Ion Irradiation-Induced Microstructural Evolution of Ni–Mo–Cr Low Alloy Steels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
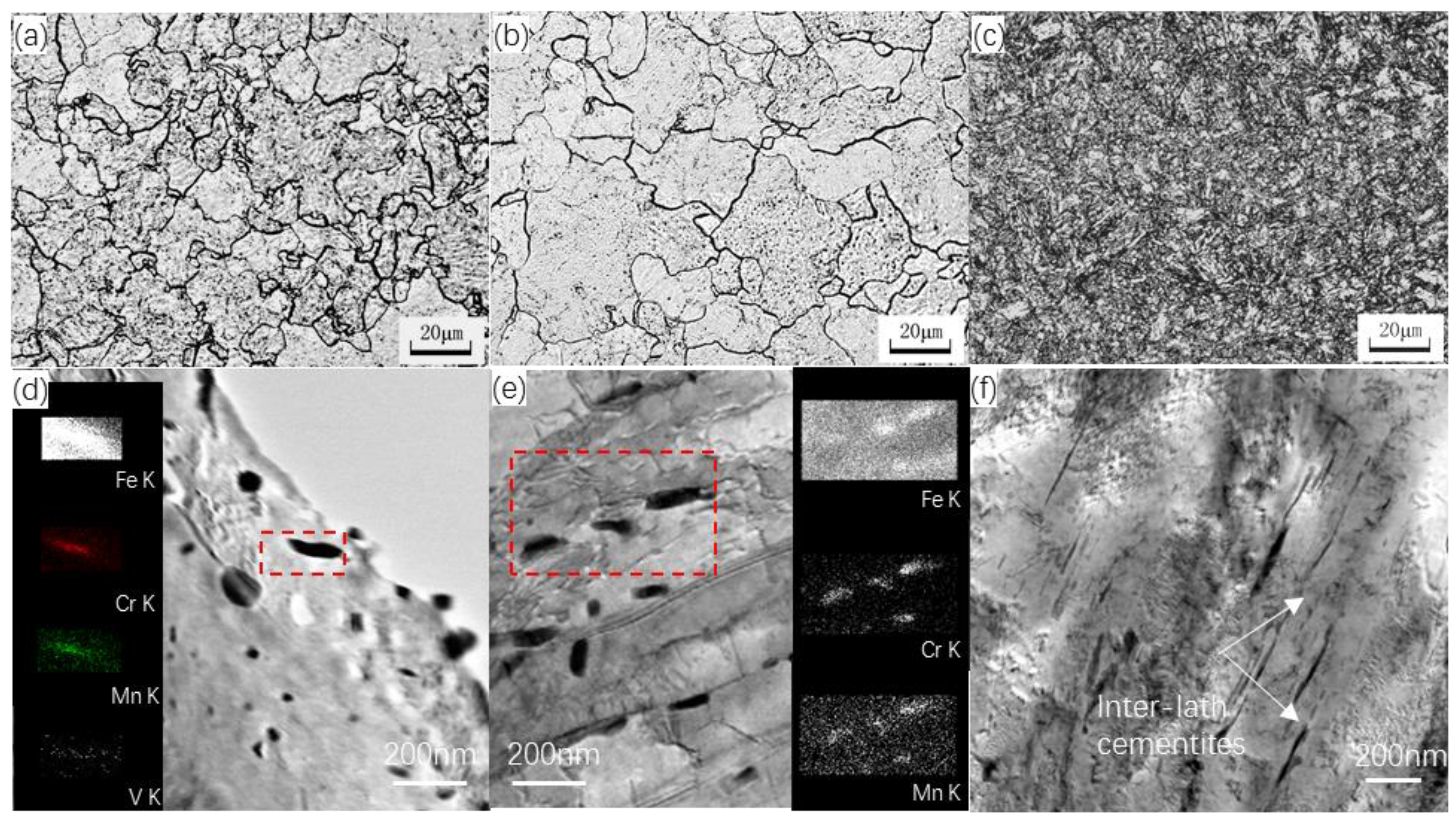
3.1. Microstructure
