A Comparison of Household Carbon Emission Patterns of Urban and Rural China over the 17 Year Period (1995–2011)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. A Brief Snapshot of China’s Emission Reduction Policy
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Estimation of Direct Household Carbon Emission (HCEs)
| Fossil fuel type | NCV (ei) (TJ/1 × 104 t) | CEF (ci) (tC/TJ) | COF (oi) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw coal | 209.08 | 26.37 | 0.94 |
| Washed coal | 94.09 | 25.41 | 0.90 |
| Moulded coal | 147.60 | 33.60 | 0.90 |
| Cooking coal | 284.35 | 29.50 | 0.93 |
| Coke oven gas | 173.54 | 13.58 | 0.99 |
| Other gas | 182.74 | 12.20 | 0.99 |
| Gasoline * | 430.70 | 18.90 | 0.98 |
| Kerosene | 430.70 | 19.60 | 0.98 |
| Diesel | 426.52 | 20.20 | 0.98 |
| Liquid petroleum gas (LPG) | 501.79 | 17.20 | 0.98 |
| Natural gas | 389.31 | 15.30 | 0.98 |
3.3. Estimation of Indirect Household Carbon Emission (HCEs)
| Items/sectors | CO2 emission factors (kg CO2/RMB) |
|---|---|
| Food | 0.095 |
| Clothing | 0.126 |
| Residence * | 0.192 |
| Household equipment | 0.156 |
| Transportation & communication | 0.160 |
| Cultural & educational entertainment | 0.177 |
| Medical care | 0.159 |
| Others | 0.064 |
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Comparison of Direct Household Carbon Emission (HCEs) from Different Sources between Urban and Rural People in China
