Different Effects of NSF and PCE Superplasticizer on Adsorption, Dynamic Yield Stress and Thixotropy of Cement Pastes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Materials and Mixing Procedures
2.2. Rheometer and Rheological Tests
2.3. Adsorption Test or Total Organic Carbon (TOC) Test
3. Results
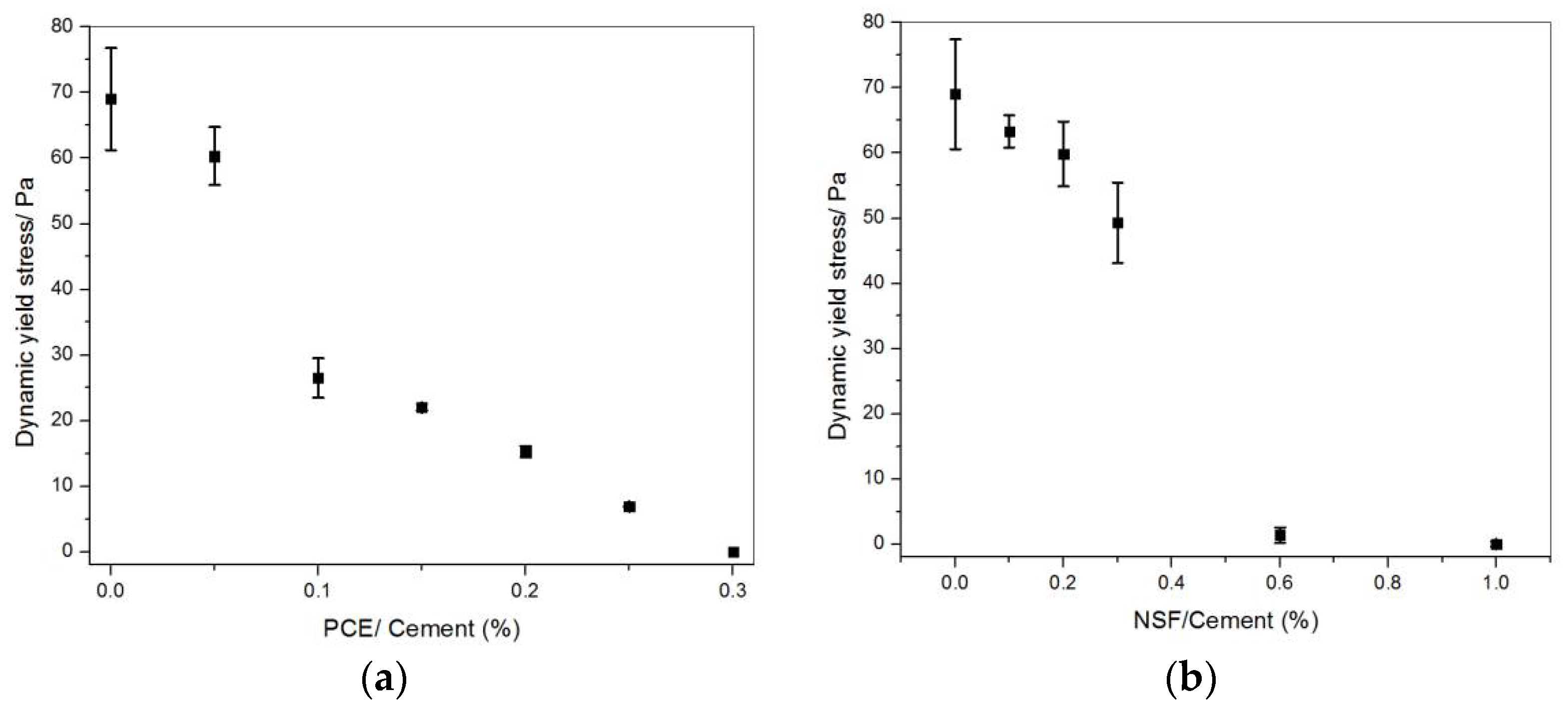
3.1. Equilibrium Flow Curve and Dynamic Yield Stress
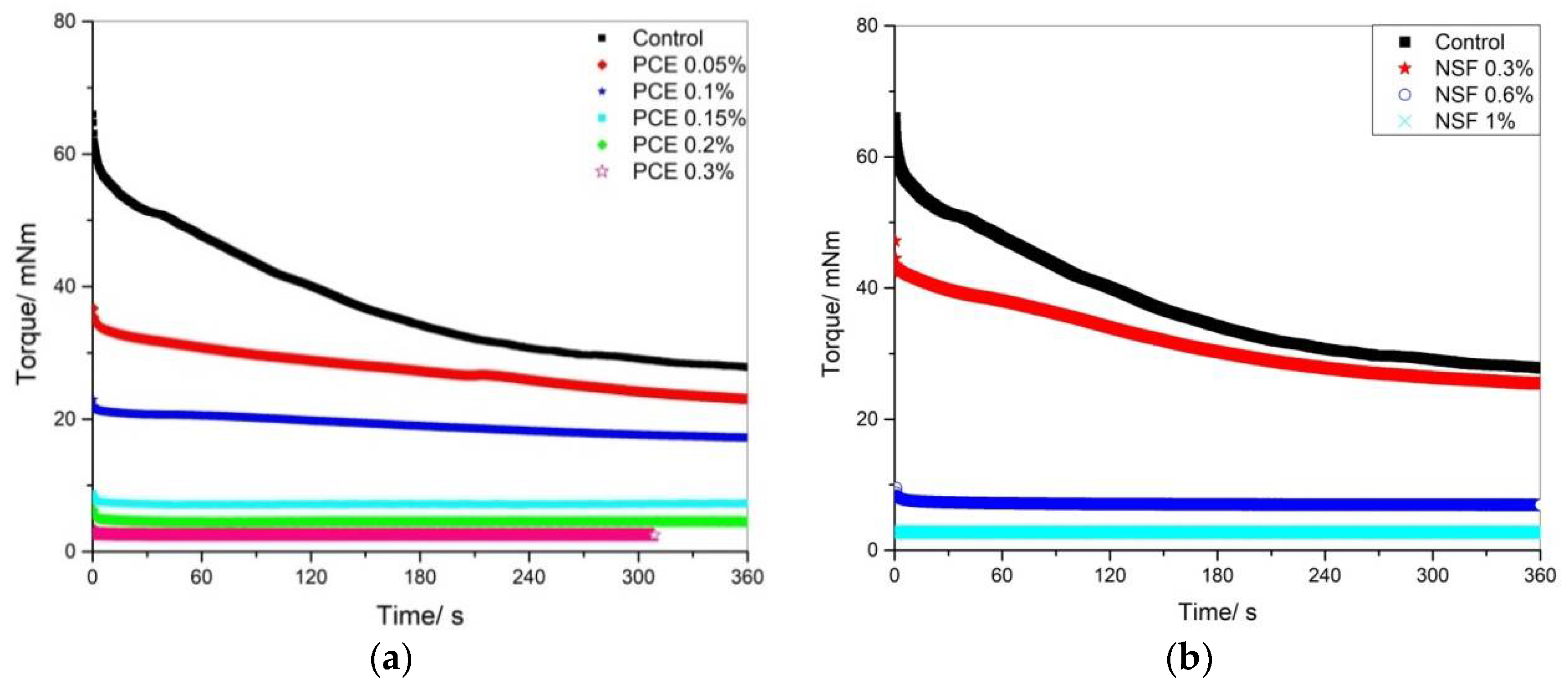
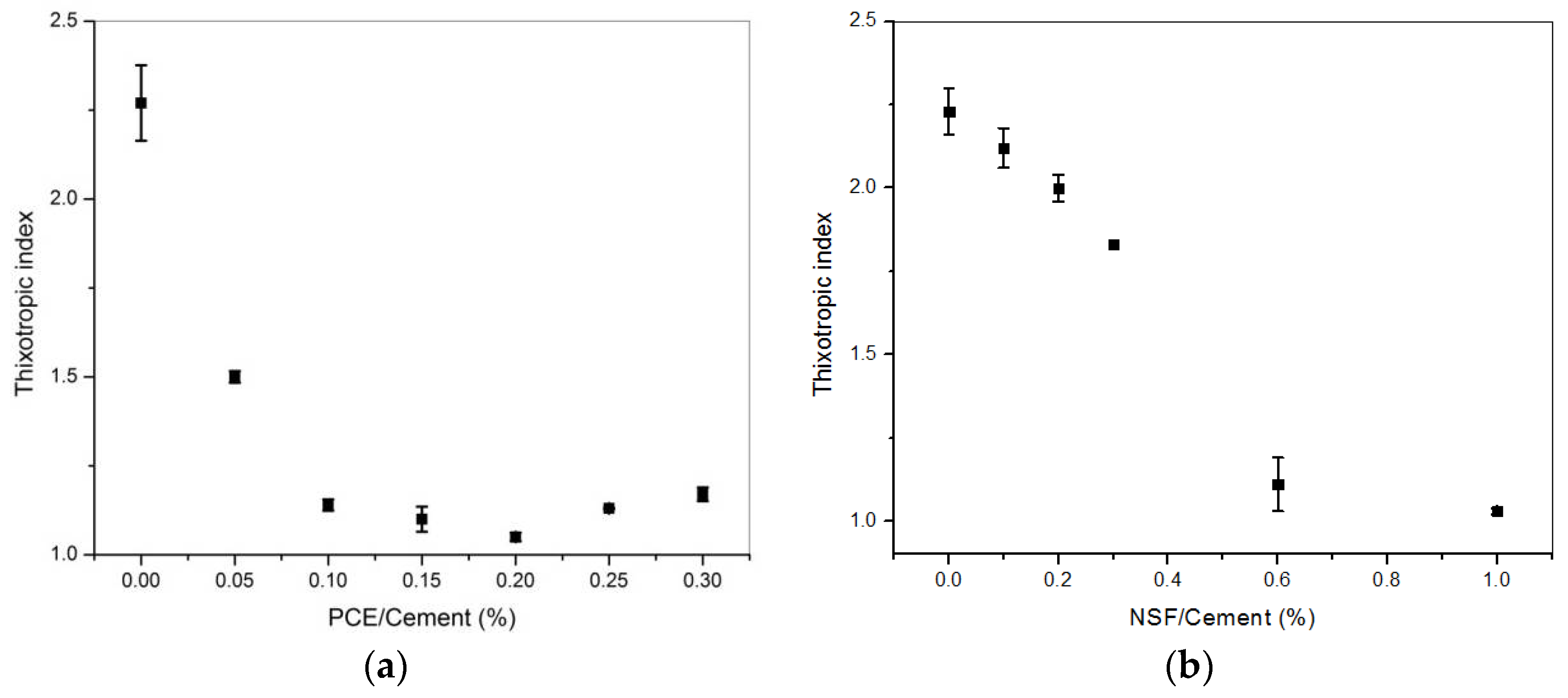
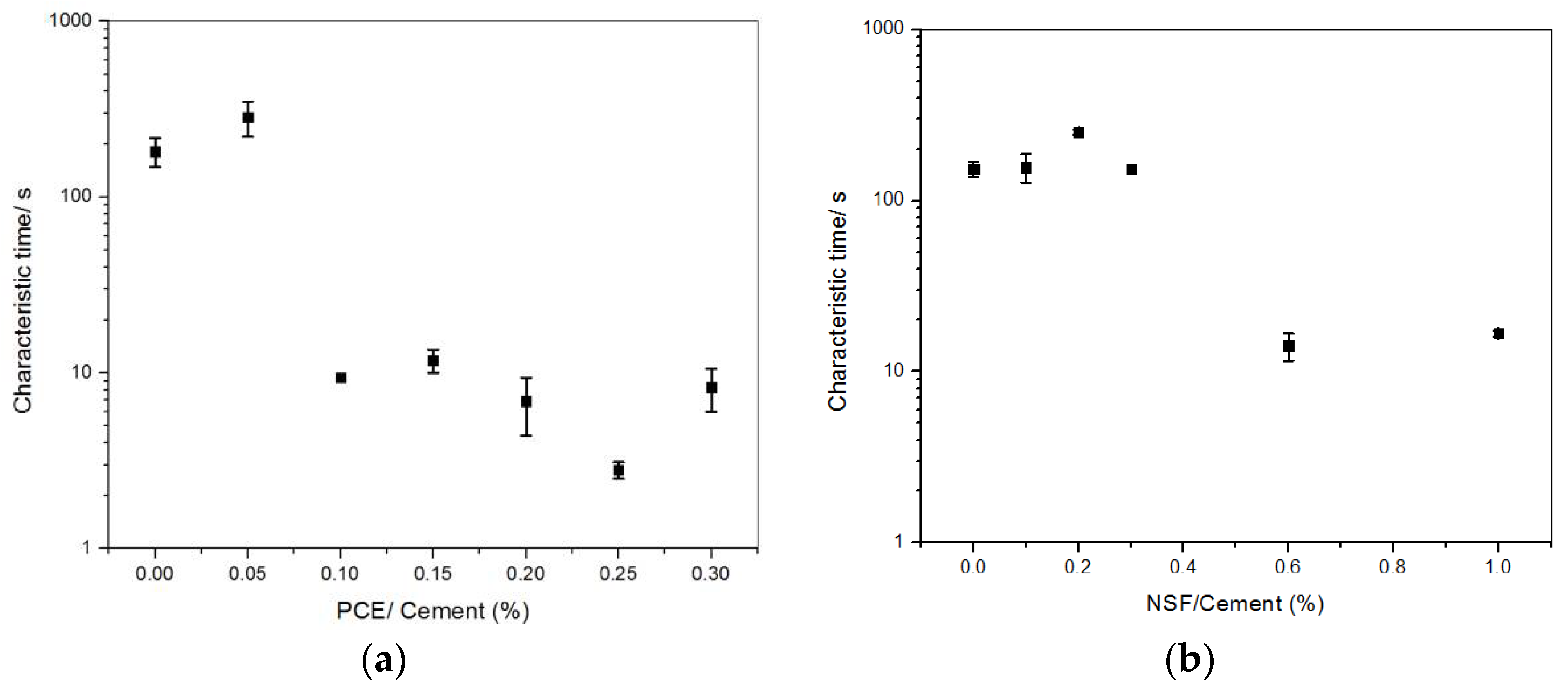
3.2. Thixotropy of Cement Pastes with Various PCE Addition
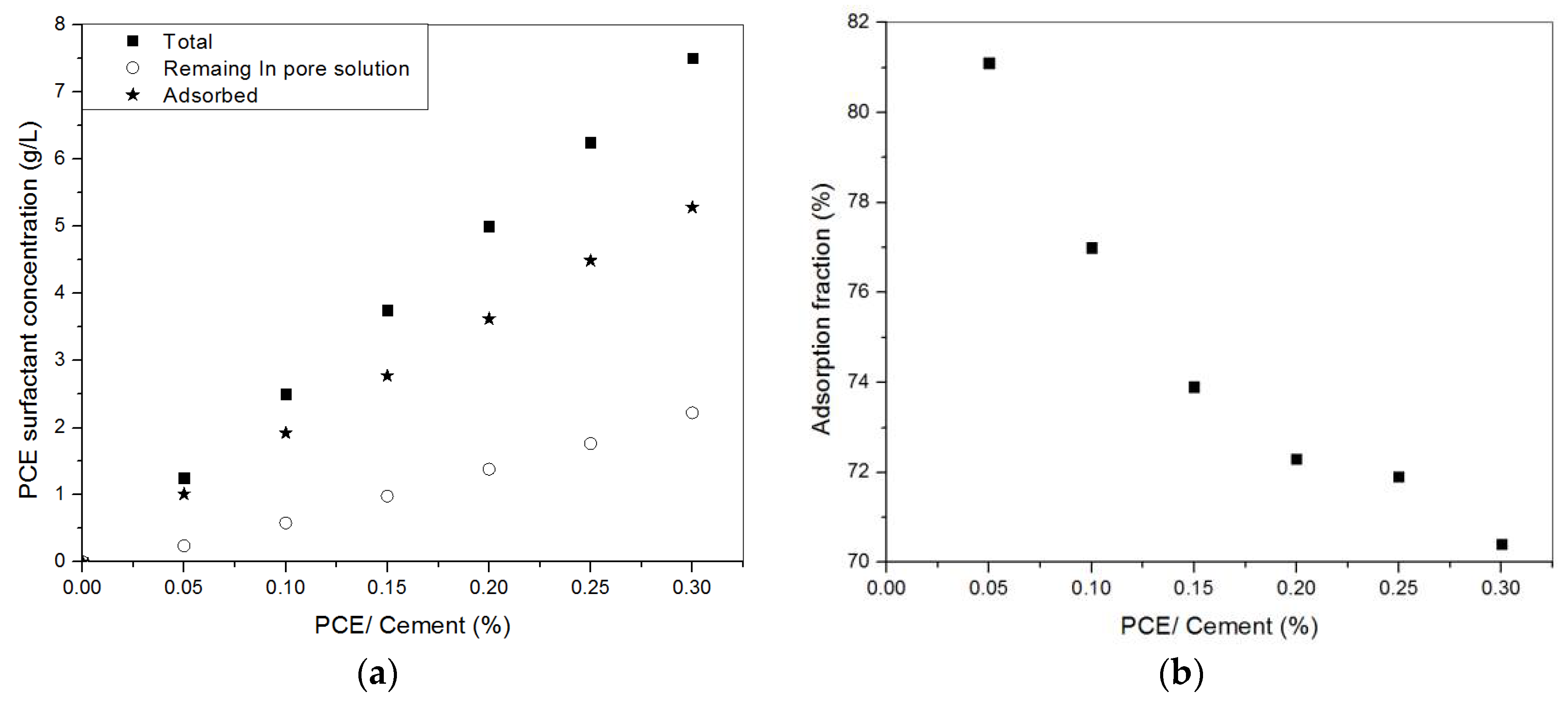
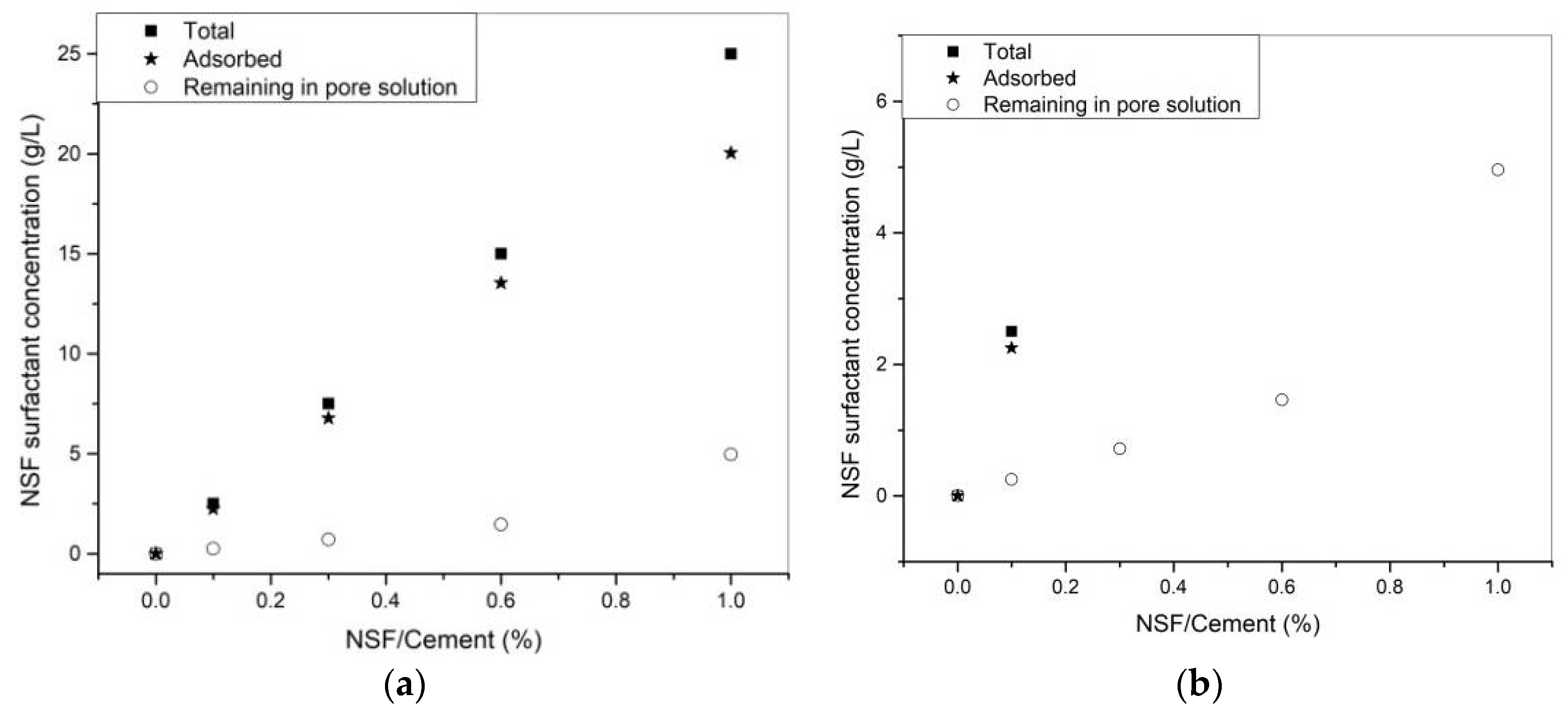
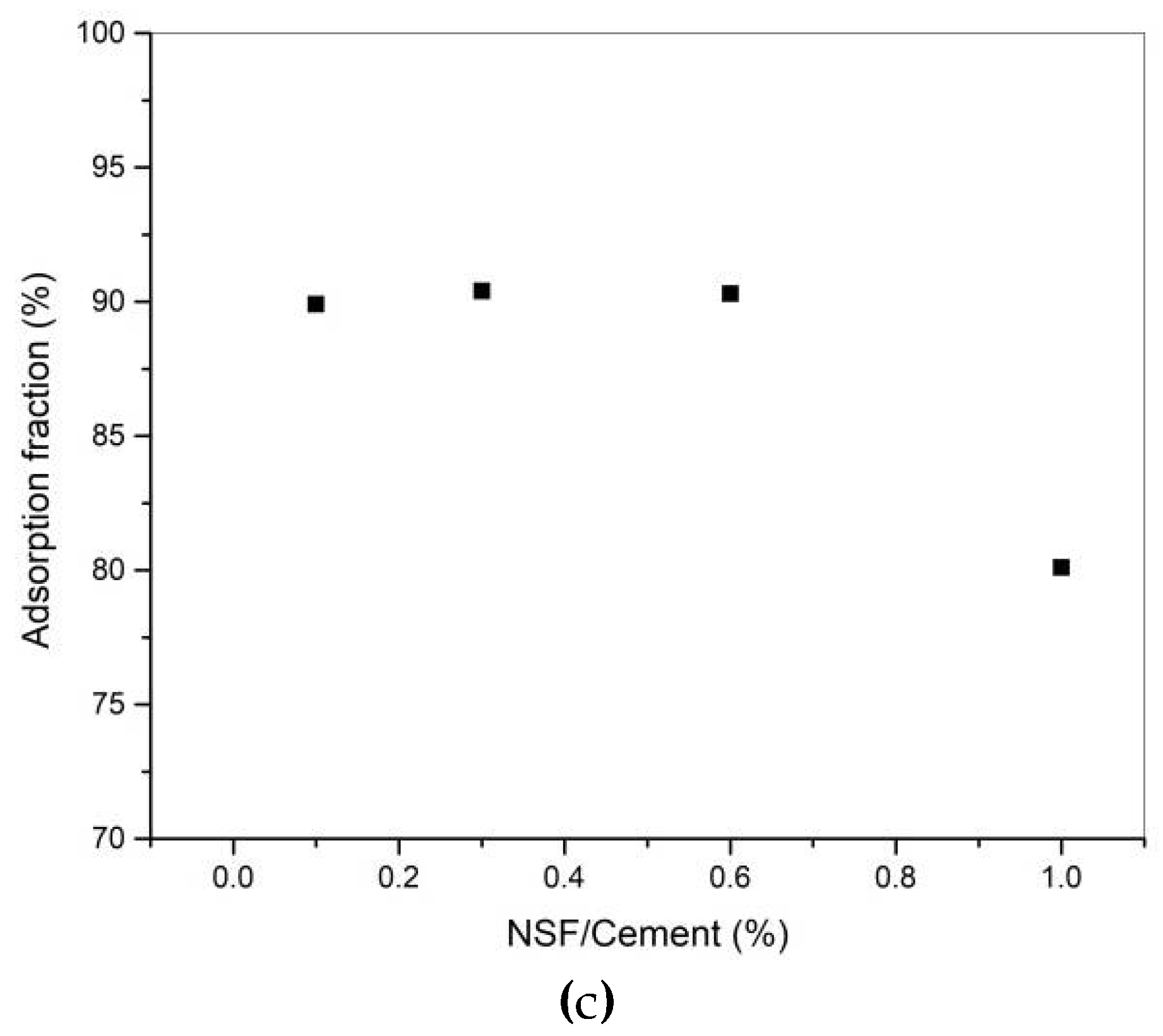
3.3. Adsorption of PCE or NSF in Cement Pastes
4. Discussions
4.1. Efficiency of NSF and PCE
4.2. Different Effect of Superplasticizers on Dynamic Yield Stress and Thixotropy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nkinamubanzi, P.-C.; Aïtcin, P.-C. Cement and superplasticizer combinations: Compatibility and robustness. Cem. Concr. Aggreg. 2004, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, R.J.; Schober, I.; Raphael, E.; Plassard, C.; Lesniewska, E. Conformation of adsorbed comb copolymer dispersants. Langmuir 2008, 25, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, K.; Tazawa, E.I.; Kawai, K.; Enohata, T. Adsorption characteristics of superplasticizers on cement component minerals. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, R.; Schober, I. Superplasticizers and the rheology of concrete. In Understanding the Rheology of Concrete; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 144–208. [Google Scholar]
- Uchikawa, H.; Hanehara, S.; Sawaki, D. The role of steric repulsive force in the dispersion of cement particles in fresh paste prepared with organic admixture. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Barbhuiya, S.A.; Charan, D.; Pandey, S.P. Characterising cement–superplasticiser interaction using zeta potential measurements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2517–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daimon, M.; Roy, D.M. Rheological properties of cement mixes: II. Zeta potential and preliminary viscosity studies. Cem. Concr. Res. 1979, 9, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Z.; Feng, N.Q.; Chen, R.J. Effects of polyethlene oxide chains on the performance of polycarboxylate-type water-reducers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perche, F.; Houst, Y.F.; Bowen, P.; Hofmann, H. Adsorption of lignosulfonates and polycarboxylates-Depletion and electroacoustic methods. In Proceedings of the 7th CANMET/ACI International Conference on Superplasticizers and Other Chemical Admixtures in concrete-Supplementary Paper, Berlin, Germany, 20–23 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, X. Correlations of the dispersing capability of NSF and PCE types of superplasticizer and their impacts on cement hydration with the adsorption in fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, S.; Hwang, S.D.; Khayat, K.H. Robustness of self-consolidating concrete incorporating different viscosity-enhancing admixtures. Mater. J. 2011, 108, 432–438. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.; Khayat, K.H. Effect of various admixture-binder combinations on workability of ready-mix self-consolidating concrete. ACI Spec. Publ. 2005, 233, 25–44. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Qu, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Wan, T. Adsorption characteristics of water-reducing agents on gypsum surface and its effect on the rheology of gypsum plaster. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Kawashima, S. Use of creep recovery protocol to measure static yield stress and structural rebuilding of fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 90, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Beacraft, M.; Shah, S.P. Effect of mineral admixtures on formwork pressure of self-consolidating concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Kawashima, S. Flow onset of fresh mortars in rheometers: Contribution of paste deflocculation and sand particle migration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 90, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemian, A.; Yuan, X.; Cochran, E.; Khoshnevis, B. Cementitious materials for construction-scale 3D printing: Laboratory testing of fresh printing mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, M.; Sonebi, M.; Amziane, S. 3D Printing of Fibre Cement-Based Materials: Fresh and Rheological Performances. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference On Bio-Based Building Materials, RILEM, ICBBM 2017, Clermont-Ferrand, France, 21–23 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Kawashima, S. Distinguishing dynamic and static yield stress of fresh cement mortars through thixotropy. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 86, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, F.; Wolfs, R.; Ahmed, Z.; Salet, T. Additive manufacturing of concrete in construction: Potentials and challenges of 3D concrete printing. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2016, 11, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfs, R.; Bos, F.; Salet, T. Early age mechanical behaviour of 3D printed concrete: Numerical modelling and experimental testing. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 106, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Lesage, K.; El Cheikh, K.; De Schutter, G. Effect of polycarboxylate ether superplasticizer (PCE) on dynamic yield stress, thixotropy and flocculation state of fresh cement pastes in consideration of the Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC). Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 107, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hot, J.; Bessaies-Bey, H.; Brumaud, C.; Duc, M.; Castella, C.; Roussel, N. Adsorbing polymers and viscosity of cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 63, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, D.; Wallevik, J.E.; Yahia, A.; Khayat, K.H.; Wallevik, O.H. Extension of the Reiner–Riwlin equation to determine modified Bingham parameters measured in coaxial cylinders rheometers. Mater. Struct. 