Biosynthetic PCL-graft-Collagen Bulk Material for Tissue Engineering Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Physico-Chemical Characterisation of Casted Films
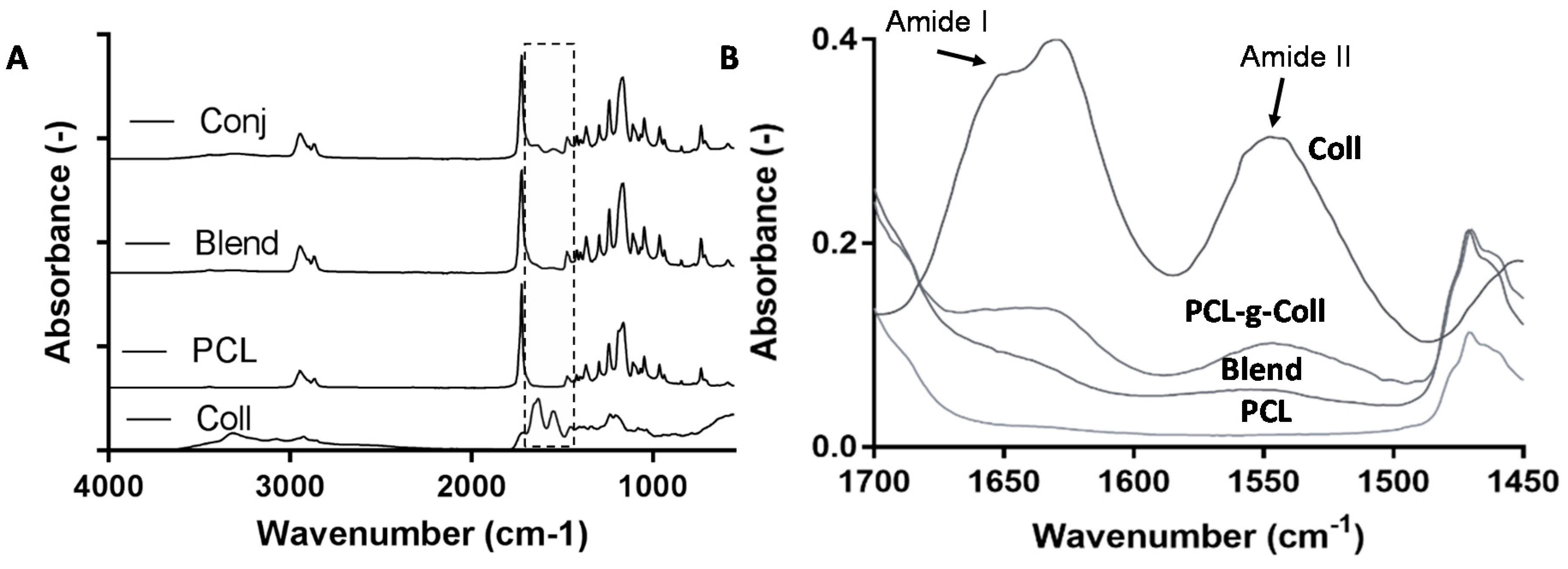
2.1.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy in Attenuated Total Reflection Mode (FT-IR/ATR)
2.1.2. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
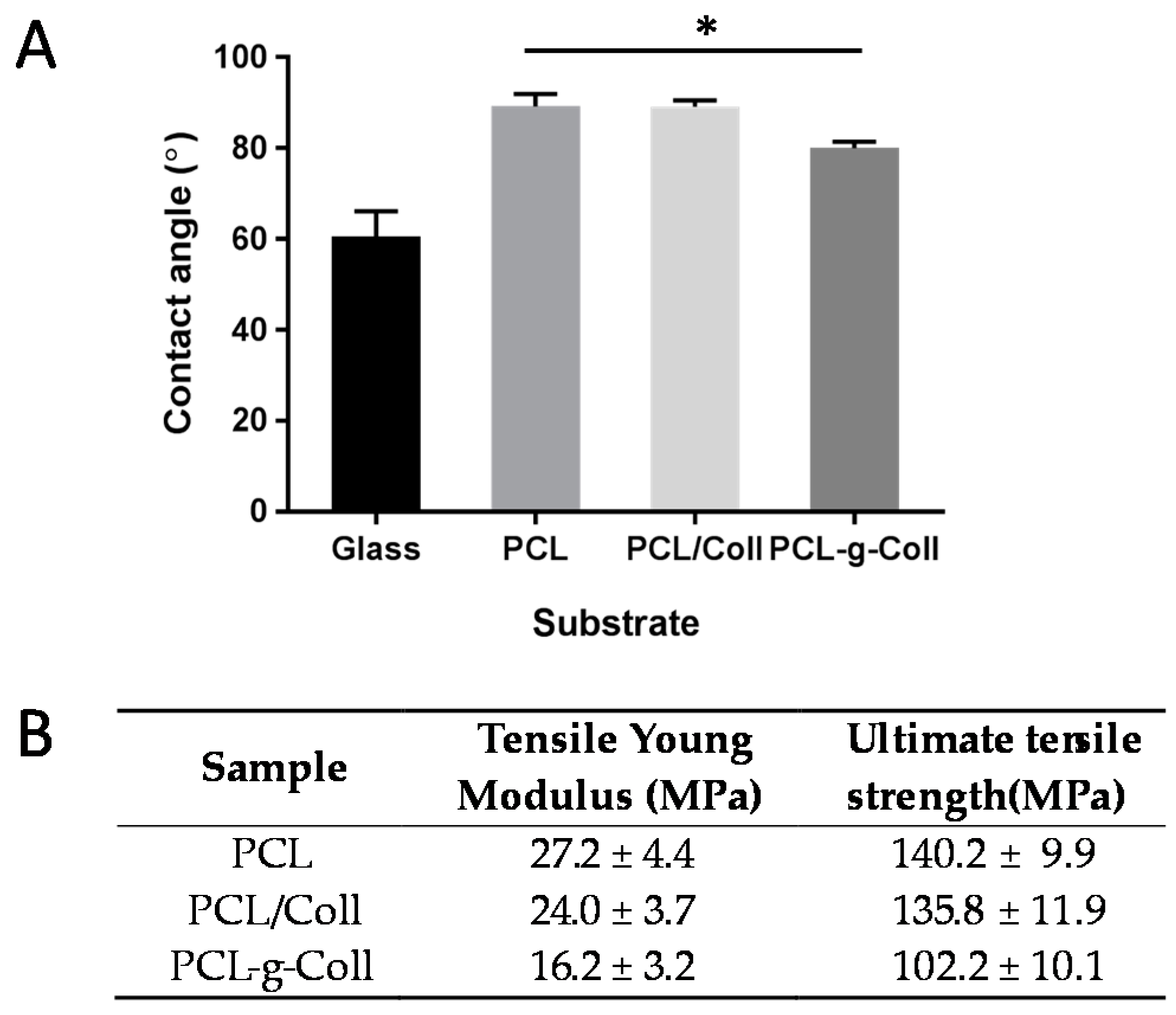
2.1.3. Contact Angle (CA) Measurement
2.1.4. Tensile Tests
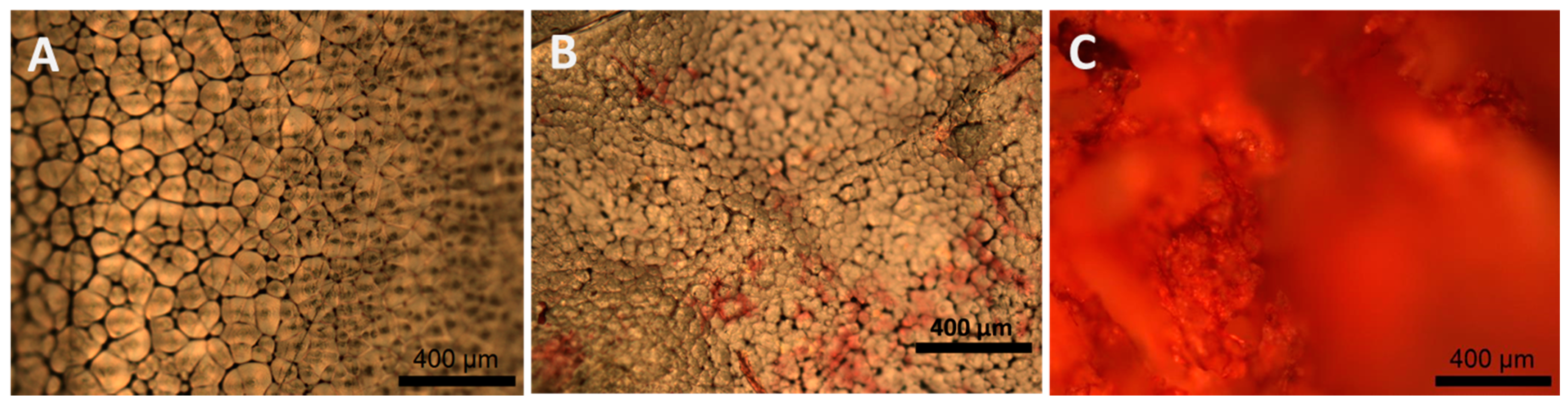
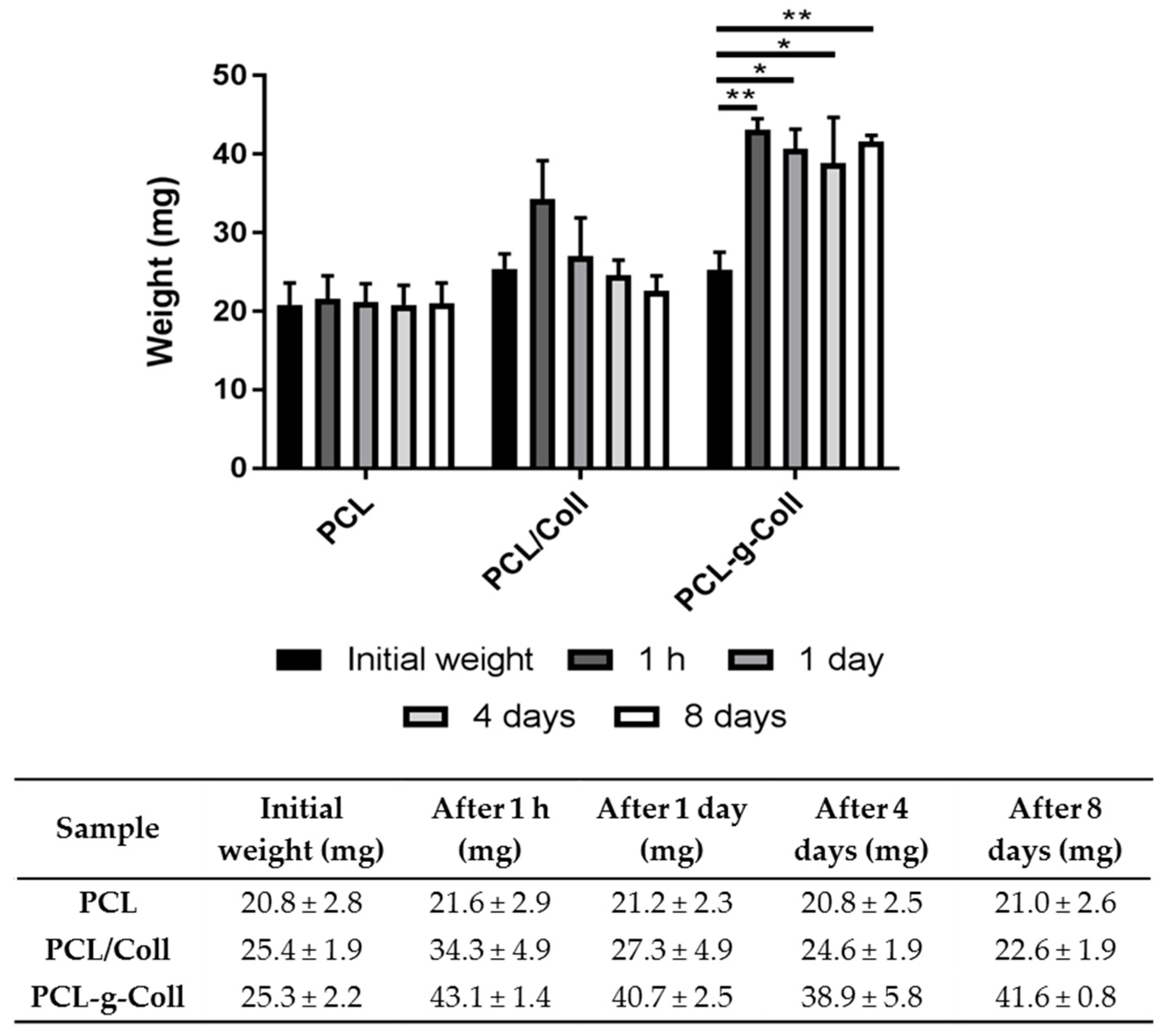
2.1.5. Collagen Staining and In Vitro Degradation Tests
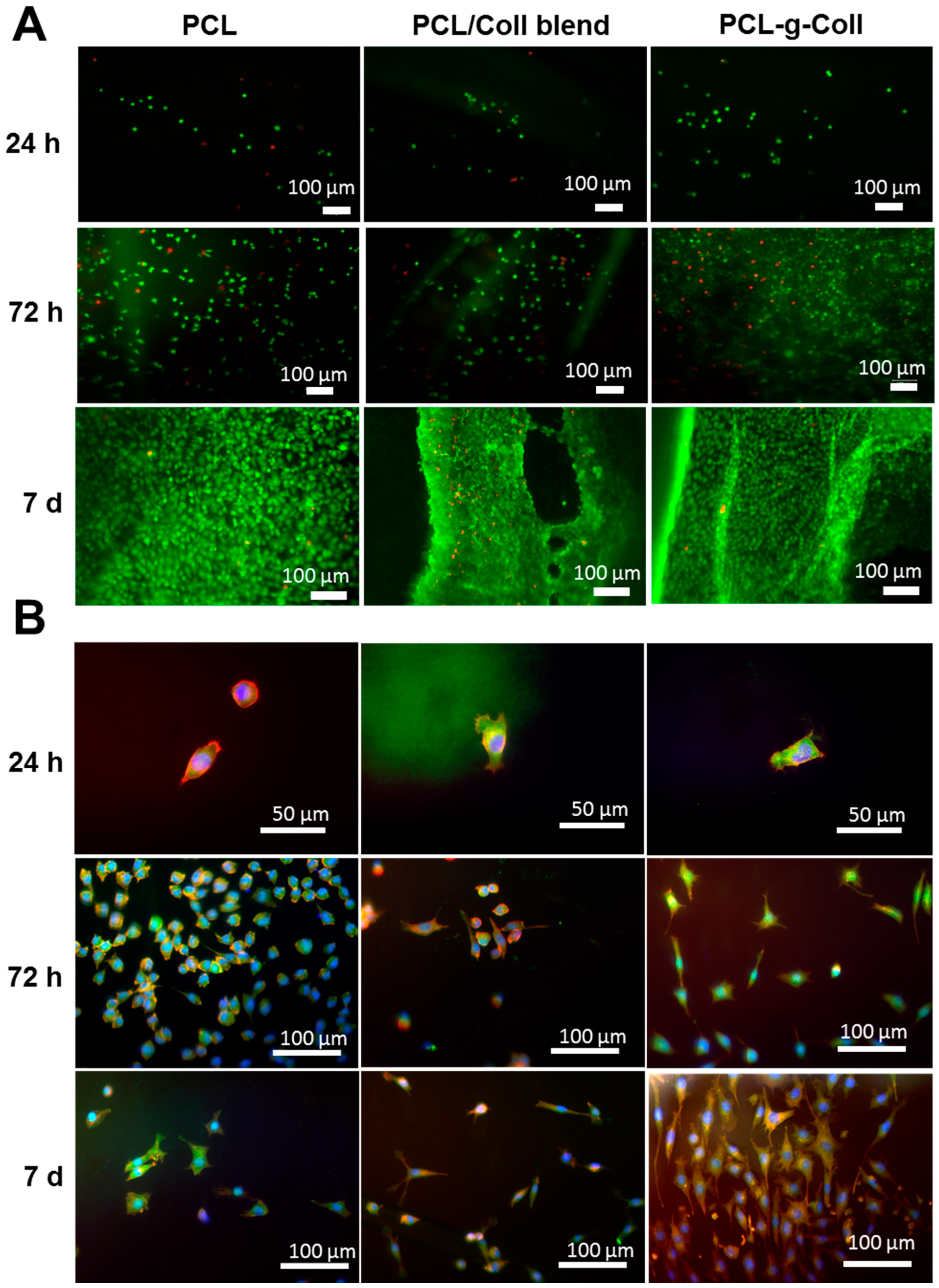
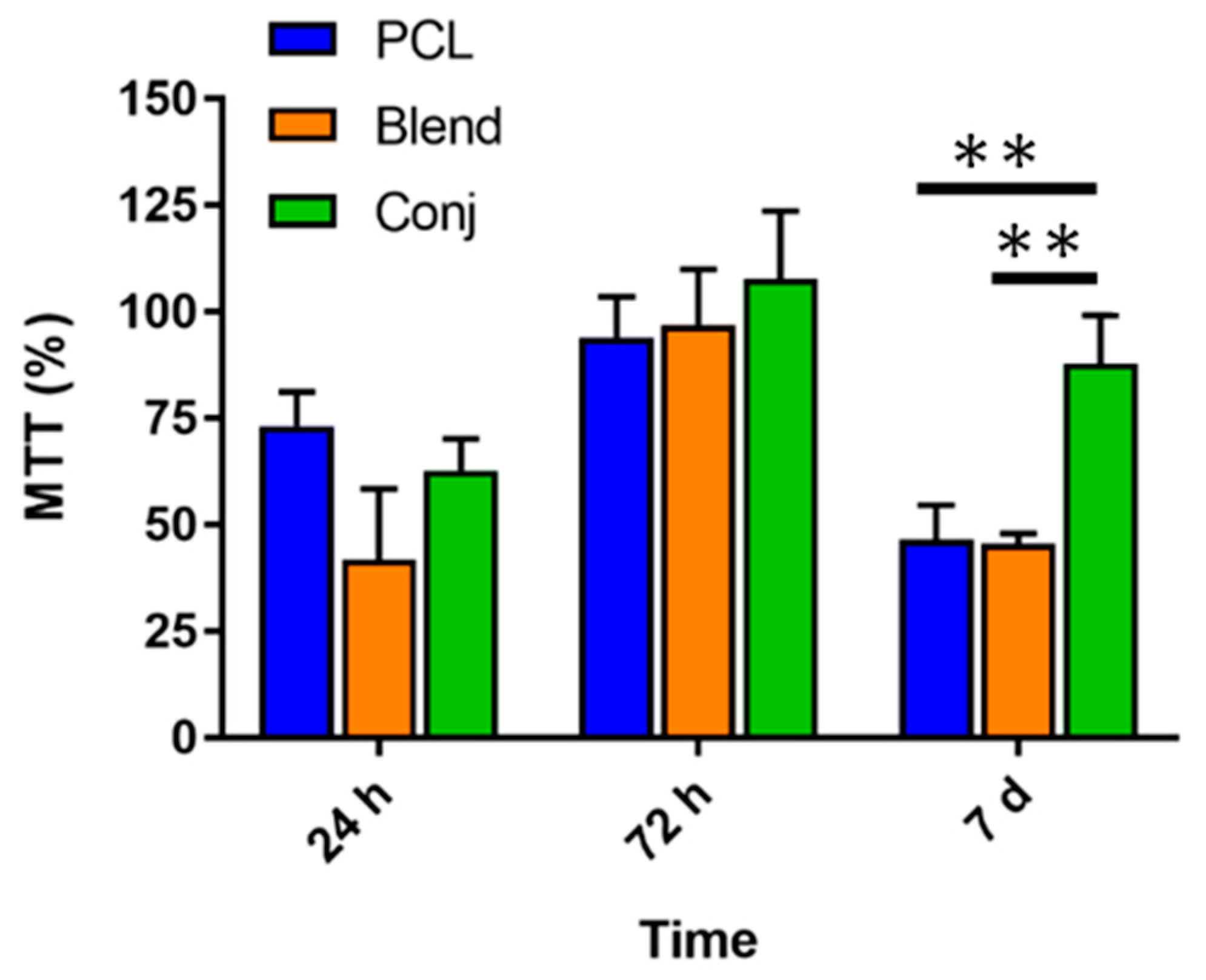
2.1.6. Cell Culture and Cytoskeletal Staining
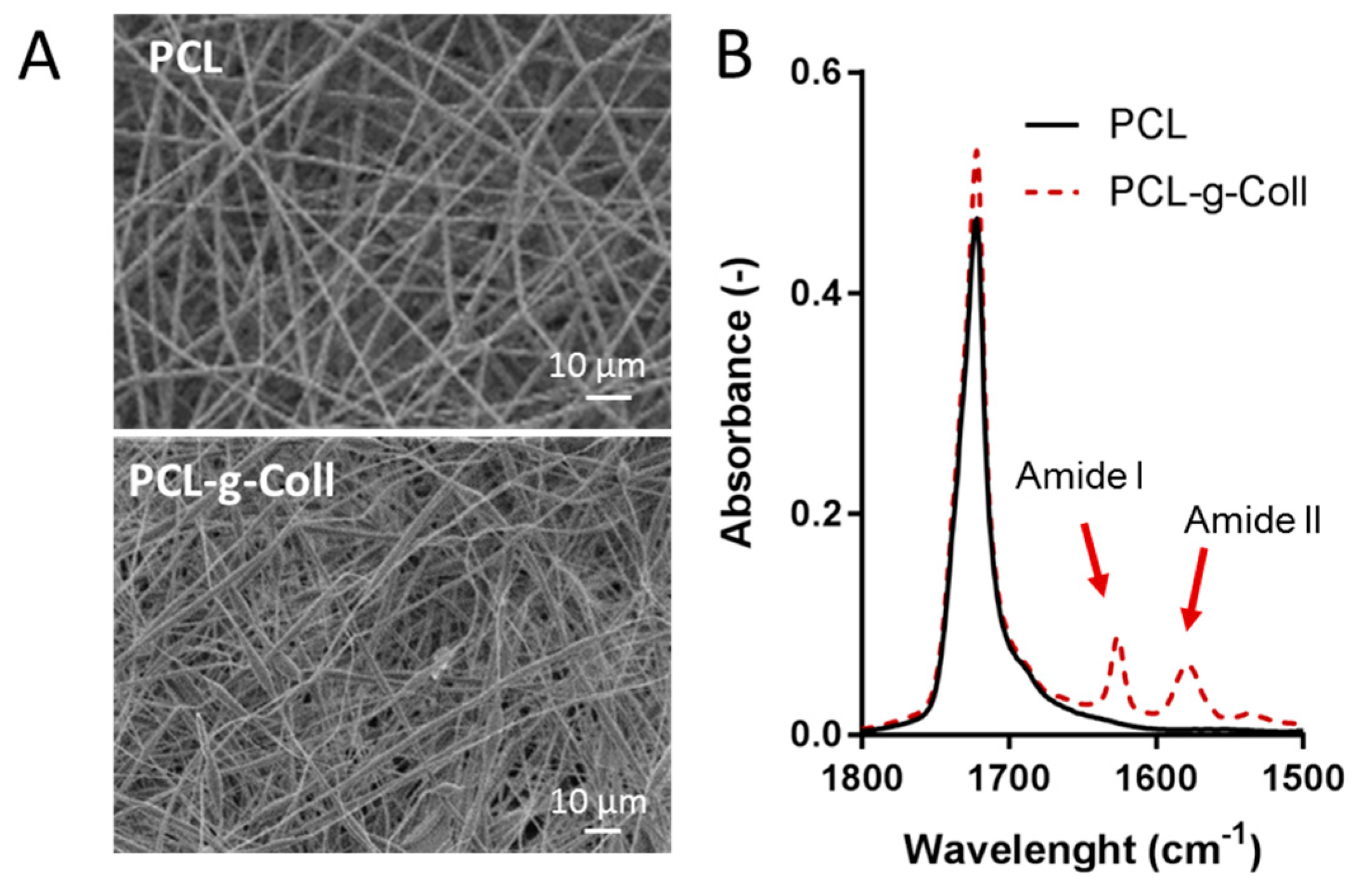
2.2. Characterisation of PCL/Coll Electrospun Membranes
3. Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of the Successful Synthesis of PCL-g-Coll
3.2. Preliminary Considerations on PCL-g-Coll as Base Materials for Electrospun Scaffolds Preparation
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
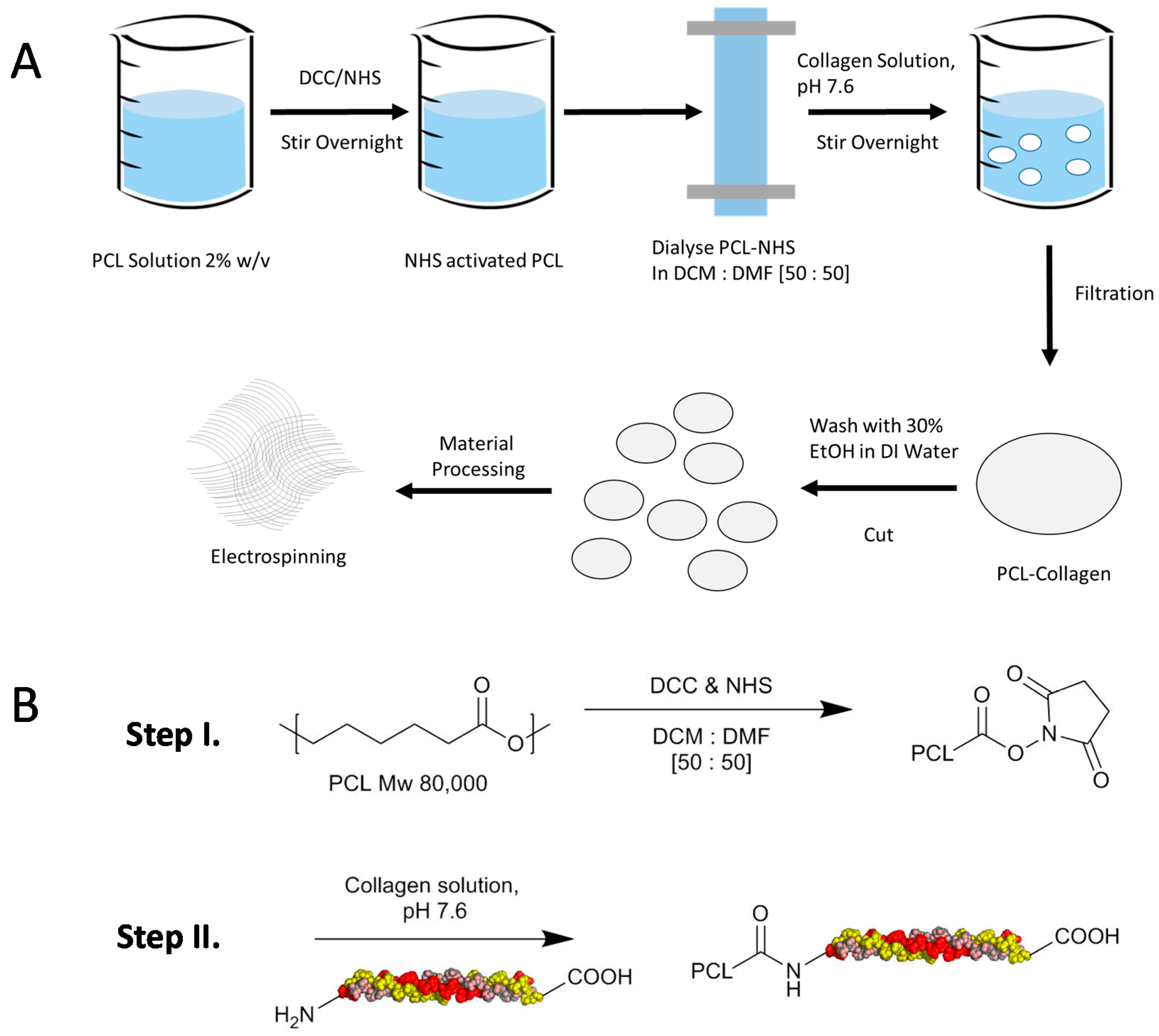
4.2. Protocol for Preparation of ε-Polycaprolactone and Collagen Type I Conjugation
4.3. Preparation of Dense Films by Solvent Casting
4.4. Preparation of Dense Films by Spin Coating
4.5. Electrospun Membranes
4.6. Physical–Chemical Characterization
4.6.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy in Attenuated Total Reflection Mode (ATR-FTIR)
4.6.2. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
4.6.3. Contact Angle Measurement
4.6.4. Sirius Red Method
4.6.5. Tensile Tests
4.6.6. In Vitro Biodegradation Studies
