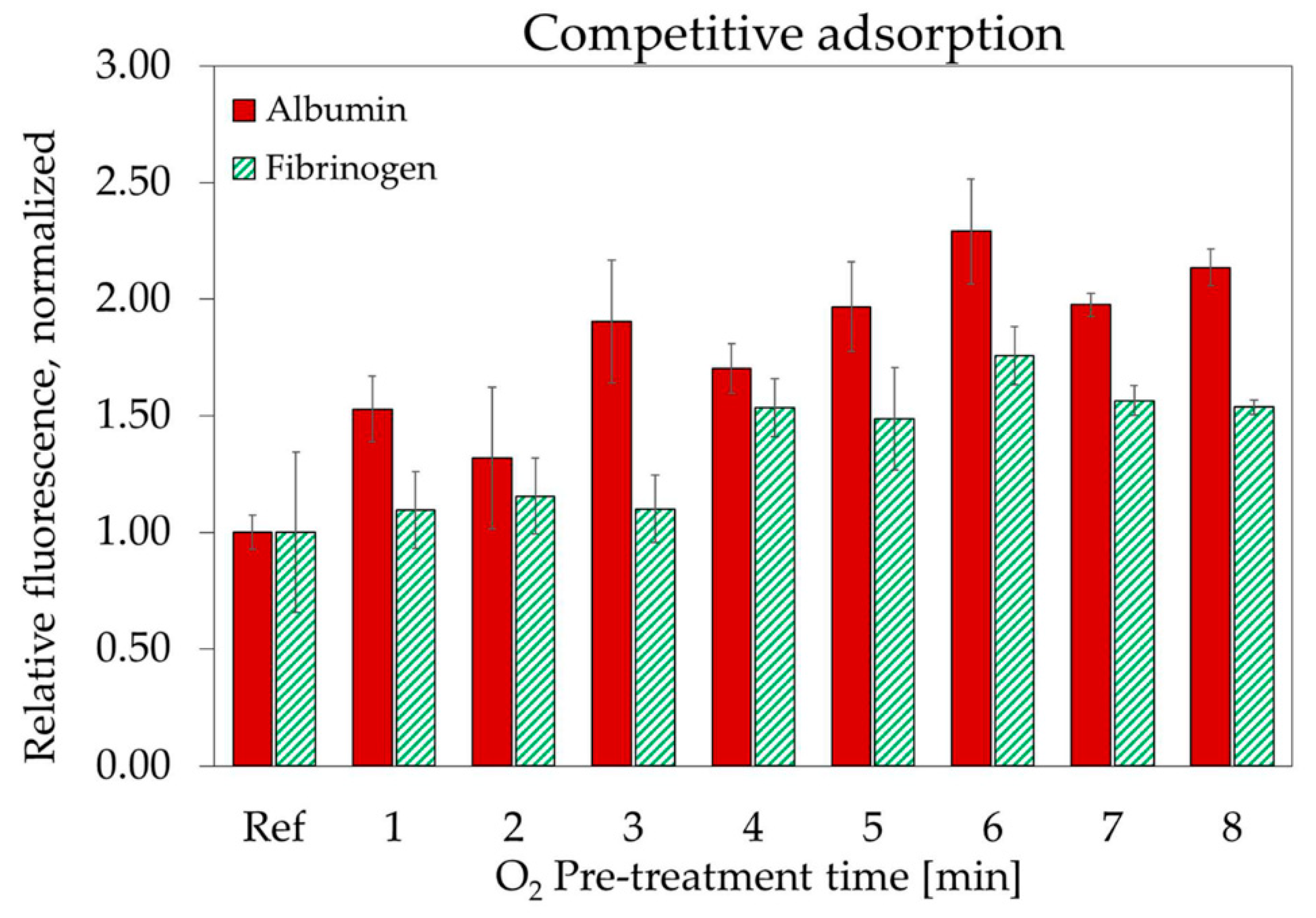
3.4. Plasma Protein Adsorption
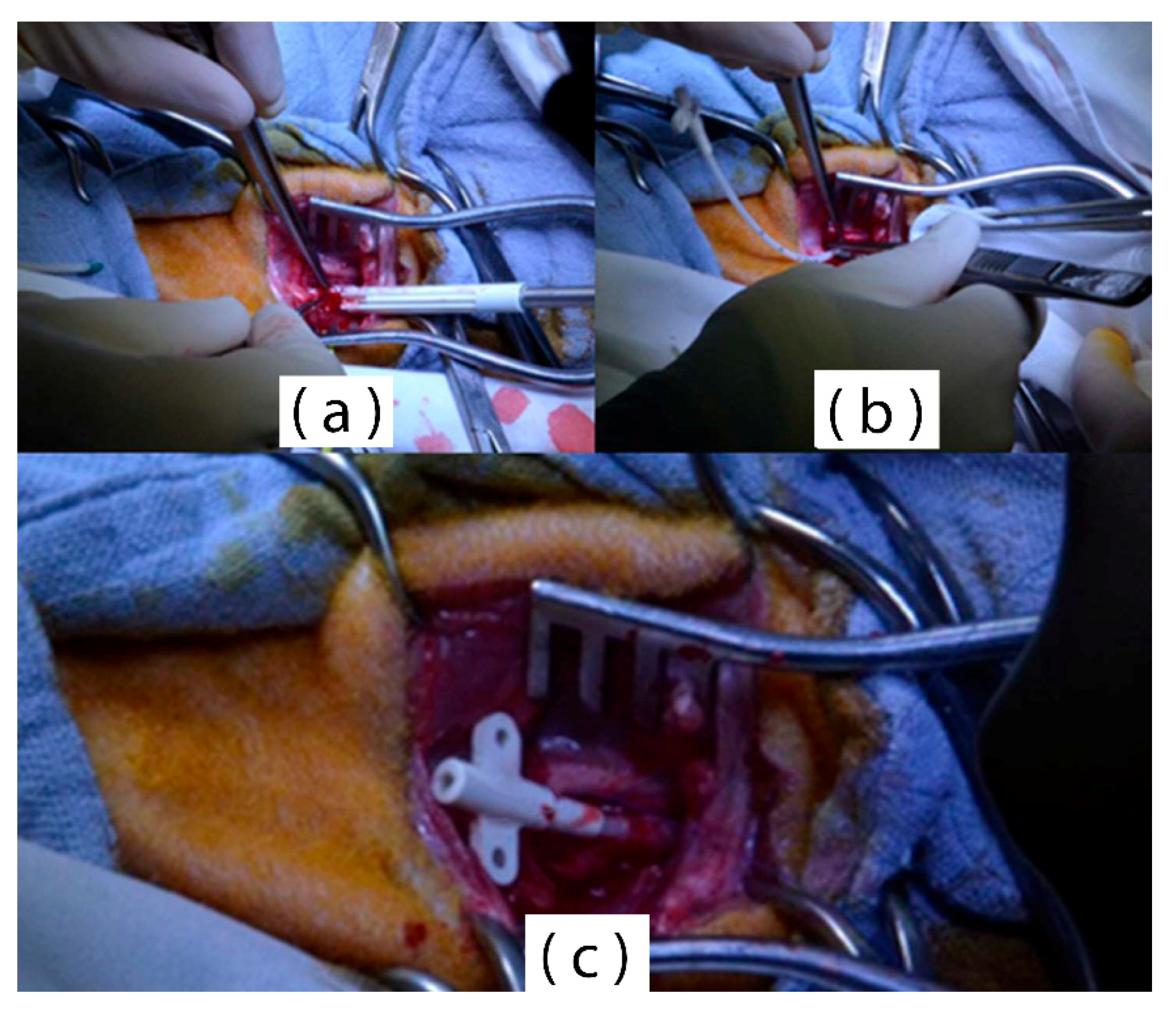
3.5. In Vivo Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Oeveren, W. Obstacles in haemocompatibility testing. Scientifica 2013, 2013, 392584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffer, I.H.; Fredenburgh, J.C.; Hirsh, J.; Weitz, J.I. Medical device-induced thrombosis: What causes it and how can we prevent it? J. Thromb Haemost 2015, 13 (Suppl. 1), S72–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.C.; Bauer, J.W.; Siedlecki, C.A. Proteins, platelets, and blood coagulation at biomaterial interfaces. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 124, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusami, S.; Oskouei, R.H. Parylene Coatings in Medical Devices and Implants: A Review. Univers. J. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 3, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-J.; Lee, D.-S.; Kim, I.-G.; Sohn, D.-W.; Park, J.-Y.; Choi, B.-K.; Kim, S.-W. Evaluation of the biocompatibility of a coating material for an implantable bladder volume sensor. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2012, 28, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Valle, J.; de la Oliva, N.; Muller, M.; Stieglitz, T.; Navarro, X. Biocompatibility evaluation of parylene C and polyimide as substrates for peripheral nerve interfaces. In Proceedings of the 2015 7th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), Montpellier, France, 22–24 April 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 442–445. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.-J.; Rodger, D.C.; Saati, S.; Humayun, M.S.; Tai, Y.-C. Microfabricated Implantable Parylene-Based Wireless Passive Intraocular Pressure Sensors. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2008, 17, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metallo, C.; White, R.D.; Trimmer, B.A. Flexible parylene-based microelectrode arrays for high resolution EMG recordings in freely moving small animals. J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 195, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancato, L.; Weydts, T.; Oosterlinck, W.; Herijgers, P.; Puers, R. Packaging of implantable accelerometers to monitor epicardial and endocardial wall motion. Biomed. Microdevices 2017, 19, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancato, L.; Weydts, T.; Soebadi, M.A.; De Ridder, D.; Puers, R. Submucosal Exploration of EMG and Physiological Parameters in the Bladder Wall. Proceedings 2017, 1, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winslow, B.D.; Christensen, M.B.; Yang, W.