Effects of Liposomes Contained in Thermosensitive Hydrogels as Biomaterials Useful in Neural Tissue Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Rheological Analysis and DSC Measurements
2.1.1. Effect of Chitosan on Pluronic F127
2.1.2. Effect of Size and Composition of Liposomes on Pluronic F127
2.1.3. Effect of Size and Composition of Liposomes on Pluronic F127/Pluronic F127-Chitosan
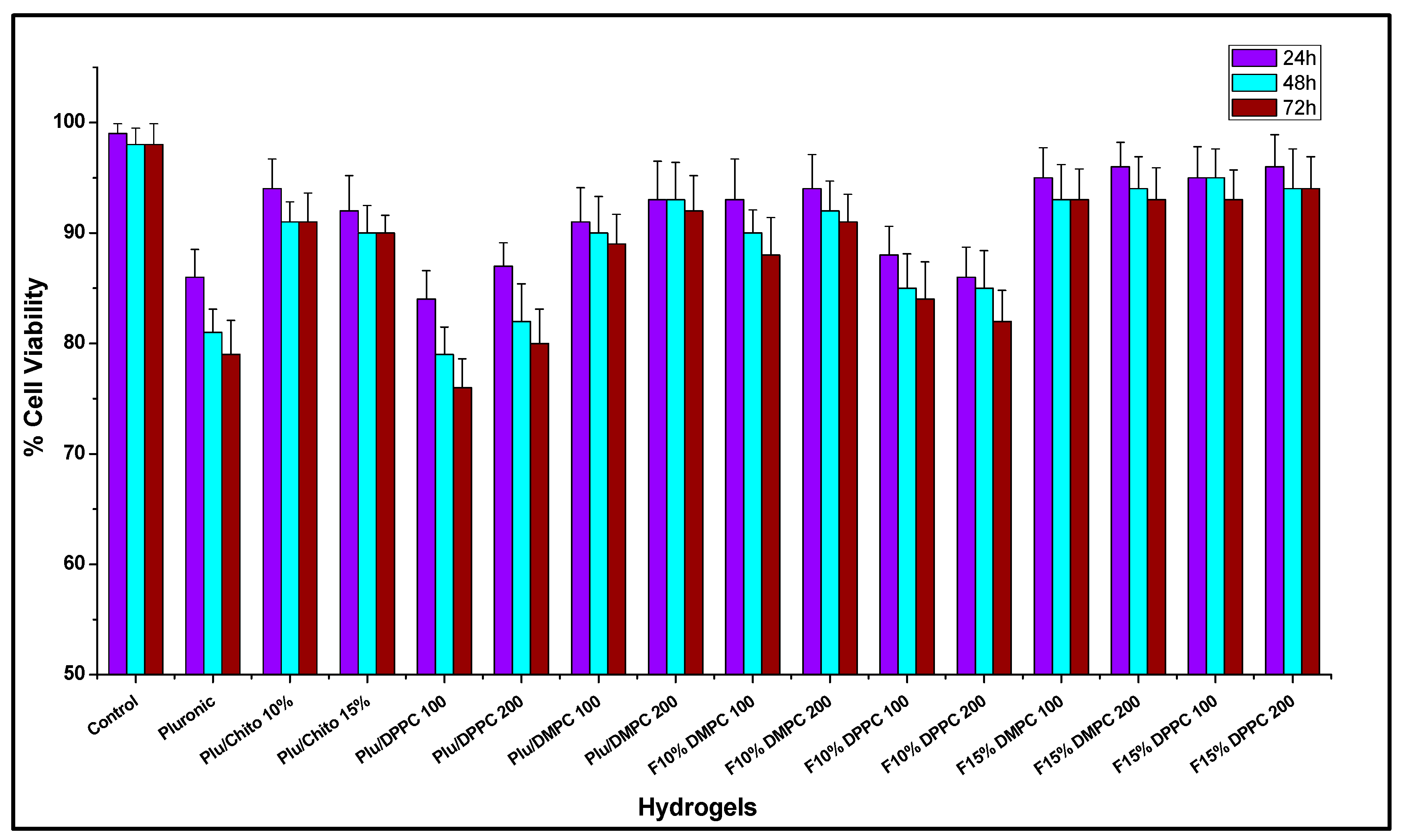
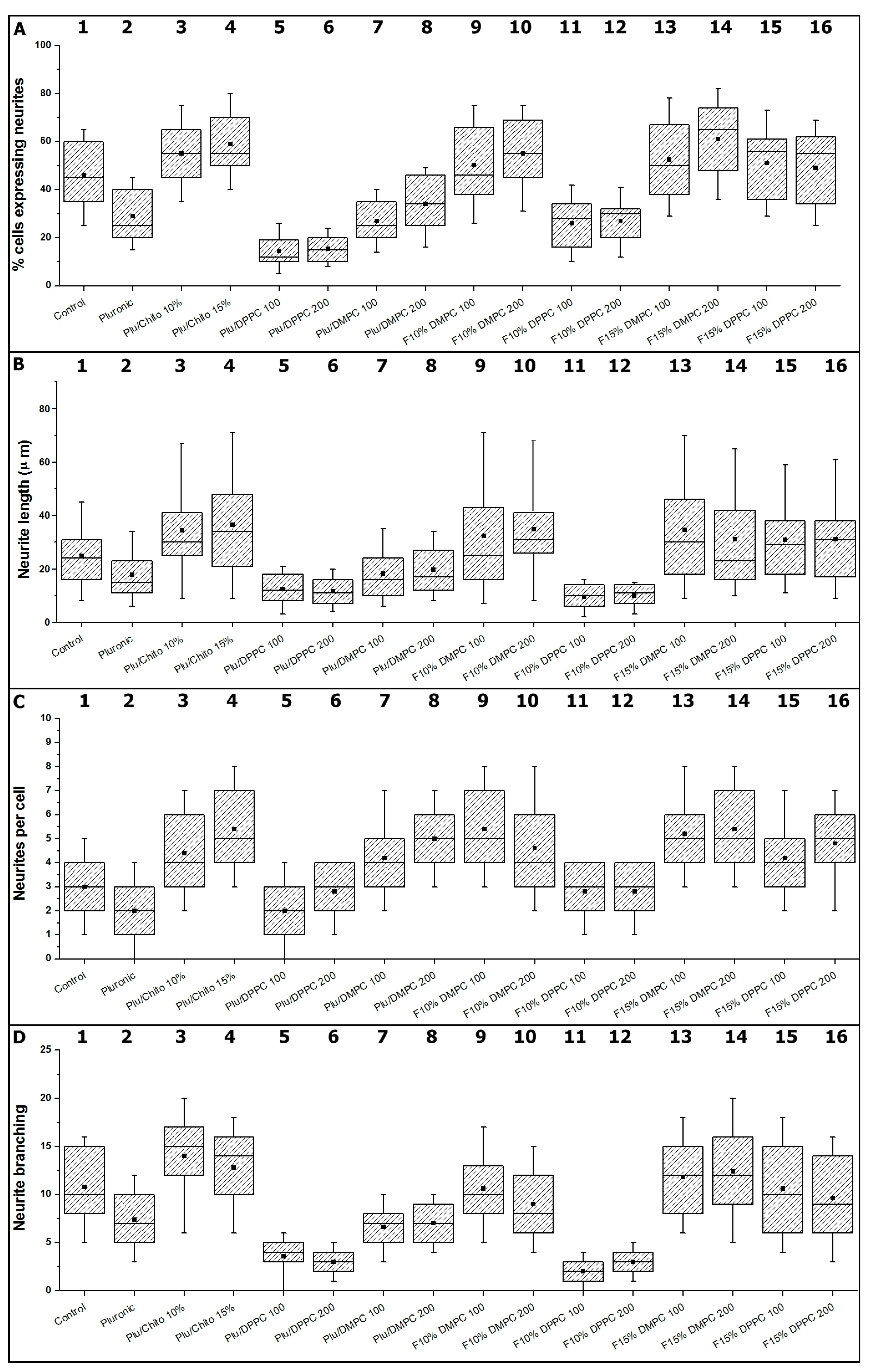
2.2. In Vitro Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Pluronic F127-Chitosan
3.3. Liposome Preparation
3.4. Rheological Analysis of Thermosensitive Hydrogels
3.5. Measurements of Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.6. Culture of PC12 Cells
3.7. Analysis of Viability of PC12 Cells and Neurite Outgrowth on Hydrogels
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphy, A.R.; Laslett, A.; O’Brien, C.M.; Cameron, N.R. Scaffolds for 3d in vitro culture of neural lineage cells. Acta Biomater. 2017, 54, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xie, L.; Lin, W.Z.Y.; Chen, Q. Biomimetic nanofibrous scaffolds for neural tissue engineering and drug development. Drug Dis. Today 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurand, E.R.; Lampe, K.J.; Bjugstad, K.B. Defining and designing polymers and hydrogels for neural tissue engineering. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 72, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, K.; Dinis, T.M.; Taourirt, S.; Vidal, G.; Kaplan, D.L.; Egles, C. Recent strategies in tissue engineering for guided peripheral nerve regeneration. Macromol. Biosci. 2016, 16, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepore, A.C.; Neuhuber, B.; Connors, T.M.; Han, S.S.; Liu, Y.; Daniels, M.P.; Rao, M.S.; Fischer, I. Long-term fate of neural precursor cells following transplantation into developing and adult cns. Neuroscience 2006, 142, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquardt, L.M.; Sakiyama-Elbert, S.E. Engineering peripheral nerve repair. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piccini, P.; Pavese, N.; Hagell, P.; Reimer, J.; Bjorklund, A.; Oertel, W.H.; Quinn, N.P.; Brooks, D.J.; Lindvall, O. Factors affecting the clinical outcome after neural transplantation in parkinson’s disease. Brain 2005, 128, 2977–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.E.; Leach, J.B. Neural tissue engineering: Strategies for repair and regeneration. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 5, 293–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabesh, H.; Amoabediny, G.; Nik, N.S.; Heydari, M.; Yosefifard, M.; Siadat, S.O.; Mottaghy, K. The role of biodegradable engineered scaffolds seeded with schwann cells for spinal cord regeneration. Neurochem. Int. 2009, 54, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet-Maheu, J.M.; Fernandes, J.C.; de Lacerda, C.A.; Shi, Q.; Benderdour, M.; Lavigne, P. Pluronic f-127 as a cell carrier for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Appl. 2009, 24, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilmann, S.; Kuchler, S.; Wischke, C.; Lendlein, A.; Stein, C.; Schafer-Korting, M. A thermosensitive morphine-containing hydrogel for the treatment of large-scale skin wounds. