Self-Assembly Synthesis of Silver Nanowires/Graphene Nanocomposite and Its Effects on the Performance of Electrically Conductive Adhesive
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment Design
2.1. Raw Materials and Experiment Equipment
2.2. Preparation of Composites
2.2.1. Preparation of Silver Nanowires (AgNWs)
2.2.2. The Preparation of AgNWs/GO Composites
2.2.3. The Preparation of AgNWs/GNs
2.2.4. Preparation of Conductive Adhesive
2.3. Experiment Tests
2.3.1. Tests on Shear Strength
2.3.2. Tests on Shear Electrical Conductivity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy) Spectra Analysis
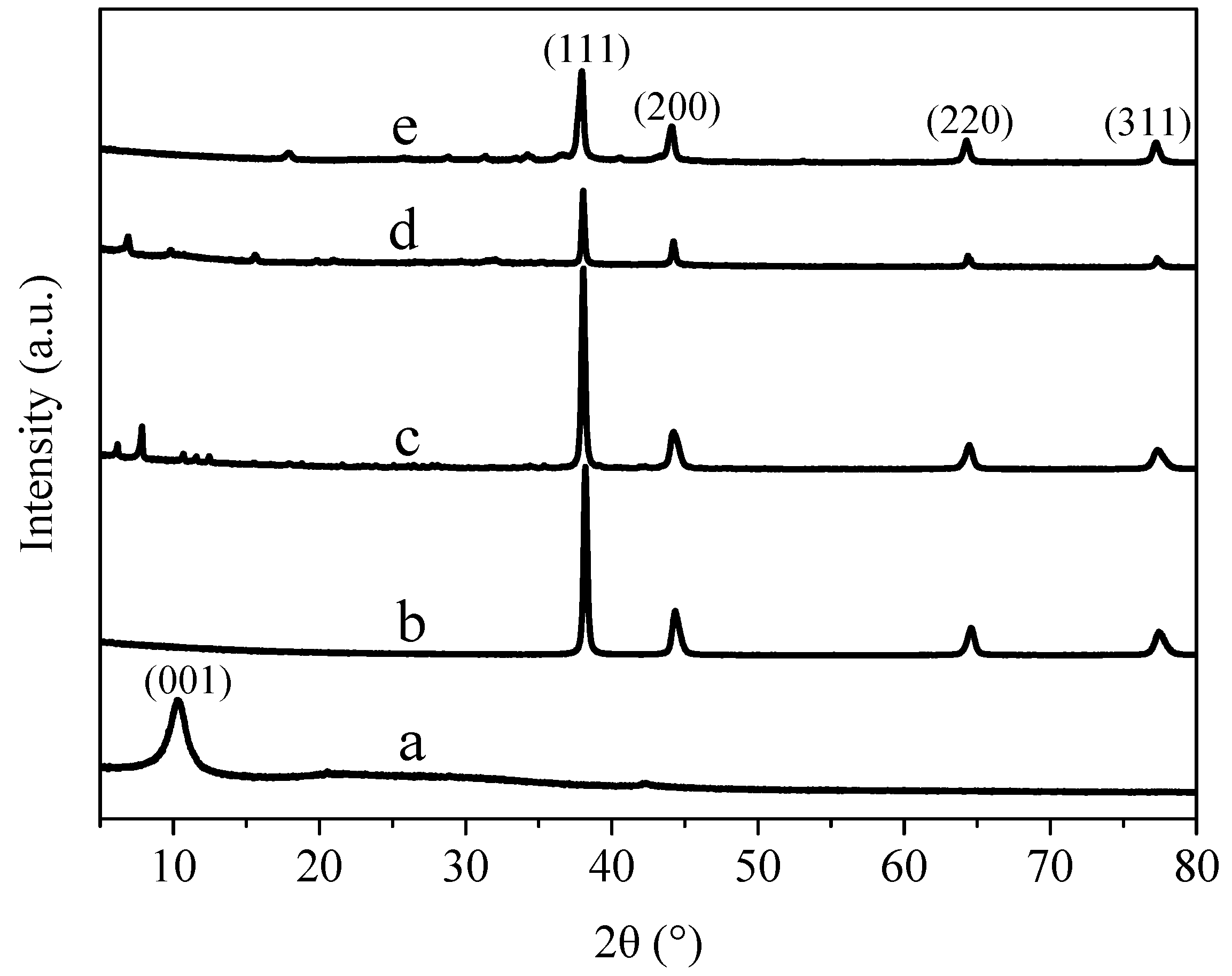
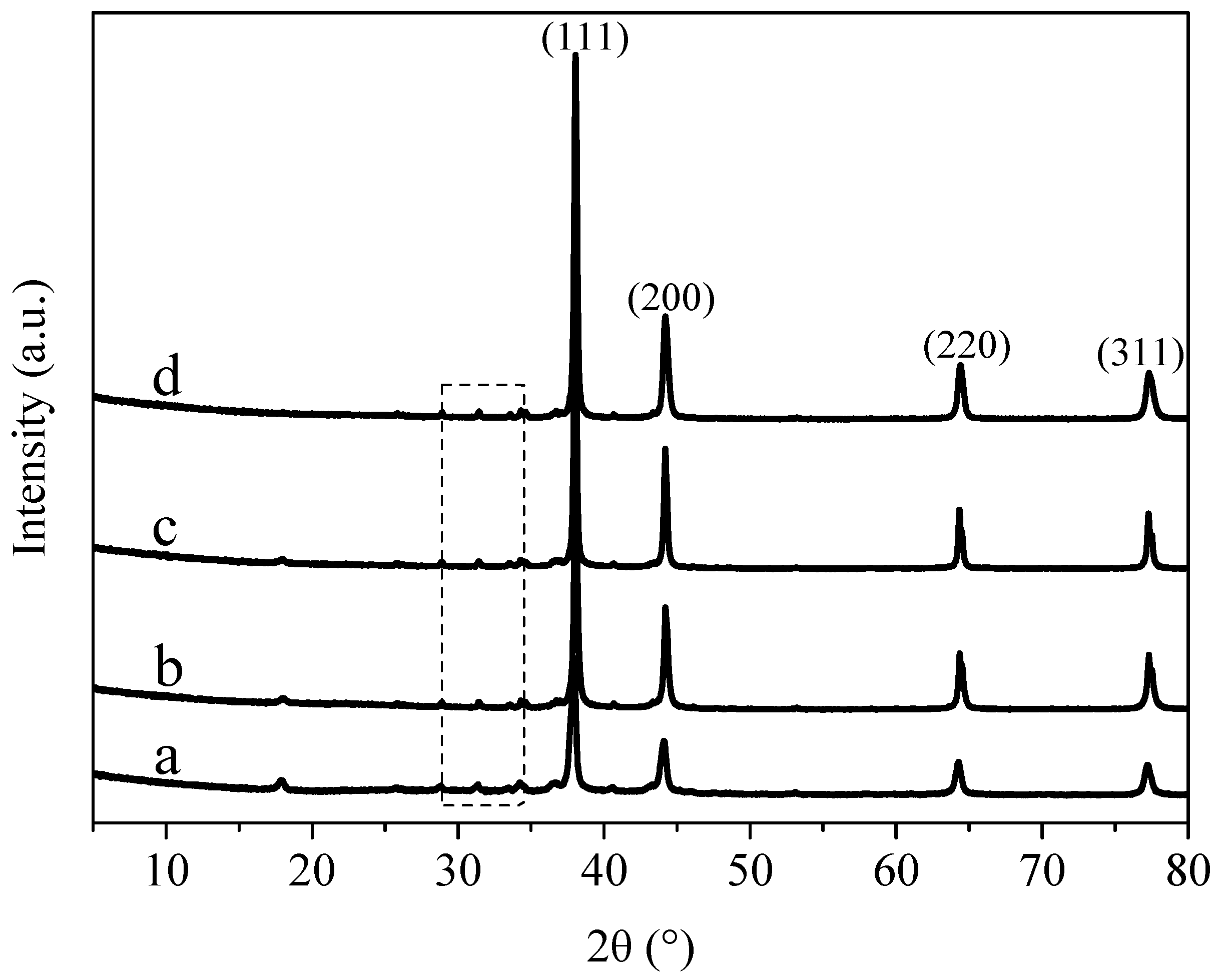
3.2. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
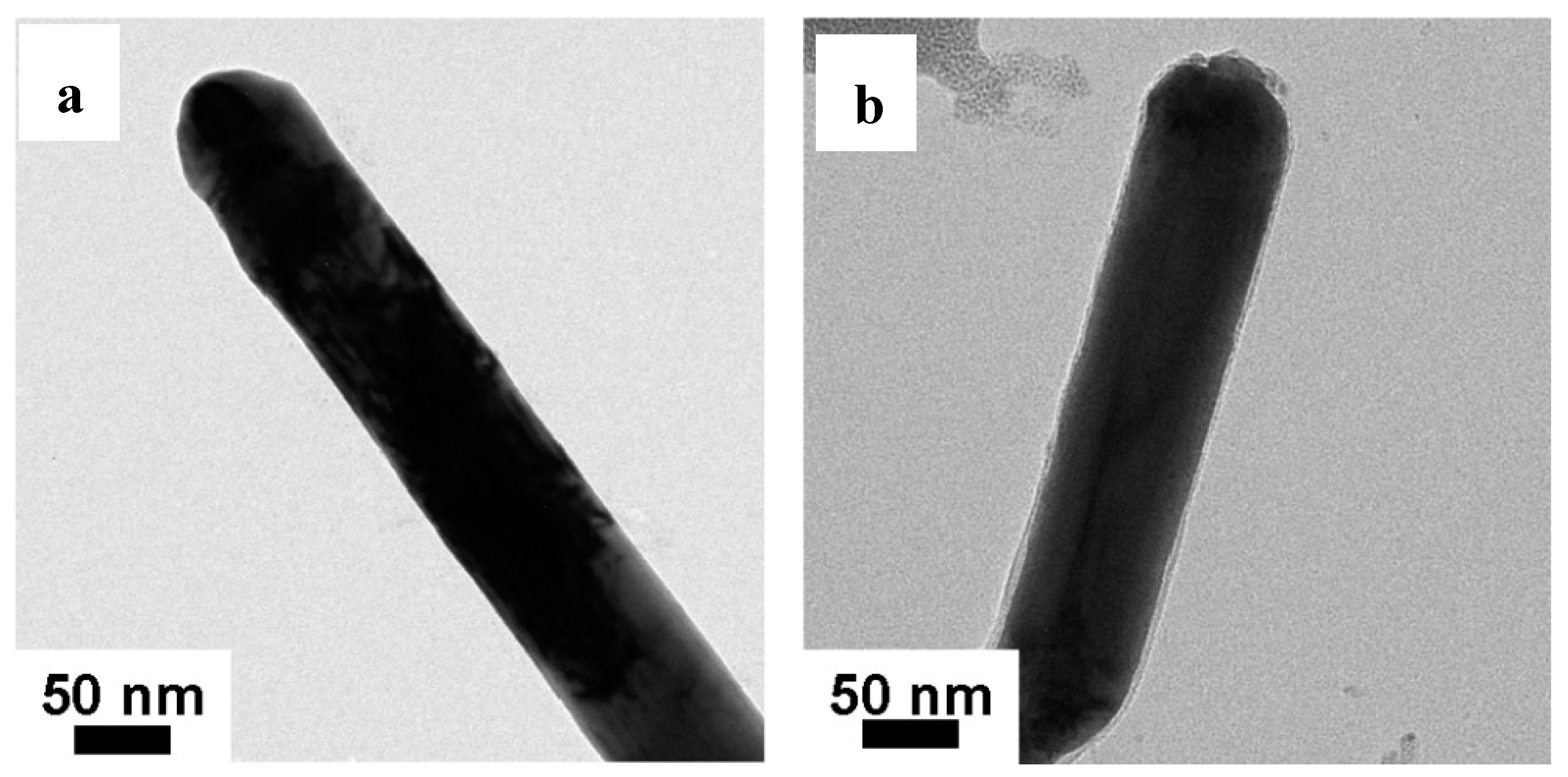