-K.; Solzbacher, F.; Tresco, P.A. A comparison of the tissue response to chronically implanted Parylene-C-coated and uncoated planar silicon microelectrode arrays in rat cortex. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 9163–9172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Rodger, D.C.; Menon, P.R.; Tai, Y.C. Corrosion Behavior of Parylene-Metal-Parylene Thin Films in Saline. ECS Trans. 2008, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beeck, M.O.; Jarboui, A.; Cauwe, M.; Declercq, H.; Uytterhoeven, G.; Cornelissen, M.; Vanfleteren, J.; Van Hoof, C. Improved chip & component encapsulation by dedicated diffusion barriers to reduce corrosion sensitivity in biological and humid environments. In Proceedings of the 2013 Eurpoean Microelectronics Packaging Conference (EMPC), Grenoble, France, 9–12 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, T.Y.; Yadav, V.G.; De Leo, S.; Mohedas, A.; Rajalingam, B.; Chen, C.-L.; Selvarasah, S.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Khademhosseini, A. Cell and Protein Compatibility of Parylene-C Surfaces. Langmuir 2007, 23, 11718–11725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisenberg, B.A.; Mooradian, D.L. Hemocompatibility of materials used in microelectromechanical systems: Platelet adhesion and morphology in vitro. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 60, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamińska, M.; Okrój, W.; Szymański, W.; Jakubowski, W.; Komorowski, P.; Nosal, A.; Szymanowski, H.; Gazicki-Lipman, M.; Jerczyńska, H.; Pawłowska, Z.; et al. Interaction of parylene C with biological objects. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2009, 11, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gołda, M.; Brzychczy-Włoch, M.; Faryna, M.; Engvall, K.; Kotarba, A. Oxygen plasma functionalization of parylene C coating for implants surface: Nanotopography and active sites for drug anchoring. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 4221–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Crum, B.P.; Li, W. Super Hydrophobic Parylene-C Produced by Consecutive O2 and SF6 Plasma Treatment. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2014, 23, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancato, L.; Keulemans, G.; Gijsenbergh, P.; Puers, R. Plasma enhanced hydrophobicity of parylene-C surfaces for a blood contacting pressure sensor. Procedia Eng. 2014, 87, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, W.I. In Vitro Measurements of the Effects of Anticoagulants on the Flow Properties of Blood: The Relationship of these Effects to Red Cell Shrinkage. Blood 1968, 31, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwok, S.C.H.; Wang, J.; Chu, P.K. Surface energy, wettability, and blood compatibility phosphorus doped diamond-like carbon films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2005, 14, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mel, A.; Cousins, B.G.; Seifalian, A.M. Surface Modification of Biomaterials: A Quest for Blood Compatibility. Int. J. Biomater. 