Effects of Processing Parameters on Surface Roughness of Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V via Electron Beam Melting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
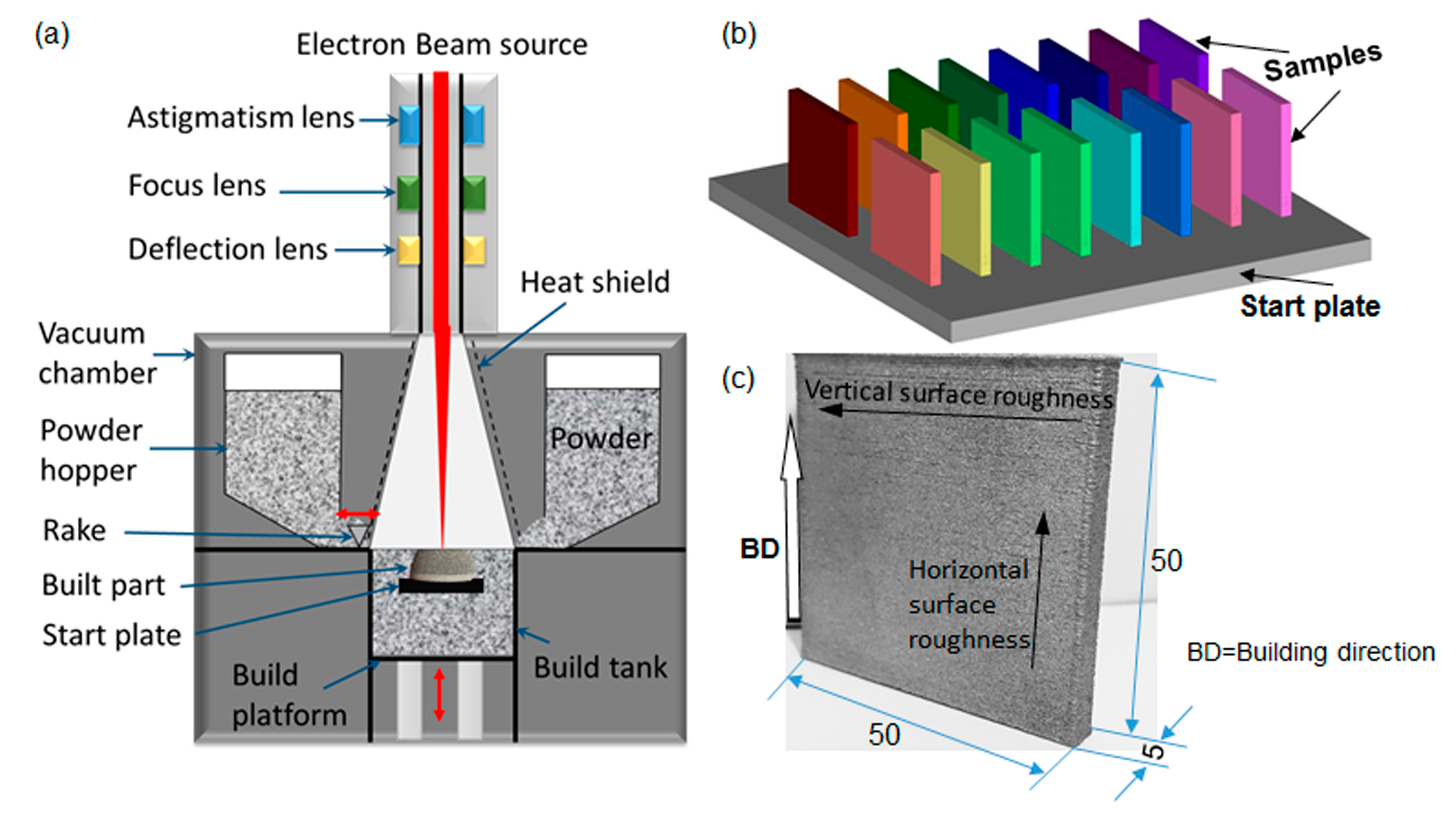
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results
