Fabrication and Characterization of 3D-Printed Highly-Porous 3D LiFePO4 Electrodes by Low Temperature Direct Writing Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
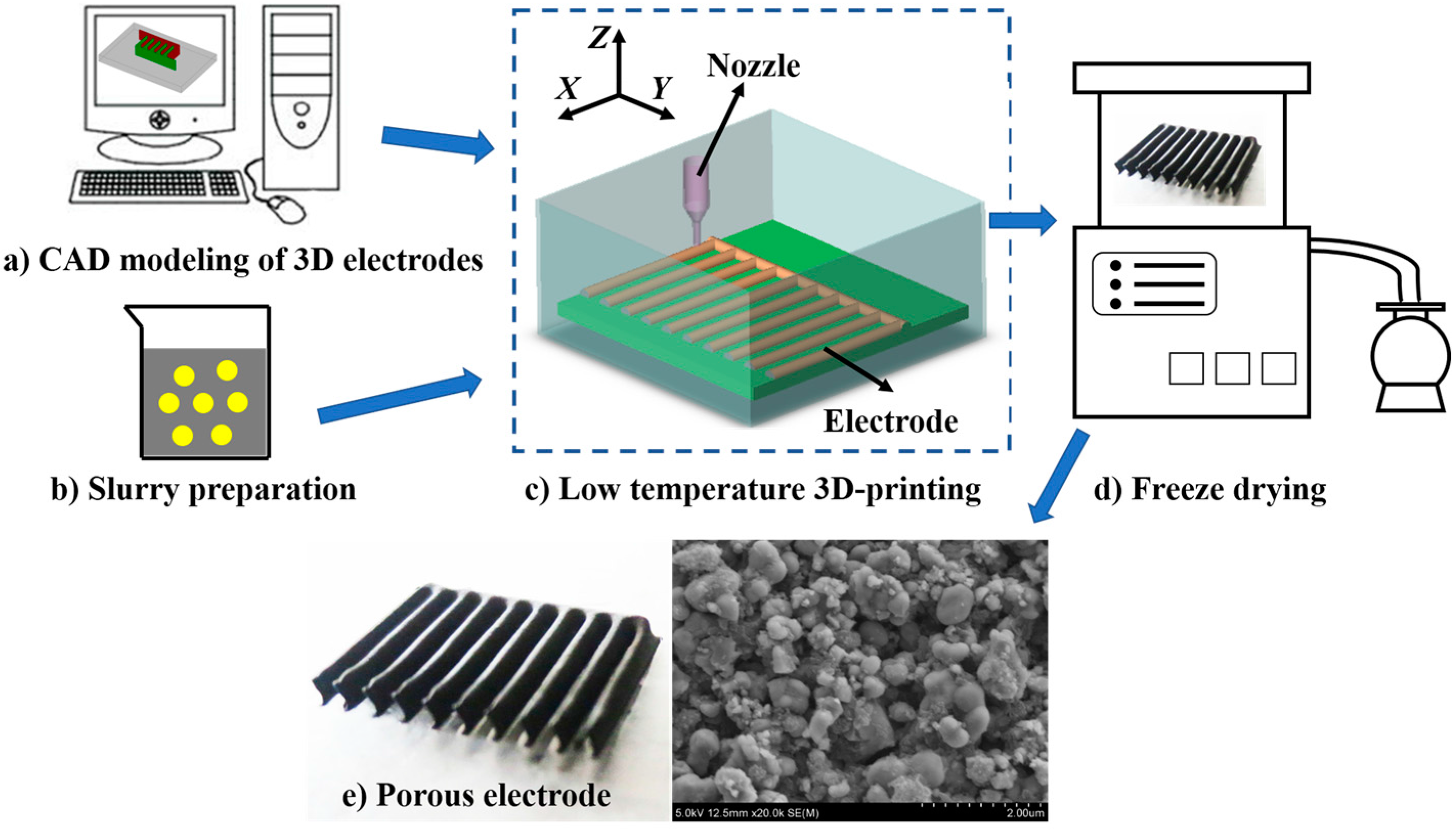
2.1. Materials Preparation
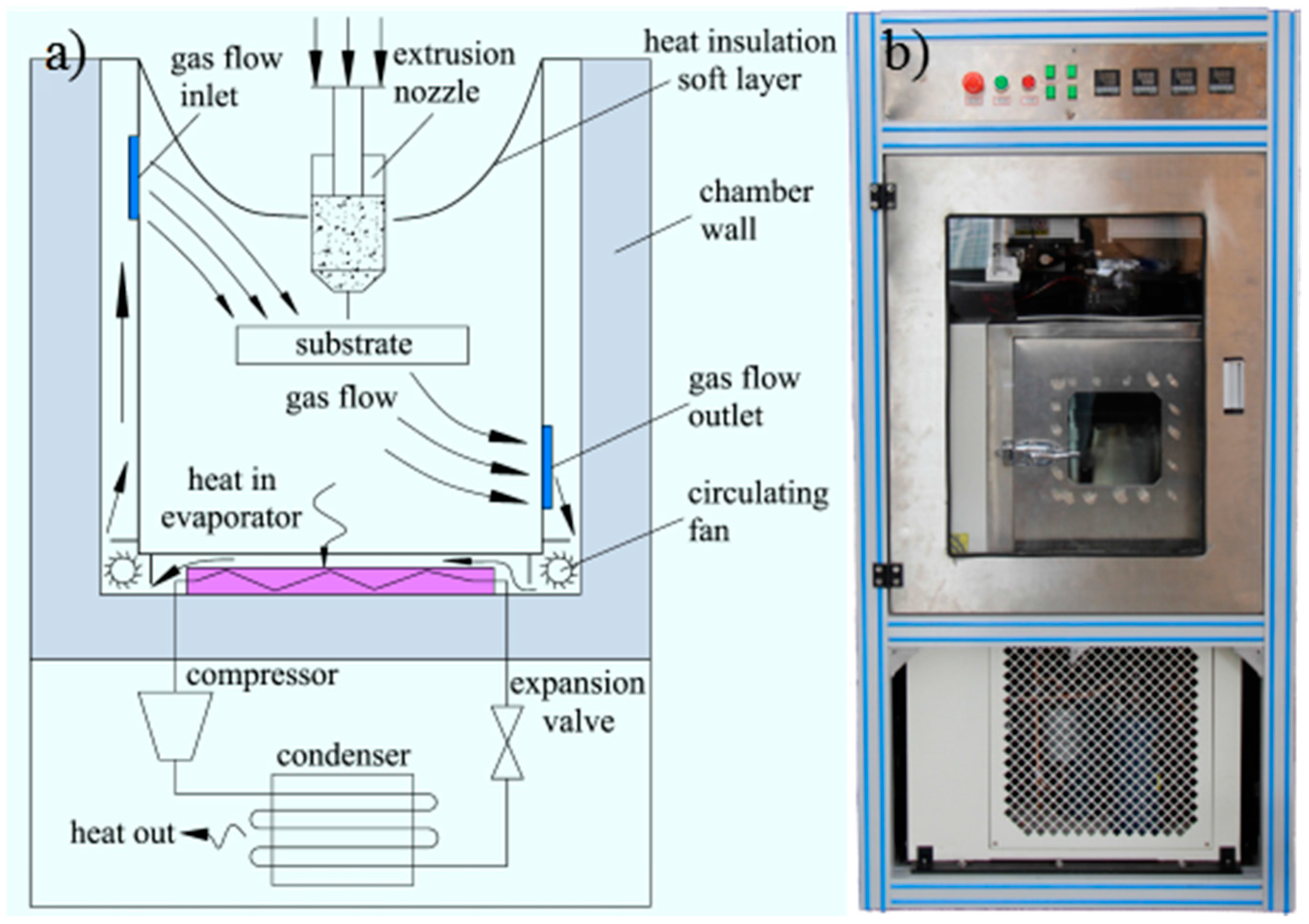
2.2. LTDW Process
2.3. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Rheological Properties of LFP Slurries
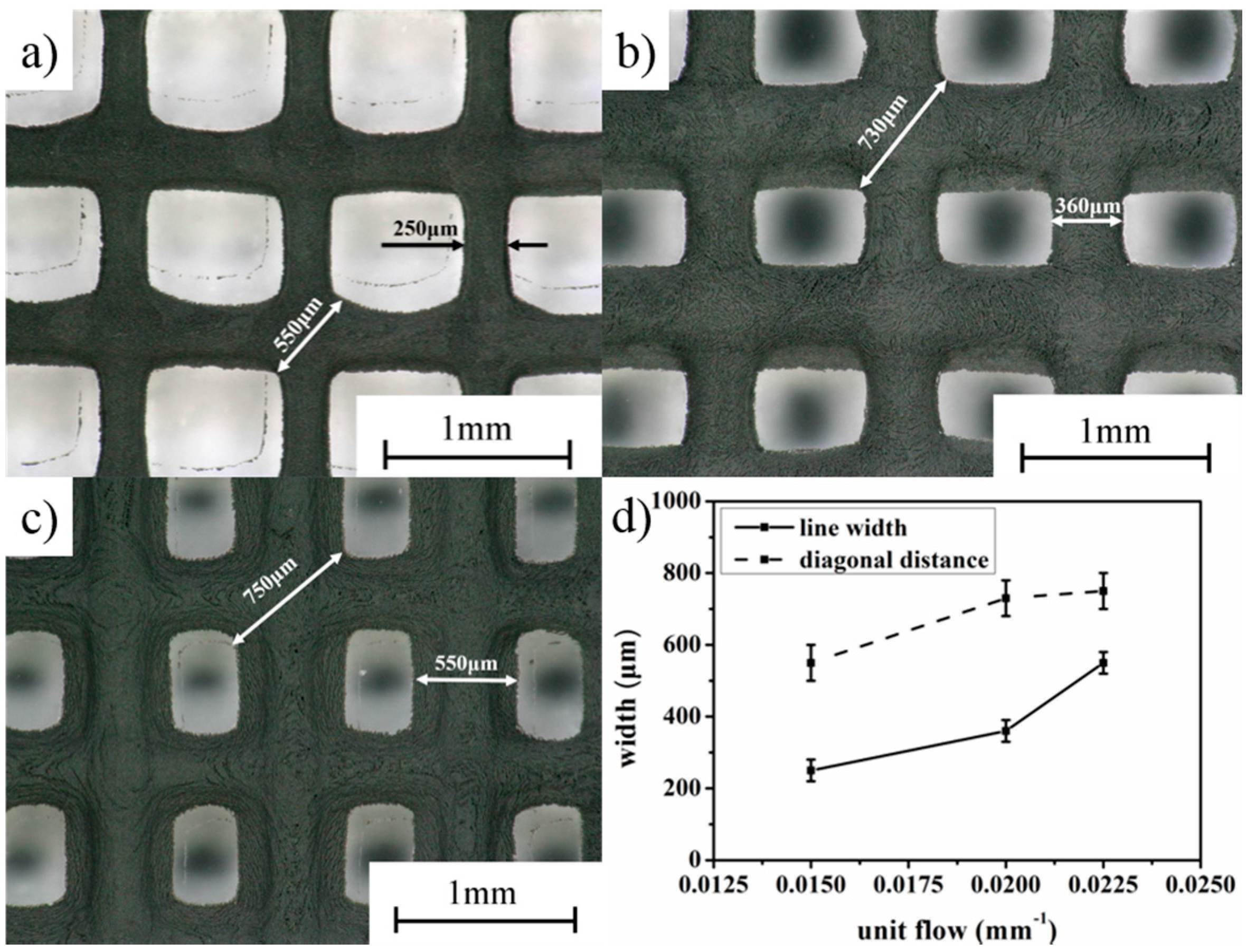
3.2. Printing Process Optimization and Accuracy Characterization
3.3. Microstructure Characterization
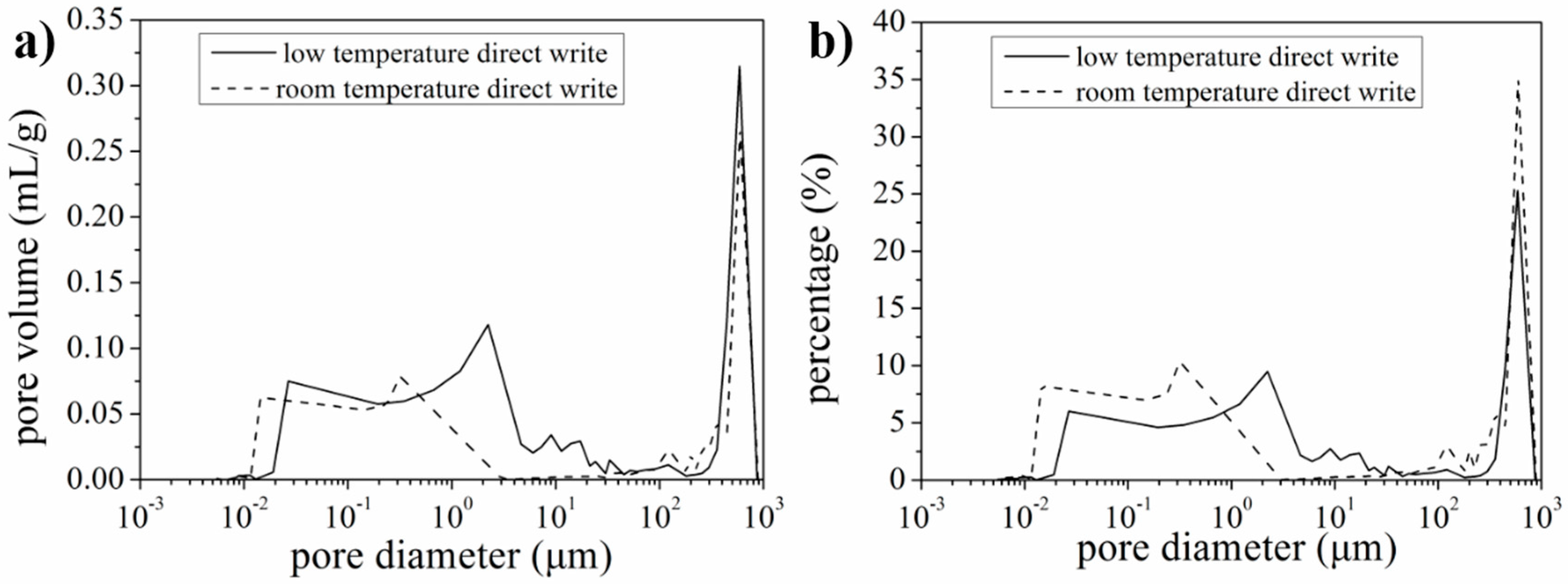
3.4. Characterization of Pore Volume, Size and Distribution
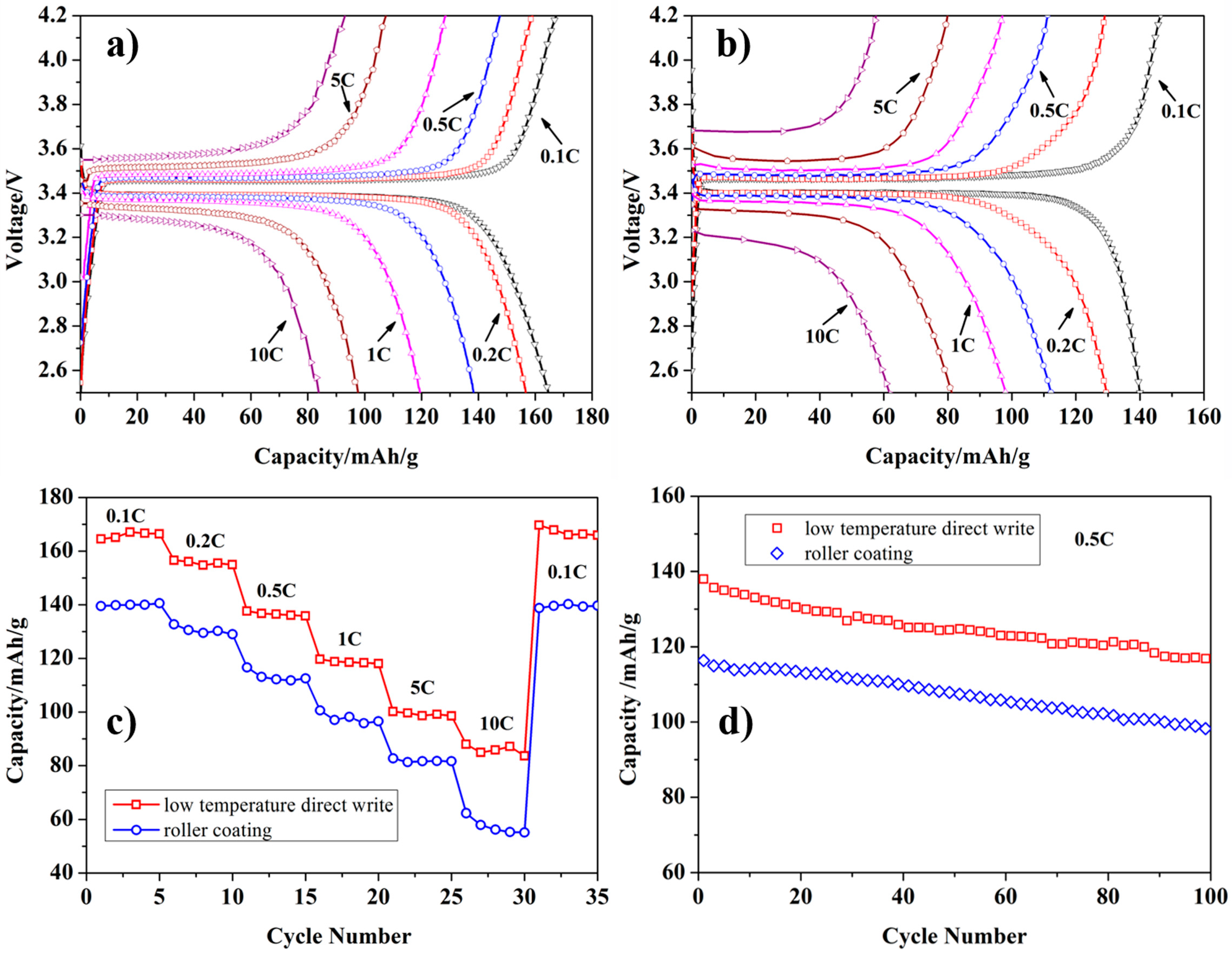
3.5. Electrochemical Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgment
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ambrosi, A.; Pumera, M. 3D-printing technologies for electrochemical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2740–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvert, P. Printing cells. Science 2007, 318, 208–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durmus, N.G.; Tasoglu, S.; Demirci, U. Bioprinting functional droplet networks. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 478–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norotte, C.; Marga, F.S.; Niklason, L.E.; Forgacs, G. Scaffold-free vascular tissue engineering using bioprinting. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5910–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, J. Fast Fabrication of Flexible Functional Circuits Based on Liquid Metal Dual-Trans Printing. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7109–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-Y.; Yang, C.; Hsu, W.; Lin, L. 3D-printed microelectronics for integrated circuitry and passive wireless sensors. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2015, 1, 15013–15021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Wang, Y.B.; Yan, C.Y.; Yao, Y.G.; Chen, Y.A.; Dai, J.Q.; Lacey, S.; Wang, Y.B.; Wan, J.Y.; Li, T.; et al. Graphene Oxide-Based Electrode Inks for 3D-Printed Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.T.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, S.H.; Duan, Y.D.; Liu, T.C.; Guo, H.; Lin, L.P.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, J.X.; Amine, K.; et al. 3D-Printed Cathodes of LiMn1-xFexPO4 Nanocrystals Achieve Both Ultrahigh Rate and High Capacity for Advanced Lithium-Ion Battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmeyer, R.R.; Blake, A.J.; Hardin, J.O.; Carmona, E.A.; Carpena-Nunez, J.; Maruyama, B.; Berrigan, J.D.; Huang, H.; Durstock, M.F. Composite batteries: a simple yet universal approach to 3D printable lithium-ion battery electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 16856–16864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Wei, T.S.; Ahn, B.Y.; Seo, J.Y.; Dillon, S.J.; Lewis, J.A. 3D printing of interdigitated Li-ion microbattery architectures. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4539–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Gorkin, R.; Beirne, S.; Shu, K.; Wallace, G.G. Three dimensional (3D) printed electrodes for interdigitated supercapacitors. Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 41, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, L.F.; Walsh, F.C.; de Leon, C.P. 3D-Printing of Redox Flow Batteries for Energy Storage: A Rapid Prototype Laboratory Cell. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, P3080–P3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.M. Building a Better Battery. Science 2010, 330, 1485–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodenough, J.B. Electrochemical energy storage in a sustainable modern society. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarascon, J.M.; Armand, M. Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 2001, 414, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armand, M.; Tarascon, J.M. Building better batteries. Nature 2008, 451, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.; Loveridge, M.; Beattie, S.D.; Jahn, M.; Dashwood, R.J.; Bhagat, R. Latest advances in the manufacturing of 3D rechargeable lithium microbatteries. J. Power Sources 2015, 286, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.W.; Dunn, B.; Rolison, D.R.; White, H.S. Three-dimensional battery architectures. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4463–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, T.S.; Bates, D.J.; Cirigliano, N.; Johnson, D.C.; Malati, P.; Mosby, J.M.; Perre, E.; Rawls, M.T.; Prieto, A.L.; Dunn, B. Three-dimensional electrodes and battery architectures. MRS Bull. 2011, 36, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, C.L.; Ho, C.C. Additive Manufacturing: Rethinking Battery Design. Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2016, 25, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.; Johns, P.; Owen, J.; Brandell, D.; Edstrom, K.; el Enany, G.; Guery, C.; Golodnitsky, D.; Lacey, M.; Lecoeur, C.; et al. 3D lithium ion batteries—From fundamentals to fabrication. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xiong, Z.; Yan, Y.N.; Hu, Y.Y.; Zhang, R.J.; Wang, S.G. Porous morphology, porosity, mechanical properties of poly(alpha-hydroxy acid)-tricalcium phosphate composite scaffolds fabricated by low-temperature deposition. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 82, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Xiong, Z.; Yan, Y.N.; Zhang, R.J.; Wang, X.H.; Jin, L. Multinozzle Low-Temperature Deposition System for Construction of Gradient Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2009, 88, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.; Yan, Y.N.; Wang, S.G.; Zhang, R.J.; Zhang, C. Fabrication of porous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering via low-temperature deposition. Scri. Mater. 2002, 46, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, A. LiFePO4/C nanocomposites for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2017, 343, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, G.; Li, Z.C.; Sheng, W.J.; Zhang, Y.C.; Gu, J.J.; Zheng, X.S.; Cao, F.F. Improved Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4@N-Doped Carbon Nanocomposites Using Polybenzoxazine as Nitrogen and Carbon Sources. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 26908–26915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, G.; Kawase, M. Numerical and experimental evaluation of the relationship between porous electrode structure and effective conductivity of ions and electrons in lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2017, 342, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

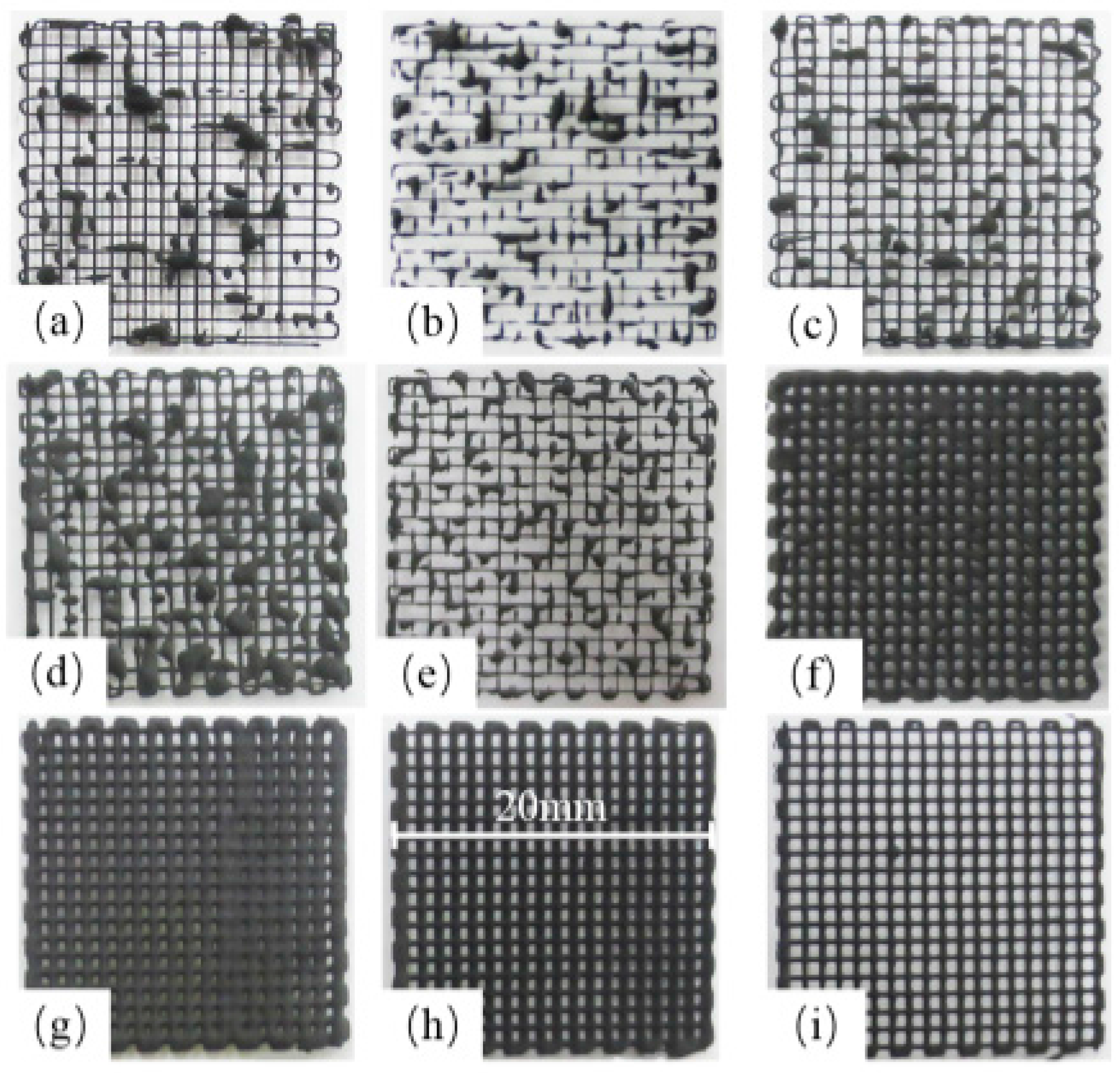
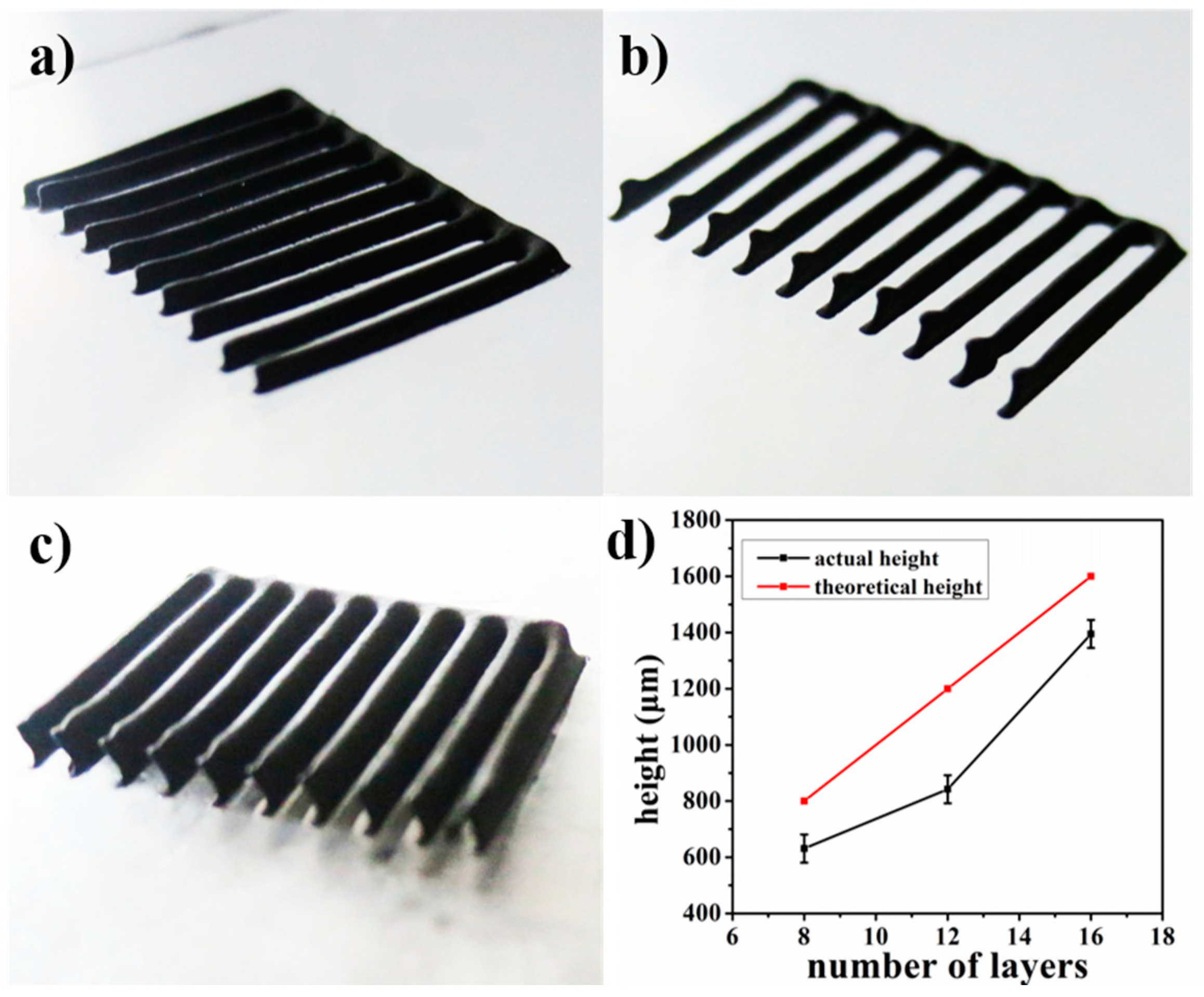
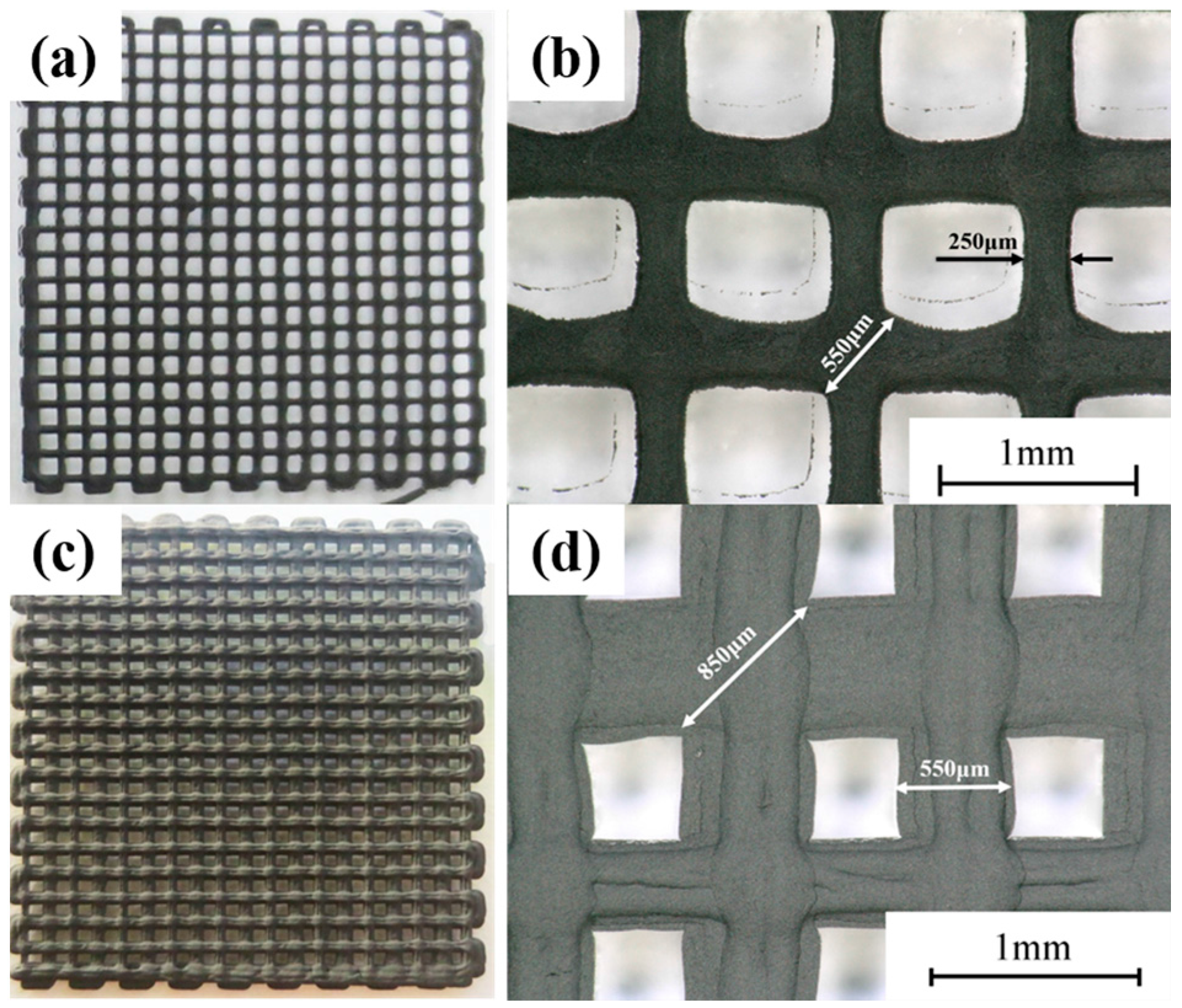
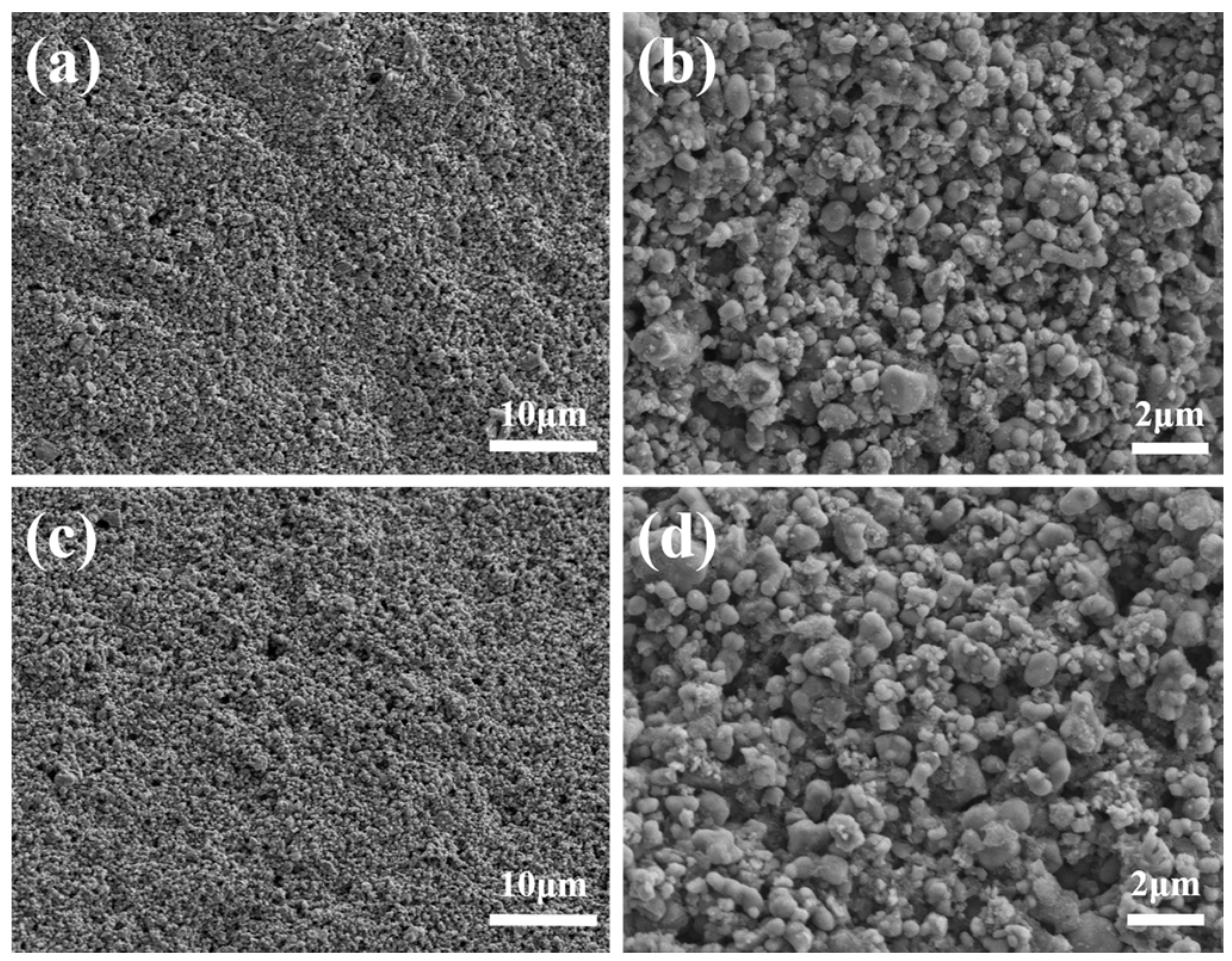
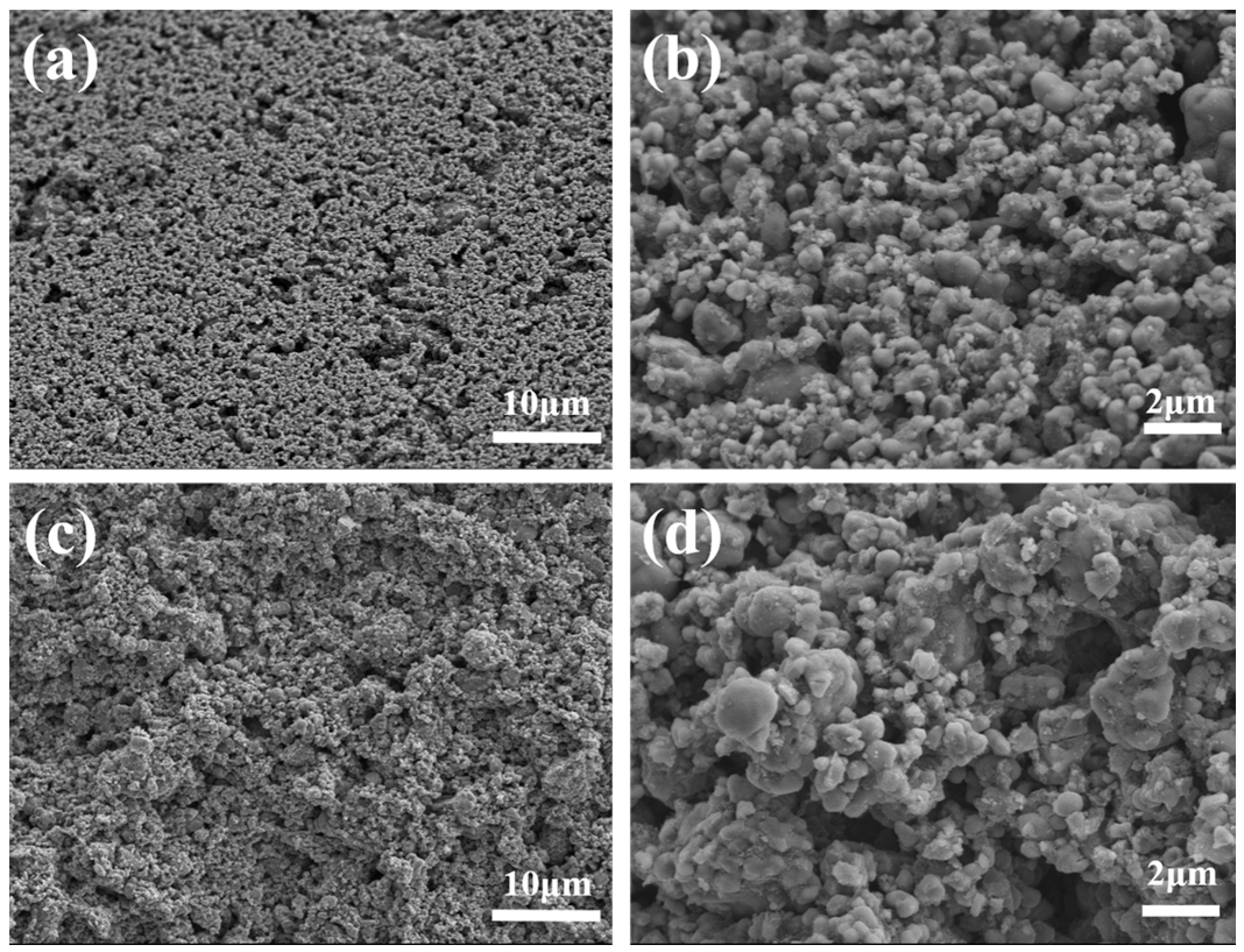

| No. | Extrusion Speed vj (mm/s) | Scanning Speed vxy (mm/s) | Layer Thickness hs (mm) | Printed Structures (Figure 4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.003 | 2 | 0.1 | (i) |
| 2 | 0.003 | 4 | 0.15 | (b) |
| 3 | 0.003 | 6 | 0.2 | (a) |
| 4 | 0.006 | 2 | 0.15 | (h) |
| 5 | 0.006 | 4 | 0.2 | (d) |
| 6 | 0.006 | 6 | 0.1 | (e) |
| 7 | 0.009 | 2 | 0.2 | (g) |
| 8 | 0.009 | 4 | 0.1 | (f) |
| 9 | 0.009 | 6 | 0.15 | (c) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Cheng, X.; Li, B.; Chen, Z.; Mi, S.; Lao, C. Fabrication and Characterization of 3D-Printed Highly-Porous 3D LiFePO4 Electrodes by Low Temperature Direct Writing Process. Materials 2017, 10, 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080934
Liu C, Cheng X, Li B, Chen Z, Mi S, Lao C. Fabrication and Characterization of 3D-Printed Highly-Porous 3D LiFePO4 Electrodes by Low Temperature Direct Writing Process. Materials. 2017; 10(8):934. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080934
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Changyong, Xingxing Cheng, Bohan Li, Zhangwei Chen, Shengli Mi, and Changshi Lao. 2017. "Fabrication and Characterization of 3D-Printed Highly-Porous 3D LiFePO4 Electrodes by Low Temperature Direct Writing Process" Materials 10, no. 8: 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080934
APA StyleLiu, C., Cheng, X., Li, B., Chen, Z., Mi, S., & Lao, C. (2017). Fabrication and Characterization of 3D-Printed Highly-Porous 3D LiFePO4 Electrodes by Low Temperature Direct Writing Process. Materials, 10(8), 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080934






