The A, B and C’s of Silicone Breast Implants: Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma, Biofilm and Capsular Contracture
Abstract
1. Introduction
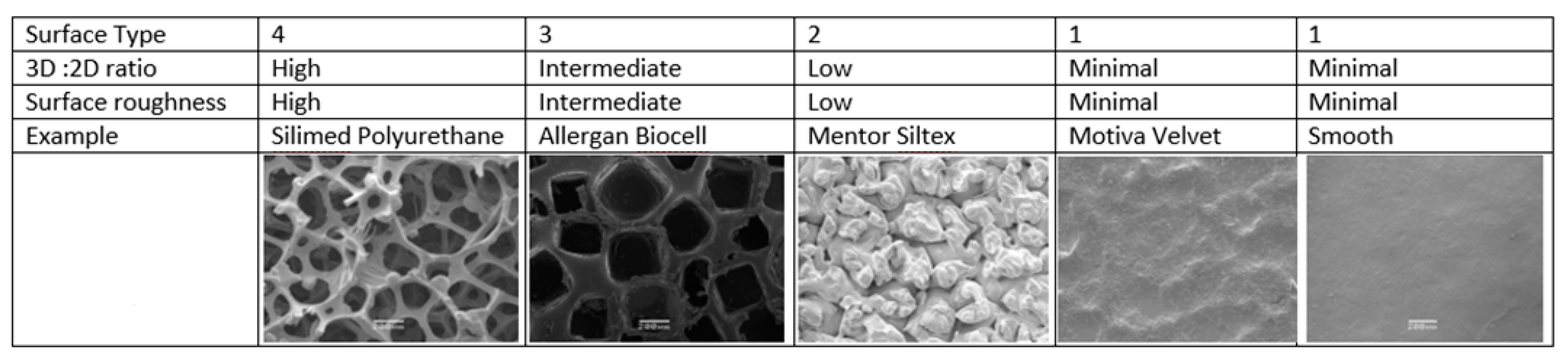
2. Breast Implants
3. Capsular Contracture
4. Aetiopathogenesis of Capsular Contracture (CC)
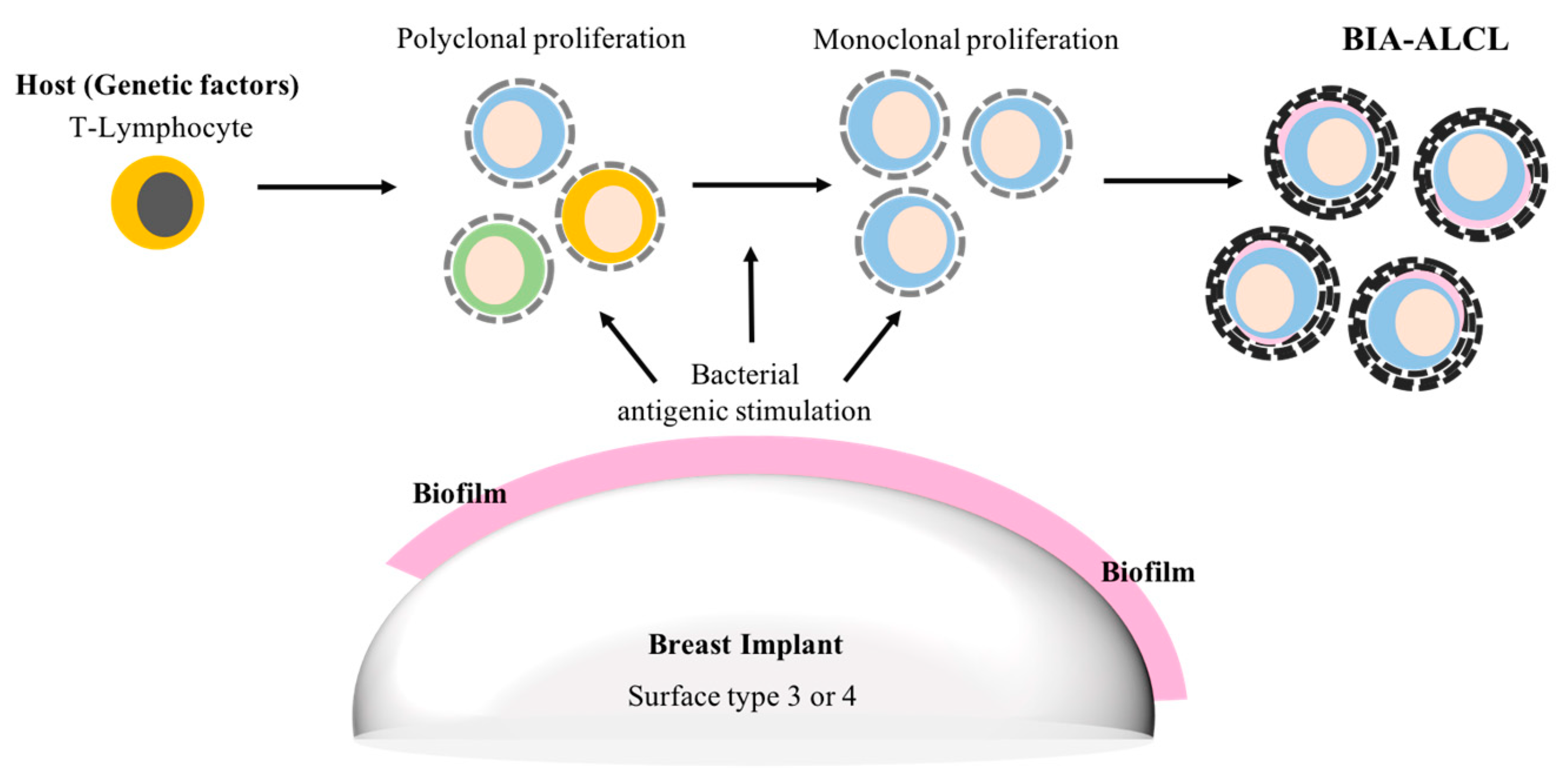
5. Breast Implant Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ASPS. ASPS Plastic Surgery Statistics Report. Available online: www.plasticsurgery.org (accessed on 30 June 2018).
- Cronin, T.D.; Gerow, F.J. Augmentation mammaplasty: A new “natural feel” prosthesis. In Proceedings of the Transactions of the Third International Congress of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Washington, DC, USA, 13–18 October 1963; Excerpta Medica: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1964; pp. 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Namnoum, J.D.; Largent, J.; Kaplan, H.M.; Oefelein, M.G.; Brown, M.H. Primary breast augmentation clinical trial outcomes stratified by surgical incision, anatomical placement and implant device type. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2013, 66, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headon, H.; Kasem, A.; Mokbel, K. Capsular contracture after breast augmentation: An update for clinical practice. Archiv. Plast. Surg. 2015, 42, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shaughnessy, K. Evolution and update on current devices for prosthetic breast reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2015, 4, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henderson, P.W.; Nash, D.; Laskowski, M.; Grant, R.T. Objective Comparison of Commercially Available Breast Implant Devices. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2015, 39, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clubb, F.J.; Ciapper, D.L.; Deferrari, D.A.; Hu, S.; Stare, W.J., Jr.; Capik, P.P.; Armstrong, J.; McGEE, M.G.; Bilings, L.A.; Fuqua, J.M. Surface texturing and coating of biomaterial implants: Effects on tissue integration and fibrosis. ASAIO J. 1999, 45, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalby, M.J.; Yarwood, S.J.; Riehle, M.O.; Johnstone, H.J.; Affrossman, S.; Curtis, A.S. Increasing fibroblast response to materials using nanotopography: Morphological and genetic measurements of cell response to 13-nm-high polymer demixed islands. Exp. Cell Res. 2002, 276, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.; Mempin, M.; Hu, H.; Chowdhury, D.; Foley, M.; Cooter, R.; Adams, W.P., Jr.; Vickery, K.; Deva, A.K. The Functional Influence of Breast Implant Outer Shell Morphology on Bacterial Attachment and Growth. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, F.L. Further studies on the natural-y breast prosthesis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1972, 49, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, T.M.; Kerrigan, C.L.; Buntic, R. Biodegradation of the polyurethane foam covering of breast implants. Plast. Reconstr. Surg 1993, 92, 1003–1013; discussion 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.C.; Birdsell, D.C.; Gradeen, C.Y. Detection of toluenediamines in the urine of a patient with polyurethane-covered breast implants. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 756–758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barr, S.; Bayat, A. Breast surgery review article: Breast implant surface development: Perspectives on development and manufacture. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2011, 31, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, F.E.; Perry, L.; Keller, T.; Maxwell, G.P. The biomechanical and histopathologic effects of surface texturing with silicone and polyurethane in tissue implantation and expansion. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1992, 90, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danino, A.M.; Basmacioglu, P.; Saito, S.; Rocher, F.; Blanchet-Bardon, C.; Revol, M.; Servant, J.-M. Comparison of the capsular response to the Biocell RTV and Mentor 1600 Siltex breast implant surface texturing: A scanning electron microscopic study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2001, 108, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, G.P.; Hammond, D.C. Breast implants: Smooth versus textured. Adv. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1993, 9, 209–220. [Google Scholar]
- Barr, S.; Hill, E.W.; Bayat, A. Functional biocompatibility testing of silicone breast implants and a novel classification system based on surface roughness. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 75, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sforza, M.; Zaccheddu, R.; Alleruzzo, A.; Seno, A.; Mileto, D.; Paganelli, A.; Sulaiman, H.; Payne, M.; Maurovich-Horvat, L. Preliminary 3-Year Evaluation of Experience with SilkSurface and VelvetSurface Motiva Silicone Breast Implants: A Single-Center Experience with 5813 Consecutive Breast Augmentation Cases. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2018, 38, S62–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deva, A.K.; Adams, W.P.; Vickery, K. The role of bacterial biofilms in device-associated infection. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Breast Implant- Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL); FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2018.
- Hopper, I.; Parker, E.; Pelligrini, B.; Mulvany, C.; Pase, M.; Ahem, S.; Earnest, A.; McNeil, J. The Australian Breast Device Registry 2016 Report; Monash University: Melbourne, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bengtson, B.P.; Van Natta, B.W.; Murphy, D.K.; Slicton, A.; Maxwell, G.P.; Style 410 U.S. Core Clinical Study Group. Style 410 highly cohesive silicone breast implant core study results at 3 years. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 120, 40S–48S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spear, S.L.; Murphy, D.K. Natrelle round silicone breast implants: Core study results at 10 years. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 133, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, W.P., Jr.; Rios, J.L.; Smith, S.J. Enhancing patient outcomes in aesthetic and reconstructive breast surgery using triple antibiotic breast irrigation: Six-year prospective clinical study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajkos, A.; Deva, A.K.; Vickery, K.; Cope, C.; Chang, L.; Cossart, Y.E. Detection of subclinical infection in significant breast implant capsules. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2003, 111, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersek, R.A. Rate and incidence of capsular contracture: A comparison of smooth and textured silicone double-lumen breast prostheses. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1991, 87, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersek, R.A.; Salisbury, A.V. Textured surface, nonsili- cone gel breast implants: Four years’ clinical outcome. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1997, 100, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handel, N.; Jensen, J.A.; Black, Q.; Waisman, J.R.; Silverstein, M.J. The fate of breast implants: A critical analysis of complications and outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1995, 96, 1521–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnsley, G.P.; Sigurdson, L.J.; Barnsley, S.E. Textured surface breast implants in the prevention of capsular contracture among breast augmentation patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117, 2182–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araco, A.; Caruso, R.; Araco, F.; Overton, J.; Gravante, G. Capsular contractures: A systematic review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 1808–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spear, S.L.; Baker, J.L., Jr. Classification of capsular contracture after prosthetic breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1995, 96, 1119–1123; discussion 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malata, C.M.; Varma, S.; Scott, M.; Liston, J.C.; Sharpe, D.T. Silicone breast implant rupture: Common/serious complication? Med. Prog. Technol. 1994, 20, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, G.P.; Gabriel, A. The evolution of breast implants. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2009, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Caldwell, E.; Reading, G.; Wray, R.C., Jr. A comparison of conventional and low-bleed implants in augmentation mammaplasty. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1992, 89, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogetti, P.; Boltri, M.; Balocco, P.; Spagnoli, G. Augmentation mammaplasty with a new cohesive gel prosthesis. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2000, 24, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heden, P.; Jernbeck, J.; Hober, M. Breast augmentation with anatomical cohesive gel implants: The world’s largest current experience. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2001, 28, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drever, J. Cohesive gel implants for breast augmentation. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2003, 23, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brown, M.H.; Shenker, R.; Silver, S.A. Cohesive silicone gel breast implants in aesthetic and reconstructive breast surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 116, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, T.F.; Fryzek, J.P.; Holmich, L.R.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Krag, C.; Karlsen, R.; Kjøller, K.; Olsen, J.H.; Friis, S. Reconstructive breast implantation after mastectomy for breast cancer: Clinical outcomes in a nationwide prospective cohort study. Arch. Surg. 2005, 140, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wong, C.-H.; Samuel, M.; Tan, B.-K.; Song, C. Capsular contracture in subglandular breast augmentation with textured versus smooth breast implants: A systematic review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, D.J.; Foo, I.T.; Sharpe, D.T. Textured or smooth implants for breast augmentation? A prospective controlled trial. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1991, 44, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakelius, L.; Ohlsen, L. Tendency to capsular contracture around smooth and textured gel-filled silicone mammary implants: A five-year follow-up. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1997, 100, 1566–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt, B.R.; Demas, C.P. The effect of Siltex texturing and povidone-iodine irrigation on capsular contracture around saline inflatable breast implants. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1994, 93, 123–128; discussion 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt, B.R.; Eades, E. The effect of Biocell texturing and povidone-iodine irrigation on capsular contracture around saline-inflatable breast implants. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1995, 96, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asplund, O.; Gylbert, L.; Jurell, G.; Ward, C. Textured or smooth implants for submuscular breast augmentation: A controlled study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1996, 97, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malata, C.M.; Feldberg, L.; Coleman, D.J.; Foo, I.T.; Sharpe, D.T. Textured or smooth implants for breast augmentation? Three year follow-up of a prospective randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1997, 50, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeppl, N.; Schreml, S.; Lichtenegger, F.; Lenich, A.; Eisenmann-Klein, M.; Prantl, L. Does the surface structure of implants have an impact on the formation of a capsular contracture? Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2007, 31, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, W.G.; Nahabedian, M.Y.; Calobrace, M.B.; Harrington, J.L.; Capizzi, P.J.; Cohen, R.; d’Incelli, R.C.; Beckstrand, M. Risk factor analysis for capsular contracture: A 5-year Sientra study analysis using round, smooth, and textured implants for breast augmentation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Pan, F.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Fan, D. Comparison of the postoperative incidence rate of capsular contracture among different breast implants: A cumulative meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt, B.R.; Fried, M.; Schnur, P.L.; Tofield, J.J. Capsules, infection, and intraluminal antibiotics. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1981, 68, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deva, A.K.; Chang, L.C. Bacterial biofilms: A cause for accelerated capsular contracture? Aesthet. Surg. J. 1999, 19, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, U.; Mesina, J.; Kalbermatten, D.; Haug, M.; Frey, H.; Pico, R.; Frei, R.; Pierer, G.; Lüscher, N.; Trampuz, A. Bacterial biofilms and capsular contracture in patients with breast implants. Br. J. Surg. 2013, 100, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Jacombs, A.; Vickery, K.; Merten, S.L.; Pennington, D.G.; Deva, A.K. Chronic biofilm infection in breast implants is associated with an increased T-cell lymphocytic infiltrate: Implications for breast implant-associated lymphoma. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 135, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fux, C.A.; Stoodley, P.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W. Bacterial biofilms: A diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Expert Rev. Antiinfect. Ther. 2003, 1, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prantl, L.; Pöppl, N.; Horvat, N.; Heine, N.; Eisenmann-Klein, M. Serologic and histologic findings in patients with capsular contracture after breast augmentation with smooth silicone gel implants: Is serum hyaluronan a potential predictor? Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2005, 29, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, Z.; Lehman, J.A., Jr.; Tan, J. Does Infection Play a Role in Breast Capsular Contracture? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1981, 68, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virden, C.P.; Dobke, M.K.; Stein, P.; Parsons, C.L.; Frank, D.H. Subclinical infection of the silicone breast implant surface as a possible cause of capsular contracture. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 1992, 16, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netscher, D.T. Subclinical infection in breast capsules. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 114, 818–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pozo, J.L.; Tran, N.V.; Petty, P.M.; Johnson, C.H.; Walsh, M.F.; Bite, U.; Clay, R.P.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Piper, K.E.; Steckelberg, J.M. Pilot study of association of bacteria on breast implants with capsular contracture. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, M.; Brown, S.A.; Cordeiro, N.D.; Rodrigues-Pereira, P.; Cobrado, M.L.; Morales-Helguera, A.; Queirós, L.; Luís, A.; Freitas, R.; Gonçalves-Rodrigues, A. Effects of coagulase-negative staphylococci and fibrin on breast capsule formation in a rabbit model. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2011, 31, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamboto, H.; Vickery, K.; Deva, A.K. Subclinical (biofilm) infection causes capsular contracture in a porcine model following augmentation mammaplasty. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 126, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darouiche, R.O.; Meade, R.; Mansouri, M.D.; Netscher, D.T. In vivo efficacy of antimicrobe-impregnated saline-filled silicone implants. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2002, 109, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacombs, A.; Allan, J.; Hu, H.; Valente, P.M.; Wessels, W.L.F.; Deva, A.K.; Vickery, K. Prevention of Biofilm-Induced Capsular Contracture with Antibiotic-Impregnated Mesh in a Porcine Model. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2012, 32, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, W.P., Jr.; Conner, W.C.H.; Barton, F.E., Jr.; Rohrich, R.J. Optimizing breast-pocket irrigation: The post-Betadine era. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2001, 107, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blount, A.L.; Martin, M.D.; Lineberry, K.D.; Kettaneh, N.; Alfonso, D.R. Capsular contracture rate in a low-risk population after primary augmentation mammaplasty. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2013, 33, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, S.; Peltoniemi, H.; Lilius, P.; Salmi, A. Povidone-iodine combined with antibiotic topical irrigation to reduce capsular contracture in cosmetic breast augmentation: A comparative study. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2013, 33, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL) in Women with Breast Implants: Preliminary FDA Findings and Analyses; Center for Devices and Radiological Health: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2011.
- Stein, H.; Foss, H.-D.; Dürkop, H.; Marafioti, T.; Delsol, G.; Pulford, K.; Pileri, S.; Falini, B. CD30+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma: A review of its histopathologic, genetic, and clinical features. Blood 2000, 96, 3681–3695. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knight, R.; Loch-Wilkinson, A.-M.; Wessels, W.; Papadopoulos, T.; Magnusson, M.; Lofts, J.; Connell, T.; Hopper, I.; Beath, K.; Lade, S. Epidemiology and risk factors for Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL) in Australia & New Zealand. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 4, 94–95. [Google Scholar]
- Loch-Wilkinson, A.; Beath, K.J.; Knight, R.J.W.; Wessels, W.L.F.; Magnusson, M.; Papadopoulos, T.; Connell, T.; Lofts, J.; Locke, M.; Hopper, I.; et al. Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma in Australia and New Zealand: High-Surface-Area Textured Implants Are Associated with Increased Risk. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doren, E.L.; Miranda, R.N.; Selber, J.C.; Garvey, P.B.; Liu, J.; Medeiros, L.J.; Butler, C.E.; Clemens, M.W. US Epidemiology of Breast Implant–Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 139, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TGA. Breast Implants and Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Update—Additional Confirmed Cases of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma; TGA: Symonston, Australia, 2018.
