Effect of Temperature and Growth Time on Vertically Aligned ZnO Nanorods by Simplified Hydrothermal Technique for Photoelectrochemical Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of ZnO Nanorods
2.2. Characterization of ZnO Nanorods
2.3. Photoelectrochemical Performance of ZnO Nanorods
3. Results and Discussion
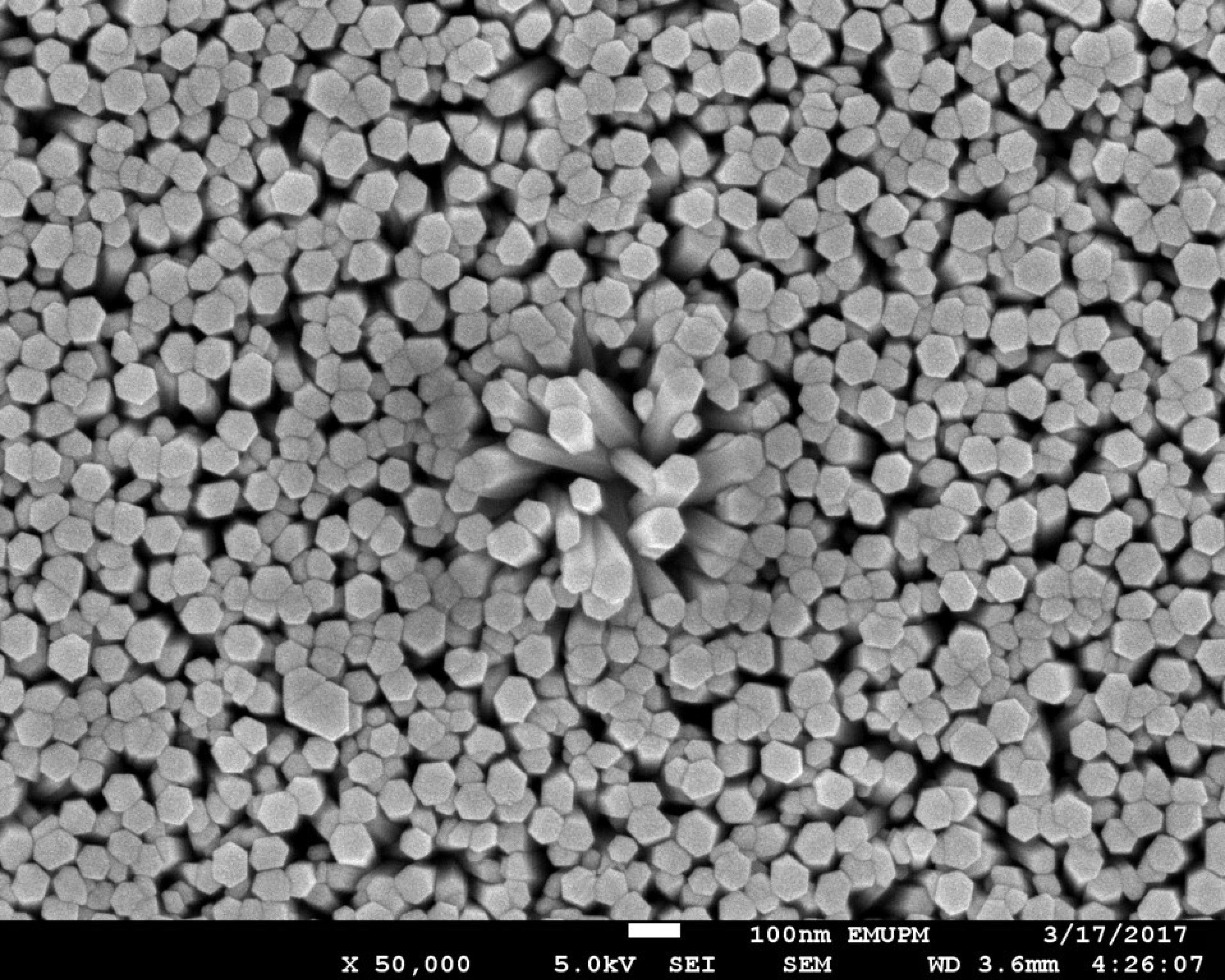
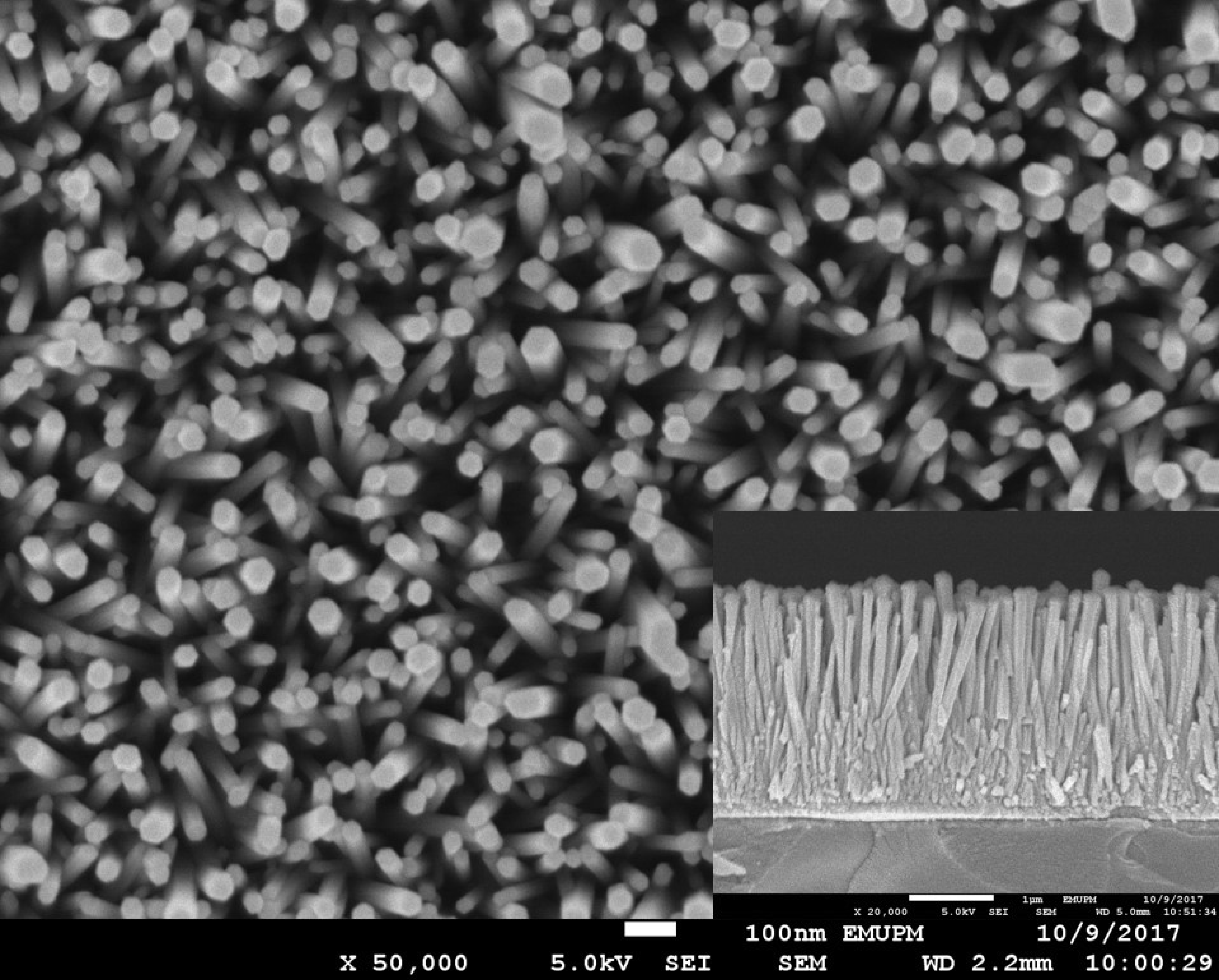
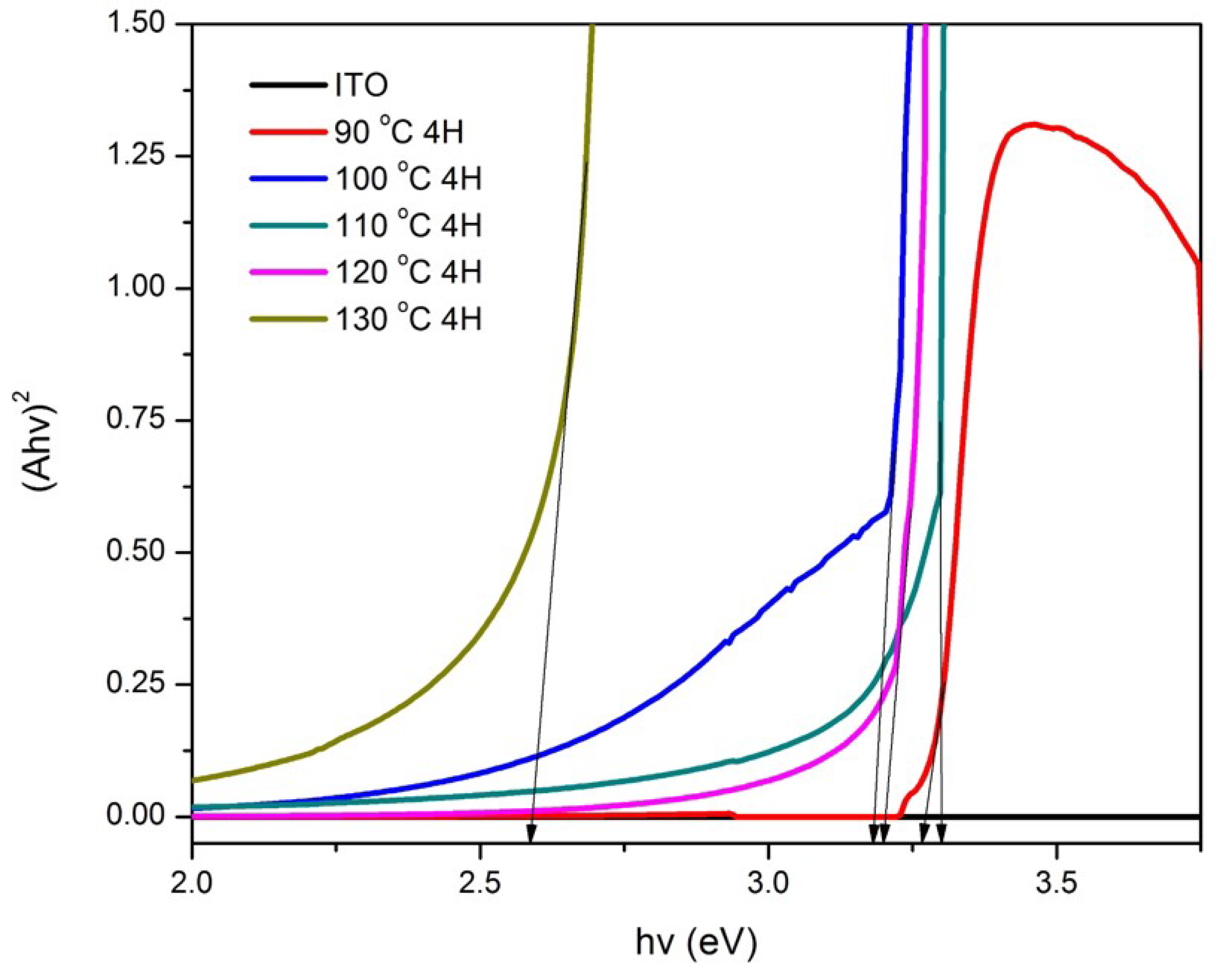
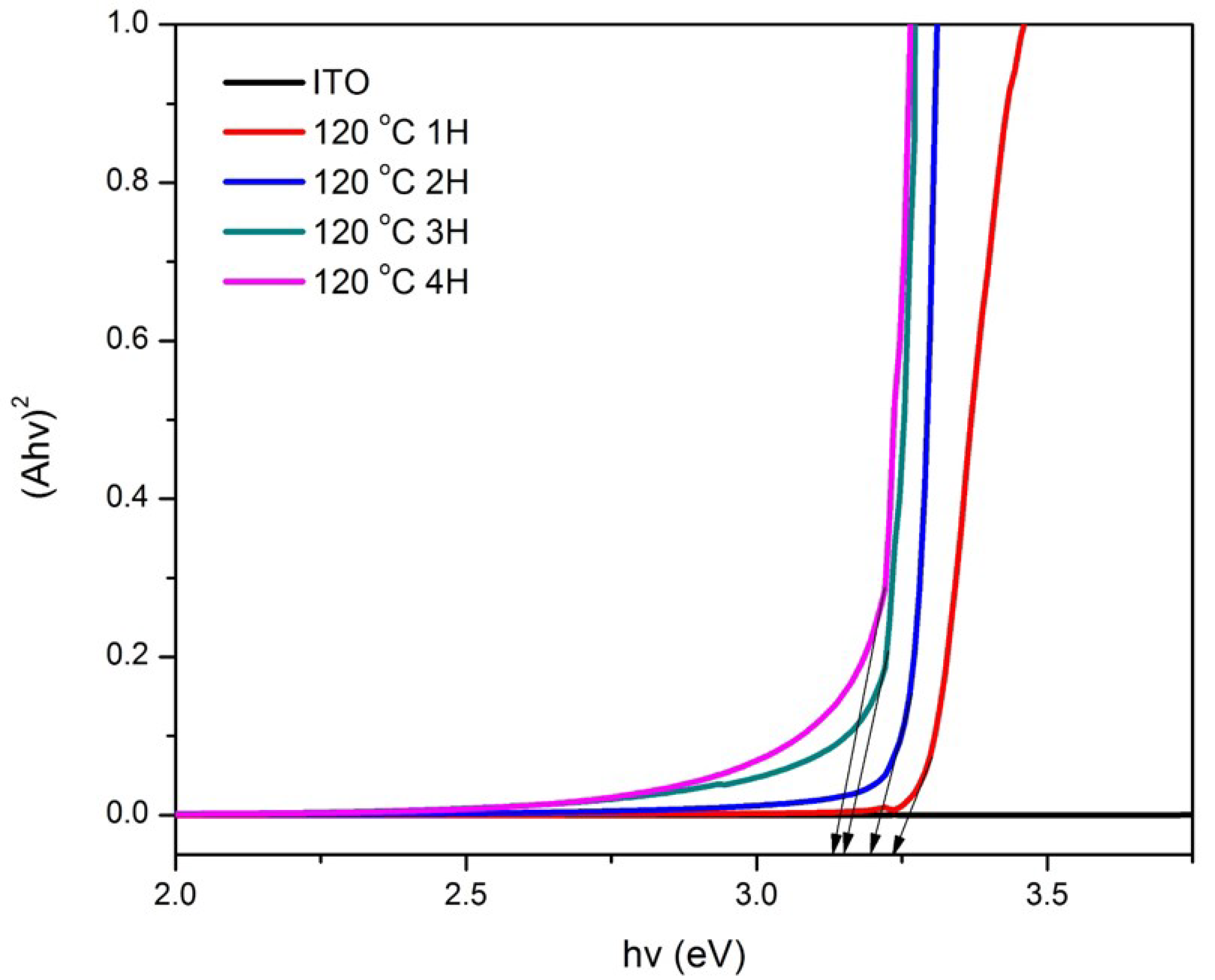
3.1. Structural and Optical Characterization of ZnO Nanorods
3.2. Photoelectrochemical Measurements of ZnO Nanorods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fortunato, E.; Gonçalves, A.; Pimentel, A.; Barquinha, P.; Gonçalves, G.; Pereira, L.; Ferreira, I.; Martins, R. Zinc oxide, a multifunctional material: From material to device applications. Appl. Phys. A 2009, 96, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, R.; Thavasi, V.; Ramakrishna, S. Metal oxides for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Fang, Y.; Pang, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, J.; Ge, W.; Yang, S. ZnO nanobelt arrays grown directly from and on zinc substrates: Synthesis, characterization, and applications. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 15303–15308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.Y.; Ding, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, Z.L. Single-crystal nanorings formed by epitaxial self-coiling of polar nanobelts. Science 2004, 303, 1348–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.X.; Ding, Y.; Mai, W.; Hughes, W.L.; Lao, C.; Wang, Z.L. Conversion of zinc oxide nanobelts into superlattice-structured nanohelices. Science 2005, 309, 1700–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holi, A.M.; Zainal, Z.; Talib, Z.A.; Lim, H.N.; Yap, C.C.; Chang, S.K.; Ayal, A.K. Hydrothermal deposition of CdS on vertically aligned ZnO nanorods for photoelectrochemical solar cell application. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 7353–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, R.F.; Feng, H.T.; Liang, Q.; Liu, J.Z.; Chen, J.T.; Yan, D.; Feng, J.J.; Li, H.J.; Cheng, S.; Geng, B.S. Morphology-controlled synthesis, growth mechanism, optical and microwave absorption properties of ZnO nanocombs. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 185405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rackauskas, S.; Klimova, O.; Jiang, H.; Nikitenko, A.; Chernenko, K.A.; Shandakov, S.D.; Kauppinen, E.I.; Tolochko, O.V.; Nasibulin, A.G. A novel method for continuous synthesis of ZnO tetrapods. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 16366–16373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Zinc oxide nanostructures: Growth, properties and applications. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2004, 16, R829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Chang, Y.; Long, Y. High performance of nanostructured ZnO film gas sensor at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnol, M.S.; Avouris, P.; Pan, Z.W.; Wang, Z.L. Field-effect transistors based on single semiconducting oxide nanobelts. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.J.; Zhou, M. Size-dependent thermal conductivity of zinc oxide nanobelts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 141921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Mei, Z.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, T.; Hou, Y.; Kuznetsov, A.Y. Controlled growth of high-quality ZnO-based films and fabrication of visible-blind and solar-blind ultra-violet detectors. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4625–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krunks, M.; Katerski, A.; Dedova, T.; Acik, I.O.; Mere, A. Nanostructured solar cell based on spray pyrolysis deposited ZnO nanorod array. Sol. Energy Mater. Solar Cells 2008, 92, 1016–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc oxide—From synthesis to application: A review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mridha, S.; Basak, D. Effect of thickness on the structural, electrical and optical properties of ZnO films. Mater. Res. Bull. 2007, 42, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, V.R.; Lokhande, C.D.; Mane, R.S.; Han, S.H. Hydrophobic and textured ZnO films deposited by chemical bath deposition: Annealing effect. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 245, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shum, K.; Salagaj, T.; Zhang, W.; Strobl, K. ZnO thin films synthesized by chemical vapor deposition. In Proceedings of the 2010 Long Island Systems, Applications and Technology Conference (LISAT), Farmingdale, NY, USA, 7 May 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, C.Z.; Yang, L.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Smith, J.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Rapid Thermal Annealing on the Structural, Electrical, and Optical Properties of Zr-Doped ZnO Thin Films Grown by Atomic Layer Deposition. Materials 2016, 9, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, B.; Yamada, A.; Konagai, M. Textured ZnO thin films for solar cells grown by a two-step process with the atomic layer deposition technique. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 37, L206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwoka, M.; Lyson-Sypien, B.; Kulis, A.; Maslyk, M.; Borysiewicz, M.A.; Kaminska, E.; Szuber, J. Surface Properties of Nanostructured, Porous ZnO Thin Films Prepared by Direct Current Reactive Magnetron Sputtering. Materials 2018, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carcia, P.F.; McLean, R.S.; Reilly, M.H.; Nunes, G., Jr. Transparent ZnO thin-film transistor fabricated by rf magnetron sputtering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, P.; Mondal, S. Structural and morphological characterization of ZnO thin films synthesized by SILAR. Prog. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2013, 1, 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, N.; Parija, B.; Panigrahi, S. Fundamental understanding and modeling of spin coating process: A review. Indian J. Phys. 2009, 83, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, M. Studies on Chemical Bath Deposited Semiconducting Copper Selenide and Iron Sulfide Thin Films Useful for Photovoltaic Application; Doctor of Philosophy, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Department of Physics Cochin University of Science and Technology: Cochin, India, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Creighton, J.R.; Ho, P. Introduction to chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Chem. Vap. Depos. 2001, 2, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Moshe, H.; Mastai, Y. Atomic layer deposition on self-assembled-monolayers. In Materials Science-Advanced Topics; InTech: London, UK, 2013; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/materials-science-advanced-topics/atomic-layer-deposition-on-self-assembled-monolayers (accessed on 10 February 2018).
