Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Tribological Properties of NiAlComposites Reinforced by CrMnFeCoNiHigh-Entropy Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
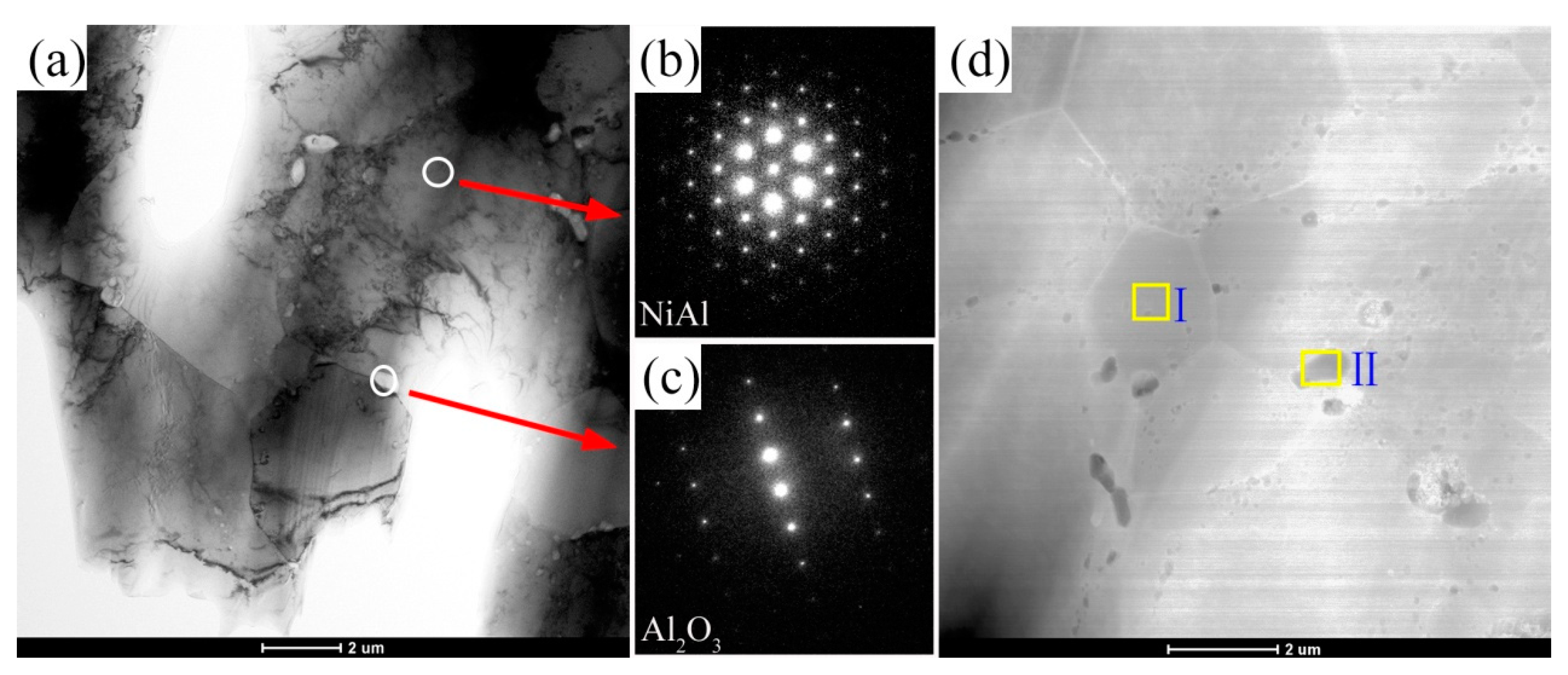
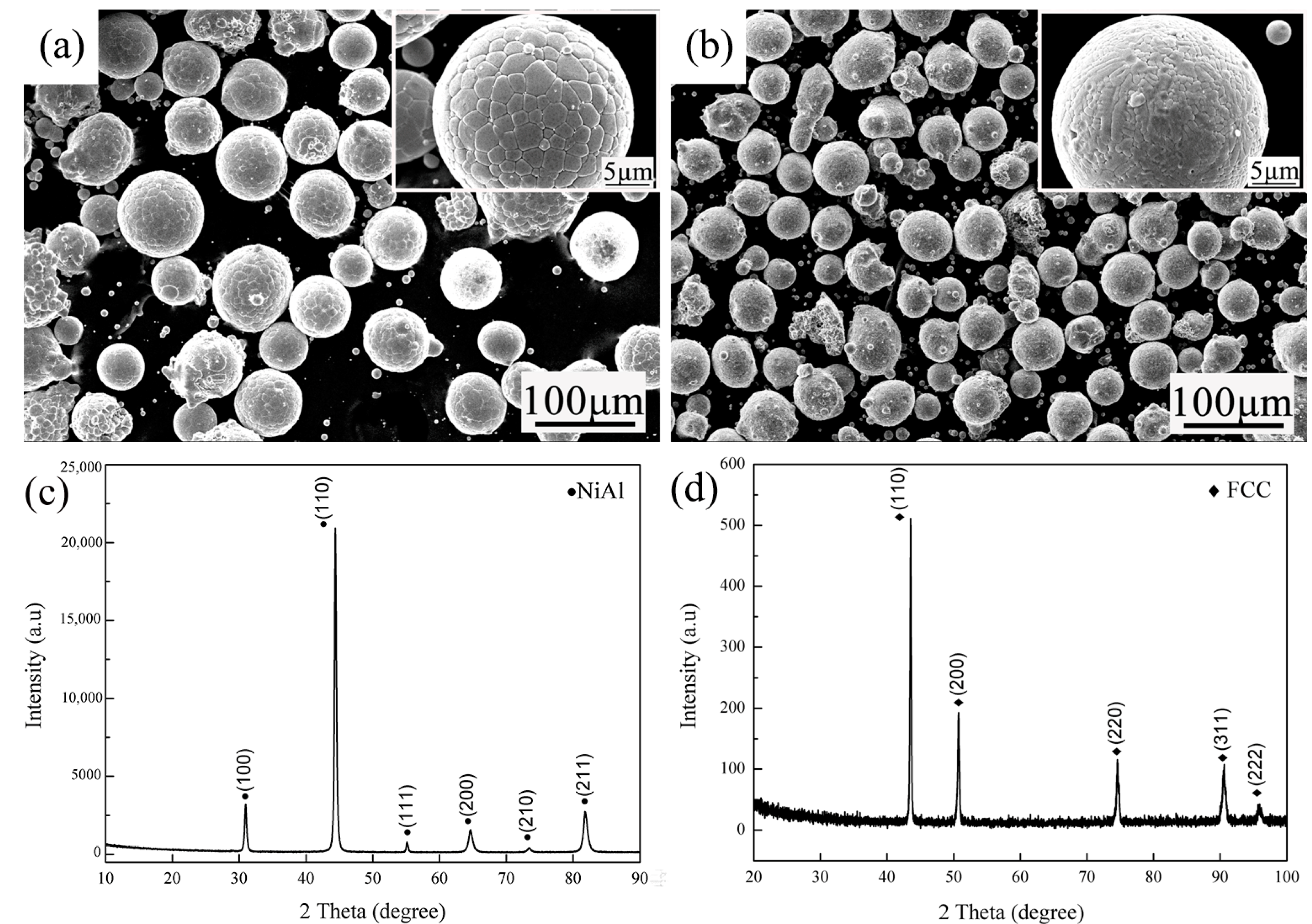
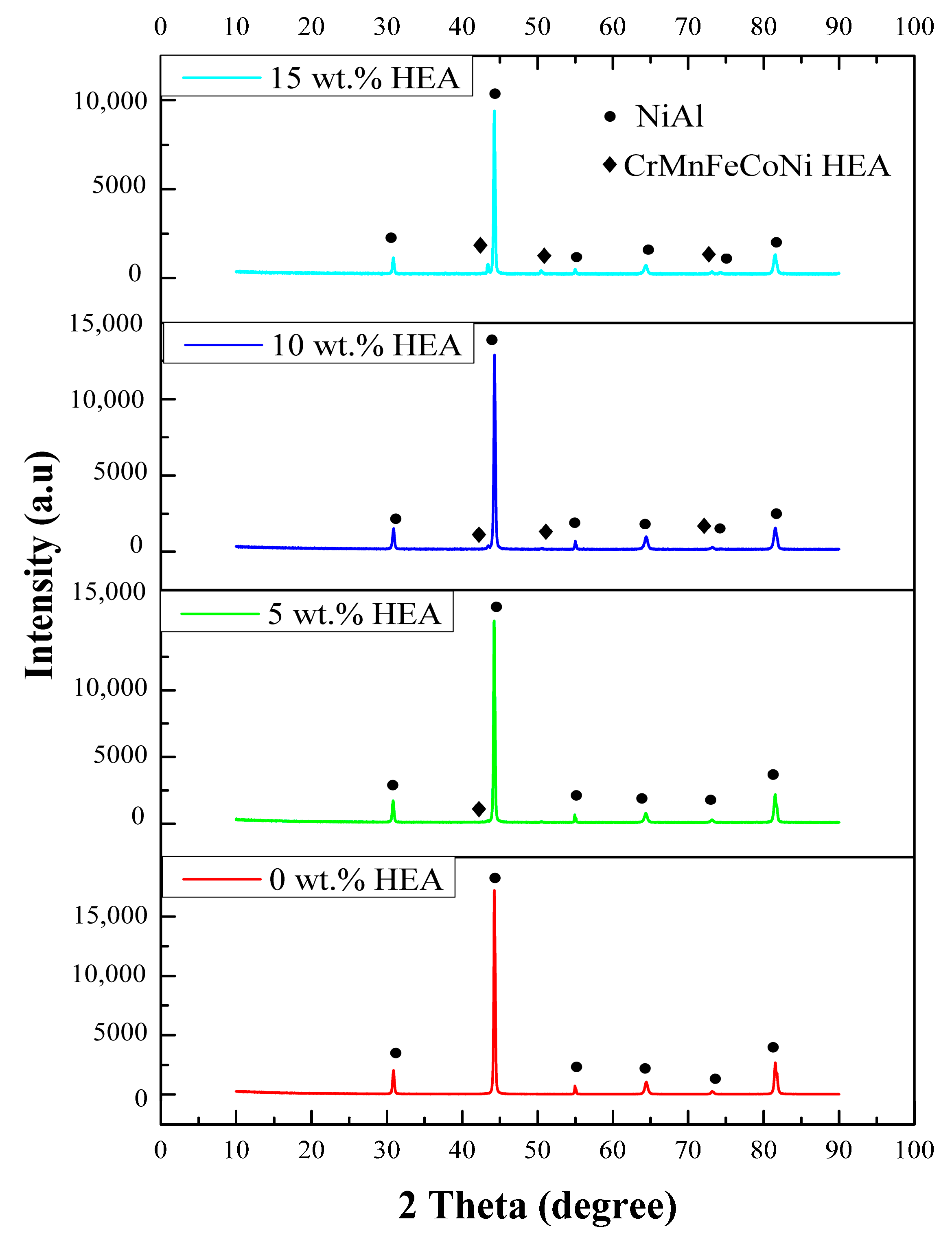
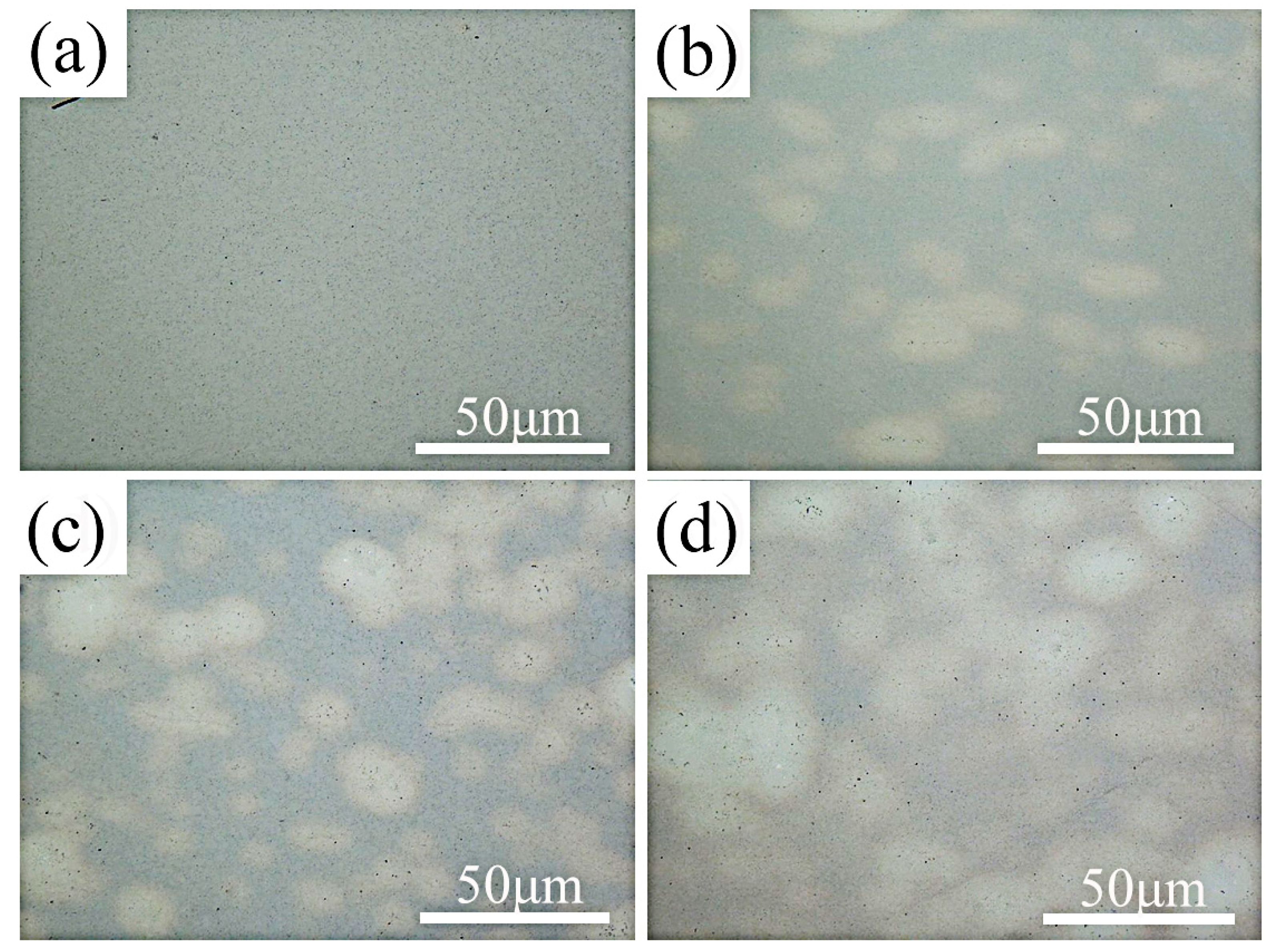
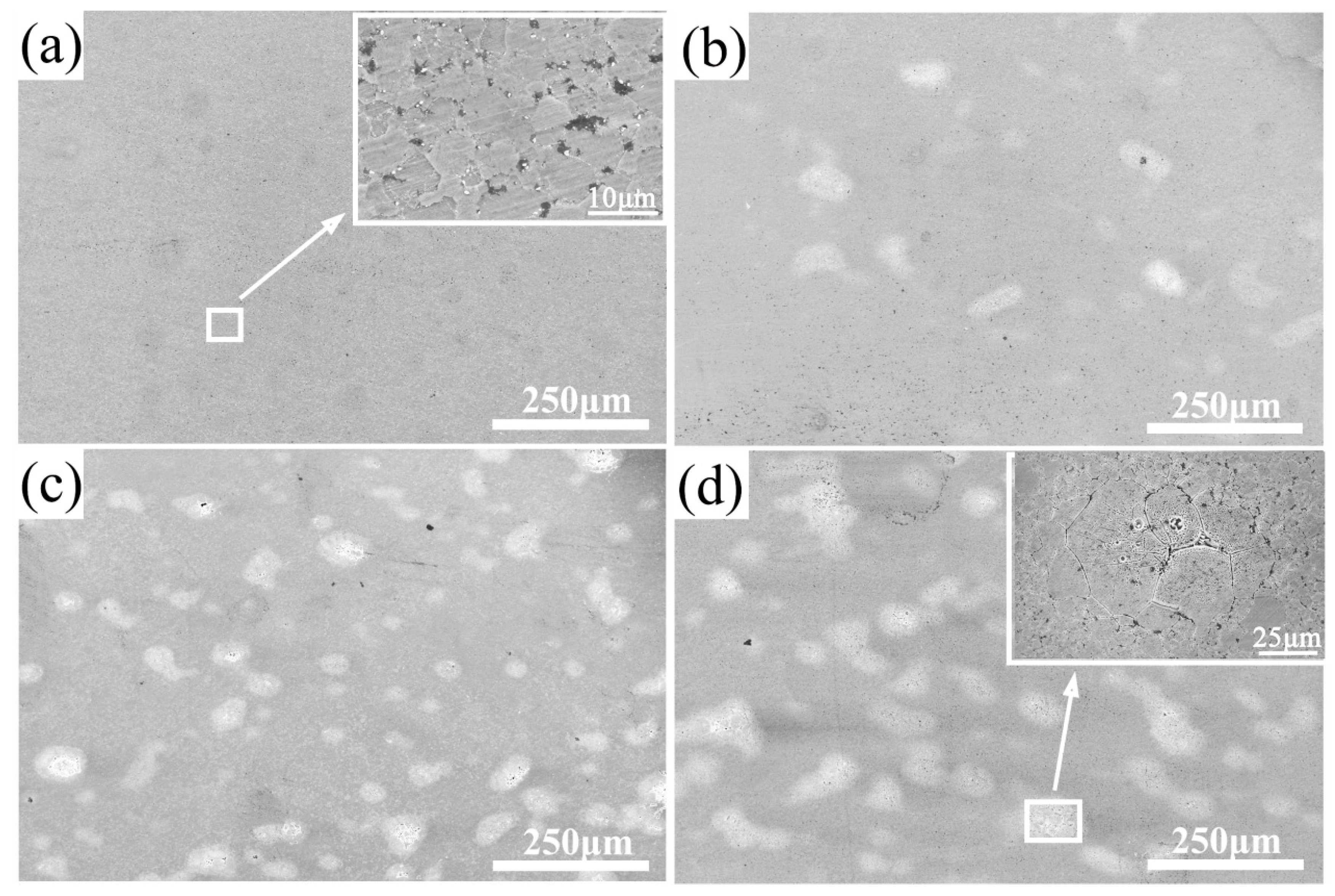
3.1. Microstucture
3.2. Mechanical Properties
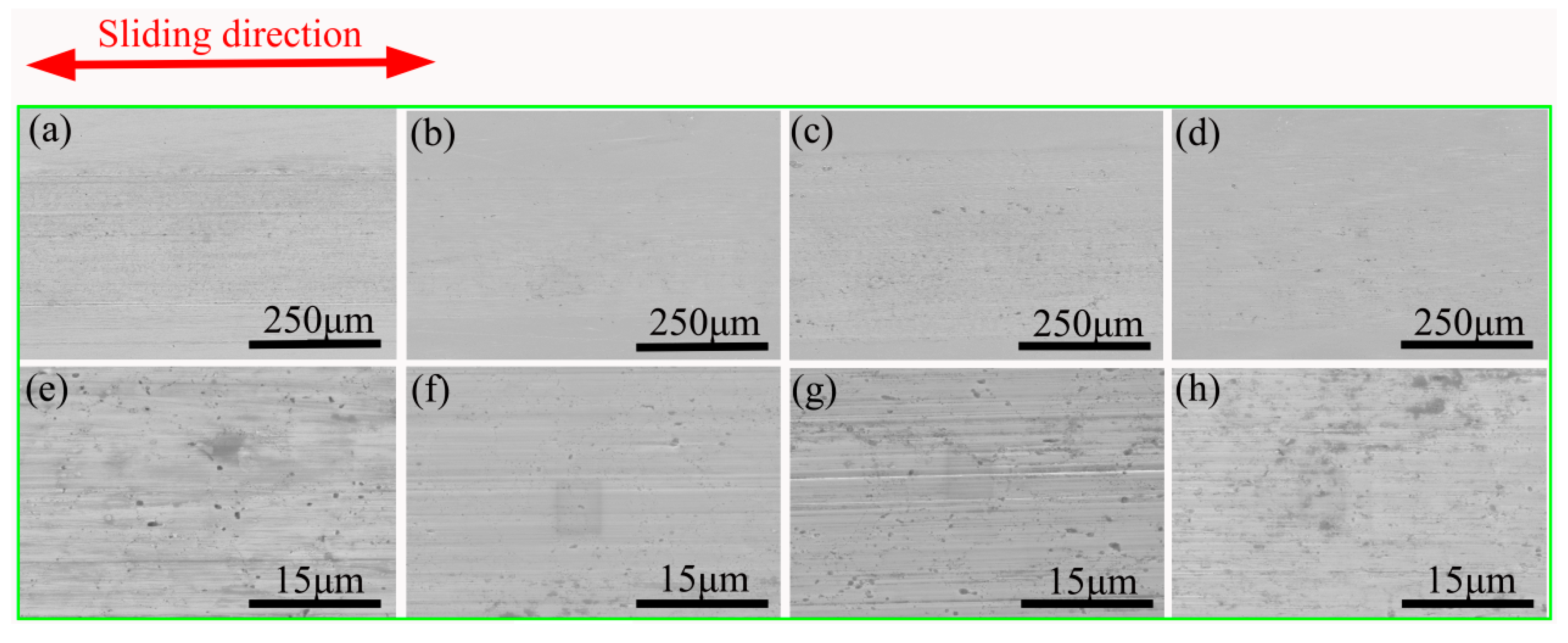
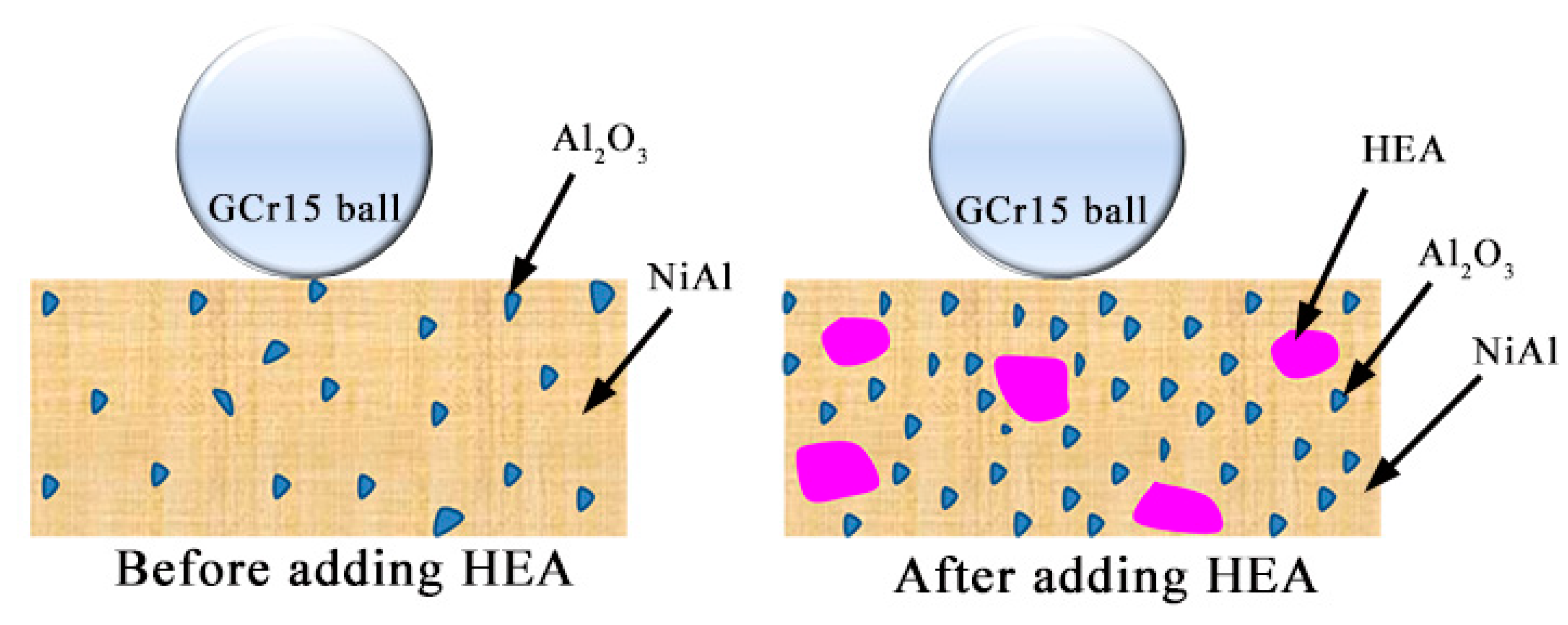
3.3. Tribological Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, G.H.; Zhang, K.F.; Huang, Z.Q. The synthesis and characterization of ultrafine grain NiAl intermetallic. Adv. Powder Technol. 2012, 23, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplin, C.; Ivanov, R.; Paliwal, M.; Jung, I.H.; Brochu, M. The effect of nanostructure on the oxidation of NiAl. Intermetallics 2014, 54, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.X.; Abbaschian, R. Microstructures and properties of in-situ NiAl-Al2O3 functionally gradient composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2000, 31, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udhayabanu, V.; Ravi, K.R.; Murty, B.S. Development of in situ NiAl-Al2O3 nanocomposite by reactive milling and spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, S223–S228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzt, E.; Grahle, P. High temperature creep behavior of oxide dispersion strengthened NiAl intermetallics. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 2717–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Sun, K. Microstructure and tribological behavior of NiAl/WC composites fabricated by thermal explosion reaction at 800 °C. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.Y.; Yang, F.; Xi, T.F.; Guo, J.T. Investigation on microstructure and wear behavior of the NiAl-TiC-Al2O3 composite fabricated by self-propagation high-temperature synthesis with extrusion. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 554, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ur, S.C.; Nash, P. Secondary recrystallization and high temperature compressive properties of ODS MA NiAl. Scr. Mater. 2002, 47, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Carrasco, J.L.; Perez, P.; Adeva, P.; Chao, J. Oxidation behaviour of an ODS NiAl-based intermetallic alloy. Intermetallics 1999, 7, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.Y.; Yang, F.; Guo, J.T.; Xi, T.F.; Ye, H.Q. Investigation on NiAl-TiC-Al2O3 composite prepared by self-propagation high temperature synthesis with hot extrusion. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 45, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, G.M.; Panikar, S.; Ram, G.J.; Kottada, R.S. Additive manufacturing of an aluminum matrix composite reinforced with nanocrystalline high-entropy alloy particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 679, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Niu, P.; Wei, T.; Hao, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, Y. Fabrication and mechanical properties of AlCoNiCrFe high-entropy alloy particle reinforced Cu matrix composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 649, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, C.L.; Zhang, C.H. Phase evolution characteristics of FeCoCrAlCuVxNi high entropy alloy coatings by laser high-entropy alloying. Mater. Lett. 2015, 141, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Koc, R. Processing and characterization of TiB2-TiNiFeCrCoAl high-entropy alloy composite. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 2803–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, J.; Shang, Z.; Fu, H. Microstructure evolution and enhancement of fracture toughness of NiAl-Cr (Mo)-(Hf, Dy) alloy with a small addition of Fe during heat treatment. Scr. Mater. 