- Bishara, M.R.; Ross, C.; Sur, M. Primary anaplastic large cell lymphoma of the breast arising in reconstruction mammoplasty capsule of saline filled breast implant after radical mastectomy for breast cancer: An unusual case presentation. Diagn. Pathol. 2009, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P.A.; Lade, S.; Webster, H.; Ryan, G.; Prince, H.M. Effusion-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma of the breast: Time for it to be defined as a distinct clinico-pathological entity. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1977–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupani, A.; Frame, J.D.; Kamel, D. Lymphomas Associated with Breast Implants: A Review of the Literature. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2015, 35, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Clemens, M.W.; Brody, G.S.; Mahabir, R.C.; Miranda, R.N. How to Diagnose and Treat Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 141, 586e–599e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roden, A.C.; Macon, W.R.; Keeney, G.L.; Myers, J.L.; Feldman, A.L.; Dogan, A. Seroma-associated primary anaplastic large-cell lymphoma adjacent to breast implants: An indolent T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder. Mod. Pathol. 2008, 21, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; WHO Classification of Tumours; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; Volume 22008, p. 439. [Google Scholar]
- Jewell, M.; Spear, S.L.; Largent, J.; Oefelein, M.G.; Adams, W.P., Jr. Anaplastic large T-cell lymphoma and breast implants: A review of the literature. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 128, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, M.G.; Lade, S.; Liebertz, D.J.; Prince, H.M.; Brody, G.S.; Webster, H.R.; Epstein, A.L. Breast implant-associated, ALK-negative, T-cell, anaplastic, large-cell lymphoma: Establishment and characterization of a model cell line (TLBR-1) for this newly emerging clinical entity. Cancer 2011, 117, 1478–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadin, M.E.; Deva, A.; Xu, H.; Morgan, J.; Khare, P.; MacLeod, R.A.; Van Natta, B.W.; Adams, W.P., Jr.; Brody, G.S.; Epstein, A.L. Biomarkers Provide Clues to Early Events in the Pathogenesis of Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2016, 36, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, M.G.; Megiel, C.; Church, C.H.; Angell, T.E.; Russell, S.M.; Sevell, R.B.; Jang, J.K.; Brody, G.S.; Epstein, A.L. Survival signals and targets for therapy in breast implant-associated ALK-anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4549–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivennikov, S.; Karin, M. Autocrine IL-6 signaling: A key event in tumorigenesis? Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, L.T.; Wright, G.; Davis, R.E.; Lenz, G.; Farinha, P.; Dang, L.; Chan, J.W.; Rosenwald, A.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Staudt, L.M. Cooperative signaling through the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and nuclear factor-κB pathways in subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2008, 111, 3701–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scuto, A.; Kujawski, M.; Kowolik, C.; Krymskaya, L.; Wang, L.; Weiss, L.M.; DiGiusto, D.; Yu, H.; Forman, S.; Jove, R. STAT3 inhibition is a therapeutic strategy for ABC-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3182–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, M.G.; Liebertz, D.J.; Epstein, A.L. Characterization of cytokine-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells from normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 2273–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, T.J.; Smyth, M.J. Improving cancer immunotherapy by targeting tumor-induced immune suppression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011, 30, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Johani, K.; Almatroudi, A.; Vickery, K.; Van Natta, B.; Kadin, M.E.; Brody, G.; Clemens, M.; Cheah, C.Y.; Lade, S.; et al. Bacterial Biofilm Infection Detected in Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 137, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.-Y.; Chen, C.; Gao, X.-Z.; Li, J.; Yue, J.; Ling, F.; Wang, X.-C.; Shao, S.-H. Distribution of Helicobacter pylori virulence markers in patients with gastroduodenal diseases in a region at high risk of gastric cancer. Microb. Pathog. 2013, 59–60, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matysiak-Budnik, T.; Fabiani, B.; Hennequin, C.; Thieblemont, C.; Malamut, G.; Cadiot, G.; Bouché, O.; Ruskoné-Fourmestraux, A. Gastrointestinal lymphomas: French Intergroup clinical practice recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up (SNFGE, FFCD, GERCOR, UNICANCER, SFCD, SFED, SFRO, SFH). Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreri, A.J.M.; Govi, S.; Pasini, E.; Mappa, S.; Bertoni, F.; Zaja, F.; Montalbán, C.; Stelitano, C.; Cabrera, M.E.; Resti, A.G.; et al. Chlamydophila Psittaci eradication with doxycycline as first-line targeted therapy for ocular adnexae lymphoma: Final results of an international phase II trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2988–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mempin, M.; Hu, H.; Chowdhury, D.; Deva, A.; Vickery, K. The A, B and C’s of Silicone Breast Implants: Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma, Biofilm and Capsular Contracture. Materials 2018, 11, 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122393
Mempin M, Hu H, Chowdhury D, Deva A, Vickery K. The A, B and C’s of Silicone Breast Implants: Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma, Biofilm and Capsular Contracture. Materials. 2018; 11(12):2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122393
Chicago/Turabian StyleMempin, Maria, Honghua Hu, Durdana Chowdhury, Anand Deva, and Karen Vickery. 2018. "The A, B and C’s of Silicone Breast Implants: Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma, Biofilm and Capsular Contracture" Materials 11, no. 12: 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122393
APA StyleMempin, M., Hu, H., Chowdhury, D., Deva, A., & Vickery, K. (2018). The A, B and C’s of Silicone Breast Implants: Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma, Biofilm and Capsular Contracture. Materials, 11(12), 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122393






