Hybrid Metasurface Based Tunable Near-Perfect Absorber and Plasmonic Sensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
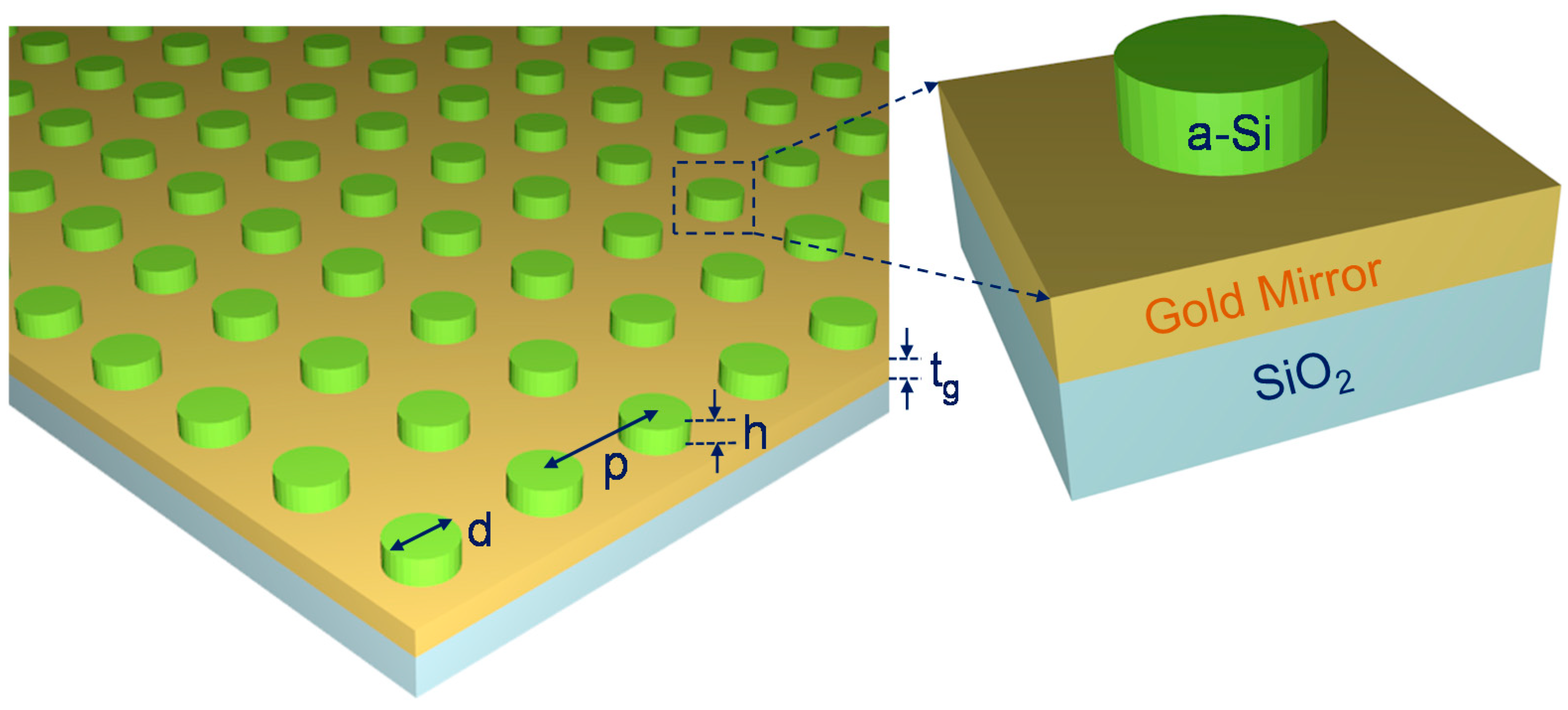
2. Structural Design and Numerical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
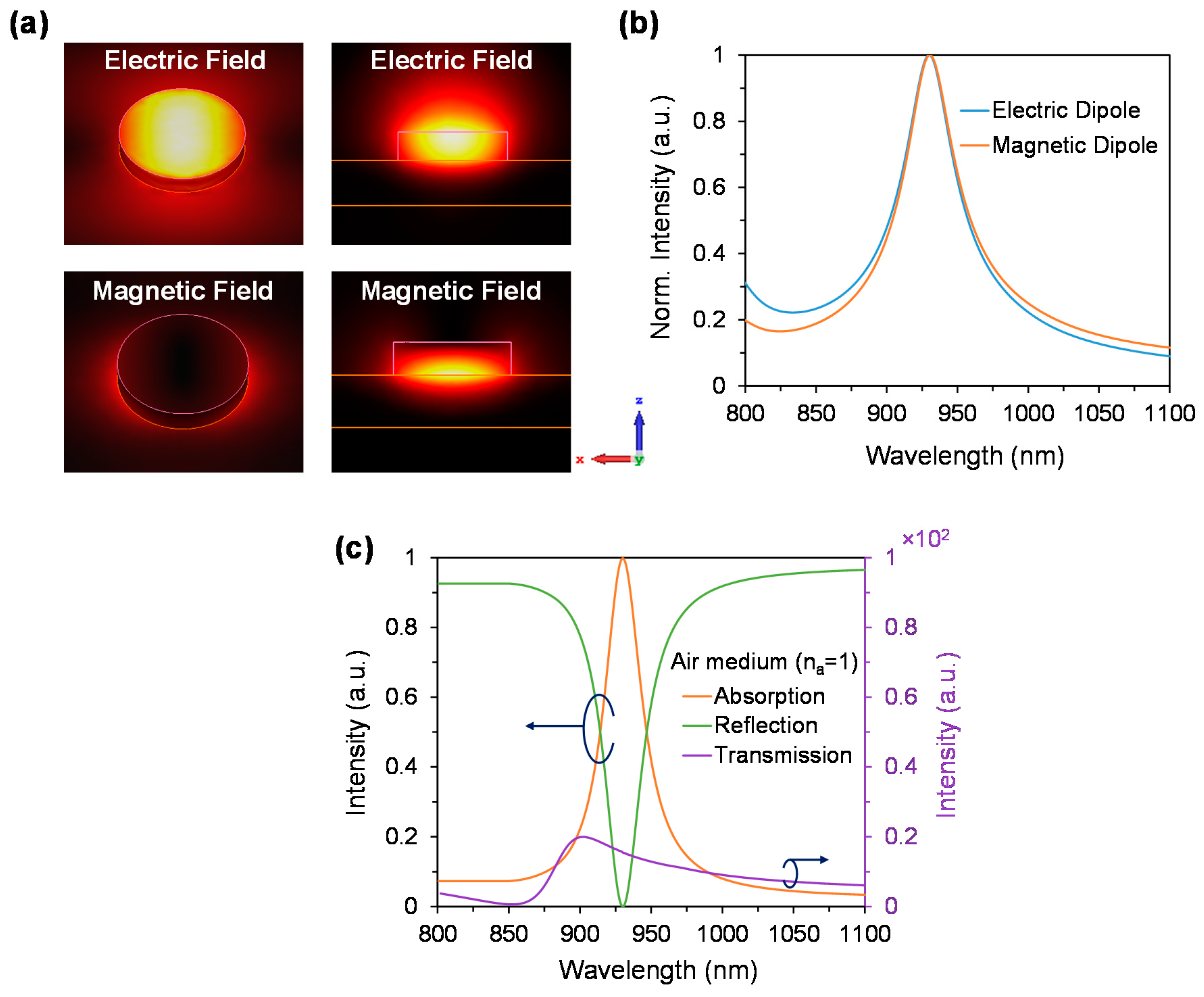
3.1. Performance Analysis with Respect to Perfect Absorber
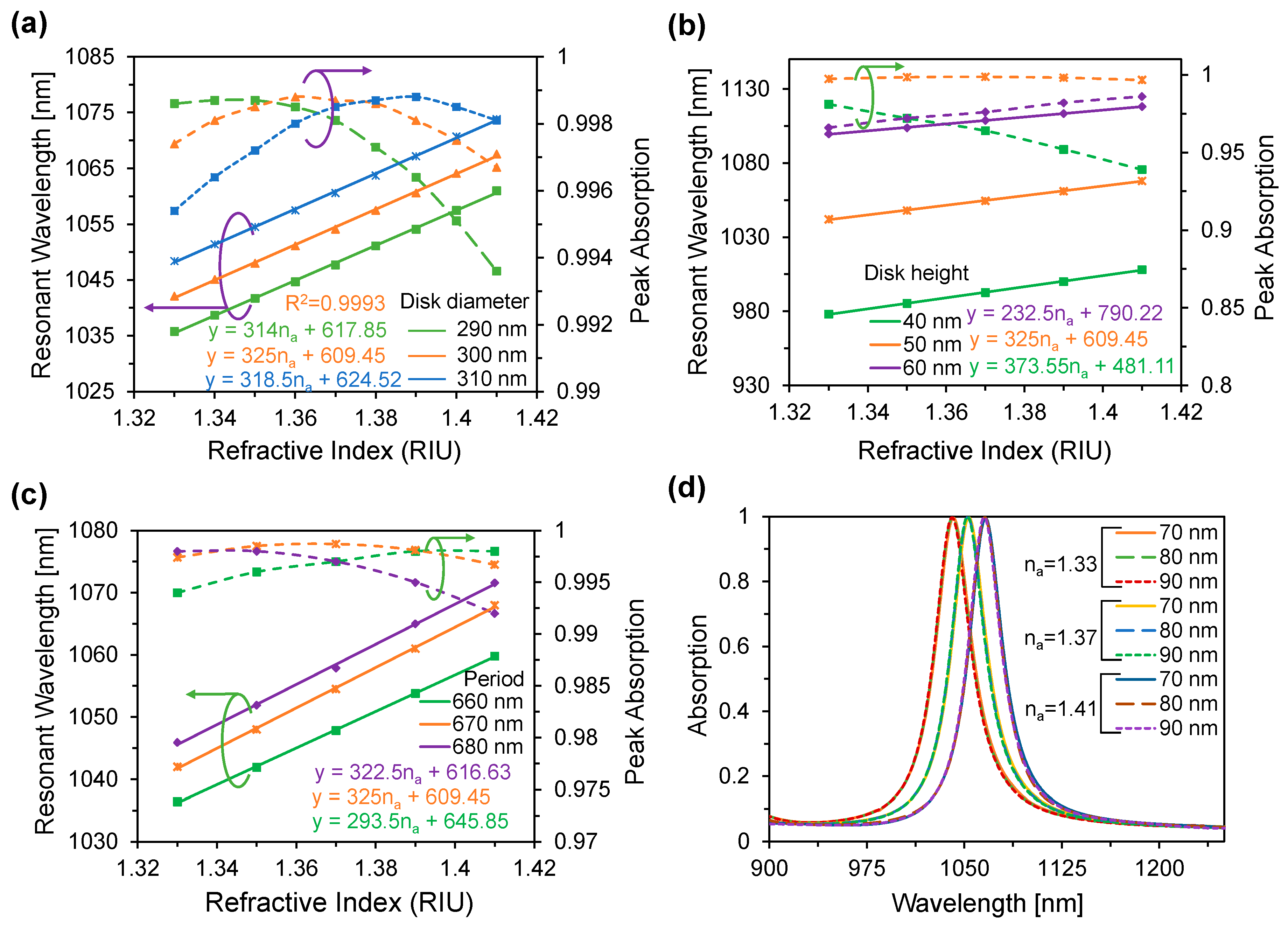
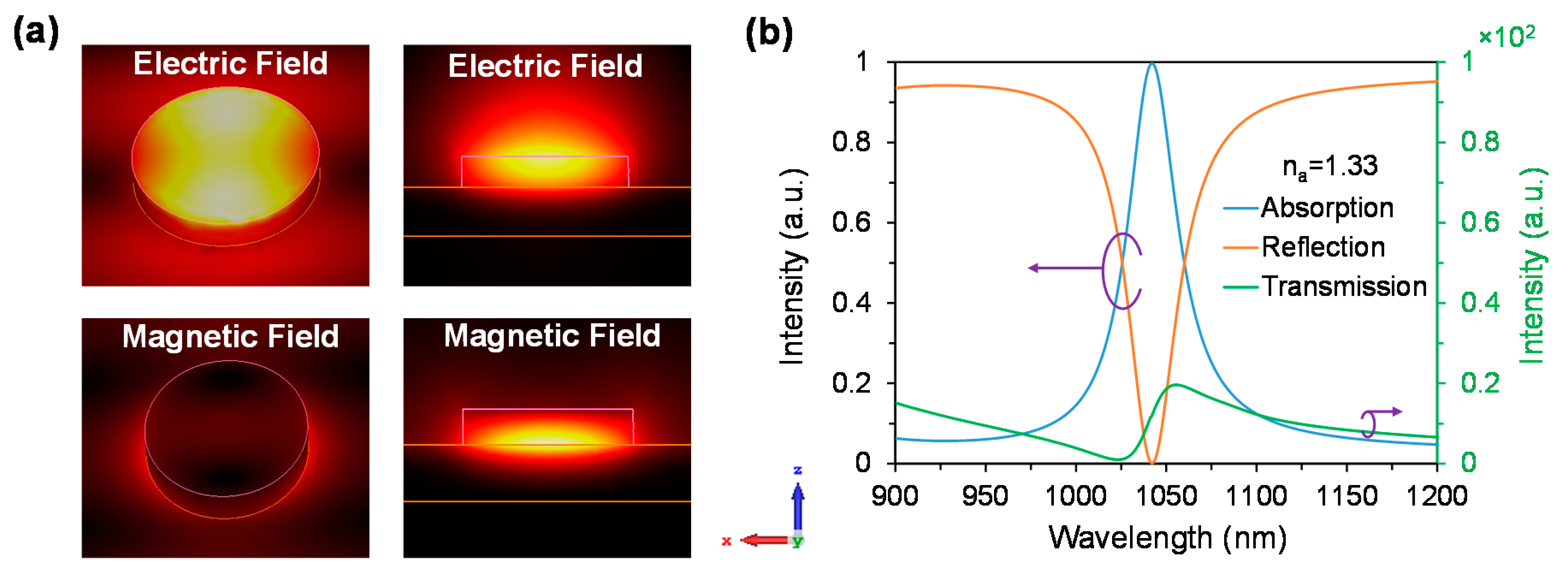
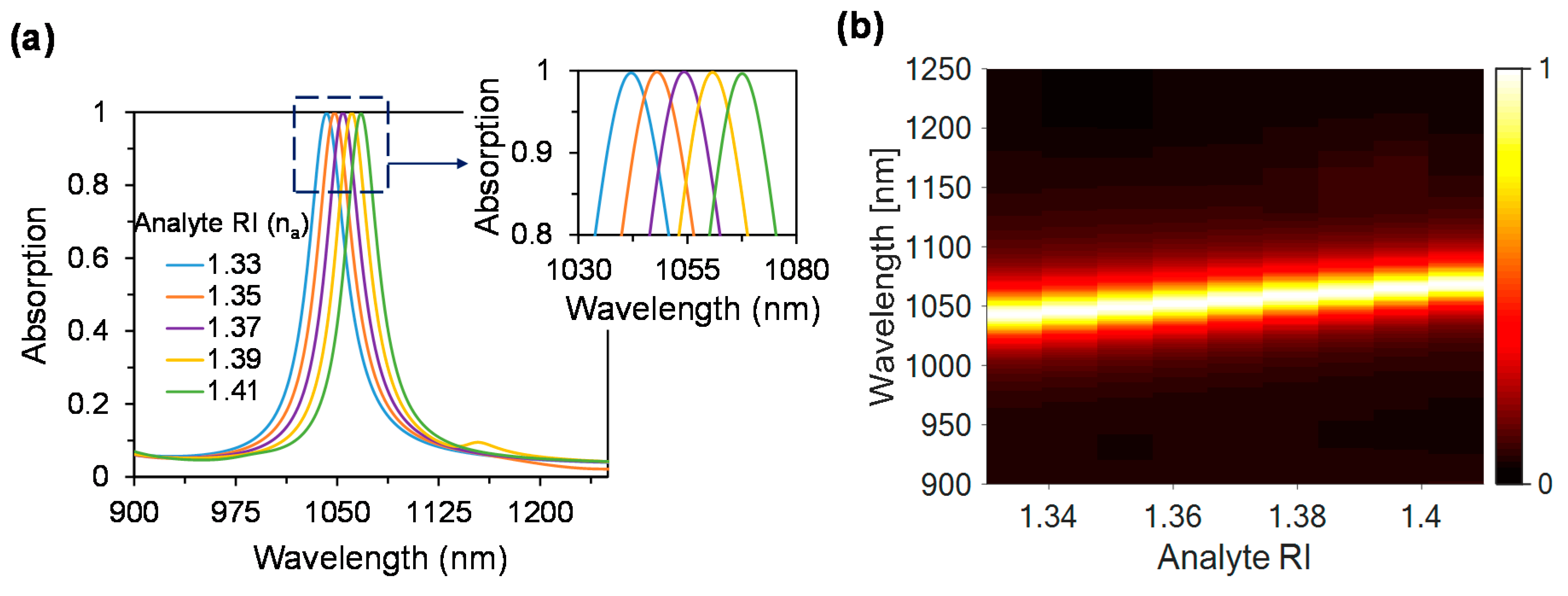
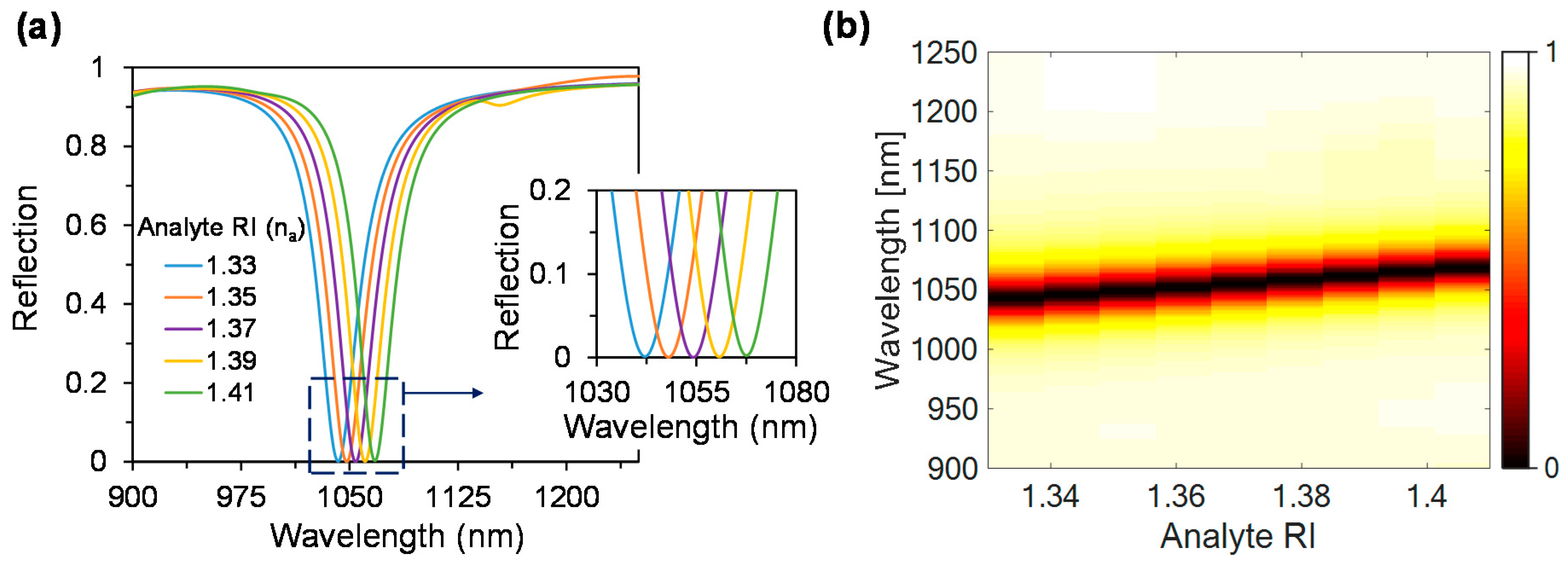
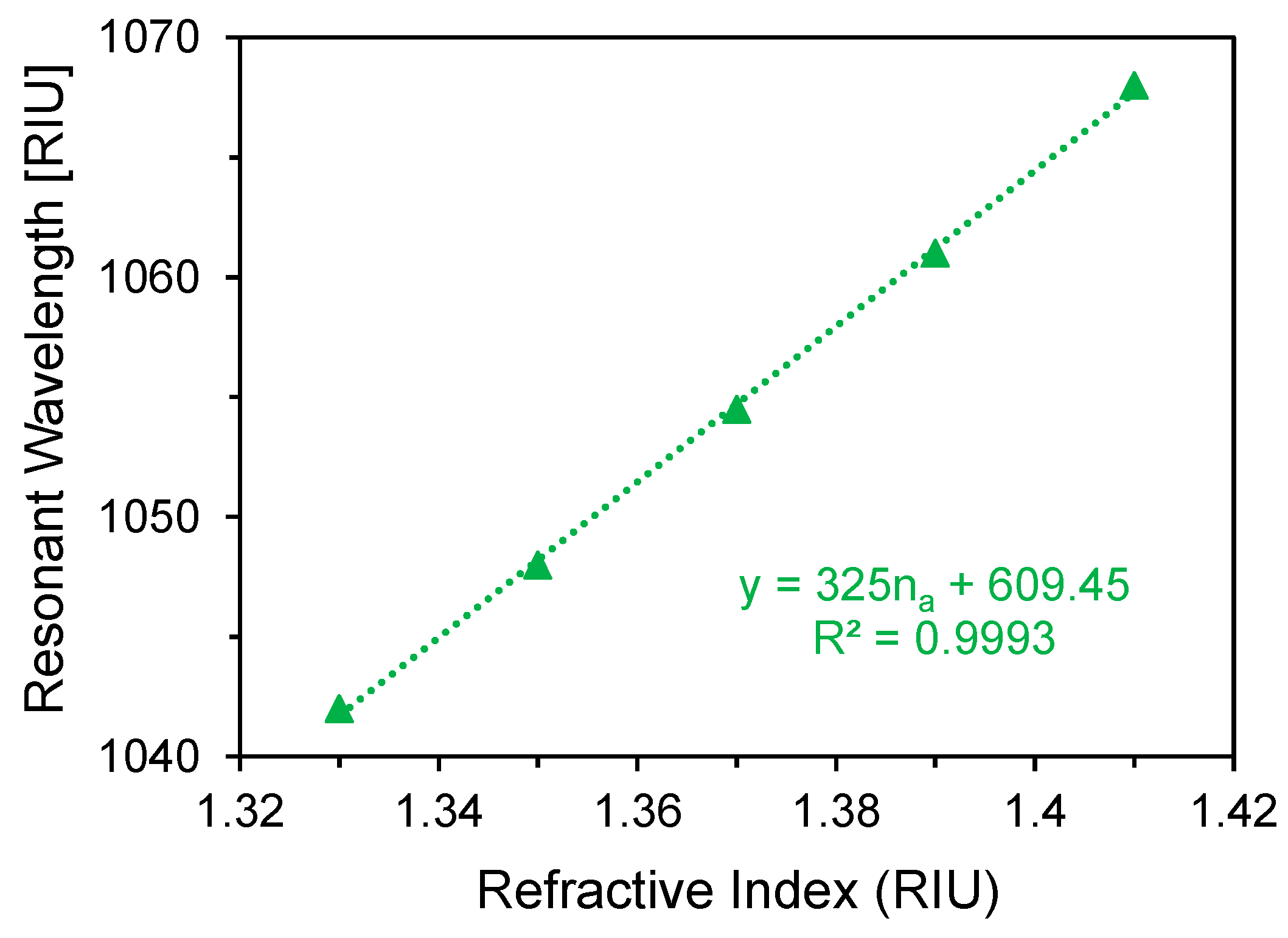
3.2. Performance Analysis with Respect to Plasmonic Sensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Pu, M.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Luo, X. Refractory metamaterial absorber for ultra-broadband, omnidirectional and polarization-independent absorption in the UV-NIR spectrum. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 8298–8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, M.; Shorokhov, A.S.; Hopkins, B.; Miroshnichenko, A.E.; Shcherbakov, M.R.; Camacho-Morales, R.; Fedyanin, A.A.; Neshev, D.N.; Kivshar, Y.S. Nonlinear symmetry breaking in symmetric oligomers. ACS Photonics 2017, 4, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.M.; Lee, D.; Rho, J. Control of light absorbance using plasmonic grating based perfect absorber at visible and near-infrared wavelengths. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Li, Z.; Stan, L.; Rosenmann, D.; Czaplewski, D.; Gao, J.; Yang, X. Broadband perfect absorber based on one ultrathin layer of refractory metal. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 2592–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Bi, K.; Li, B.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, J. Metamaterial perfect absorber based on artificial dielectric atoms. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 20454–20460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.K.; Lai, Y.-C.; Tu, M.-H.; Chen, B.-R.; Fu, S.M.; Yu, P.; Lin, A. Omnidirectional, polarization-independent, ultra-broadband metamaterial perfect absorber using field-penetration and reflected-wave-cancellation. Opt. Express 2016, 24, A832–A845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivshar, Y.; Miroshnichenko, A. Meta-optics with Mie resonances. Opt. Photonics News 2017, 28, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroshnichenko, A.E.; Flach, S.; Kivshar, Y.S. Fano resonances in nanoscale structures. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010, 82, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minovich, A.E.; Miroshnichenko, A.E.; Bykov, A.Y.; Murzina, T.V.; Neshev, D.N.; Kivshar, Y.S. Functional and nonlinear optical metasurfaces. Laser Photonics Rev. 2015, 9, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, A.I.; Miroshnichenko, A.E.; Brongersma, M.L.; Kivshar, Y.S.; Luk’yanchuk, B. Optically resonant dielectric nanostructures. Science 2016, 354, aag2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, M.; Xu, L.; Miroshnichenko, A.E.; Komar, A.; Camacho-Morales, R.; Chen, H.; Zárate, Y.; Kruk, S.; Zhang, G.; Neshev, D.N.; et al. Reversible thermal tuning of all-dielectric metasurfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.; Sedighy, S. Broadband wide-angle polarization-insensitive metasurface solar absorber. JOSA A 2018, 35, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, K.; Ferry, V.E.; Briggs, R.M.; Atwater, H.A. Broadband polarization-independent resonant light absorption using ultrathin plasmonic super absorbers. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Q.; Sun, T.; Yan, Y.; Wang, C. Large-area wide-incident-angle metasurface perfect absorber in total visible band based on coupled mie resonances. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Mesch, M.; Weiss, T.; Hentschel, M.; Giessen, H. Infrared perfect absorber and its application as plasmonic sensor. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2342–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, R.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Hao, Y.; Lei, M.; Bi, K. Wideband terahertz absorber based on Mie resonance metasurface. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 115310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Dong, G.; Hao, Y.; Lei, M.; Bi, K. Multi-band terahertz metasurface absorber. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2017, 31, 1750354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Xie, Z.; Chen, W.; Lei, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, K.; Li, L. Metasurface with multi-sized structure for multi-band coherent perfect absorption. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 7066–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yu, P.; Tang, C.; Cheng, H.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Tian, J. Bidirectional perfect absorber using free substrate plasmonic metasurfaces. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Shankar, R.; Kats, M.A.; Song, Y.; Kong, J.; Loncar, M.; Capasso, F. Electrically tunable metasurface perfect absorbers for ultrathin mid-infrared optical modulators. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 6526–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Lee, D.; Lim, S. A fluidically tunable metasurface absorber for flexible large-scale wireless ethanol sensor applications. Sensors 2016, 16, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berini, P. Long-range surface plasmon polaritons. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2009, 1, 484–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homola, J. Surface plasmon resonance sensors for detection of chemical and biological species. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 462–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baquedano, E.; González, M.; Paniagua-Domínguez, R.; Sánchez-Gil, J.A.; Postigo, P.A. Low-cost and large-size nanoplasmonic sensor based on Fano resonances with fast response and high sensitivity. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 15967–15976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupin, O.; Wong, W.R.; Adikan, F.R.M.; Berini, P. Detection of small molecules using long-range surface plasmon polariton waveguides. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantume Electron. 2017, 23, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontempi, N.; Chong, K.E.; Orton, H.W.; Staude, I.; Choi, D.