Synthesis of Hollow Sphere and 1D Structural Materials by Sol-Gel Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
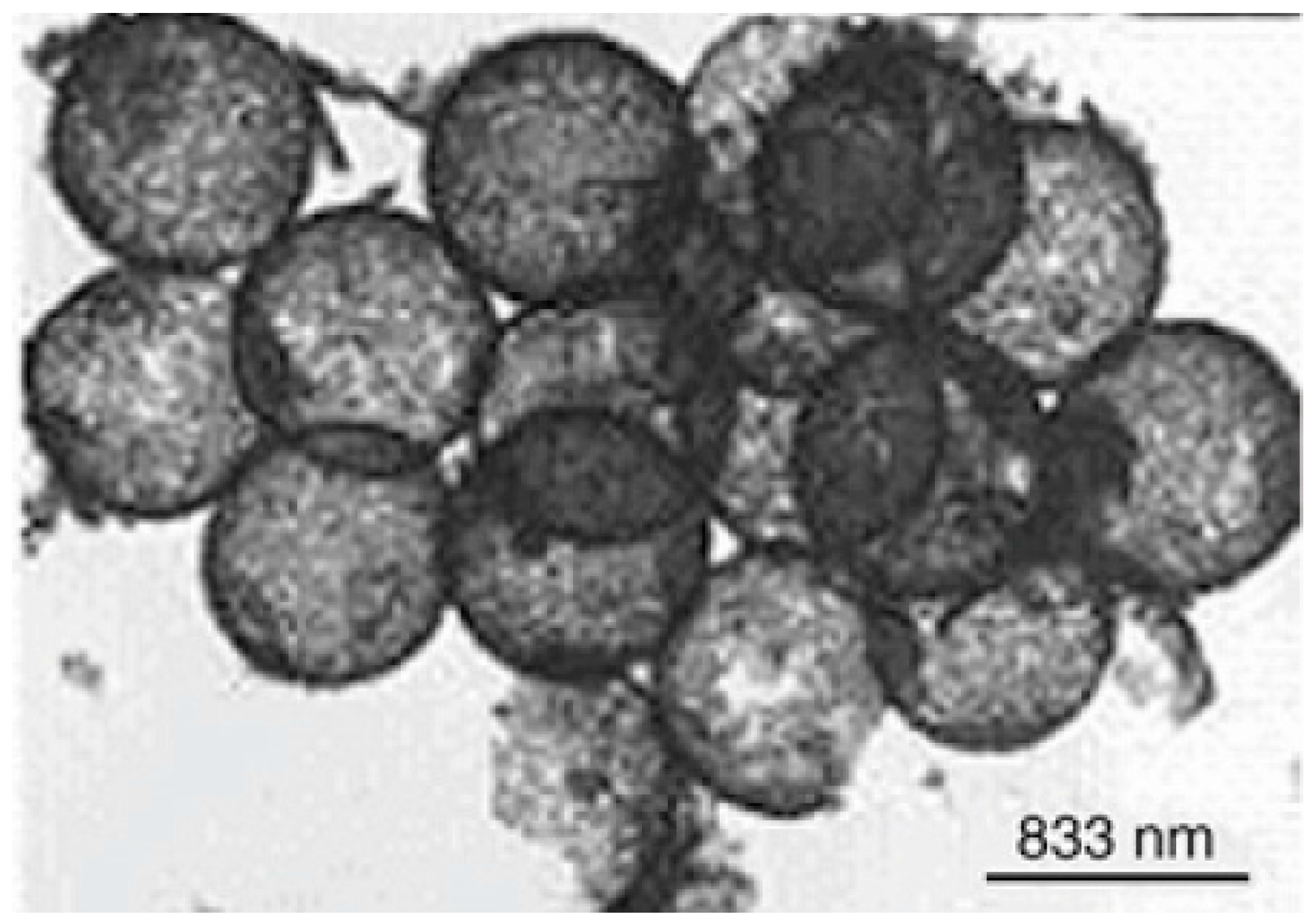
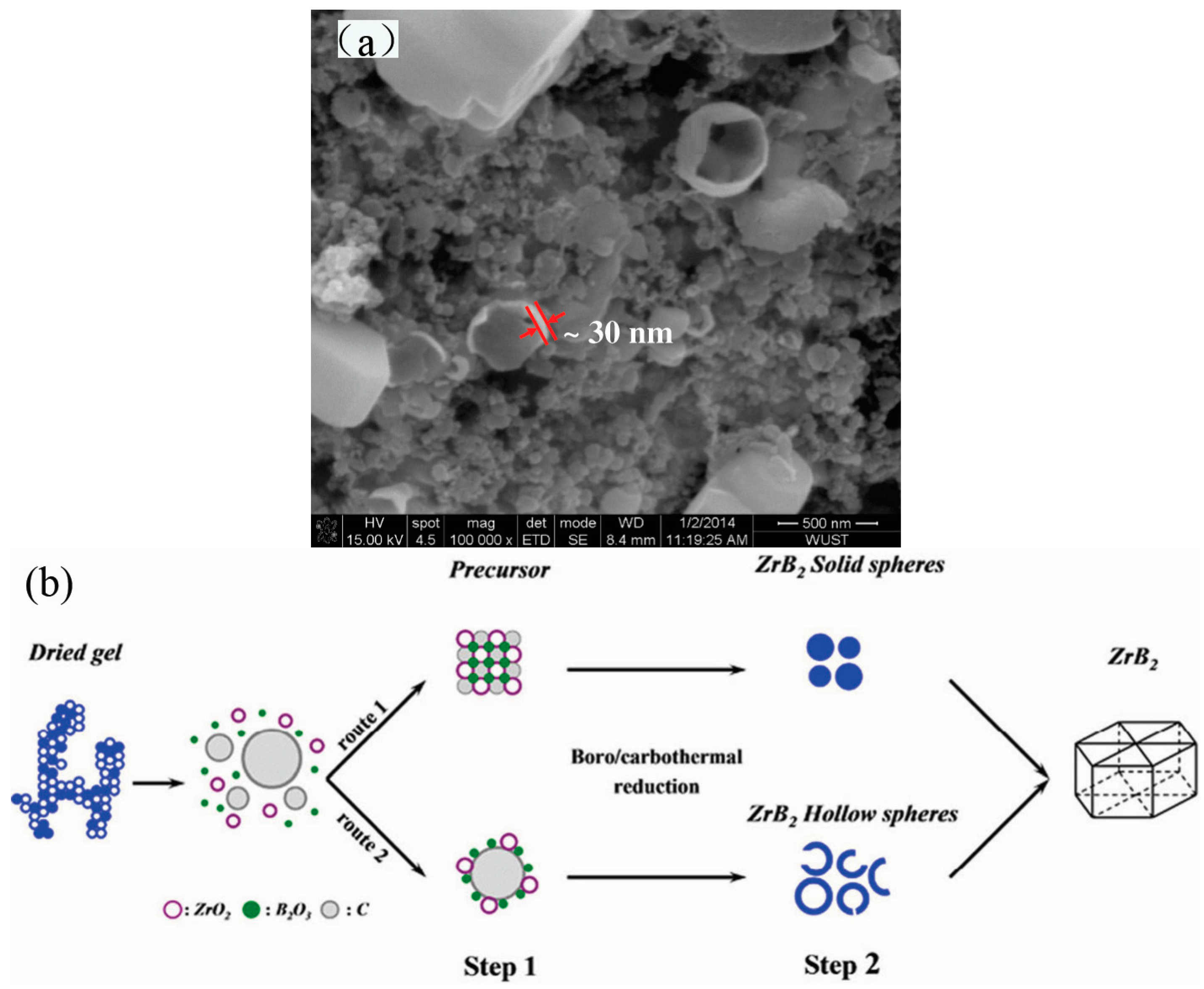
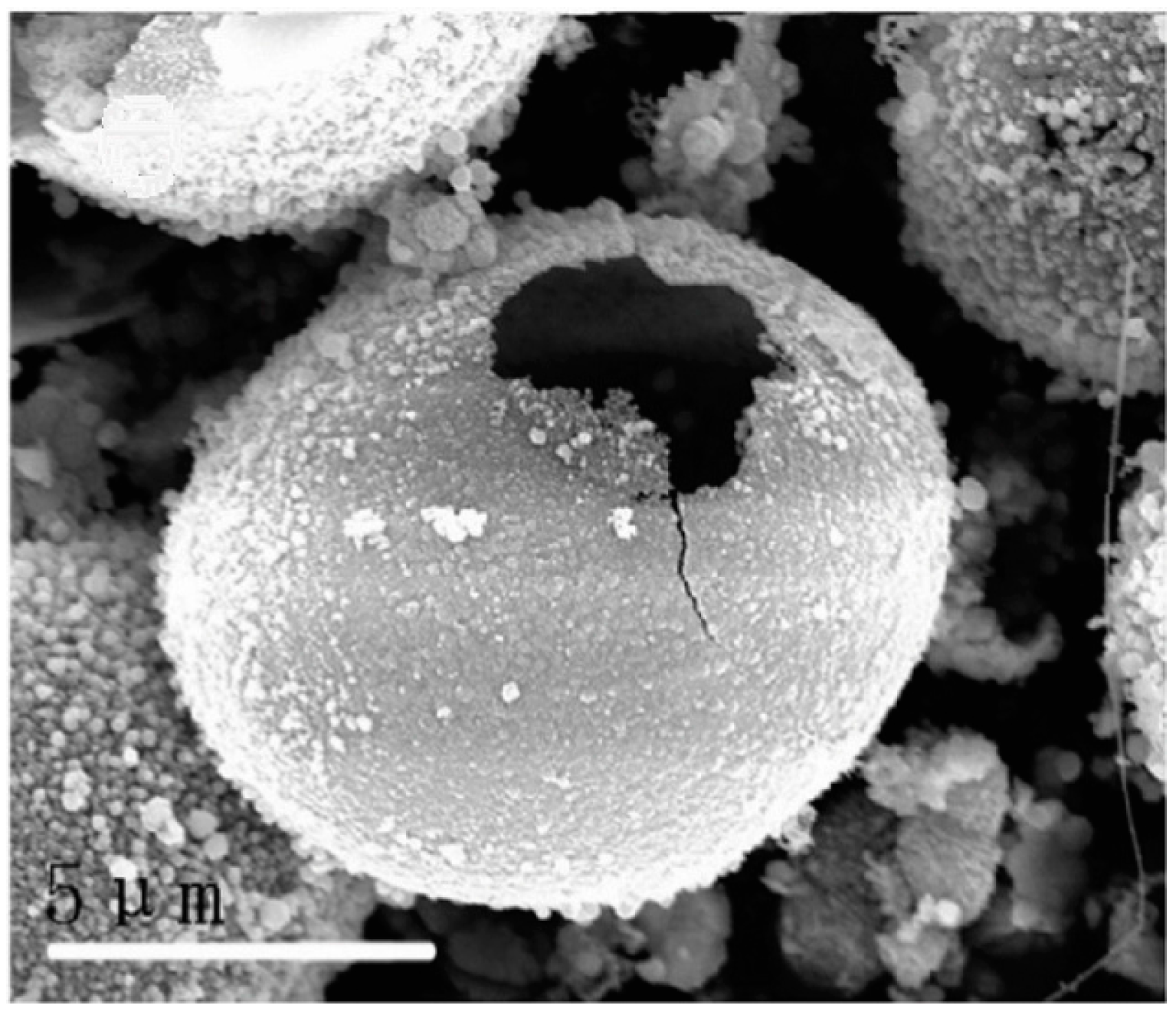
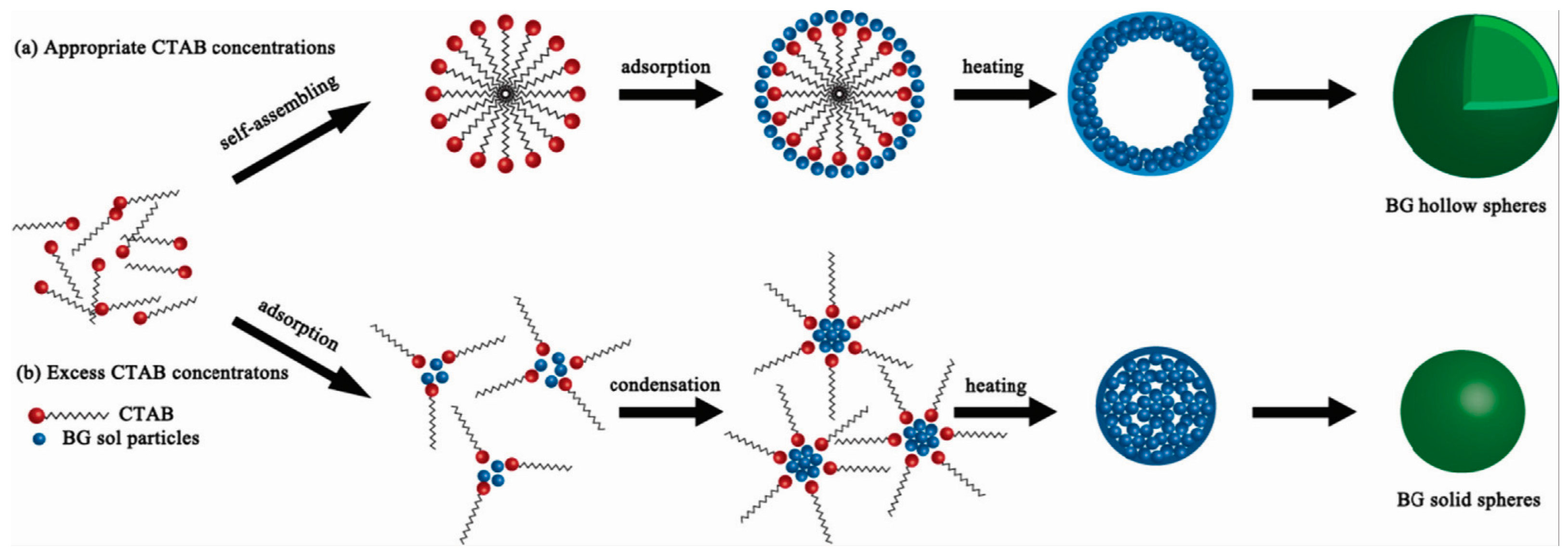
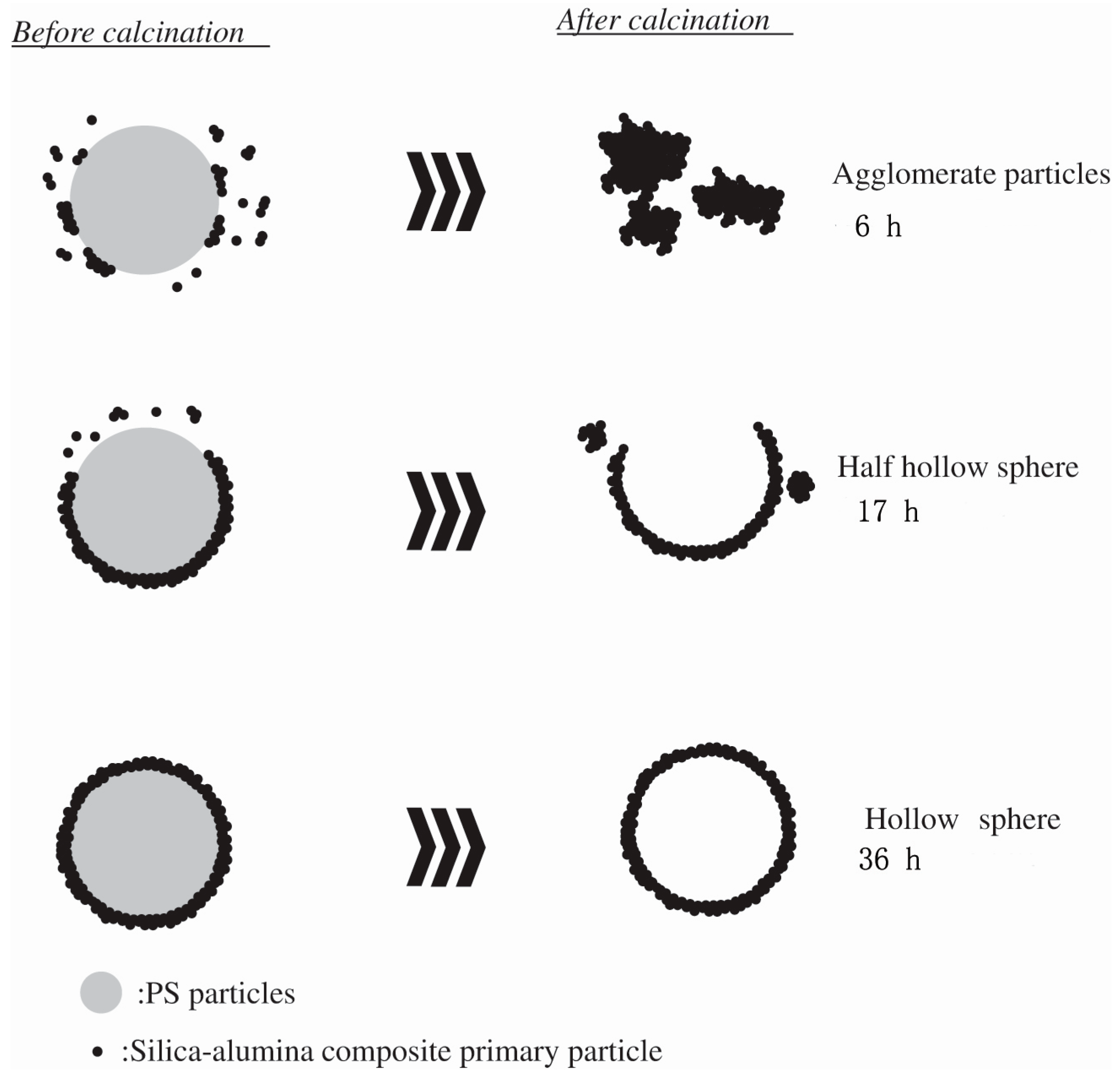
2. Synthesis of Hollow Sphere Materials by the Sol-Gel Method
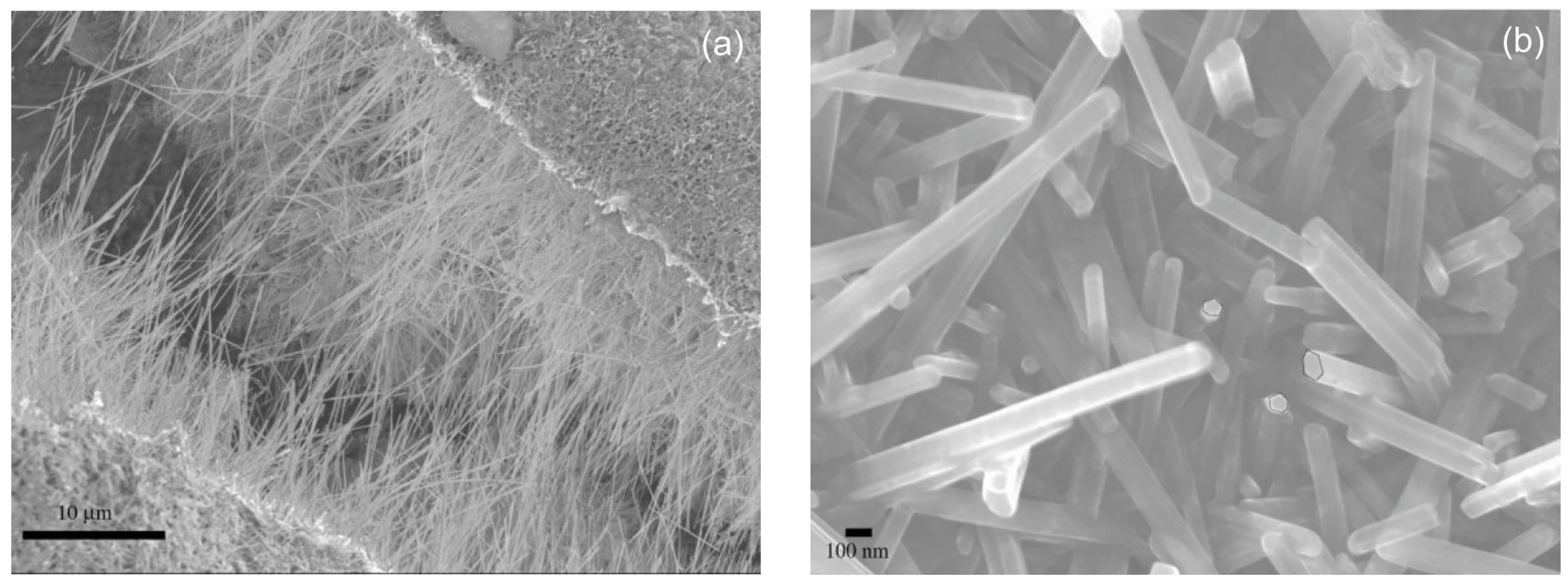
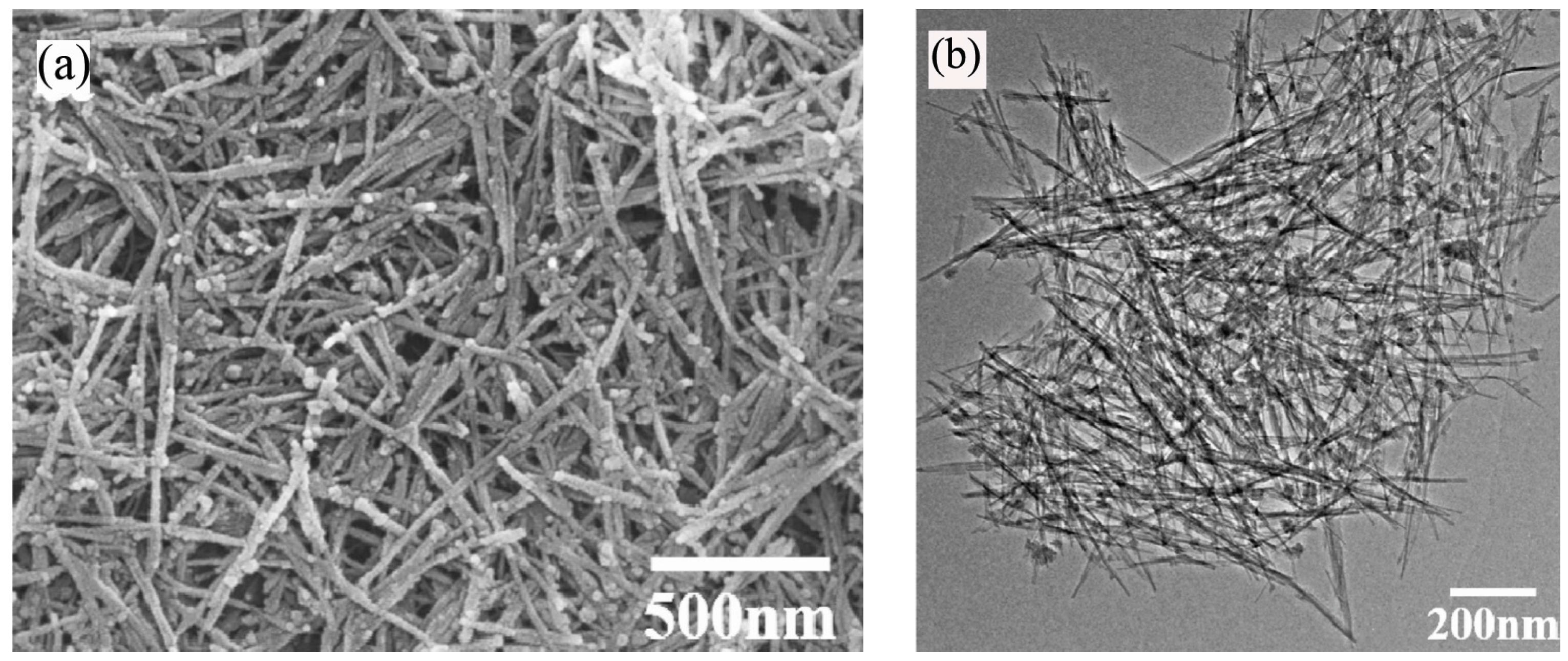
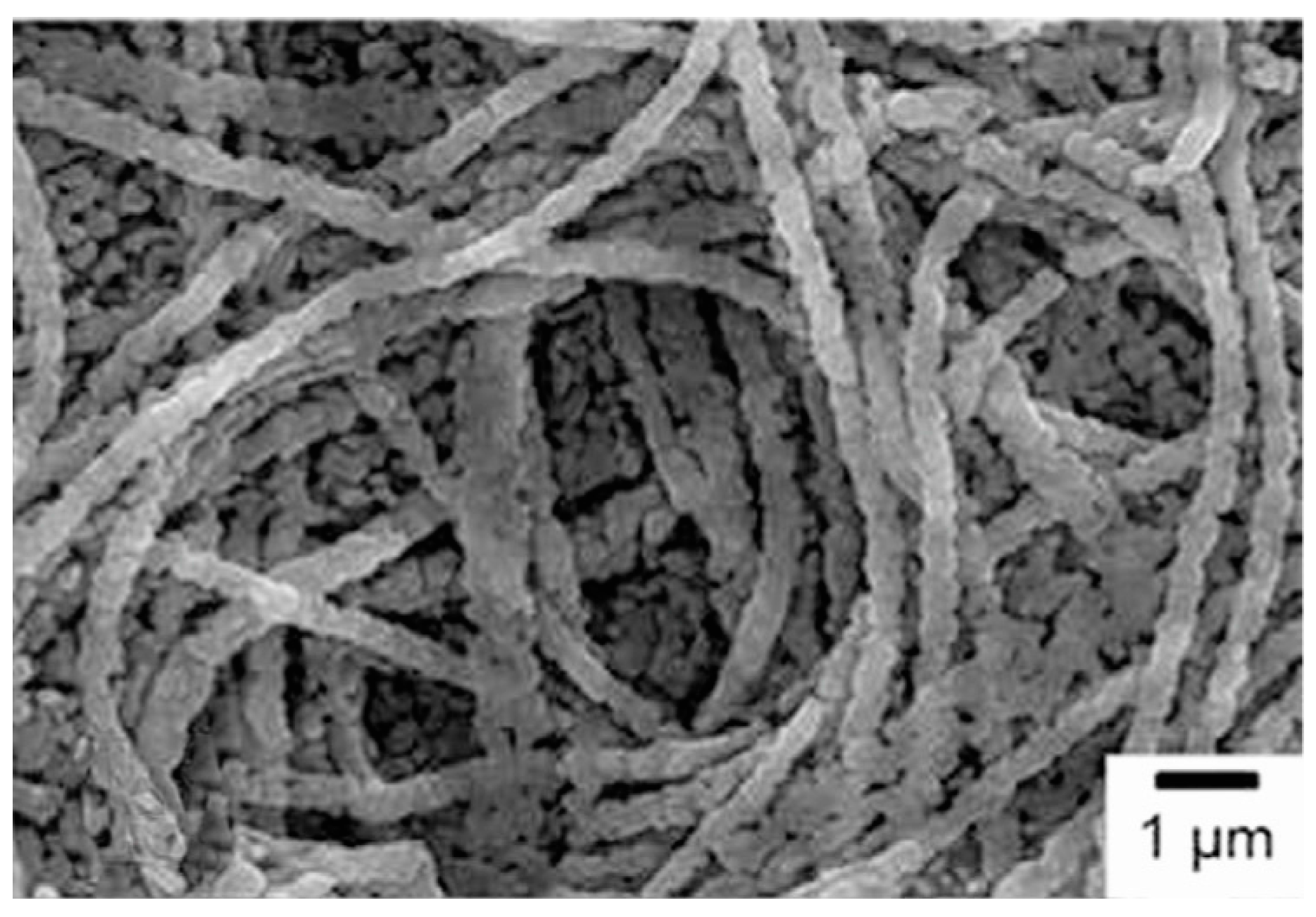
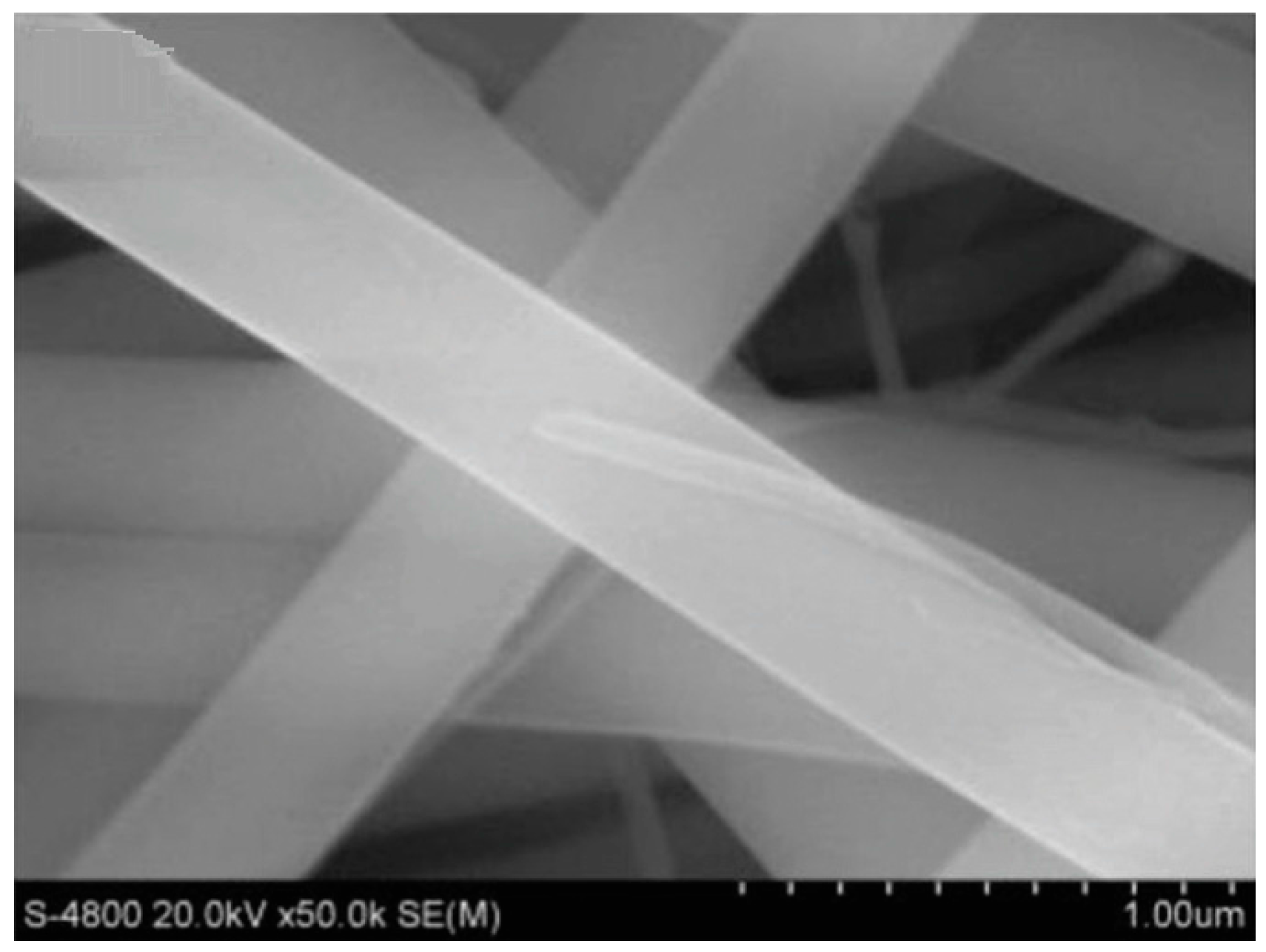
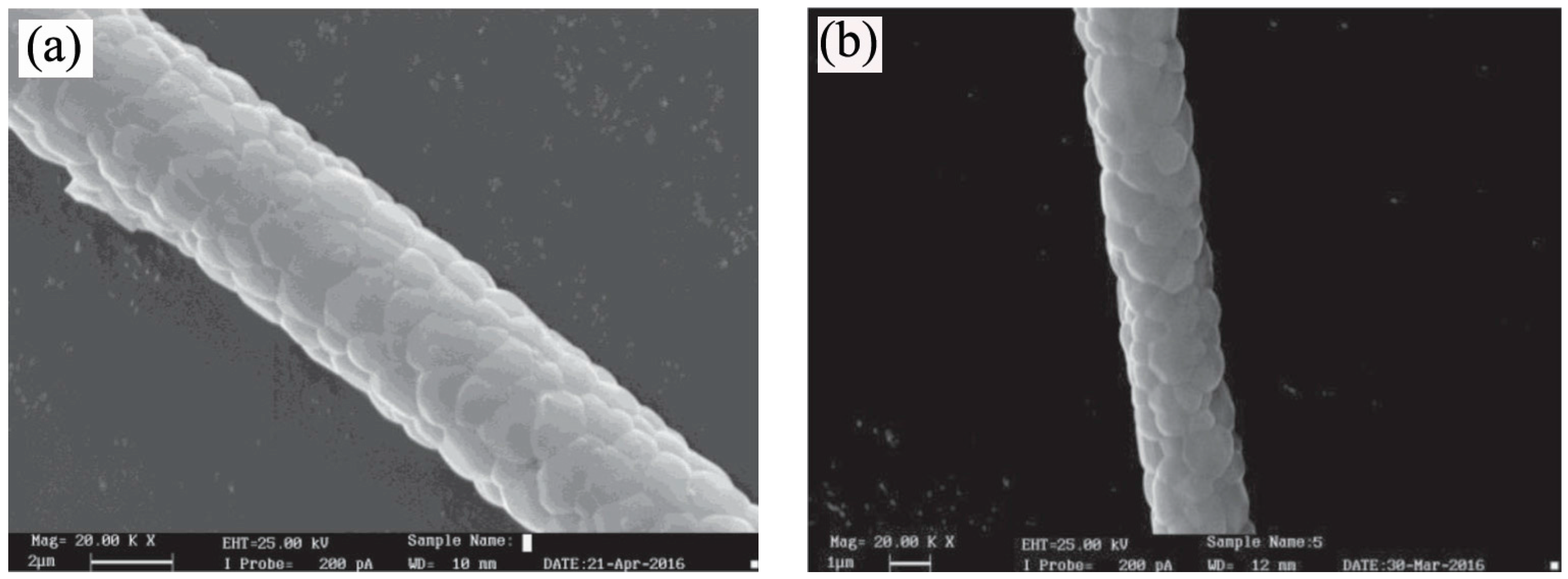
3. Synthesis of 1D Structural Materials by the Sol-Gel Method
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeynali, H.; Akbari, H. Magnetic Properties of L10(FePt)100−xAgx Nanoparticles Synthesized by the Sol-Gel Method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2016, 29, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.S.; Roh, I.J.; Park, J.M.; Kang, C.Y.; Choi, W.J.; Baek, S.H.; Park, S.S.; Yoo, J.W.; Lee, K.S. Dramatic enhancement of the saturation magnetization of a sol-gel synthesized Y3Fe5O12 by a mechanical pressing process. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 711, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Ma, C.; Yao, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, M. Preparation and microwave properties of Co- and Ti-doped barium ferrite by citrate sol-gel process. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 80, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Yao, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, M. Dielectric and magnetic properties of ZnCo-substituted X hexaferrites prepared by citrate sol-gel process. Mater. Res. Bull. 2003, 38, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Ma, C.; Yao, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, M. Complex permittivity, permeability, and microwave absorption of Zn- and Ti-substituted barium ferrite by citrate sol-gel process. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2002, 96, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Yao, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, M. The Synthesis, Characterization and Microwave Properties of ZnCo-Substituted W-Type Barium Hexaferrite, from a Sol-Gel Precursor. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2003, 27, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, X.; Zhang, L. The preparation and microwave properties of BaZn2−ZCoZFe16O27 ferrite obtained by a sol-gel process. Ceram. Int. 2002, 28, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, X.; Zhang, L. The preparation and microwave properties of Ba2ZnZCo2−ZFe12O22 hexaferrites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 22, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, X.; Zhang, L. The preparation and