Microstructure of High-Performance Aluminum Alloy Surface Processed by the Single-Excitation Same-Frequency Longitudinal–Torsional Coupled Ultrasonic Vibration Milling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The System of LTCUV
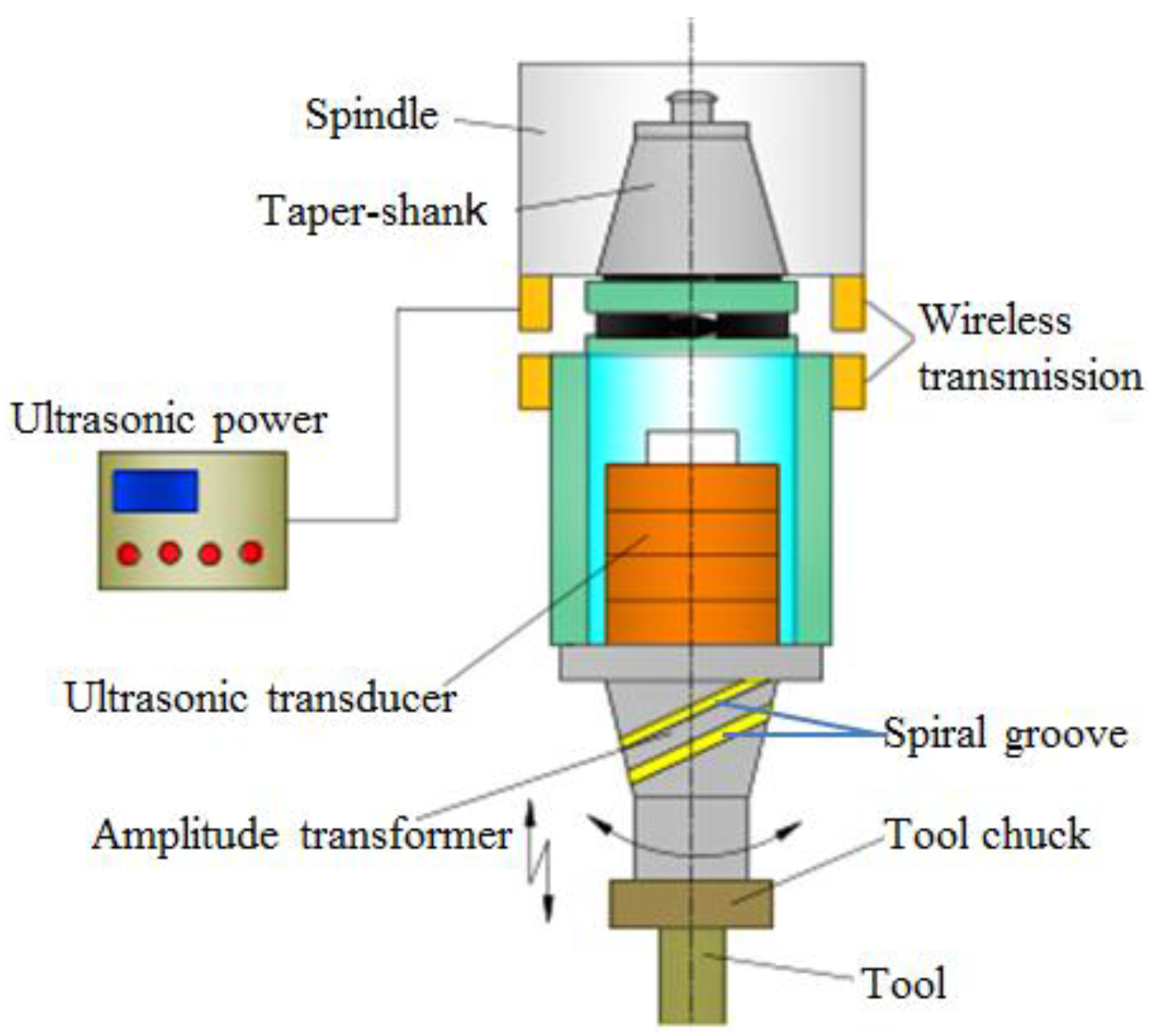
2.1. Constitution of LTCUV System
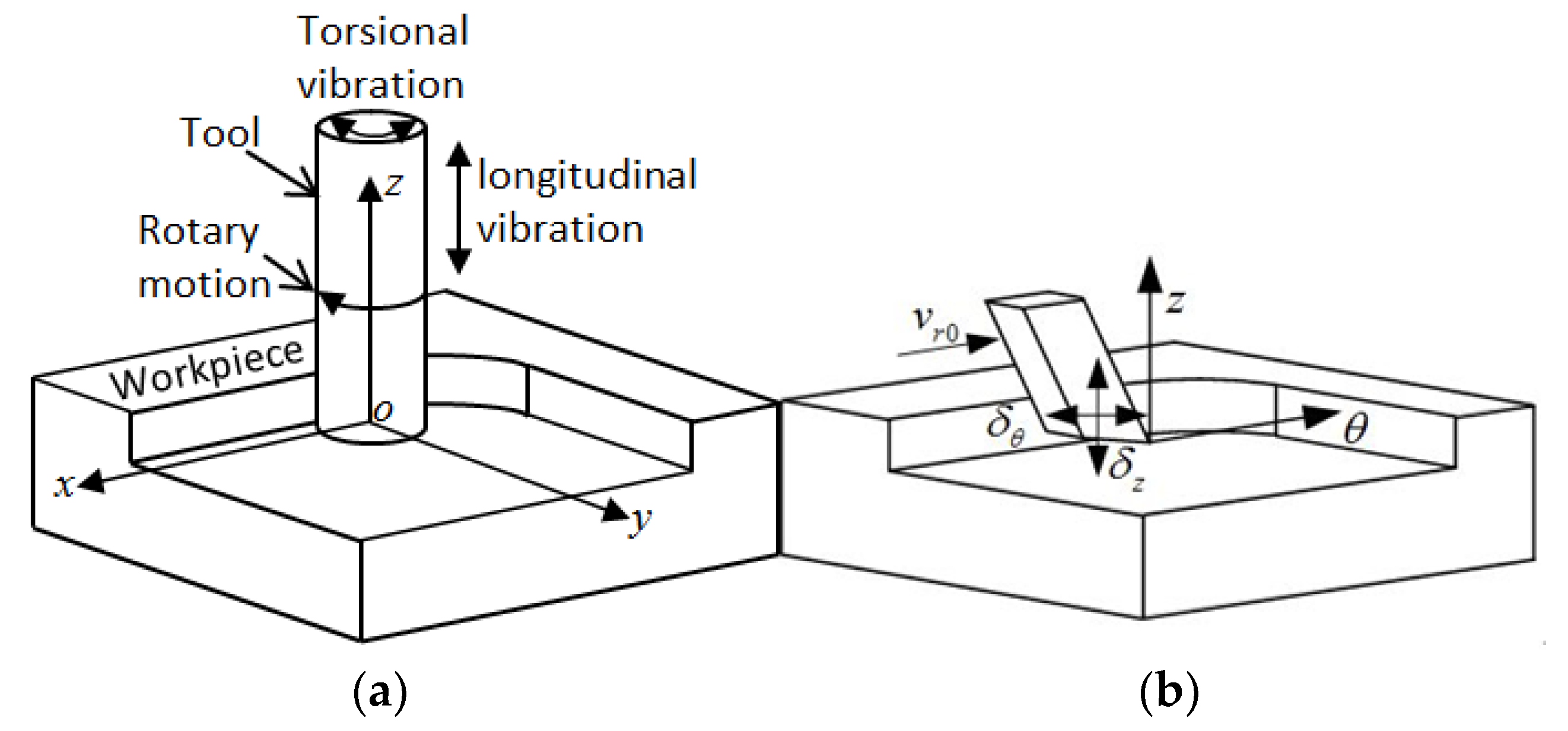
2.2. Motion Path Model of Ultrasonic Longitudinal–Torsional Milling Tool
3. Methods and Results
3.1. Methods
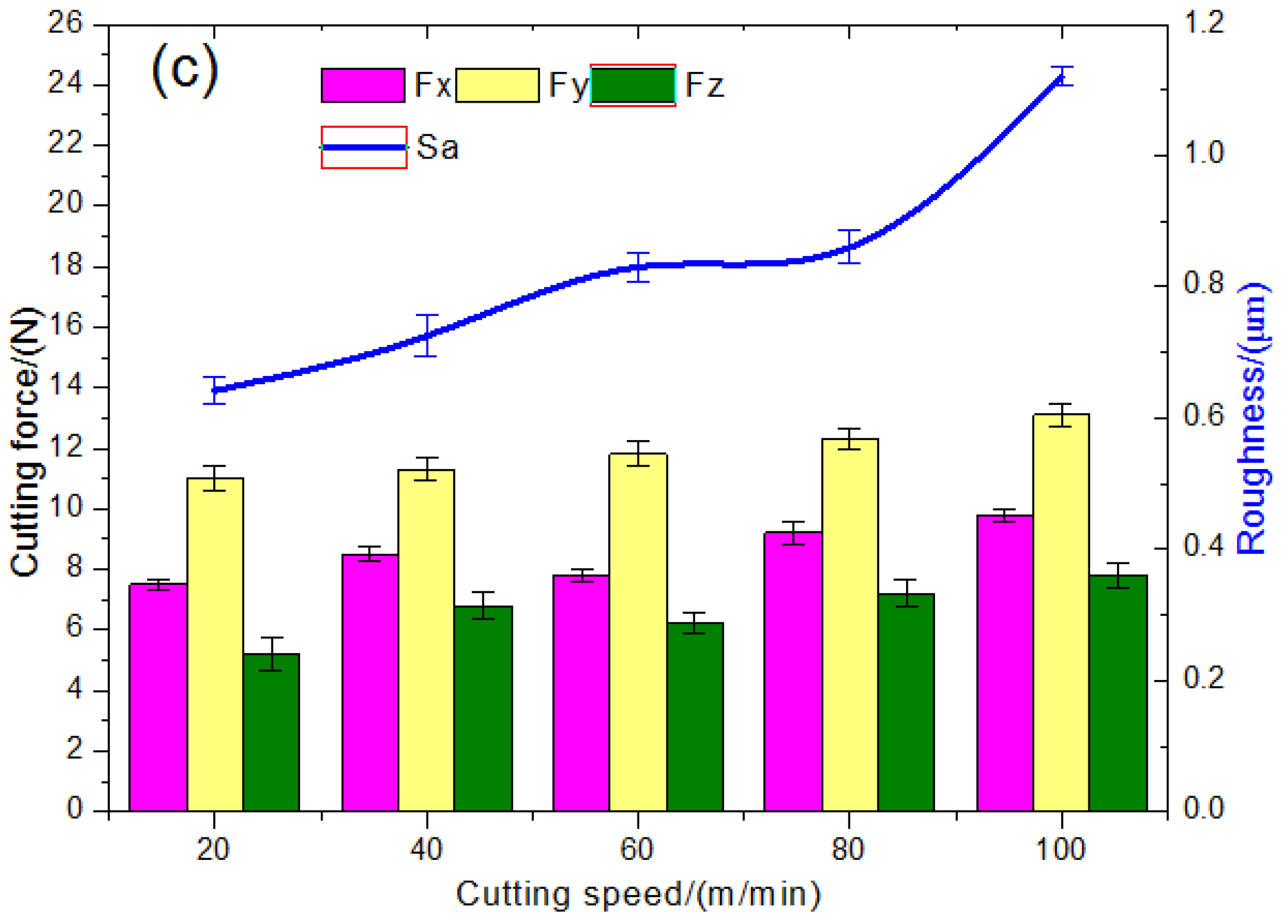
3.2. Impact of Processing Parameters on the Cutting Force and Surface Roughness
3.3. Effects of Processing Parameters on Surface Wettability
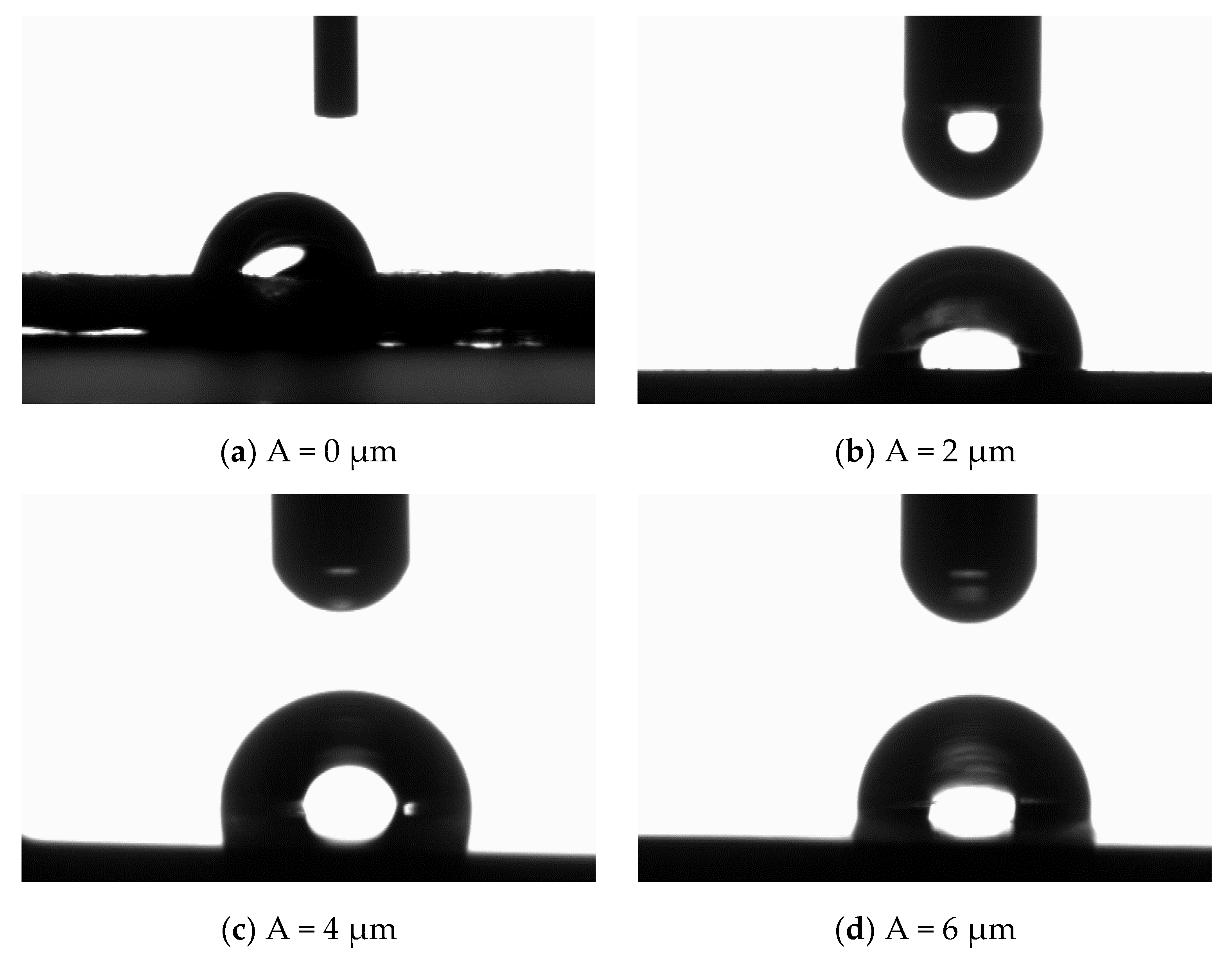
3.3.1. Effects of Processing Parameters on Water Contact Angle
3.3.2. Ultrasonic Amplitude Effect on the Water Contact Angle
3.4. Wear Resistance of Surfaces Processed by Ultrasonic Longitudinal Torsion Milling
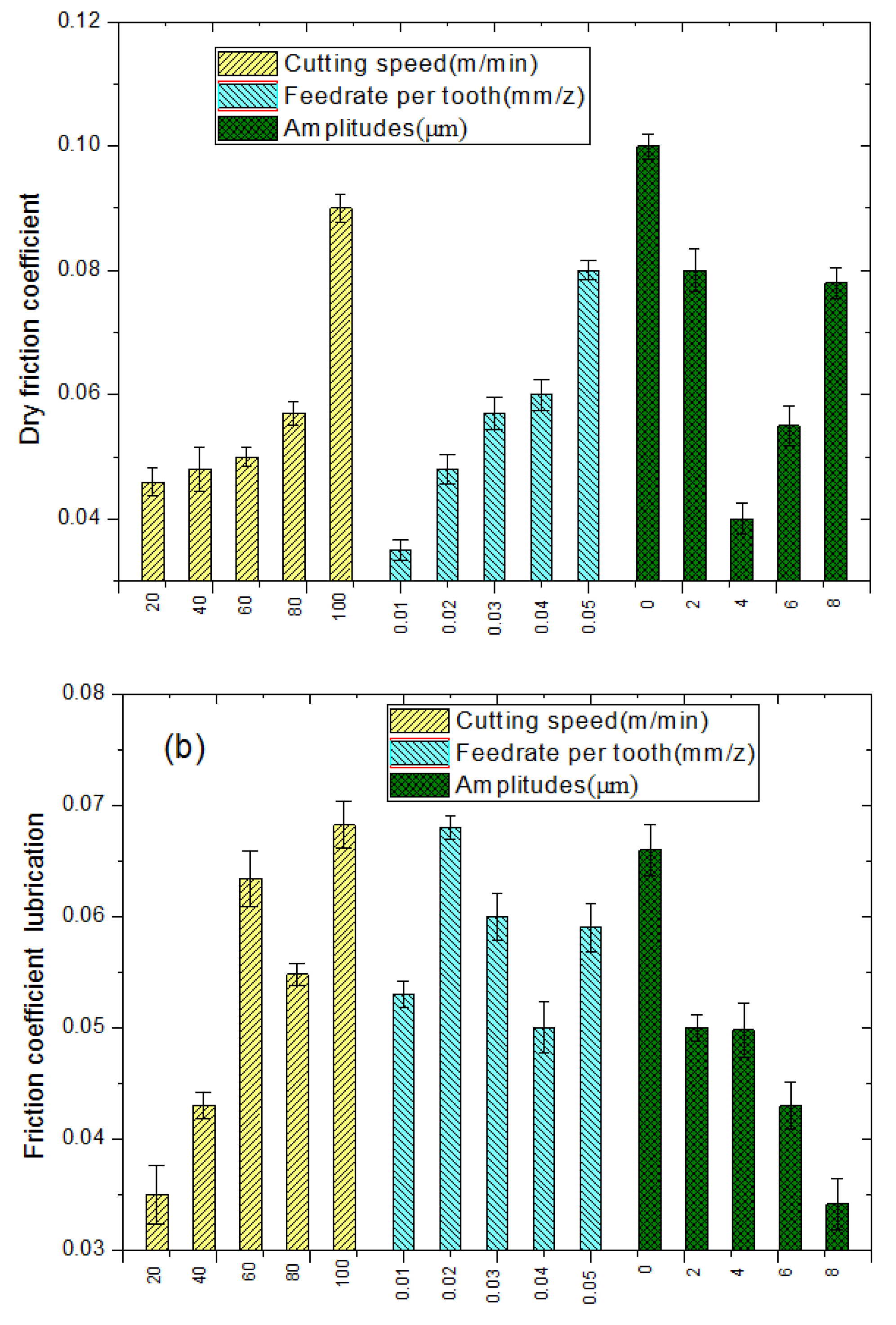
3.4.1. Effect of Processing Parameters on the Friction Coefficient
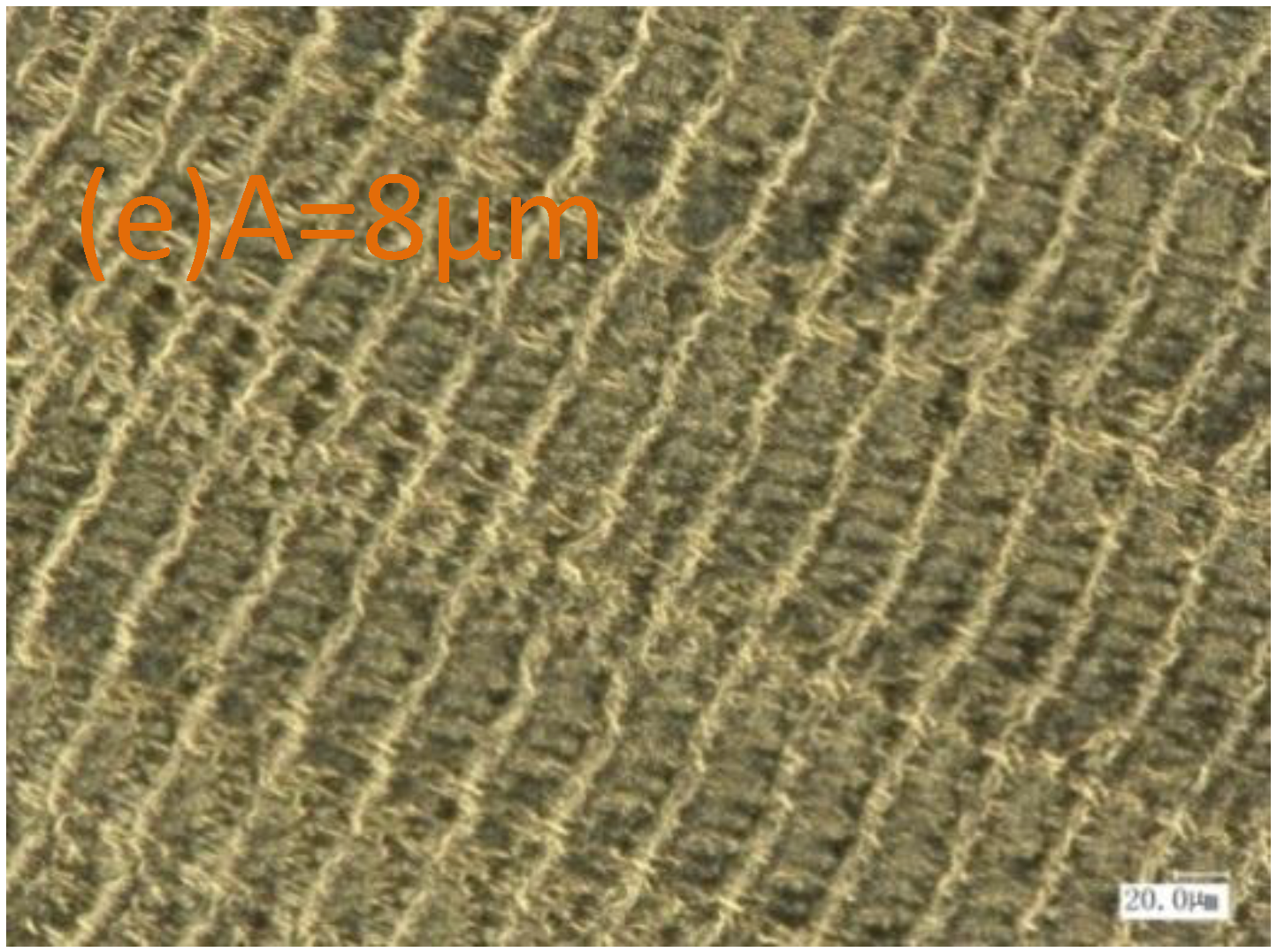
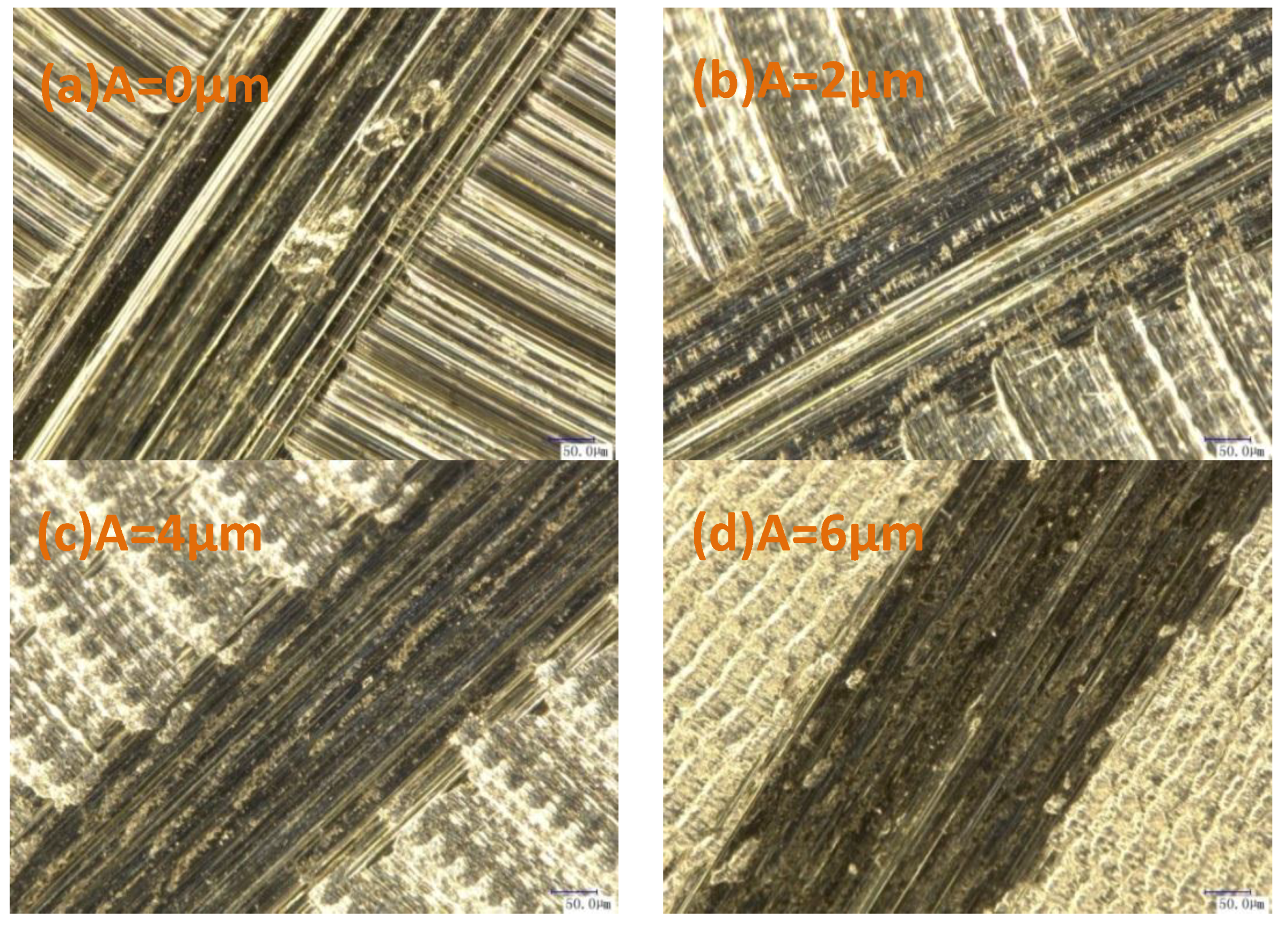
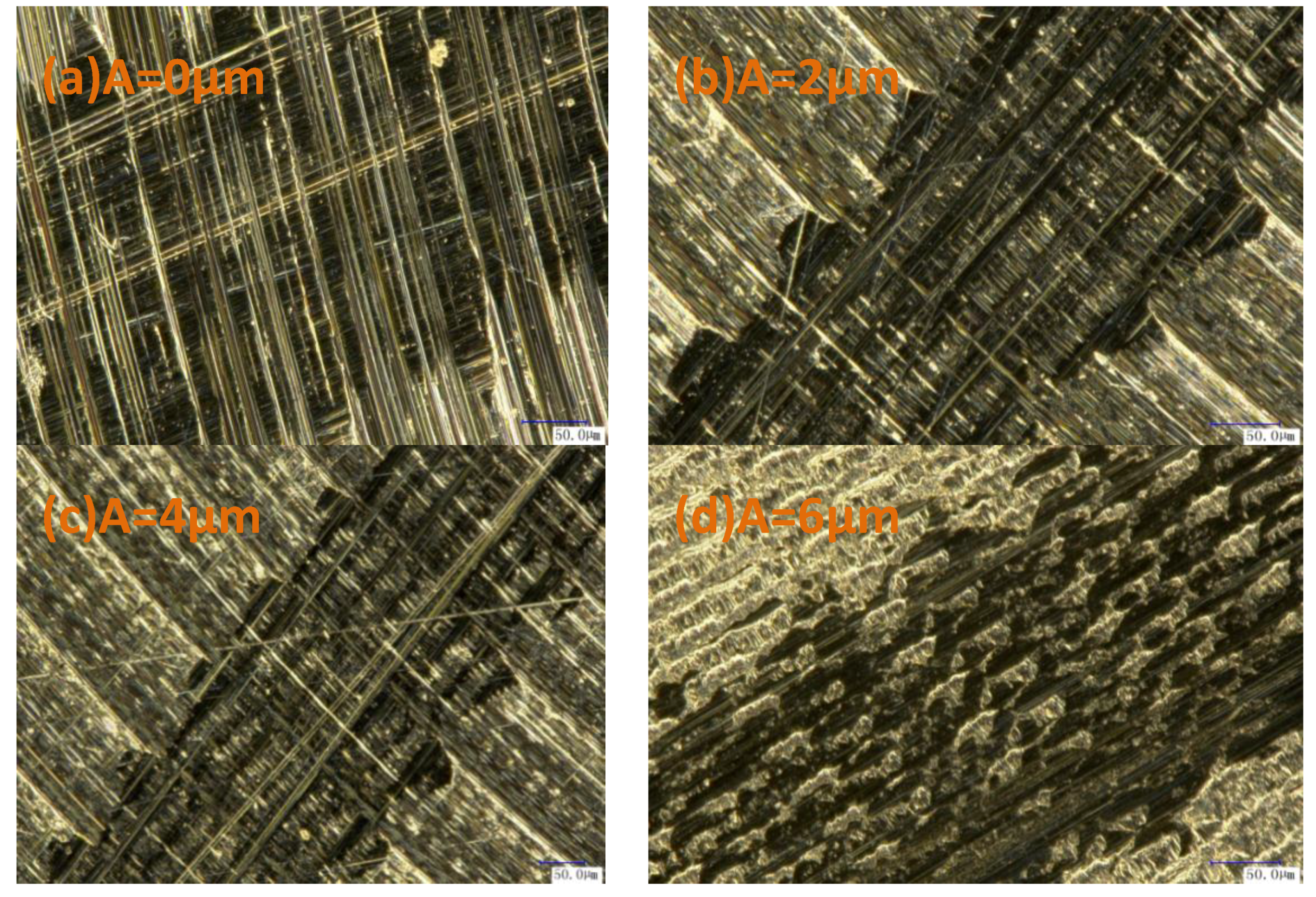
3.4.2. Frictional Wear Microstructures of Samples Treated by Different Processing Methods
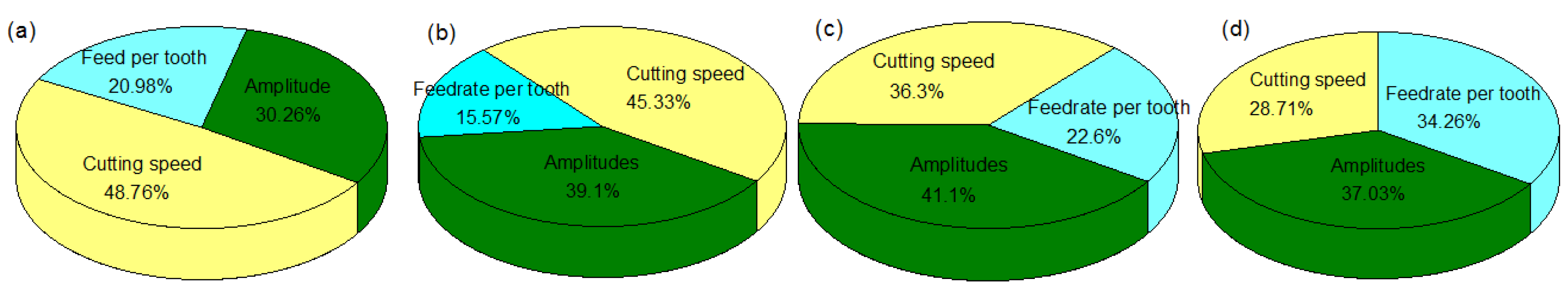