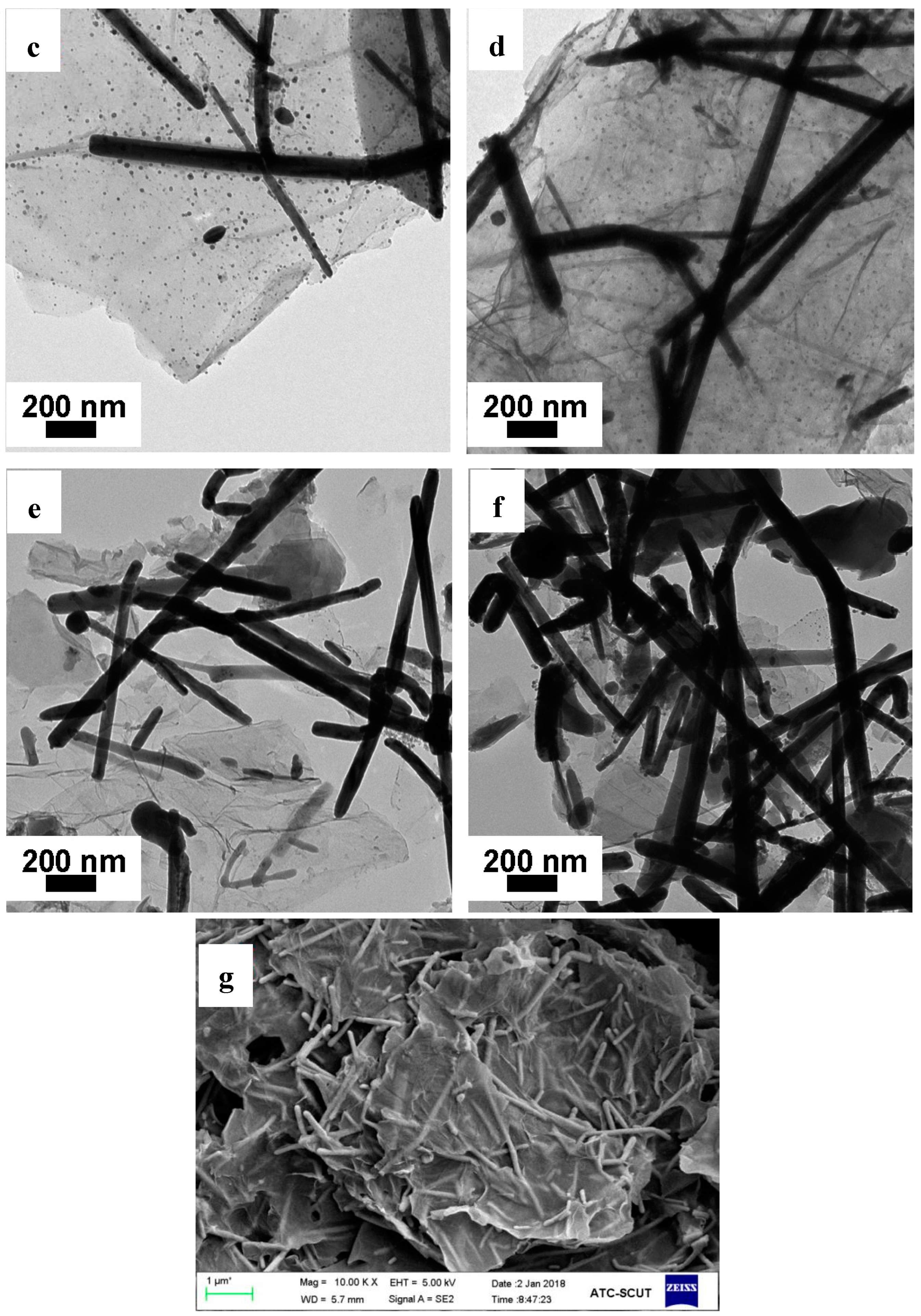
3.3. SEM and TEM Analysis
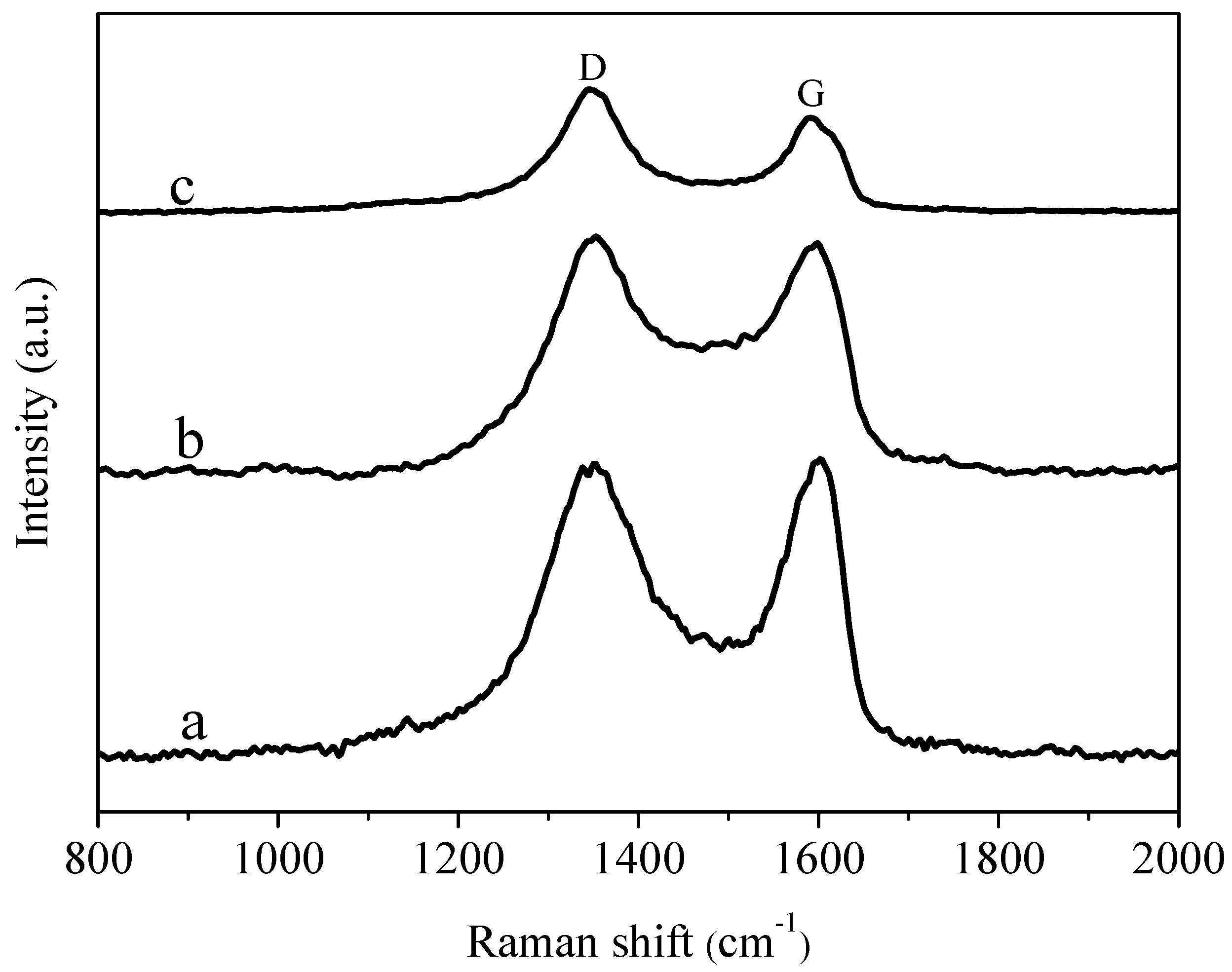
3.4. Raman Spectra Analysis
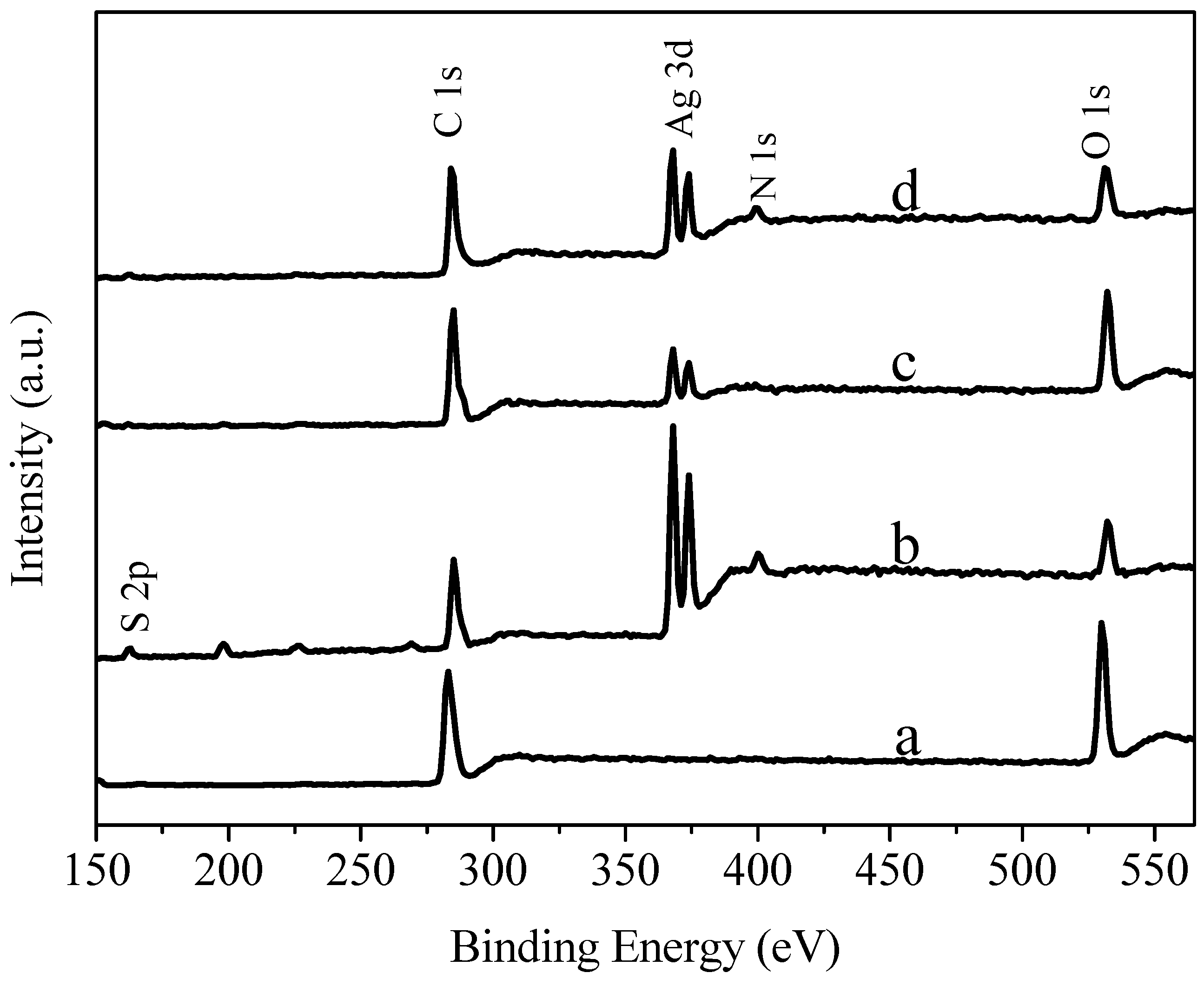
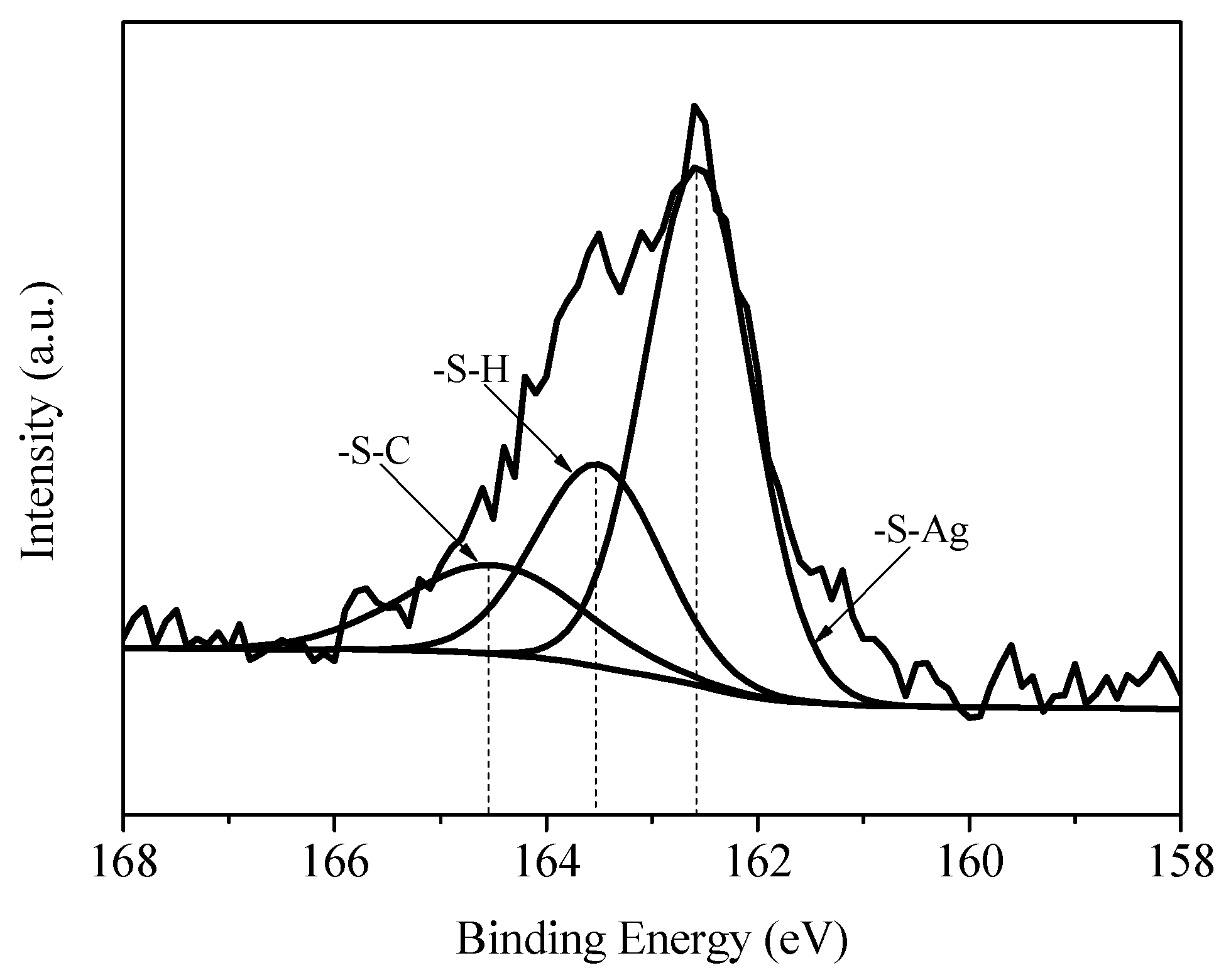
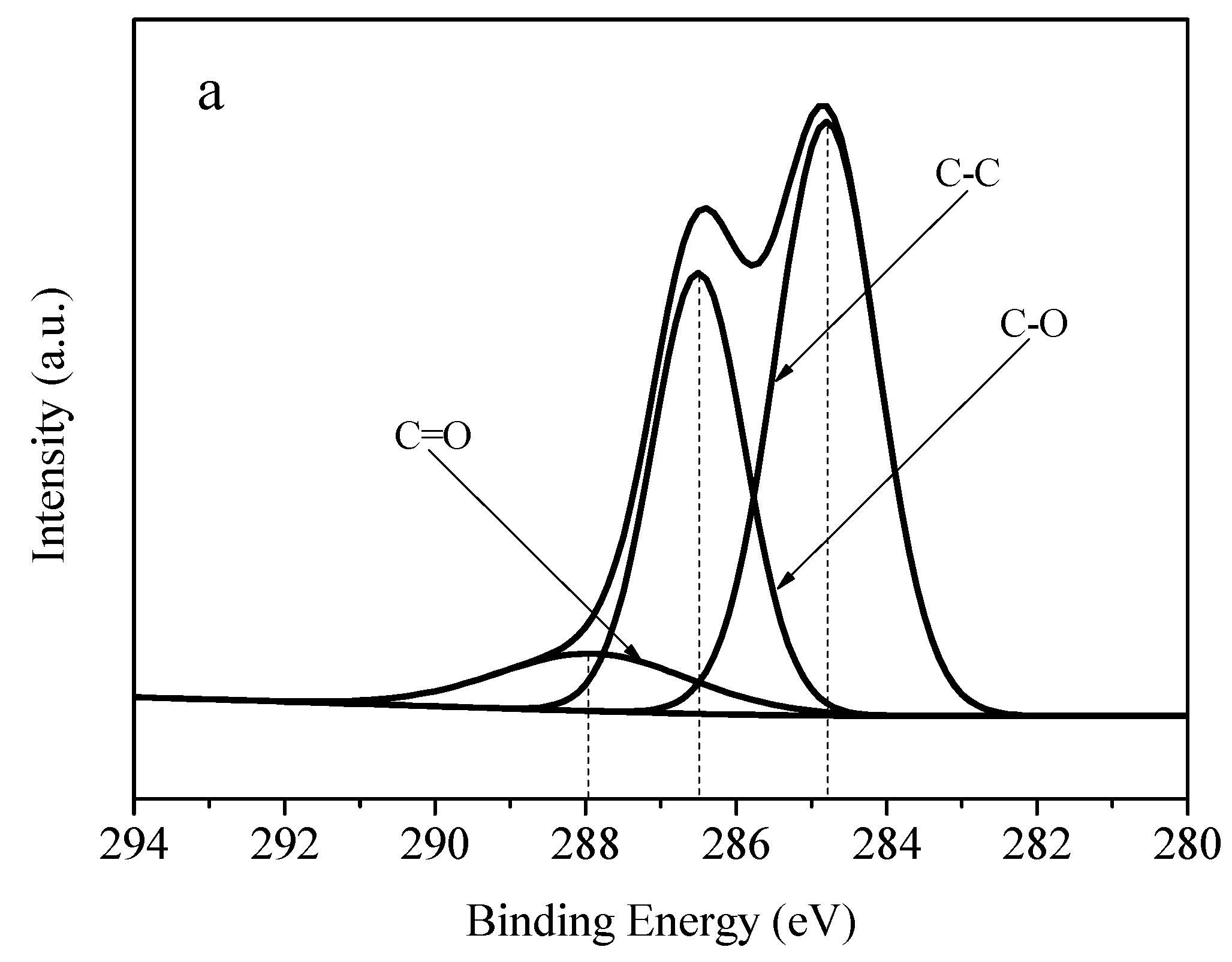