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 444, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruel-Gariepy, E.; Leroux, J.C. In situ-forming hydrogels—Review of temperature-sensitive systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cellesi, F. Thermoresponsive hydrogels for cellular delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2012, 3, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, I.M.; Chen, C.; Xu, X.; Ansari, S.; Zadeh, H.H.; Marques, M.M.; Shi, S.; Moshaverinia, A. Pluronic f-127 hydrogel as a promising scaffold for encapsulation of dental-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinand, C.; Neville, C.M.; Weinberg, E.; Tabata, Y.; Vacanti, J.P. Optimizing biomaterials for tissue engineering human bone using mesenchymal stem cells. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 137, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Atyabi, F.; Dinarvand, R.; Ostad, S.N. Chitosan-pluronic nanoparticles as oral delivery of anticancer gemcitabine: Preparation and in vitro study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.M.P.; Pham, V.P.; Dang, T.M.L.; La, T.H.; Le, T.H.; Le, Q.H. Preparation of curcumin-loaded pluronic f127/chitosan nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 025001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Gilstrap, K.; Wu, L.; Remant Bahadur, K.C.; Moss, M.A.; Wang, Q.; Lu, X.; He, X. Synthesis and characterization of thermally responsive pluronic f127-chitosan nanocapsules for controlled release and intracellular delivery of small molecules. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6747–6759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.M.; Bae, J.W.; Joung, Y.K.; Shin, J.W.; Park, K.D. Nanoaggregate of thermosensitive chitosan-pluronic for sustained release of hydrophobic drug. Colloids and surfaces. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 63, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshosaz, J.; Tabbakhian, M.; Salmani, Z. Designing of a thermosensitive chitosan/poloxamer in situ gel for ocular delivery of ciprofloxacin. Open Drug Deliv. J. 2008, 2, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Go, D.; Bae, J.; Jung, I.; Lee, J.; Park, K. Synthesis and characterization of pluronic® grafted chitosan copolymer as a novel injectable biomaterial. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2005, 5, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Kim, D.; Bae, J.; Joung, Y.; Shin, J.; Park, K. Injectable chitosan-pluronic hydrogel releasing osteogenic protein-1 for the regeneration of intervetebral disc. Biomater. Res. 2008, 12, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Joung, Y.K.; Na, J.S.; Lee, M.C.; Park, K.D. Thermosensitive chitosan-pluronic hydrogel as an injectable cell delivery carrier for cartilage regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grijalvo, S.; Mayr, J.; Eritja, R.; Diaz, D.D. Biodegradable liposome-encapsulated hydrogels for biomedical applications: A marriage of convenience. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 555–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battista, S.; Guarnieri, D.; Borselli, C.; Zeppetelli, S.; Borzacchiello, A.; Mayol, L.; Gerbasio, D.; Keene, D.R.; Ambrosio, L.; Netti, P.A. The effect of matrix composition of 3d constructs on embryonic stem cell differentiation. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6194–6207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertassoni, L.E.; Cecconi, M.; Manoharan, V.; Nikkhah, M.; Hjortnaes, J.; Cristino, A.L.; Barabaschi, G.; Demarchi, D.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Yang, Y.; et al. Hydrogel bioprinted microchannel networks for vascularization of tissue engineering constructs. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2202–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamour, G.; Journiac, N.; Soues, S.; Bonneau, S.; Nassoy, P.; Hamraoui, A. Influence of surface energy distribution on neuritogenesis. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 72, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skop, N.B.; Calderon, F.; Cho, C.H.; Gandhi, C.D.; Levison, S.W. Improvements in biomaterial matrices for neural precursor cell transplantation. Mol. Cell. Ther. 2014, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soman, P.; Tobe, B.T.; Lee, J.W.; Winquist, A.A.; Singec, I.; Vecchio, K.S.; Snyder, E.Y.; Chen, S. Three-dimensional scaffolding to investigate neuronal derivatives of human embryonic stem cells. Biomed. Microdevices 2012, 14, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Ao, Q.; Gong, K.; Wang, A.; Zheng, L.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, X. The effect of topology of chitosan biomaterials on the differentiation and proliferation of neural stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3630–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamour, G.; Eftekhari-Bafrooei, A.; Borguet, E.; Soues, S.; Hamraoui, A. Neuronal adhesion and differentiation driven by nanoscale surface free-energy gradients. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3762–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monticelli, F.; Preiss, U.; Hitzl, W.; Keller, T. Pupil function as an indicator of being under the influence of central nervous system-acting substances from a traffic-medicine perspective—Part II. Med. Sci. Law 2016, 56, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.P.; Freudenrich, T.M.; Mundy, W.R. Assessment of pc12 cell differentiation and neurite growth: A comparison of morphological and neurochemical measures. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2004, 26, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, L. Multiple phase transition and scaling law for poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide)-poly(ethylene oxide) triblock copolymer in aqueous solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 2688–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Du, Y.; Hu, X.; Shi, X.; Kennedy, J. Rheological characterisation of a novel thermosensitive chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend hydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 67, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, J. Conformational structure of triblock copolymers by ft-raman and ftir spectroscopy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 209, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, H.W.; Hsu, Y.H.; Wang, J.H.; Chen, L.J. Novel behavior of heat of micellization of pluronics f68 and f88 in aqueous solutions. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2008, 24, 13858–13862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, J.; Kumar, S.; Nath, S.; Ganguly, R.; Aswal, V.K.; Ismail, K. Additive induced core and corona specific dehydration and ensuing growth and interaction of pluronic f127 micelles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 415, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artzner, F.; Geiger, S.; Olivier, A.; Allais, C.; Finet, S.; Agnely, F. Interactions between poloxamers in aqueous solutions: Micellization and gelation studied by differential scanning calorimetry, small angle x-ray scattering, and rheology. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2007, 23, 5085–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kamel, A.H. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of pluronic f127-based ocular delivery system for timolol maleate. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 241, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.S.; Choi, J.S.; Quan, Q.Z.; Rhee, J.D.; Kim, C.K.; Lim, S.J.; Kim, K.M.; Oh, P.S.; Choi, H.G. Effect of sodium chloride on the gelation temperature, gel strength and bioadhesive force of poloxamer gels containing diclofenac sodium. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 226, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Rezaei-Sadabady, R.; Davaran, S.; Joo, S.W.; Zarghami, N.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Samiei, M.; Kouhi, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K. Liposome: Classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frezard, F. Liposomes: From biophysics to the design of peptide vaccines. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1999, 32, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, D.C.; Meyer, O.; Hong, K.; Kirpotin, D.B.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Optimizing liposomes for delivery of chemotherapeutic agents to solid tumors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 691–743. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, N.; Martins, A.; Reis, R.L.; Neves, N.M. Liposomes in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, S.; Hsiao, W.L.; Pan, W.; Yang, Z. Thermoreversible pluronic f127-based hydrogel containing liposomes for the controlled delivery of paclitaxel: In vitro drug release, cell cytotoxicity, and uptake studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 151–166. [Google Scholar]
