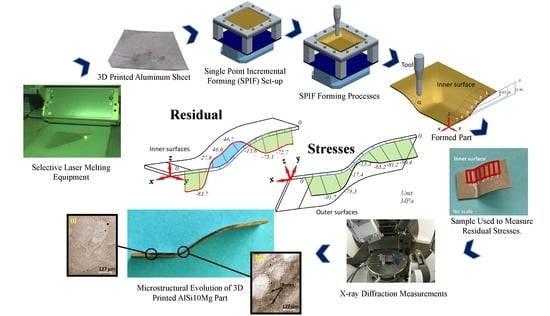
Experimental Determination of Residual Stresses Generated by Single Point Incremental Forming of AlSi10Mg Sheets Produced Using SLM Additive Manufacturing Process
Abstract
Share and Cite
López, C.; Elías-Zúñiga, A.; Jiménez, I.; Martínez-Romero, O.; R. Siller, H.; Diabb, J.M. Experimental Determination of Residual Stresses Generated by Single Point Incremental Forming of AlSi10Mg Sheets Produced Using SLM Additive Manufacturing Process. Materials 2018, 11, 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122542
López C, Elías-Zúñiga A, Jiménez I, Martínez-Romero O, R. Siller H, Diabb JM. Experimental Determination of Residual Stresses Generated by Single Point Incremental Forming of AlSi10Mg Sheets Produced Using SLM Additive Manufacturing Process. Materials. 2018; 11(12):2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122542
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez, Cecilio, Alex Elías-Zúñiga, Isaac Jiménez, Oscar Martínez-Romero, Héctor R. Siller, and José M. Diabb. 2018. "Experimental Determination of Residual Stresses Generated by Single Point Incremental Forming of AlSi10Mg Sheets Produced Using SLM Additive Manufacturing Process" Materials 11, no. 12: 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122542
APA StyleLópez, C., Elías-Zúñiga, A., Jiménez, I., Martínez-Romero, O., R. Siller, H., & Diabb, J. M. (2018). Experimental Determination of Residual Stresses Generated by Single Point Incremental Forming of AlSi10Mg Sheets Produced Using SLM Additive Manufacturing Process. Materials, 11(12), 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122542