2012, 2012, 707863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong-Van, E.; Rodriguez, I.; Low, H.Y.; Elmouelhi, N.; Lowenhaupt, B.; Natarajan, S.; Lim, C.T.; Prajapati, R.; Vyakarnam, M.; Cooper, K. Review: Micro- and nanostructured surface engineering for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 28, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, Y.-H.; Shutov, D.A.; Baek, K.-H.; Do, L.-M.; Kim, K.; Lee, C.-W.; Kwon, K.-H. Surface characteristics of parylene-C films in an inductively coupled O2/CF4 gas plasma. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 6378–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.T.; Chuang, C.T.; Li, T.C.; Yu, P.C. Study of Parylene-C Thin Film Deposited on Flat Substrates. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 217–219, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontziampasis, D.; Trantidou, T.; Regoutz, A.; Humphrey, E.J.; Carta, D.; Terracciano, C.M.; Prodromakis, T. Effects of Ar and O2 Plasma Etching on Parylene C: Topography versus Surface Chemistry and the Impact on Cell Viability. Plasma Process. Polym. 2016, 13, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solouk, A.; Cousins, B.G.; Mirzadeh, H.; Solati-Hashtjin, M.; Najarian, S.; Seifalian, A.M. Surface modification of POSS-nanocomposite biomaterials using reactive oxygen plasma treatment for cardiovascular surgical implant applications. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2011, 58, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, P.K.; Chen, J.Y.; Wang, L.P.; Huang, N. Plasma-surface modification of biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2002, 36, 143–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.P.; Craighead, H.G. Surface Engineering and Patterning Using Parylene for Biological Applications. Materials 2010, 3, 1803–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosina, J.; Kvasnák, E.; Suta, D.; Kolárová, H.; Málek, J.; Krajci, L. Temperature dependence of blood surface tension. Physiol. Res. 2007, 56 (Suppl. 1), S93–S98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhunia, S.; Majerus, S.; Sawan, M. Implantable Biomedical Microsystems: Design Principles and Applications; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 9780323261906. [Google Scholar]
