Graded Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Ti/N-Implanted M50 Steel with Polyenergy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Samples
2.2. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
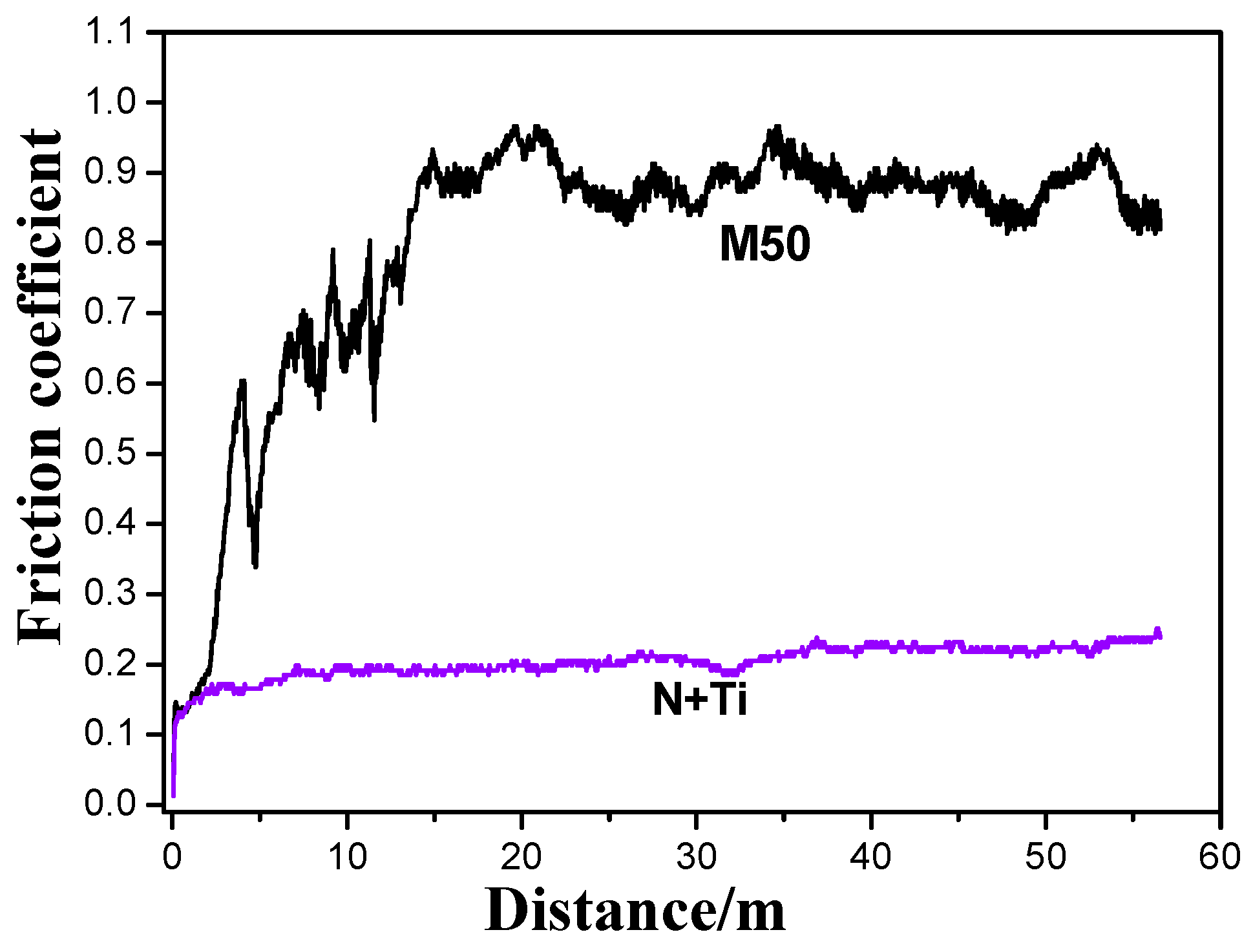
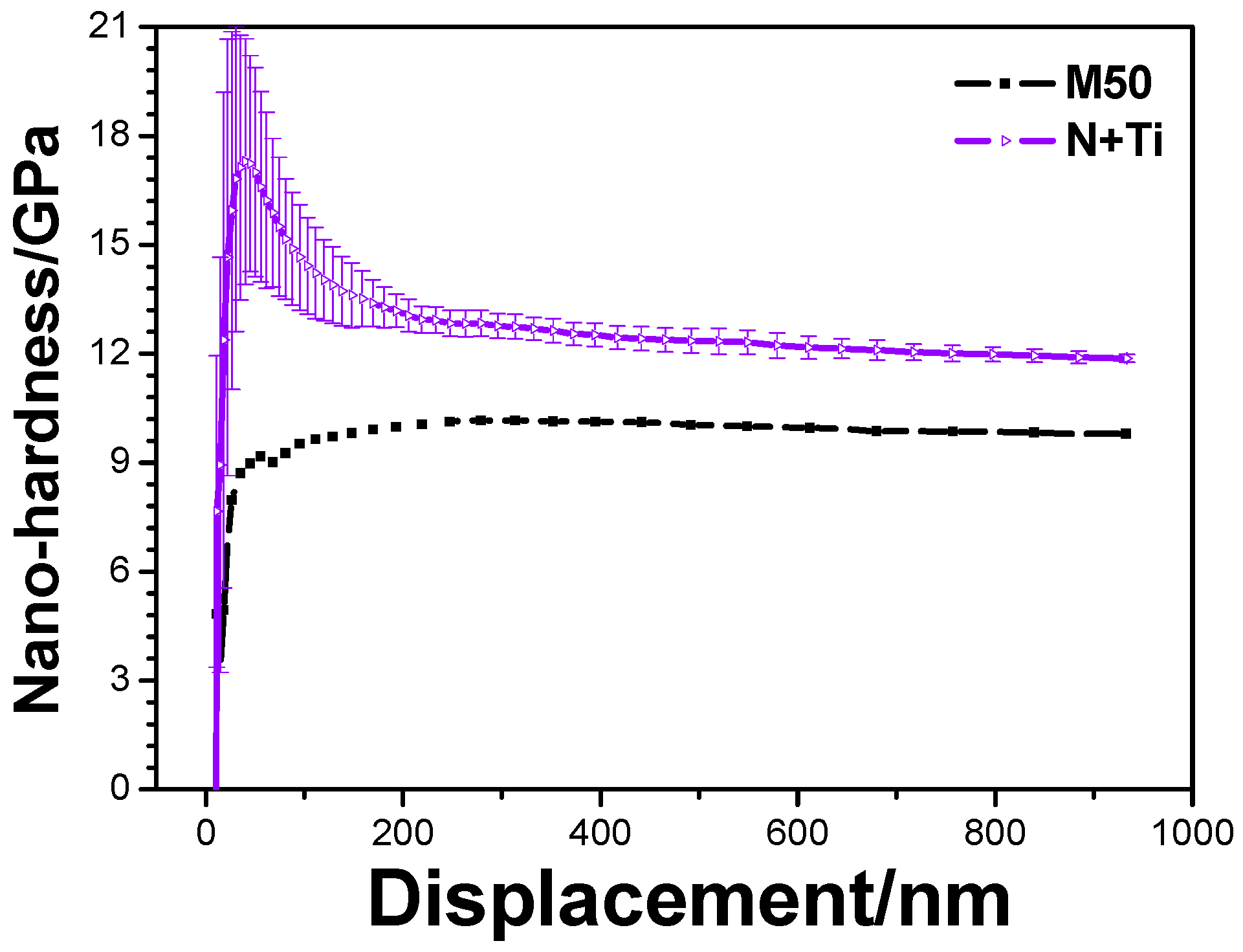
3.1. Mechanical Performance
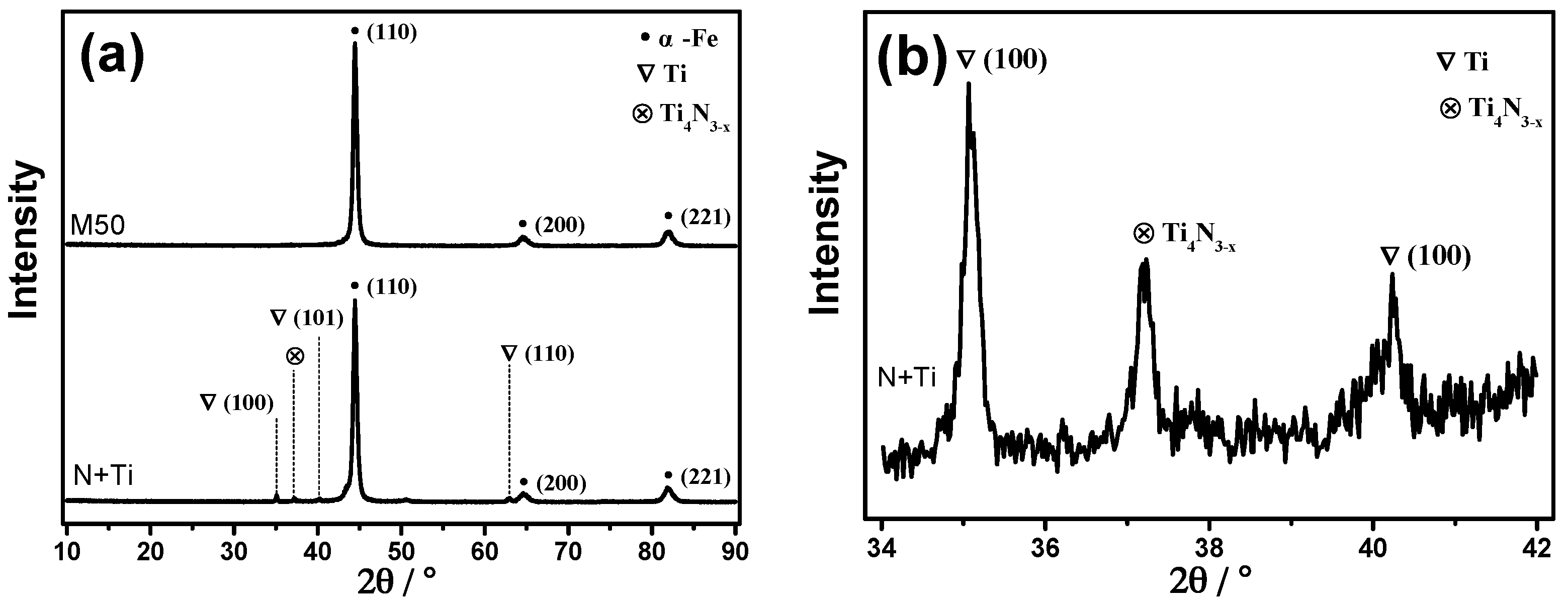
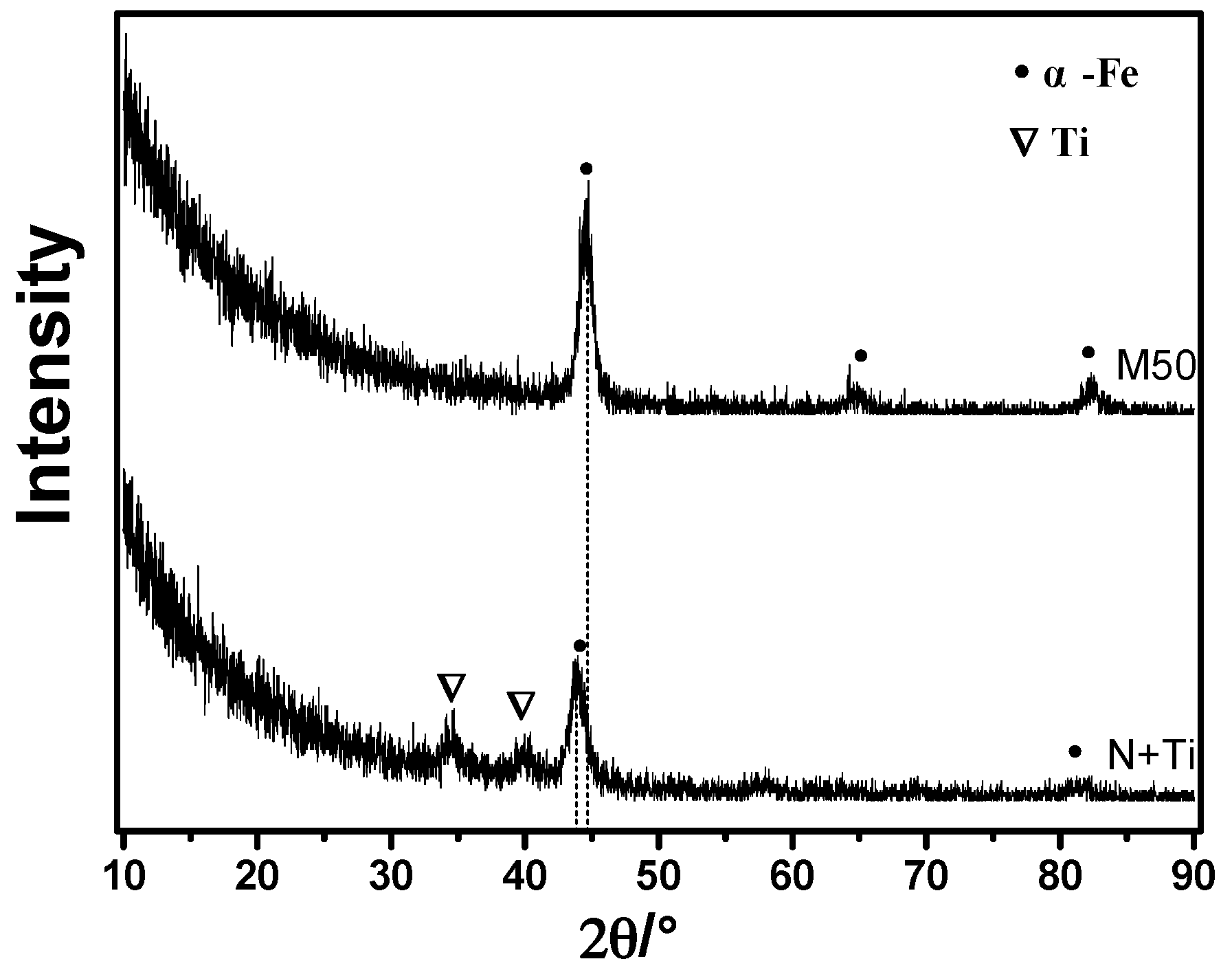
3.2. Phase Constitution of Surface Layer
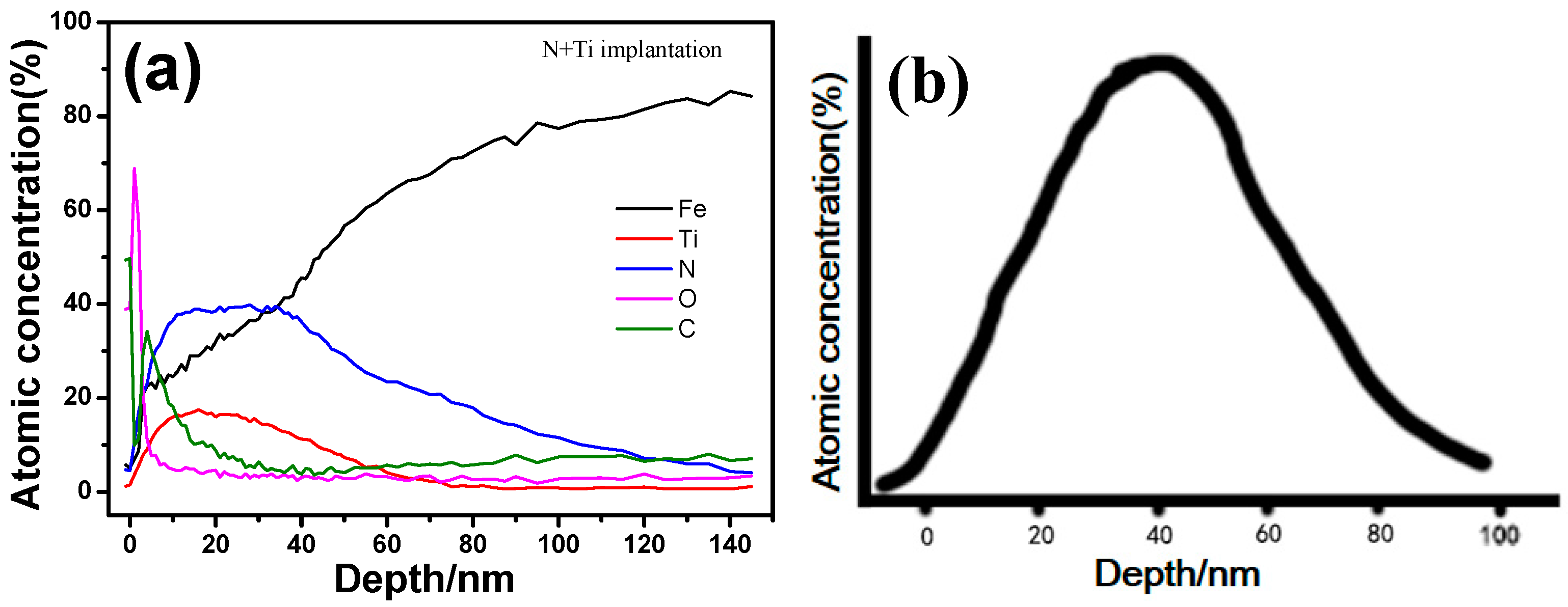
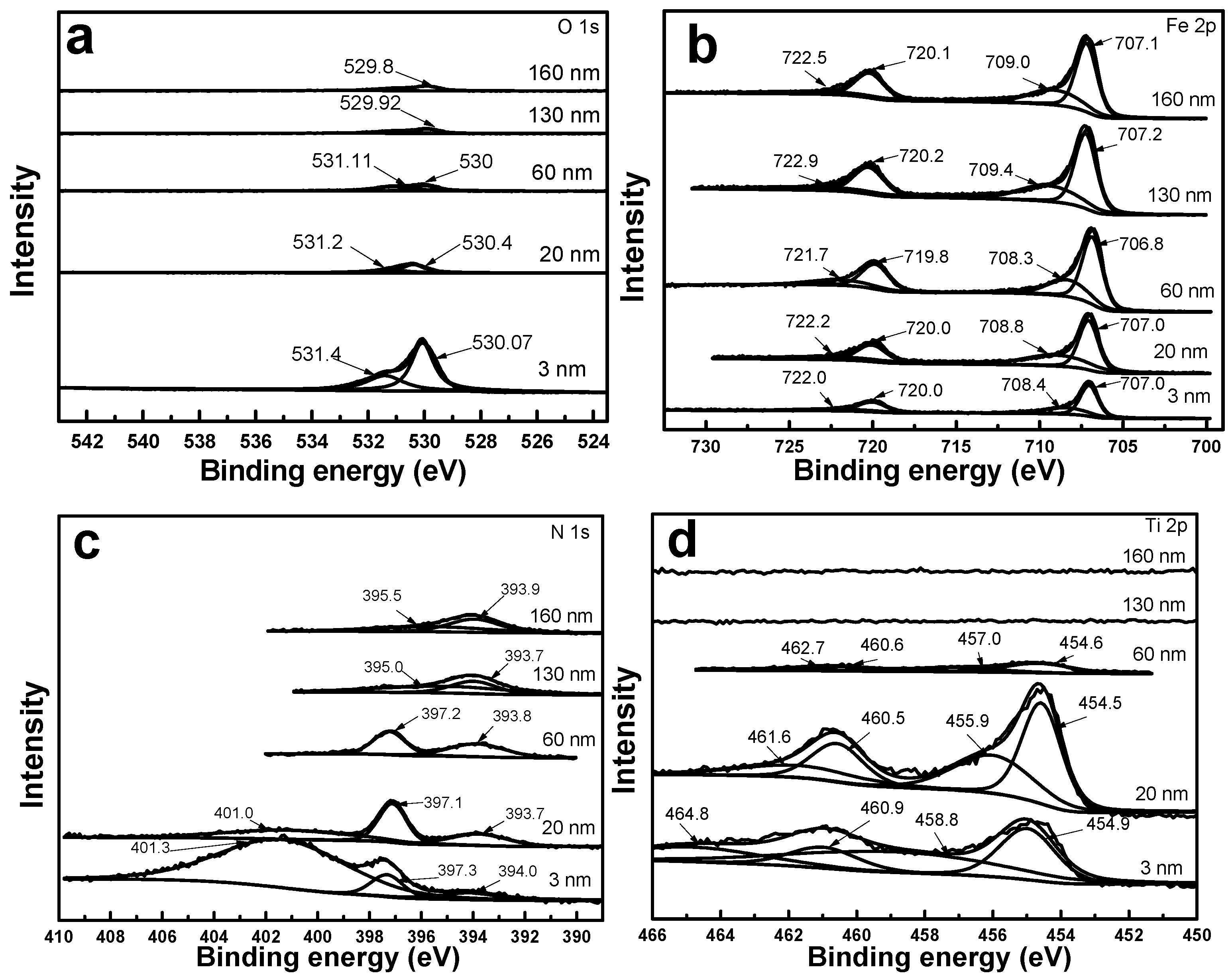
3.3. Chemical Composition
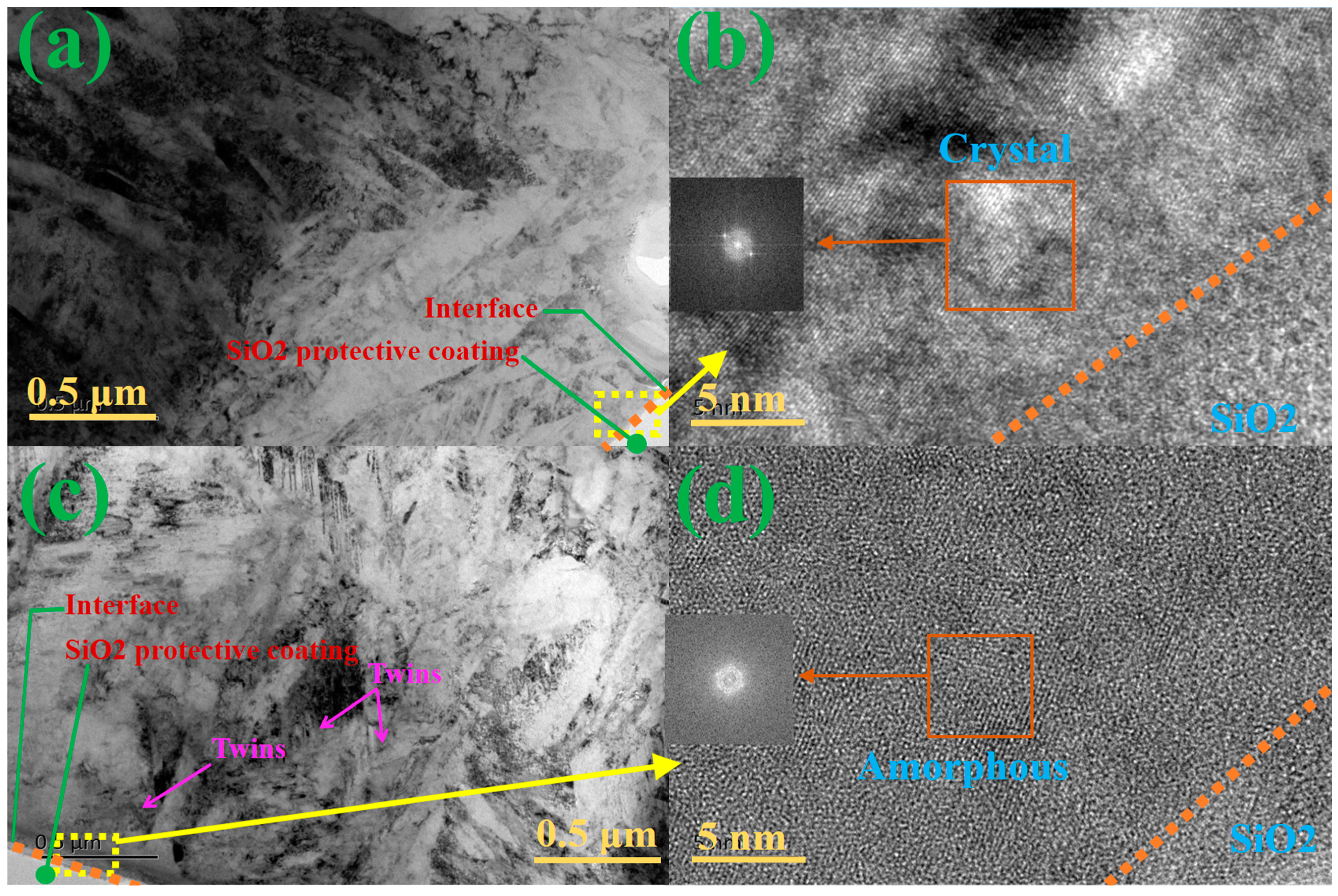
3.4. TEM Microstructure Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Z.L.; Ma, C.M. Failure Analysis and Prevention of Aircraft Engine Spindle Bearing; Science and Technology Documents Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, N.H. Rolling contact fatigue life and spall propagation of AlSi M50, M50NiL, and AlSi 52100, Part I: Experimental results. Tribol. Trans. 