4.2. Comparison of Indirect Household Carbon Emission (HCEs) from Different Sources between Urban and Rural China
| Year | Emission 100 million tCO2 | Raw coal | Washed coal | Moulded coal | Cooking coal | Coke oven gas | Other gas | Gasoline | Kerosene | Diesel | LPG | Natural gas | Electric power |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Percentage share of direct HCEs in urban China | |||||||||||||
| 1995 | 1.77 | 55.20 | 4.84 | 0.25 | 0.66 | 0.23 | 0.33 | 0.53 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 5.21 | 0.20 | 32.45 |
| 1996 | 1.67 | 32.01 | 4.37 | 6.96 | 0.71 | 0.26 | 0.56 | 1.66 | 0.07 | 0.90 | 7.00 | 0.23 | 45.27 |
| 1997 | 1.67 | 27.94 | 4.15 | 6.74 | 0.73 | 0.44 | 0.75 | 1.77 | 0.05 | 0.94 | 7.47 | 0.23 | 48.77 |
| 1998 | 1.69 | 25.43 | 3.81 | 5.86 | 0.79 | 0.40 | 0.89 | 1.85 | 0.12 | 1.12 | 8.36 | 0.26 | 51.11 |
| 1999 | 1.68 | 24.01 | 3.88 | 5.96 | 0.76 | 0.38 | 0.87 | 1.96 | 0.07 | 1.30 | 8.24 | 0.28 | 52.30 |
| 2000 | 1.70 | 22.18 | 4.09 | 5.11 | 0.73 | 0.40 | 0.95 | 1.99 | 0.07 | 1.38 | 8.25 | 0.35 | 54.52 |
| 2001 | 1.77 | 21.07 | 4.11 | 4.90 | 0.70 | 0.36 | 0.85 | 2.05 | 0.07 | 1.45 | 7.89 | 0.43 | 56.11 |
| 2002 | 1.87 | 19.15 | 3.17 | 4.80 | 0.58 | 0.35 | 0.86 | 2.14 | 0.06 | 1.55 | 8.32 | 0.45 | 58.57 |
| 2003 | 2.11 | 17.97 | 2.85 | 4.50 | 0.49 | 0.34 | 0.79 | 2.27 | 0.05 | 1.58 | 8.35 | 0.45 | 60.36 |
| 2004 | 2.38 | 16.67 | 2.62 | 4.12 | 0.42 | 0.31 | 0.73 | 2.63 | 0.02 | 2.09 | 8.61 | 0.51 | 61.28 |
