A Novel Nanocomposite as an Efficient Adsorbent for the Rapid Adsorption of Ni(II) from Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Sulfhydryl-Lignocellulose (SL)
2.3. Preparation of the Sulfhydryl-Lignocellulose/Montmorillonite (SLT) Nanocomposite
2.4. Standard Work Curve of Ni(II) Ions
2.5. Adsorption Experiment
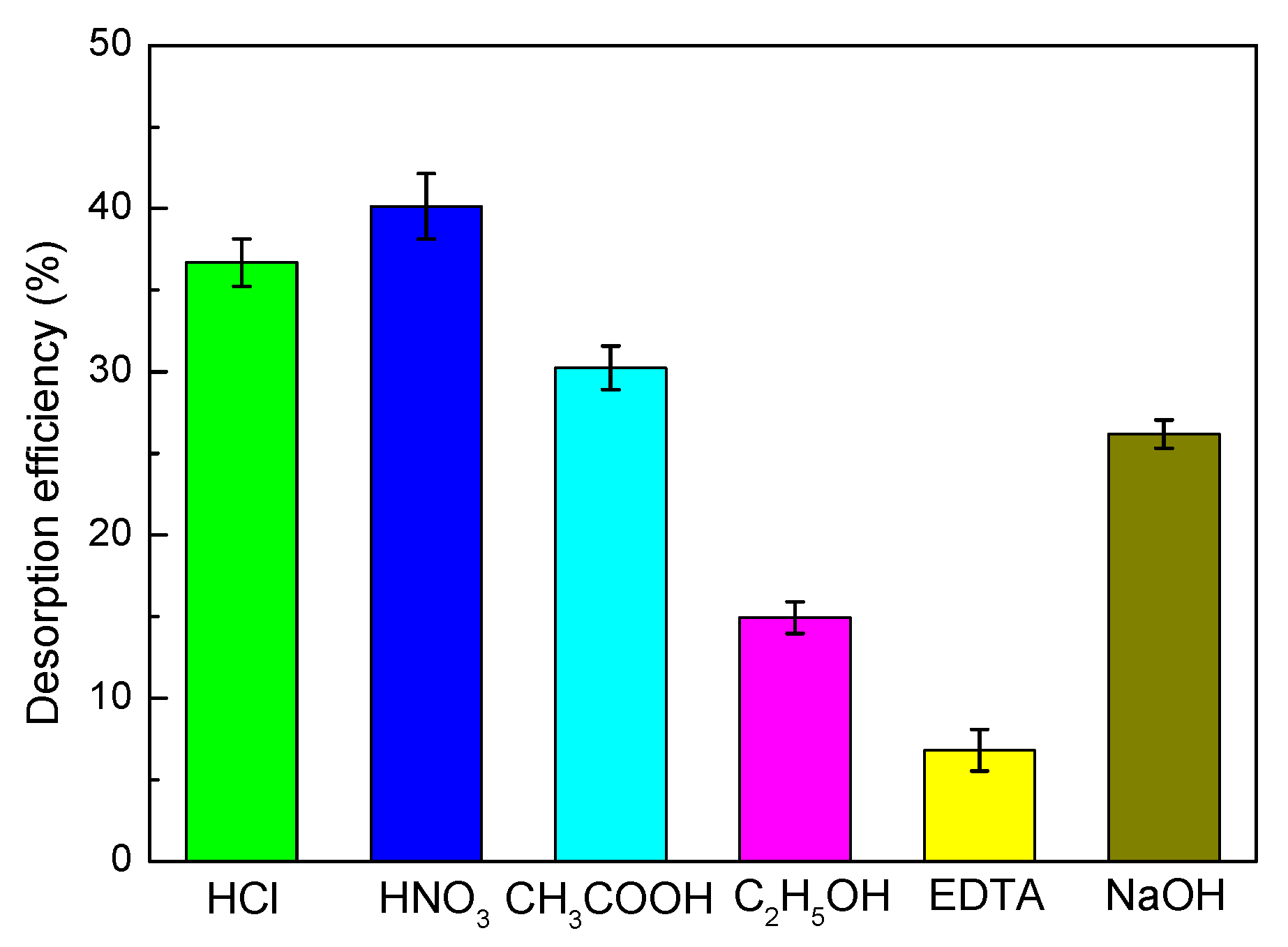
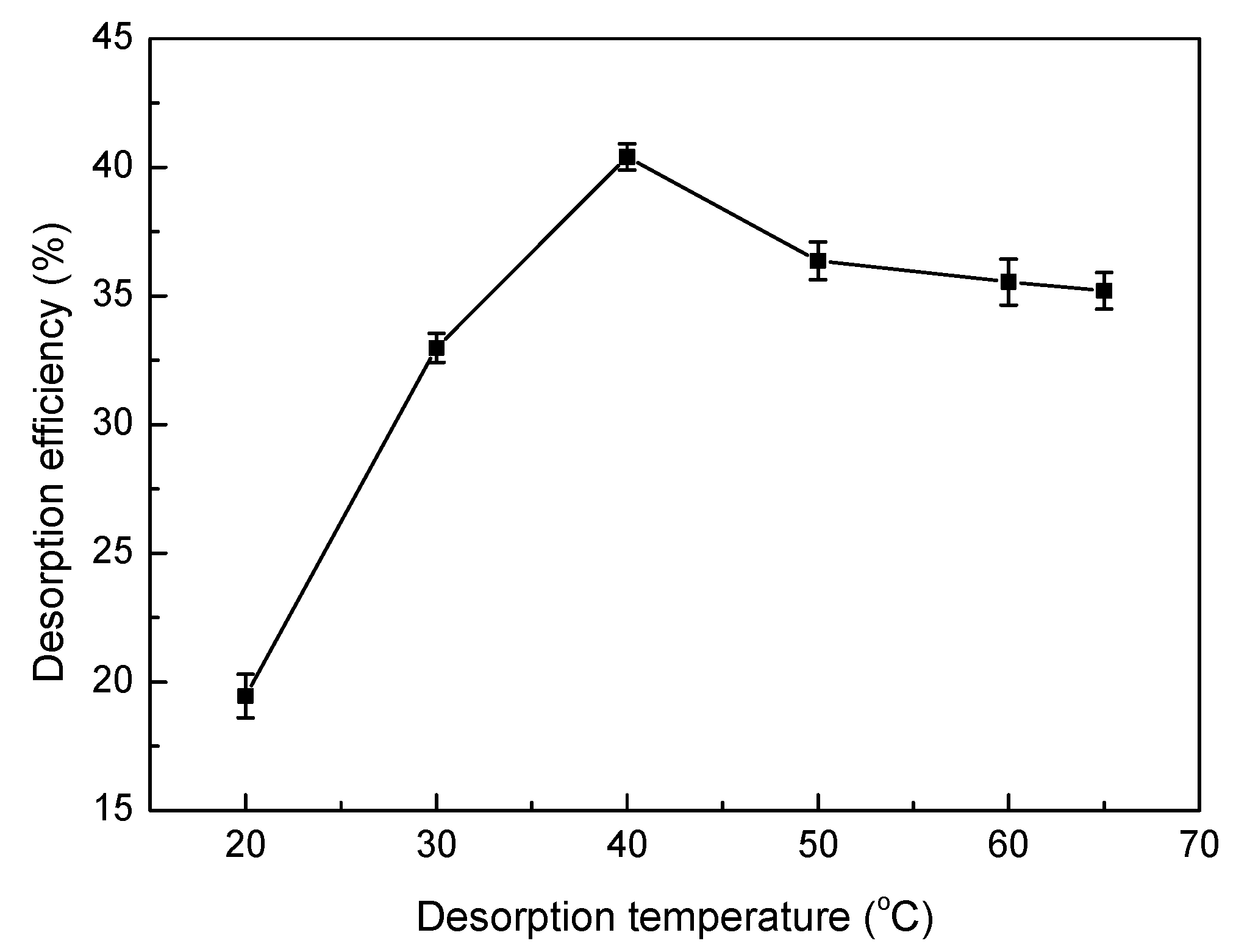
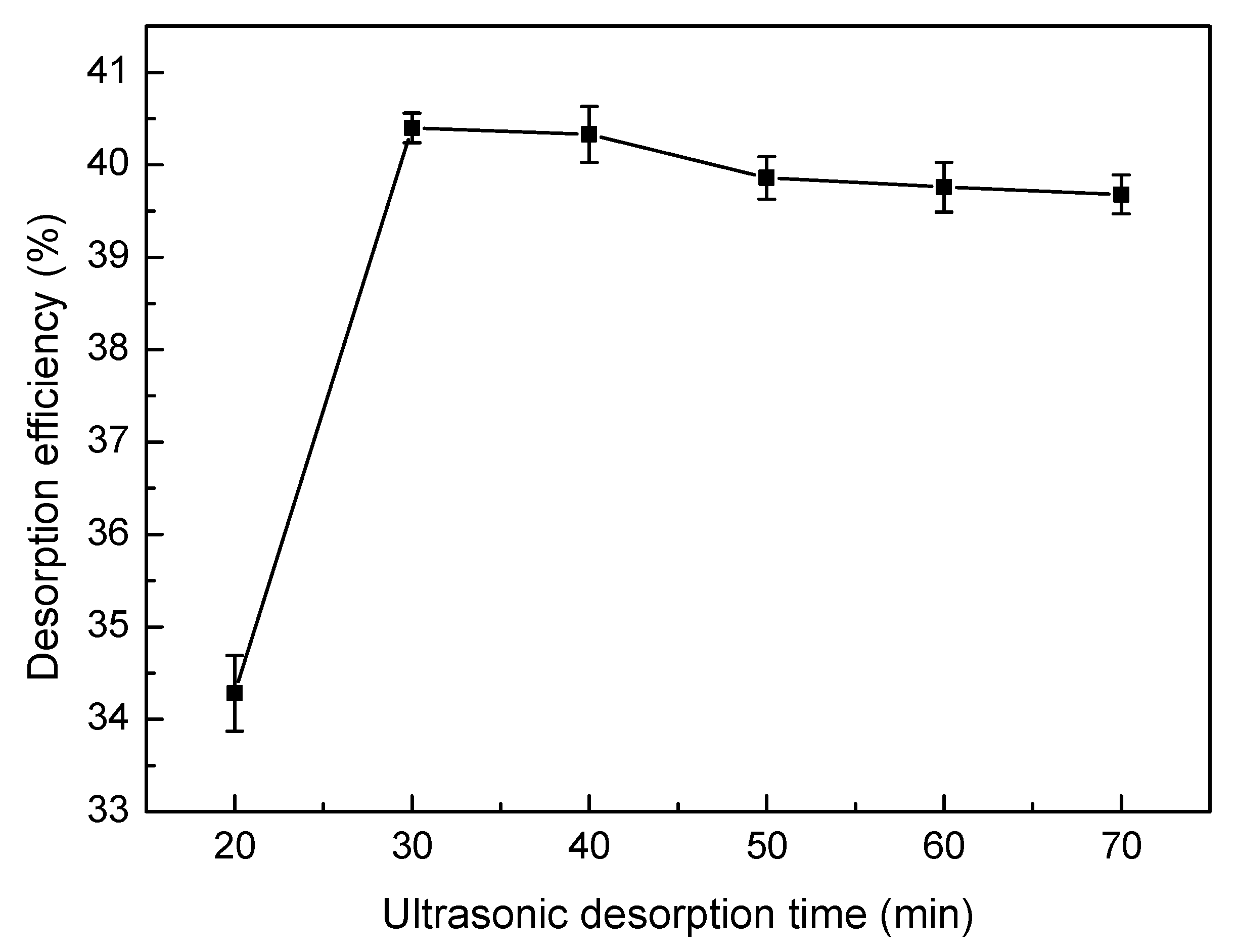
2.6. Desorption and Regeneration Experiments
2.7. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR Analysis of SLT
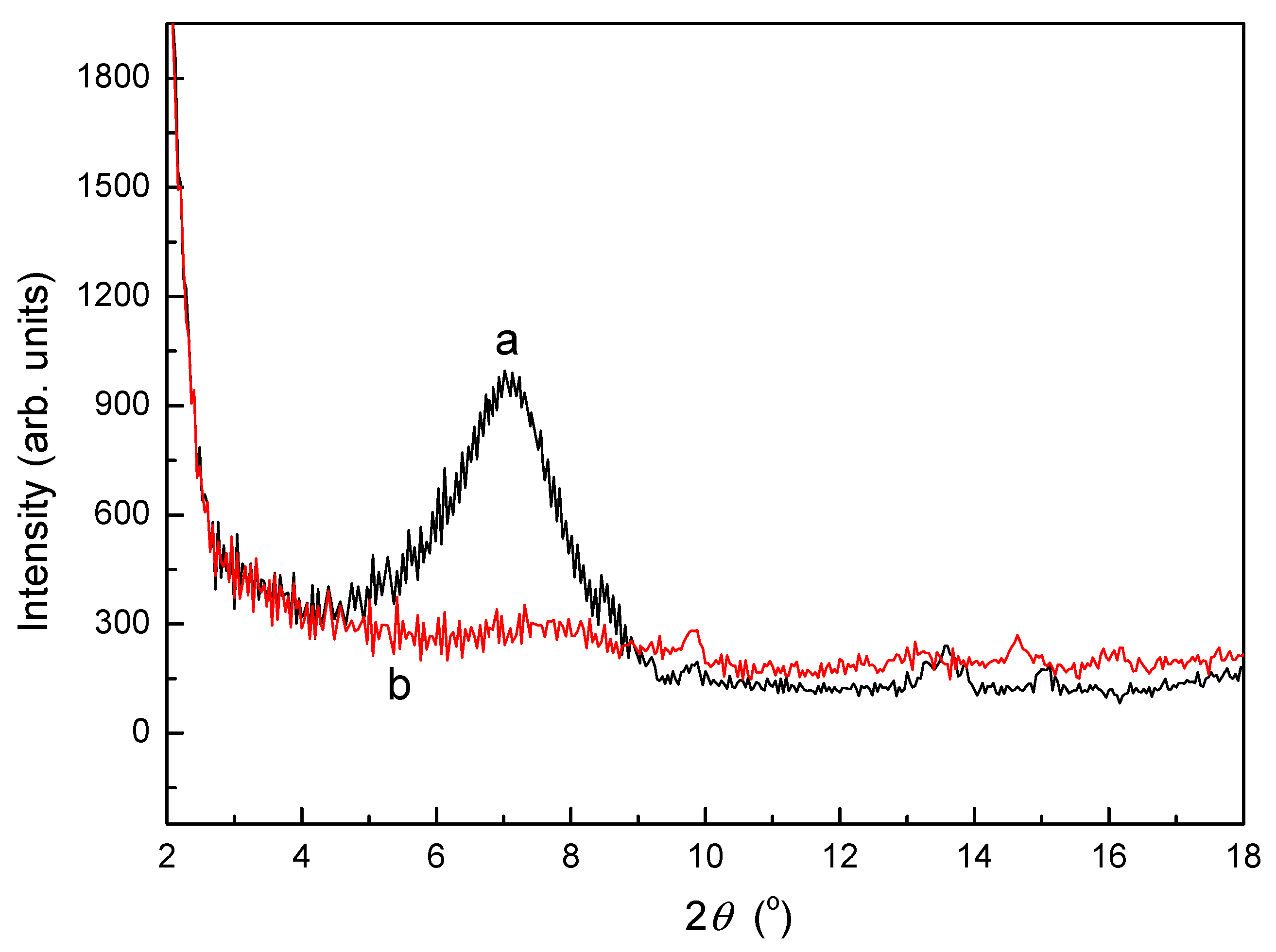
3.2. XRD Analysis of SLT
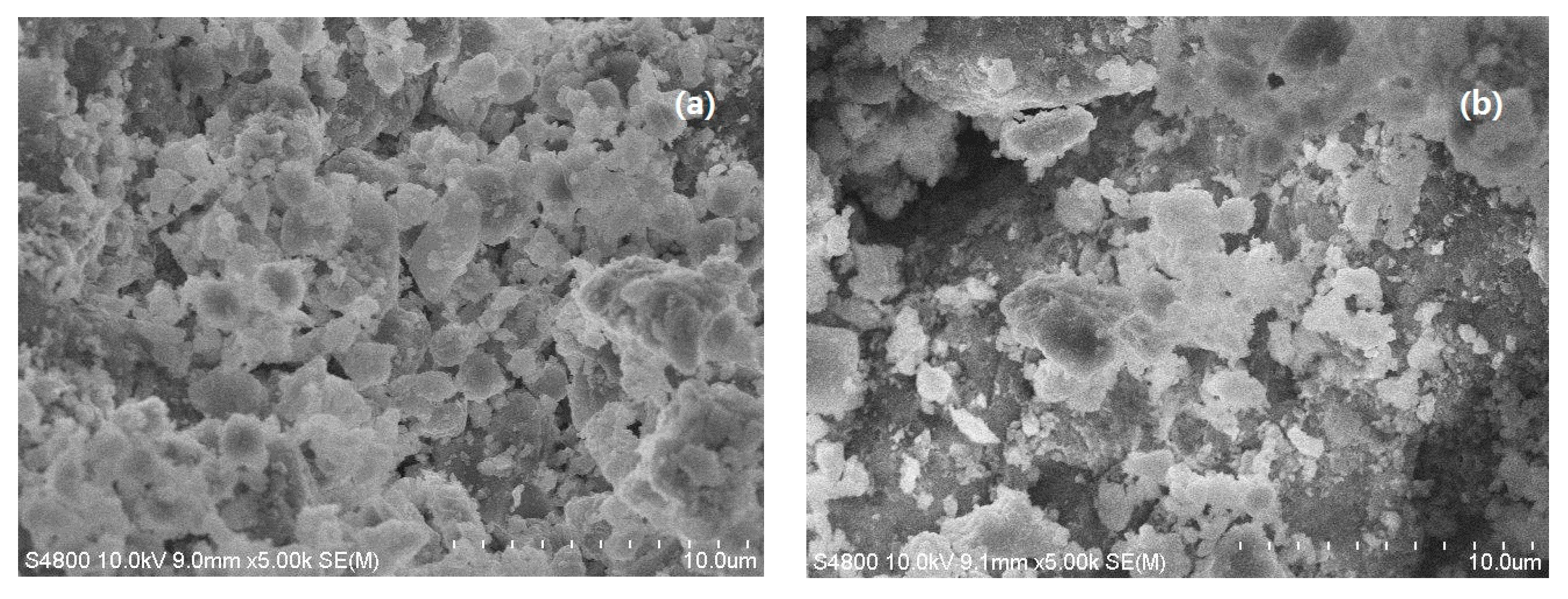
3.3. SEM Analysis of SLT
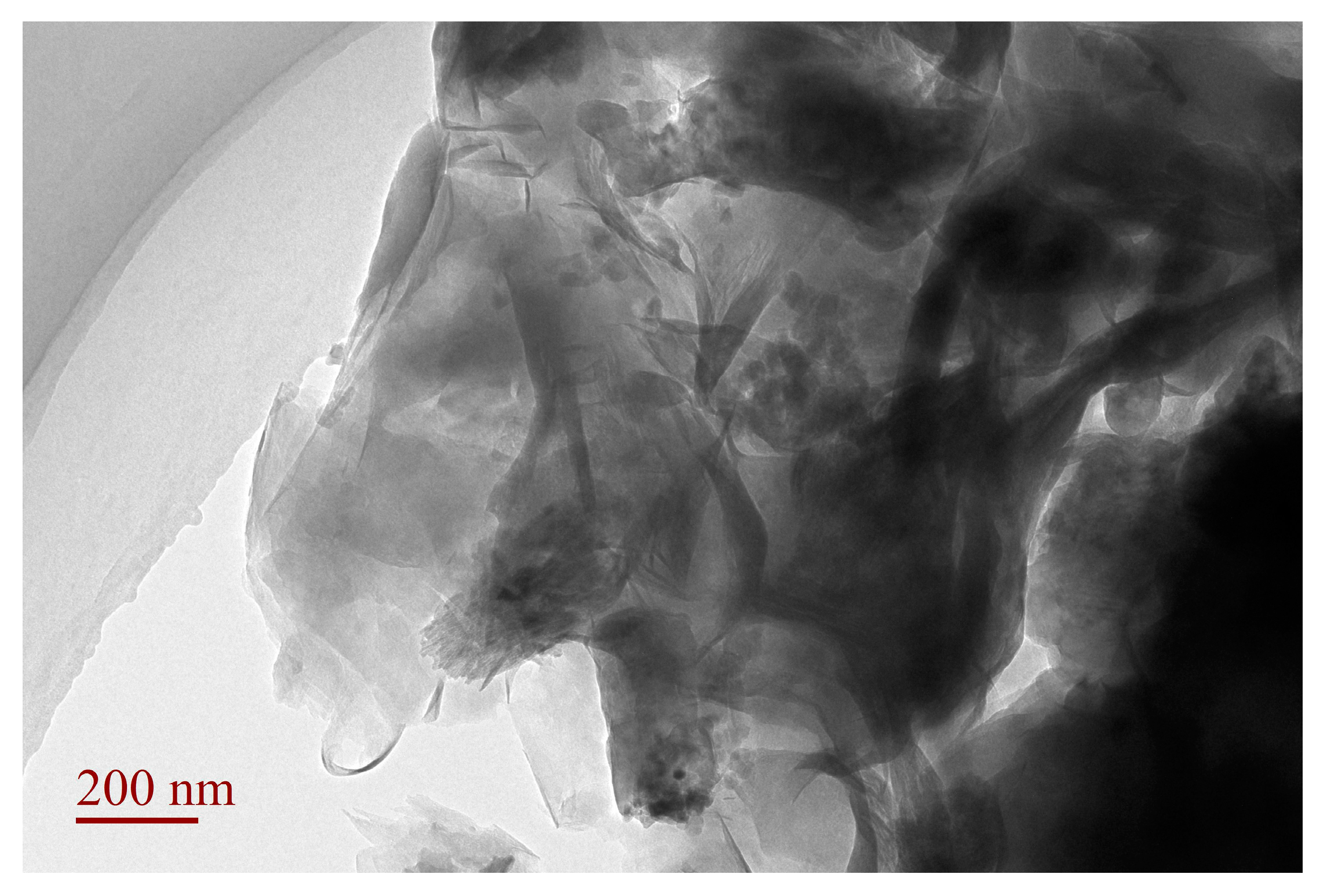
3.4. TEM Analysis of SLT
3.5. Influencing Factors on Ni(II) Adsorption
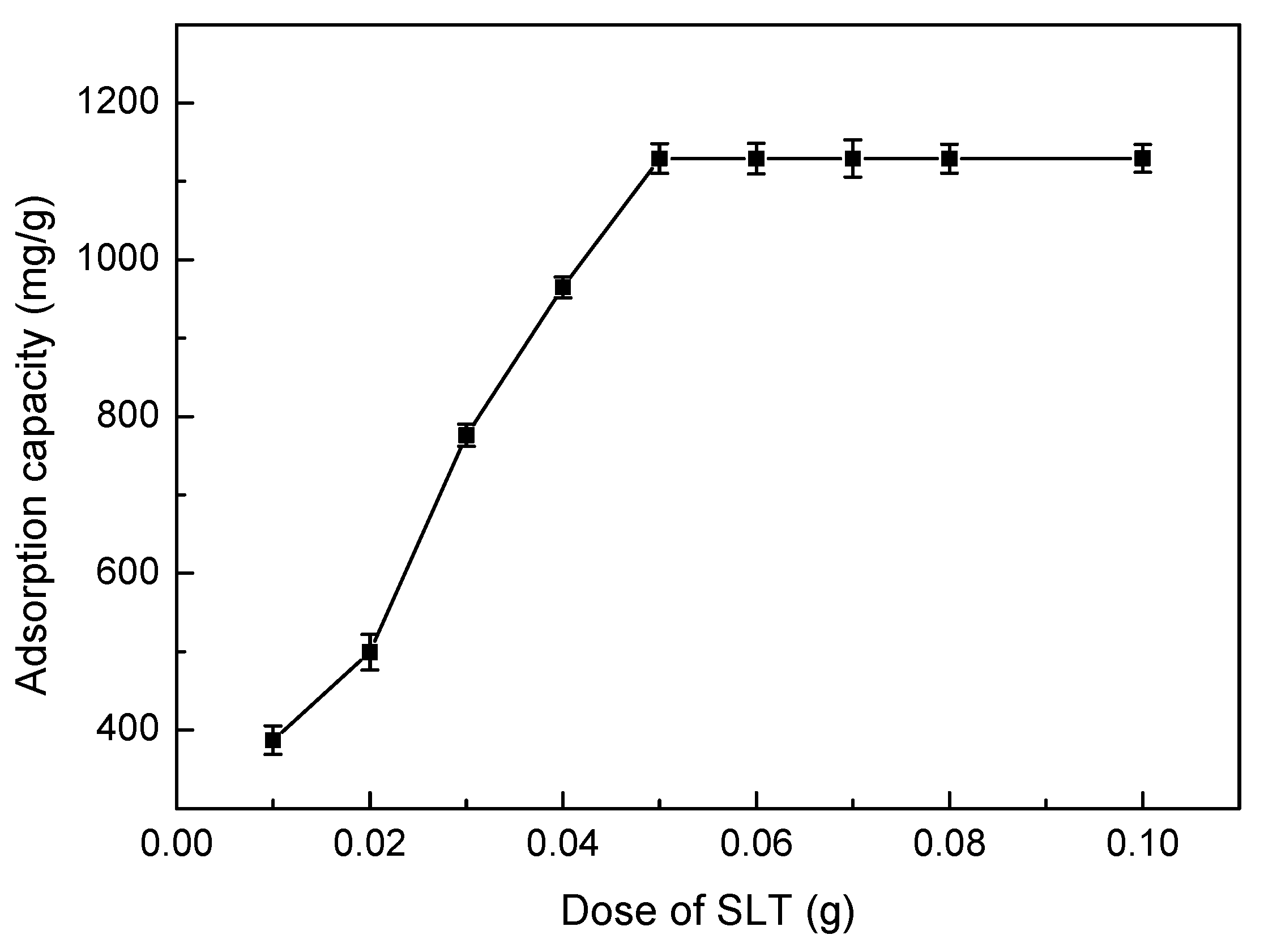
3.5.1. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
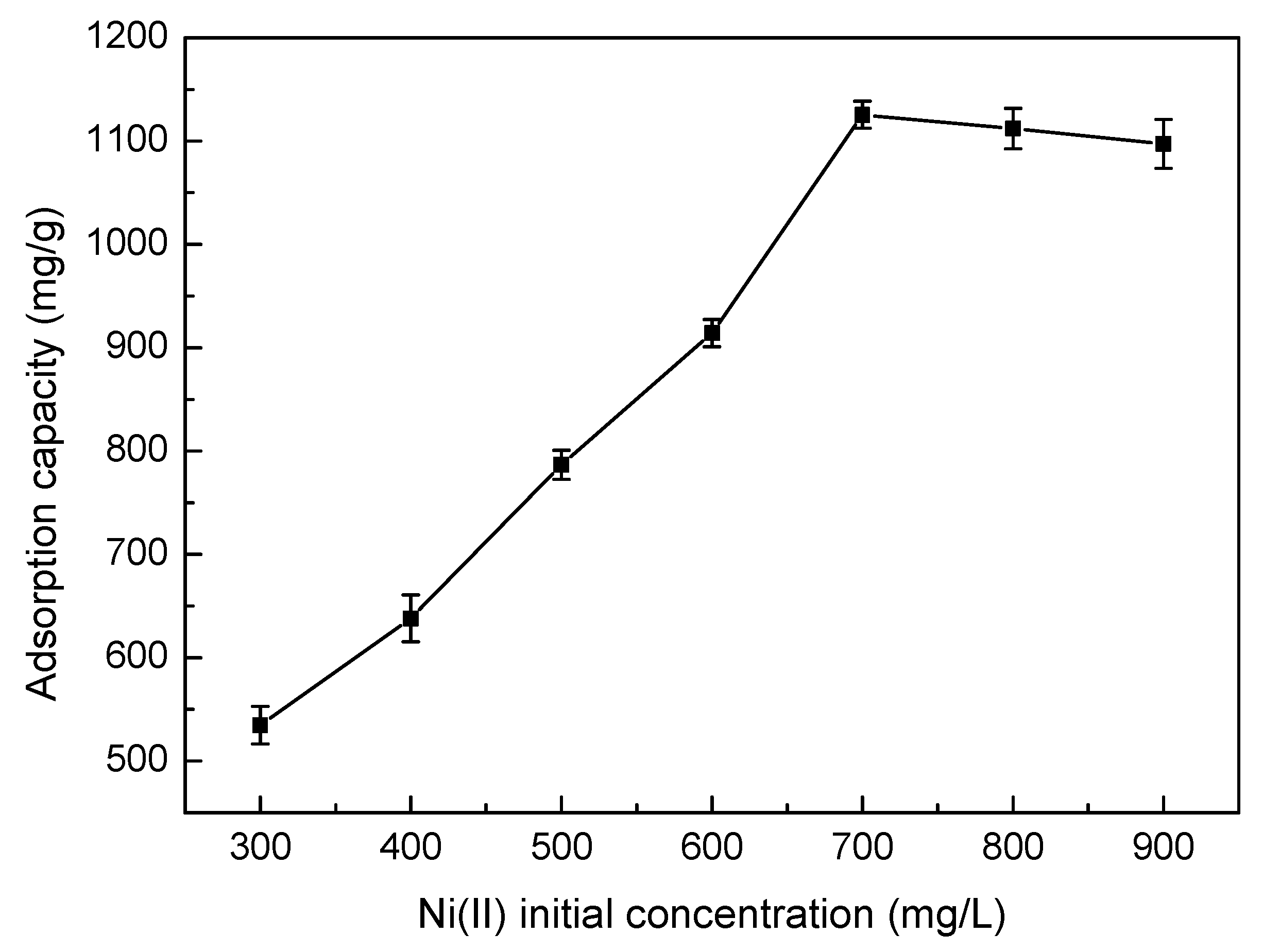
3.5.2. Effect of Ni(II) Initial Concentration
3.5.3. Effect of pH
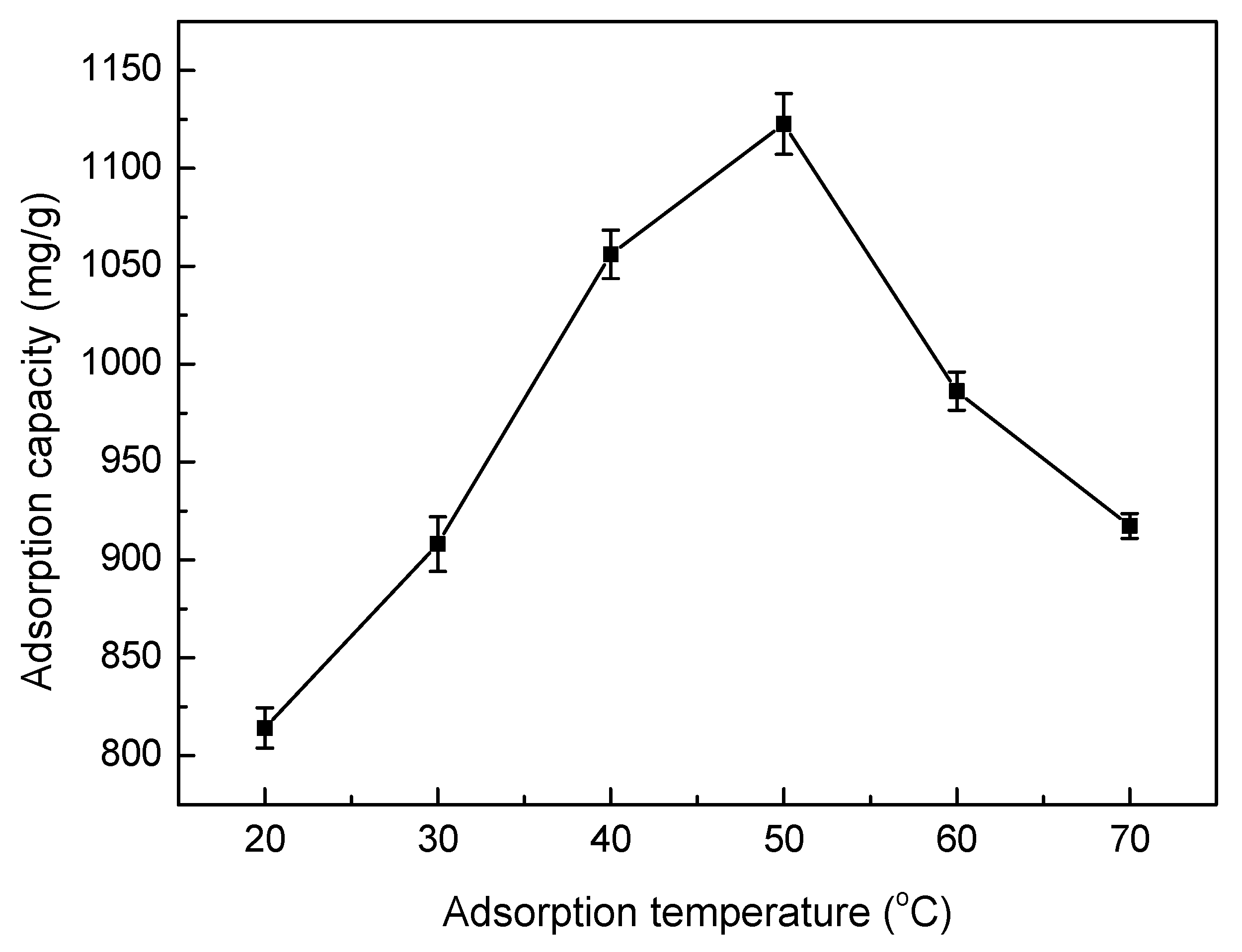
3.5.4. Effect of Adsorption Temperature
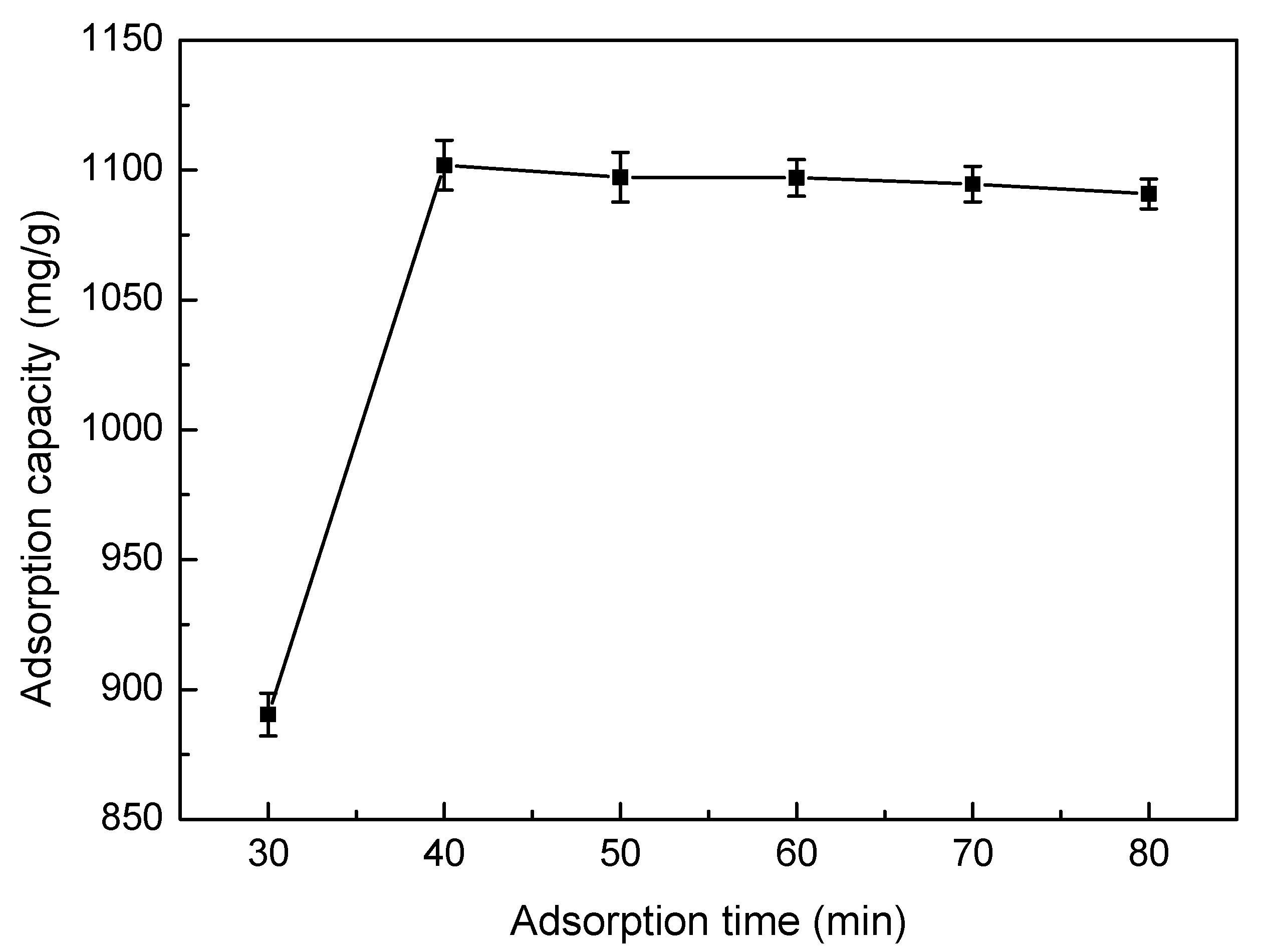
3.5.5. Effect of Adsorption Time
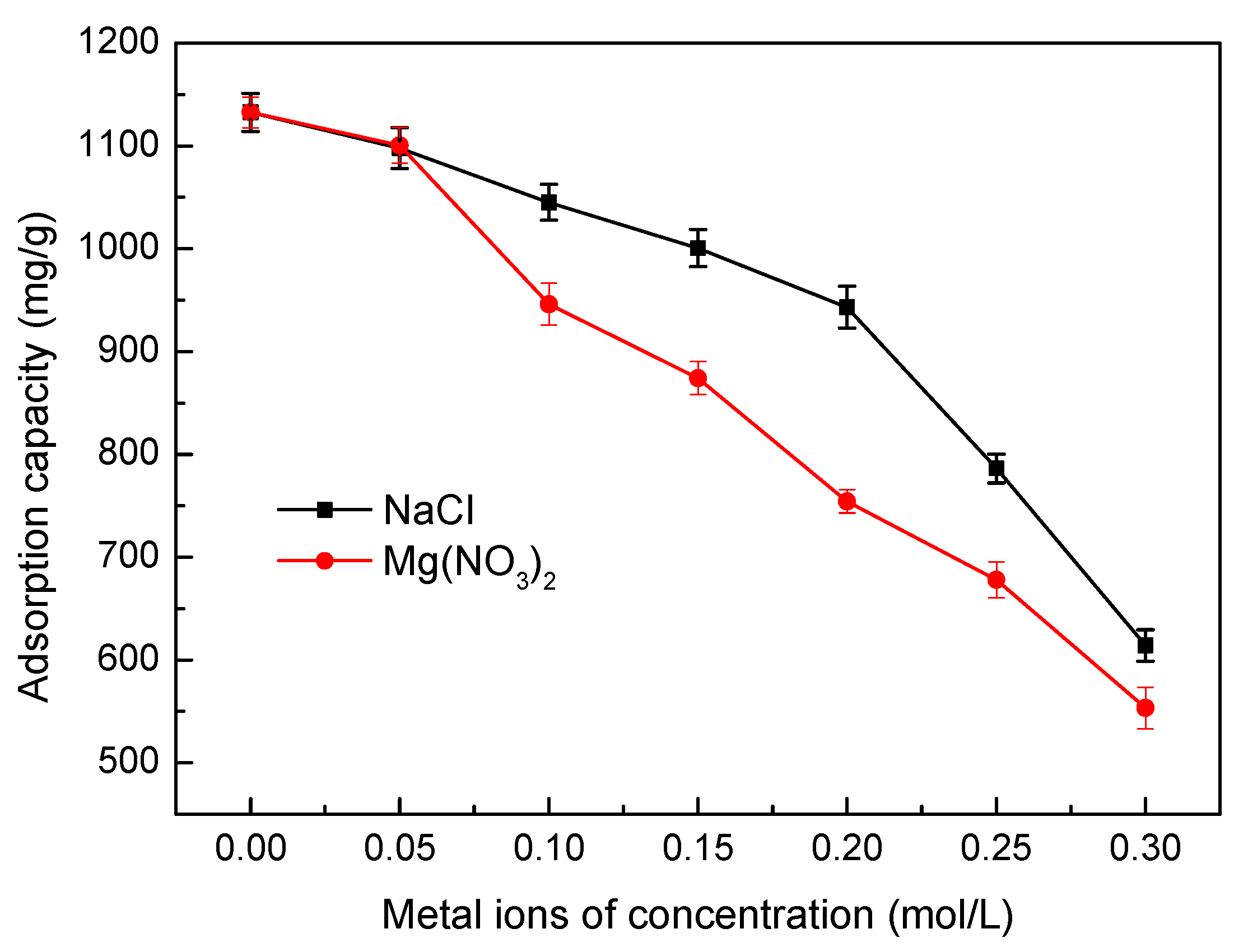
3.5.6. Effect of Ionic Strength
3.6. Adsorption Kinetics
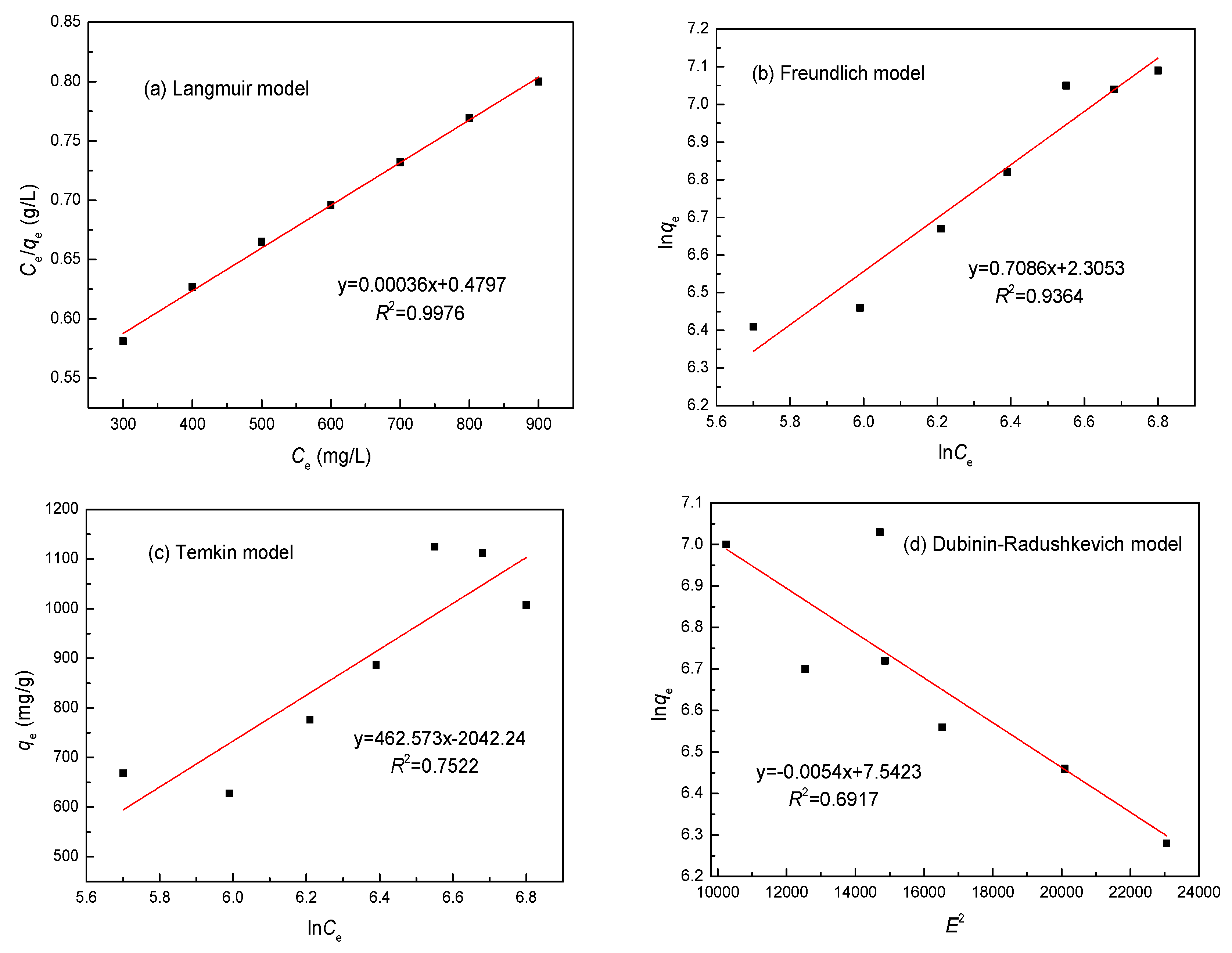
3.7. Adsorption Isotherm
3.8. Desorption and Regeneration
3.9. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ngah, W.S.W.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3935–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febrianto, J.; Kosasih, A.N.; Sunarso, J.; Ju, Y.H.; Indraswati, N.; Ismadji, S. Equilibrium and kinetic studies in adsorption of heavy metals using biosorbent: A summary of recent studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 616–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehaqui, H.; Larraya, U.P.; Liu, P.; Pfenninger, N.; Mathew, A.P.; Zimmermann, T.; Tingaut, P. Enhancing adsorption of heavy metal ions onto biobased nanofibers from waste pulp residues for application in wastewater treatment. Cellulose 2014, 21, 2831–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielczyk, F.; Bartczak, P.; Wieszczycka, K.; Siwinska-Stefanska, K.; Nowacka, M.; Jesionowski, T. Adsorption of Ni(II) from model solutions using co-precipitated inorganic oxides. Adsorption 2013, 19, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, S.; Kumar, S.H.; Jyothi, N.V.V. Rapid removal of Ni(II) from aqueous solution using 3-Mercaptopropionic acid functionalized bio magnetite nanoparticles. Water Resour. Ind. 2015, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Farha, S.A.; Abdel-Aal, A.Y.; Ashourb, I.A.; Garamon, S.E. Removal of some heavy metal cations by synthetic resin purolite C100. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Ooi, B.S. A study on acid reclamation and copper recovery using low pressure nanofiltration membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 56, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Choi, S.S.; Tiwari, D. Simultaneous removal of Hg(II) and phenol using functionalized activated carbon derived from areca nut waste by metals. Materials 2017, 7, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, S.T.; Yetimoglu, Y.; Gedikbey, T. Removal of chromium (VI) ions from aqueous solutions by using Turkish montmorillonite clay: Effect of activation and modification. Desalination 2009, 244, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Tao, X.; Xu, J.; Yin, N. Novel