Development of SiC Nanoparticles and Second Phases Synergistically Reinforced Mg-Based Composites Processed by Multi-Pass Forging with Varying Temperatures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Fabrication of Nano-SiCp/AZ91 Composite
2.2. Multi-Pass Forging of Nano-SiCp/AZ91 Composite
2.3. Microstructures Characterization
2.4. Tensile Test
3. Results and Discussion
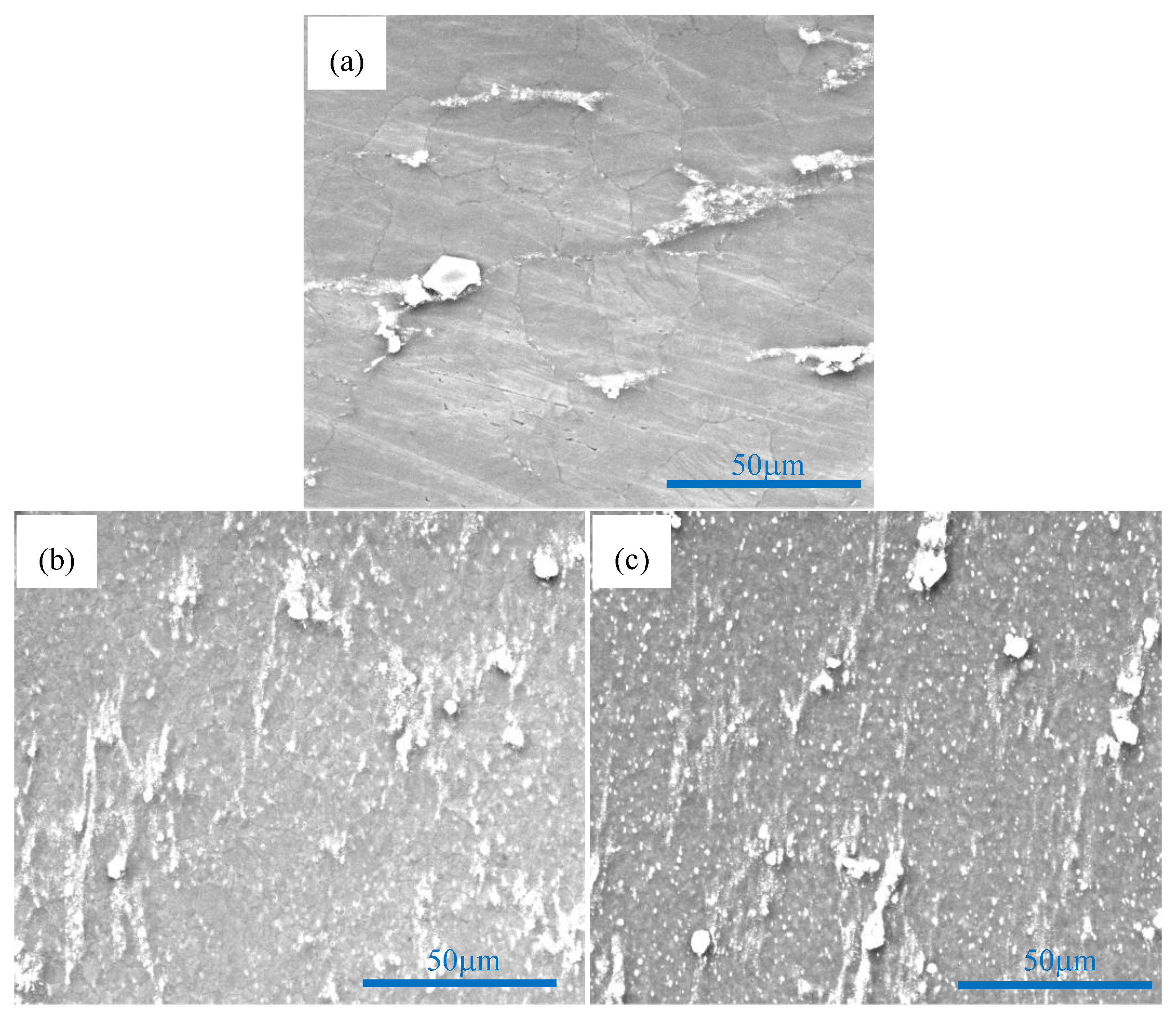
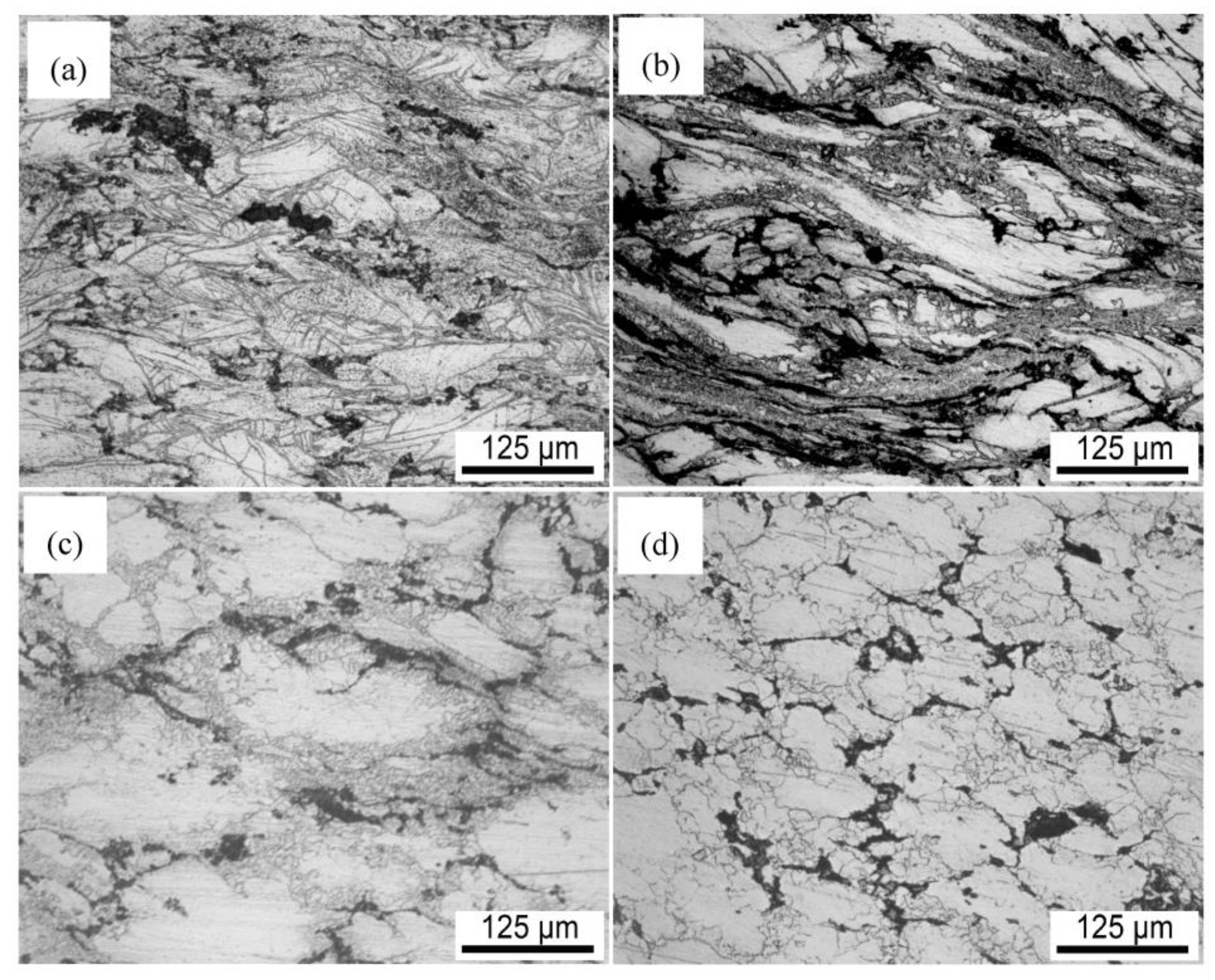
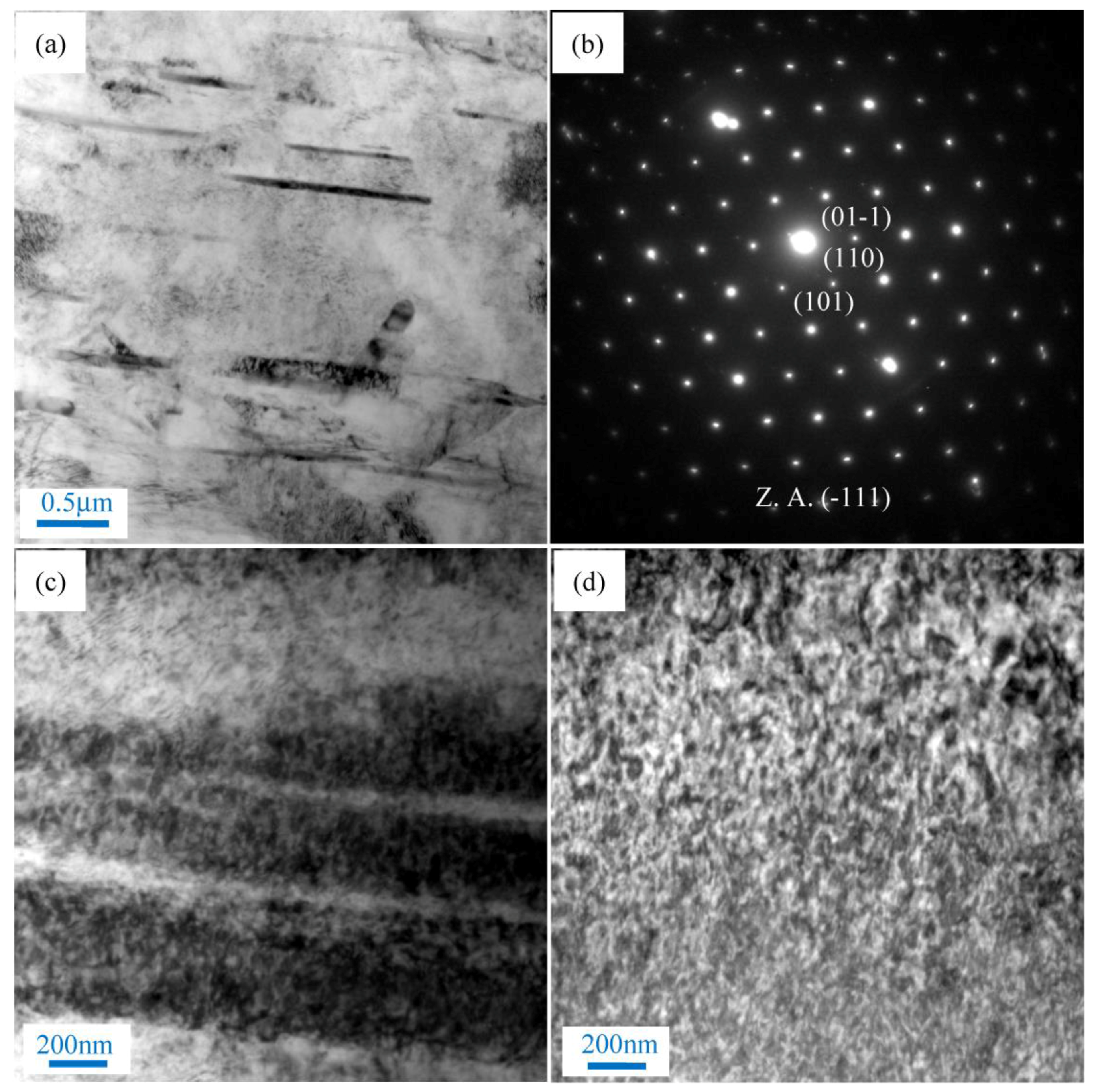
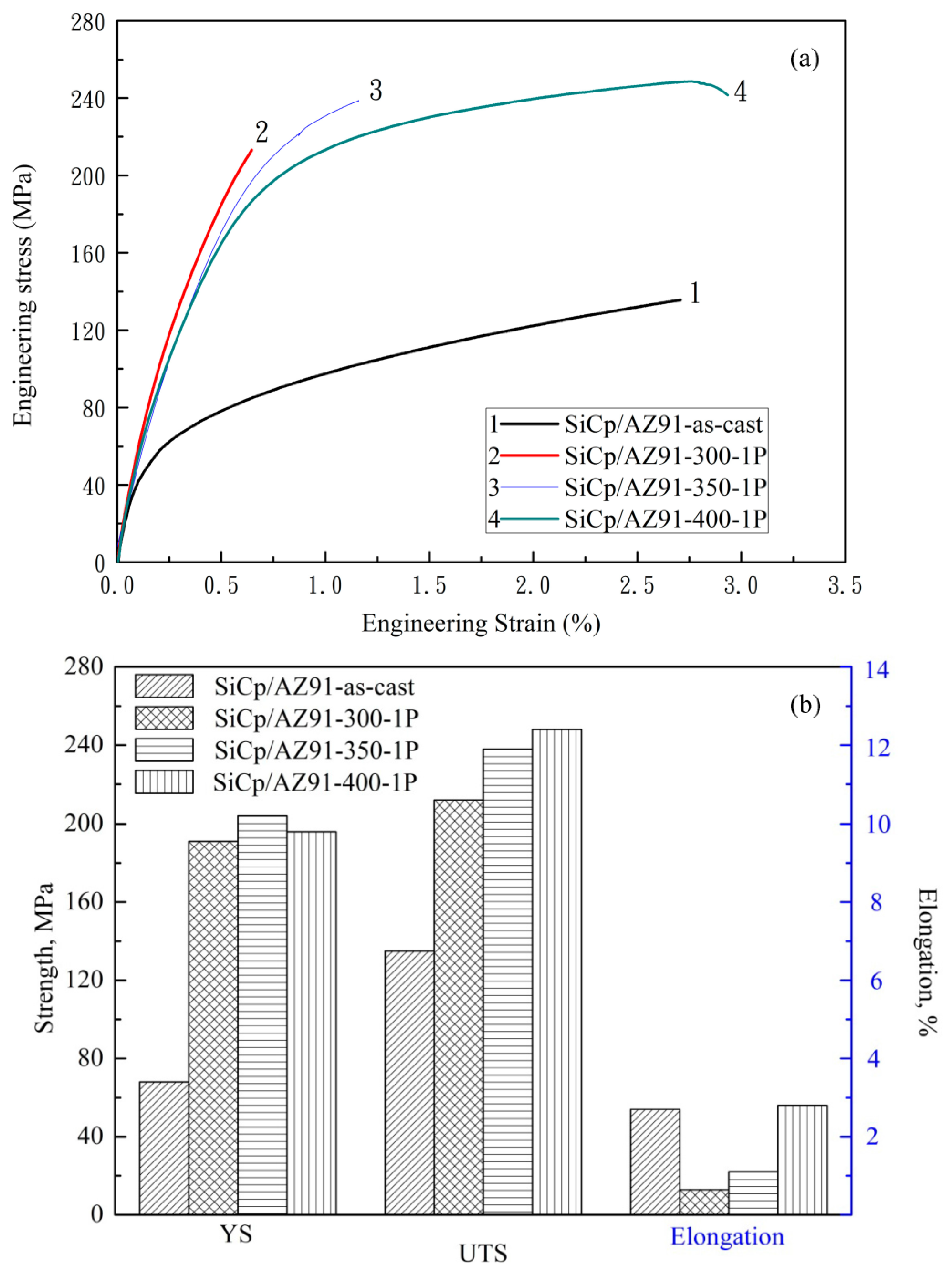
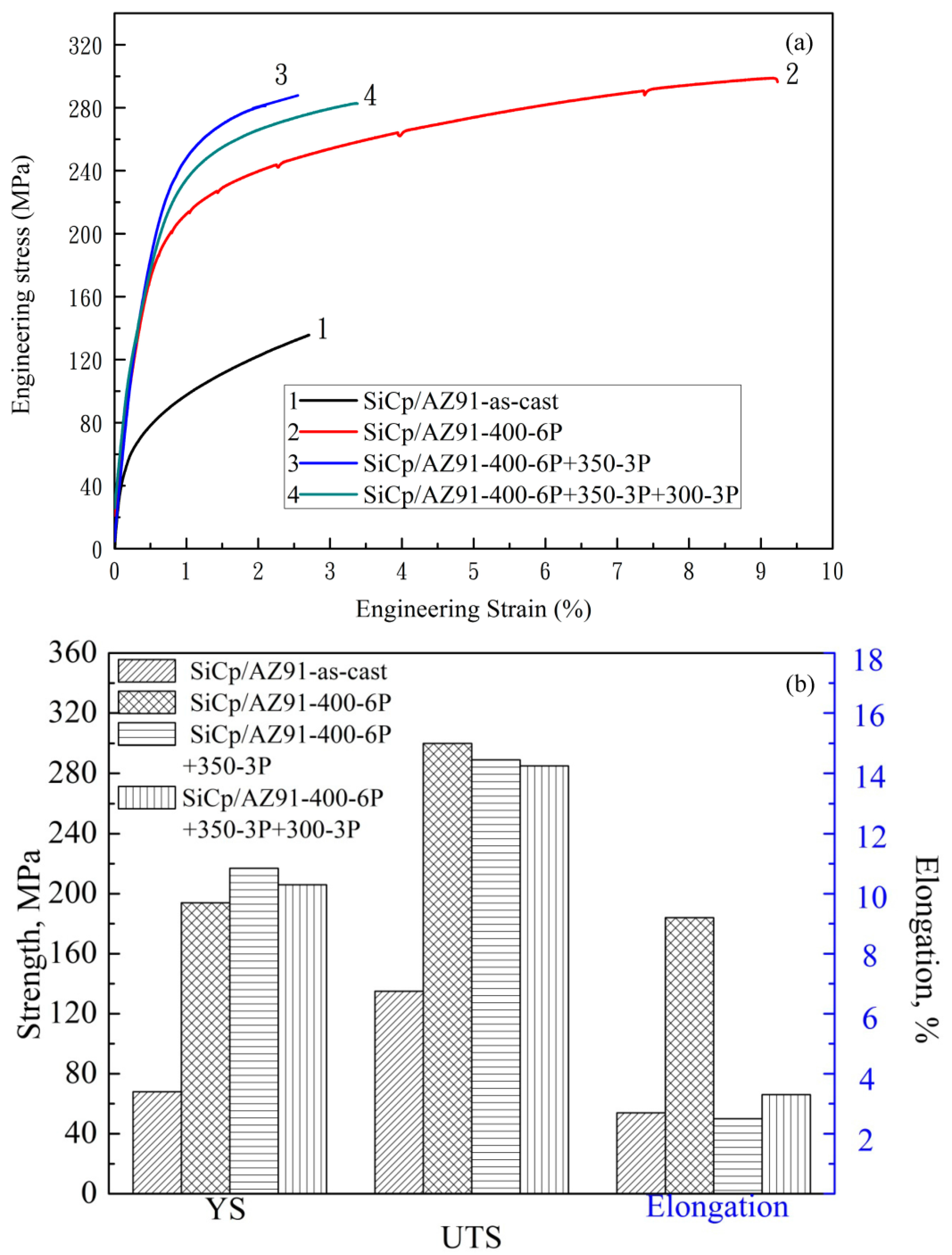
3.1. Microstructure and Tensile Properties after Single-Pass Forging at Different Temperatures
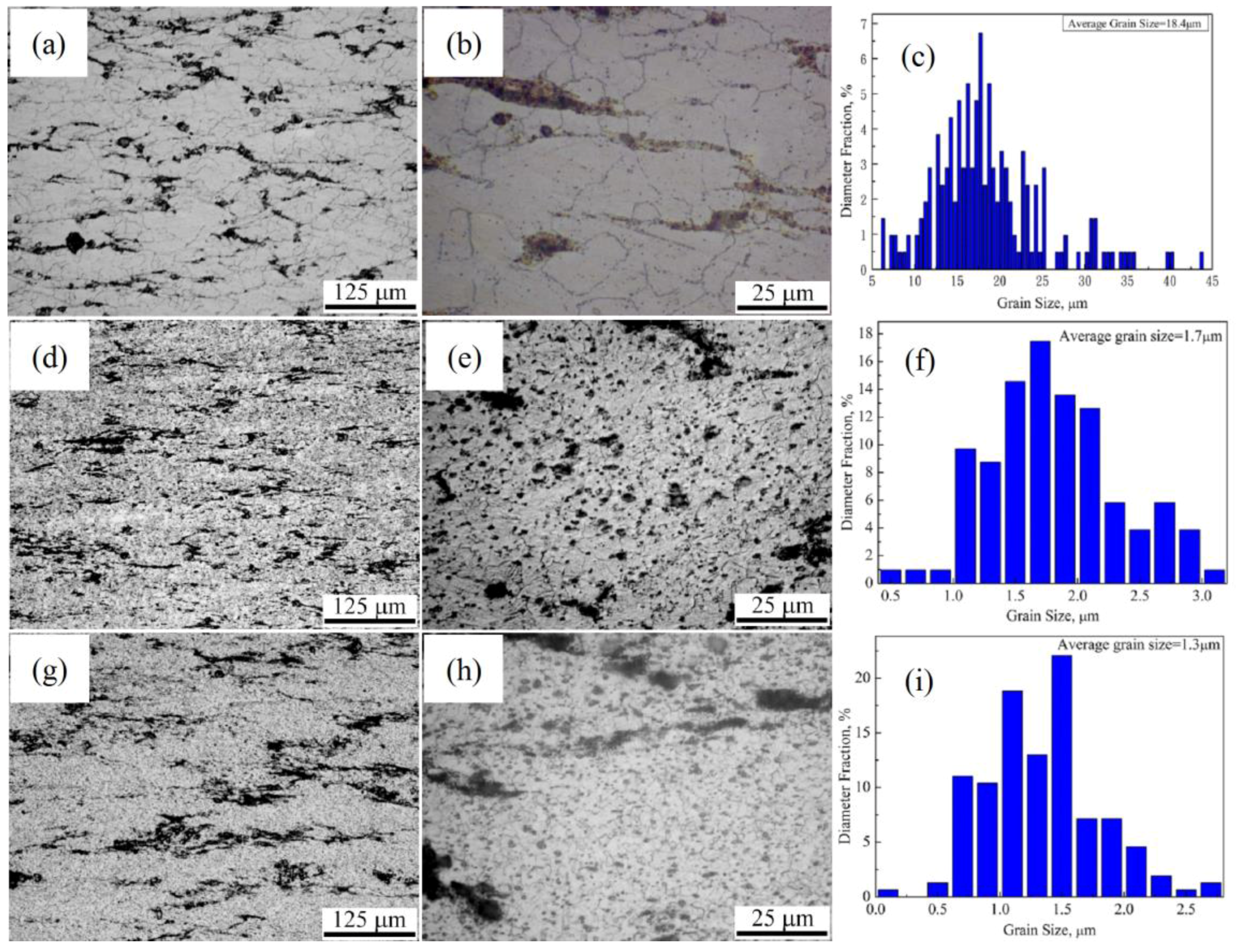
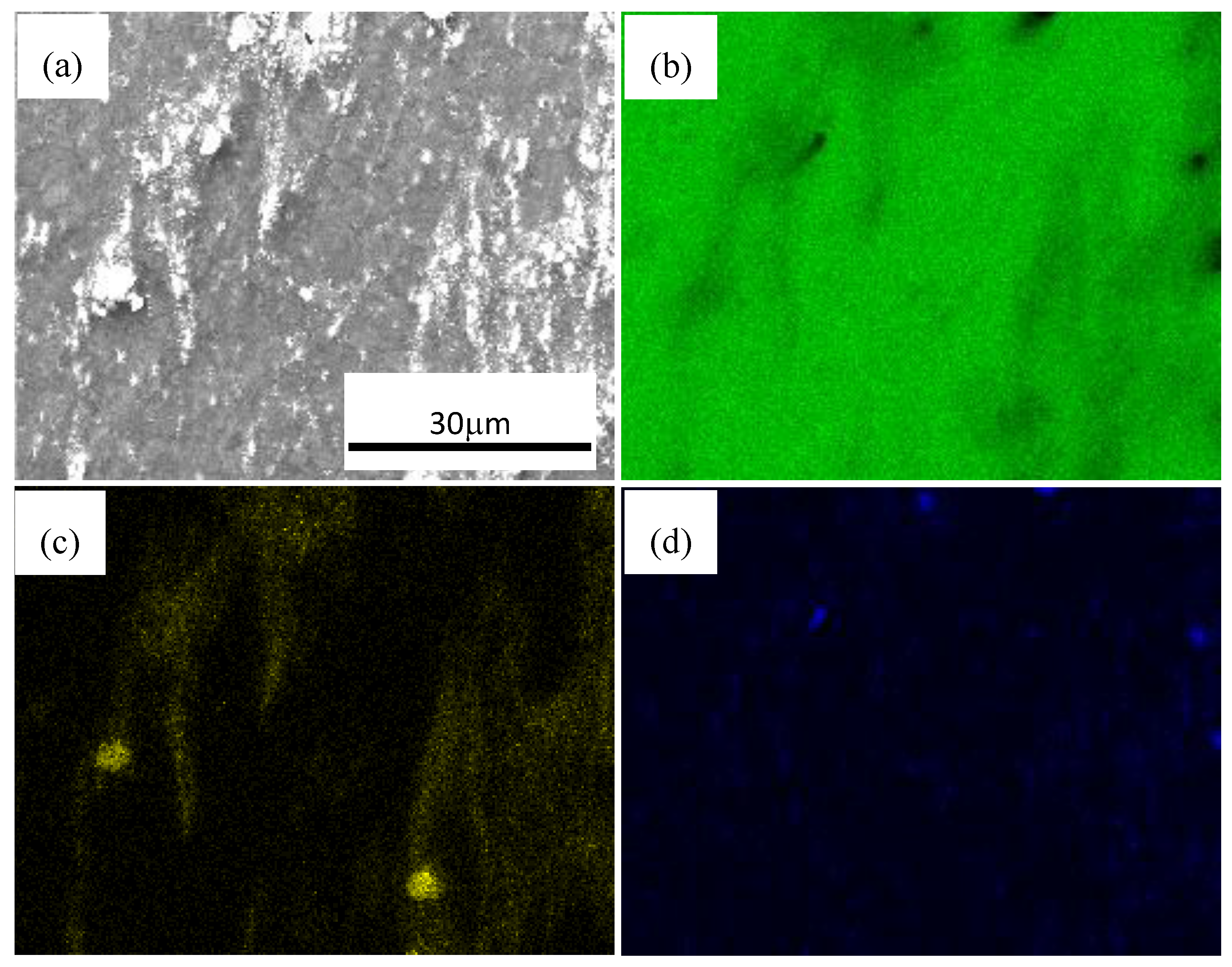
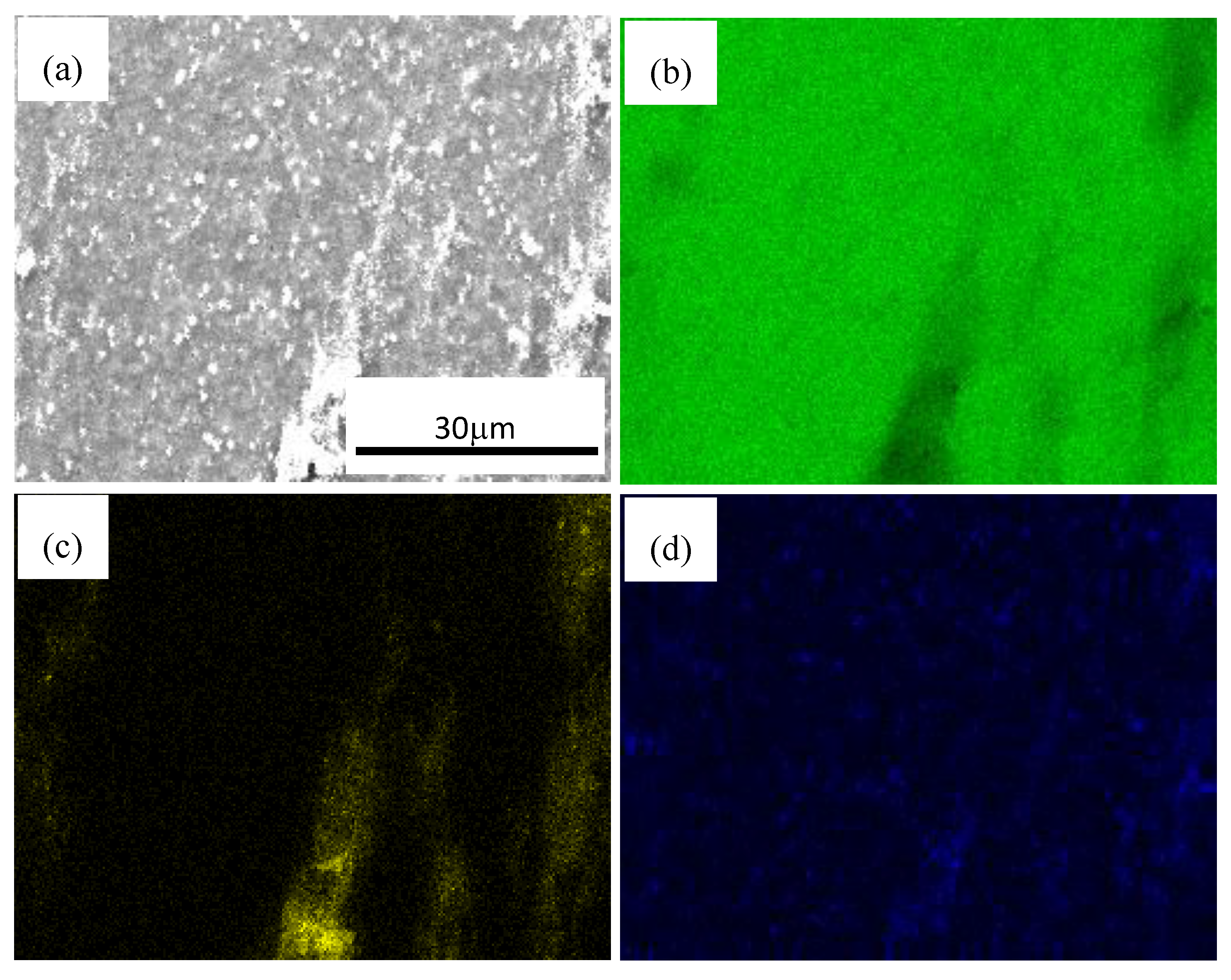
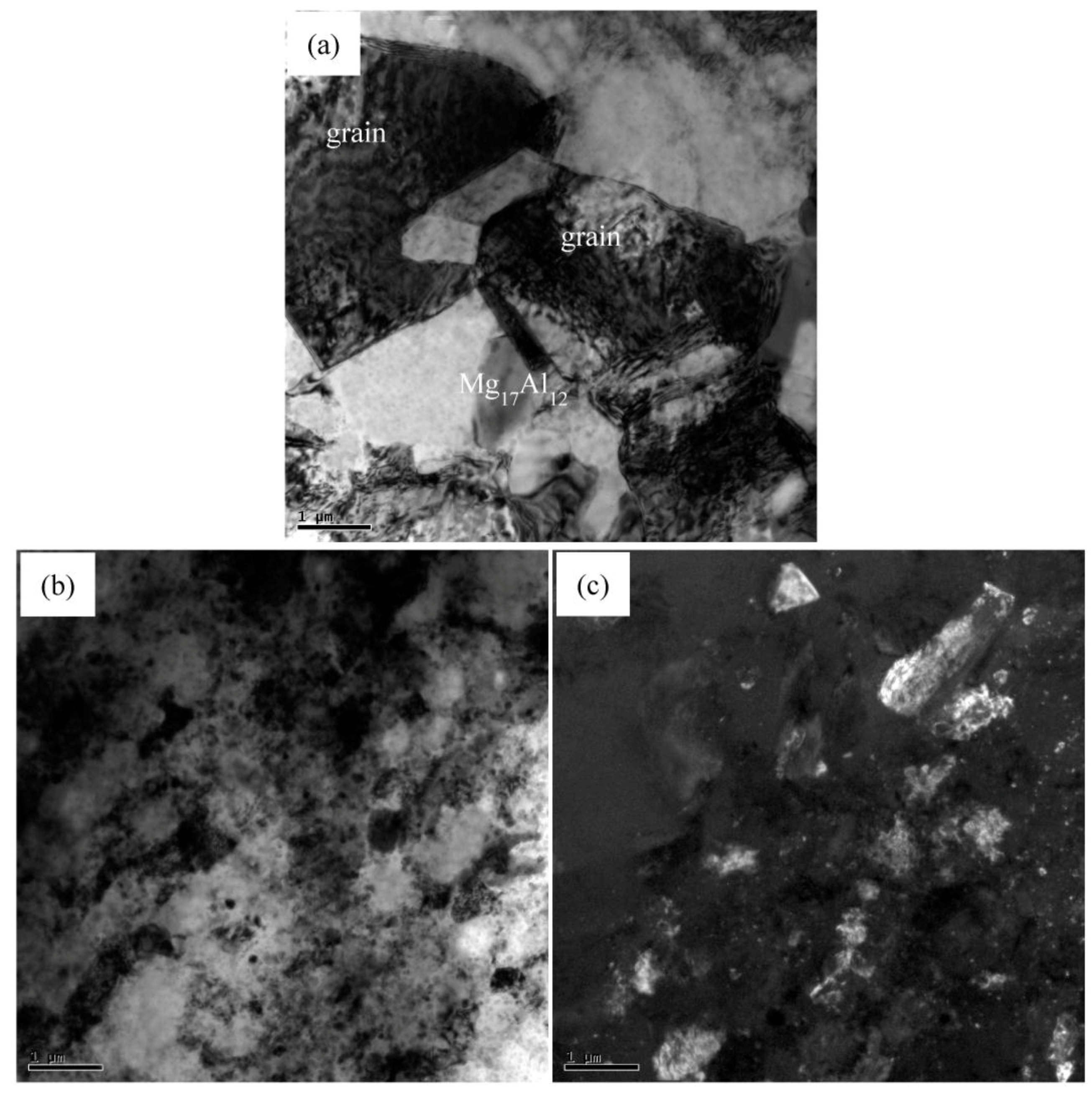
3.2. SiC Nanoparticles and Second Phases Synergistically Reinforced Composite Processed by Multi-Pass Forging with Varying Temperatures
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The distribution of SiC nanoparticles is improved while the amount of dispersed nanoparticles is increased with the increase of single-pass forging temperature for the present composite, resulting in an increased DRX degree and refined grains.
- (2)
- SiC nanoparticle dense zones with twins may deform by twinning in the matrix while nanoparticle sparse zones with deformation bands and high density dislocations deform mainly by dislocation slip.
- (3)
- Yield strength and ultimate tensile strength are gradually enhanced with the increase of the single-pass forging temperature from 300 °C to 400 °C. This indicates that an initial high forging temperature is beneficial to improve the tensile properties.