| 2005 | 2.71 | 14.38 | 2.43 | 3.43 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.67 | 2.62 | 0.01 | 2.02 | 7.17 | 0.53 | 66.12 |
| 2006 | 2.99 | 13.82 | 1.91 | 2.79 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.73 | 2.68 | 0.01 | 2.14 | 7.11 | 0.62 | 67.60 |
| 2007 | 3.39 | 11.48 | 1.89 | 2.22 | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.77 | 2.95 | 0.01 | 2.16 | 6.92 | 0.77 | 70.35 |
| 2008 | 3.46 | 10.01 | 1.71 | 1.09 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.74 | 3.20 | 0.01 | 2.31 | 5.83 | 0.89 | 73.77 |
| 2009 | 3.71 | 8.09 | 1.57 | 0.91 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.62 | 3.45 | 0.01 | 2.41 | 5.60 | 0.87 | 76.13 |
| 2010 | 3.86 | 6.61 | 1.52 | 0.83 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 0.53 | 3.98 | 0.01 | 2.70 | 5.17 | 1.07 | 77.21 |
| 2011 | 4.11 | 5.59 | 1.31 | 0.81 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.48 | 4.38 | 0.01 | 2.87 | 5.43 | 1.17 | 77.68 |
| B. Percentage share of direct HCEs in rural China | |||||||||||||
| 1995 | 1.86 | 70.02 | 4.89 | 0.22 | 0.66 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.56 | 0.11 | 0.27 | 0.00 | 23.13 |
| 1996 | 1.47 | 66.13 | 5.06 | 4.61 | 0.80 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.34 | 0.72 | 0.33 | 0.88 | 0.00 | 21.12 |
| 1997 | 1.53 | 61.41 | 4.86 | 4.47 | 0.83 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.38 | 0.69 | 0.39 | 0.94 | 0.00 | 26.03 |
