Corrosion Behavior of Silver-Plated Circuit Boards in a Simulated Marine Environment with Industrial Pollution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Morphology Analyses of the Specimens
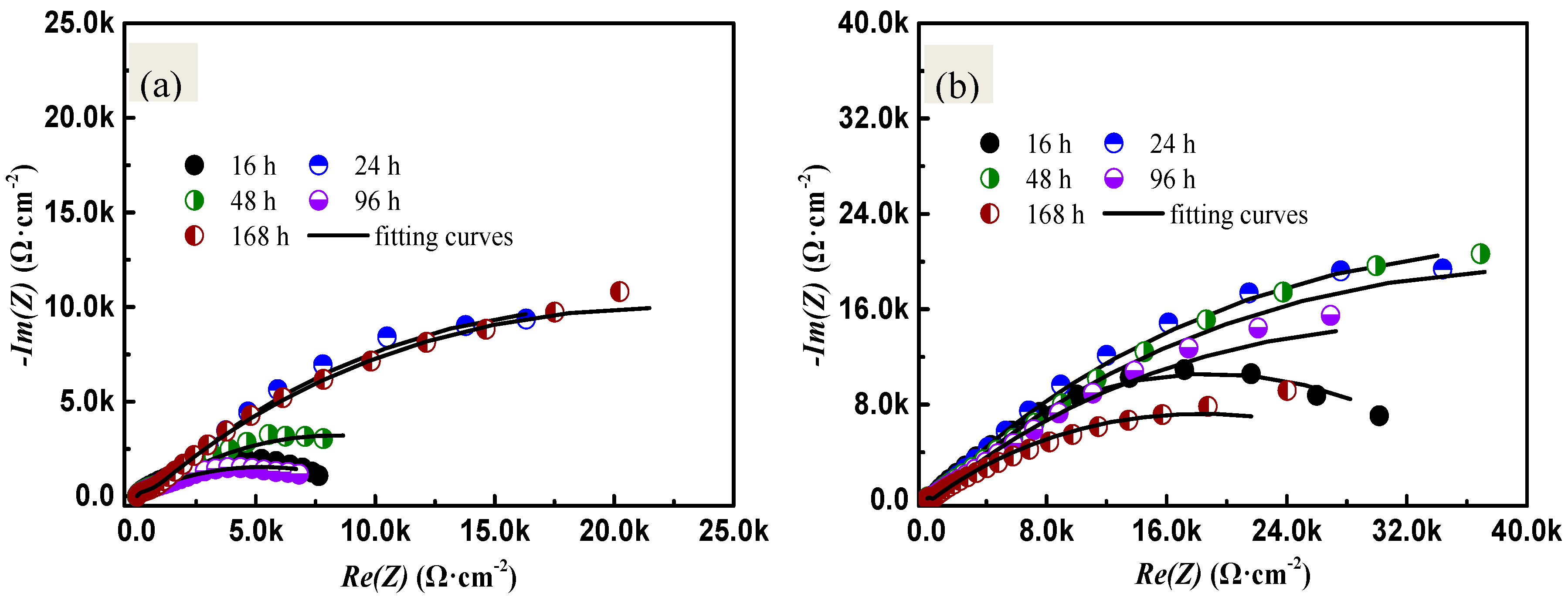
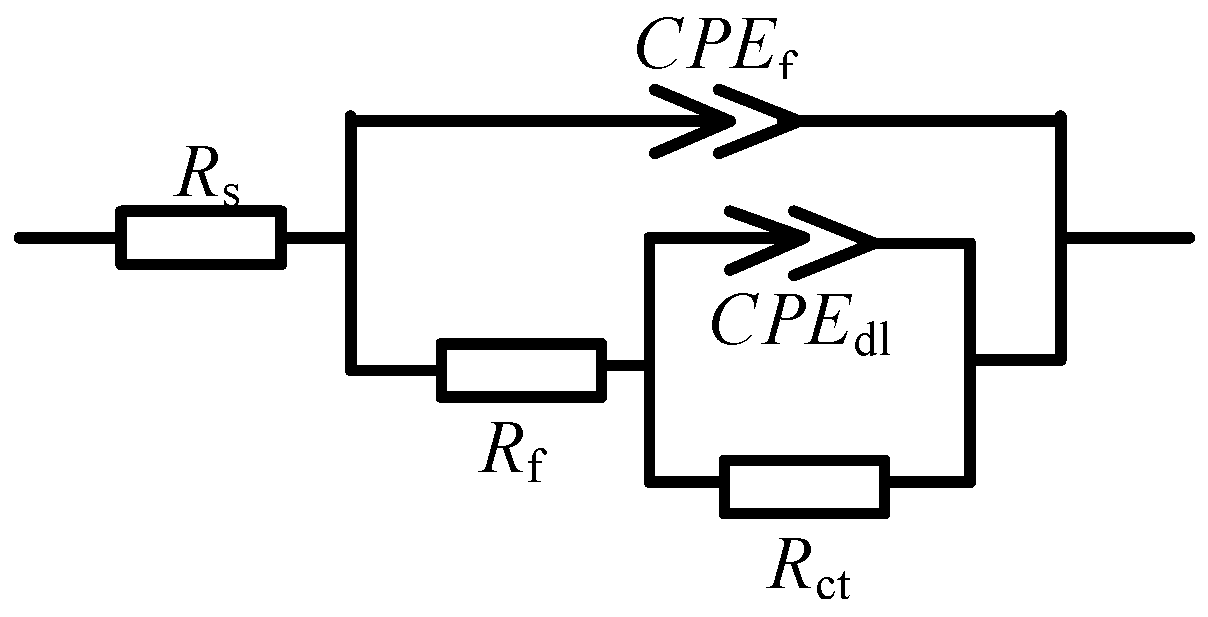
2.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Analysis
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements in Different Types of Solutions
3. Discussions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Design of the Experimental Setup
4.2. Surface Analysis Methods
4.3. Electrochemical Measurements
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Cl− mainly induces the microporous corrosion. The silver coating is not sensitive to Cl−. Also, the settlements of salt particles on the surface of PCB-ImAg act as the corrosion-active points.
- (2)
- SO2 mainly induces general corrosion of silver coating. The color of silver changes significantly under the influence of SO2. Then, the silver coating protection of the copper substrate decreases quickly.
- (3)
- The lower charge transfer resistance obtained in a test containing SO2 demonstrates that the corrosion rate is accelerated in a mixed atmosphere.
- (4)
- The corrosion potential is lower in mixed solutions, which indicates that the corrosion tendency increases with the increase of HSO3− concentration. Addition of HSO3− ions results in current fluctuation at the potential near the corrosion potential.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H. Corrosion process of silver in environments containing 0.1 ppm H2S and 1.2 ppm NO2. Mater. Corros. 2003, 54, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Li, X.; Dong, C.; Ding, K.; Xiao, K. Electrochemical migration, whisker formation, and corrosion behavior of printed circuit board under wet H2S environment. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 114, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comizzoli, R.; Frankenthal, R.; Milner, P.; Sinclair, J. Corrosion of electronic materials and devices. Science 1986, 234, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesinger, R.; Martina, I.; Kleber, C.; Schreiner, M. Influence of relative humidity and ozone on atmospheric silver corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2013, 77, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromans, D.; Sun, R.H. Anodic behavior of copper in weakly alkaline solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1992, 139, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Pan, Z.; Guo, X.; Qiu, Y. Effects of direct current electric field on corrosion behaviour of copper, Cl− ion migration behaviour and dendrites growth under thin electrolyte layer. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickett, B.; Payer, J. Composition of copper tarnish products formed in moist air with trace levels of pollutant gas: Sulfur dioxide and sulfur dioxide/nitrogen dioxide. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 3713–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kear, G.; Barker, B.; Walsh, F. Electrochemical corrosion of unalloyed copper in chloride media––A critical review. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 109–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warraky, A.E.; Shayeb, H.E.; Sherif, E. Pitting corrosion of copper in chloride solutions. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 2004, 51, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Cao, F.; Zheng, L.; Liu, W.; Chen, A.; Zhang, J.; Cao, C. Corrosion behaviour of copper under chloride-containing thin electrolyte layer. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 3289–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfantazi, A.; Ahmed, T.; Tromans, D. Corrosion behavior of copper alloys in chloride media. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 2425–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, S.; Li, W. Experimental and theoretical studies on the corrosion inhibition of copper by two indazole derivatives in 3.0% NaCl solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 472, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Luo, H.; Dong, C.; Xiao, K.; Li, X. The electrochemical behaviour of brass in NaHSO3 solution without and with Cl. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 11123–11136. [Google Scholar]
- Betova, I.; Bojinov, M.; Lilja, C. Influence of chloride on the long-term interaction of copper with deoxygenated neutral aqueous solutions. Corros. Sci. 2013, 76, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahal, C.; Masmoudi, M.; Abdelhedi, R.; Sabot, R.; Jeannin, M.; Bouaziz, M.; Refait, P. Olive leaf extract as natural corrosion inhibitor for pure copper in 0.5 M NaCl solution: A study by voltammetry around OCP. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 769, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, N.; Fuys, J., Jr.; Stanford, J. The chloride corrosion behavior of silver-base casting alloys. J. Dent. Res. 1979, 58, 1572–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, H.; Payer, J. The effect of silver chloride formation on the kinetics of silver dissolution in chloride solution. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Lu, J.; Liu, P.; Tong, H. The electrochemical formation and reduction of a thick AgCl deposition layer on a silver substrate. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2003, 542, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graedel, T. Corrosion mechanisms for silver exposed to the atmosphere. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1992, 139, 1963–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changjiang, Y.; Chenghao, L.; Peng, W. Investigation of the tarnish on the surface of a panda gold coin. R. Metals 2007, 26, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, L.; Peterson, P. The atmospheric sulfidation of silver in a tubular corrosion reactor. Corros. Sci. 1989, 29, 1179–1187, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odnevall, I.; Leygraf, C. Atmospheric corrosion of copper in a rural atmosphere. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 3682–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliú, S., Jr.; Mariaca, L.; Simancas, J.; González, J.; Morcillo, M. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of the effect of nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide on the atmospheric corrosion of copper at low relative humidity values. Corrosion 2005, 61, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidblad, J.; Leygraf, C. Atmospheric corrosion effects of SO2 and NO2 a comparison of laboratory and field-exposed copper. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Kui, X.; Ding, K.; Gang, L.; Dong, C.; Li, X. In situ investigation of atmospheric corrosion behavior of PCB-ENIG under adsorbed thin electrolyte layer. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, H.; Buitrago, C.; Echavarría, A. Characterization of atmospheric corrosion products formed on silver in tropical-mountain environments. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2015, 19, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, K. Determination and generation of the corrosion compounds on silver exposed to the atmospheres. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 2336–2354. [Google Scholar]