3.5. Contribution Degree of Parameters to Microstructure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Li, C.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, Q.; Yu, L.; Li, H. Corrosion behavior of Al–Mg2Si alloys with/without addition of Al–P master alloy. Mater. Charact. 2015, 110, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Z.; Mao, Q.; Fang, B.; Song, R.; Zheng, Z. The intergranular corrosion susceptibility of a heavily overaged Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloy. Corros. Sci. 2016, 107, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Huang, Y.T.; Zhang, J. Analysis of light alloy forming manufacturing technology. Modern Manuf. 2017, 24, 100–101. [Google Scholar]
- Delijic, K.; Markoli, B. The influence of the chemical composition on the corrosion performances of a medium strength Al-Mg-Si (6XXX) type alloys. Metal. Mater. Eng. 2014, 20, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.D. Ultrasonic Processing and its Application; National Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, X.; Wu, R. Feasibility study of high-speed ultrasonic vibration cutting titanium alloy. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 247, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanbi, D.; Ogam, E.; Amara, S.E.; Fellah, Z.E.A. Synthesis and Mechanical Characterization of Binary and Ternary Intermetallic Alloys Based on Fe-Ti-Al by Resonant Ultrasound Vibrational Methods. Materials 2018, 11, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Telang, A.; Gill, A.S.; Suslov, S.; Idell, Y.; Zweiacker, K.; Vasudevan, V.K. Gradient nanostructure and residual stresses induced by Ultrasonic Nano-crystal Surface Modification in 304 austenitic stainless steel for high strength and high ductility. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 613, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkena, B.; Vehmeyer, J.; Niederwestberg, D.; Maaß, P. Identification of the specific cutting force for geometrically defined cutting edges and varying cutting conditions. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2014, 82, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zębala, W.; Kowalczyk, R. Estimating the effect of cutting data on surface roughness and cutting force during WC-Co turning with PCD tool using Taguchi design and ANOVA analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 77, 2241–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Huang, J.; Gao, C.; Chang, W. Empirical models for cutting forces in finish dry hard turning of hardened tool steel at different hardness levels. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 76, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przestacki, D.; Chwalczuk, T.; Wojciechowski, S. The study on minimum uncut chip thickness and cutting forces during laser-assisted turning of WC/NiCr clad layers. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 3887–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitzig-Frank, H.; Tawakoli, T.; Azarhoushang, B. Material removal mechanism in ultrasonic-assisted grinding of Al2O3, by single-grain scratch test. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 2949–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Niu, Y.; Liu, X. Effect of ultrasonic vibration on surface white layer in ultrasonic aided turning of hardened GCr15 bearing steel. Mater. Res. Innov. 2015, 19, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.; Ma, C.; Shen, X.; Zhang, J. Experimental and modeling study on cutting forces of feed direction ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 90, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.H.; Ehmann, K.F. Investigation of the effect of tooling axial ultrasonic vibration assistance on meso-scale milled surfaces. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference of the European Society for Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology, Berlin, Germany, 1 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, Y.; Cong, W.L.; Stanco, M.R.; Xu, Z.G.; Pei, Z.J.; Treadwell, C.; Li, Z.C. Rotary ultrasonic machining of alumina dental ceramics: A preliminary experimental study on surface and subsurface damages. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. 2012, 134, 064501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruda, R.W.; Krolczyk, G.M.; Wojciechowski, S.; Zak, K.; Habrat, W.; Nieslony, P. Effects of extreme pressure and anti-wear additives on surface topography and tool wear during MQCL turning of AISI 1045 steel. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.S.; Yang, K.S.; Chung, C.K.; Lin, J.F. Surface quality, microstructure, and mechanical properties of the SKD 61 tool steel with prior heat treatment affected by single- and double-pass continuous wave laser polishing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghjari, S.H.; Mousavi, S.A. Effects of pulsed Nd: YAG laser welding parameters and subsequent post-weld heat treatment on microstructure and hardness of AISI 420 stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2013, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhatha, M.E.; Fatoba, O.S.; Akinlabi, E.T. Effects of rapid solidification on the microstructure and surface analyses of laser-deposited Al-Sn coatings on AISI 1015 steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 94, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özşahin, O.; Ertürk, A.; Özgüven, H.N.; Budak, E. A closed-form approach for identification of dynamical contact parameters in spindle–holder–tool assemblies. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2009, 49, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunç, L.T.; Ozkirimli, O.M.; Budak, E. Machining strategy development and parameter selection in 5-axis milling based on process simulations. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 85, 1483–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Suzuki, N.; Shamoto, E. Investigation on Machining Performance of Amplitude Control Sculpturing Method in Elliptical Vibration Cutting. Procedia CIRP 2013, 8, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shamoto, E. Elliptical vibration cutting of hardened steel with large nose radius single crystal diamond tool (mini special issue on machining control and process monitoring). Int. J. Autom. Technol. 2014, 8, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaise, T.; Li, J.; Nelias, D.; Kubler, R.; Taheri, S.; Douchet, G.; Gilles, P. Modelling of multiple impacts for the prediction of distortions and residual stresses induced by ultrasonic shot peening (USP). J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 2080–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.H.; Shaw, K.C.; Chua, H.K.; Lin, R.M. The effect of one directional ultrasonic vibration assistance in high speed meso-scale milling process. Key Eng. Mater. 2010, 447, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babitsky, V.I.; Mitrofanov, A.V.; Silberschmidt, V.V. Ultrasonically assisted turning of aviation materials: Simulations and experimental study. Ultrasonics 2004, 42, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Mitrofanov, A.V.; Babitsky, V.I.; Silberschmidt, V.V. 3D finite element analysis of ultrasonically assisted turning. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2007, 39, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Huang, C.; Wen, L.; Zhang, W. Influence of Ultrasonic Surface Rolling on Microstructure and Wear Behavior of Selective Laser Melted Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials 2017, 10, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation Stress (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| ≥560 | ≥495 | ≥6 |
| Diameter (mm) | Helix Angle (°) | Cutter Teeth |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | 55 | 3 |
| Rang Ability (KN) | Sensitivity (pc/N) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fx | Fy | Fz | Fx | Fy | Fz |
| ±5 | ±5 | ±10 | −7.929 | −7.931 | −3.712 |
| Number | Cutting Speed V (m/min) | Feed Per Tooth Fz (mm/z) | Amplitude A (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 0.01 | 0 |
| 2 | 40 | 0.02 | 2 |