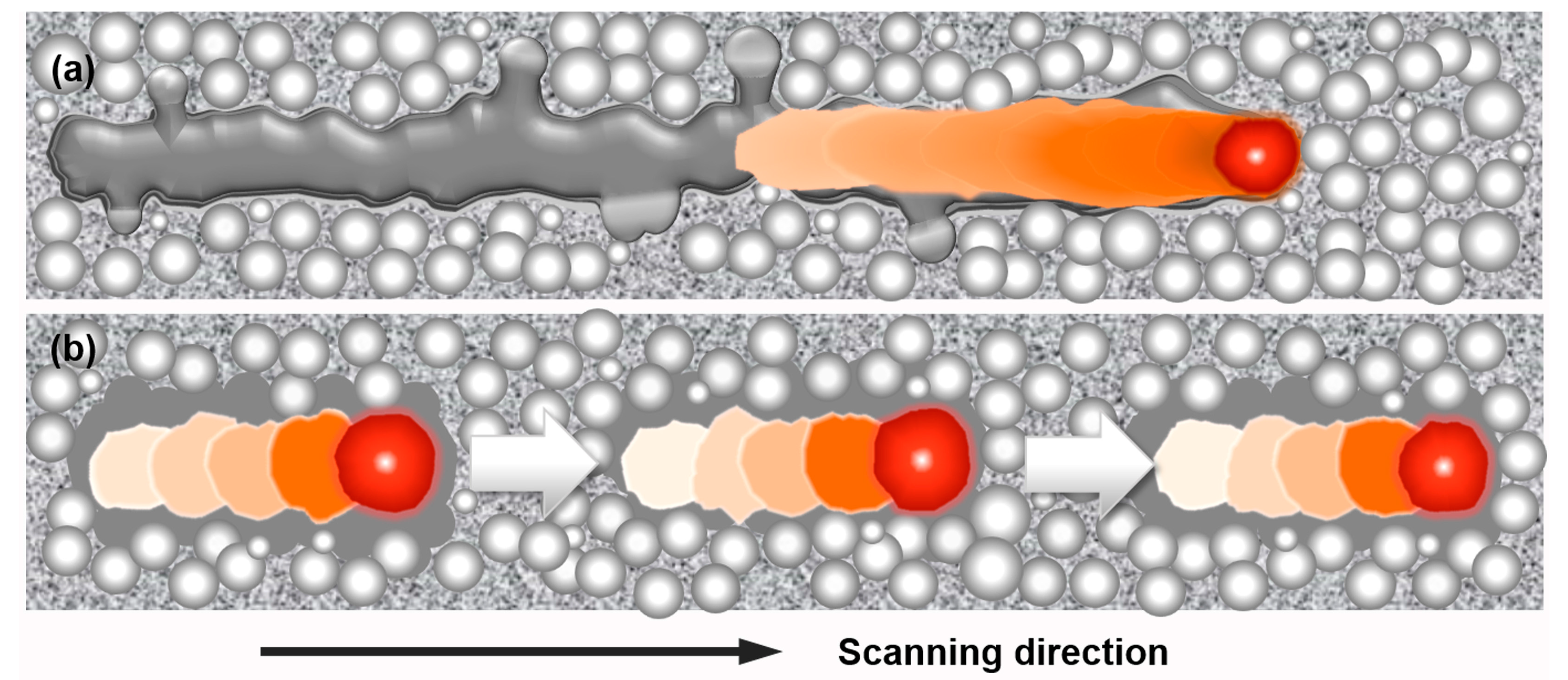
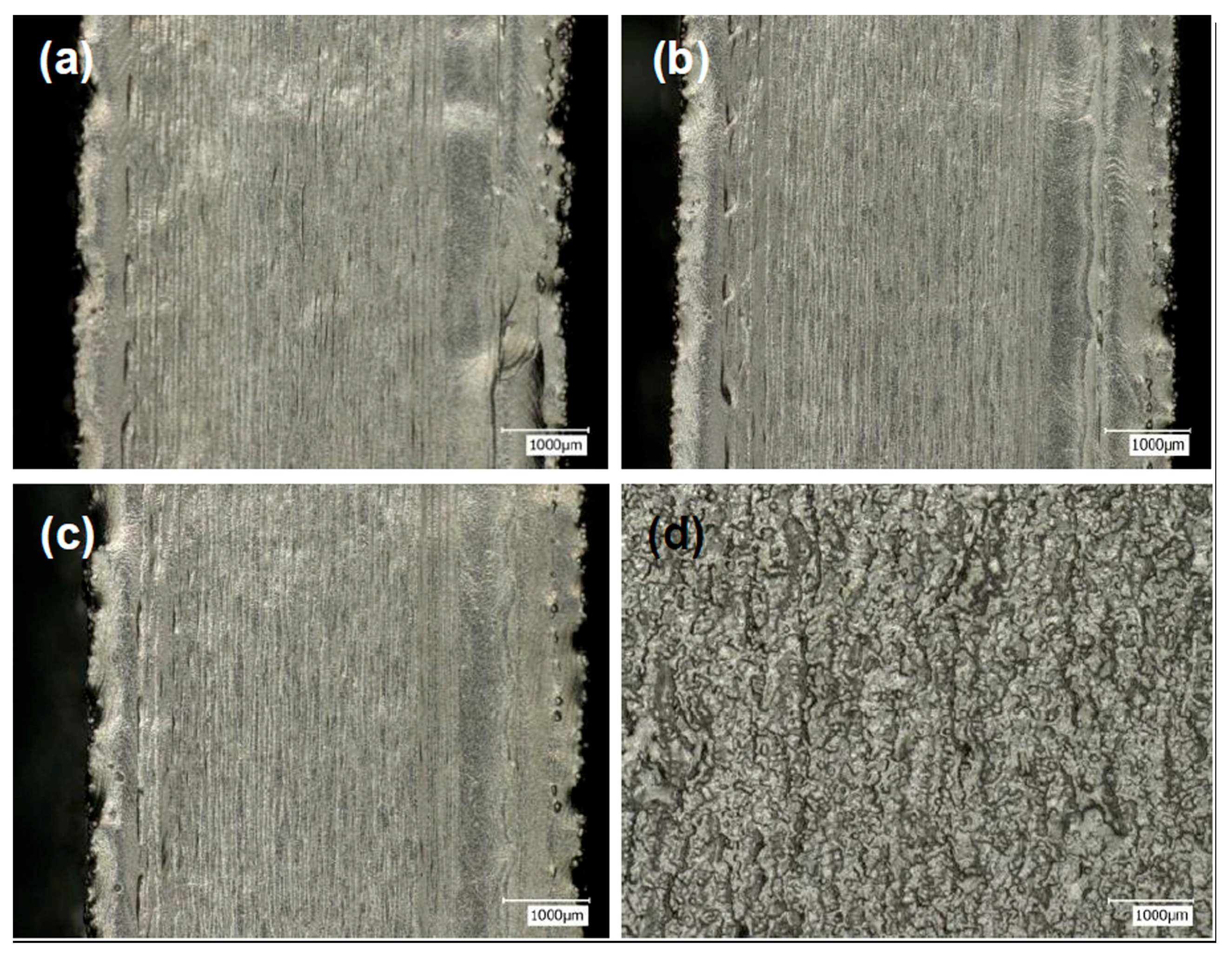
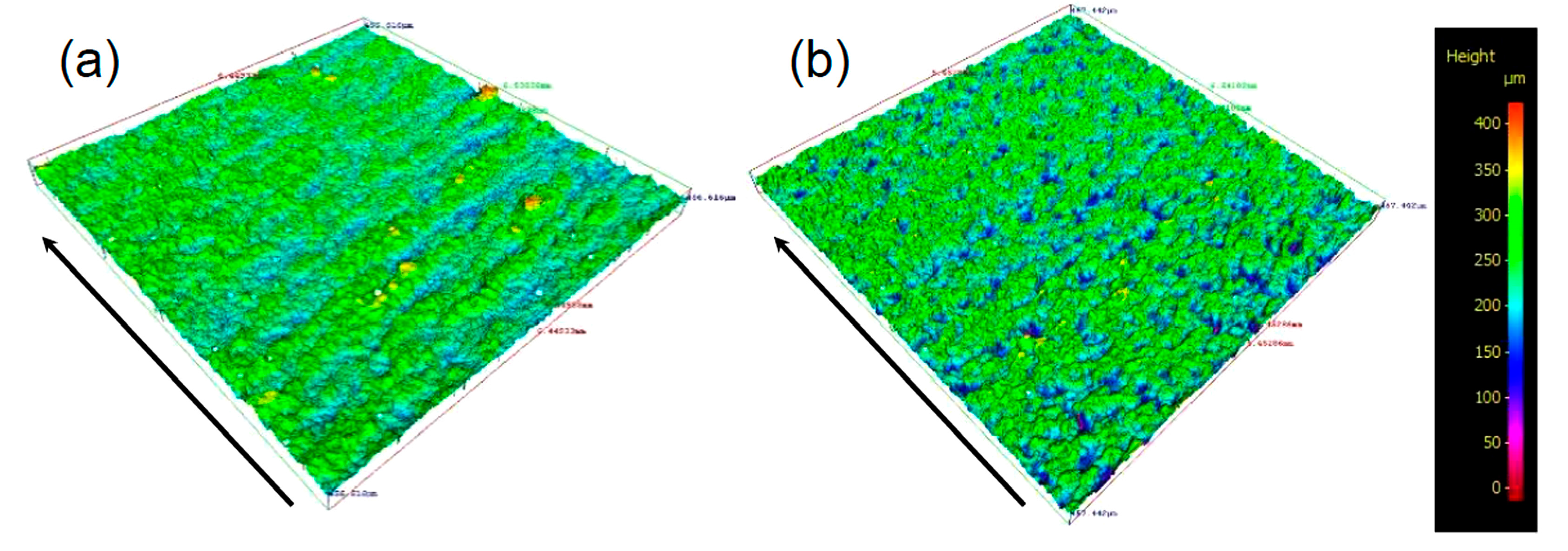
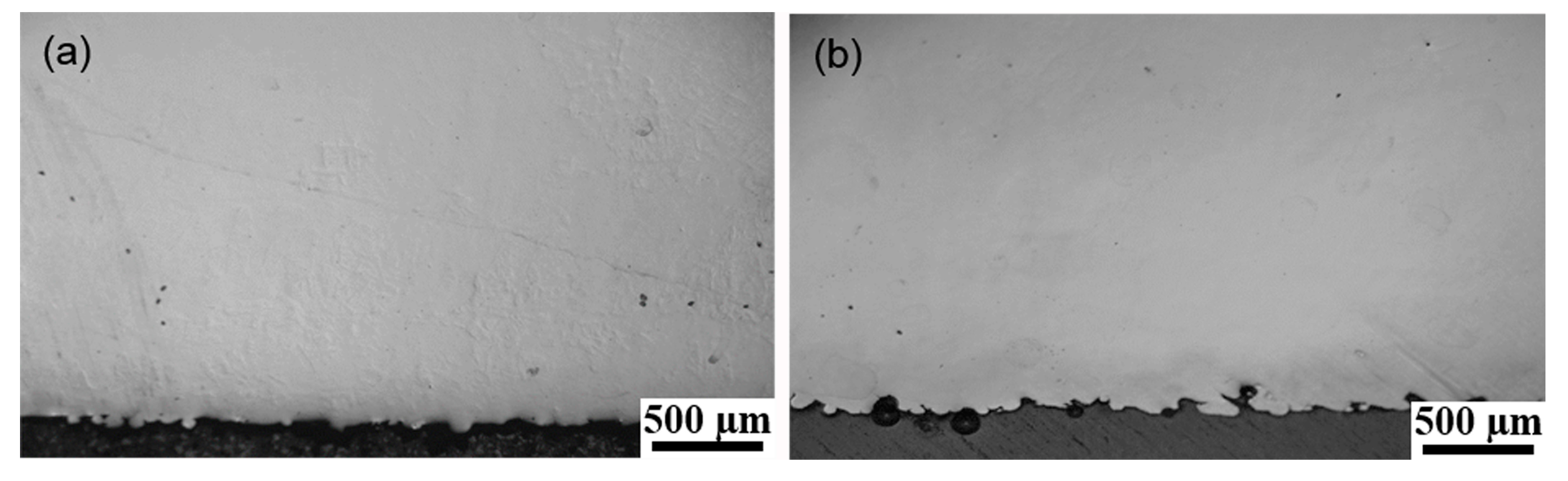
3.1. Non-Multispot Contouring
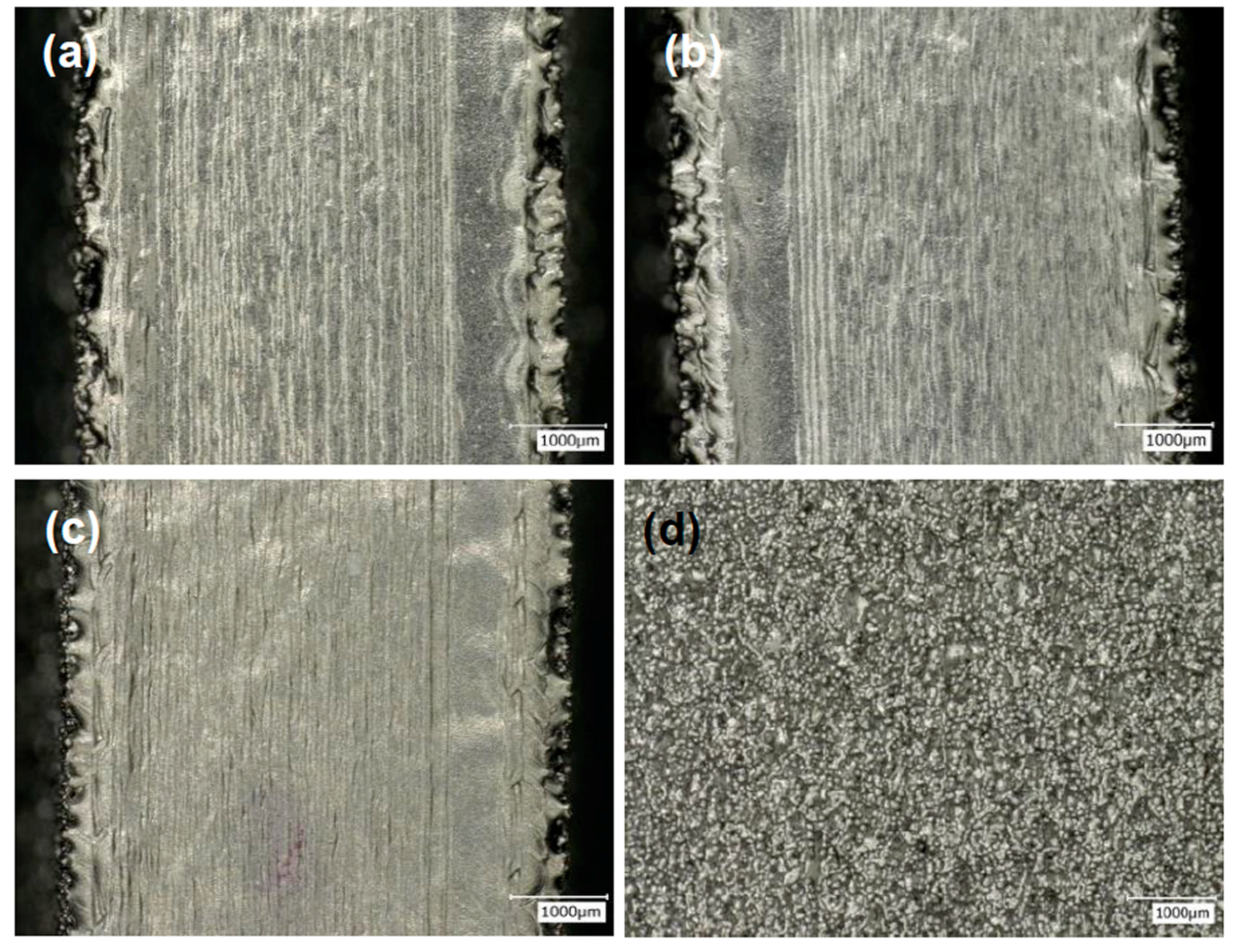
3.2. Multispot Contouring
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The non-multispot contouring strategy produced lower as-built surface roughness but compromised dimensional accuracy while the multispot contouring strategy had higher as-built roughness but better dimensional accuracy. Moreover, an anisotropic surface roughness was observed in the sample with non-multispot contouring strategy, which was caused by the unstable melting pool. The vertical surface roughness values were around 30% higher than the horizontal surface roughness values in non-multispot samples.
- (2)
- For the non-multispot contouring scanning strategy, lower beam current and speed function resulted in better as-built surface roughness. The vertical and horizontal surface roughness values of optimized conditions were 24 µm and 20 µm, respectively.