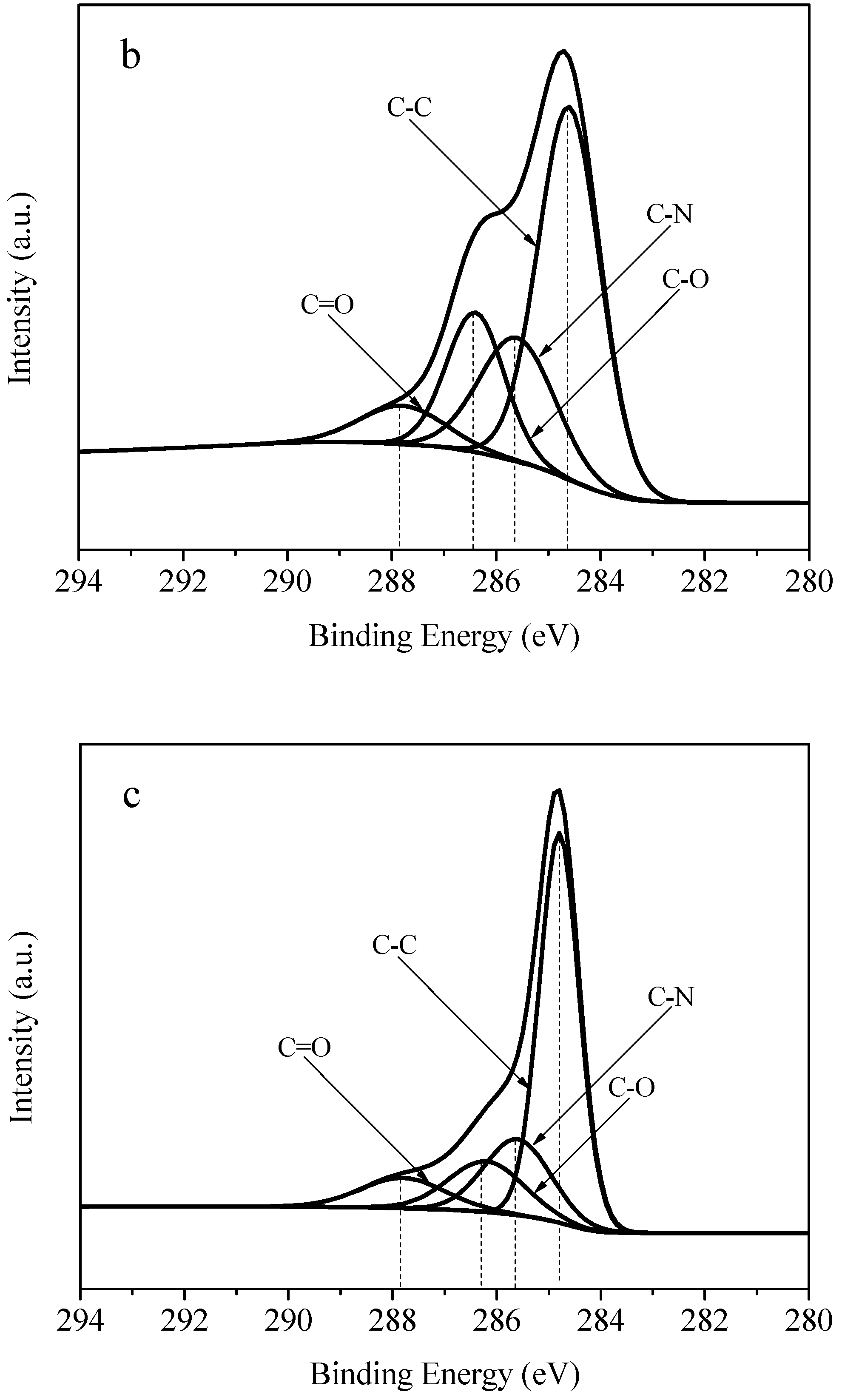
3.5. XPS (X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy) Spectra Analysis
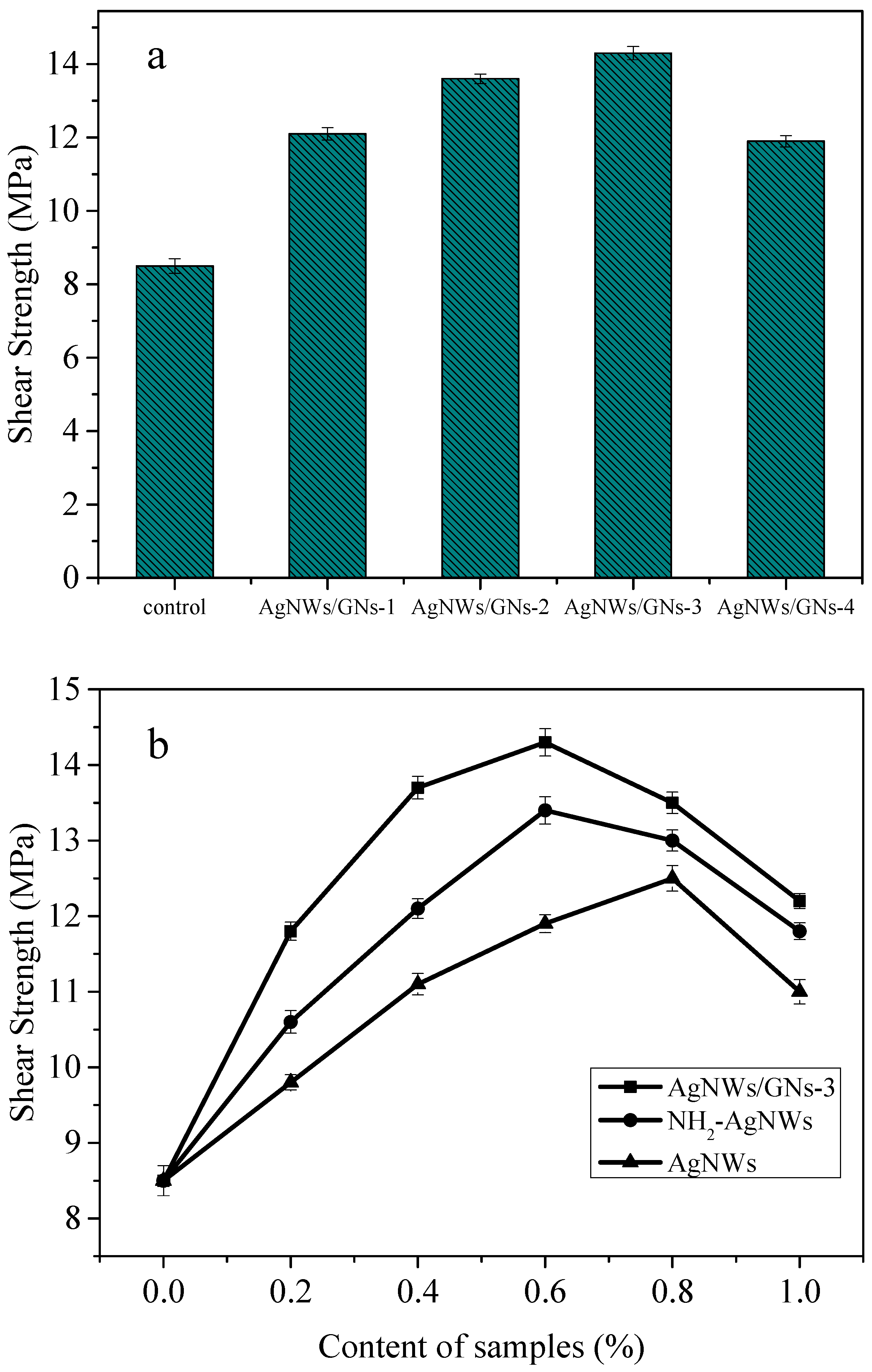
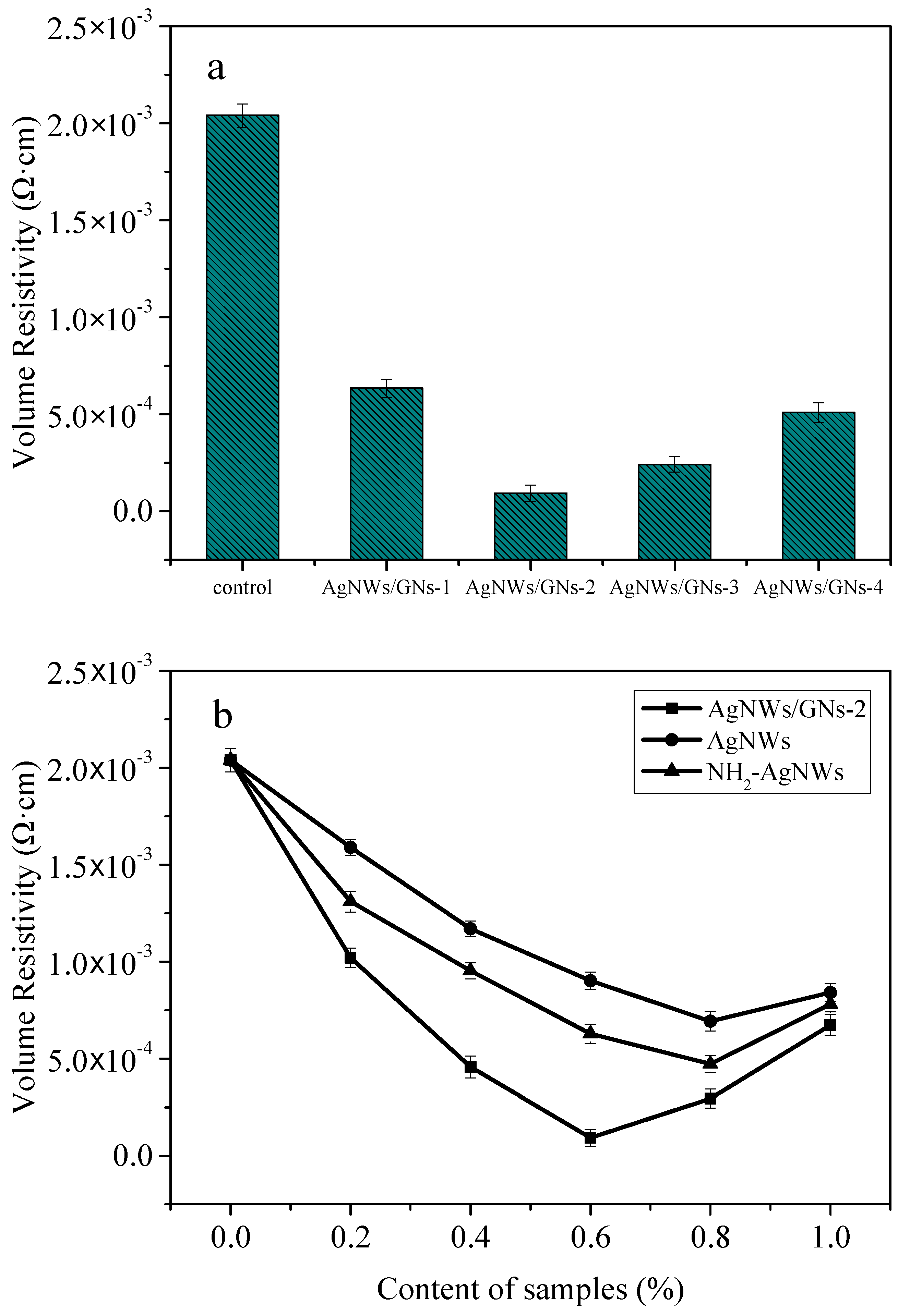
3.6. Performance Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Regarding the structure of the silver nanowires/graphene composite, the silver nanowires are uniformly dispersed on the surface of the graphene sheet layer. Such distribution can effectively form a two-dimensional nanocomposite structure and prevent graphene sheets from stacking.