- (4)
- During multi-pass forging with varying temperatures, the value of grain size is gradually reduced and the distribution is more even with increasing the forging passes and lowering the deformation temperature. The amount of the precipitated second phases is significantly increased compared with that after multi-pass forging at a constant temperature.
- (5)
- The improvement in yield strength could be attributed to grain refinement strengthening and Orowan strengthening, which are related to synergistical enhancement by precipitated second phases and SiC nanoparticles.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lü, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, X.; Ding, W.; Zhai, C.; Zhu, Y. Effects of rare earths on the microstructure, properties and fracture behavior of Mg-Al alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 278, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.X.; Pan, F.; Li, Z.; Luo, X. Effect of composition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Al alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 456, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Xu, D.K.; Wu, R.Z.; Chen, X.B.; Peng, Q.M.; Jin, L.; Xin, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.H.; et al. What is going on in magnesium alloys? J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzadeh, H. Constitutive behaviors of magnesium and Mg–Zn–Zr alloy during hot deformation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 152, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Wong, W.L.E. Magnesium-based nanocomposites: Lightweight materials of the future. Mater. Charact. 2015, 105, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhang, D.; Sun, J.; Luo, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Pan, F. Improving mechanical properties of ZM61 magnesium alloy by aging before extrusion. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 690, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Nakata, T.; Qiao, X.G.; Zheng, M.Y.; Wu, K.; Kamado, S. Ageing behavior of extruded Mg-8.2Gd-3.8Y-1.0Zn-0.4Zr (wt. %) alloy containing LPSO phase and γ′ precipitates. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Ye, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Guo, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, W. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of SiC nanoparticles reinforced magnesium matrix composite processed by cyclic closed-die forging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 642, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelliah, N.M.; Singh, H.; Surappa, M.K. Microstructural evolution and strengthening behavior in in-situ magnesium matrix composites fabricated by solidification processing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 194, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.L.; Gupta, M.; Wang, X.J.; Wang, L.D.; Hu, X.S.; Wu, K. Enhanced overall strength and ductility of magnesium matrix composites by low content of graphene nanoplatelets. Compos. Part A 2017, 100, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Wang, C.; Shi, J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, K. Microstructure evolution mechanism of micron particle reinforced magnesium matrix composite at room temperature. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 134, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-J.; Deng, K.