- Pradines, B.; Djabourov, M.; Vauthier, C.; Loiseau, P.M.; Ponchel, G.; Bouchemal, K. Gelation and micellization behaviors of pluronic((r)) f127 hydrogel containing poly(isobutylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles specifically designed for mucosal application. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Bhatia, S.R. Effect of anti-inflammatories on pluronic f127: Micellar assembly, gelation and partitioning. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 278, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.H.; Park, K.; Han, D.K. Preparation of tgf-beta1-conjugated biodegradable pluronic f127 hydrogel and its application with adipose-derived stem cells. J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoni, D.; Burckel, H.; Josset, E.; Noel, G. Three-dimensional cell culture: A breakthrough in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 5517–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadri, S.; Khazaei, M.; Ghanbari, A.; Khazaei, M.R.; Shah, P. Neuronal differentiation of pc12 and embryonic stem cells in two- and three-dimensional in vitro culture. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 52, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Krishnan, U.M.; Sethuraman, S. Development of biomaterial scaffold for nerve tissue engineering: Biomaterial mediated neural regeneration. J. Biomed. Sci. 2009, 16, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.Z.; Jiang, X.; Xiao, J.; Lin, Q.; Yu, W.Z.; Tian, F.R.; Mao, K.L.; Yang, W.; Wong, H.L.; Lu, C.T. Using ngf heparin-poloxamer thermosensitive hydrogels to enhance the nerve regeneration for spinal cord injury. Acta Biomater. 2016, 29, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Jo, S.; Shin, E.; Kim, D.; Noh, I. Evaluations of nerve cell compatibility of self cross-linking chitosan-poly(ethylene oxide) hydrogel. Tissue Eng. Regener. Med. 2012, 9, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickett, T.A.; Amoozgar, Z.; Tuchek, C.A.; Park, J.; Yeo, Y.; Shi, R. Rapidly photo-cross-linkable chitosan hydrogel for peripheral neurosurgeries. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.L.; Tian, F.R.; Lu, C.T.; Xu, J.; Fan, Z.L.; Yang, J.J.; Chen, P.P.; Huang, Y.D.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, Y.Z. Thermo-sensitive hydrogels combined with decellularised matrix deliver bfgf for the functional recovery of rats after a spinal cord injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.K.; Cho, K.Y.; Song, H.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kwon, J.W.