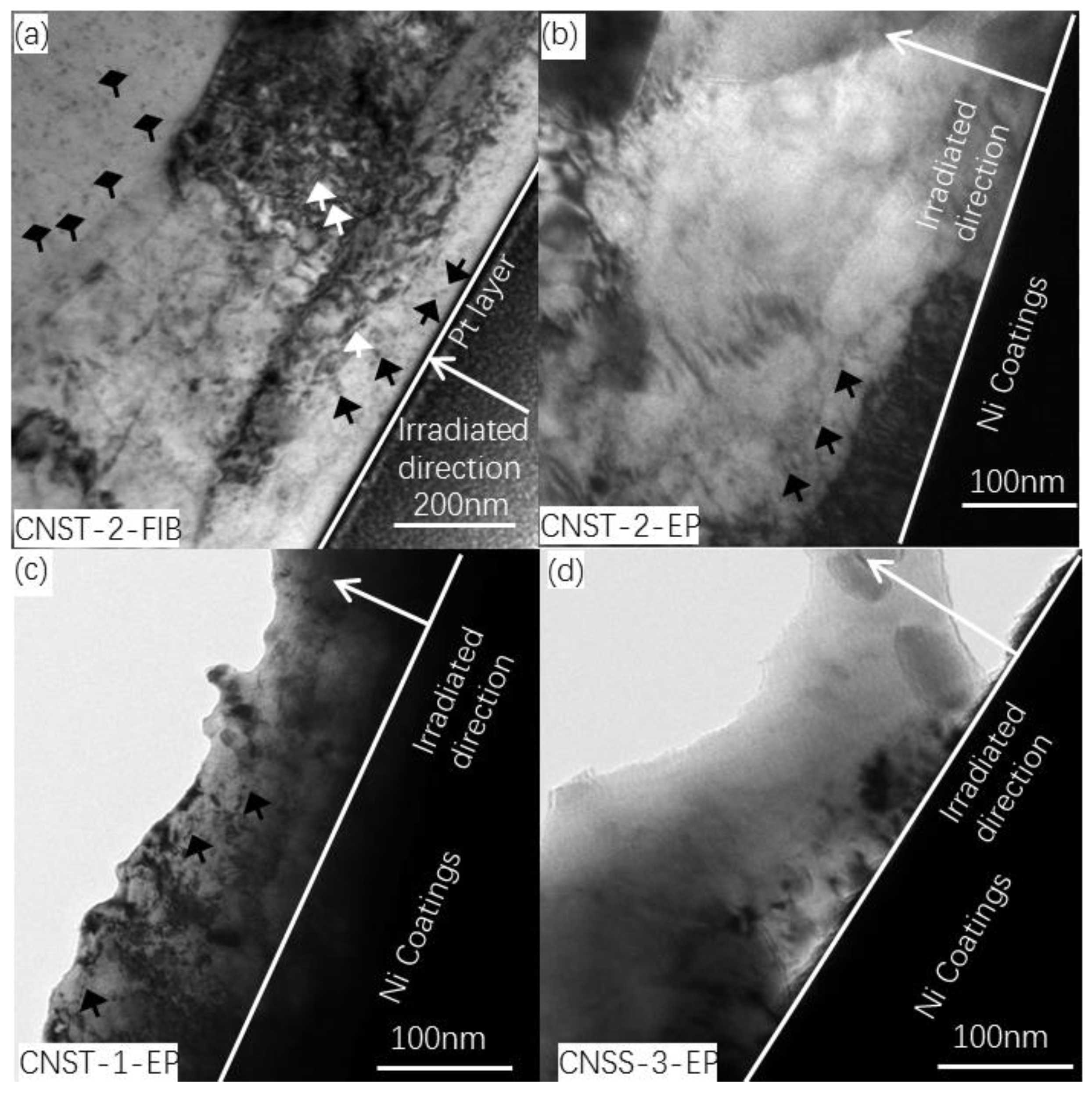
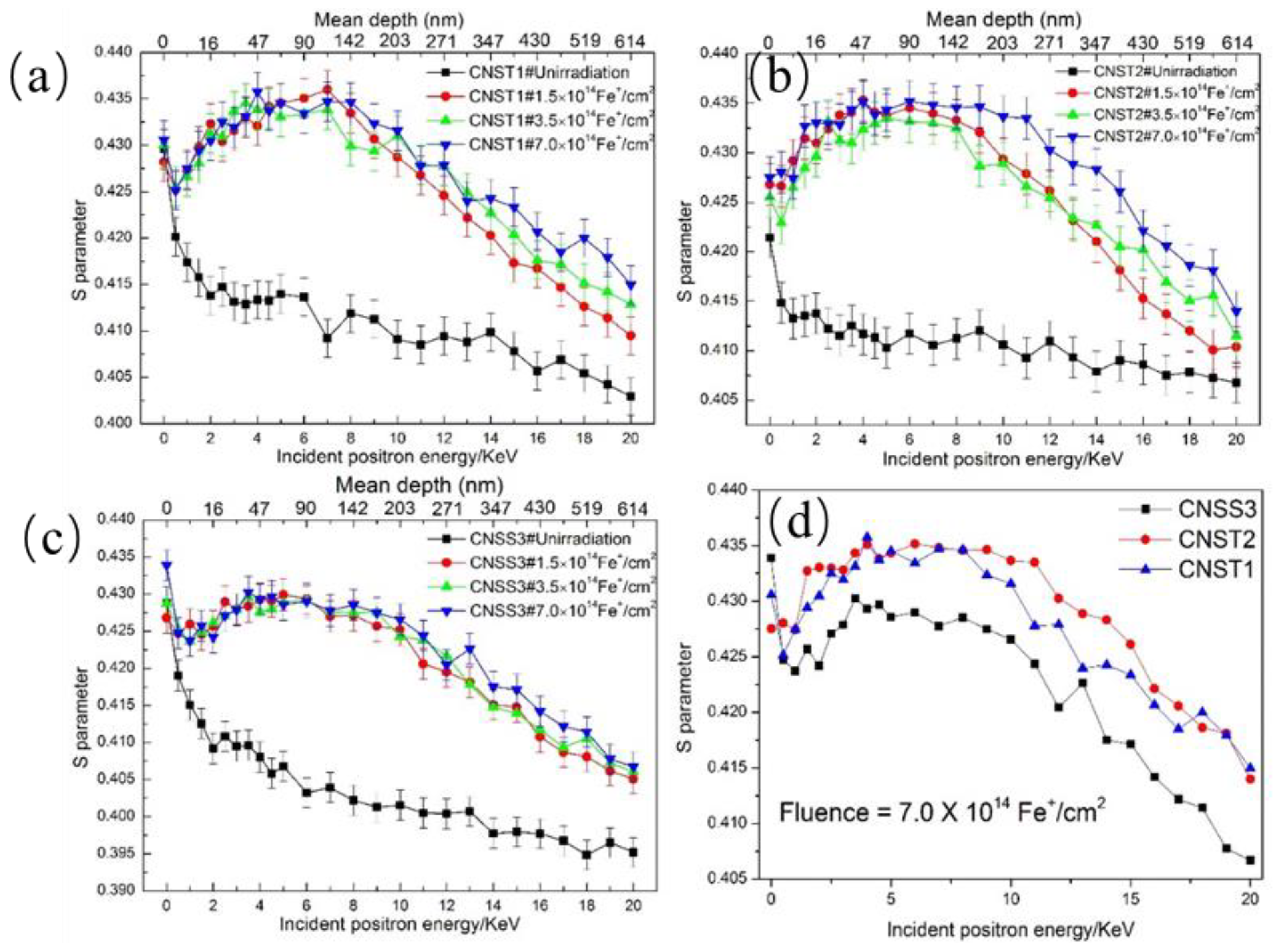
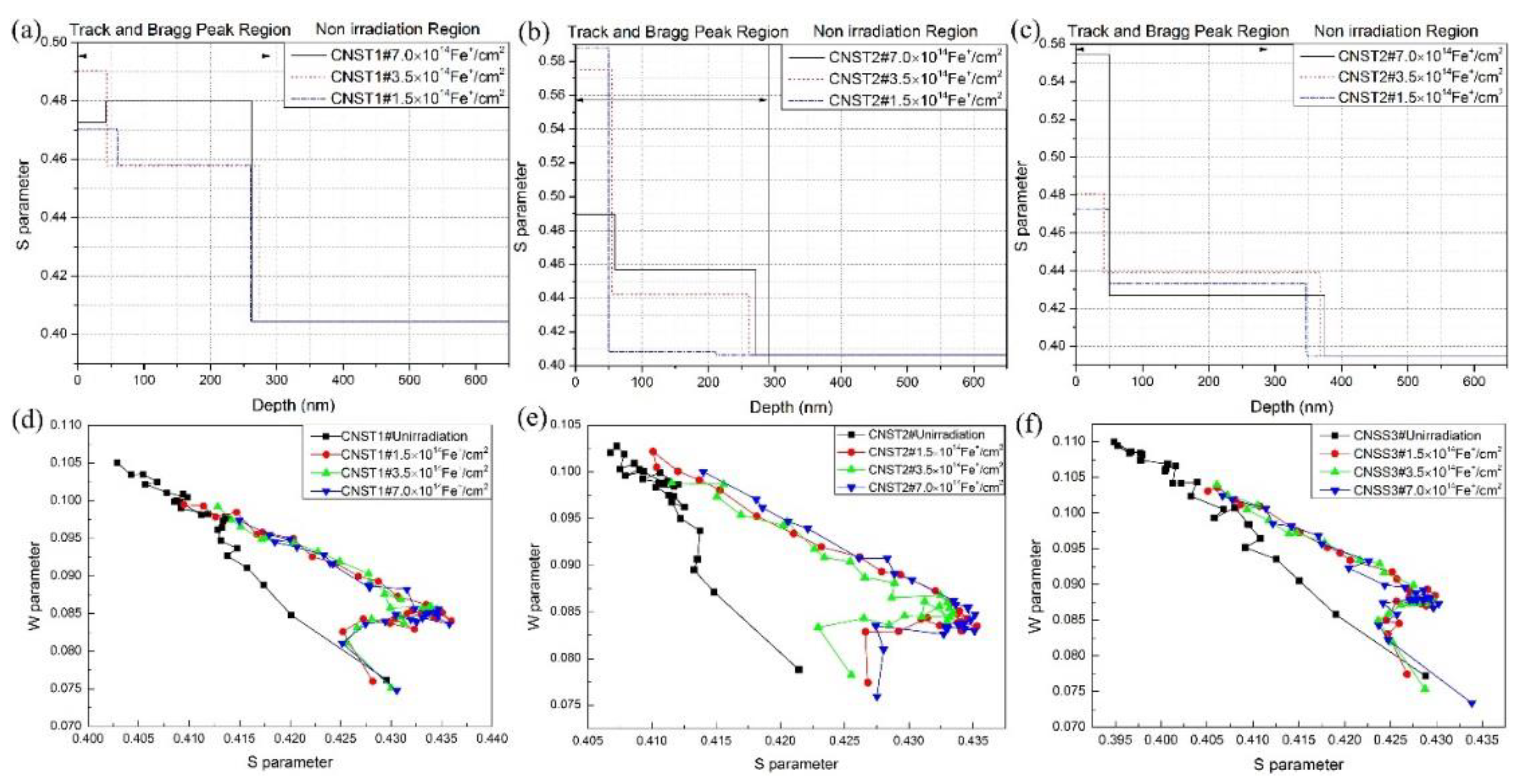
3.2. Irradiation-Induced Defects
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Point defects and dislocation loops were observed in the cross-sectional samples of CNST2 steel prepared by FIB but few similar defects in the sample prepared by ETE method. The bombardment of energetic focused Ga+ could introduce artificial defects into TEM samples that were not the actual defects induced by Fe+ irradiation, while ETE method provided a better way to prepare irradiated TEM samples with lesser or no damage for these materials.