chitosan-MOF composite adsorbent for the removal of heavy metal ions. Chem. Lett. 2016, 45, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgel, L.V.A.; Júnior, O.K.; Gil, R.P.D.F.; Gil, L.F. Adsorption of Cu(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II) from aqueous single metal solutions by cellulose and mercerized cellulose chemically modified with succinic anhydride. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3077–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelgawad, A.M.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Hudson, S.M.; Rojas, O.J. Fabrication and characterization of bactericidal thiol-chitosan and chitosan iodoacetamide nanofibres. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 94, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.L.; Xiong, W.; Xu, Y.F.; Kun, X.; Yang, Q.; Yu, Q.D.; Li, W.N. Removal of trace Cu(II) from aquatic condiment using sulfhydryl lignin. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 554–556, 1979–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.K.; Bolan, N.S.; Lombi, E.; Skinner, W.; Guibal, E. Sulfur-containing chitin and chitosan derivatives as trace metal adsorbents: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 43, 1741–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavilan, K.C.; Pestov, A.V.; Garcia, H.M.; Yatluk, Y.; Roussy, J.; Guibal, E. Mercury sorption on a thiocarbamoyl derivative of chitosan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leodopoulos, C.; Doulia, D.; Gimouhopoulos, K. Study on adsorption behavior of humic acid on acidified montmorillonite: Kinetic and equilibrium modeling, comparison of linear and non-linear methods. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2013, 22, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.T.; Wang, X.M. Adsorption and desorption of Nickel(II) ions from aqueous solution by a lignocellulose/montmorillonite nanocomposite. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, A.Q. Removal of congo red from aqueous solution using a chitosan/organomontmorillonite nanocomposite. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2007, 82, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, M. Application of synthetic layered sodium silicate magadiite nanosheets for environmental remediation of methylene blue dye in water. Materials 2017, 10, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Patra, A.S.; Ghorai, S.; Sarkar, A.K.; Mahato, V.; Sarkar, S.; Singh, R.P. Efficient and rapid adsorption characteristics of templating modified guar gum and silica nanocomposite toward removal of toxic reactive blue and Congo red dyes. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 191, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, K.S.; Filho, E.C.S.; Airoldi, C. Ethylenesulfide as a useful agent for incorporation into the biopolymer chitosan in a solvent-free reaction for use in cation removal. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, S.K.; Bolan, N.; Lombi, E.; Skinner, W. Synthesis and characterization of thiolated chitosan beads for removal of Cu(II) and Cd(II) from wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1720–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadlia, A.; Mohamed, K.; Najah, L.; Farouk, M.M. Preparation and characterization of new succinicanhydride grafted Posidonia for the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1579–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.H.; Kuo, C.Y.; Guan, S.S. Adsorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by waste coffee residues: Kinetics, equilibrium, and thermodynamics. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 5056–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutzenkirchen, J. Ionic strength effects on cation sorption to oxides: Macroscopic observations and their significance in microscopic interpretation. J. Collid Interface Sci. 1997, 195, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudasir, M.; Karelius, K.; Aprilita, N.H.; Wahyuni, E.T. Adsorption of mercury(II) on dithizone-immobilized natural zeolite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.; Lee, S.-M. Surface-functionalized activated sericite for the simultaneous removal of cadmium and phenol from aqueous solutions: Mechanistic insights. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 1414–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokce, Y.; Aktas, Z. Nitric acid modification of activated carbon produced from waste tea and adsorption of methylene blue and phenol. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 313, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasojevic, P.M.; Panic, V.V.; Jovic, M.D.; Markovic, J.; Roost, C.V.; Popovice, I.G.; Velickovice, S.J. Biomimic hybrid polymer networks based on casein and poly(methacrylic acid). Case study: Ni2+ removal. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1680–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G. The kinetics of sorption of divalent metal ions into sphagnum moss peat. Water Res. 2002, 34, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhong, L.L.; Yang, S.W.; Liu, D.X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.S.; Han, X.L.; Zhang, X.M. Adsorption of Ni(II) ion on Ni(II) ion-imprinted magnetic chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladipo, A.A.; Gazi, M. Uptake of Ni2+ and rhodamine B by nano-hydroxyapatite/alginate composite beads: Batch and continuous-flow systems. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2015, 98, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandia, D.; Saha, I.; Ray, S.S.; Maity, A. Development of a reduced-graphene-oxide based superparamagnetic nanocomposite for the removal of nickel(II) from an aqueous medium via a fluorescence sensor platform. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 454, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghani, A.N.; Mahvi, A.H.; Gholami, M.; Rastkari, N.; Delikhoon, M. One-Pot synthesis, characterization and adsorption studies of amine-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles for removal of Cr(VI) and Ni(II) ions from aqueous solution: Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Health Sci. 2016, 14, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare-Dorabei, R.; Ferdowsi, S.M.; Barzin, A.; Tadjarodi, A. Highly efficient simultaneous ultrasonic-assisted adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) ions from aqueous solutions by graphene oxide modified with 2,2′-dipyridylamine: Central composite design optimization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 32, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, C.; Wang, H.; Han, L.; Wang, C.; Jie, X.M.; Chen, Y. Modified adsorbent hydroxypropyl cellulose xanthate for removal of Cu2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solution. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 27419–27431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Li, N.; Wang, W.; Nan, J.; Zhao, Z.W.; Cui, F.Y. Highly efficient removal of bivalent heavy metals from aqueous systems by magnetic porous Fe3O4-MnO2: Adsorption behavior and process study. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, F.F.; Meng, M.J.; Liu, Z.C.; Ni, L.; Zhong, G.X. Synthesis of a Ni(II) ion imprinted polymer based on macroporous-mesoporous silica with enhanced dynamic adsorption capacity: Optimization by response surface methodology. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 3821–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.; Laldanwngliana, C.; Choi, C.-H.; Lee, S.M. Manganese-modified natural sand in the remediation of aquatic environment contaminated with heavy metal toxic ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


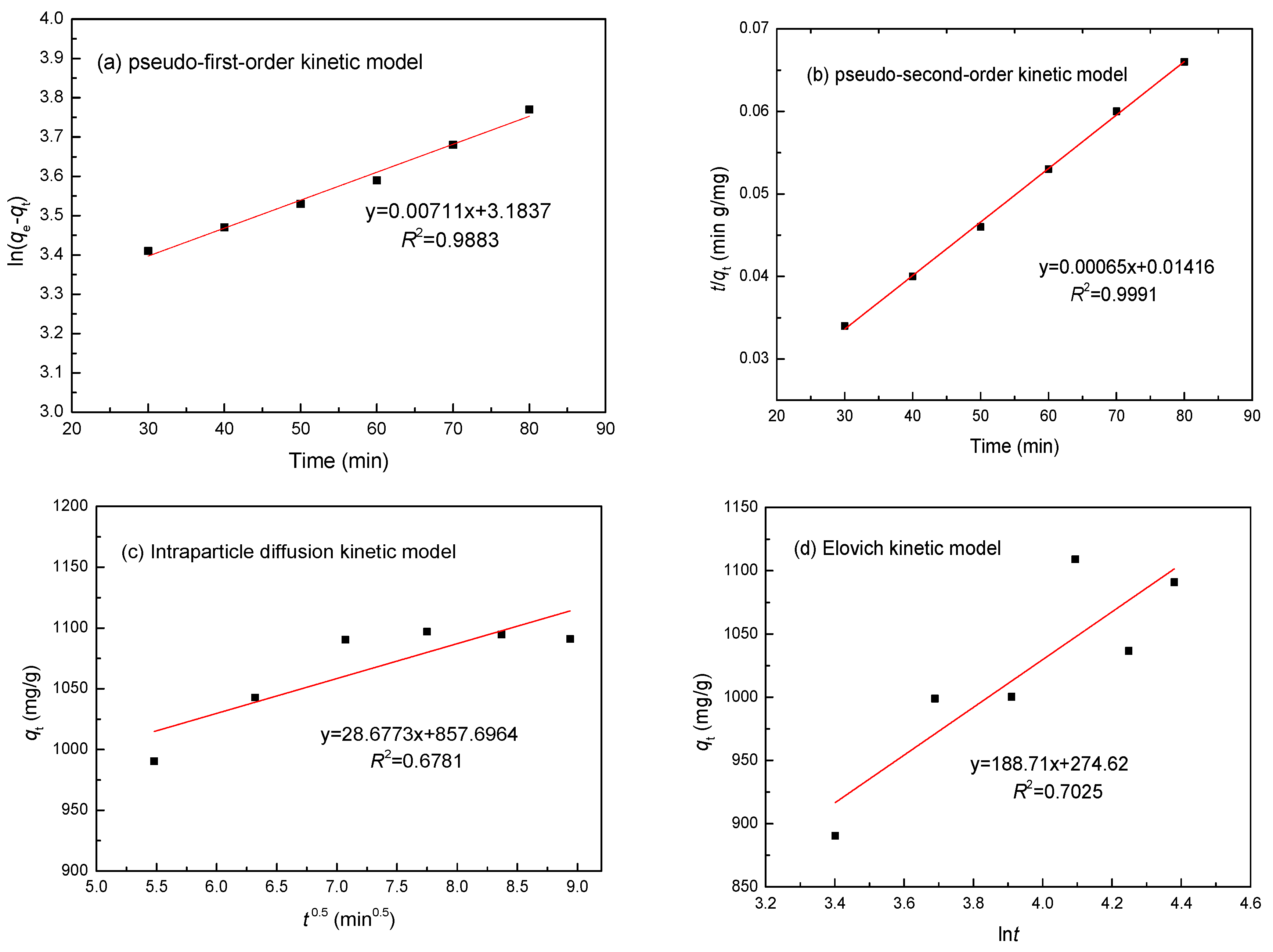



| Metal | Parameters | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | Intraparticle Diffusion | Elovich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni(II) | R2 | 0.9883 | 0.9991 | 0.6781 | 0.7025 | ||||
| Constants | k1 | 0.0059 min−1 | k2 | 0.0779 min−1 | ki | 9.274 mg/(g min0.5) | α | 22.51 mg/(g min) | |
| qe | 943.02 mg/g | qe | 1109.84 mg/g | β | 0.0097 g/mg | ||||
| Metal | Parameters | Langmuir | Freundlich | Temkin | Dubinin–Radushkevichl | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni(II) | R2 | 0.9976 | 0.9364 | 0.7522 | 0.6917 | ||||
| Constants | KL | 0.0173 L/mg | Kf | 90.64 L/g | bt | 40.87 J/mol | B | 1.374 × 10−8 mol2·2 | |
| RL | 0.165 | ||||||||
| qmax | 1120.33 mg/g | 1/n | 0.139 | at | 2.061 × 109 L/g | qmax | 815.32 g/mg | ||
| Adsorbents | qmax (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| SLT nanocomposite | 1134.08 | This paper |
