Effects of UV-Ozone Treatment on Sensing Behaviours of EGFETs with Al2O3 Sensing Film
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
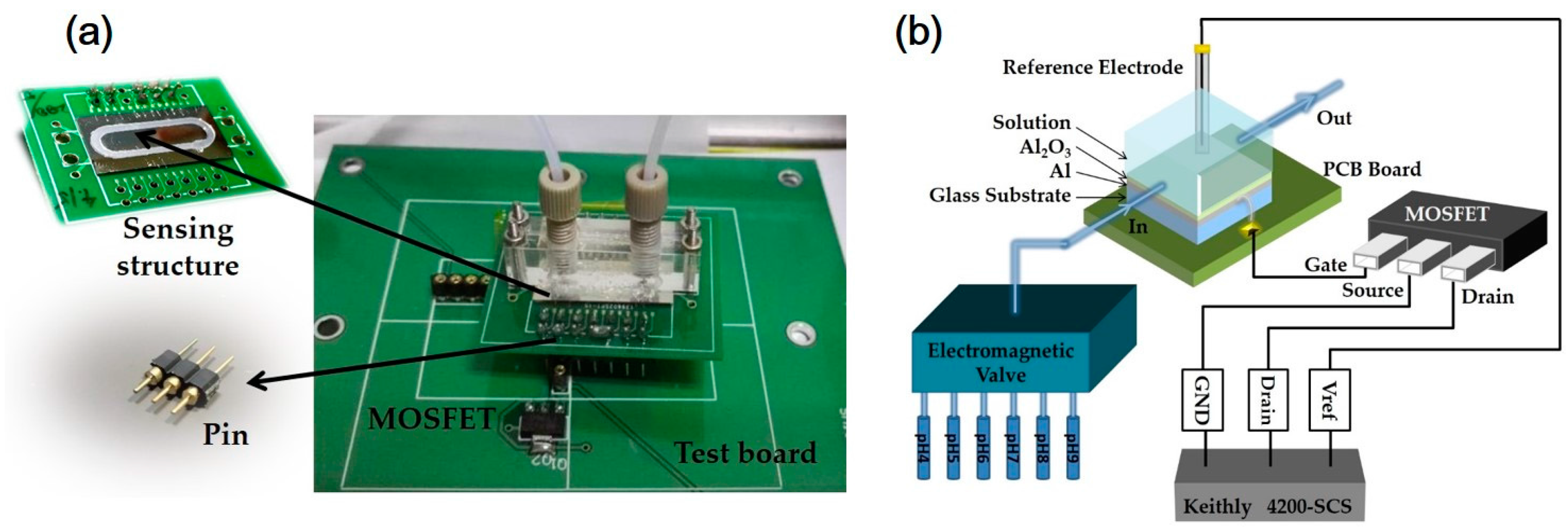
2.1. Fabrication Process
2.2. Electrical and Physical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
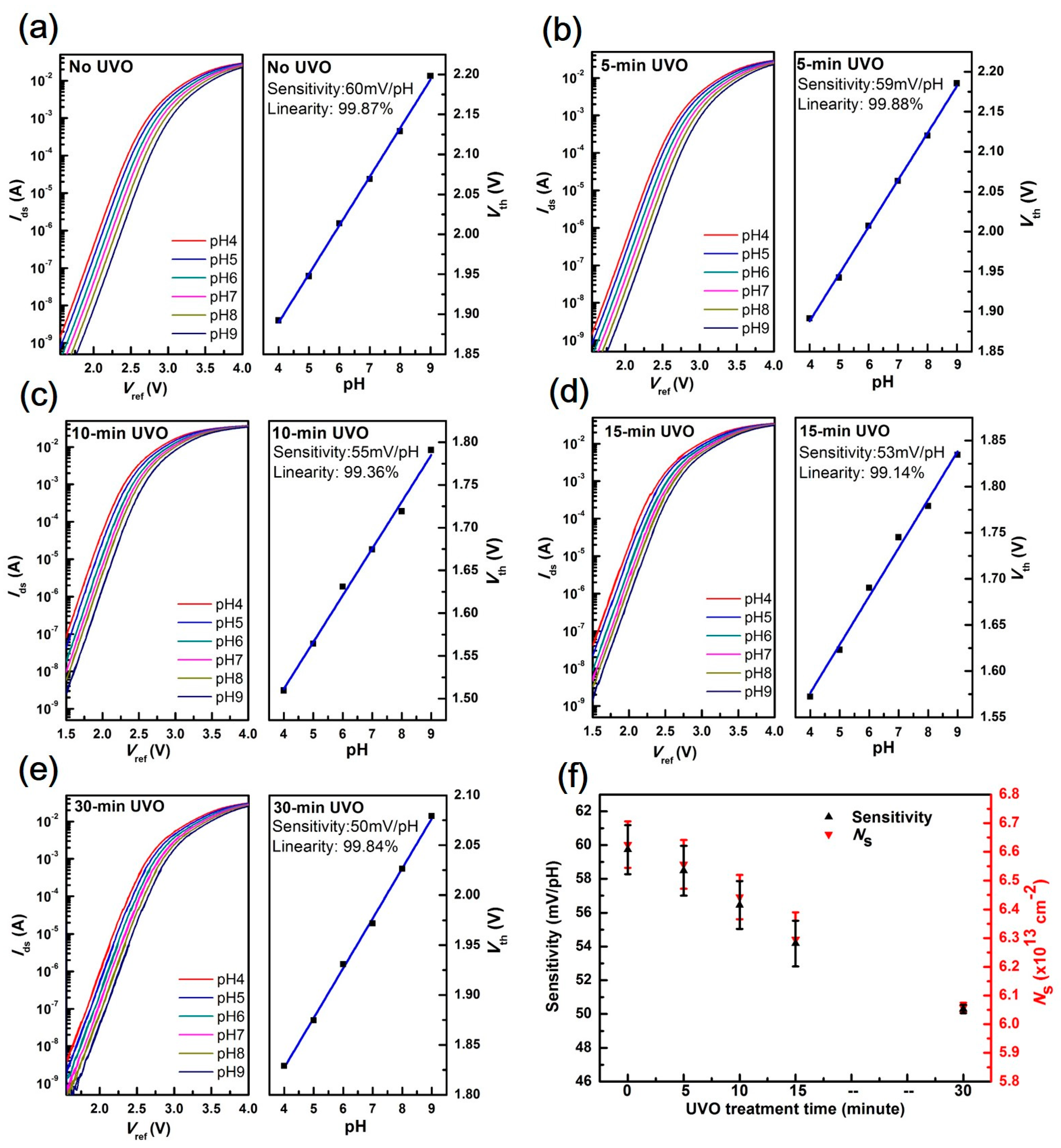
3.1. EGFET Sensing Behaviours
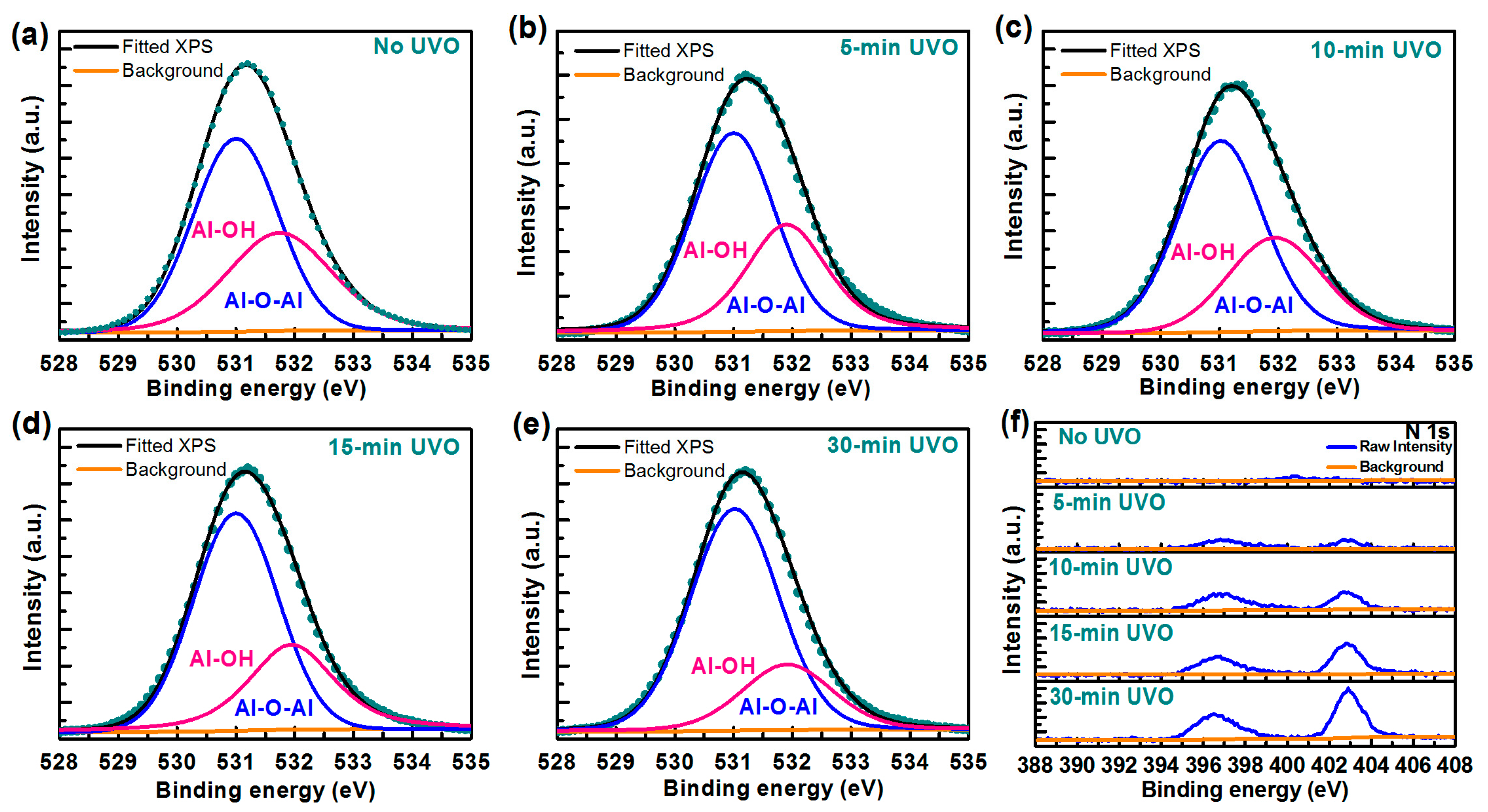
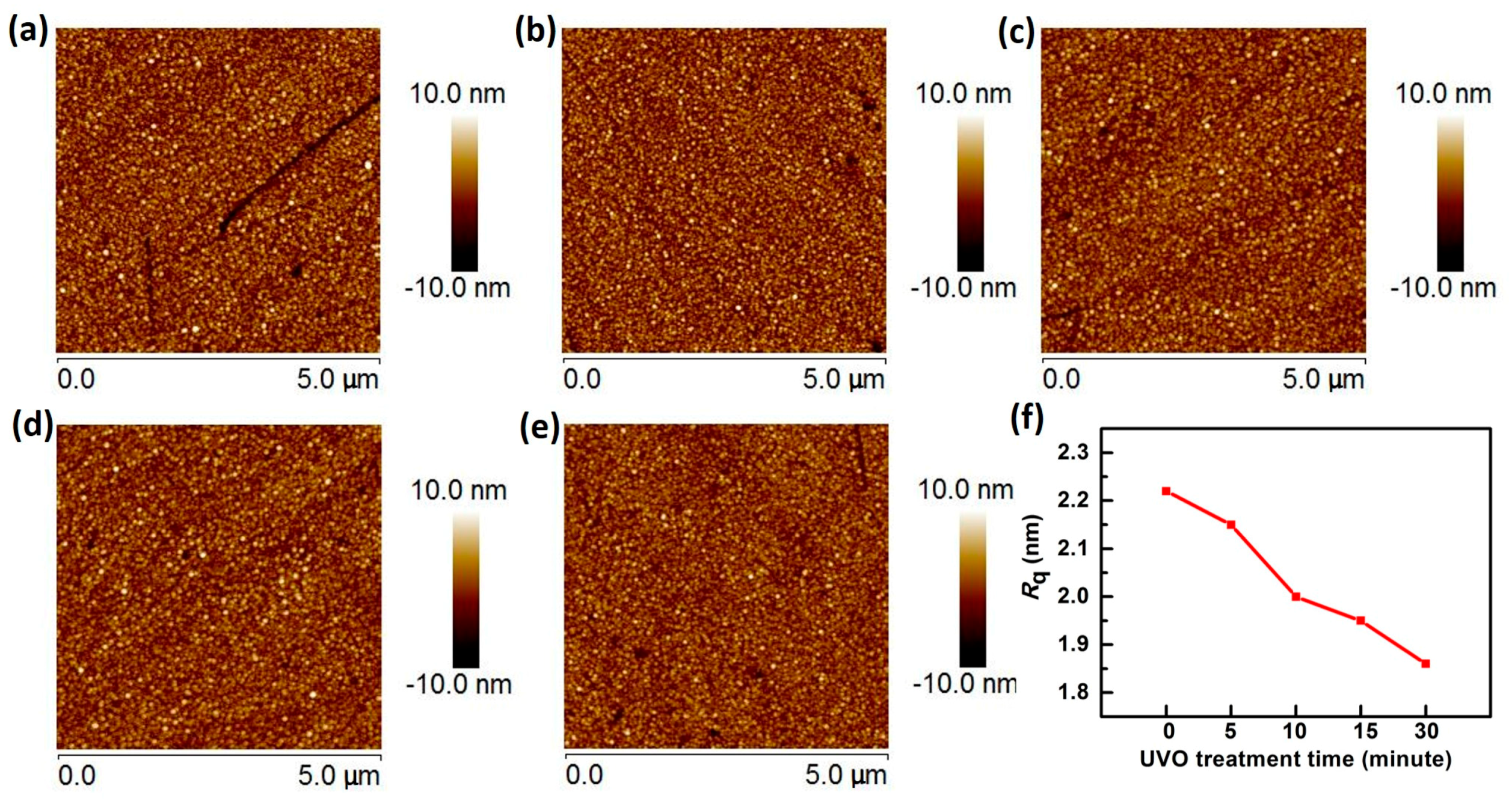
3.2. Sensing Film Surface Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergveld, P. Thirty years of ISFETOLOGY: What happened in the past 30 years and what may happen in the next 30 years. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 88, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergveld, P. Development, operation, and application of the ion-sensitive field-effect transistor as a tool for electrophysiology. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1972, 19, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang-Soo Lee, S.K.K. Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor for Biological Sensing. Sensors 2009, 9, 7111–7131. [Google Scholar]
- Shinwari, M.W.; Deen, M.J.; Landheer, D. Study of the electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor field-effect transistor (EISFET) with applications in biosensor design. Microelectron. Reliab. 2007, 47, 2025–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, J.V.D.; Lauks, I.; Chan, P.; Babic, D. The extended gate chemically sensitive field effect transistor as multi-species microprobe. Sens. Actuators 1983, 4, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Wang, J.C.; Chiang, T.W.; Lin, Y.T.; Juan, T.W.; Chen, T.G.; Shih, M.Y.; Lue, C.E.; Lai, C.S. Hydrogen ion sensing characteristics of IGZO/Si electrode in EGFET. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2013, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, L.L.; Chou, J.C.; Chung, W.Y.; Sun, T.P.; Hsiung, S.K. Study on extended gate field effect transistor with tin oxide sensing membrane. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2000, 63, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.T.; Chou, J.C.; Chung, W.Y.; Sun, T.P.; Hsiung, S.K. Separate structure extended gate H+-ion sensitive field effect transistor on a glass substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 71, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, E.M.; Silva, G.R.; Mulato, M. Extended gate field effect transistor using V2O5 xerogel sensing membrane by sol–gel method. Solid State Sci. 2009, 11, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.V.; Branquinho, R.; Barquinha, P.; Alves, E.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Extended-Gate ISFETs Based on Sputtered Amorphous Oxides. J. Disp. Technol. 2013, 9, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Esashi, M.; Matsuo, T. ISFET’s using inorganic gate thin films. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1979, 26, 1939–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, P.D. An embedded measurement system for electrical characterization of EGFET as pH sensor. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2013, 25, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.G.; Kim, A.; Chan, W.P.; Ah, C.S.; Yang, J.H.; Kim, T.Y.; Jang, M.; Sung, G.Y. Modified ion sensitive field effect transistor sensors having an extended gate on a thick dielectric. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I. High-performance extended gate field-effect-transistor-based dissolved carbon dioxide sensing system with a packaged microreference electrode. J. Micro Nanolithogr. MEMS MOEMS 2014, 13, 4005–4014. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.H.; Chu, C.P.; Lin, C.F.; Liao, H.H.; Tsai, H.H.; Juang, Y.Z. Extended-gate field-effect transistor packed in micro channel for glucose, urea and protein biomarker detection. Biomed. Microdevices 2015, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, V.K. Remedial and adaptive solutions of ISFET non-ideal behaviour. Sens. Rev. 2013, 33, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Kawarada, H. Low drift and small hysteresis characteristics of diamond electrolyte-solution-gate FET. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 374020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woias, P.; Meixner, L.; Fröstl, P. Slow pH response effects of silicon nitride ISFET sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1998, 48, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-N.; Chou, J.-C.; Sun, T.-P.; Hsiung, S.-K. Study on the time-dependent slow response of the tin oxide pH electrode. IEEE Sens. J. 2006, 6, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Rasaiah, J.C. Proton transfer and the mobilities of the H+ and OH− ions from studies of a dissociating model for water. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 124505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grattarola, M.; Massobrio, G.; Martinoia, S. Modeling H+ -sensitive FETs with SPICE. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1992, 39, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousse, L.; Bergveld, P. The role of buried OH sites in the response mechanism of inorganic-gate pH-sensitive ISFETs. Sens. Actuators 1984, 6, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.C.; Weng, C.Y. Sensitivity and hysteresis effect in Al2O3 gate pH-ISFET. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2001, 71, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.V.D.; Bergveld, P.; Reinhoudt, D.N.; Sudhölter, E.J. Sensitivity control of ISFETs by chemical surface modification. Sens. Actuators 1985, 8, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, A.; Wipf, M.; Stoop, R.L.; Bedner, K.; Fu, W.; Guzenko, V.A.; Knopfmacher, O.; Calame, M.; Schönenberger, C. Understanding the electrolyte background for biochemical sensing with ion-sensitive field-effect transistors. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9291–9298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Bu, Y.; Ao, J.-P. Effect of oxygen plasma treatment on the performance of AlGaN/GaN ion-sensitive field-effect transistors. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 73, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.-T.; Chou, J.-C.; Chung, W.-Y.; Sun, T.-P.; Hsiung, S.-K. Characteristics of silicon nitride after O/sub 2/plasma surface treatment for pH-ISFET applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 48, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.F.; Wang, J.C.; Yang, C.M.; Chang, C.P.; Ho, K.I.; Ai, C.F.; Lai, C.S. Non-ideal effects improvement of SF 6 plasma treated hafnium oxide film based on electrolyte & ndash;insulator– semiconductor structure for pH-sensor application. Microelectron. Reliab. 2010, 50, 742–746. [Google Scholar]
- Dipalo, M.; Pietzka, C.; Denisenko, A.; El-Hajj, H.; Kohn, E. O-terminated nano-diamond ISFET for applications in harsh environment. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2008, 17, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastidar, S.; Agarwal, A.; Kumar, N.; Bal, V. Sensitivity Enhancement of Electrolyte–Insulator–Semiconductor Sensors Using Mesotextured and Nanotextured Dielectric Surfaces. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 2039–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengdee, P.; Chaisriratanakul, W.; Bunjongpru, W.; Sripumkhai, W.; Srisuwan, A.; Jeamsaksiri, W.; Hruanun, C.; Poyai, A.; Promptmas, C. Surface modification of silicon dioxide, silicon nitride and titanium oxynitride for lactate dehydrogenase immobilization. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Bomer, J.G.; Carlen, E.T.; Berg, A.V.D. Al2O3/Silicon Nano ISFET with Near Ideal Nernstian Response. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2334–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanu, A.; Lai, S.; Cosseddu, P.; Tedesco, M.; Martinoia, S.; Bonfiglio, A. An organic transistor-based system for reference-less electrophysiological monitoring of excitable cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Zine, N.; Baraket, A.; Zabala, M.; Campabadal, F.; Caruso, R.; Trivella, M.G.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Errachid, A. A novel biosensor based on hafnium oxide: Application for early stage detection of human interleukin-10. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 175, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-C.; Yang, P.-H.; Lu, M.S.-C. CMOS open-gate ion-sensitive field-effect transistors for ultrasensitive dopamine detection. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2010, 57, 2761–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braik, M.; Dridi, C.; Ali, M.B.; Ali, M.; Abbas, M.; Zabala, M.; Bausells, J.; Zine, N.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Errachid, A. Development of a capacitive chemical sensor based on Co (II)-phthalocyanine acrylate-polymer/HfO2/SiO2/Si for detection of perchlorate. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2015, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braeken, D.; Rand, D.R.; Andrei, A.; Huys, R.; Spira, M.E.; Yitzchaik, S.; Shappir, J.; Borghs, G.; Callewaert, G.; Bartic, C. Glutamate sensing with enzyme-modified floating-gate field effect transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2384–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoop, R.L.; Wipf, M.; Müller, S.; Bedner, K.; Wright, I.A.; Martin, C.J.; Constable, E.C.; Fanget, A.; Schönenberger, C.; Calame, M. Implementing Silicon Nanoribbon Field-Effect Transistors