| 1998 | 1.54 | 60.12 | 4.47 | 4.15 | 0.90 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 0.73 | 0.49 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 27.73 |
| 1999 | 1.56 | 57.20 | 4.73 | 3.76 | 0.85 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.47 | 0.75 | 0.55 | 1.0 | 0.00 | 30.65 |
| 2000 | 1.59 | 55.43 | 4.99 | 2.97 | 0.80 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.48 | 0.75 | 0.57 | 1.03 | 0.00 | 32.98 |
| 2001 | 1.67 | 51.85 | 4.96 | 2.98 | 0.72 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.49 | 0.74 | 0.64 | 0.96 | 0.00 | 36.66 |
| 2002 | 1.75 | 50.51 | 4.79 | 3.14 | 0.58 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.56 | 0.36 | 0.57 | 1.17 | 0.00 | 38.32 |
| 2003 | 1.95 | 48.45 | 4.69 | 3.48 | 0.52 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.70 | 0.28 | 0.60 | 1.34 | 0.00 | 39.94 |
| 2004 | 2.23 | 46.55 | 4.53 | 3.56 | 0.41 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.92 | 0.21 | 0.82 | 1.82 | 0.00 | 41.17 |
| 2005 | 2.47 | 43.93 | 4.35 | 3.49 | 0.30 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.99 | 0.17 | 0.78 | 1.94 | 0.00 | 44.04 |
| 2006 | 2.71 | 40.07 | 3.84 | 2.99 | 0.27 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 1.18 | 0.14 | 0.80 | 1.94 | 0.00 | 48.76 |
| 2007 | 3.05 | 34.70 | 3.08 | 3.05 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 1.36 | 0.10 | 0.85 | 2.07 | 0.00 | 54.58 |
| 2008 | 3.20 | 32.45 | 3.32 | 2.41 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 1.40 | 0.06 | 0.87 | 1.99 | 0.00 | 57.35 |