| m-CTS/PVA/Ni(II)s composite | 500 | [31] |
| nano-hydroxyapatite/alginate composite | 360 | [32] |
| GC nanocomposite | 228 | [33] |
| Fe3O4-NH2 nanoparticle | 232.51 | [34] |
| GO-DPA composite | 180.893 | [35] |
| HCX | 114.29 | [36] |
| LNC/MMT | 94.86 | [17] |
| chitosan-MOF composite | 60 | [10] |
| Fe3O4-MnO2 nanoplates | 55.63 | [37] |
| Ni(II)-IIP polymer | 12.96 | [38] |
| Recycle Times | First | Second | Third | Fourth | Fifth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorption qe (mg/g) | 1134.08 | 1104.79 | 1006.51 | 830.65 | 422.13 |
| Desorption qe (mg/g) | 458.21 | 441.06 | 297.23 | 187.91 | 76.04 |
| Desorption Efficiency (%) | 40.40 | 39.92 | 29.53 | 22.62 | 18.01 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z. A Novel Nanocomposite as an Efficient Adsorbent for the Rapid Adsorption of Ni(II) from Aqueous Solution. Materials 2017, 10, 1124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101124
Zhang X, Wang X, Chen Z. A Novel Nanocomposite as an Efficient Adsorbent for the Rapid Adsorption of Ni(II) from Aqueous Solution. Materials. 2017; 10(10):1124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101124
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaotao, Ximing Wang, and Zhangjing Chen. 2017. "A Novel Nanocomposite as an Efficient Adsorbent for the Rapid Adsorption of Ni(II) from Aqueous Solution" Materials 10, no. 10: 1124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101124
APA StyleZhang, X., Wang, X., & Chen, Z. (2017). A Novel Nanocomposite as an Efficient Adsorbent for the Rapid Adsorption of Ni(II) from Aqueous Solution. Materials, 10(10), 1124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101124