-Y.; Alessandri, I.; Kivshar, Y.S.; Neshev, D.N. Highly sensitive biosensors based on all-dielectric nanoresonators. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 4972–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, M.; Rahmani, M.; Zhang, L.; Lei, D.Y.; Roschuk, T.R.; Giannini, V.; Qiu, C.W.; Hong, M.; Schlücker, S.; Maier, S.A. Unveiling the correlation between nanometer-thick molecular monolayer sensitivity and near-field enhancement and localization in coupled plasmonic oligomers. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9188–9198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rifat, A.A.; Ahmed, R.; Mahdiraji, G.A.; Adikan, F.M.; Miroshnichenko, A.E. Highly sensitive selectively coated photonic crystal fiber-based plasmonic sensor. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rifat, A.A.; Hasan, M.R.; Ahmed, R.; Butt, H. Photonic crystal fiber-based plasmonic biosensor with external sensing approach. J. Nanophotonics 2017, 12, 012503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifat, A.A.; Mahdiraji, G.A.; Chow, D.M.; Shee, Y.G.; Ahmed, R.; Adikan, F.R.M. Photonic crystal fiber-based surface plasmon resonance sensor with selective analyte channels and graphene-silver deposited core. Sensors 2015, 15, 11499–11510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.R.; Akter, S.; Rifat, A.A.; Rana, S.; Ali, S. A highly sensitive gold-coated photonic crystal fiber biosensor based on surface plasmon resonance. Photonics 2017, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caucheteur, C.; Guo, T.; Albert, J. Review of plasmonic fiber optic biochemical sensors: Improving the limit of detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 3883–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.B.; Christy, R.-W. Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 6, 4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xifré-Pérez, E.; Shi, L.; Tuzer, U.; Fenollosa, R.; Ramiro-Manzano, F.; Quidant, R.; Meseguer, F. Mirror-image-induced magnetic modes. ACS Nano 2012, 7, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mock, J.J.; Hill, R.T.; Tsai, Y.-J.; Chilkoti, A.; Smith, D.R. Probing dynamically tunable localized surface plasmon resonances of film-coupled nanoparticles by evanescent wave excitation. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rifat, A.A.; Mahdiraji, G.; Sua, Y.M.; Ahmed, R.; Shee, Y.; Adikan, F.M. Highly sensitive multi-core flat fiber surface plasmon resonance refractive index sensor. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 2485–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, M.; Lei, D.Y.; Giannini, V.; Lukiyanchuk, B.; Ranjbar, M.; Liew, T.Y.F.; Hong, M.; Maier, S.A. Subgroup decomposition of plasmonic resonances in hybrid oligomers: Modeling the resonance lineshape. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2101–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rifat, A.A.; Rahmani, M.; Xu, L.; Miroshnichenko, A.E. Hybrid Metasurface Based Tunable Near-Perfect Absorber and Plasmonic Sensor. Materials 2018, 11, 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071091
Rifat AA, Rahmani M, Xu L, Miroshnichenko AE. Hybrid Metasurface Based Tunable Near-Perfect Absorber and Plasmonic Sensor. Materials. 2018; 11(7):1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071091
Chicago/Turabian StyleRifat, Ahmmed A., Mohsen Rahmani, Lei Xu, and Andrey E. Miroshnichenko. 2018. "Hybrid Metasurface Based Tunable Near-Perfect Absorber and Plasmonic Sensor" Materials 11, no. 7: 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071091
APA StyleRifat, A. A., Rahmani, M., Xu, L., & Miroshnichenko, A. E. (2018). Hybrid Metasurface Based Tunable Near-Perfect Absorber and Plasmonic Sensor. Materials, 11(7), 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071091