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Wee, W.R.; Cho, C.S. Release of ciprofloxacin from chondroitin 6-sulfate-graft-poloxamer hydrogel in vitro for ophthalmic drug delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2005, 31, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Shankarappa, S.A.; Chang, H.H.; Tong, R.; Kohane, D.S. Biodegradable mesostructured polymer membranes. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 4410–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; He, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, H.; Lin, Q.; He, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; et al. A thermosensitive heparin-poloxamer hydrogel bridges afgf to treat spinal cord injury. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 6725–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudry, D.; Stork, P.J.; Lazarovici, P.; Eiden, L.E. Signaling pathways for pc12 cell differentiation: Making the right connections. Science 2002, 296, 1648–1649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flores-Merino, M.V.; Chirasatitsin, S.; Lopresti, C.; Reilly, G.C.; Battaglia, G.; Engler, A.J. Nanoscopic mechanical anisotropy in hydrogel surfaces. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 4466–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, J.D.; Grunwald, E.W.; Nealey, P.F.; Murphy, C.J. Cooperative modulation of neuritogenesis by pc12 cells by topography and nerve growth factor. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3639–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.R.; Garcia, A.J. Cellular mechanotransduction: Sensing rigidity. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 539–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balgude, A.P.; Yu, X.; Szymanski, A.; Bellamkonda, R.V. Agarose gel stiffness determines rate of drg neurite extension in 3D cultures. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, J.W.; Turner, S.D.; Mann, B.K. Adhesive and mechanical properties of hydrogels influence neurite extension. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2005, 72, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, T.W.; DiMilla, P.A. Spreading and motility of human glioblastoma cells on sheets of silicone rubber depend on substratum compliance. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2000, 38, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willits, R.K.; Skornia, S.L. Effect of collagen gel stiffness on neurite extension. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2004, 15, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leach, J.B.; Brown, X.Q.; Jacot, J.G.; Dimilla, P.A.; Wong, J.Y. Neurite outgrowth and branching of pc12 cells on very soft substrates sharply decreases below a threshold of substrate rigidity. J. Neural Eng. 2007, 4, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.-H.; Yang, J.; Li, B.; Jiang, Y.-W.; Lu, X.; Chen, Z. Biodegradable and injectable polymer–liposome hydrogel: A promising cell carrier. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 2037–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charras, G.; Sahai, E. Physical influences of the extracellular environment on cell migration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, A.; Kumar, S. Transforming potential and matrix stiffness co-regulate confinement sensitivity of tumor cell migration. Integr. Biol. 2013, 5, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Kechai, N.; Bochot, A.; Huang, N.; Nguyen, Y.; Ferrary, E.; Agnely, F. Effect of liposomes on rheological and syringeability properties of hyaluronic acid hydrogels intended for local injection of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 487, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourtas, S.; Aggelopoulos, C.A.; Klepetsanis, P.; Tsakiroglou, C.D.; Antimisiaris, S.G. Complex hydrogel systems composed of polymers, liposomes, and cyclodextrins: Implications of composition on rheological properties and aging. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2009, 25, 8480–8488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourtas, S.; Haikou, M.; Theodoropoulou, M.; Tsakiroglou, C.; Antimisiaris, S.G. The effect of added liposomes on the rheological properties of a hydrogel: A systematic study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 317, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.; Chung, T.; Kim, B.; Kim, M.; Lee, L.; Wee, W.; Cho, C. Release of ciprofloxacin from poloxamer-graft-hyaluronic acid hydrogels in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 260, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguin, Y.; Carrascosa, L.G.; Lechuga, L.M.; Young, M. The effects of lipids and surfactants on tlr5-proteoliposome functionality for flagellin detection using surface plasmon resonance biosensing. Talanta 2014, 126, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olguin, Y.; Villalobos, P.; Carrascosa, L.G.; Young, M.; Valdez, E.; Lechuga, L.; Galindo, R. Detection of flagellin by interaction with human recombinant tlr5 immobilized in liposomes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bercea, M.; Darie, R.; Niţă, L.; Morariu, S. Temperature responsive gels based on pluronic f127 and poly(vinyl alcohol). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

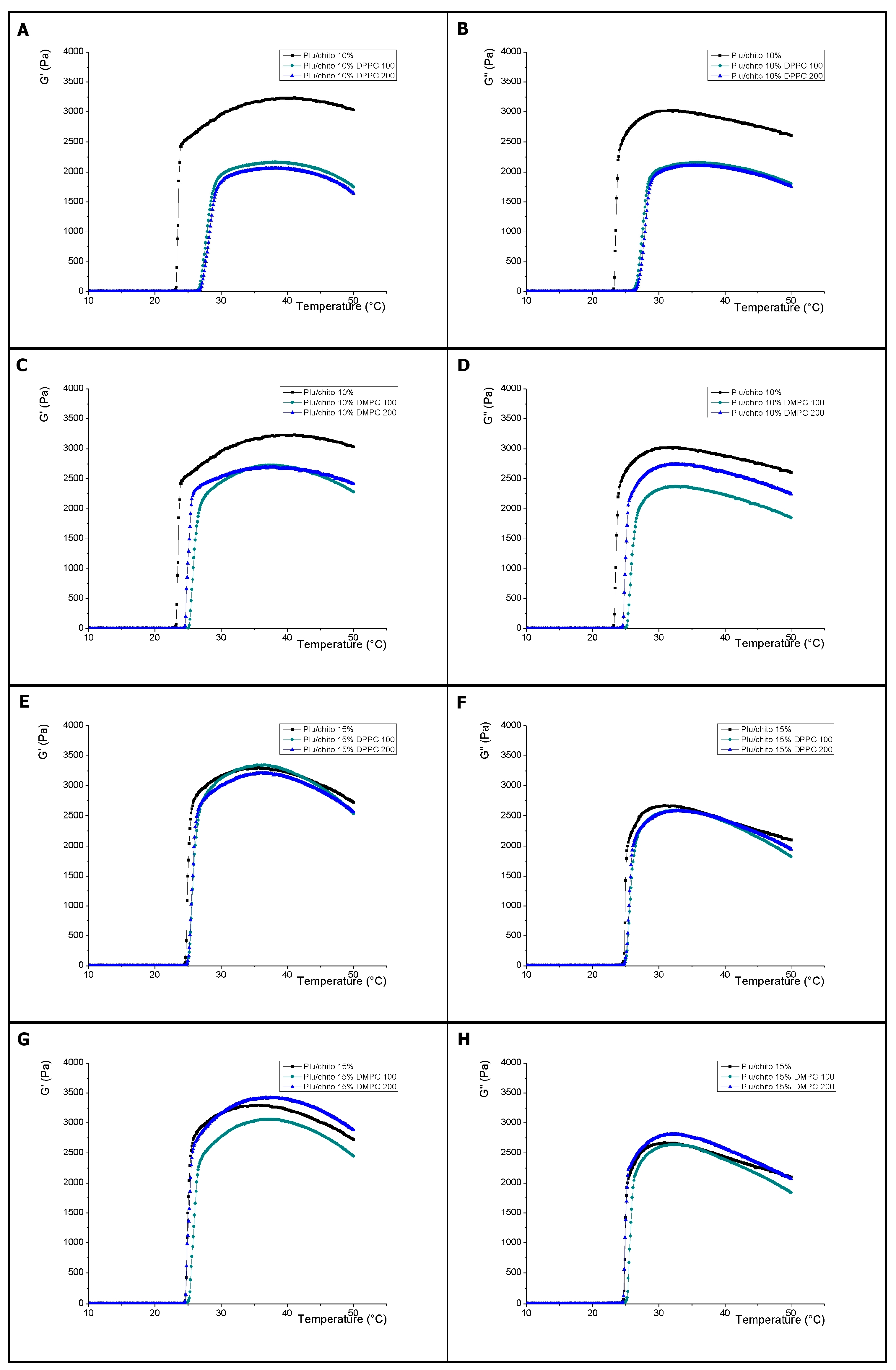


| Sample | G′ = G″ (°C) | SD (±) | G′ 37 °C (Pa) | SD (±) | G″ 37 °C (Pa) | SD (±) | tanδ 37 °C | SD (±) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pluronic F127 control | 25.62 | 0.37 | 1798 | 103 | 2346 | 28 | 1.299 | 0.272 |
| PLU/CHITO 10% | 23.89 | 0.29 | 3189 | 106 | 2944 | 28 | 0.917 | 0.264 |
| PLU/CHITO 15% | 24.57 | 0.33 | 3297 | 143 | 2536 | 35 | 0.772 | 0.245 |
| PLU DPPC 100 | 28.41 | 0.26 | 1545 | 121 | 1781 | 27 | 1.153 | 0.223 |
| PLU DPPC 200 | 28.38 | 0.31 | 1674 | 106 | 1859 | 31 | 1.111 | 0.292 |
| PLU DMPC 100 | 24.73 | 0.52 | 2526 | 133 | 2526 | 34 | 0.979 | 0.256 |