4.6.7. Morphological Analysis by Scanning Electron Microscopy
4.7. Biological Evaluation
4.7.1. Cell Culture
4.7.2. Cytocompatibility Assays
4.7.3. Cytoskeletal Staining
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhandayuthapani, B.; Yoshida, Y.; Maekawa, T.; Sakthi Kumar, D. Polymeric scaffolds in tissue engineering application: A review. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2011, 2011, 290602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.P.; Sharma, U.; Mikos, A.G. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: A review. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, I.; Sefat, F.; Deshpande, P.; Paterson, T.; Ramachandran, C.; Ryan, A.J.; MacNeil, S.; Claeyssens, F. Combination of microstereolithography and electrospinning to produce membranes equipped with niches for corneal regeneration. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 91, 51826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sefat, F.; McKean, R.; Deshpande, P.; Ramachandran, C.; Hill, C.J.; Sangwan, V.S.; Ryan, A.J.; MacNeil, S. Production, sterilisation and storage of biodegradable electrospun PLGA membranes for delivery of limbal stem cells to the cornea. Procedia Eng. 2013, 59, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, P.; Ramachandran, C.; Sefat, F.; Mariappan, I.; Johnson, C.; McKean, R.; Hannah, M.; Sangwan, V.S.; Claeyssens, F.; Ryan, A.J. Simplifying corneal surface regeneration using a biodegradable synthetic membrane and limbal tissue explants. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5088–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, P.; Ferreira, A.M.; Callaghan, J.T.; Miller, C.A.; Atkinson, J.; Freeman, C.; Hatton, P.V. Multilayer nanoscale encapsulation of biofunctional peptides to enhance bone tissue regeneration in vivo. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Venugopal, J.; Huang, Z.M.; Lim, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S. Characterization of the surface biocompatibility of the electrospun PCL-collagen nanofibers using fibroblasts. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2583–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Gentile, P.; Toumpaniari, S.; Ciardelli, G.; Birch, M.A. Impact of collagen/heparin multilayers for regulating bone cellular functions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 29923–29932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedalwafa, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Li, C. Biodegradable poly-epsilon-caprolactone (PCL) for tissue engineering applications: A review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2013, 34, 123–140. [Google Scholar]
- Cipitria, A.; Skelton, A.; Dargaville, T.R.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Design, fabrication and characterization of PCL electrospun scaffolds—A review. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 9419–9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Yang, F.; Seyednejad, H.; Chen, Z.; Hennink, W.E.; Anderson, J.M.; van den Beucken, J.J.J.P.; Jansen, J.A. Biocompatibility and degradation characteristics of PLGA-based electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds with nanoapatite incorporation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6604–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Gentile, P.; Chiono, V.; Ciardelli, G. Collagen for bone tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, N.T.; Williamson, M.R.; Khammo, N.; Adams, E.F.; Coombes, A.G.A. Composite cell support membranes based on collagen and polycaprolactone for tissue engineering of skin. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4263–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahjour, S.B.; Sefat, F.; Polunin, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Improved cell infiltration of electrospun nanofiber mats for layered tissue constructs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2016, 104, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dippold, D.; Cai, A.; Hardt, M.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Horch, R.; Beier, J.P.; Schubert, D.W. Novel approach towards aligned PCL-collagen nanofibrous constructs from a benign solvent system. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 72, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Liu, J.; Oh, S.H.; Soker, S.; Atala, A.; Yoo, J.J. Development of a composite vascular scaffolding system that withstands physiological vascular conditions. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2891–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillman, B.W.; Yazdani, S.K.; Lee, S.J.; Geary, R.L.; Atala, A.; Yoo, J.J. The In Vivo stability of electrospun polycaprolactone-collagen scaffolds in vascular reconstruction. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çapkın, M.; Çakmak, S.; Kurt, F.Ö.; Gümüşderelioğlu, M.; Şen, B.H.; Türk, B.T.; Deliloğlu-Gürhan, S.