2013, 46, 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, M. Deformation and Flow: An Elementary Introduction to Theoretical Rheology; HK Lewis: London, UK, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Flatt, R.J.; Houst, Y.F. A simplified view on chemical effects perturbing the action of superplasticizers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Schutter, G.D. Enhancing thixotropy with nanoclay in presence of Polycarboxylate ether superplasticizer (PCE). Cem. Concr. Res 2018. (submitted). [Google Scholar]
- Roussel, N. Steady and transient flow behaviour of fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattersall, G. The rheology of Portland cement pastes. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 1955, 6, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papo, A. The thixotropic behavior of white Portland cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1988, 18, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapasin, R.; Longo, V.; Rajgelj, S. Thixotropic behaviour of cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1979, 9, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.-C.; Chiu, J.-J.; Chen, S.-D.; Tseng, Y.-C. Effect of addition time of a superplasticizer on cement adsorption and on concrete workability. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1999, 21, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, C. Untersuchungen zur Wechselwirkung Zwischen Polymeren Fliessmitteln und Zementen bzw. Mineralphasen der Frühen Zementhydratation; Technische Universität München: Munich, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Iida, S. Interaction of calcium ion and maleic acid copolymer. Biophys. Chem. 1995, 53, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, M.; Ooya, T.; Yui, N. Controlling the mechanism of trypsin inhibition by the numbers of α-cyclodextrins and carboxyl groups in carboxyethylester-polyrotaxanes. J. Control. Release 2004, 96, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingg, A.; Winnefeld, F.; Holzer, L.; Pakusch, J.; Becker, S.; Gauckler, L. Adsorption of polyelectrolytes and its influence on the rheology, zeta potential, and microstructure of various cement and hydrate phases. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 323, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.R.; Pan, L.S.; Wang, C.M.; Xu, N. Effects of polycarboxylate superplasticizers with different molecular structure on the hydration behavior of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 105, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Kong, X.M.; Lu, Z.B.; Lu, Z.C.; Hou, S.S. Effects of the charge characteristics of polycarboxylate superplasticizers on the adsorption and the retardation in cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, S.; Chaouche, M.; Corr, D.J.; Shah, S.P. Influence of purified attapulgite clays on the adhesive properties of cement pastes as measured by the tack test. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 48, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, Y.; De Schutter, G. Different Effects of NSF and PCE Superplasticizer on Adsorption, Dynamic Yield Stress and Thixotropy of Cement Pastes. Materials 2018, 11, 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050695
Qian Y, De Schutter G. Different Effects of NSF and PCE Superplasticizer on Adsorption, Dynamic Yield Stress and Thixotropy of Cement Pastes. Materials. 2018; 11(5):695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050695
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Ye, and Geert De Schutter. 2018. "Different Effects of NSF and PCE Superplasticizer on Adsorption, Dynamic Yield Stress and Thixotropy of Cement Pastes" Materials 11, no. 5: 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050695
APA StyleQian, Y., & De Schutter, G. (2018). Different Effects of NSF and PCE Superplasticizer on Adsorption, Dynamic Yield Stress and Thixotropy of Cement Pastes. Materials, 11(5), 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050695