| 2009 | 3.46 | 31.36 | 3.24 | 2.06 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 1.55 | 0.09 | 0.85 | 1.85 | 0.00 | 58.88 |
| 2010 | 3.63 | 31.18 | 3.18 | 2.05 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.85 | 0.09 | 0.99 | 1.80 | 0.00 | 58.76 |
| 2011 | 3.98 | 29.28 | 2.95 | 1.92 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.14 | 0.09 | 1.13 | 1.74 | 0.00 | 60.64 |
| Year | Emission 100 million tCO2 | Food | Clothing | Residence | Household equipment | Transportation & communication | Cultural & educational entertainment | Medical care | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage share of indirect HCEs in urban China | |||||||||
| 1995 | 1.53 | 38.56 | 13.73 | 12.42 | 9.80 | 6.54 | 13.73 | 3.92 | 1.31 |
| 1996 | 1.66 | 37.95 | 13.86 | 10.84 | 10.24 | 7.23 | 13.25 | 4.82 | 1.81 |
| 1997 | 1.86 | 36.02 | 12.37 | 10.75 | 10.22 | 8.06 | 15.05 | 5.38 | 2.15 |
| 1998 | 2.10 | 34.76 | 10.95 | 10.95 | 10.95 | 9.05 | 16.19 | 5.71 | 1.43 |
| 1999 | 2.44 | 32.79 | 10.25 | 10.66 | 11.48 | 10.25 | 17.21 | 5.74 | 1.64 |
| 2000 | 2.92 | 30.48 | 9.25 | 10.96 | 9.59 | 13.36 | 18.49 | 6.85 | 1.03 |
| 2001 | 3.24 | 29.32 | 9.57 | 11.11 | 9.57 | 14.51 | 17.90 | 7.10 | 0.93 |
| 2002 | 3.93 | 28.50 | 9.41 | 9.67 | 8.65 | 16.28 | 18.83 | 7.63 | 1.02 |
| 2003 | 4.41 | 27.21 | 9.52 | 9.75 | 8.62 | 17.91 | 18.14 | 7.94 | 0.91 |
| 2004 | 4.96 | 25.81 | 9.68 | 9.27 | 8.06 | 19.76 | 18.35 | 8.27 | 0.81 |