İ. Random/aligned electrospun PCL/PCL-collagen nanofibrous membranes: Comparison of neural differentiation of rat AdMSCs and BMSCs. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 7, 045013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, E.J.; Phan, T.T.; Lim, I.J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Bay, B.H.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lim, C.T. Evaluation of electrospun PCL/gelatin nanofibrous scaffold for wound healing and layered dermal reconstitution. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Kim, G.H. Electrohydrodynamic direct printing of PCL/collagen fibrous scaffolds with a core/shell structure for tissue engineering applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Li, J.; Poh, C.K.; Tan, H.C.; San Thian, E.; Fuh, J.Y.H.; Sun, J.; Tay, B.Y.; Wang, W. Collagen grafted 3D polycaprolactone scaffolds for enhanced cartilage regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5971–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiens, M.; Elkhooly, T.A.; Schröder, H.-C.; Mohamed, T.H.A.; Müller, W.E.G. Characterization and osteogenic activity of a silicatein/biosilica-coated chitosan-graft-polycaprolactone. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4456–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Gentile, P.; Sartori, S.; Pagliano, C.; Cabrele, C.; Chiono, V.; Ciardelli, G. Biomimetic soluble collagen purified from bones. Biotechnol. J. 2012, 7, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sionkowska, A.; Kozłowska, J. Characterization of collagen/hydroxyapatite composite sponges as a potential bone substitute. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, F.; Chang, S.; Toh, Y.C.; Teoh, S.H.; Yu, H. Development of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-collagen scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.R.; Noda, I.; Jung, Y.M. Positional fluctuation of IR absorption peaks: Frequency shift of a single band or relative intensity changes of overlapped bands. Am. Lab. 2011, 43, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Sionkowska, A. Current research on the blends of natural and synthetic polymers as new biomaterials: Review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1254–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, M.I.; Xu, X.; Li, L. A review on biodegradable polymeric materials for bone tissue engineering applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 5713–5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutolf, M.P.; Hubbell, J.A. Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, S.; Hiltner, A.; Lando, J.B.; Baer, E. Interaction of water with native collagen. Biopolymers 1977, 16, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noris-Suárez, K.; Lira-Olivares, J.; Ferreira, A.M.; Feijoo, J.L.; Suárez, N.; Hernández, M.C.; Barrios, E. In vitro deposition of hydroxyapatite on cortical bone collagen stimulated by deformation-induced piezoelectricity. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul-E-Noor, F.; Singh, C.; Papaioannou, A.; Sinha, N.; Boutis, G.S. The behavior of water in collagen and hydroxyapatite sites of cortical bone: Fracture, mechanical wear, and load bearing studies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 21528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyman, J.S.; Roy, A.; Shen, X.; Acuna, R.L.; Tyler, J.H.; Wang, X. The influence of water removal on the strength and toughness of cortical bone. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Even-Ram, S.; Yamada, K.M. Cell migration in 3D matrix. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005, 17, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Wu, Y.-P.; Fu, Z.-F.; Tian, Y.; Li, C.-J.; Gao, C.-Y.; Chen, Z.-L.; Feng, X.-Z. Cell adhesive and growth behavior on electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds by designed multifunctional composites. Coll. Surf. B 2011, 84, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, I.; Mendes, A.; Pereira, R.F.; Bártolo, P.J. Collagen surface modified poly(ε-caprolactone) scaffolds with improved hydrophilicity and cell adhesion properties. Mater. Lett. 2014, 134, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-J.; Yu, H.-S.; Hong, S.-J.; Jeong, I.; Jang, J.-H.; Kim, H.-W. Nanofibrous membrane of collagen–polycaprolactone for cell growth and tissue regeneration. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 20, 1927–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deitzel, J.M.; Kleinmeyer, J.; Harris, D.E.A.; Tan, N.C.B. The effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun nanofibers and textiles. Polymer 2001, 42, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Feng, B.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, G.; Liu, W.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.J. Engineering of epidermis skin grafts using electrospun nanofibrous gelatin/polycaprolactone membranes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar]
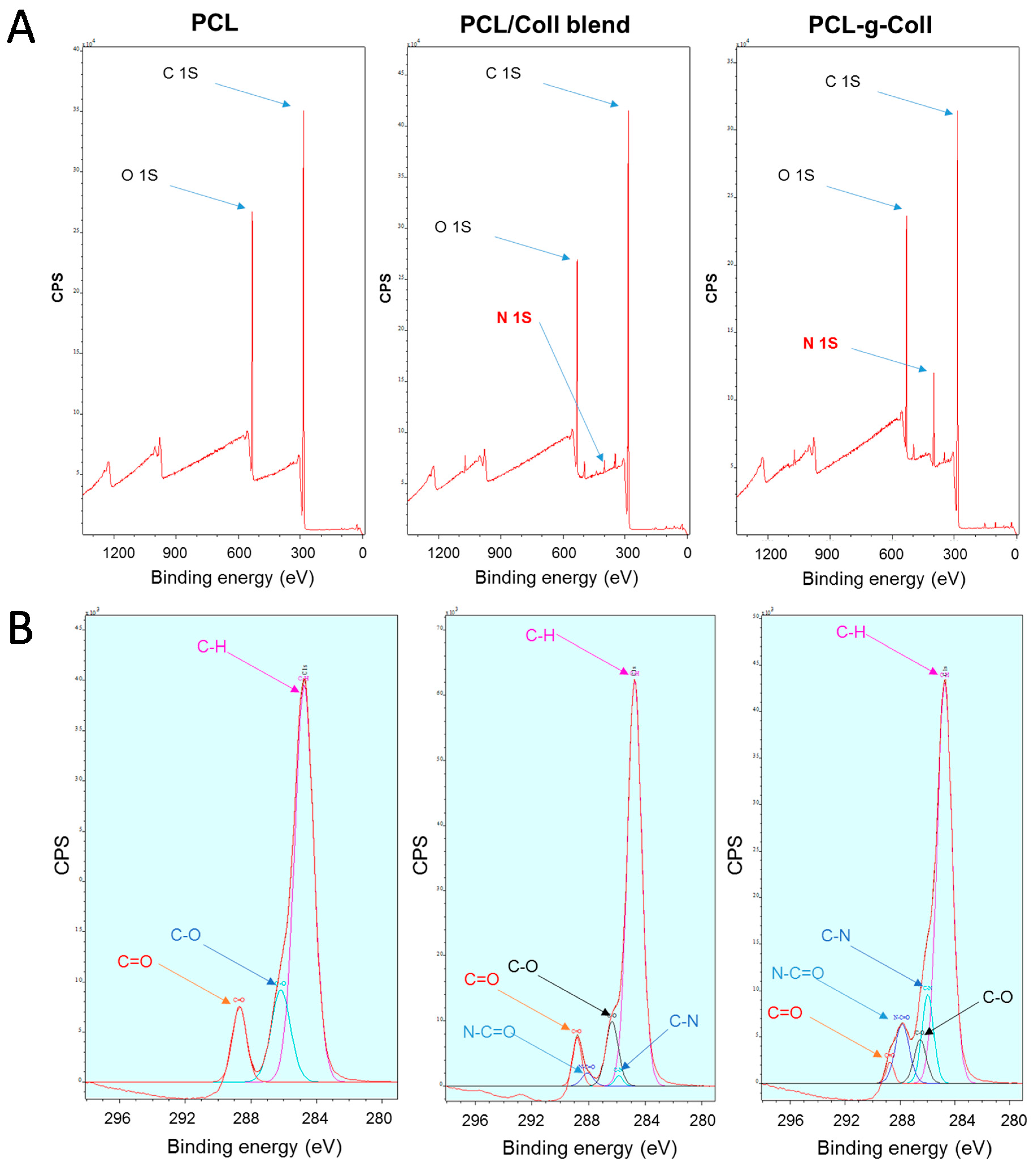
| Sample | 288.9 eV C=O (%) | 288.4 eV N–C=O (%) | 286.5 eV C–O (%) | 286.1 eV C–N (%) | 284.9 eV C–H (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCL | 10.17 ± 0.13 | - | 16.52 ± 0.42 | – | 73.31 ± 0.41 |
| PCL/Coll | 4.93 ± 0.42 | 3.59 ± 0.87 | 9.69 ± 1.65 | 1.55 ± 0.19 | 76.91 ± 1.73 |
| PCL-g-Coll | 2.86 ± 0.81 | 8.52 ± 0.63 | 7.64 ± 1.78 | 8.96 ± 2.02 | 71.82 ± 1.27 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gentile, P.; McColgan-Bannon, K.; Gianone, N.C.; Sefat, F.; Dalgarno, K.; Ferreira, A.M. Biosynthetic PCL-graft-Collagen Bulk Material for Tissue Engineering Applications. Materials 2017, 10, 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070693
Gentile P, McColgan-Bannon K, Gianone NC, Sefat F, Dalgarno K, Ferreira AM. Biosynthetic PCL-graft-Collagen Bulk Material for Tissue Engineering Applications. Materials. 2017; 10(7):693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070693
Chicago/Turabian StyleGentile, Piergiorgio, Kegan McColgan-Bannon, Nicolò Ceretto Gianone, Farshid Sefat, Kenneth Dalgarno, and Ana Marina Ferreira. 2017. "Biosynthetic PCL-graft-Collagen Bulk Material for Tissue Engineering Applications" Materials 10, no. 7: 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070693
APA StyleGentile, P., McColgan-Bannon, K., Gianone, N. C., Sefat, F., Dalgarno, K., & Ferreira, A. M. (2017). Biosynthetic PCL-graft-Collagen Bulk Material for Tissue Engineering Applications. Materials, 10(7), 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070693