- (3)
- For the multispot contouring scanning strategy, high number of spots, with a spot time of 0.4 ms, and high spot overlap had contributed to better as-built part’s roughness. Amongst all of the tested processing parameters, number of spots was the dominating factor. The results from the optimized sample, M25, were ~27 µm for both the vertical roughness and horizontal roughness.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biamino, S.; Penna, A.; Ackelid, U.; Sabbadini, S.; Tassa, O.; Fino, P.; Pavese, M.; Gennaro, P.; Badini, C. Electron beam melting of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy: Microstructure and mechanical properties investigation. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Kok, Y.; Toh, W.Q.; Tan, Y.J.; Descoins, M.; Mangelinck, D.; Tor, S.B.; Leong, K.F.; Chua, C.K. Revealing martensitic transformation and α/β interface evolution in electron beam melting three-dimensional-printed Ti-6Al-4V. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Formanoir, C.; Suard, M.; Dendievel, R.; Martin, G.; Godet, S. Improving the mechanical efficiency of electron beam melted titanium lattice structures by chemical etching. Addit. Manuf. 2016, 11, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Tan, X.; Nai, M.L.S.; Tor, S.B.; Wei, J. Spatial and geometrical-based characterization of microstructure and microhardness for an electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V component. Mater. Des. 2016, 95, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Nai, M.L.S.; Tan, X.; Vastola, G.; Srinivasan, R.; Sin, W.J.; Tor, S.B.; Pei, Q.X.; Wei, J. Recent Progress of Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V by Electron Beam Melting. In Proceedings of the 2016 Annual International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium (SFF Symp 2016), Austin, TX, USA, 8–10 August 2016; pp. 691–704. [Google Scholar]
- Reports, G. The FAA Cleared the First 3D Printed Part to Fly in a Commercial Jet Engine from GE. Available online: http://www.gereports.com/post/116402870270/the-faa-cleared-the-first-3d-printed-part-to-fly (accessed on 14 April 2015).
- Reports, G. World’s First Plant to Print Jet Engine Nozzles in Mass Production. 2014. Available online: http://www.gereports.com/post/91763815095/worlds-first-plant-to-print-jet-engine-nozzles-in (accessed on 12 September 2017).
- Murr, L.; Esquivel, E.; Quinones, S.; Gaytan, S.; Lopez, M.; Martinez, E.; Medina, F.; Hernandez, D.; Martinez, E.; Martinez, J. Microstructures and mechanical properties of electron beam-rapid manufactured Ti-6Al-4V biomedical prototypes compared to wrought Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bermani, S.; Blackmore, M.; Zhang, W.; Todd, I. The origin of microstructural diversity, texture, and mechanical properties in electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 3422–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.L.; Qian, M.; Tang, H.P.; Yan, M.; Wang, J.; StJohn, D.H. Massive transformation in Ti–6Al–4V additively manufactured by selective electron beam melting. Acta Mater. 2016, 104, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchini, L.; Magalini, E.; Robotti, P.; Molinari, A. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V produced by electron beam melting of pre-alloyed powders. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2009, 15, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juechter, V.; Scharowsky, T.; Singer, R.F.; Körner, C. Processing window and evaporation phenomena for Ti-6Al-4V produced by selective electron beam melting. Acta Mater. 2014, 76, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Nai, M.L.S.; Sin, W.J.; Wei, J. Effect of Building Height on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Big-Sized Ti-6Al-4V Plate Fabricated by Electron Beam Melting. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Material Science and Engineering Technology (ICMSET 2015), Singapore, 26–28 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Kok, Y.; Tan, Y.J.; Descoins, M.; Mangelinck, D.; Tor, S.B.; Leong, K.F.; Chua, C.K. Graded microstructure and mechanical properties of additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V via electron beam melting. Acta Mater. 