- (2)
- The distribution of vacancy clusters was heterogeneous with irradiation depth. The S parameter of CNST1 and CNST2 was obviously higher than that of CNSS3 at the same dose.
- (3)
- The change character of S parameter in candidate steels with increasing irradiation doses was not obvious as the Fe+ showed a trend towards a clear saturation. The S-W plot showed that two types of defects were formed after ion implantation, which contained small-sized defects such as vacancies, vacancy-solute complexes, dislocation loops, and large-sized point defects.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rauch, R.; Kapl, S.; Posch, G.; Radlmayr, K. High Strength Low Alloy Steel Weldments with Accommodated Qualities to the Base Metal. BHM Berg 2012, 157, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-C.; Park, S.-G.; Lee, K.-H.; Lee, B.-S. Comparison of fracture properties in SA508 Gr.3 and Gr.4N high strength low alloy steels for advanced pressure vessel materials. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2015, 131, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, T.D.; Bodnar, R.; Fielding, J.E. Critical Assessment of ASTM A508 Class 2 Steel for Pressure Vessel Applications. In Proceedings of the 32nd Mechanical Working and Steel Processing, Cincinnati OH, USA, 21–24 October 1990; Volume 28, pp. 323–341. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, P.; Druce, S.G.; Knott, J.F. Effects of microstructure on cleavage fracture in pressure vessel steel. Acta Met. 1986, 34, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, Y.-R.; Jun Oh, Y.; Lee, B.-J.; Hwa Hong, J.; Lee, H.-C. Effects of carbide precipitation on the strength and Charpy impact properties of low carbon Mn–Ni–Mo bainitic steels. J. Nucl. Mater. 2001, 297, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Im, Y.-R.; Lee, H.-C.; Oh, Y.J.; Hong, J.H. Effects of alloying elements on mechanical and fracture properties of base metals and simulated heat-affected zones of SA 508 steels. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2001, 32, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Druce, S.G.; Edwards, B. Development of PWR pressure vessel steels. Nucl. Energy 1980, 19, 347–360. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.; McMahon, C.J. Mechanisms of stress relief cracking in a ferritic steel. Acta Met. 1984, 32, 1535–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yoshiie, T.; Sato, K. Temperature dependence of Cu precipitation in neutron irradiated Fe-Cu alloys. In Physica Status Solidi C—Current Topics in Solid State Physics; Knights, A.P., Mascher, P., Simpson, P.J., Eds.; Wiley-V C H Verlag Gmbh: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; Volume 4, p. 3573. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, M.N.; Rihan, R.; Al-Hadhrami, L. Evaluation of the corrosion resistance of SA-543 and X65 steels in emulsions containing H2S and CO2 using a novel emulsion flow loop. Corros. Sci. 2015, 94, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Xin, Y.; Ju, X.; Guo, L.P.; Wang, B.Y.; Zhong, Y.R.; Huang, Q.Y.; Wu, Y.C. Investigation by slow positron beam of defects in CLAM steel induced by helium and hydrogen implantation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 2009, 267, 3162–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, S.B.; Harbottle, J.E.; Aldridge, N. Radiation hardening in magnox pressure-vessel steels. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1985, 315, 301–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, T.; Nagai, Y.; Tang, Z.; Hasegawa, M.; Almazouzi, A.; van Walle, E.; Gerard, R. Nanostructural evolution in surveillance test specimens of a commercial nuclear reactor pressure vessel studied by three-dimensional atom probe and positron annihilation. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 6852–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, M.; Hono, K.; Katayama, Y. Microstructural evolution in a 17-4 PH stainless steel after aging at 400 °C. Met. Mater. Trans. A 1999, 30, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldrup, M.; Singh, B.N. Studies of defects and defect agglomerates by positron annihilation spectroscopy. J. Nucl. Mater. 1997, 251, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinkle, S.J.; Was, G.S. Materials challenges in nuclear energy. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 735–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, M.; Almazouzi, A. Positron annihilation study of neutron irradiated model alloys and of a reactor pressure vessel steel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2009, 385, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, Y.; Tang, Z.; Hassegawa, M.; Kanai, T.; Saneyasu, M. Irradiation-induced Cu aggregations in Fe: An origin of embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel steels. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 134110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SRIM-The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter. Available online: http://www.srim.org/ (accessed on 20 June 2018).