- Hassler, C.; von Metzen, R.; Stieglitz, T. Deposition Parameters Determining Insulation Resistance and Crystallinity of Parylene C in Neural Implant Encapsulation. In Proceedings of the 4th European Conference of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering, Antwerp, Belgium, 23–27 November 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 2439–2442. [Google Scholar]
- Sadique, S.E.; Mollah, M.H.; Ali, M.M.; Haque, M.M.; Basri, S.; Ahmad, M.M.H.M.; Sapuan, S.M. Influence of Aluminium Additions on the Rate of Oxidation of Iron-Chromium Alloys. J. Corros. Sci. Eng. 2000, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Siedlecki, C.A. Protein adsorption, platelet adhesion, and bacterial adhesion to polyethylene-glycol-textured polyurethane biomaterial surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, D.L. Encyclopedic Handbook of Biomaterials and Bioengineering: v. 1–2. Applications; Encyclopedic Handbook of Biomaterials and Bioengineering; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1995; ISBN 9780824795962. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, S.L.; Cooper, S.L.; Albrecht, R.M. Integrin receptors and platelet adhesion to synthetic surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1993, 27, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delivopoulos, E.; Ouberai, M.M.; Coffey, P.D.; Swann, M.J.; Shakesheff, K.M.; Welland, M.E. Serum protein layers on parylene-C and silicon oxide: Effect on cell adhesion. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 126, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goda, T.; Konno, T.; Takai, M.; Ishihara, K. Photoinduced phospholipid polymer grafting on Parylene film: Advanced lubrication and antibiofouling properties. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 54, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, A.; Cha, P.; Liu, Y.-H.; Allara, D.; Vogler, E.A. Interfacial energetics of blood plasma and serum adsorption to a hydrophobic self-assembled monolayer surface. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3187–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.I.; McColl, I.R.; Grant, D.M.; Parker, K.G.; Parker, T.L. Protein adsorption and platelet attachment and activation, on TiN, TiC, and DLC coatings on titanium for cardiovascular applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonckreman, C.J.; Fleith, S.; Rouxhet, P.G.; Dupont-Gillain, C.C. Competitive adsorption of fibrinogen and albumin and blood platelet adhesion on surfaces modified with nanoparticles and/or PEO. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 77, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minges, M.L.; ASM International. Electronic Materials Handbook; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1989; ISBN 0871702851. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Li, X. Superhydrophobic surfaces for corrosion protection: A review of recent progresses and future directions. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2016, 13, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, D.; Qiu, R.; Wan, Y.; Wu, J. Green approach to fabrication of a super-hydrophobic film on copper and the consequent corrosion resistance. Corros. Sci. 2014, 80, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, D.; Qiu, R.; Wu, J.; Wan, Y. Super-hydrophobic film prepared on zinc and its effect on corrosion in simulated marine atmosphere. Corros. Sci. 2013, 69, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandner, B.D.; Hansson, P.M.; Swerin, A.; Claesson, P.M.; Wåhlander, M.; Schoelkopf, J.; Gane, P.A.C. Solvent segregation and capillary evaporation at a superhydrophobic surface investigated by confocal Raman microscopy and force measurements. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancato, L.; Keulemans, G.; Verbelen, T.; Meyns, B.; Puers, R. An Implantable Intravascular Pressure Sensor for a Ventricular Assist Device. Micromachines 2016, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Substrate | Coating | O2 Plasma Duration (min) | SF6 Plasma Duration (min) | Surface Roughness (RMS) (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | Glass | - | - | - | 2 ± 1.2 |
| A1 | Glass | Parylene-C | - | - | 10.96 ± 2.4 |
| A2 | Glass | Parylene-C | 5 | 1 | 30.13 ± 6.2 |
| A3 | Glass | Parylene-C | 10 | 1 | 53.48 ± 9.5 |
| Sample | O2 Plasma Duration (s) | SF6 Plasma Duration (s) |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | - | - |
| S2 | 30 | 30 |
| S3 | 30 | 60 |
| S4 | 30 | 120 |
| S5 | 60 | 30 |
| S6 | 120 | 30 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brancato, L.; Decrop, D.; Lammertyn, J.; Puers, R. Surface Nanostructuring of Parylene-C Coatings for Blood Contacting Implants. Materials 2018, 11, 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071109
Brancato L, Decrop D, Lammertyn J, Puers R. Surface Nanostructuring of Parylene-C Coatings for Blood Contacting Implants. Materials. 2018; 11(7):1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071109
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrancato, Luigi, Deborah Decrop, Jeroen Lammertyn, and Robert Puers. 2018. "Surface Nanostructuring of Parylene-C Coatings for Blood Contacting Implants" Materials 11, no. 7: 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071109
APA StyleBrancato, L., Decrop, D., Lammertyn, J., & Puers, R. (2018). Surface Nanostructuring of Parylene-C Coatings for Blood Contacting Implants. Materials, 11(7), 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071109