| PLU DMPC 200 | 24.62 | 0.43 | 2651 | 145 | 2561 | 42 | 0.981 | 0.29 |
| PLU/CHITO 10% DPPC 100 | 28.57 | 0.49 | 2156 | 128 | 2144 | 36 | 0.995 | 0.281 |
| PLU/CHITO 10% DPPC 200 | 28.71 | 0.63 | 2059 | 143 | 2097 | 41 | 1.021 | 0.287 |
| PLU/CHITO 10% DMPC 100 | 26.89 | 0.38 | 2725 | 166 | 2303 | 37 | 0.844 | 0.223 |
| PLU/CHITO 10% DMPC 200 | 26.68 | 0.42 | 2690 | 139 | 2677 | 38 | 0.995 | 0.273 |
| PLU/CHITO 15% DPPC 100 | 25.04 | 0.25 | 3339 | 146 | 2517 | 30 | 0.754 | 0.205 |
| PLU/CHITO 15% DPPC 200 | 25.13 | 0.27 | 3206 | 172 | 2514 | 42 | 0.784 | 0.244 |
| PLU/CHITO 15% DMPC 100 | 25.36 | 0.23 | 3061 | 137 | 2518 | 39 | 0.822 | 0.285 |
| PLU/CHITO 15% DMPC 200 | 24.56 | 0.19 | 3.421 | 158 | 2.689 | 47 | 0.787 | 0.297 |
| Sample | Tonset (°C) | SD (±) | Tend (°C) | SD (±) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plu control | 11.47 | 0.61 | 24.31 | 0.47 |
| PLU/CHITO 10% | 8.61 | 0.21 | 23.17 | 0.26 |
| PLU/CHITO 15% | 8.07 | 0.19 | 24.37 | 0.25 |
| PLU DPPC 100 | 20.12 | 0.31 | 28.01 | 0.26 |
| PLU DPPC 200 | 20.43 | 0.24 | 27.92 | 0.23 |
| PLU DMPC 100 | 16.23 | 0.34 | 25.23 | 0.42 |
| PLU DMPC 200 | 16.31 | 0.37 | 24.76 | 0.35 |
| PLU/CHITO 10% DPPC 100 | 12.37 | 0.42 | 20.71 | 0.26 |
| PLU/CHITO 10% DPPC 200 | 12.81 | 0.37 | 21.49 | 0.34 |
| PLU/CHITO 10% DMPC 100 | 11.12 | 0.43 | 20.93 | 0.32 |
| PLU/CHITO 10% DMPC 200 | 11.93 | 0.33 | 20.64 | 0.29 |
| PLU/CHITO 15% DPPC 100 | 9.79 | 0.17 | 25.19 | 0.28 |
| PLU/CHITO 15% DPPC 200 | 12.68 | 0.31 | 20.92 | 0.32 |
| PLU/CHITO 15% DMPC 100 | 15.09 | 0.48 | 21.03 | 0.35 |
| PLU/CHITO 15% DMPC 200 | 12.54 | 0.35 | 20.56 | 0.38 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olguín, Y.; Campos, C.; Catalán, J.; Velásquez, L.; Osorio, F.; Montenegro, I.; Madrid, A.; Acevedo, C. Effects of Liposomes Contained in Thermosensitive Hydrogels as Biomaterials Useful in Neural Tissue Engineering. Materials 2017, 10, 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101122
Olguín Y, Campos C, Catalán J, Velásquez L, Osorio F, Montenegro I, Madrid A, Acevedo C. Effects of Liposomes Contained in Thermosensitive Hydrogels as Biomaterials Useful in Neural Tissue Engineering. Materials. 2017; 10(10):1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101122
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlguín, Yusser, Cristian Campos, Javiera Catalán, Luís Velásquez, Fernando Osorio, Iván Montenegro, Alejandro Madrid, and Cristian Acevedo. 2017. "Effects of Liposomes Contained in Thermosensitive Hydrogels as Biomaterials Useful in Neural Tissue Engineering" Materials 10, no. 10: 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101122
APA StyleOlguín, Y., Campos, C., Catalán, J., Velásquez, L., Osorio, F., Montenegro, I., Madrid, A., & Acevedo, C. (2017). Effects of Liposomes Contained in Thermosensitive Hydrogels as Biomaterials Useful in Neural Tissue Engineering. Materials, 10(10), 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101122