- Lei, J.; Ding, H.; Shu, G.-G.; Wan, Q.-M. Study on the mechanical properties evolution of A508-3 steel under proton irradiation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 2014, 338, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.S.; Liu, J.L.; Zhang, J.X.; Wu, J.S. TEM investigation of FIB induced damages in preparation of metal material TEM specimens by FIB. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitzman, L.E.; Wang, L.M.; Griffin, R.D.; Komissarov, A.P.; Kulcinski, G.L.; Dodd, R.A. Cross-section specimen preparation technique for nickel alloys and stainless steels. Ultramicroscopy 1989, 29, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, Y.C.; Liu, X.B.; Wang, R.S.; Nagai, Y.; Inoue, K.; Shimizu, Y.; Toyama, T. Microstructural evolution of RPV steels under proton and ion irradiation studied by positron annihilation spectroscopy. J. Nucl. Mater. 2015, 458, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, C.; Sitaud, B.; Zhang, X.; Dimitrov, O.; Dedek, U.; Dworschak, F. Radiation-induced defects in solid solutions and intermetallic compounds based on the Ni-Al system. J. Phys. 1992, 4, 10211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, P.J.; Lynn, K.G. Interaction of positron beams with surfaces, thin films, and interfaces. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1988, 60, 701–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Code | Si | Mn | P | Cu | V | Cr | Ni | Mo | Ti | C | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNST1 | 0.19 | 0.4 | 0.009 | 0.028 | 0.062 | 1.01 | 2.91 | 0.24 | 0.008 | 0.085 | <0.005 |
| CNST2 | 0.21 | 0.41 | 0.01 | 0.018 | 0.058 | 0.93 | 2.87 | 0.22 | 0.016 | 0.079 | <0.005 |
| CNSS3 | 0.26 | 0.58 | 0.007 | 0.092 | 0.059 | 0.99 | 4.14 | 0.46 | 0.01 | 0.1 | <0.005 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; Lei, P.; Ran, G.; Wang, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, S. Ion Irradiation-Induced Microstructural Evolution of Ni–Mo–Cr Low Alloy Steels. Materials 2018, 11, 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112268
Sun H, Lei P, Ran G, Wang H, Zheng J, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Qiu S. Ion Irradiation-Induced Microstructural Evolution of Ni–Mo–Cr Low Alloy Steels. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112268
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Hongying, Penghui Lei, Guang Ran, Hui Wang, Jiyun Zheng, Yiyong Zhang, Zhigang Wang, and Shui Qiu. 2018. "Ion Irradiation-Induced Microstructural Evolution of Ni–Mo–Cr Low Alloy Steels" Materials 11, no. 11: 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112268
APA StyleSun, H., Lei, P., Ran, G., Wang, H., Zheng, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., & Qiu, S. (2018). Ion Irradiation-Induced Microstructural Evolution of Ni–Mo–Cr Low Alloy Steels. Materials, 11(11), 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112268