- (2)
- Adding silver nanowires/graphene composite can effectively improve the electrical conductivity and mechanical properties of the conductive adhesive. When the mass ratio of silver nanowires to graphite oxide is 4:1 and the mass fraction of the filled composite is 0.8%, the volume resistivity can reach the minimum of 9.31 × 10−5 Ω·cm, which is 95.4% lower than that of the reference sample. When the mass ratio of silver nanowires to graphite oxide is 6:1 and the mass fraction of the filled composite is 0.6%, the shear strength can reach the maximum of 14.3 MPa, which is 68.2% higher than that of the reference sample.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, T.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z. Research progress and trends of electronic packaging materials. J. Nanjing Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2010, 14, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Gu, M.; Jin, Y. Current Status of Research on Electronic Packaging Materials. Mater. Rev. 2000, 14, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wong, C.P. Recent advances of conductive adhesives as a lead-free alternative in electronic packaging: Materials, processing, reliability and applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2006, 51, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, M.J.; Li, Y.; Moon, K.; Paik, K.W.; Wong, C.P. Review of recent advances in electrically conductive adhesive materials and technologies in electronic packaging. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2008, 22, 1593–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y. The Study and Development of Electrically Conductive Adhesive. Chem. Adhes. 2008, 30, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yim, M.J.; Moon, K.S.; Wong, C.P. Novel nano-scale conductive films with enhanced electrical performance and reliability for high performance fine pitch interconnect. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 2009, 32, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Moon, K.S.; Wong, C.P. Electronics without lead. Science 2005, 308, 1419–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramkumar, S.M.; Srihari, K. A novel anisotropic conductive adhesive for lead-free surface mount electronics packaging. J. Electron. Packag. 2007, 129, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.K.; Jeong, S.; Kim, D.; Moon, J.; Lim, S.; Kim, J.S. Synthesis and size control of monodisperse copper nanoparticles by polyol method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 311, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Moon, K.S.; Wong, C.P. A novel approach to stabilize contact resistance of electrically conductive adhesives on lead-free alloy surfaces. J. Electron. Mater. 2004, 33, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Moon, K.S.; Wong, C.P. Monolayer-protected silver nano-particle-based anisotropic conductive adhesives: Enhancement of electrical and thermal properties. J. Electron. Mater. 2005, 34, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolvgard, A.; Malmodin, J.; Liu, J.; Lai, Z. A reliable and environmentally friendly packaging technology-flip-chip joining using anisotropically conductive adhesive. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 1999, 22, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Moon, K.; Li, Y.; Wong, C. Surface functionalized silver nanoparticles for ultrahigh conductive polymer composites. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 2969–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.P.; Wu, X.J.; Ge, M.Y.; Zhang, G.Q.; Wang, Y.W.; Jiang, J.Z. Effect analysis of filler sizes on percolation threshold of isotropical conductive adhesives. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Moon, K.S.; Lin, W.; Wong, C.P. Preparation of highly conductive polymer nanocomposites by low temperature sintering of silver nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 2018–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Chou, K.S.; Shih, Z.W. Effect of nano-sized silver particles on the resistivity of polymeric conductive adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2005, 25, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Jia, D.M. In-situ preparation of epoxy/silver nanocomposites by thermal decomposition of silver-imidazole complex. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 3529–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wong, C.P.; Yuen, M.M.F. Printed electrically conductive composites: Conductive filler designs and surface engineering. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 4052–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polavarapu, L.; Manga, K.K.; Cao, H.D.; Loh, K.P.; Xu, Q.H. Preparation of conductive silver films at mild temperatures for printable organic electronics. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 3273–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, T.; Kim, W.S. Reversibly stretchable transparent conductive coatings of spray-deposited silver nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1855–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.P.; Liu, J.F.; Wu, X.J.; Ge, M.Y. High conductivity of isotropic conductive adhesives filled with silver nanowires. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2006, 26, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ma, C.M.; Yuen, S.; Teng, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, I.; Wei, M. Morphology, electrical, and rheological properties of silane-modified silver nanowire/polymer composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Li, R.; Jiang, G.; Yu, H.; Chen, T. Effect of silver nanowires on electrical conductance of system composed of silver particles. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 3172–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Qiao, X.; Qiu, X.; Tan, F.; Chen, J.; Jiang, R. Effect of silver nanostructures on the resistivity of electrically conductive adhesives composed of silver flakes. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2010, 21, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Xiong, N.N.; Li, Z.L.; Xie, H.; Liu, J.Z.; Dong, J.; Li, J.Z. A comprehensive study of silver nanowires filled electrically conductive adhesives. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 7927–7935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zeng, J.; Harrington, S.; Ma, L.; Ma, M.; Guo, X.; Ma, Y. Hydrothermal fabrication of silver nanowires-silver nanoparticles-graphene nanosheets composites in enhancing electrical conductive performance of electrically conductive adhesives. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Xiao, F. The sintering behavior of electrically conductive adhesives filled with surface modified silver nanowires. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2011, 25, 1465–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Grigorieva, S.V.; Dubonos, S.V.; Firson, A.A. Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nature 2005, 438, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Jin, Y.; Tan, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J. A simple approach for fabricating a superhydrophobic surface based on poly(methyl methacrylate). J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2008, 22, 1841–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajid, A.S.; Ahmed, H.S.T.; Das, S.; Irin, F.; Jankowski, A.F.; Green, M.J. High-performance pristine graphene/epoxy composites with enhanced mechanical and electrical properties. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcq, F.; Demont, P.; Monfraix, P.; Peigney, A.; Laurent, Ch.; Falat, T.; Courtade, F.; Jamin, T. Carbon nanotubes and silver flakes filled epoxy resin for new hybrid conductive adhesives. Microelectron. Reliab. 2011, 51, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, V.H.; Tien, H.N.; Cuong, T.V.; Kong, B.S.; Chung, J.S.; Kim, E.J.; Hur, S.H. Novel conductive epoxy composites composed of 2-D chemically reduced graphene and 1-D silver nanowire hybrid fillers. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 8649–8653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Chun, K.Y.; Lee, E.; Kim, Y.J.; Baik, S. Functionalized nano-silver particles assembled on one-dimensional nanotube scaffolds for ultra-highly conductive silver/polymer composites. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 3579–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.P.; Wu, X.J.; Ge, M.Y.; Zhang, G.Q.; Wang, Y.W.; Jiang, J. Properties investigation on isotropical conductive adhesives filled with silver coated carbon nanotubes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoli, B.M.; Trinidad, J.; Hu, A.; Zhou, Y.N.; Zhao, B. Highly electrically conductive adhesives using silver nanoparticle (Ag NP)-decorated graphene: The effect of NPs sintering on the electrical conductivity improvement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Qiao, X.; Qiu, X.; Chen, J.; Jiang, R. Convenient synthesis of silver nanowires with adjustable diameters via a solvothermal method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 344, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tien, H.W.; Hsiao, S.T.; Liao, W.H.; Yu, Y.H.; Lin, F.C.; Wang, Y.S.; Li, S.M.; Ma, C.C.M. Using self-assembly to prepare a graphene-silver nanowire hybrid film that is transparent and electrically conductive. Carbon 2013, 58, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Techane, S.D.; Gamble, L.J.; Castner, D.G. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy characterization of gold nanoparticles functionalized with amine-terminated alkanethiols. Biointerphases 2011, 6, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sookhakian, M.; Ridwan, N.A.; Zalnezhad, E.; Yoon, G.H.; Azarang, M.; Mahmoudian, M.R.; Alias, Y. Layer-by-layer electrodeposited reduced graphene oxide-copper nanopolyhedra films as efficient platinum-free counter electrodes in high efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, D154–D159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, M.A.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S.; Cancado, L.G.; Jorio, A.; Saito, R. Studying disorder in graphite-based systems by Raman spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 1276–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Piner, R.D.; Kohlhaas, K.A.; Kleinhammes, A.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 2007, 45, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prolongo, S.G.; Campo, M.; Gude, M.R.; Chaos-Morán, R.; Ureña, A. Thermo-physical characterisation of epoxy resin reinforced by amino-functionalized carbon nanofibers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fang, Z.; Gu, A.; Xu, L.; Liu, F. Effect of amino-functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the dispersion with epoxy resin matrix. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Materials | Supplier |
|---|---|
| Mercaptoethylamine (β-cysteamine) | Aladdin Chemical Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| graphite oxide (GO) | Aladdin Chemical Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| Hydrazine hydrate | Damao Chemisty Co. Ltd. (Tianjin, China) |
| Ethanediol | Damao Chemisty Co. Ltd. (Tianjin, China) |
| AgNO3 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| FeCl3 | Guangdong Guanghuang Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd. (Shantou, China) |
| Absolute ethyl alcohol | Guangdong Guanghuang Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd. (Shantou, China) |
| Acetone | Guangzhou Chemical Reagent Factory (Guangzhou, China) |
| MeH-HPA | Shanghai Macklin Bioc-tech Inc. (Shanghai, China) |
| 2-Ethyl-4-methylimiadazole (2E4MZ) | Shanghai Macklin Bioc-tech Inc. (Shanghai, China) |
| Bisphenol-A epoxy resin (DGEBA, E-51, epoxy value = 0.54 ) | Shanghai Balin petrochemical epoxy resin Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| Equipment | Model | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Electric thermostat blast drying oven | DHG-9240A | Shanghai Shenxian Thermostatic Equipment (Shanghai, China) |
| Vacuum drying oven | DZF-6050 | Shanghai Shenxian Thermostatic Equipment (Shanghai, China) |
| Ultrasonic cleaner | KII2200 | Kunshan Hechuang Ultrasonic Instrument (Suzhou, China) |
| Electric blender | JJ-1A | Changzhou Aohua Instrument Co., Ltd. (Changzhou, China) |
| Constant temperature magnetic stirrer | Feb-85 | Shanghai Sile Instrument Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| High speed desktop centrifuge | TG1650-WS | Xiangyi Centrifuge Instrument (Changsha, China) |
| Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) | Merlin | Zeiss, Germany (Oberkochen, Germany) |
| Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) | JEM-2100F | Japan Electronics Corporation (Tokyo, Japan) |
| Automatic X-ray diffractometer | AXS D8 | Bruker, Germany (Karlsruhe, Germany) |
| Fourier transform infrared spectrometer | Equinox-55 | Bruker, Germany (Karlsruhe, Germany) |
| Raman spectrometer | LabRAM Aramis | H.J.Y, France (Paris, France) |
| X-ray photoelectron spectrometer | Axis Ultra | Shimadzu Kratos, Japan (Kyoto, Japan) |
| Electronic universal testing machine | AG-IC50kN | Suzhou Shimading Instrument Co., Ltd. (Suzhou, China) |
| Double electric logging four-point probe tester | RTS-9 | Beijing Jinshisu Instrument Equipment Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, T.; Chen, J.; Yuan, W.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhou, X. Self-Assembly Synthesis of Silver Nanowires/Graphene Nanocomposite and Its Effects on the Performance of Electrically Conductive Adhesive. Materials 2018, 11, 2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102028
Xu T, Chen J, Yuan W, Liu Y, Sun Y, Wu H, Zhou X. Self-Assembly Synthesis of Silver Nanowires/Graphene Nanocomposite and Its Effects on the Performance of Electrically Conductive Adhesive. Materials. 2018; 11(10):2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102028
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Tao, Jiayu Chen, Wenhui Yuan, Yinhua Liu, Yongjun Sun, Huijun Wu, and Xiaoqing Zhou. 2018. "Self-Assembly Synthesis of Silver Nanowires/Graphene Nanocomposite and Its Effects on the Performance of Electrically Conductive Adhesive" Materials 11, no. 10: 2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102028
APA StyleXu, T., Chen, J., Yuan, W., Liu, Y., Sun, Y., Wu, H., & Zhou, X. (2018). Self-Assembly Synthesis of Silver Nanowires/Graphene Nanocomposite and Its Effects on the Performance of Electrically Conductive Adhesive. Materials, 11(10), 2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102028