| 2005 | 5.66 | 24.38 | 10.60 | 8.66 | 8.13 | 21.38 | 17.49 | 8.48 | 0.88 |
| 2006 | 6.41 | 23.24 | 10.92 | 8.42 | 8.11 | 22.78 | 17.47 | 8.11 | 0.94 |
| 2007 | 7.50 | 21.60 | 11.33 | 7.87 | 8.67 | 24.40 | 17.33 | 7.87 | 0.93 |
| 2008 | 8.23 | 20.78 | 12.03 | 8.14 | 8.99 | 24.18 | 16.77 | 8.14 | 0.97 |
| 2009 | 9.57 | 19.23 | 12.02 | 8.25 | 9.09 | 26.23 | 16.41 | 7.84 | 0.94 |
| 2010 | 10.92 | 17.58 | 12.55 | 7.69 | 9.52 | 28.30 | 16.39 | 7.05 | 0.92 |
| 2011 | 12.21 | 16.63 | 13.10 | 7.21 | 9.66 | 28.26 | 17.12 | 7.04 | 0.98 |
| Percentage share of indirect HCEs in rural China | |||||||||
| 1995 | 1.37 | 45.99 | 6.57 | 21.90 | 6.57 | 2.92 | 10.95 | 4.38 | 0.73 |
| 1996 | 1.55 | 42.58 | 7.10 | 21.29 | 7.10 | 4.52 | 11.61 | 4.52 | 1.29 |
| 1997 | 1.59 | 41.51 | 6.92 | 21.38 | 6.92 | 5.03 | 11.95 | 5.03 | 1.26 |
| 1998 | 1.57 | 41.40 | 5.73 | 22.29 | 6.37 | 5.10 | 14.01 | 4.46 | 0.64 |
| 1999 | 1.60 | 40.63 | 5.63 | 20.63 | 6.88 | 6.88 | 14.38 | 4.38 | 0.63 |
| 2000 | 1.74 | 37.36 | 5.75 | 20.69 | 5.75 | 8.62 | 14.94 | 5.75 | 1.15 |
| 2001 | 1.77 | 36.72 | 5.65 | 20.90 | 5.65 | 10.17 | 14.12 | 5.65 | 1.13 |
| 2002 | 1.84 | 35.87 | 5.43 | 21.20 | 5.43 | 10.87 | 14.67 | 5.43 | 1.09 |
| 2003 | 1.91 | 34.03 | 5.76 | 20.42 | 5.76 | 13.09 | 14.66 | 5.76 | 0.52 |
| 2004 | 2.01 | 33.33 | 5.47 | 19.40 | 5.47 | 14.93 | 14.43 | 5.97 | 1.00 |
| 2005 | 2.27 | 31.72 | 6.17 | 18.06 | 6.17 | 16.30 | 14.10 | 7.05 | 0.44 |