2015, 97, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabe, N.; Quinn, T. Effects of processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of a titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) fabricated using electron beam melting (EBM), Part 2: Energy input, orientation, and location. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 573, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murr, L.E.; Quinones, S.A.; Gaytan, S.M.; Lopez, M.I.; Rodela, A.; Martinez, E.Y.; Hernandez, D.H.; Martinez, E.; Medina, F.; Wicker, R.B. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of Ti-6Al-4V produced by rapid-layer manufacturing, for biomedical applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 2, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Nai, M.L.S.; Tan, X.; Sin, W.J.; Tor, S.B.; Wei, J. Anisotropic Mechanical Properties In A Big-Sized Ti-6Al-4V Plate Fabricated By Electron Beam Melting. In Proceedings of the TMS 2016 145th Annual Meeting & Exhibition, Nashville, TN, USA, 14–18 February 2016; pp. 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ladani, L. Local and Global Mechanical Behavior and Microstructure of Ti-6Al-4V Parts Built Using Electron Beam Melting Technology. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 3835–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, W.; Wang, P.; Tan, X.; Nai, M.; Liu, E.; Tor, S. Microstructure and Wear Properties of Electron Beam Melted Ti-6Al-4V Parts: A Comparison Study against As-Cast Form. Metals 2016, 6, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S.; Nai, M.L.S.; Wang, P.; Sin, W.J.; Li, T.; Wei, J. Heat Treatment of Electron Beam Melted (EBM) Ti-6Al-4V: Microstructure to Mechanical Property Correlations. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, M.T.; Teo, T.J.; Yeo, S.H.; Wang, P.; Nai, M.L.S. A 3D-printed Ti-6Al-4V 3-DOF compliant parallel mechanism for high precision manipulation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Nai, M.L.S.; Lu, S.; Bai, J.; Zhang, B.; Wei, J. Study of direct fabrication of Ti-6Al-4V impeller on a wrought Ti-6Al-4V plate by electron beam melting. JOM 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidambe, A.T. Three dimensional surface topography characterization of the electron beam melted Ti6Al4V. Met. Powder Rep. 2017, 72, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Gulizia, S.; Oh, C.H.; Fraser, D.; Leary, M.; Yang, Y.F.; Qian, M. The Influence of As-Built Surface Conditions on Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Additively Manufactured by Selective Electron Beam Melting. JOM 2016, 68, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllou, A.; Giusca, C.L.; Macaulay, G.D.; Roerig, F.; Hoebel, M.; Leach, R.K.; Tomita, B.; Milne, K.A. Surface texture measurement for additive manufacturing. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2015, 3, 024002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suard, M.; Lhuissier, P.; Dendievel, R.; Blandin, J.J.; Vignat, F.; Villeneuve, F. Towards stiffness prediction of cellular structures made by electron beam melting (EBM). Powder Metall. 2014, 57, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suard, M.; Martin, G.; Lhuissier, P.; Dendievel, R.; Vignat, F.; Blandin, J.J.; Villeneuve, F. Mechanical equivalent diameter of single struts for the stiffness prediction of lattice structures produced by Electron Beam Melting. Addit. Manuf. 2015, 8, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhuissier, P.; de Formanoir, C.; Martin, G.; Dendievel, R.; Godet, S. Geometrical control of lattice structures produced by EBM through chemical etching: Investigations at the scale of individual struts. Mater. Des. 2016, 110, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, A.; He, H.; Wei, L.-Y.; Snis, A.; Chavez de Paz, L.E. Effect of process parameters settings and thickness on surface roughness of EBM produced Ti-6Al-4V. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2012, 18, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaucamp, A.T.; Namba, Y.; Charlton, P.; Jain, S.; Graziano, A.A. Finishing of additively manufactured titanium alloy by shape adaptive grinding (SAG). Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2015, 3, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcam. Arcam EBM A2X—For Aerospace Production and Materials R & D. Available online: http://www.arcam.com/technology/products/arcam-a2x-3/ (accessed on 21 August 2017).
