Coercivity Mechanism of (Nd0.8Ce0.2)2.4Fe12Co2B Ribbons with Ferromagnetic Grain Boundary Phase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
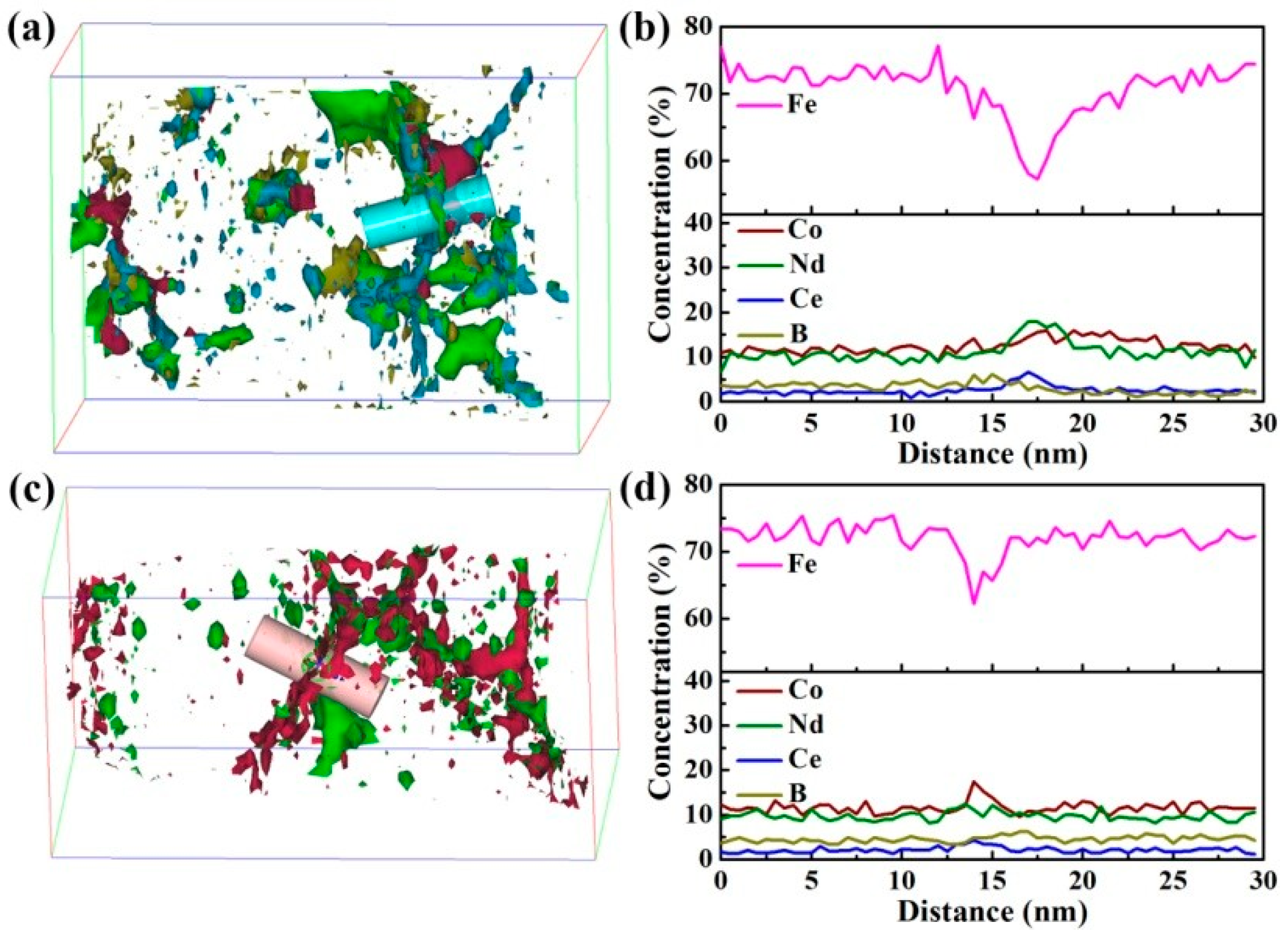
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Exchange Coupling Interaction through Ferromagnetic GB Phase
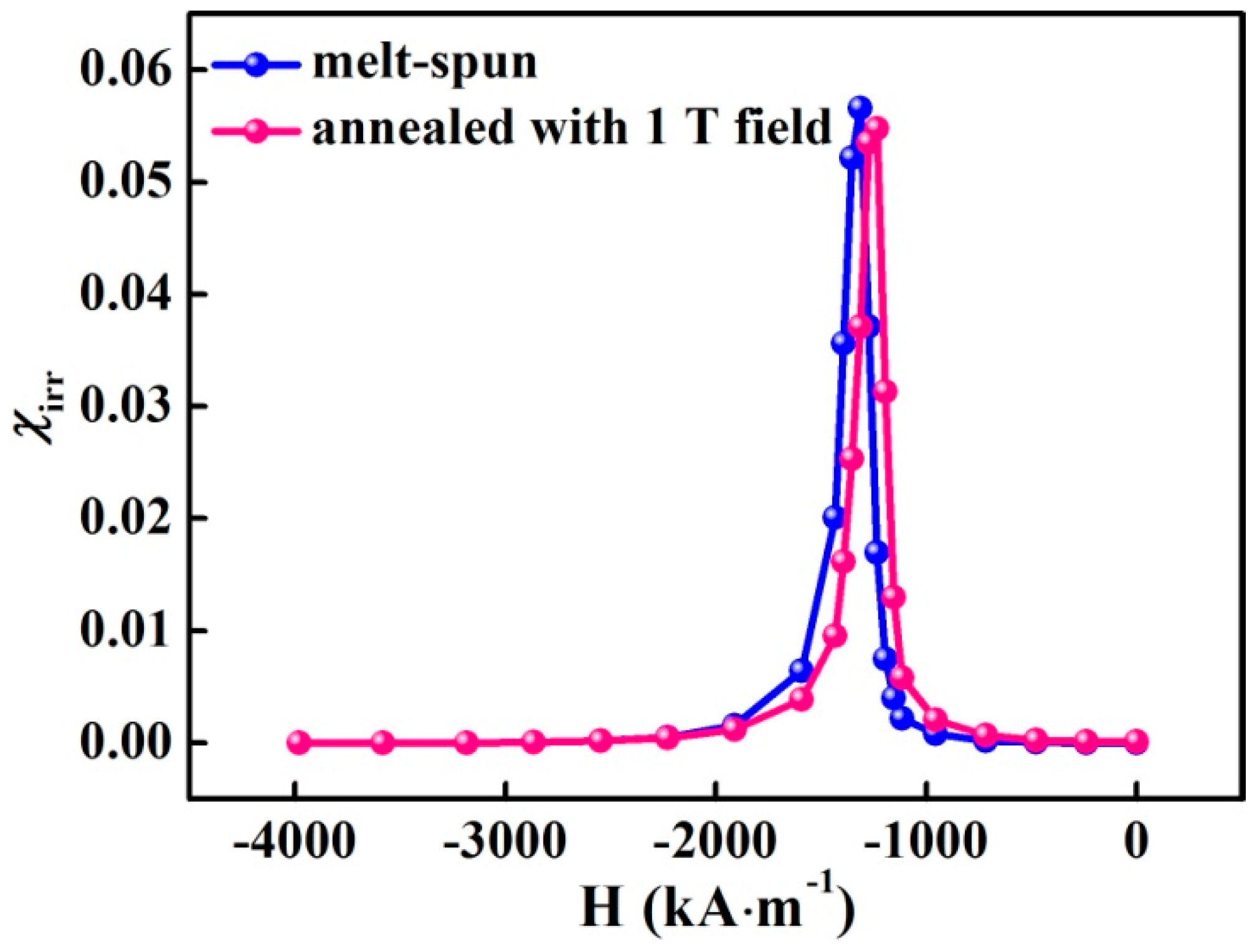
4.2. The Coercivity Mechanism
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Croat, J.J.; Herbst, J.F.; Lee, R.W.; Pinkerton, F.E. Pr-Fe and Nd-Fe-based materials: A new class of high-performance permanent magnets. J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 55, 2078–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, M.; Fujimura, S.; Togawa, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Matsuura, Y. New material for permanent magnets on a base of Nd and Fe. J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 55, 2083–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutfleisch, O.; Willard, M.A.; Brück, E.; Chen, C.H.; Sankar, S.G.; Liu, J.P. Magnetic materials and devices for the 21st century: stronger, lighter, and more energy efficient. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 821–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, J.F. R2Fe14B materials: Intrinsic properties and technological aspects. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1991, 63, 819–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D. Permanent magnets: plugging the gap. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hono, K.; Sepehri-Amin, H. Strategy for high-coercivity Nd-Fe-B magnets. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.Q.; Zha, S.S.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, D.T.; Yue, M.; Zhang, J.X.; Huang, X.L. Effects of CE substitution on the microstructures and intrinsic magnetic properties of Nd-Fe-B alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 393, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Zhu, M.G.; Li, W.; Zheng, L.Y.; Guo, Z.H.; Du, X.; Du, A. Effects of the ingot phase transition on microstructure and magnetic properties of CeNdFeB melt-spun ribbons. Physica B 2015, 476, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.B.; Shen, B.G.; Zhang, M.; Hu, F.X.; Sun, J.R. Substitution of Ce for Nd in preparing R2Fe14B nanocrystalline magnets. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 628, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.K.; Khan, M.; Gschneidner, K.A., Jr.; McCallum, R.W.; Zhou, L.; Sun, K.; Dennis, K.W.; Zhou, C.; Pinkerton, F.E.; Kramer, M.J.; et al. Cerium: An unlikely replacement of dysprosium in high performance Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2663–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.T.; Ohkubo, T.; Takada, Y.; Sato, T.; Kato, A.; Kaneko, Y.; Hono, K. Formation of non-ferromagnetic grain boundary phase in a Ga-doped Nd-rich Nd-Fe-B sintered magnet. Scr. Mater. 2016, 113, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.P.; Ma, T.Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X.L.; Yan, M. Coercivity enhancement of Dy-free Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets by intergranular adding Ho63.4Fe36.6 alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 397, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri-Amin, H.; Ohkubo, T.; Hono, K. The mechanism of coercivity enhancement by the grain boundary diffusion process of Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri-Amin, H.; Prabhu, D.; Hayashi, M.; Ohkubo, T.; Hioki, K.; Hattori, A.; Hono, K. Coercivity enhancement of rapidly solidified Nd-Fe-B magnet powders. Scr. Mater. 2013, 68, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Ohkubo, T.; Hioki, K.; Hattori, A.; Schrefl, T.; Hono, K. Effect of Nd content on the microstructure and coercivity of hot-deformed Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 5387–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri-Amin, H.; Ohkubo, T.; Shima, T.; Hono, K. Grain boundary and interface chemistry of an Nd-Fe-B-based sintered magnet. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Tanigaki, T.; Sasaki, T.T.; Takeno, Y.; Park, H.S.; Matsuda, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Hono, K.; Shindo, D. Magnetism of ultrathin intergranular boundary regions in Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets. Acta Mater. 2014, 71, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohashi, T.; Motai, K.; Nishiuchi, T.; Hirosawa, S. Magnetism in grain-boundary phase of a NdFeB sintered magnet studied by spin-polarized scanning electron microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 232408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Yasui, A.; Kotani, Y.; Fukagawa, T.; Nishiuchi, T.; Iwai, H.; Akiya, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Gohda, Y.; Hono, K.; et al. Direct observation