PLA- and PLA/PLGA-Emulsion Composite Biomaterial Sheets for the Controllable Sustained Release of Hydrophilic Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
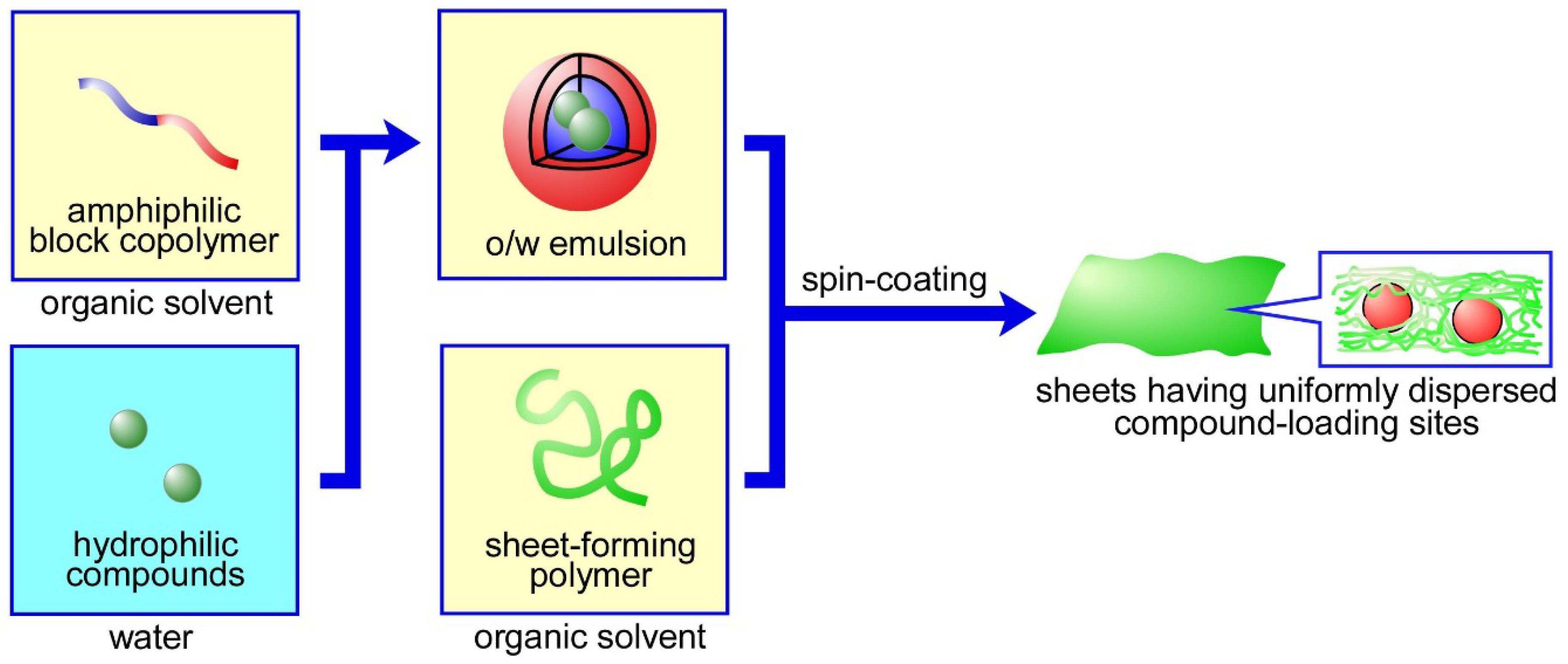
2.2. Preparation of the Sheets
2.3. Characterization of the Emulsions and Sheets
2.4. Release of FITC-Dex from the Sheets in Which W/O Emulsions Containing FITC-Dex Were Dispersed
3. Results and Discussion
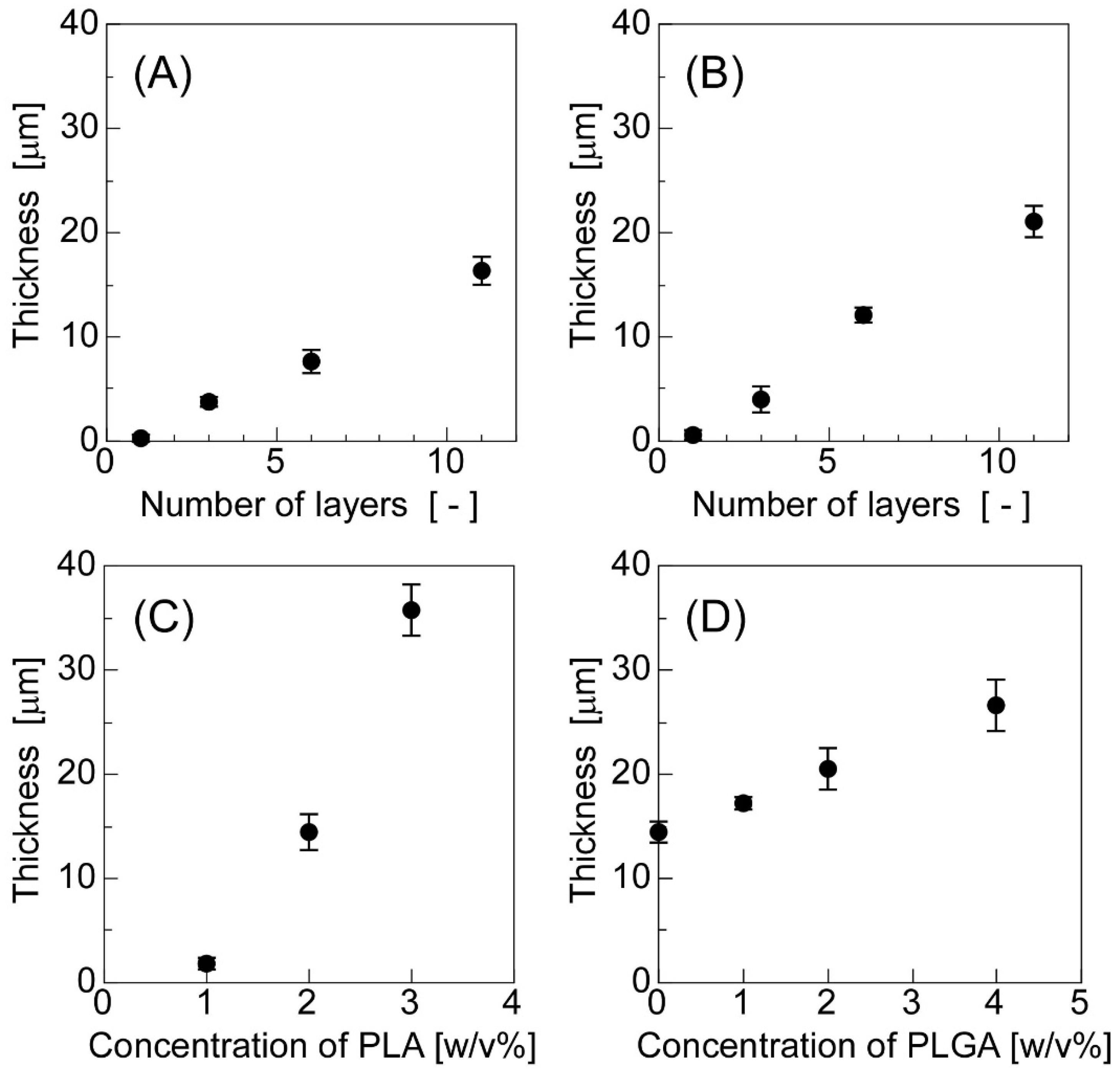
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of the Sheets in Which W/O Emulsions Were Dispersed
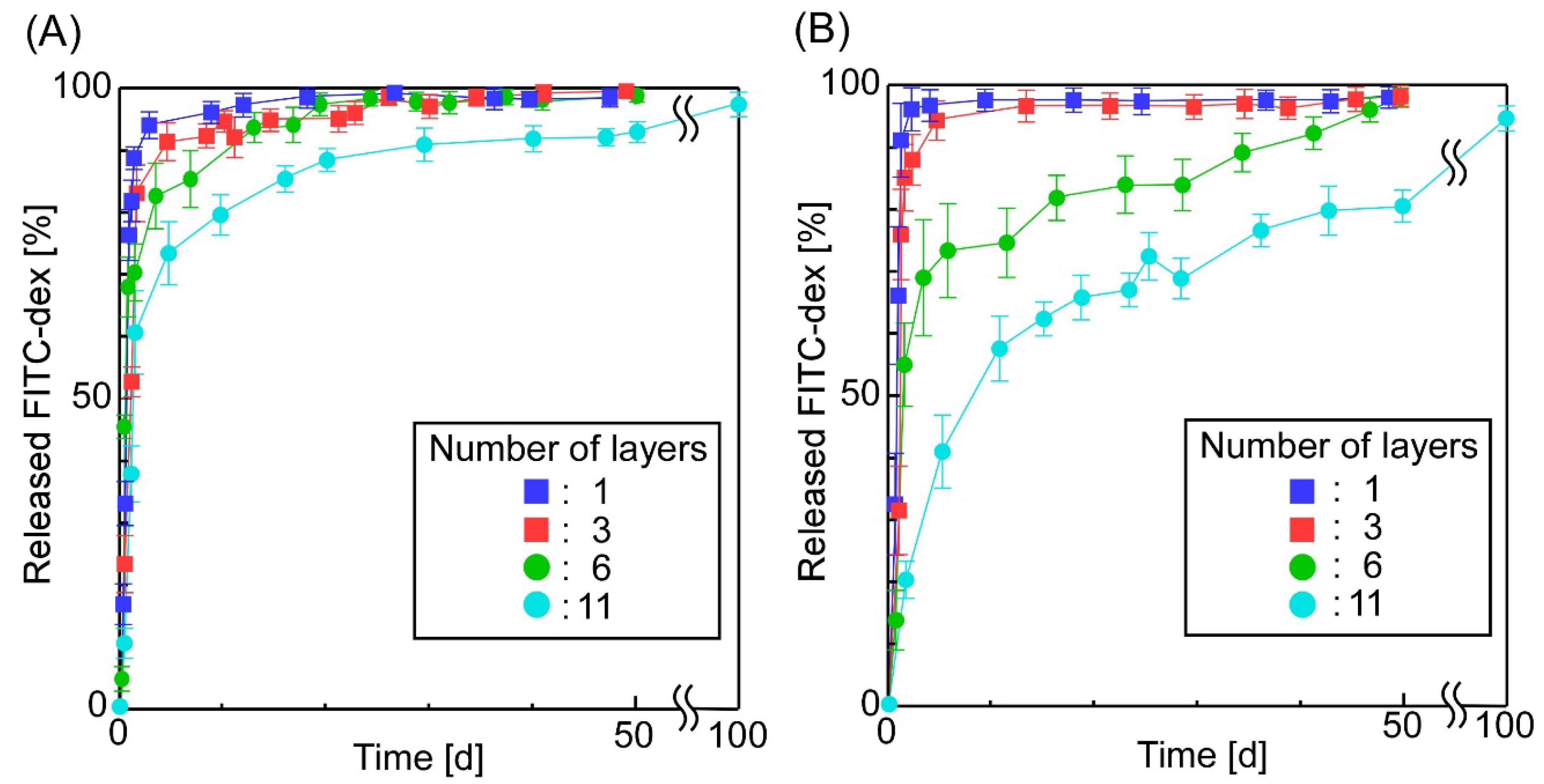
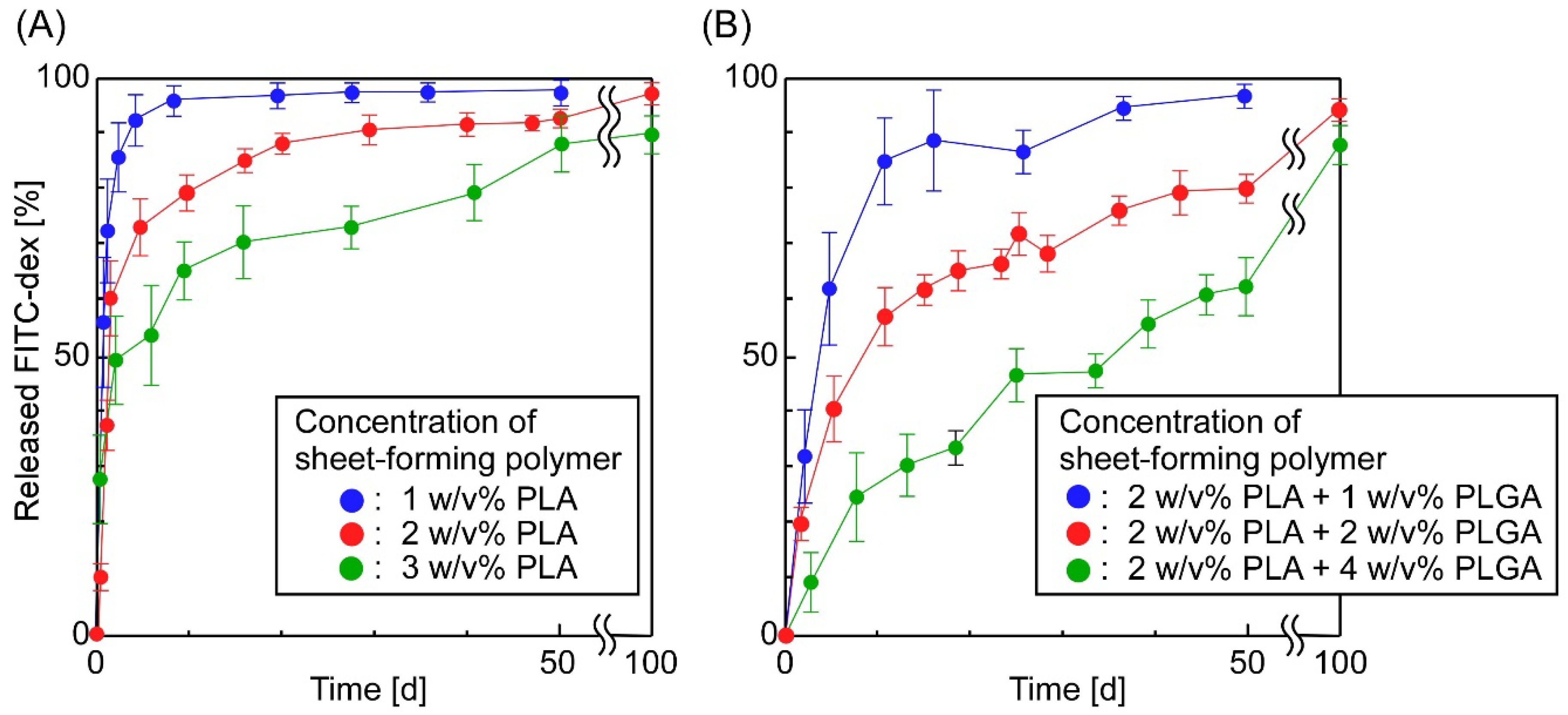
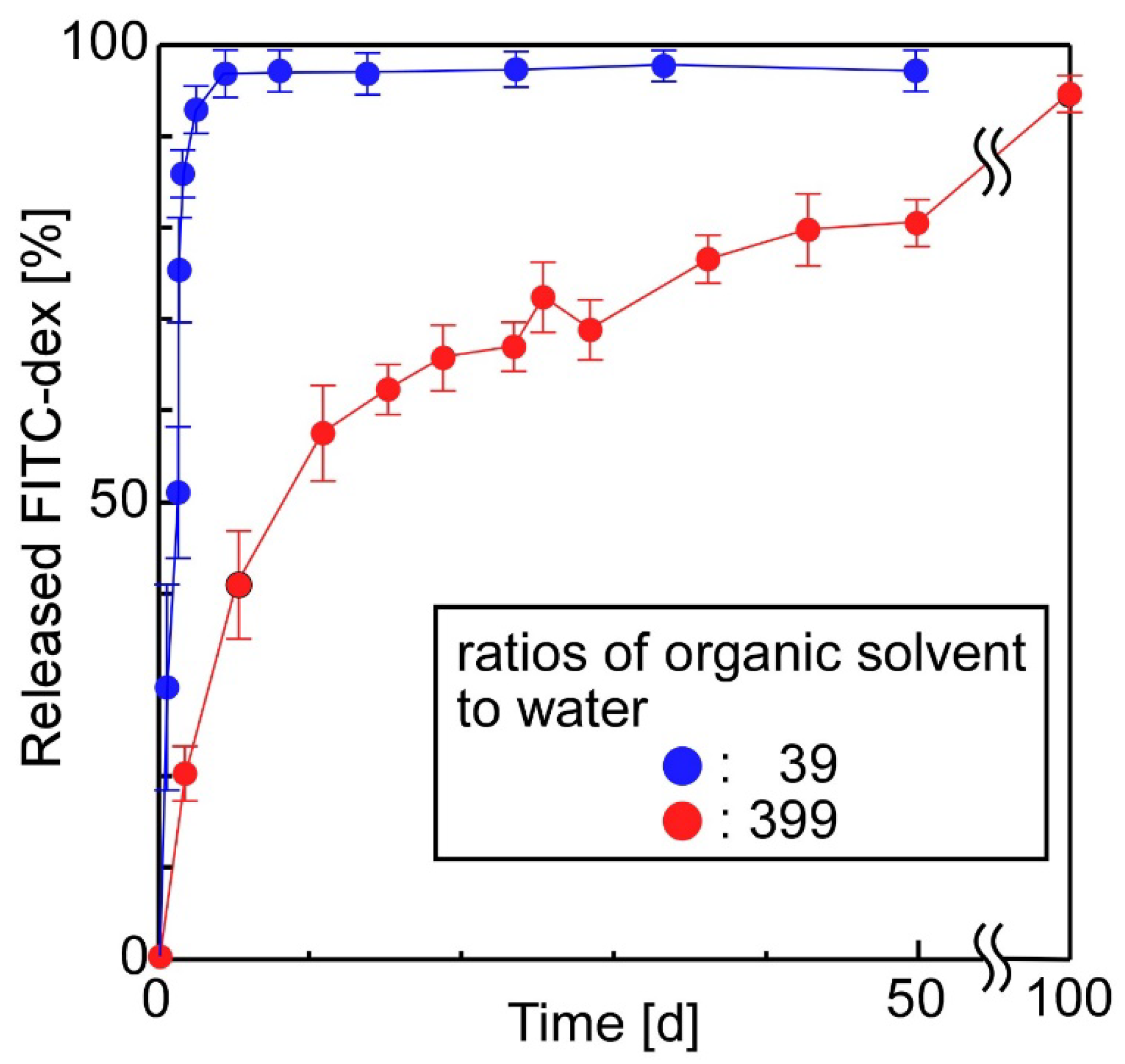
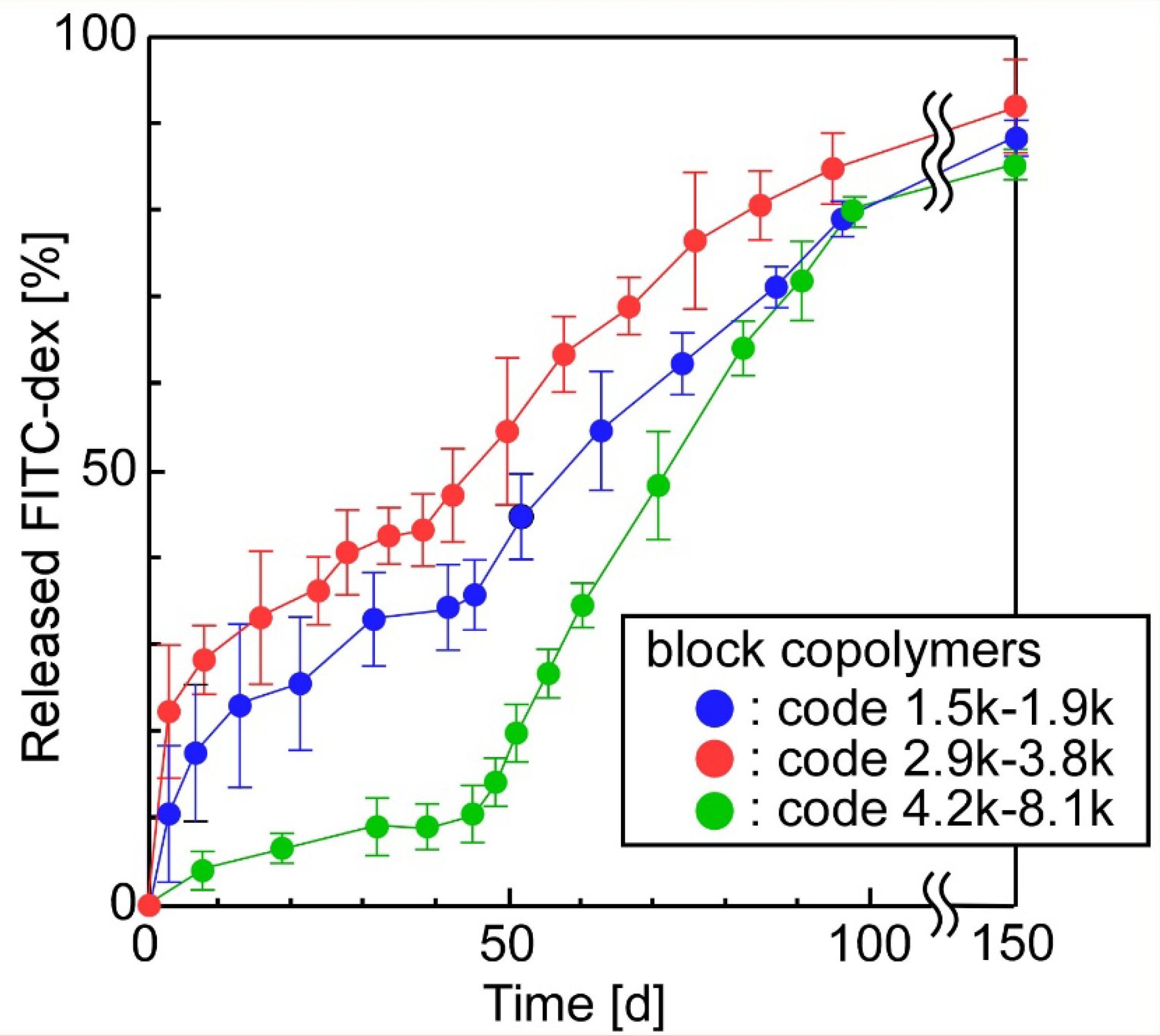
3.2. The Release of FITC-Dex from the Sheets in Which W/O Emulsions Containing FITC-Dex Were Dispersed
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saha, K.; Tsuji, H. Effects of rapid crystallization on hydrolytic degradation and mechanical properties of poly(l-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone). React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Kong, L.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, X. Improvement of mechanical properties of poly(DL-lactide) films by blending of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate). Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yuan, D.; Fu, L.; Chen, Y. Physical blend of PLA/NR with co-continuous phase structure: Preparation, rheology property, mechanical properties and morphology. Polym. Test. 2014, 37, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.S.; Djokic, J.; McCoy, C.P.; Gorman, S.P. Poly(ε-caprolactone) and poly(ε-caprolactone)-polyvinylpyrrolidoneiodine blends as ureteral biomaterials: Characterisation of mechanical and surface properties, degradation and resistance to encrustation in vitro. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4449–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, J.; Sun, J.; Bian, X.; Feng, L.; Xiang, S.; Sun, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, G.; Chen, X. Improved mechanical and thermal properties of PLLA by solvent blending with PDLA-b-PEG-b-PDLA. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 101, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orava, E.; Korventausta, J.; Rosenberg, M.; Jokinen, M.; Rosling, A. In vitro degradation of porous poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA)/bioactive glass composite foams with a polar structure. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.B.; Sakamoto, J.; Sung, M.H.; Uyama, H. pH-controlled degradation and thermal stability of a porous poly(γ-glutamic acid) monolith crosslinked with an oxazoline-functionalized polymer. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 99, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, L.I.; Dias, A.M.; Carvalho, E.; de Sousa, H.C. Recent advances on the development of wound dressings for diabetic foot ulcer treatment: A review. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7093–7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajardo, A.R.; Lopes, L.C.; Caleare, A.O.; Britta, E.A.; Nakamura, C.V.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Silver sulfadiazine loaded chitosan/chondroitin sulfate films for a potential wound dressing application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakos, I.; Rizzello, L.; Scurr, D.J.; Pompa, P.P.; Bayer, I.S.; Athanassiou, A. All-natural composite wound dressing films of essential oils encapsulated in sodium alginate with antimicrobial properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 463, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felgueiras, H.P.; Amorim, M.T.P. Functionalization of electrospun polymeric wound dressings with antimicrobial peptides. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 156, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, D.; Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Coutinho, P.; Mendonça, A.G.; Correia, I.J. Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, L.L.; Venkatraman, S.S. Paclitaxel release from single and double-layered poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide)/poly(L-lactide) film for biodegradable coronary stent application. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 87A, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Meng, S.; Zhong, W.; Cai, R.; Du, Q.; Tomasik, P. Novel drug-loaded gelatin films and their sustained-release performance. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 90B, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Liu, X.; Guo, S.; Tang, M.; Cheng, L.; Tian, L. 5-Fluorouracil-loaded multilayered films for drug controlled releasing stent application: Drug release, microstructure, and ex vivo permeation behaviors. J. Controll. Release 2010, 146, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, T.W.J.; Huang, C.L.; Widjaja, E.; Boey, F.Y.C.; Loo, J.S.C.; Venkatraman, S.S. The effect of polyethylene glycol structure on paclitaxel drug release and mechanical properties of PLGA thin films. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ro, A.J.; Falotico, R.; Dave, V. Microstructure and drug-release studies of sirolimus-containing poly(lactide-co-glycolide) films. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2011, 97B, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Hou, J.; Lei, L.; Liu, X.; Guo, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, K. Preparation, characterization and properties of partially hydrolyzed ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer films for controlled drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 400, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Ku, Y.; Chung, C.P.; Lee, S.J. Controlled release of platelet-derived growth factor from porous poly(L-lactide) membranes for guided tissue regeneration. J. Controll. Release 1998, 51, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.J.; Macdonald, M.L.; Beben, Y.M.; Padera, R.F.; Samuel, R.E.; Hammond, P.T. Tunable dual growth factor delivery from polyelectrolyte multilayer films. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6183–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Okano, T.; Nishida, H.; Tomizawa, Y.; Endo, M.; Kurosawa, H. A novel synthetic tissue-adhesive hydrogel using a crosslinkable polymeric micelle. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2007, 80A, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Nishida, H.; Tomizawa, Y.; Kurosawa, H. A simple hemostasis model for the quantitative evaluation of hydrogel-based local hemostatic biomaterials on tissue surface. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 65, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Nishida, H.; Tomizawa, Y.; Kurosawa, H. In vivo and in vitro evaluation of gelation and hemostatic properties of a novel tissue-adhesive hydrogel containing a cross-linkable polymeric micelle. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 91, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, Y.; Fukuda, K.; Murakami, Y. The hydrogel containing a novel vesicle-like soft crosslinker, a “trilayered” polymeric micelle, shows characteristic rheological properties. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2013, 51, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Yoshida, C.; Murakami, Y. Design of novel sheet-shaped chitosan hydrogel for wound healing: A hybrid biomaterial consisting of both PEG-grafted chitosan and crosslinkable polymeric micelles acting as drug containers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3697–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Uchida, Y.; Takami, T.; Ito, T.; Anzai, R.; Sonotaki, S.; Murakami, Y. Dual drug release from hydrogels covalently containing polymeric micelles that possess different drug release properties. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 153, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, C.; Uchida, Y.; Ito, T.; Takami, T.; Murakami, Y. Chitosan gel sheet containing polymeric micelles: Synthesis and gelation properties of PEG-grafted chitosan. Materials 2017, 10, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Takami, T.; Uchida, Y.; Murakami, Y. Chitosan gel sheet containing drug carriers with controllable drug-release properties. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 2018, 163, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroishi, H.; Yoshida, C.; Murakami, Y. A free-standing, sheet-shaped, “hydrophobic” biomaterial containing polymeric micelles formed from poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic acid) block copolymer for possible incorporation/release of “hydrophilic” compounds. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzai, R.; Murakami, Y. Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL)-polymeric micelle hybrid sheets for the incorporation and release of hydrophilic compounds. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 127, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzai, R.; Takami, T.; Uchida, Y.; Murakami, Y. Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) hybrid sheets containing polymeric micelles: Effects of inner structures on the material properties of the sheet. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 72, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanakubo, Y.; Ito, F.; Murakami, Y. Novel one-pot facile technique for preparing nanoparticles modified with hydrophilic polymers on the surface via block polymer-assisted emulsification/evaporation process. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 78, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takami, T.; Murakami, Y. Development of PEG-PLA/PLGA microparticles for pulmonary drug delivery prepared by a novel emulsification technique assisted with amphiphilic block copolymers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 87, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takami, T.; Murakami, Y. Unexpected and successful “one-step” formation of porous polymeric particles only by mixing organic solvent and water under “low-energy-input” conditions. Langmuir 2014, 30, 3329–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneki, N.; Takami, T.; Ito, T.; Anzai, R.; Fukuda, K.; Kinoshita, K.; Sonotaki, S.; Murakami, Y. One-pot facile preparation of PEG-modified PLGA nanoparticles: Effects of PEG and PLGA on release properties of the particles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 469, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, S.; Takami, T.; Murakami, Y. Porous PLGA microparticles formed by “one-step” emulsification forpulmonary drug delivery: The surface morphology and theaerodynamic properties. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, Y.; Murakami, Y. Trilayered polymeric micelle: A newly developed macromolecular assembly that can incorporate hydrophilic compounds. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, Y.; Murakami, Y. Successful preferential formation of a novel macromolecular assembly–trilayered polymeric micelle–that can incorporate hydrophilic compounds: The optimization of factors affecting the micelle formation from amphiphilic block copolymers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 84, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Du, H.-L.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Zhai, Y.-J.; Zhai, G.-X. Polymer-drug conjugates: Present state of play and future perspectives. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolate, A.; Baradia, D.; Patil, S.; Vhora, I.; Kore, G.; Misra, A. PEG: A versatile conjugating ligand for drugs and drug delivery systems. J. Controll. Release 2014, 192, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Hirata, A. Complex between α-chymotrypsin and poly(ethylene glycol) catalytically active in organic media. Biotechnol. Tech. 1999, 13, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Hoshi, R.; Hirata, A. Borate buffer dramatically enhances the activity of poly(ethylene glycol)-α-chymotrypsin complex catalytically active in anhydrous isooctane than conventional phosphate buffer even at low concentration. Biotechnol. Lett. 2001, 23, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Hirata, A. Enzymatic synthesis of peptides: Review. Seibutsu-Kogaku Kais. 1998, 76, 238–254. [Google Scholar]
- Wanga, B.; Zheng, H.; Chang, M.-W.; Ahmad, Z.; Li, J.-S. Hollow polycaprolactone composite fibers for controlled magnetic responsive antifungal drug release. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Lin, H.; Rothrauff, B.B.; Yu, S.; Tuan, R.S. Multilayered polycaprolactone/gelatin fiber-hydrogel composite for tendon tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2016, 35, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Gao, H.; Zhu, G.; Cao, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y. The preparation and characterization of polycaprolactone/graphene oxide biocomposite nanofiber scaffolds and their application for directing cell behaviors. Carbon 2015, 95, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lv, S.; Lu, J.; Jiang, S.; Lin, L. Characterization of polycaprolactone/collagen fibrous scaffolds by electrospinning and their bioactivity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 76, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramot, Y.; Haim-Zada, M.; Domb, A.J.; Nyska, A. Biocompatibility and safety of PLA and its copolymers. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.K.; Yun, Y.; Park, K. PLA micro- and nano-particles. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, B.; Gullotti, D.; Mangraviti, A.; Utsuki, T.; Brem, H. Polylactic acid (PLA) controlled delivery carriers for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chereddy, K.K.; Payen, V.L.; Préat, V. PLGA: From a classic drug carrier to a novel therapeutic activity contributor. J. Controll. Release 2018, 289, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, M.; Ahmed, N.; Rehman, A.U. Recent applications of PLGA based nanostructures in drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Jin, K.; Liu, W.; Qiu, X.; Li, C. Fabrication of functional PLGA-based electrospun scaffolds and their applications in biomedical engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, F.A.; Lulianelli, G.C.V.; Tavares, M.I.B. Development and properties evaluation of bio-based PLA/PLGA blend films reinforced with microcrystalline cellulose and organophilic silica. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2017, 57, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, M.; Kadota, K.; Kajihara, M.; Sano, A.; Fujioka, K. Sustained release of human growth hormone (hGH) from collagen film and evaluation of effect on wound healing in db/db mice. J. Controll. Release 2001, 77, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, K.; Takada, Y.; Sato, S.; Miyata, T. Novel delivery system for proteins using collagen as a carrier material: The minipellet. J. Controll. Release 1995, 33, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijkhuizen-Radersma, R.; Métairie, S.; Roosma, J.R.; de Groot, K.; Bezemer, J.M. Controlled release of proteins from degradable poly(ether-ester) multiblock copolymers. J. Controll. Release 2005, 101, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.-S.; Park, S.W.; Hammond, P.T. Hydrogen-bonding layer-by-layer-assembled biodegradable polymeric micelles as drug delivery vehicles from surfaces. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakizawa, Y.; Nishio, R.; Hirano, T.; Koshi, Y.; Nukiwa, M.; Koiwa, M.; Michizoe, J.; Ida, N. Controlled release of protein drugs from newly developed amphiphilic polymer-based microparticles composed of nanoparticles. J. Controll. Release 2010, 142, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakeji, Y.; Oki, E.; Egashira, A.; Sadanaga, N.; Takahashi, I.; Morita, M.; Emi, Y.; Maehara, Y. Phase II study of biweekly docetaxel and S-1 combination therapy for advanced or recurrent gastric cancer. Oncology 2009, 77, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathe, O.F.; Ernst, S.; Sutherland, F.R.; Dixon, E.; Butts, C.; Bigam, D.; Porter, G.A.; Koppel, J.; Dowden, S. A phase II experience with neoadjuvant irinotecan (CPT-11), 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and leucovorin (LV) for colorectal liver metastases. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.B.; Kundu, S.C. Calcium alginate beads embedded in silk fibroin as 3D dual drug releasing scaffolds. Biomaterials 2009, 28, 5170–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, T.; Tominaga, K.; Kidoaki, S. Time-programmed dual release formulation by multilayered drug-loaded nanofiber meshes. J. Controll. Release 2010, 143, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Cai, C.; Lin, J.; Chen, T. Dual-drug delivery system based on hydrogel/micelle composites. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2606–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Code 1 | PEG (Including Methoxy Terminus) | PCL | PEG-b-PCL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn2 | Mw/Mn2 | Mn3 | Mn2,3 | Mw/Mn2 | |
| 1.6k–0.7k | 1600 | 1.11 | 700 | 2300 | 1.11 |
| 1.5k–1.9k | 1500 | 1.10 | 1900 | 3400 | 1.24 |
| 3.0k–0.6k | 3000 | 1.05 | 600 | 3600 | 1.08 |
| 3.2k–1.9k | 3200 | 1.04 | 1900 | 5100 | 1.11 |
| 2.9k–3.8k | 2900 | 1.05 | 3800 | 6700 | 1.13 |
| 4.2k–8.1k | 4200 | 1.04 | 8100 | 12,300 | 1.19 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moroishi, H.; Sonotaki, S.; Murakami, Y. PLA- and PLA/PLGA-Emulsion Composite Biomaterial Sheets for the Controllable Sustained Release of Hydrophilic Compounds. Materials 2018, 11, 2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122588
Moroishi H, Sonotaki S, Murakami Y. PLA- and PLA/PLGA-Emulsion Composite Biomaterial Sheets for the Controllable Sustained Release of Hydrophilic Compounds. Materials. 2018; 11(12):2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122588
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoroishi, Hitomi, Seiichi Sonotaki, and Yoshihiko Murakami. 2018. "PLA- and PLA/PLGA-Emulsion Composite Biomaterial Sheets for the Controllable Sustained Release of Hydrophilic Compounds" Materials 11, no. 12: 2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122588
APA StyleMoroishi, H., Sonotaki, S., & Murakami, Y. (2018). PLA- and PLA/PLGA-Emulsion Composite Biomaterial Sheets for the Controllable Sustained Release of Hydrophilic Compounds. Materials, 11(12), 2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122588