- Stratmann, M.; Streckel, H. On the atmospheric corrosion of metals which are covered with thin electrolyte layers—I. Verification of the experimental technique. Corros. Sci. 1990, 30, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Hokazono, A.; Handa, T.; Ichino, T.; Kuwaki, N. Corrosion of copper and silver plates by volcanic gases. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 3759–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, C.O.; Landolt, D. Passive films on stainless steels—Chemistry, structure and growth. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
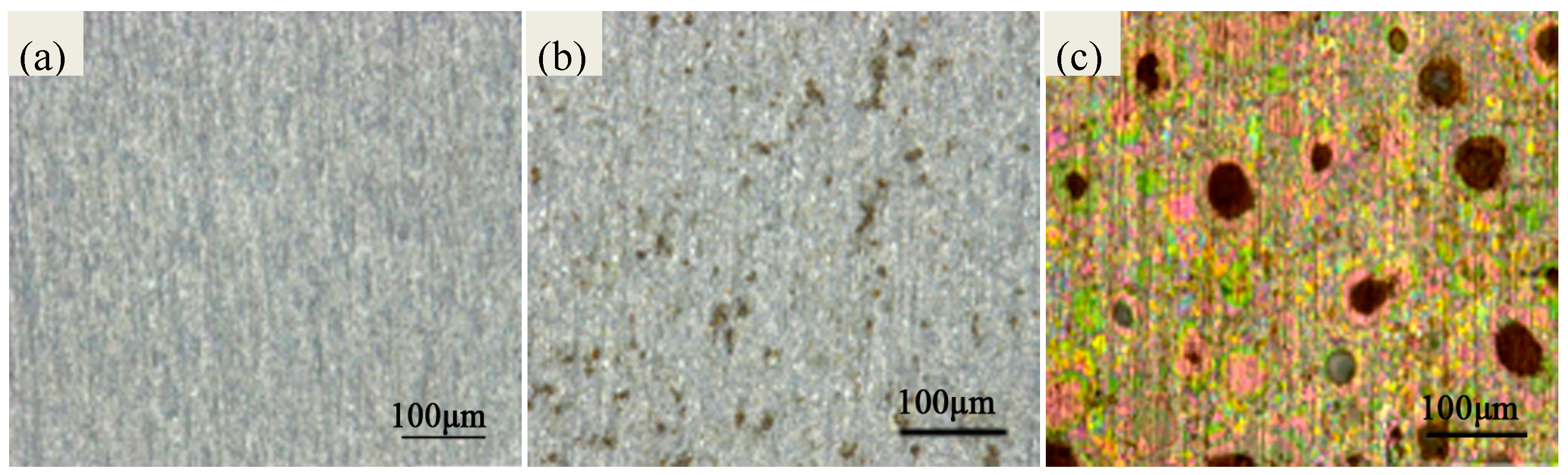
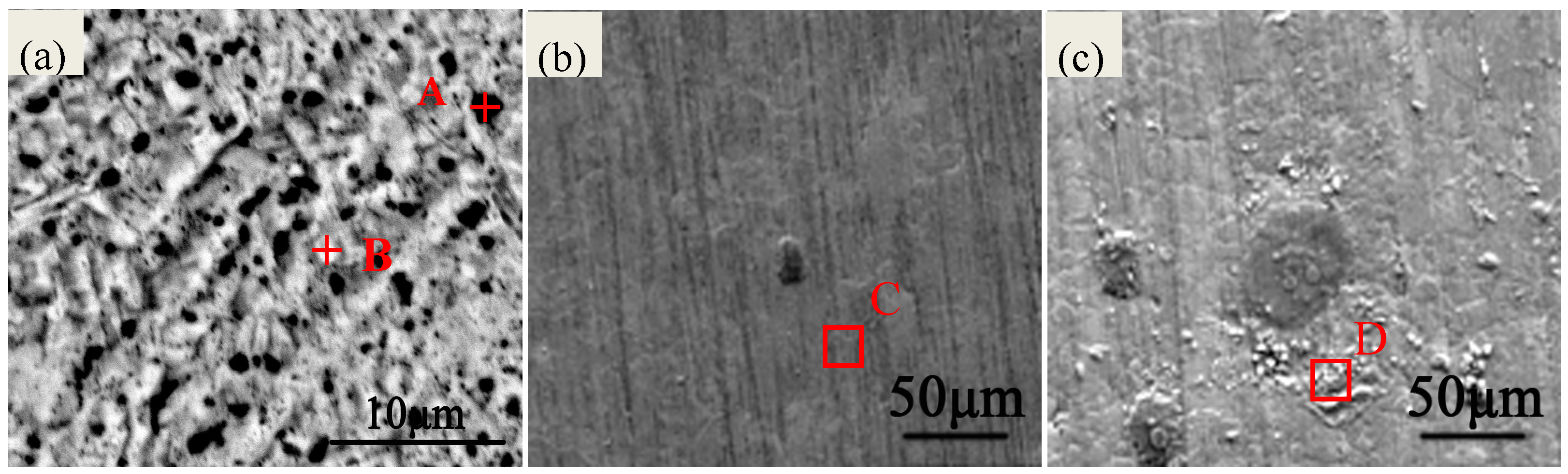

| Chemical Elements | Ag | Cu | O | S | C | Cl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 26.62 | 73.38 | - | - | - | - |
| B | 57.91 | 42.09 | - | - | - | - |
| C | 38.93 | 45.53 | 0.83 | - | 13.56 | 1.15 |
| D | 17.84 | 33.26 | 42.75 | 0.28 | 5.33 | 0.55 |
| Experimental Period/h | Rs/Ω | Qdl/Ω−1·cm−2·s−n | n2 | Rdl/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 10.30 | 1.831 × 10−6 | 1 | 9.847 × 103 |
| 24 | 12.27 | 1.856 × 10−4 | 0.5660 | 4.823 × 104 |
| 48 | 11.90 | 2.417 × 10−4 | 0.4971 | 1.525 × 104 |
| 96 | 11.42 | 5.765 × 10−5 | 0.9799 | 1.048 × 104 |
| 168 | 13.67 | 1.080 × 10−4 | 0.5461 | 4.293 × 104 |
| Experimental Period/h | Rs/Ω | Qdl/Ω−1·cm−2·s−n | n2 | Rdl/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 9.600 | 7.216 × 10−5 | 0.6620 | 3.701 × 104 |
| 24 | 13.24 | 8.508 × 10−5 | 0.5957 | 8.368 × 104 |
| 48 | 9.860 | 6.759 × 10−5 | 0.5569 | 8.267 × 104 |
| 96 | 10.01 | 6.956 × 10−5 | 0.5288 | 6.609 × 104 |
| 168 | 11.02 | 7.768 × 10−5 | 0.4876 | 3.589 × 104 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, K.; Yi, P.; Yan, L.; Bai, Z.; Dong, C.; Dong, P.; Gao, X. Corrosion Behavior of Silver-Plated Circuit Boards in a Simulated Marine Environment with Industrial Pollution. Materials 2017, 10, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070762
Xiao K, Yi P, Yan L, Bai Z, Dong C, Dong P, Gao X. Corrosion Behavior of Silver-Plated Circuit Boards in a Simulated Marine Environment with Industrial Pollution. Materials. 2017; 10(7):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070762
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Kui, Pan Yi, Lidan Yan, Ziheng Bai, Chaofang Dong, Pengfei Dong, and Xiong Gao. 2017. "Corrosion Behavior of Silver-Plated Circuit Boards in a Simulated Marine Environment with Industrial Pollution" Materials 10, no. 7: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070762
APA StyleXiao, K., Yi, P., Yan, L., Bai, Z., Dong, C., Dong, P., & Gao, X. (2017). Corrosion Behavior of Silver-Plated Circuit Boards in a Simulated Marine Environment with Industrial Pollution. Materials, 10(7), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070762