2009, 53, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, L. Rolling contact fatigue life and spall propagation characteristics of AlSi M50, M50 NiL, and AISI 52100, Part III: Metallurgical examination. Tribol. Trans. 2009, 53, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, N.; Reddy, D.M. An integrated tribological and vibration signal behaviour of TiN and AlCrN based PVD coatings for roller bearings. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, X.L.; Wang, Y. M50nil Material Linear Ion Implantation Method of Surface Modification. China Patent CN103757598A, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dodd, A.; Kinder, J.; Torp, B.; Nielsen, B.R.; Rangel, C.M.; Silva, M.F.D. The effect of ion implantation on the fatigue life and corrosion resistance of M50 steel bearings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1995, 74–75, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Chen, Y.B.; Gao, K.W. Effects of different metal ion implantation on friction and wear of Cr4Mo4V. China Surf. Eng. 2014, 27, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Chen, Y.; Gao, K.; Huang, X. The effect of ion implantation on tribology and hot rolling contact fatigue of Cr4Mo4Ni4V bearing steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 305, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, J.; Jin, J.; Zhou, G.; Qiu, W.; Tao, Q. Surface structures and mechanical properties of 9Cr18Mo stainless steels implanted with nitrogen ions. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2013, 42, 1838–1843. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, B.; Kankeleit, E.; Walter, G. Implantation induced phase formation in stainless steel. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 2003, 211, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzynski, P.; Youssef, A.A.; Sielanko, J. Surface modification of Ti–6Al–4V alloy by nitrogen ion implantation. Wear 2006, 261, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didenko, A.; Rjabchikov, A.; Isaev, G.; Arzubov, N.; Sharkeev, Y.P.; Kozlov, E.; Pushkareva, G.; Nikonova, I.; Ligachev, A. Dislocation structure in near-surface layers of pure metals formed by ion implantation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1989, 115, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.D.; Vilaithong, T.; Yotsombat, B.; Thongtem, S.; Han, J.G.; Lee, J.S. Surface modification of tool steels by combined Cr- and N-ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1998, 103–104, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torp, B.; Nielsen, B.R.; Dodd, A.; Kinder, J.; Rangel, C.M.; Dasilva, M.F.; Courage, B. Improvement of rolling contact fatigue life of ion implanted M50 steel. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 1993, 80–81, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzynski, P.; Youssef, A.A.; Kamienska, B. Influence of nitrogen and titanium implantation on the tribological properties of steel. Vacuum 2003, 70, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R. Low energy, high current density ion implantation of materials at elevated temperatures for tribological applications. China Surf. Eng. 1998, 83, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.M.; Bull, S.J. Changing the tribological performance of steels using low energy, high temperature nitrogen ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1996, 83, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, V.; Grant, W.A.; Procter, R.P.M. Ion implantation into metals. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Modification of Surface Properties of Metals by Ion Implantation, UMIST, Manchester, UK, 23–26 June 1981; pp. 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sharkeev, Y.P.; Kozlov, E.V. The long-range effect in ion implanted metallic materials: Dislocation structures, properties, stresses, mechanisms. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 158, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkeev, Y.P.; Kozlov, E.V.; Didenko, A.N.; Kolupaeva, S.N.; Vihor, N.A. The mechanisms of the long-range effect in metals and alloys by ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1996, 83, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.H.; Li, W.L.; Tao, N.R.; Lu, K. Revealing extraordinary intrinsic tensile plasticity in gradient nano-grained copper. Science 2011, 331, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Jiang, P.; Chen, L.; Yuan, F.; Zhu, Y.T. Extraordinary strain hardening by gradient structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7197–7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, S. Graded materials for resistance to contact deformation and damage. Science 2001, 292, 2447–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, I.L.; Carosella, C.A.; Reed, J.R. Friction behavior of 52100 steel modified by ion implanted Ti. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 1981, 182, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ji, C.; Shen, J.; Ju, C.; Tan, F.; Gao, Y. The influence of Ti, N and Ti + N implantation on phase change, microstructure, growth of metallic compounds and correlated effects in hardness and wear resistance in H13 steel. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1992, 72, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.L.; Jin, J.; Qiu, W.W.; Meng, X.Y.; Meng, H. Effects of metal and nitrogen combined ion implantation treatment on tribological properties of inconel 718. China Surf. Eng. 2017, 30, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
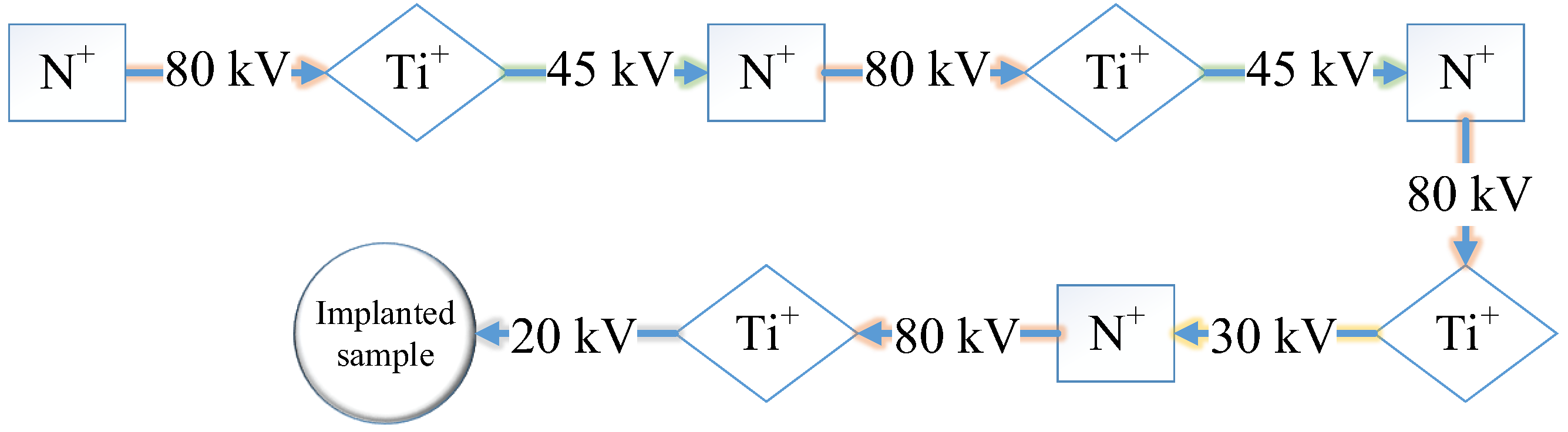
| Element | C | Cr | Mo | V | Mn | Si | P | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content% | 0.8 | 3.97 | 4.37 | 1.04 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.01 | allowance |
| Implantation Parameter | Parameter Values |
|---|---|
| Base vacuum | 3.0 × 10−4 Pa |
| Sample temperature | 150–180 °C |
| N ion acceleration voltage | 80 kV |
| N ion implantation dose | 2 × 1017 ions/cm2 |
| Ti ion acceleration voltage | 45–20 kV |
| Ti ion implantation dose | 2 × 1017 ions/cm2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jie, J.; Shao, T. Graded Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Ti/N-Implanted M50 Steel with Polyenergy. Materials 2017, 10, 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101204
Jie J, Shao T. Graded Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Ti/N-Implanted M50 Steel with Polyenergy. Materials. 2017; 10(10):1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101204
Chicago/Turabian StyleJie, Jin, and Tianmin Shao. 2017. "Graded Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Ti/N-Implanted M50 Steel with Polyenergy" Materials 10, no. 10: 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101204
APA StyleJie, J., & Shao, T. (2017). Graded Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Ti/N-Implanted M50 Steel with Polyenergy. Materials, 10(10), 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101204