-K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.-J.; Kang, J.-W.; Nie, K.-B.; Liang, W. Microstructures, tensile properties and work hardening behavior of SiCp/Mg-Zn-Ca composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-Y.; Xu, J.-Q.; Choi, H.; Pozuelo, M.; Ma, X.; Bhowmick, S.; Yang, J.-M.; Mathaudhu, S.; Li, X.-C. Processing and properties of magnesium containing a dense uniform dispersion of nanoparticles. Nature 2015, 528, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.J.; Geng, L.; Peng, H.X. Microstructurally inhomogeneous composites: Is a homogeneous reinforcement distribution optimal? Prog. Mater Sci. 2015, 71, 93–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.B.; Wang, X.J.; Wu, K.; Xu, L.; Zheng, M.Y.; Hu, X.S. Processing, microstructure and mechanical properties of magnesium matrix nanocomposites fabricated by semisolid stirring assisted ultrasonic vibration. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 8664–8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Q.; Hu, X.S.; Wang, X.J.; Wu, K.; Zheng, M.Y. Evolution of microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of SiC/AZ31 nanocomposite during hot rolling process. Mater. Des. 2016, 93, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Alba-Baena, N.; Nimityongskul, S.; Jones, M.; Wood, T.; Sahoo, M.; Lakes, R.; Kou, S.; Li, X. Characterization of hot extruded Mg/SiC nanocomposites fabricated by casting. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 2991–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.B.; Wang, X.J.; Xu, L.; Wu, K.; Hu, X.S.; Zheng, M.Y. Effect of hot extrusion on microstructures and mechanical properties of SiC nanoparticles reinforced magnesium matrix composite. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 512, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Estrin, Y.; Horita, Z.; Langdon, T.G.; Zehetbauer, M.J.; Zhu, Y.T. Producing bulk ultrafine-grained materials by severe plastic deformation: Ten years later. JOM 2016, 68, 1216–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, R.B.; Langdon, T.G. Principles of grain refinement in magnesium alloys processed by equal-channel angular pressing. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 4758–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Ji, D.; Xiao, H. Microstructures and tensile properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy during multidirectional forging at 773 K. Mater. Des. 2013, 50, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Okabe, Y.; Miura, H.; Sakai, T. Effect of pass strain and temperature on recrystallisation in magnesium alloy AZ31 after interrupted cold deformation. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 2823–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuloria, D.; Nageswararao, P.; Jayaganthana, R.; Jha, S.; Srivastava, D. An investigation of deformed microstructure and mechanical properties of Zircaloy-4 processed through multiaxial forging. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 173, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.G.; Yan, H.; Chen, R.S. Twinning, recrystallization and texture development during multi-directional impact forging in an AZ61 Mg alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 650, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, J.; Cui, Z. Microstructures and mechanical properties of AZ61 magnesium alloy after isothermal multidirectional forging with increasing strain rate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 643, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.B.; Wang, X.J.; Deng, K.K.; Xu, F.J.; Wu, K.; Zheng, M.Y. Multidirectional forging of AZ91 magnesium alloy and its effects on microstructures and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 624, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, K. Microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of coarse-grained Mg-Gd-Y-Nd-Zr alloy processed by multidirectional forging. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 623, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshzaban Khosroshahi, H.; Fereshteh Saniee, F.; Abedi, H.R. Mechanical properties improvement of cast AZ80 Mg alloy/nano-particles composite via thermomechanical processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 595, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.B.; Wu, K.; Wang, X.J.; Deng, K.K.; Wu, Y.W.; Zheng, M.Y. Multidirectional forging of magnesium matrix composites: Effect on microstructures and tensile properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 7364–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.B.; Wang, X.J.; Hu, X.S.; Wu, Y.W.; Deng, K.K.; Wu, K.; Zheng, M.Y. Effect of multidirectional forging on microstructures and tensile properties of a particulate reinforced magnesium matrix composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 7133–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, C.S.; Wei, J.; Lee, L.C.; Gupta, M. Properties and deformation behaviour of Mg-Y2O3 nanocomposites. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 5115–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Shu, D.; Hua, C.K.; Zhao, Z.D.; Yuan, B.G. Grain refinement in an as-cast AZ61 magnesium alloy processed by multi-axial forging under the multitemperature processing procedure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 541, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, G.; Mashhadi, M.M.; Kim, H.S. Microstructure inhomogeneity in ultra-fine grained bulk AZ91 produced by accumulative back extrusion (ABE). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 4312–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changizian, P.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Abedi, H.R. On the recrystallization behavior of homogenized AZ81 magnesium alloy: The effect of mechanical twins and γ precipitates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 558, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.B.; Deng, K.K.; Wang, X.J.; Gan, W.M.; Xu, F.J.; Wu, K.; Zheng, M.Y. Microstructures and mechanical properties of SiCp/AZ91 magnesium matrix nanocomposites processed by multidirectional forging. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 622, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.B.; Wang, X.J.; Xu, F.J.; Wu, K.; Zheng, M.Y. Microstructure and tensile properties of SiC nanoparticles reinforced magnesium matrix composite prepared by multidirectional forging under decreasing temperature conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 639, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, D.L. Consideration of Orowan strengthening effect in particulate-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites: A model for predicting their yield strength. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.B.; Deng, K.K.; Wang, X.J.; Wu, K. Characterization and strengthening mechanism of SiC nanoparticles reinforced magnesium matrix composite fabricated by ultrasonic vibration assisted squeeze casting. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 2609–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F.; Dong, J.; Zeng, X.Q.; Lu, C.; Ding, W.J. Influence of Mg17Al12 intermetallic compounds on the hot extruded microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg-9Al-1Zn alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 466, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nie, K.; Guo, Y.; Deng, K.; Wang, X.; Wu, K. Development of SiC Nanoparticles and Second Phases Synergistically Reinforced Mg-Based Composites Processed by Multi-Pass Forging with Varying Temperatures. Materials 2018, 11, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010126
Nie K, Guo Y, Deng K, Wang X, Wu K. Development of SiC Nanoparticles and Second Phases Synergistically Reinforced Mg-Based Composites Processed by Multi-Pass Forging with Varying Temperatures. Materials. 2018; 11(1):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010126
Chicago/Turabian StyleNie, Kaibo, Yachao Guo, Kunkun Deng, Xiaojun Wang, and Kun Wu. 2018. "Development of SiC Nanoparticles and Second Phases Synergistically Reinforced Mg-Based Composites Processed by Multi-Pass Forging with Varying Temperatures" Materials 11, no. 1: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010126
APA StyleNie, K., Guo, Y., Deng, K., Wang, X., & Wu, K. (2018). Development of SiC Nanoparticles and Second Phases Synergistically Reinforced Mg-Based Composites Processed by Multi-Pass Forging with Varying Temperatures. Materials, 11(1), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010126