| 3 | 60 | 0.03 | 4 |
| 4 | 80 | 0.04 | 6 |
| 5 | 100 | 0.05 | 8 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, B.; Jiao, F. Microstructure of High-Performance Aluminum Alloy Surface Processed by the Single-Excitation Same-Frequency Longitudinal–Torsional Coupled Ultrasonic Vibration Milling. Materials 2018, 11, 1975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101975
Zhao C, Wang X, Zhao B, Jiao F. Microstructure of High-Performance Aluminum Alloy Surface Processed by the Single-Excitation Same-Frequency Longitudinal–Torsional Coupled Ultrasonic Vibration Milling. Materials. 2018; 11(10):1975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101975
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Chongyang, Xiaobo Wang, Bo Zhao, and Feng Jiao. 2018. "Microstructure of High-Performance Aluminum Alloy Surface Processed by the Single-Excitation Same-Frequency Longitudinal–Torsional Coupled Ultrasonic Vibration Milling" Materials 11, no. 10: 1975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101975
APA StyleZhao, C., Wang, X., Zhao, B., & Jiao, F. (2018). Microstructure of High-Performance Aluminum Alloy Surface Processed by the Single-Excitation Same-Frequency Longitudinal–Torsional Coupled Ultrasonic Vibration Milling. Materials, 11(10), 1975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101975