| Beam Current (mA) | Speed Function | Focus Offset (mA) | Vertical Surface Roughness (µm) | Horizontal Surface Roughness (µm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 33.6 ± 2.1 | 22.8 ± 1.9 |
| N2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 29.3 ± 1.3 | 23.1 ± 2.2 |
| N3 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 33.3 ± 1.3 | 23.6 ± 1.1 |
| N4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 28.1 ± 1.8 | 21.6 ± 1.1 |
| N5 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 24.1 ± 2.3 | 19.7 ± 1.3 |
| N6 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 25.4 ± 2.1 | 21.7 ± 0.7 |
| N7 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 33.5 ± 6.5 | 25.1 ± 3.3 |
| N8 | 4 | 6 | 3 | 32.1 ± 4.6 | 31.2 ± 4.9 |
| N9 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 31.0 ± 5.8 | 24.9 ± 5.2 |
| N10 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 33.0 ± 4.9 | 24.3 ± 4.7 |
| N11 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 33.8 ± 3.3 | 24.3 ± 2.7 |
| N12 | 6 | 6 | 3 | 39.3 ± 6.7 | 30.9 ± 2.8 |
| Number of Spots | Spot Time (ms) | Spot Overlap (mm) | Focus Offset (mA) | Beam Current (mA) | Vertical Surface Roughness (µm) | Horizontal Surface Roughness (µm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 10 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 1 | 4 | 40.5 ± 2.7 | 32.3 ± 2.3 |
| M2 | 10 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 1 | 6 | 37.7 ± 2.9 | 29.2 ± 2.8 |
| M3 | 10 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 3 | 4 | 38.2 ± 2.1 | 31.4 ± 2.9 |
| M4 | 10 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 3 | 6 | 37.3 ± 3.5 | 28.4 ± 3.9 |
| M5 | 10 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 3 | 4 | 32.6 ± 1.7 | 30.0 ± 1.4 |
| M6 | 40 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 1 | 4 | 31.8 ± 1.9 | 31.5 ± 2.1 |
| M7 | 40 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 1 | 6 | 31.8 ± 2.6 | 30.5 ± 2.9 |
| M8 | 40 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 3 | 4 | 29.6 ± 2.3 | 28.9 ± 2.2 |
| M9 | 40 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 3 | 6 | 33.6 ± 1.6 | 31.4 ± 1.3 |
| M10 | 40 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1 | 6 | 29.8 ± 1.5 | 29.7 ± 3.7 |
| M11 | 40 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 1 | 6 | 33.0 ± 1.2 | 30.3 ± 1.4 |
| M12 | 40 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 3 | 6 | 30.7 ± 1.4 | 29.1 ± 2.4 |
| M13 | 40 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 1 | 4 | 31.6 ± 1.4 | 30.5 ± 2.0 |
| M14 | 40 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 1 | 6 | 34.7 ± 3.1 | 33.0 ± 1.7 |
| M15 | 40 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 3 | 4 | 30.9 ± 1.2 | 30.6 ± 2.0 |
| M16 * | 40 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 3 | 4 | 31.7 ± 1.9 | 31.0 ± 1.9 |
| M17 | 55 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 3 | 4 | 27.3 ± 1.7 | 25.5 ± 3.2 |
| M18 | 55 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 3 | 4 | 26.1 ± 0.9 | 27.0 ± 2.9 |
| M19 | 55 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 3 | 4 | 32.4 ± 1.3 | 31.5 ± 2.1 |
| M20 | 55 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 3 | 4 | 32.9 ± 1.3 | 30.6 ± 2.4 |
| M21 | 70 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 3 | 4 | 28.9 ± 2.0 | 27.8 ± 1.9 |
| M22 | 70 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 3 | 4 | 28.4 ± 1.2 | 25.8 ± 1.9 |
| M23 | 70 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 3 | 4 | 35.1 ± 3.8 | 33.3 ± 2.3 |
| M24 | 70 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 3 | 4 | 33.6 ± 1.9 | 32.3 ± 1.6 |
| M25 | 80 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 3 | 4 | 27.9 ± 1.4 | 27.1 ± 1.9 |
| M26 | 80 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 3 | 4 | 29.3 ± 1.7 | 28.0 ± 2.5 |
| M27 | 80 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 3 | 4 | 34.2 ± 1.7 | 32.6 ± 2.0 |
| M28 | 80 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 3 | 4 | 34.7 ± 1.5 | 33.5 ± 1.9 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Sin, W.J.; Nai, M.L.S.; Wei, J. Effects of Processing Parameters on Surface Roughness of Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V via Electron Beam Melting. Materials 2017, 10, 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101121
Wang P, Sin WJ, Nai MLS, Wei J. Effects of Processing Parameters on Surface Roughness of Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V via Electron Beam Melting. Materials. 2017; 10(10):1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101121
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Pan, Wai Jack Sin, Mui Ling Sharon Nai, and Jun Wei. 2017. "Effects of Processing Parameters on Surface Roughness of Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V via Electron Beam Melting" Materials 10, no. 10: 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101121
APA StyleWang, P., Sin, W. J., Nai, M. L. S., & Wei, J. (2017). Effects of Processing Parameters on Surface Roughness of Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V via Electron Beam Melting. Materials, 10(10), 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101121







