Load-Deflection and Friction Properties of PEEK Wires as Alternative Orthodontic Wires
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
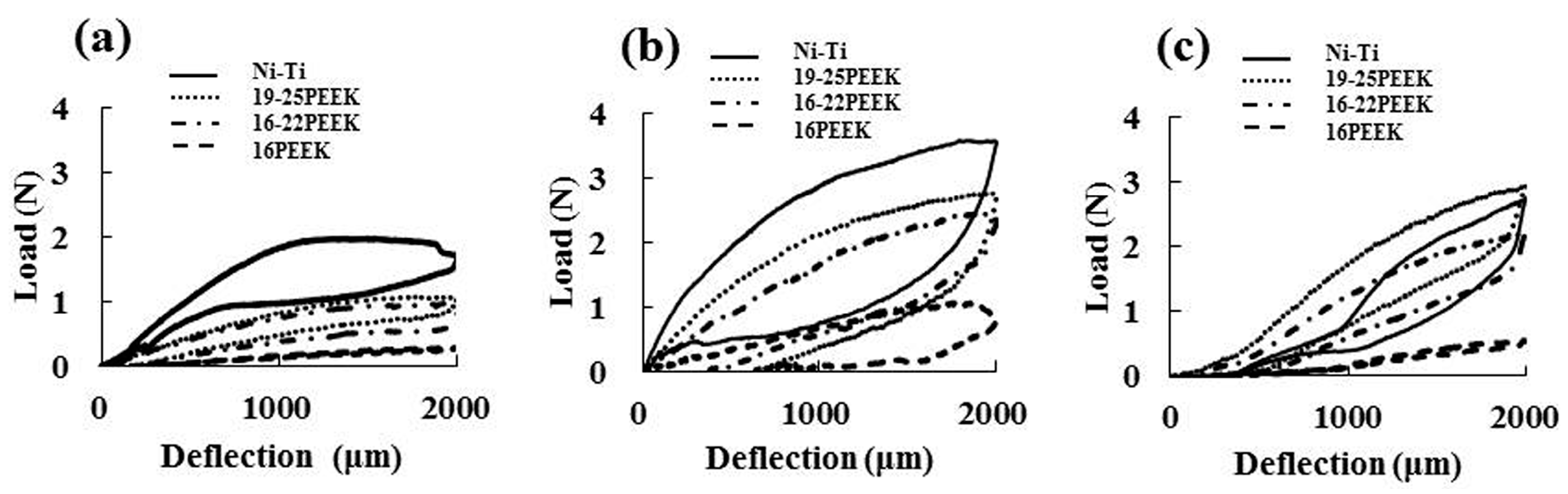
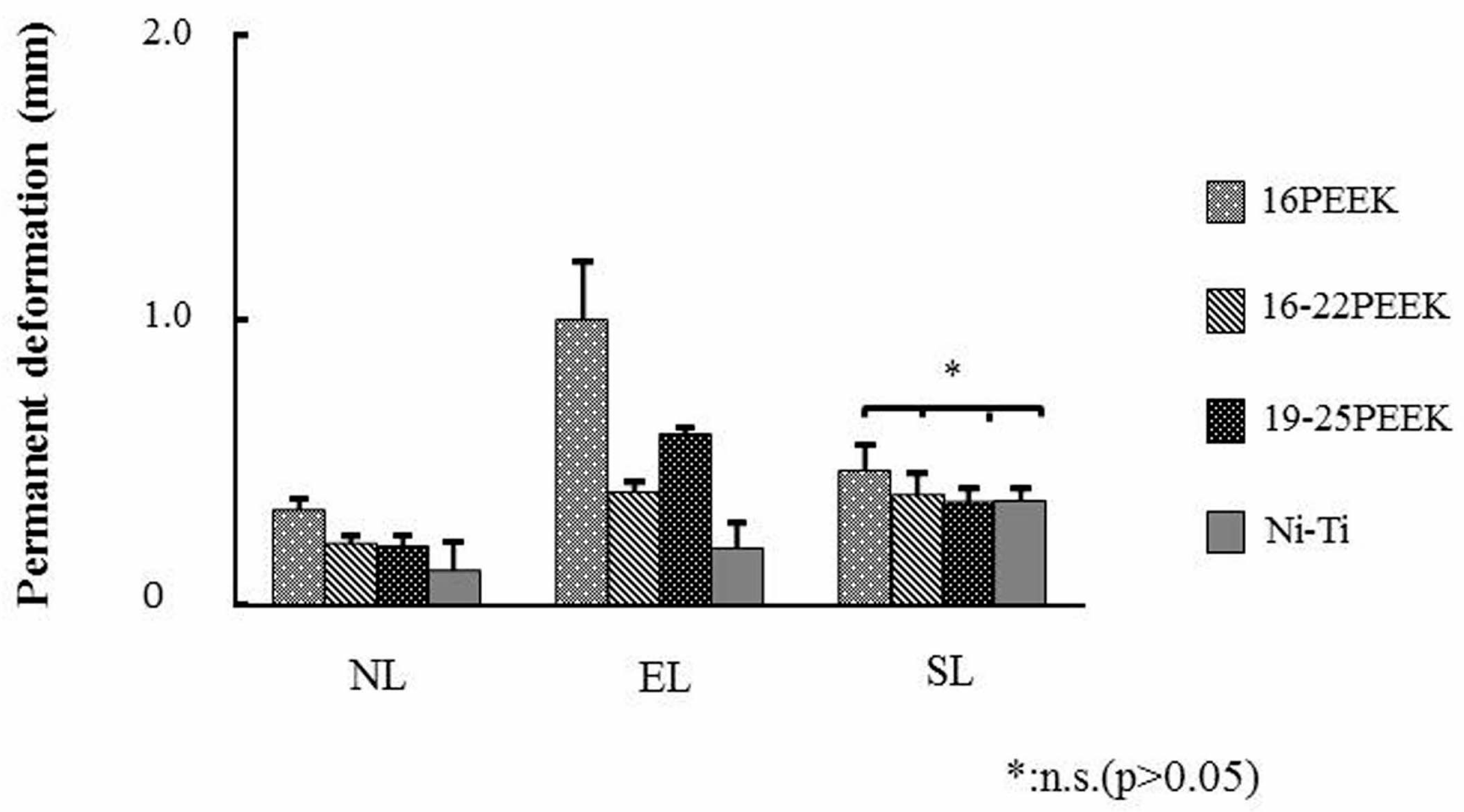
2.1. Three-Point Bending Tests
2.2. Stress Relaxation Tests
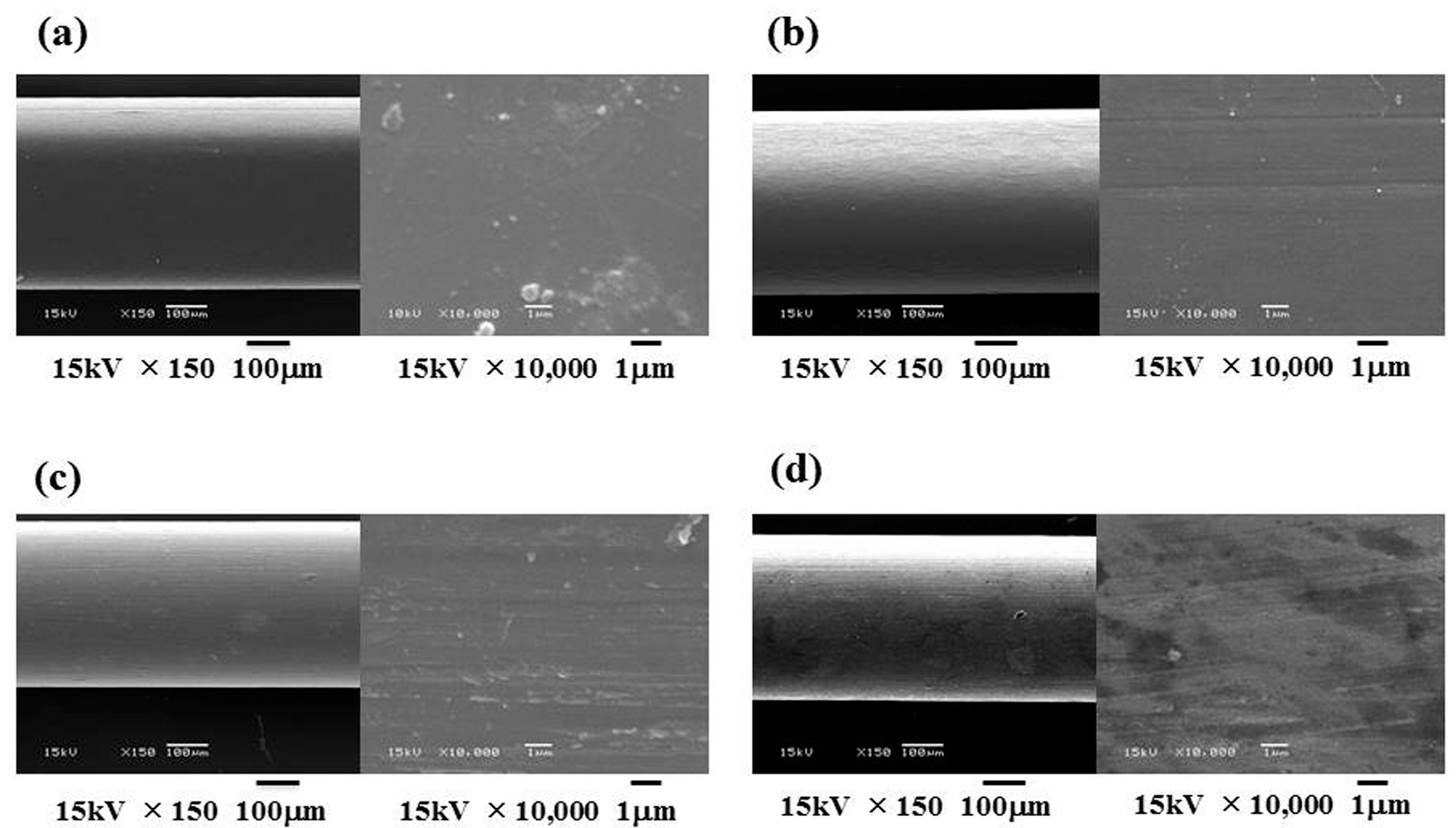
2.3. Static Friction Tests
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
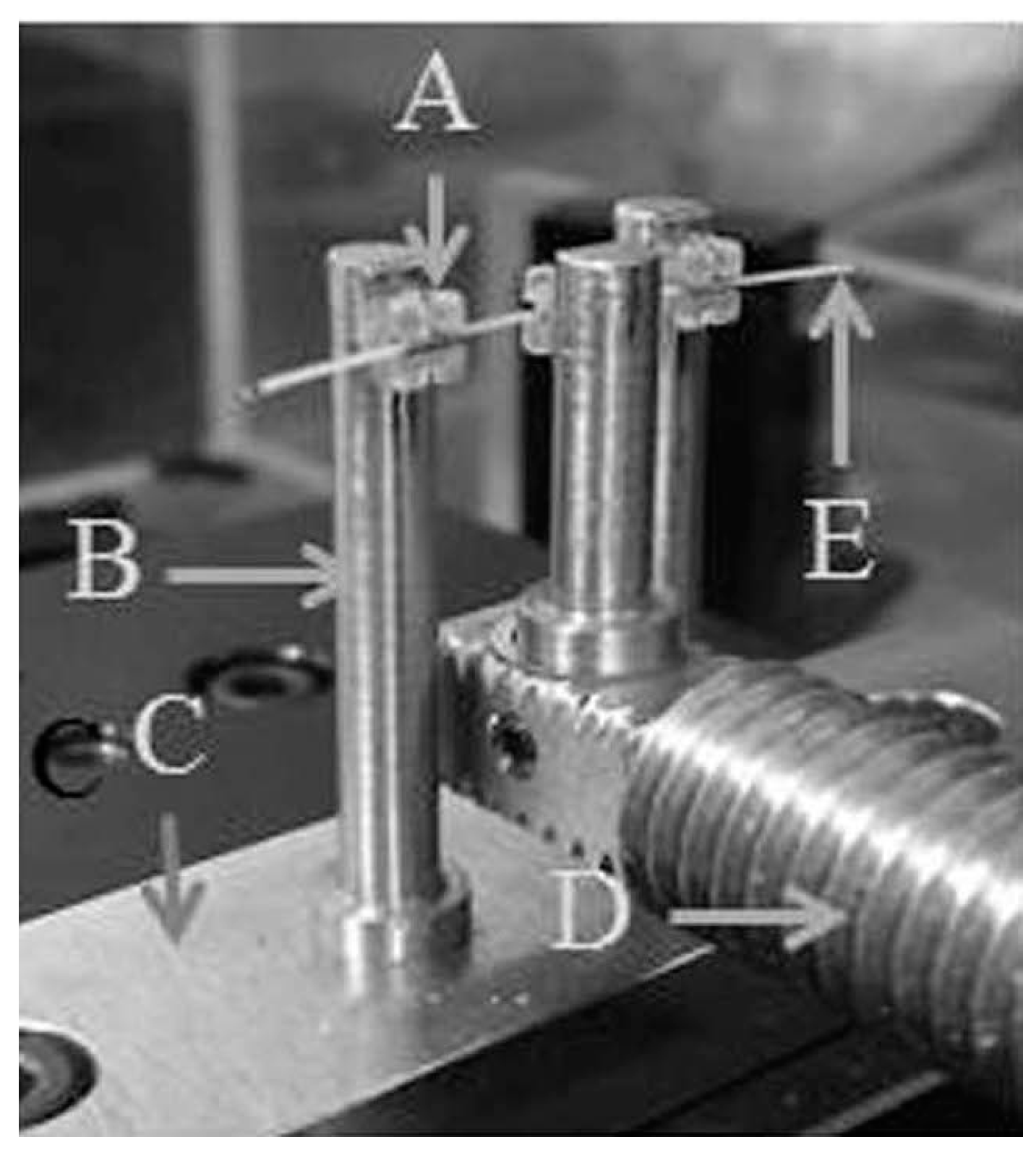
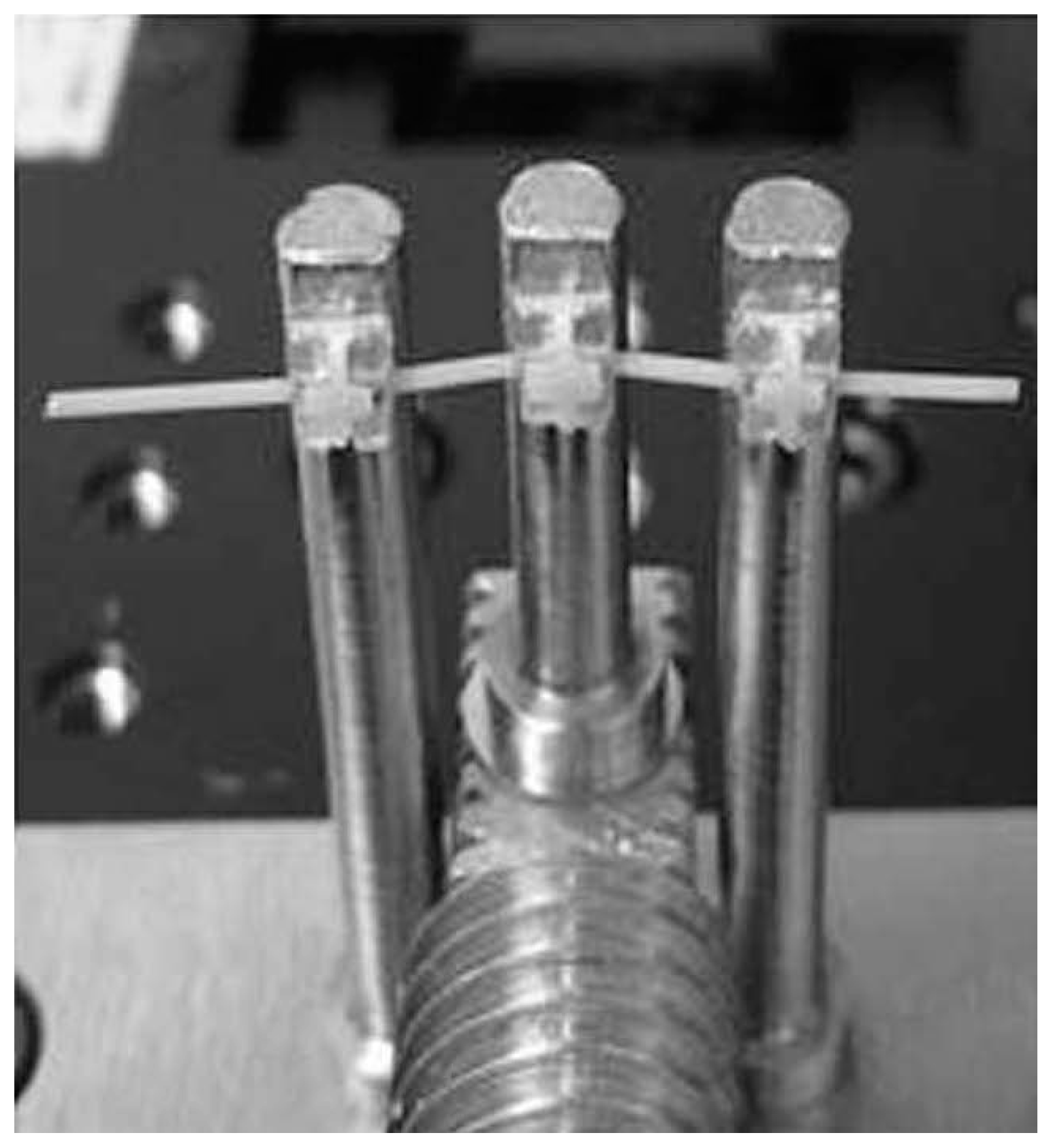
4.2. Three-Point Bending Tests
4.3. Stress Relaxation Tests
4.4. Static Friction Tests
4.5 Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Proffit, W.R. The basis of orthodontic therapy. In Contemporary Orthodontics, 5th ed.; Proffit, W.R., Fields, H.W., Sarver, D.M., Eds.; Mosby Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2012; pp. 312–318. [Google Scholar]
- Waters, N.E. Superelastic nickel-titanium wires. Br. J. Orthod. 1992, 19, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.A. An overview of nickel-titanium alloys used in dentistry. Int. Endod. J. 2000, 33, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walia, H.M.; Brantley, W.A.; Gerstein, H. An initial investigation of the bending and torsional properties of Nitinol root canal files. J. Endod. 1988, 14, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, F.; Mogi, M.; Ohura, Y.; Hamanaka, H. The super-elastic property of the Japanese NiTi alloy wire for use in orthodontics. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1986, 90, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieminen, T.; Kallela, I.; Wuolijoki, E.; Kainulainen, H.; Hiidenheimo, I.; Rantala, I. Amorphous and crystalline polyetheretherketone: Mechanical properties and tissue reactions during a 3-year follow-up. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 84, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, V.; Wagner, C.; Merk, S.; Roos, M.; Schmidlin, P.R.; Eichberger, M.; Stawarczyk, B. Retention force of differently fabricated telescopic PEEK crowns with different tapers. Dent. Mater. J. 2016, 35, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidlin, P.R.; Stawarczyk, B.; Wieland, M.; Attin, T.; Hämmerle, C.H.; Fischer, J. Effect of different surface pre-treatments and luting materials on shear bond strength to PEEK. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.S.; Torrents, N.J.; Brufau, B.M.; Cabratosa, T.J. Use of polyetheretherketone in the fabrication of a maxillary obturator prosthesis: A clinical report. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najeeb, S.; Zafar, M.S.; Khurshid, Z.; Siddiqui, F. Applications of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) in oral implantology and prosthodontics. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2016, 60, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, M.; Kanno, Z.; Wada, T.; Hongo, T.; Doi, H.; Hanawa, T.; Ono, T.; Uo, M. Mechanical properties of orthodontic wires made of super engineering plastic. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasuya, S.; Nagasaka, S.; Hanyuda, A.; Ishimura, S.; Hirashita, A. The effect of ligation on the load deflection characteristics of nickel titanium orthodontic wire. Eur. J. Orthod. 2007, 29, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapila, S.; Angolkar, P.V.; Duncanson, M.G.; Nanda, R.S. Evaluation of friction between edgewise stainless steel brackets and orthodontic wires of four alloys. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1990, 98, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ding, P.; Lin, J. Effects of bracket design on critical contact angle. Angle Orthod. 2013, 83, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drescher, D.; Bourauel, C.; Schumacher, H.A. Frictional forces between bracket and arch wire. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1989, 96, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, G.F.; Quevedo, F.R. Evaluation of friction forces in the 0.022 × 0.028 edgewise bracket in vitro. J. Biomech. 1970, 3, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayotov, I.V.; Orti, V.; Cuisinier, F.; Yachouh, J. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) for medical applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2016, 27, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Rodriguez, E.; Cebriána, J.L.; Nietoa, M.J.; Del Castilloa, J.L.; Hernández-Godoyb, J.; Burgueñoa, M. Polyetheretherketone custom-made implants for craniofacial defects: Report of 14 cases and review of the literature. J. Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg. 2015, 43, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Matinlinna, J.P.; Siddiqui, F.; Nassani, M.Z.; Baroudi, K. Nanomodified Peek Dental Implants: Bioactive Composites and Surface Modification—A Review. Int. J. Dent. 2015, 2015, 381759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfondrini, M.F.; Cacciafesta, V.; Maffia, E.; Scribante, A.; Alberti, G.; Biesuz, R.; Klersy, C. Nickel release from new conventional stainless steel, recycled, and nickel-free orthodontic brackets: An in vitro study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2010, 137, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfondrini, M.F.; Cacciafesta, V.; Maffia, E.; Massironi, S.; Scribante, A.; Alberti, G.; Biesuz, R.; Klersy, C. Chromium Release from New Stainless Steel, Recycled and Nickel-free Orthodontic Brackets. Angle Orthod. 2009, 79, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasbi, S.; Sheikh, T.; Hemmati, Y.B. Ion Release and Galvanic Corrosion of Different Orthodontic Brackets and Wires in Artificial Saliva. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2017, 18, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarul, M.; Rutkowska-Gorczyca, M.; Detyna, J.; Zięty, A.; Kawala, M.; Antoszewska-Smith, J. Do Mechanical and Physicochemical Properties of Orthodontic NiTi Wires Remain Stable In Vivo? Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5268629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hain, M.; Dhopatkar, A.; Rock, P. The effect of ligation method on friction in sliding mechanics. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2003, 123, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanyuda, A.; Nagasaka, S.; Yoshida, T. Long-term time effect on load–deflection characteristics of orthodontic wires. Orthod. Waves 2006, 65, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, S.; Hayakawa, T.; Kobayashi, D.; Aono, Y.; Hirata, A.; Hiratsuka, M.; Nakamura, Y. Reduction in static friction by deposition of a homogeneous diamond-like carbon (DLC) coating on orthodontic brackets. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaike, S.; Kobayashi, D.; Aono, Y.; Hiratsuka, M.; Hirata, A.; Hayakawa, T.; Nakamura, Y. Relationship between static friction and surface wettability of orthodontic brackets coated with diamond-like carbon (DLC), fluorine- or silicone-doped DLC coatings. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2016, 61, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahnel, S.; Wieser, A.; Lang, R.; Rosentritt, M. Biofilm formation on the surface of modern implant abutment materials. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 1297–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tateishi, T.; Kyomoto, M.; Kakinoki, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Ishihara, K. Reduced platelets and bacteria adhesion on poly (ether ether ketone) by photoinduced and self-initiated graft polymerization of 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimer, S.; Schmidlin, P.R.; Stawarczyk, B. Discoloration of PMMA, composite, and PEEK. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 21, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arun, A.V.; Vaz, A.C. Frictional characteristics of the newer orthodontic elastomeric ligatures. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2011, 22, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.H.; Luk, H.S.; Hsu, Y.C.; Kao, C.T. An in vitro comparison of the frictional forces between archwires and self-ligating brackets of passive and active types. Eur. J. Orthod. 2012, 34, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasaka, S.; Hanyuda, A.; Yoshida, T. A modified three-point bending system and its validity. Tsurumi Univ. Dent. J. 2006, 32, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Redlich, M.; Mayer, Y.; Harari, D.; Lewinstein, I. In vitro study of frictional forces during sliding mechanics of “reduced-friction” brackets. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2003, 124, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


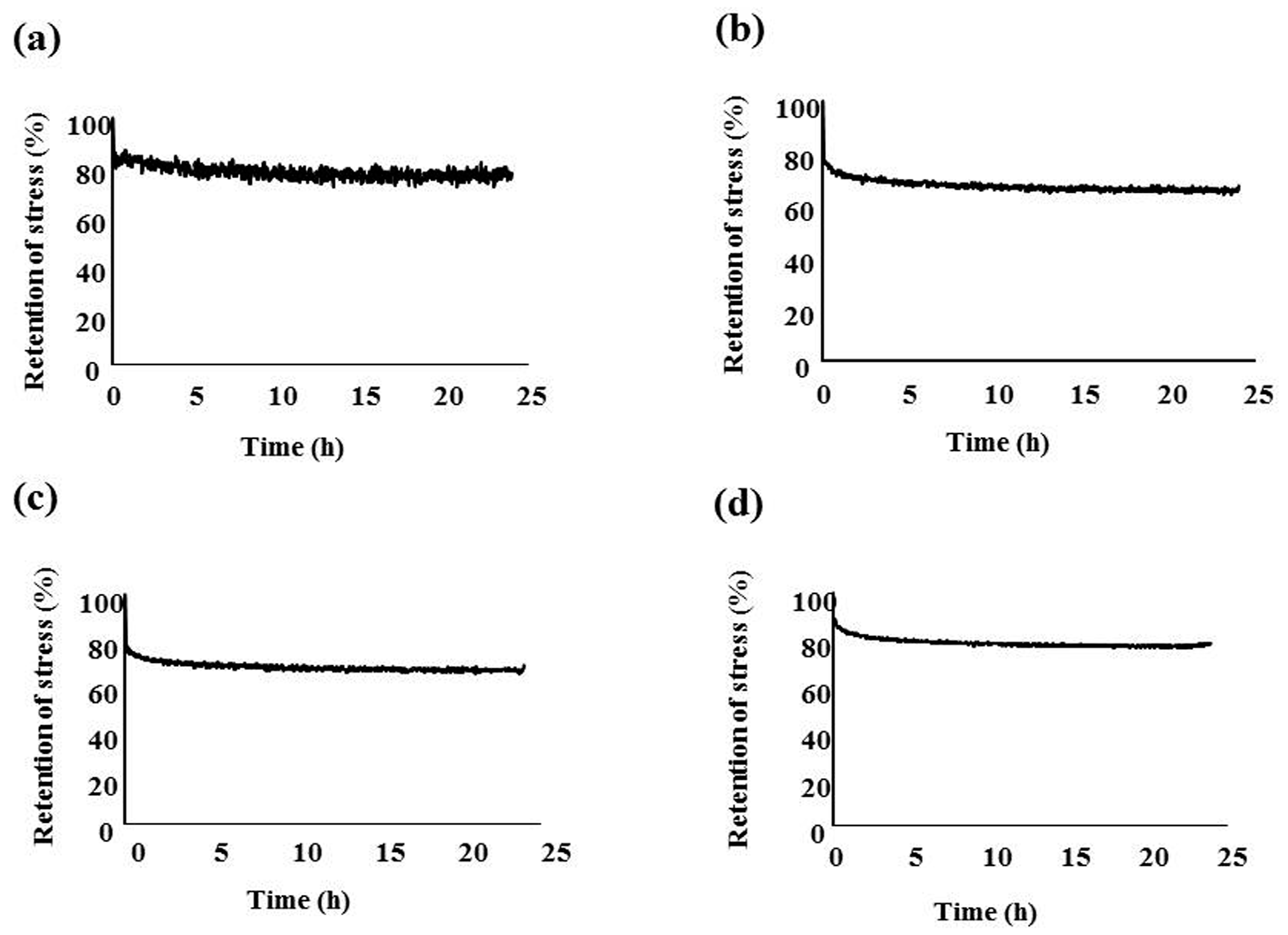




| Wire | Rate of Retention Stress (%) |
|---|---|
| 16PEEK | 77.48 (1.13) a |
| 16-22PEEK | 67.24 (5.20) a,b |
| 19-25PEEK | 69.34 (4.92) |
| Ni-Ti | 78.34 (0.53) b |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tada, Y.; Hayakawa, T.; Nakamura, Y. Load-Deflection and Friction Properties of PEEK Wires as Alternative Orthodontic Wires. Materials 2017, 10, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080914
Tada Y, Hayakawa T, Nakamura Y. Load-Deflection and Friction Properties of PEEK Wires as Alternative Orthodontic Wires. Materials. 2017; 10(8):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080914
Chicago/Turabian StyleTada, Yoshifumi, Tohru Hayakawa, and Yoshiki Nakamura. 2017. "Load-Deflection and Friction Properties of PEEK Wires as Alternative Orthodontic Wires" Materials 10, no. 8: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080914
APA StyleTada, Y., Hayakawa, T., & Nakamura, Y. (2017). Load-Deflection and Friction Properties of PEEK Wires as Alternative Orthodontic Wires. Materials, 10(8), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080914




