Polymerizable Microsphere-Induced High Mechanical Strength of Hydrogel Composed of Acrylamide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Material
2.2. Synthesis of Acrylamide/2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate Microspheres
2.3. Treatment of the Acrylamide/2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate Microspheres
2.4. Preparation of the Microsphere Hydrogel
2.5. Rheological Measurements
2.6. Strain–Stress Measurements
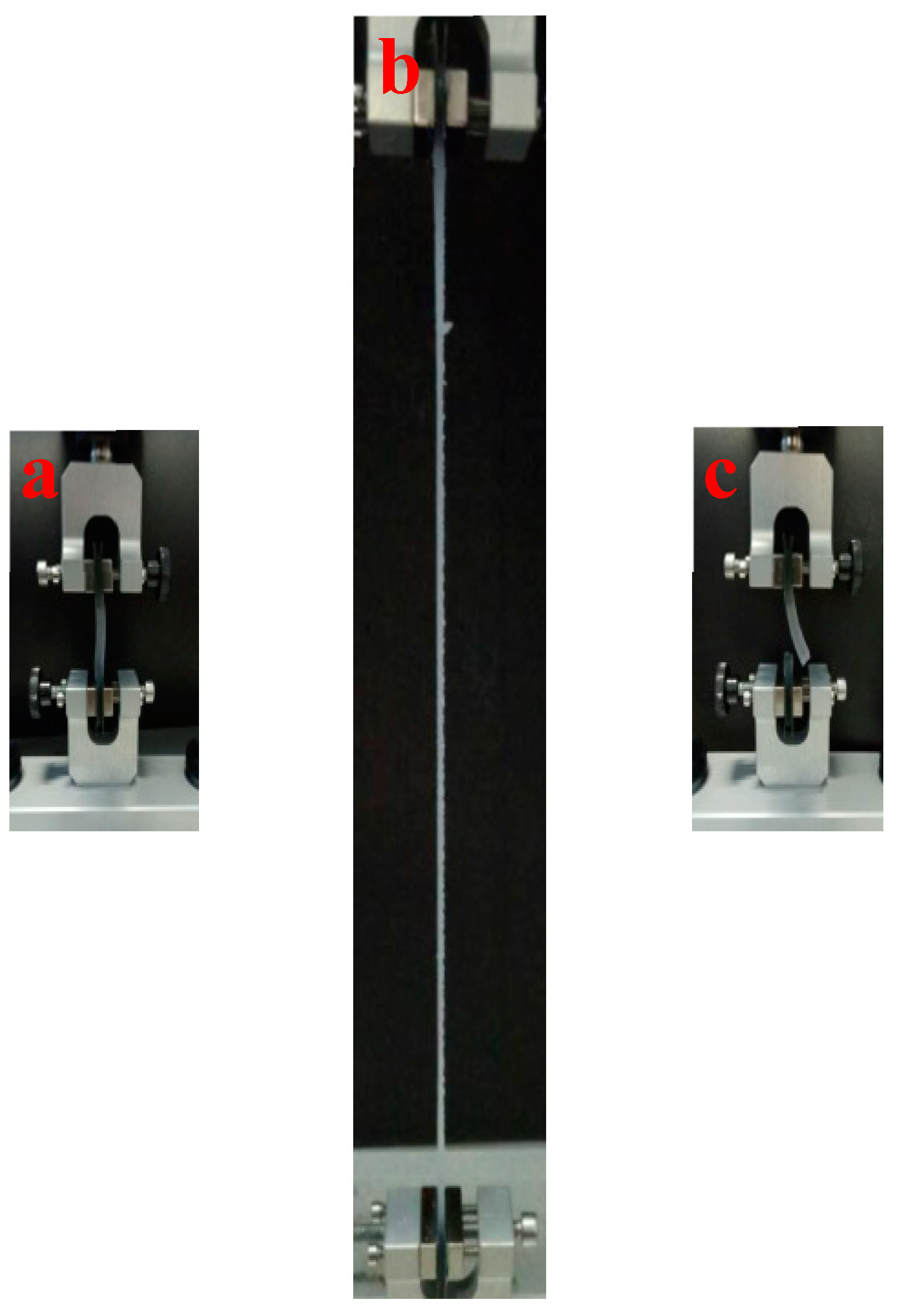
2.7. Tensile Test
2.8. Compression Strength Measurements
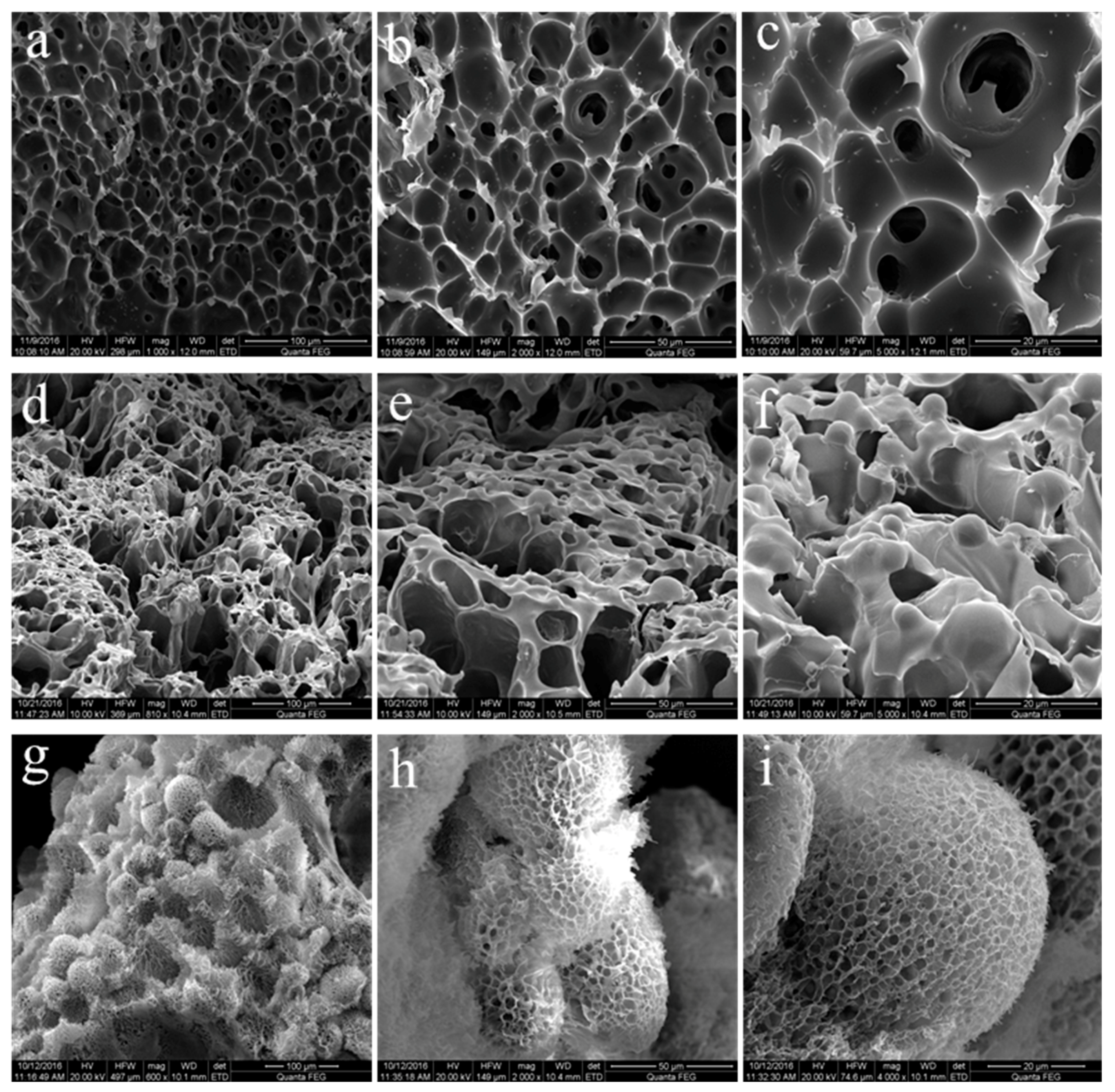
2.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results and Discussion
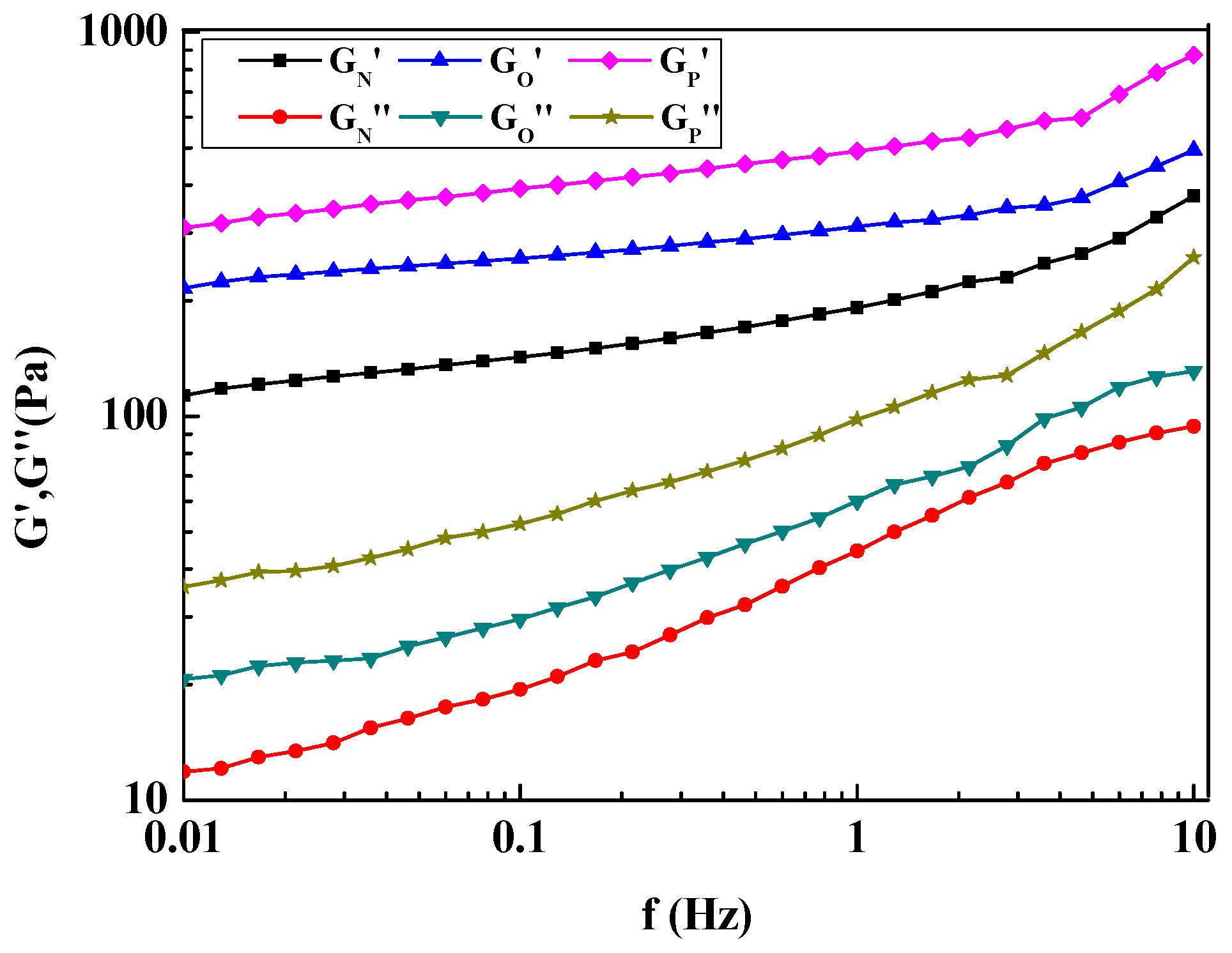
3.1. Rheological Behavior of Microsphere Hydrogel
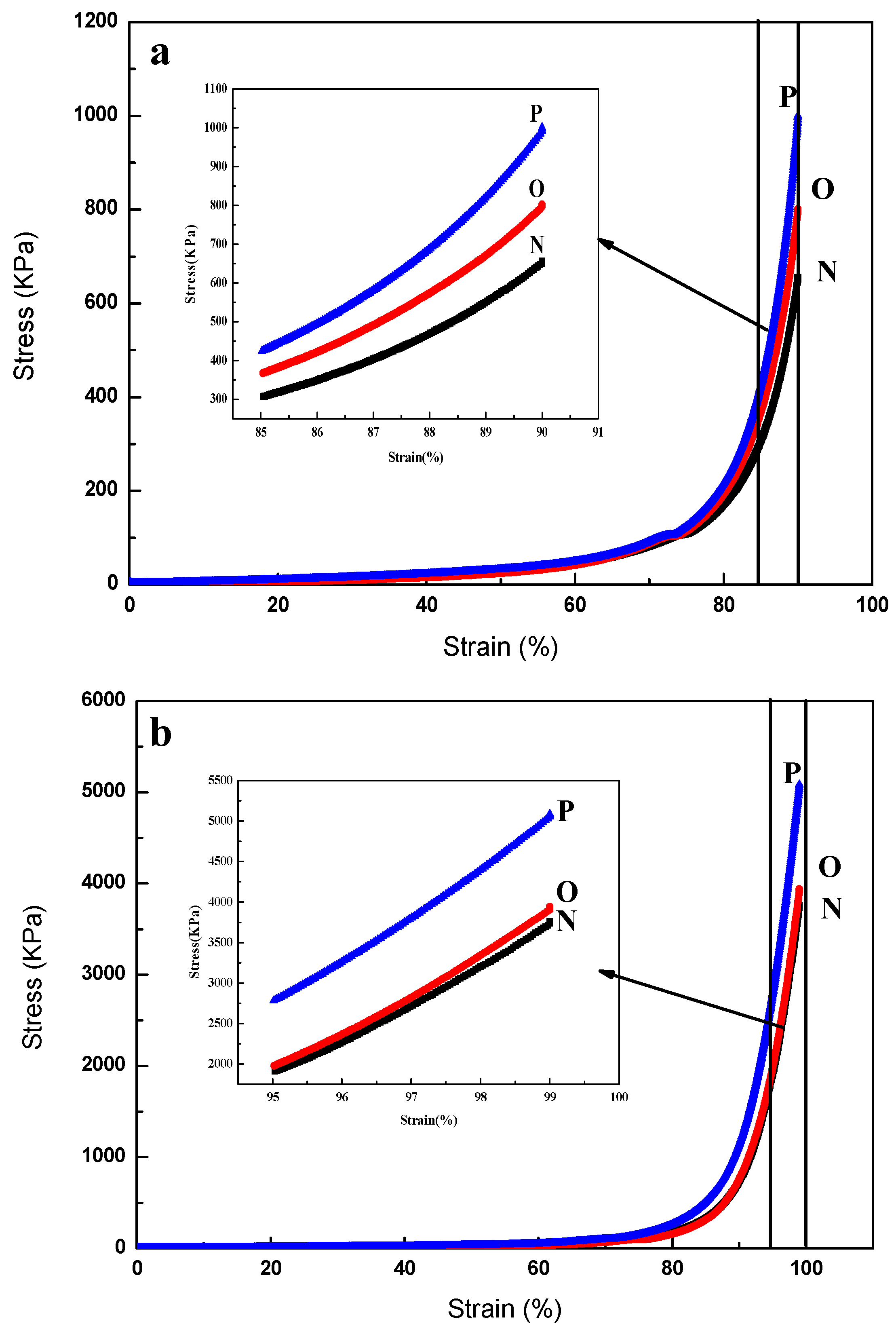
3.2. Strain–Stress Properties of Microsphere Hydrogels
3.3. Tensile Properties of Microsphere Hydrogels
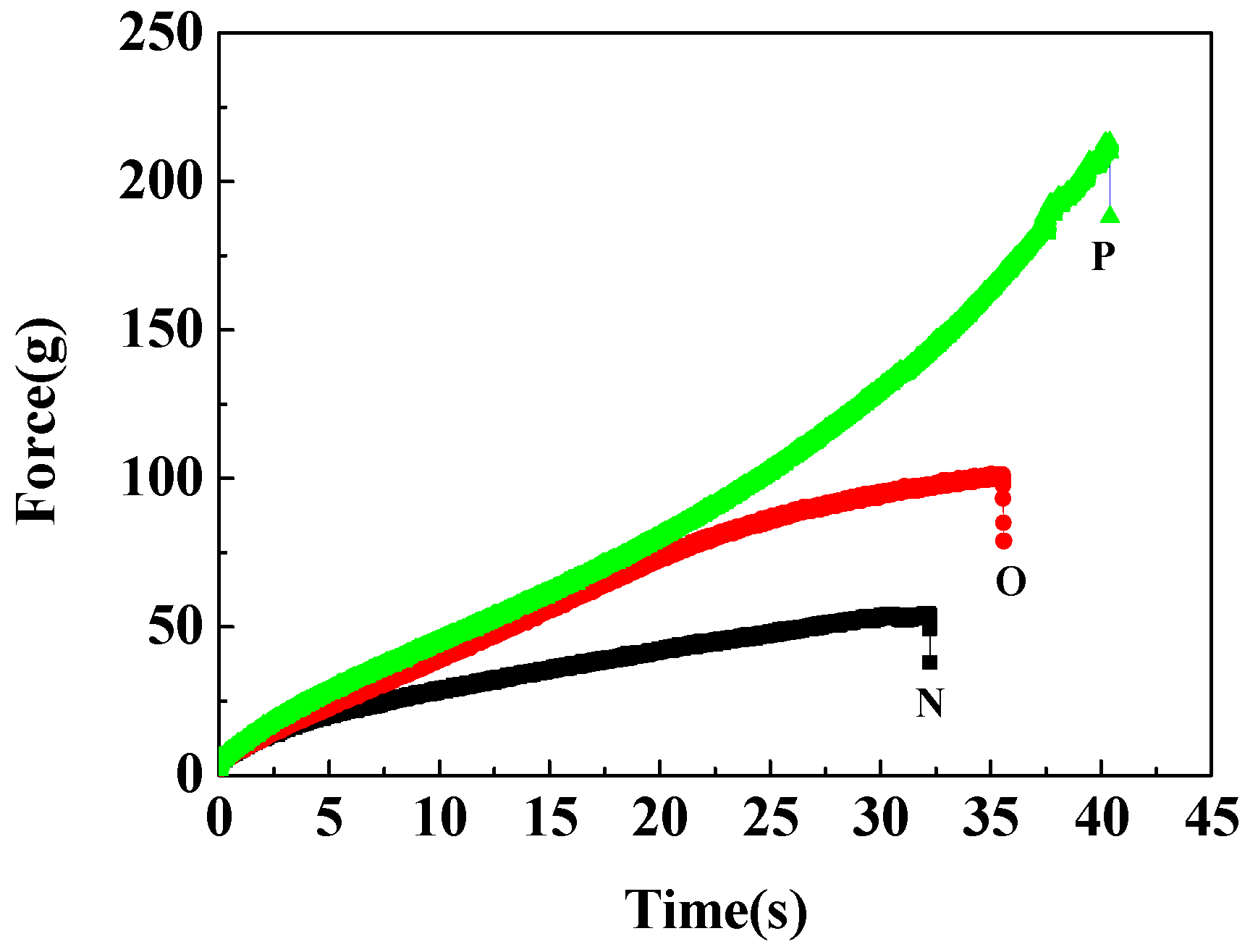
3.4. Compression Strength of Microsphere Hydrogel
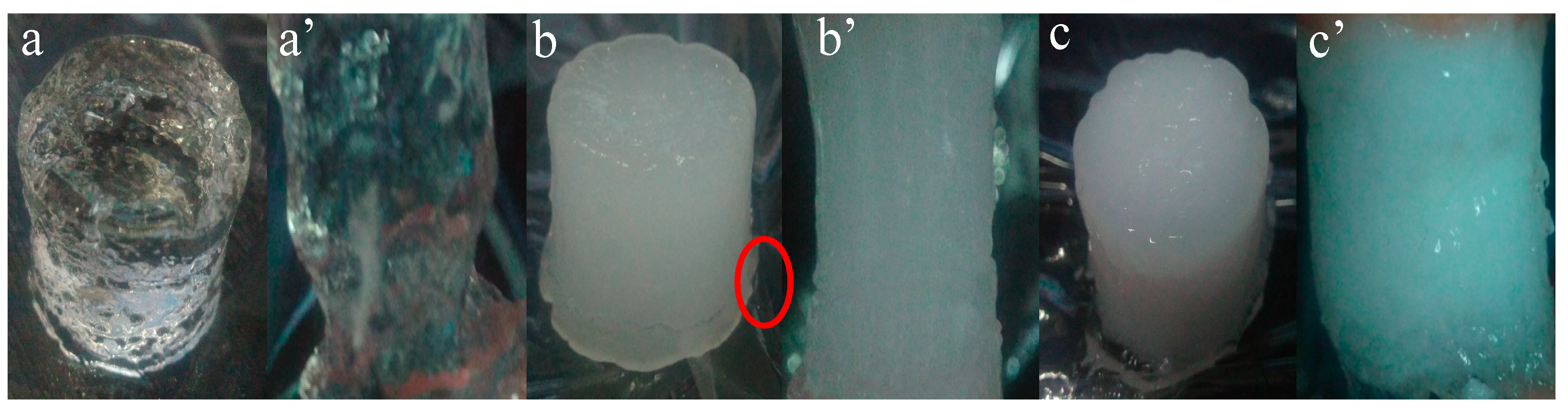
3.5. Morphology and Gelling Mechanism of Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, F.; Lin, M.