- Minami, T.; Nanto, H.; Shooji, S.; Takata, S. The stability of zinc oxide transparent electrodes fabricated by RF magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 1984, 111, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, M.A.; Suryawanshi, M.P.; Nikam, S.S.; Bhosale, C.H.; Kim, J.H.; Moholkar, A.V. Influence of Zn concentration and dye adsorption time on the photovoltaic performance of M-SILAR deposited ZnO-based dye sensitized solar cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2016, 329, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J.; Grigorovici, R.; Vancu, A. Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys. Status Solidi 1966, 15, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viezbicke, B.D.; Patel, S.; Davis, B.E.; Birnie, D.P. Evaluation of the Tauc method for optical absorption edge determination: ZnO thin films as a model system. Phys. Status Solidi 2015, 252, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, G.; Asif, M.H.; Zainelabdin, A.; Zaman, S.; Nur, O.; Willander, M. Influence of pH, precursor concentration, growth time, and temperature on the morphology of ZnO nanostructures grown by the hydrothermal method. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, A.; Samouco, A.; Nunes, D.; Araújo, A.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Ultra-Fast Microwave Synthesis of ZnO Nanorods on Cellulose Substrates for UV Sensor Applications. Materials 2017, 10, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.J.; Lee, S.; Yu, Y.; Hong, S.M.; Choi, H.C.; Choi, M.Y. Low-temperature hydrothermal growth of ZnO nanorods on sol–gel prepared ZnO seed layers: Optimal growth conditions. Thin Solid Films 2012, 524, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




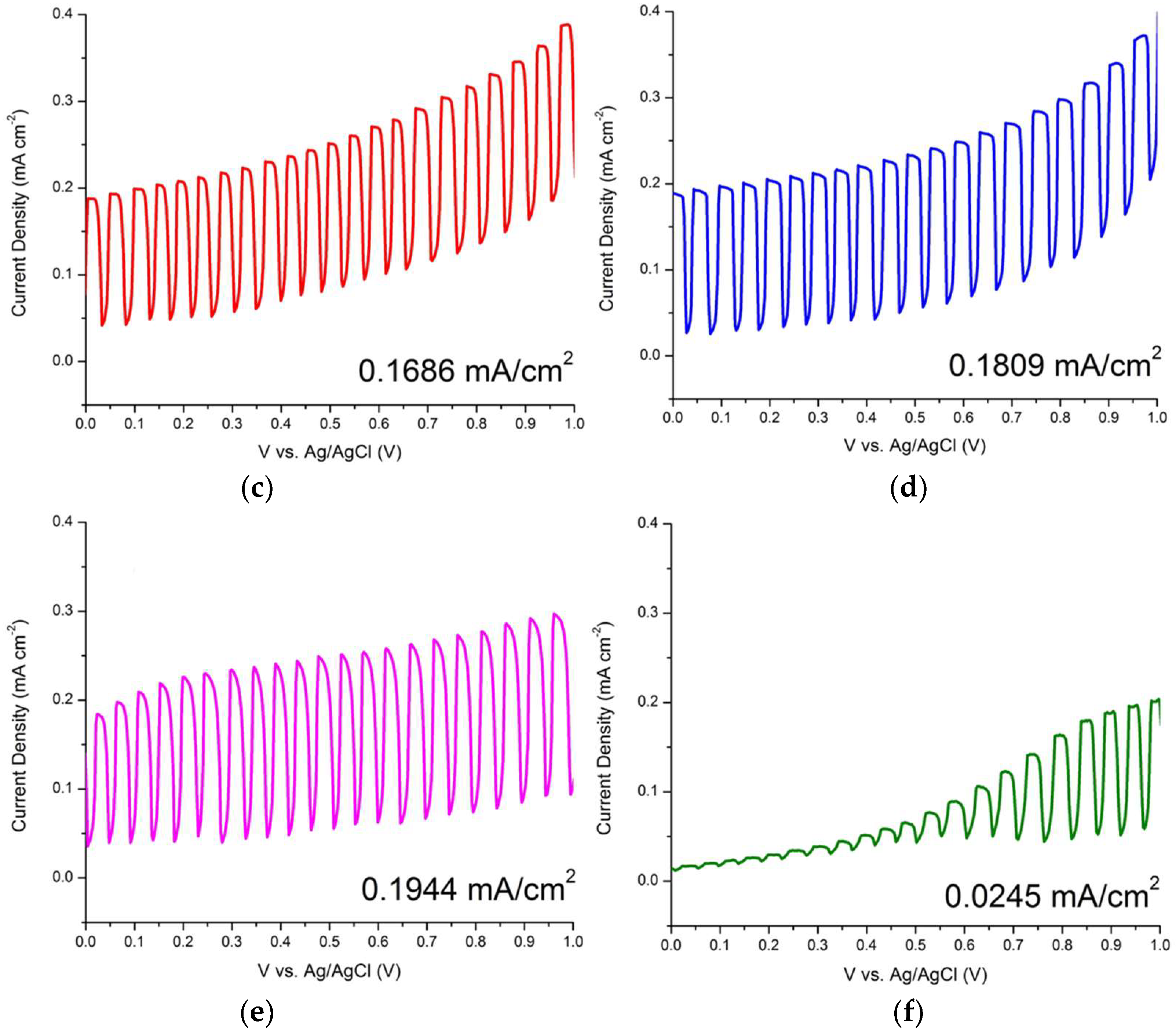


| ZnO/ITO Nanorods Prepared at Various Hydrothermal Temperatures (°C) | Photocurrent Density (mA/cm2) |
|---|---|
| 90 | 0.1061 |
| 100 | 0.1686 |
| 110 | 0.1809 |
| 120 | 0.1944 |
| 130 | 0.0245 |
| ITO | 0.0028 |
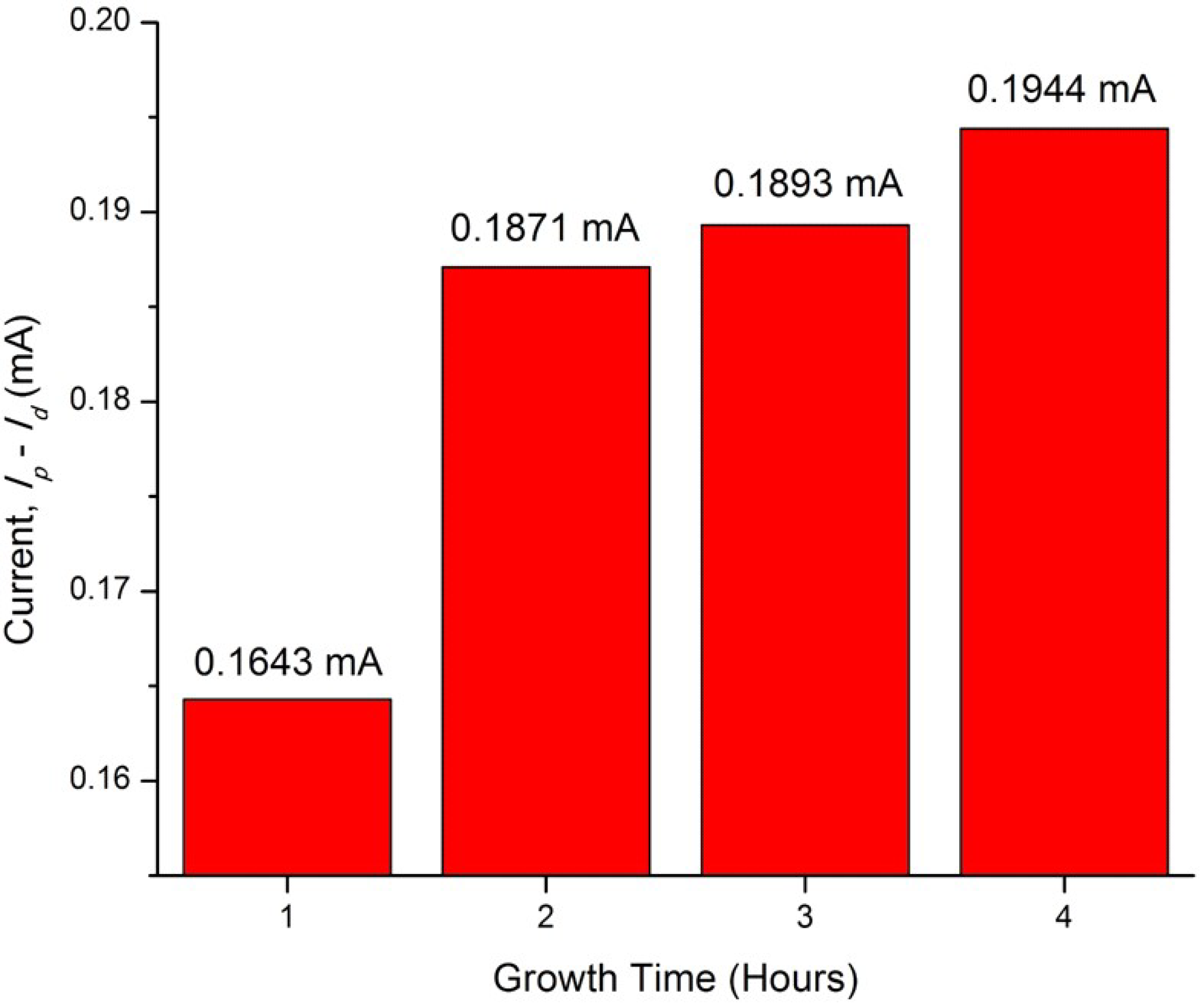
| ZnO/ITO Nanorods Prepared at Various Growth Time (h) | Photocurrent Density (mA/cm2) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1643 |
| 2 | 0.1871 |
| 3 | 0.1893 |
| 4 | 0.1944 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohd Fudzi, L.; Zainal, Z.; Lim, H.N.; Chang, S.