microwave properties of Ba2ZnxCo2−xFe28O46 hexaferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 241, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.P.; Zabotto, F.L.; Garcia, D.; Kiminami, R.H.G.A. In Situ sol-gel co-synthesis at as low hydrolysis rate and microwave sintering of PZT/Fe2CoO4 magnetoelectric composite ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 5925–5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahouadji, B.; Guerbous, L.; Boukerika, A.; Dolić, S.D.; Jovanović, D.J.; Dramićanin, M.D. Sol gel synthesis and pH effect on the luminescent and structural properties of YPO4: Pr3+ nanophosphors. Opt. Mater. 2017, 70, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, M.S.; Kompany, A.; Khorsand Zak, A.; Khorrami, Gh.H. Characterization of Ce(1−x)ZrxO2 yellow nanopigments synthesized by a green sol-gel method. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 8482–8487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almamoun, O.; Ma, S. Effect of Mn doping on the structural, morphological and optical properties of SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by Sol-gel method. Mater. Lett. 2017, 199, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, J. Synthesis of SnO2/rGO hybrid materials by sol-gel/thermal reduction method and its application in electrochemical capacitors. Mater. Lett. 2017, 197, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, E.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Hao, W.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced ethanol sensing performance for chlorine doped nanocrystalline LaFeO3-δ powders by citric sol-gel method. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 251, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Liang, F.; Liu, J.; Cao, Y. Low-temperature preparation of ZrC powders using a combined sol-gel and microwave carbothermal reduction method. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 124, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Lu, L.; Zhang, S.; Cao, Y. Preparation and characterization of ultrafine ZrB2-SiC composite powders by a combined sol-gel and microwave boro/carbothermal reduction method. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 7823–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Fu, F.; Lu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Preparation and artificial neural networks analysis of ultrafine β-Sialon powders by microwave-assisted carbothermal reduction nitridation of sol-gel derived powder precursors. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Jia, Q.; Ye, G. Preparation of titanium carbide powders by sol-gel and microwave carbothermal reduction methods at low temperature. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 46, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, F. Preparation and microstructure evolution of diboride ultrafine powder by sol-gel and microwave carbothermal reduction method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 45, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Synthesis of O’-SiAlON ultrafine powder. Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 2007, 86, 9401–9408. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Miao, J.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Q.; Jia, X. Preparation of Ultrafine β-Sialon Powder by Citrate Sol-Gel and Carbothermal Reduction Nitridation. Key Eng. Mater. 2007, 336–338, 927–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Z. Effect of seeds on the synthesis of mullite powder by the citrate sol-gel method. Interceram 2005, 54, 328–331. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Jia, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, D.; Li, Z. The effect of the concentration of citric acid and pH values on the preparation of MgAl2O4 ultrafine powder by citrate sol-gel process. Mater. Res. Bull. 2004, 39, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jia, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z. The low temperature preparation of nanocrystalline MgAl2O4 spinel by citrate sol-gel process. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 1625–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhang, L. Clewlike ZnV2O4 hollow spheres: Nonaqueous sol-gel synthesis, formation mechanism, and lithium storage properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 9442–9450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Jiao, X.; Chen, D. Preparation of Y-TZP ceramic fibers by electrolysis-sol-gel method. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 5562–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Sha, J.; Ma, X.; Yang, D. Synthesis of NiO nanowires by a sol-gel process. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 1967–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelouche, A.; Touam, T.; Tazerout, M.; Djouadi, D.; Boudjouan, F. Effect of Li codoping on highly oriented sol-gel Ce-doped ZnO thin films properties. J. Lumin. 2017, 188, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Xu, B.; Shen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Nan, C. Improvement of the conductivity of sol-gel derived Li-La-Zr-O thin films by the addition of surfactant. Ceram. Int. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, T.; Harizanova, A.; Koutzarova, T.; Vertruyen, B. Optical characterization of sol-gel ZnO:Al thin films. Superlattice Microstruct. 2015, 85, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, Z.N.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Study of Nickel Nitride Thin Films Deposited by Sol-Gel Route. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2017, 70, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predoana, L.; Stanciu, I.; Anastasescu, M.; Calderon-Moreno, J.M.; Stoica, M.; Preda, S.; Gartner, M.; Zaharescu, M. Structure and properties of the V-doped TiO2 thin films obtained by sol-gel and microwave-assisted sol-gel method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 78, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, G.; Dong, X.; Tang, X. Structure and magnetic properties of La0.67Sr0.33MnO3 thin films prepared by sol-gel method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, X.; Shen, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H. Synthesis and application of several sol-gel-derived materials via sol-gel process combining with other technologies: A review. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 79, 328–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fu, F.; Cao, Y.; Du, S.; Lu, L.; Zhang, S. Sol-Gel Process Synthesis of High-Temperature Non-oxide Ultrafine Powders. Interceram 2013, 62, 282–286. [Google Scholar]
- Livage, J.; Ganguli, D. Sol-gel electrochromic coatings and devices:A review. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2001, 68, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoldas, B.E. Technological significance of Sol-Gel process and process-induced variations in Sol-Gel materials and coatings. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 1993, 1, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; He, J. Facile preparation of titania hollow spheres by combination of the mixed solvent method and the sol-gel process and post-calcination. Mater. Res. Bull. 2009, 44, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobó, D.G.; Berkesi, D.; Kukovecz, Á. Morphology conserving aminopropyl functionalization of hollow silica nanospheres in toluene. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1140, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Meiser, F.; Möhwald, H. Nanoengineering of iron oxide and iron oxide/silica hollow spheres by sequential layering combined with a sol-gel process. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2005, 288, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, M.; Wu, S.; Chen, Q.; Shen, J. Novel triethanolamine assisted sol-gel synthesis of N-doped TiO2 hollow spheres. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 1398–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, T.; Cao, S.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, X. Synthesis of uniform hollow TiO2 and SiO2 microspheres via a freezing assisted reverse microemulsion-templated sol-gel method. Mater. Lett. 2015, 151, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Han, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, F.; Yang, W. Preparation of hollow mesoporous silica spheres by a sol-gel/emulsion approach. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 127, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Yuan, Q.; Zhao, H. Self-doped TiO2 hierarchical hollow spheres with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 640, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y. Silicone rubber/hollow silica spheres composites with enhanced mechanical and electrical insulating performances. Mater. Lett. 2017, 205, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, Y.; Xie, T. Sol-gel synthesis of titania hollow spheres. Mater. Res. Bull. 2005, 40, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Lei, Z.; Jia, H.; Zhao, X. Sol-gel synthesis, microstructure and adsorption properties of hollow silica spheres. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1811–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashuri, M.; He, Q.; Zhang, K.; Emani, S.; Shaw, L.L. Synthesis of hollow silicon nanospheres encapsulated with a carbon shell through sol-gel coating of polystyrene nanoparticles. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Chen, D.; Chen, L. Synthesis of monodisperse CeO2 hollow spheres with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 11570–11575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Rong, F.; Ji, X.; Fu, D. Visible light photocatalytic activity and Photoelectrochemical property of Fe-doped TiO2 hollow spheres by sol-gel method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2011, 59, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullar, R.C.; Taylor, M.D.; Bhattacharya, A.K. Blow spun strontium zirconate fibers produced from a sol-gel precursor. J. Mater. Sci. 1998, 33, 3229–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, R.; Ramanan, S.R. Effect of organic additives on the properties of sol-gel spun alumina fibers. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 20, 2543–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandradass, J.; Balasubramanian, M. Extrusion of alumina fiber using sol-gel precursor. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 6026–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.J. Hydroxyapatite nanofibers fabricated through electrospinning and sol-gel process. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 3361–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Ding, Y.; Yang, J. Mullite fibers preparation by aqueous sol-gel process and activation energy of mullitization. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 492, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, G.; Restoin, C.; Roy, P.; Jamier, R.; Roungier, S.; Lecomte, A.; Blondy, J.M. Nanostructured optical fibers in the SiO2/SnO2 system by the sol-gel method. Mater. Lett. 2014, 120, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Ma, X.; Fu, M. Preparation of continuous alumina gel fibers by aqueous sol-gel process. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2013, 36, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wan, L.; Xu, D. Preparation of continuous TiO2 fibers by sol-gel method and its photocatalytic degradation on formaldehyde. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3469–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S. Sol-gel template synthesis of LiV3O8 nanowires. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil, T.; Anandhan, S. Structure-property relationship of sol-gel electrospun ZnO nanofibers developed for ammonia gas sensing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 432, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Admaiai, L.F.; Daza, L.; Grange, P.; Delmon, B. Synthesis of YBa2Cu3O7−x superconductor with fiber structure by the sol-gel method. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1994, 13, 668–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, J.M.; Jones, K.; Emblem, H.G. The preparation of spinel fiber by a sol-gel route. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1990, 9, 914–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Ji, H.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Sun, X. Synthesis of zirconium diboride nano-powders by novel complex sol-gel technology at low temperature. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Du, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Lu, L.; Zhang, S.; Deng, X. Preparation of zirconium diboride ultrafine hollow spheres by a combined sol-gel and boro/carbothermal reduction technique. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2014, 72, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Tong, Y.; Li, F.; Wu, J.C.S.; Wang, X. Openmouthed β-SiC hollow-sphere with highly photocatalytic activity for reduction of CO2 with H2O. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 206, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ma, W.; Shangguan, J.; Jiang, W.; Zhong, Q. Controllable synthesis of hollow mesoporous silica spheres and application as support of nano-gold. J. Solid State Chem. 2014, 215, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Luo, J.; Wu, M.; Jiu, H.; Chen, Q. Synthesis of Eu2O3 hollow submicrometer spheres through a sol-gel template approach. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 4452–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syoufian, A.; Manako, Y.; Nakashima, K. Sol-gel preparation of photoactive srilankite-type zirconium titanate hollow spheres by templating sulfonated polystyrene latex particles. Powder Technol. 2015, 280, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chaki, T.K. Millimetre-sized hollow spheres of lead zirconate titanate by a sol-gel method. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 2563–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, N.; Ning, C.; Chen, X. Facile synthesis of hollow mesoporous bioactive glass sub-micron spheres with a tunable cavity size. Mater. Lett. 2014, 134, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, N.; Ohki, S.; Tansho, S.; Shimizu, T.; Umegaki, T.; Kojima, Y. Influence of alcohol solvents on morphology of hollow silica–alumina composite spheres and their activity for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Kao, C.T.; Tang, B.; Chang, W.; Wu, R. Efficient hydrogen production by photocatalytic water-splitting using Pt-doped TiO2 hollow spheres under visible light. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 6749–6754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.T.; Tseng, I.H. Fabrication of organosilica hollow spheres using organosiloxane-templated sol-gel process. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 76, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhalid, I.A.; Abdulsalam, A.A. Photocatalytic reduction of Hg using core-shell Fe/CeO2 hollow sphere nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 5614–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, K.; Kamiya, J.; Koumoto, K.; Inumaru, K. Preparation of hollow titania and strontium titanate spheres using sol-gel derived silica gel particles as templates. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2012, 63, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronakis, I.S. Novel nanocomposites and nanoceramics based on polymer nanofibers using electrospinning process-A review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2005, 167, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamatsu, J.; Nakagawa, N.; Muranaka, T.; Zenitani, Y.; Akimitsu, J. Superconductivity at 39 K in magnesium diboride. Nature 2001, 410, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, M.; Parkinson, B.A. A Simple Sol-Gel Synthesis of Superconducting MgB2 Nanowires. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1865–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G. Preparation and characterization of SiBON fiber. Mater. Lett. 2012, 89, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Shan, X.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y. Sol-gel process for the synthesis of ultrafine MnO2 nanowires and nanorods. Mater. Lett. 2014, 132, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Kang, Y.S. Synthesis and structural properties of manganese titanate MnTiO3 nanoparticle. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2004, 24, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhowong, R. Fabrication and characterization of MnTiO3 nanofibers by sol-gel assisted electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2015, 161, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamitha, C.; Senthil, T.; Wu, L.; Kumar, B.S.; Anandhan, S. Sol-gel electrospun mesoporous ZnMn2O4 nanofibers with superior specific surface area. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Sang, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Bu, J.; Dong, G. Synthesis of flexible mullite nanofibers by electrospinning based on nonhydrolytic sol-gel method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Lv, Z.; Tan, H.; Nan, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, X. Preparation and grain-growth of chromia-yttrium aluminum garnet composites fibers by sol-gel method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 83, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.H.; Li, K.; Chan, H.L.W. Lead magnesium niobate-lead titanate fibers by a modified sol-gel method. Mater. Res. Bull. 2005, 40, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lin, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, D. Fabrication of calcium zirconate fibers by the sol-gel method. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 12525–12531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaie-Bahaabad, M.; Taheri-Nassaj, E.; Naghizadeh, R. An alumina-YAG nanostructured fiber prepared from an aqueous sol-gel precursor: Preparation, rheological behavior and spinnability. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, G.; Anandhan, S. Comparison of structural, spectral and magnetic properties of NiO nanofibers obtained by sol-gel electrospinning from two different polymeric binders. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 32, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Nomura, N.; Kawasaki, A. Synthesis of n-type Mg2Si/CNT Thermoelectric Nanofibers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, K.; Takasuka, Y.; Kamiya, K.; Nasu, H. Preparation of NbN fibers by nitridation of sol-gel derived Nb2O5 fibers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 1994, 5, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.-L.; Zhang, H.-J. Synthesis of Hollow Sphere and 1D Structural Materials by Sol-Gel Process. Materials 2017, 10, 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10090995
Li F-L, Zhang H-J. Synthesis of Hollow Sphere and 1D Structural Materials by Sol-Gel Process. Materials. 2017; 10(9):995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10090995
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Fa-Liang, and Hai-Jun Zhang. 2017. "Synthesis of Hollow Sphere and 1D Structural Materials by Sol-Gel Process" Materials 10, no. 9: 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10090995
APA StyleLi, F.-L., & Zhang, H.-J. (2017). Synthesis of Hollow Sphere and 1D Structural Materials by Sol-Gel Process. Materials, 10(9), 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10090995