2014, 89, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Jia, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, W.; Gao, Y. Study on preparation and mechanical property of nanocrystalline NiAl intermetallic. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Fang, Q.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S. Preparation of superfine-grained high entropy alloy by spark plasma sintering gas atomized powder. Intermetallics 2016, 68, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.Y.; Tsai, M.H.; Yeh, J.W. Sluggish diffusion in Co-Cr-Fe-Mn-Ni high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4887–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucza, W.; Dąbrowa, J.; Cieślak, G.; Berent, K.; Kulik, T.; Danielewski, M. Studies of “sluggish diffusion” effect in Co-Cr-Fe-Mn-Ni, Co-Cr-Fe-Ni and Co-Fe-Mn-Ni high entropy alloys; determination of tracer diffusivities by combinatorial approach. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 731, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.R.; Razavi, S.H.; Shabestari, S.G. Development of a novel Al-Cu-Ti metallic glass reinforced Al matrix composite consolidated through equal channel angular pressing (ECAP). J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 673, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosdidier, T.; Ji, G.; Launois, S. Processing dense hetero-nanostructured metallic materials by spark plasma sintering. Scr. Mater. 2007, 57, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yin, H.; Xu, Y. Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened High-Entropy Alloys. Materials 2017, 10, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povarova, K.B.; Kazanskaya, N.K.; Drozdov, A.A.; Morozov, A.E. Physicochemical laws of the interaction of nickel aluminides with alloying elements: I. Formation of nickel aluminide-based solid solutions. Russ. Metall. (Met.) 2006, 5, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chérif, A.; Bachaga, T.; Saurina, J.; Suñol, J.J.; Khitouni, M.; Makhlouf, T. Morphology and structure effect of Ti additive on the solid-state reaction between Ni and Al powders during mechanical alloying. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 86, 2937–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, I.M.; Duncan, A.J.; Bentley, J. Site-distributions of Fe alloying additions to B2-ordered NiAl. Intermetallics 1999, 7, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, B.L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.Y. Microstructure evolution and elemental diffusion of SiCp/Al-Cu-Mg composites prepared from elemental powder during hot pressing. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 6783–6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Geng, L.; Li, A.B.; Yang, F.Y.; Peng, H.X. In situ TiBw/Ti-6Al-4V composites with novel reinforcement architecture fabricated by reaction hot pressing. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 996–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Gao, Y.; Jia, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, W. Microstructure and mechanical properties of in situ NiAl-Mo2C nanocomposites prepared by hot-pressing sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 592, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Qi, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, J.; Li, H. Interfacial microstructure and tensile properties of carbon fiber reinforced Mg-Al-RE matrix composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 663, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Chang, W.; Zhou, Y. Design of friction and wear resistant titanium-and cobalt-modified nickel-base repair alloys by spray forming. Mater. Des. 2017, 116, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, R.M.; Kuhlenbeck, H.; Freund, H.J.; Wuttig, M.; Hoffmann, W.; Franchy, R.; Ibach, H. Formation of a well-ordered aluminium oxide overlayer by oxidation of NiAl (110). Surf. Sci. 1991, 259, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudino, S.; Liu, G.; Prashanth, K.G.; Bartusch, B.; Surreddi, K.B.; Murty, B.S.; Eckert, J. Mechanical properties of Al-based metal matrix composites reinforced with Zr-based glassy particles produced by powder metallurgy. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 2029–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
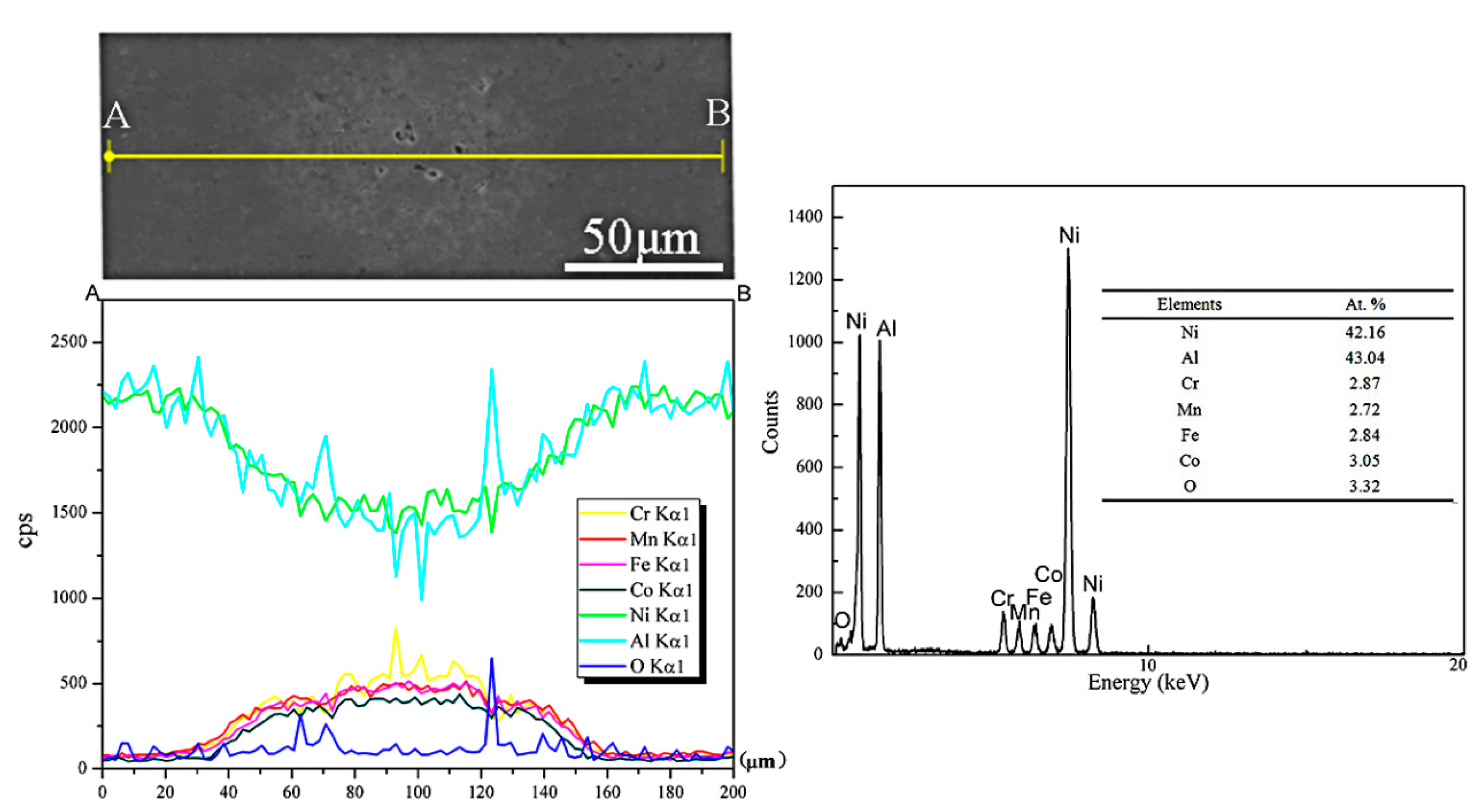

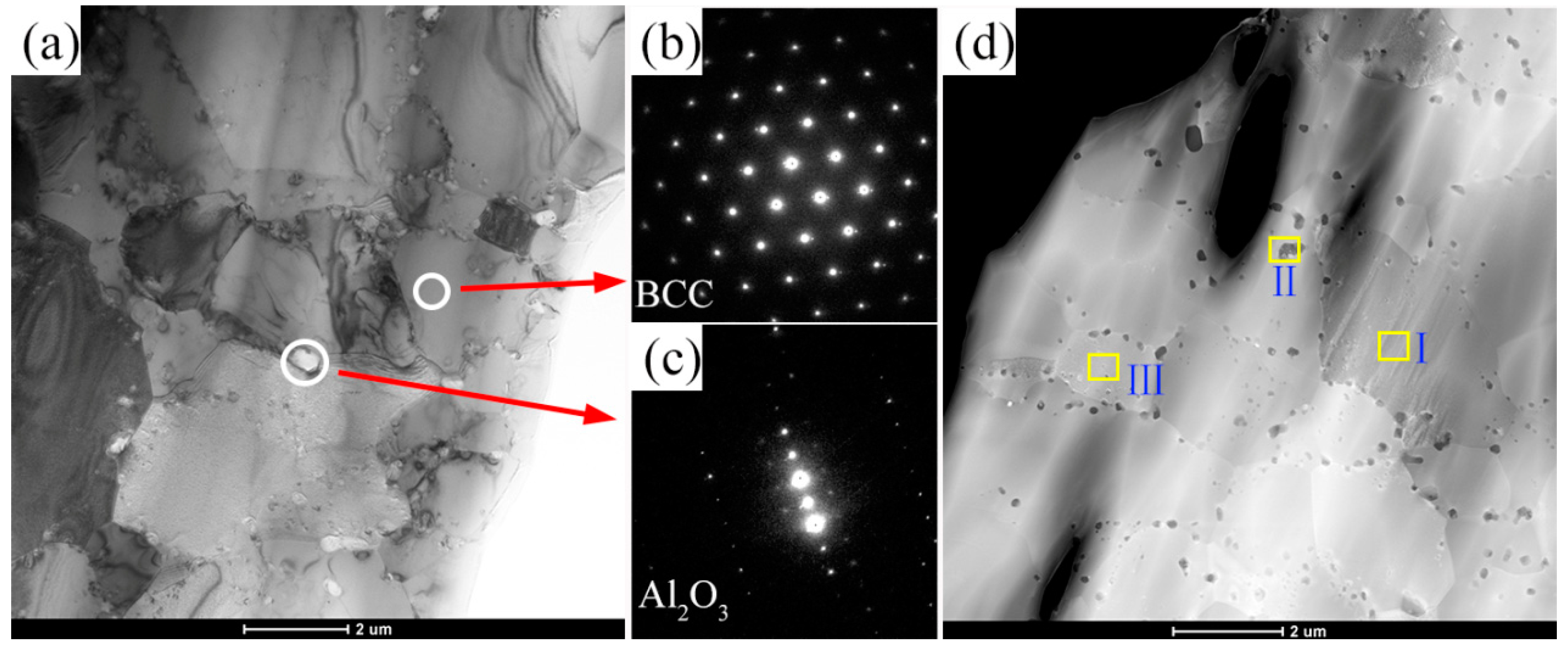
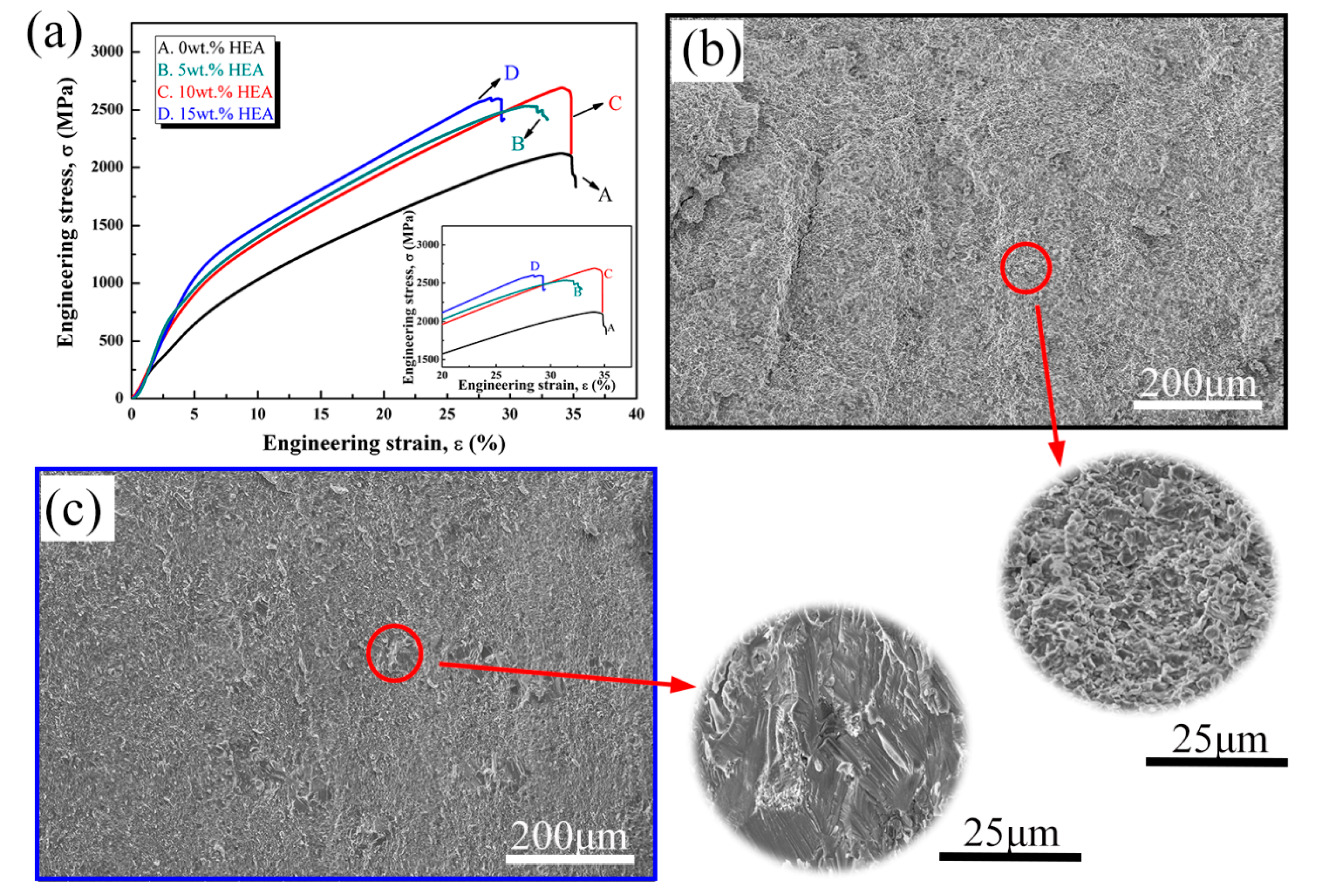
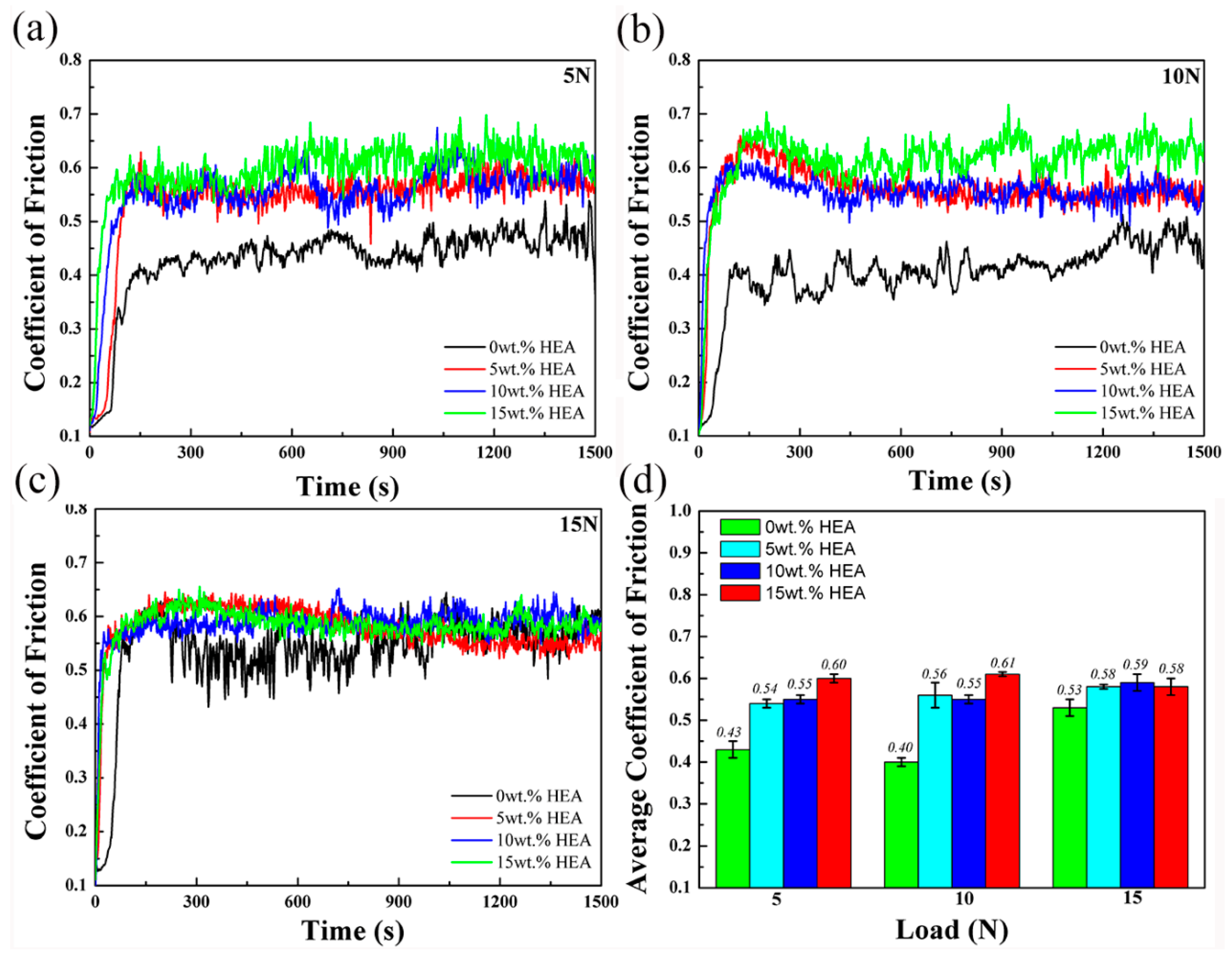


| Sample | Place of Analysis | Element (at.%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Al | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | O | ||
| 0 wt.% HEA | Figure 5dI | 49.21 | 51.79 | - | - | - | - | - |
| II | - | 33.55 | - | - | - | - | 66.45 | |
| 10 wt.% HEA | Figure 6dI | 27.77 | 41.51 | 1.21 | 0.95 | 1.05 | 0.38 | 27.10 |
| II | - | 36.07 | - | - | - | - | 63.92 | |
| III | 53.01 | 30.28 | 4.22 | 2.72 | 3.33 | 3.72 | 2.68 | |
| Samples | Density (g/cm3) | Hardness (HV) | YS (MPa) | UTS (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 wt.% HEA | 5.85 ± 0.03 | 451 ± 15 | 779 ± 45 | 2121 ± 55 |
| 5 wt.% HEA | 5.96 ± 0.05 | 469 ± 21 | 1417 ± 52 | 2531 ± 51 |
| 10 wt.% HEA | 6.06 ± 0.05 | 515 ± 25 | 1347 ± 54 | 2692 ± 45 |
| 15 wt.% HEA | 6.12 ± 0.02 | 525 ± 21 | 1566 ± 42 | 2600 ± 48 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Tribological Properties of NiAlComposites Reinforced by CrMnFeCoNiHigh-Entropy Alloy. Materials 2018, 11, 1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101850
Zhou S, Liu X, Xu Y. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Tribological Properties of NiAlComposites Reinforced by CrMnFeCoNiHigh-Entropy Alloy. Materials. 2018; 11(10):1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101850
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, ShuQiang, XinYu Liu, and Yi Xu. 2018. "Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Tribological Properties of NiAlComposites Reinforced by CrMnFeCoNiHigh-Entropy Alloy" Materials 11, no. 10: 1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101850
APA StyleZhou, S., Liu, X., & Xu, Y. (2018). Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Tribological Properties of NiAlComposites Reinforced by CrMnFeCoNiHigh-Entropy Alloy. Materials, 11(10), 1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101850