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Song, F. Nanosilica-induced high mechanical strength of nanocomposite hydrogel for killing fluids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 458, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangwan, W.; Petcharoen, K.; Paradee, N.; Lerdwijitjarud, W.; Sirivat, A. Electrically responsive materials based on polycarbazole/sodium alginate hydrogel blend for soft and flexible actuator application. Carbohyd. Polym. 2016, 151, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Braschler, T.; Anker, R.; Wildhaber, F.; Bertsch, A.; Brugger, J.; Renaud, P. Composite hydrogel-loaded alumina membranes for nanofluidic molecular filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 477, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, D.; Liu, Z.; Li, J. Calcium alginate hydrogel filtration membrane with excellent anti-fouling property and controlled separation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 492, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tao, L.; Shuxi, L.; Wei, Y. Synthesis of Multiresponsive and Dynamic Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Controlled Release of Bioactive Molecules. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2894–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Xu, Z.; Yang, X.; He, Y.; Lin, R. Construction and characterization of a pure protein hydrogel for drug delivery application. Int. J. Biol. Marcomol. 2017, 95, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, V. Crosslinking of poly(vinylpyrrolidone/acrylic acid with tragacanth gum for hydrogels formation for use in drug delivery applications. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 157, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Tsang, W.P.; Wan, C.; Wu, C. Fabrication of injectable high strength hydrogel based on 4-arm star PEG for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2017, 120, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Ma, Y.; Tan, H.; Jia, Y.; Zou, S.; Guo, S.; Zhao, M.; Huang, H.; Ling, Z.; Chen, Y. Covalent and injectable chitosan-chondroitin sulfate hydrogels embedded with chitosan microspheres for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Chen, D. A new polymer/clay nano-composite hydrogel with improved response rate and tensile mechanical properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 2125–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, K.; Takehisa, T. Nanocomposite hydrogels: A unique organic–inorganic network structure with extraordinary mechanical, optical, and swelling/de-swelling properties. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, K.; Takehisa, A.T.; Fan, S. Effects of clay content on the properties of nanocomposite hydrogels composed of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and clay. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 10162–10171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, K.; Li, H.J. Mechanical properties and structure of polymer−clay nanocomposite gels with high clay content. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 1898–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, J. Preparation and mechanical properties of silica nanoparticles reinforced composite hydrogels. Mater. Lett. 2014, 120, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ji, S.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Yang, H. Synthesis of mesoporous γ-AlOOH@Fe3O4 magnetic nanomicrospheres. Particuology 2012, 10, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Pi, F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Photocatalytic degradation of Acephate, Omethoate, and Methyl parathion by Fe3O4@SiO2@mTiO2 nanomicrospheres. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 315, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wang, C. Multihollow nanocomposite microspheres with tunable pore structures by templating Pickering double emulsions. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazan, Y.D.; Märkl, V.; Heinecke, J.; Aneziris, C.; Graule, T. Functional ceramic and nanocomposite fibers, cellular articles and microspheres via radiation curable colloidal dispersions. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 2601–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tong, Z. Facile fabrication of nanocomposite microspheres with polymer cores and magnetic shells by Pickering suspension polymerization. React. Funct. Polym. 2009, 69, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, K.; Li, H.J.; Matsuda, K.; Takehisa, T.; Elliott, E. Mechanism of forming organic/inorganic network structures during in-situ free-radical polymerization in PNIPA−clay nanocomposite hydrogels. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhu, M.; Hu, X.; Liu, X.; Tong, Z. Ultrahigh deformability and transparence of hectorite clay nanocomposite hydrogels with nimble pH response. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 3811–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Du, B.; Oppermann, W. Influence of formation conditions on spatial inhomogeneities in poly(N-isopropylacrylamide. Hydrogels. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 6558–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lu, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, C. Polymer gel nanoparticle networks. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lu, X.; Gao, J. Hydrogel Opals. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 1708–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, N.; Endo, T.; Iwasaki, Y.; Akiyoshi, K. Design of hybrid hydrogels with self-assembled nanogels as cross-linkers: interaction with proteins and chaperone-like activity. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Xu, H.G.; Jiao, K.X.; Zhu, L.P.; Brown, H.R.; Wang, H.L. A novel hydrogel with high mechanical strength: A macromolecular microsphere composite hydrogel. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 1622–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Song, S.; Ren, X.; Gao, G. Highly tough, anti-fatigue and rapidly self-recoverable hydrogels reinforced by core-shell inorganic-organic hybrid latex particles. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 6059–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Liang, X.; Li, P.; Deng, Y.; Pei, X.; Tan, Y.; Zhai, K.; Wang, P. Tough, stretchable chemically cross-linked hydrogel using core–shell polymer microspheres as cross-linking junctions. Polymer 2017, 118, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Hydrogel Sample | AM % (Mass Fraction) | Polymeric Microsphere % (Mass Fraction) | MBA % (Mass Fraction) | Compression Strength (kPa·m−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N sample | 8 | 0 | 0.05 | 100.44 |
| O sample | 6 | 2 | 0.05 | 202.45 |
| P sample | 6 | 2 | 0.05 | 248.00 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Lin, M.; Wang, M.; Song, X.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z. Polymerizable Microsphere-Induced High Mechanical Strength of Hydrogel Composed of Acrylamide. Materials 2018, 11, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11060880
Wang Z, Lin M, Wang M, Song X, Zhang C, Dong Z, Zhang J, Yang Z. Polymerizable Microsphere-Induced High Mechanical Strength of Hydrogel Composed of Acrylamide. Materials. 2018; 11(6):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11060880
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhiyong, Meiqin Lin, Menghan Wang, Xia Song, Chuqiao Zhang, Zhaoxia Dong, Juan Zhang, and Zihao Yang. 2018. "Polymerizable Microsphere-Induced High Mechanical Strength of Hydrogel Composed of Acrylamide" Materials 11, no. 6: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11060880
APA StyleWang, Z., Lin, M., Wang, M., Song, X., Zhang, C., Dong, Z., Zhang, J., & Yang, Z. (2018). Polymerizable Microsphere-Induced High Mechanical Strength of Hydrogel Composed of Acrylamide. Materials, 11(6), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11060880