of ferromagnetism in grain boundary phase of Nd-Fe-B sintered magnet using soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 202404(1–4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.Z.; Han, K.; Garmestani, H.; Su, J.H.; Schneider-Muntau, H.J.; Liu, J.P. Enhancement of exchange coupling and hard magnetic properties in nanocomposites by magnetic annealing. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 4155–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.V.; Rong, C.B.; Ding, Y.; Liu, J.P. Effect of magnetic fields on melt-spun Nd2Fe14B-based ribbons. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07A731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, R.; Yasuda, H.; Miyoshi, T.; Kanekiyo, H.; Hirosawa, S. Effects of magnetic field annealing on magnetic properties and microstructure of Nd-Fe-B-Ti-C based nanocomposite permanent magnet. Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 2007, 204, 4145–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Otero, J.; Porto, M.; Rivas, J. Henkel plots of single-domain ferromagnetic particles. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 7376–7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaunt, P. Ferromagnetic domain wall pinning by a random array of inhomogeneities. Philos. Mag. B 1983, 48, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinek, G.; Kronmüller, H. Influence of grain orientation on the coercive field in Fe-Nd-B permanent magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1990, 86, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.H.; Li, H.Y.; Xu, H.; Han, K.; Li, W.D.; Zhang, F. A cost-effective approach to optimizing microstructure and magnetic properties in Ce17Fe78B6 alloys. Materials 2017, 10, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, M.J.; Lewis, L.H.; Fabietti, L.M.; Tang, Y.; Miller, W.; Dennis, K.W.; McCallum, R.W. Solidification, microstructural refinement and magnetism in Nd2Fe14B. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 241, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.E.; O’Grady, K.; Mayo, P.L.; Chantrell, R.W. Switching mechanisms in cobalt-phosphorus thin films. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1989, 25, 3881–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, J.D. Magnetic domains in sintered FeNdB magnets. J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 57, 4137–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croat, J.J.; Herbst, J.F.; Lee, R.W.; Pinkerton, F.E. High-energy product Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1984, 44, 148–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, P.G.; Ding, J.; Feutrill, E.H.; Street, R. Mechanically alloyed hard magnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1996, 157–158, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkerton, F.E.; Fuerst, C.D. Temperature dependence of coercivity in melt-spun and die upset neodymium-iron-boron. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 67, 4753–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.J.; Pan, M.X.; Zhang, P.Y.; Ge, H.L. The origin of coercivity enhancement of sintered NdFeB magnets prepared by Dy addition. J. Magn. 2013, 18, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wu, Y.Q.; Dennis, K.W.; Kramer, M.J.; Anderson, I.E.; McCallum, R.W. Effect of TiC addition on microstructure and magnetic properties for MRE2(Fe,Co)14B melt-spun ribbons (MRE = Nd + Y + Dy). J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 08B510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| (Nd0.8Ce0.2)2.4Fe12Co2B Alloy | Hci (kA∙m−1) | Br (T) | (BH)max (kJ∙m−3) | αk | Neff |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melt-spun sample | 1285 | 0.76 | 96 | 0.67 | 0.58 |
| Annealed sample | 1189 | 0.82 | 111 | 0.66 | 0.61 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Liang, Y.; Tan, X.; Xu, H.; Hu, P.; Ren, K. Coercivity Mechanism of (Nd0.8Ce0.2)2.4Fe12Co2B Ribbons with Ferromagnetic Grain Boundary Phase. Materials 2017, 10, 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091062
Li H, Liang Y, Tan X, Xu H, Hu P, Ren K. Coercivity Mechanism of (Nd0.8Ce0.2)2.4Fe12Co2B Ribbons with Ferromagnetic Grain Boundary Phase. Materials. 2017; 10(9):1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091062
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Heyun, Yang Liang, Xiaohua Tan, Hui Xu, Pengfei Hu, and Kezhi Ren. 2017. "Coercivity Mechanism of (Nd0.8Ce0.2)2.4Fe12Co2B Ribbons with Ferromagnetic Grain Boundary Phase" Materials 10, no. 9: 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091062
APA StyleLi, H., Liang, Y., Tan, X., Xu, H., Hu, P., & Ren, K. (2017). Coercivity Mechanism of (Nd0.8Ce0.2)2.4Fe12Co2B Ribbons with Ferromagnetic Grain Boundary Phase. Materials, 10(9), 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10091062