as Arrays for Multiple Ion Detection. Biosensors 2016, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Klapperich, C.M. Mechanical and chemical analysis of plasma and ultraviolet–ozone surface treatments for thermal bonding of polymeric microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.S.; Wang, H.T.; Ren, F.; Hlad, M.; Gila, B.P.; Abernathy, C.R.; Pearton, S.J.; Li, C.; Low, Z.N.; Lin, J. Role of gate oxide in AlGaN/GaN high-electron-mobility transistor pH sensors. J. Electron. Mater. 2008, 37, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusilawati, A.N.; Maizirwan, M.; Hamzah, M.S.; Ng, K.H.; Wong, C.S. Surface modification of polystyrene beads by ultraviolet/ozone treatment and its effect on gelatin coating. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 7, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milgrew, M.J.; Cumming, D.R. Matching the transconductance characteristics of CMOS ISFET arrays by removing trapped charge. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2008, 55, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, P.; Toumazou, C. ISFET characteristics in CMOS and their application to weak inversion operation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 143, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousse, L.; De Rooij, N.F.; Bergveld, P. Operation of chemically sensitive field-effect sensors as a function of the insulator-electrolyte interface. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1983, 30, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hal, R.E.G.; Eijkel, J.C.T.; Bergveld, P. A novel description of ISFET sensitivity with the buffer capacity and double-layer capacitance as key parameters. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1995, 24, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, C.D.; Cheung, P.W.; Ko, W.H. A generalized theory of an electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor field-effect transistor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1986, 33, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woias, P.; Meixner, L.; Amandi, D.; Schönberger, M. Modelling the short-time response of ISFET sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1995, 24, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-G.; Yeo, J.-H.; Jo, Y.-W. Structural and Electrical Properties of an Electrolyte-insulator-metal Device with Variations in the Surface Area of the Anodic Aluminum Oxide Template for pH Sensors. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2015, 10, 2364–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiraldelli, E.; Pelosi, C.; Gombia, E.; Chiavarotti, G.; Vanzetti, L. ALD growth, thermal treatments and characterisation of Al2O3 layers. Thin Solid Films 2008, 517, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhang, H.L.; Xiao, H.; Guo, L.Q. Atomic layer deposited Al2O3 films for anti-reflectance and surface passivation applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 288, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatsunskyi, I.; Kempiński, M.; Jancelewicz, M.; Załęski, K.; Jurga, S.; Smyntyna, V. Structural and XPS characterization of ALD Al2O3 coated porous silicon. Vacuum 2015, 113, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, W. Science, Technology, and Applications. In Handbook of Semiconductor Wafer Cleaning Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Vig, J.R. UV/ozone cleaning of surfaces. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1985, 3, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, A.; Feldmann, F.; Krugel, G.; Zimmer, M.; Rentsch, J.; Hermle, M.; Roth-Fölsch, A.; Kai, K.; Hagendorf, C. Simple Cleaning and Conditioning of Silicon Surfaces with UV/Ozone Sources. Energy Procedia 2014, 55, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.F.; Chuang, H.C.; Wang, J.C.; Yang, C.M.; Kuo, P.C.; Lai, C.S. Effects of Thickness Effect and Rapid Thermal Annealing on pH Sensing Characteristics of Thin HfO2 Films Formed by Atomic Layer Deposition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