-K.; Holi, A.M.; Sarif@Mohd Ali, M. Effect of Temperature and Growth Time on Vertically Aligned ZnO Nanorods by Simplified Hydrothermal Technique for Photoelectrochemical Cells. Materials 2018, 11, 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050704
Mohd Fudzi L, Zainal Z, Lim HN, Chang S-K, Holi AM, Sarif@Mohd Ali M. Effect of Temperature and Growth Time on Vertically Aligned ZnO Nanorods by Simplified Hydrothermal Technique for Photoelectrochemical Cells. Materials. 2018; 11(5):704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050704
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohd Fudzi, Laimy, Zulkarnain Zainal, Hong Ngee Lim, Sook-Keng Chang, Araa Mebdir Holi, and Mahanim Sarif@Mohd Ali. 2018. "Effect of Temperature and Growth Time on Vertically Aligned ZnO Nanorods by Simplified Hydrothermal Technique for Photoelectrochemical Cells" Materials 11, no. 5: 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050704
APA StyleMohd Fudzi, L., Zainal, Z., Lim, H. N., Chang, S.-K., Holi, A. M., & Sarif@Mohd Ali, M. (2018). Effect of Temperature and Growth Time on Vertically Aligned ZnO Nanorods by Simplified Hydrothermal Technique for Photoelectrochemical Cells. Materials, 11(5), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050704