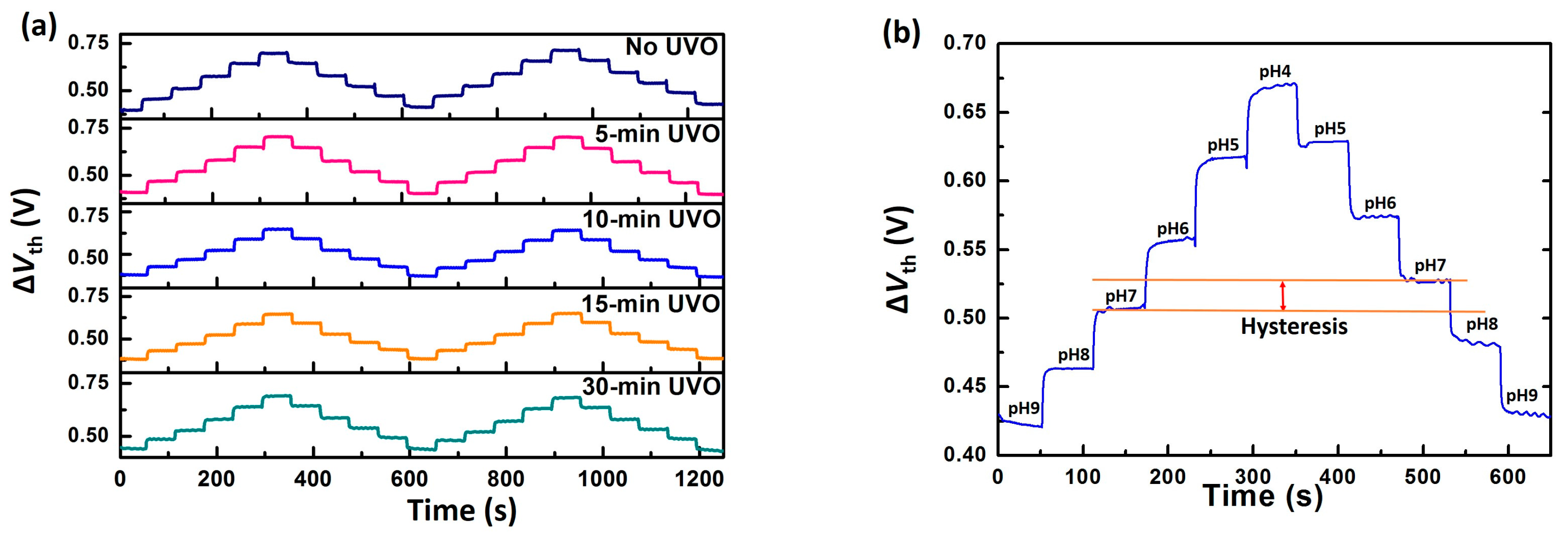
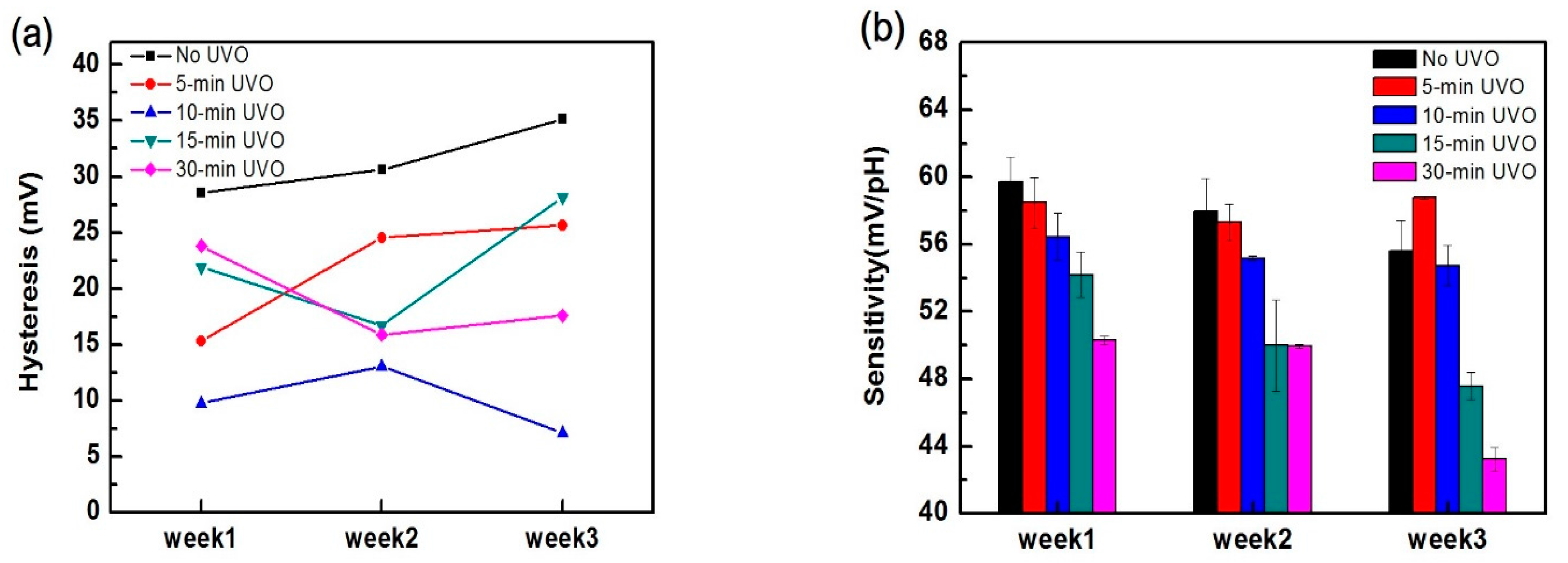
| Treatment | No UVO | 5-min UVO | 10-min UVO | 15-min UVO | 30-min UVO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hysteresis (mV) | 28 | 15 | 10 | 22 | 24 |
| Treatment | Surface | Bulk | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C (Atom %) | Al-O-Al (Area %) | Al-OH (Area %) | Al-O-Al/Al-OH (Area Radio) | |
| No UVO | 12.59 | 59.35 | 40.65 | 1.46 |
| 5-min UVO | 12.21 | 62.76 | 37.24 | 1.69 |
| 10-min UVO | 9.56 | 65.62 | 34.38 | 1.91 |
| 15-min UVO | 9.45 | 66.91 | 33.09 | 2.02 |
| 30-min UVO | 9.27 | 75.72 | 24.28 | 3.12 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, C.; Zeng, R.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, Z.-J.; Wu, D. Effects of UV-Ozone Treatment on Sensing Behaviours of EGFETs with Al2O3 Sensing Film. Materials 2017, 10, 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121432
Sun C, Zeng R, Zhang J, Qiu Z-J, Wu D. Effects of UV-Ozone Treatment on Sensing Behaviours of EGFETs with Al2O3 Sensing Film. Materials. 2017; 10(12):1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121432
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Cuiling, Ruixue Zeng, Junkai Zhang, Zhi-Jun Qiu, and Dongping Wu. 2017. "Effects of UV-Ozone Treatment on Sensing Behaviours of EGFETs with Al2O3 Sensing Film" Materials 10, no. 12: 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121432
APA StyleSun, C., Zeng, R., Zhang, J., Qiu, Z.-J., & Wu, D. (2017). Effects of UV-Ozone Treatment on Sensing Behaviours of EGFETs with Al2O3 Sensing Film. Materials, 10(12), 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121432