| 2006 | 2.48 | 29.44 | 6.45 | 19.76 | 6.05 | 16.94 | 13.71 | 7.26 | 0.40 |
| 2007 | 2.60 | 27.31 | 6.92 | 21.54 | 6.54 | 17.69 | 12.69 | 6.92 | 0.38 |
| 2008 | 2.75 | 25.82 | 6.91 | 22.18 | 6.91 | 18.18 | 12.36 | 7.27 | 0.36 |
| 2009 | 3.01 | 23.59 | 6.98 | 23.59 | 7.31 | 18.60 | 11.63 | 7.64 | 0.66 |
| 2010 | 3.14 | 22.61 | 7.32 | 21.97 | 7.96 | 19.75 | 11.78 | 7.96 | 0.64 |
| 2011 | 3.51 | 20.51 | 8.26 | 21.08 | 9.12 | 20.51 | 11.11 | 8.83 | 0.57 |
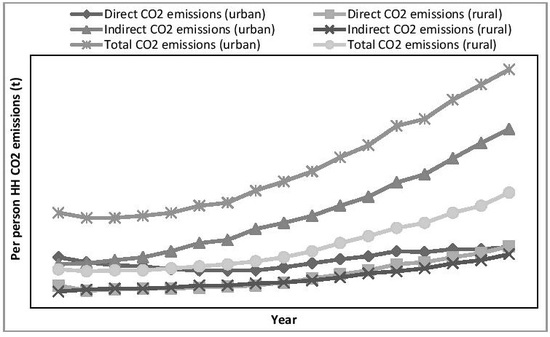
4.3. Comparison of Per Person Direct and Indirect Household Carbon Emission (HCEs) between Urban and Rural People in China
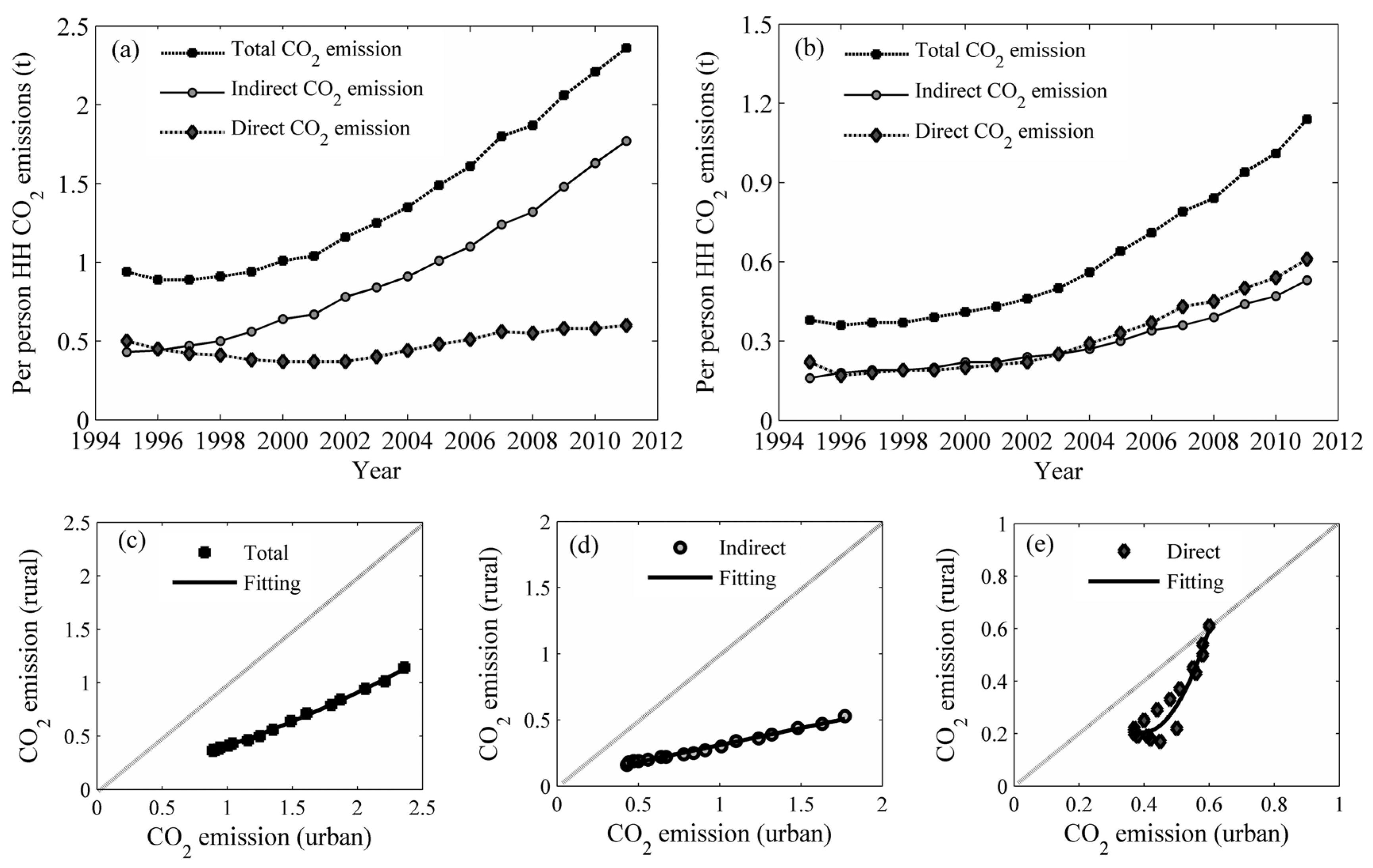
4.4. Income Effect on Per Person Household Carbon Emission (HCEs) in Urban and Rural China
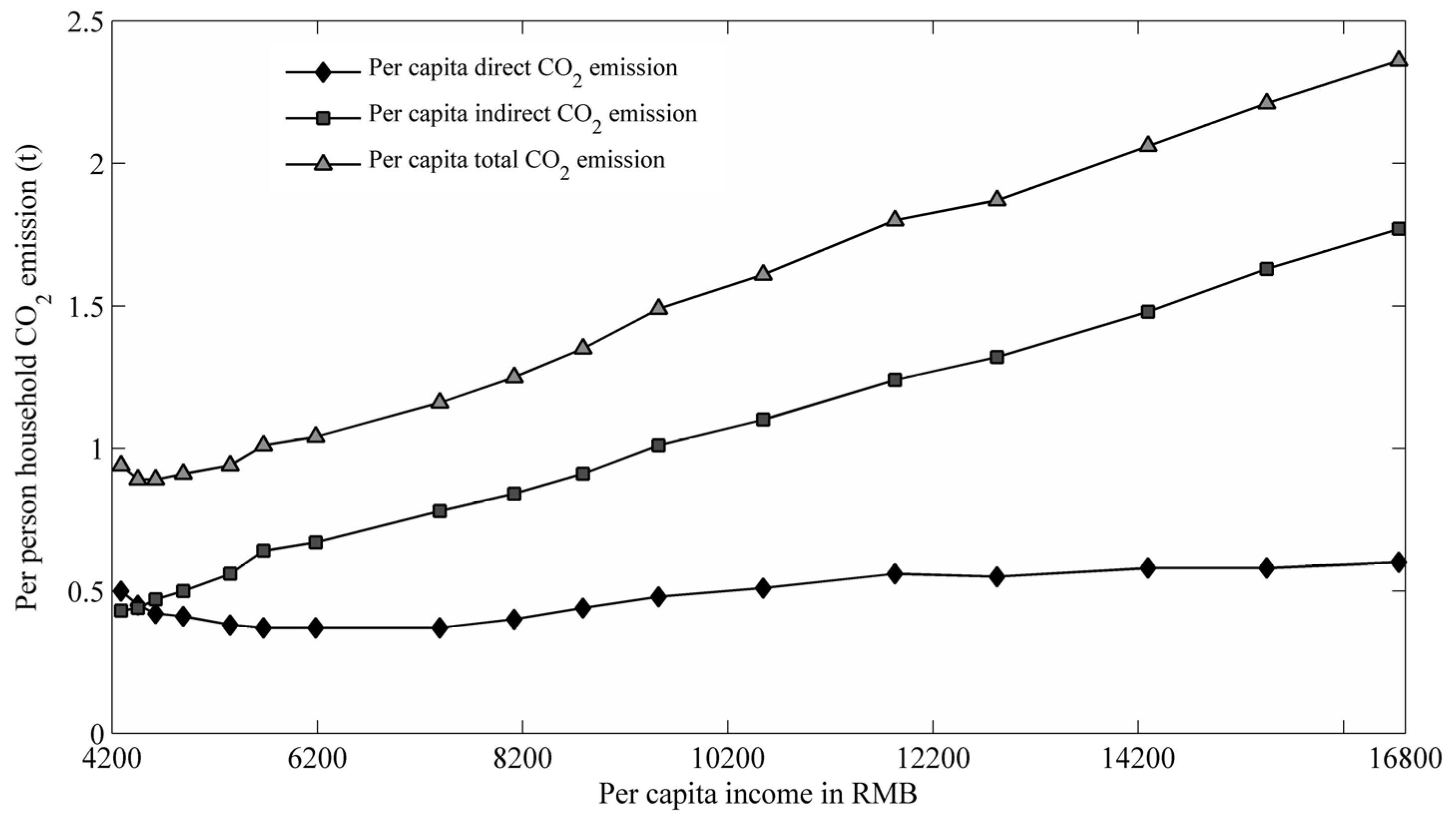
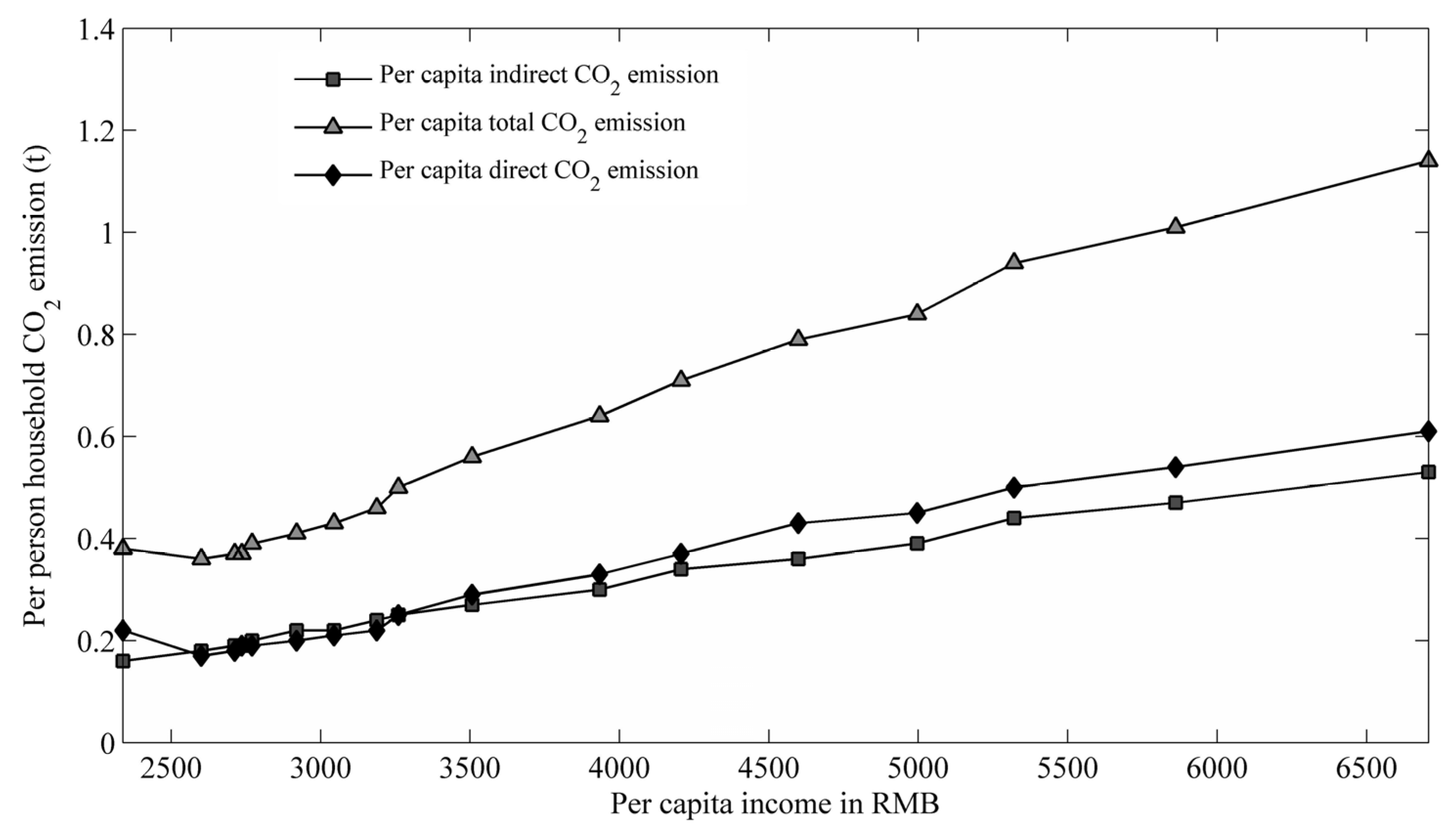
4.5. Urbanization Effect on Household Carbon Emission (HCEs)
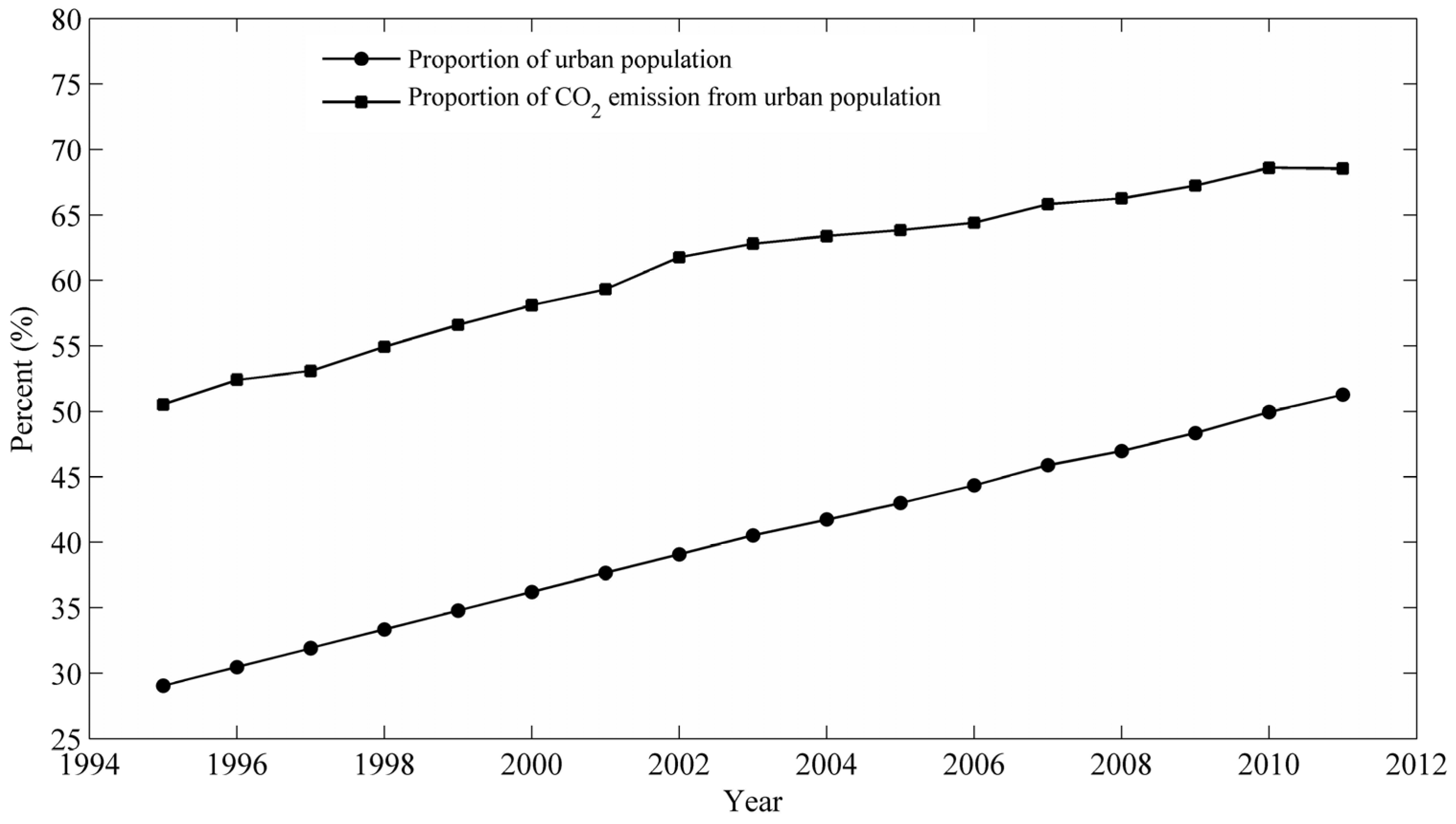
4.6. Household Size Effect on Per Person Household Carbon Emission (HCEs) in Urban and Rural China
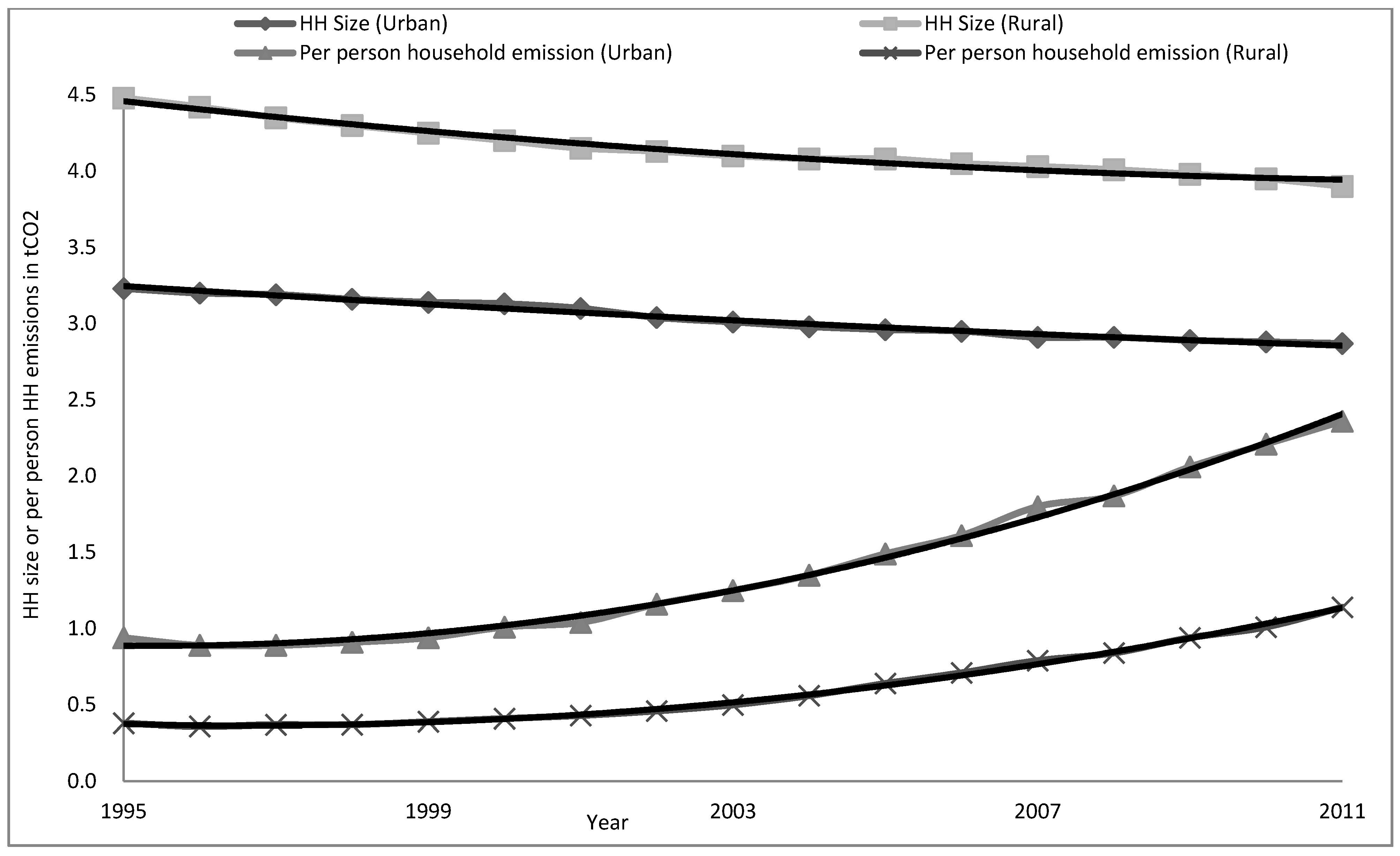
4.7. Combined Effect of Per Capita Income (PCI) and Household Size on Per Person Household Carbon Emission (HCEs)
| Area | Effects of due to | Best fitted equations | R2 | AdjR2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | PCI | 0.995 | 0.985 | |
| HHsize | 0.870 | 0.862 | ||
| PCI plus HHsize | 0.997 | 0.996 | ||
| Rural | PCI | 0.989 | 0.988 | |
| HHsize | 0.738 | 0.720 | ||
| PCI plus HHsize | 0.989 | 0.988 |
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qu, J.S.; Zeng, J.J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Maraseni, T.; Zhang, L.H.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Clarke-Sather, A. Household carbon dioxide emissions from peasants and herdsmen in northwestern arid-alpine regions, China. Energy Policy 2011, 57, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.S.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Zeng, J.J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.H.; Qiu, J.L.; Liu, L.N.; Dong, L.P.; Tang, X. Household carbon emission differences and their driving factors in north-western China. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 260–266. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.C.; Wu, G.; Wang, J.N.; Wei, Y.M. China’s carbon emissions from urban and rural households during 1992–2007. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vringer, K.; Blok, K. The direct and indirect energy requirements of households in the Netherlands. Energy Policy 1995, 23, 893–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munksgaard, J.; Pedersen, K.A.; Wier, M. Impact of household consumption on CO2 emissions. Energy Econ. 2000, 22, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachauri, S.; Spreng, D. Direct and indirect energy requirements of households in India. Energy Policy 2002, 30, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinders, A.H.M.E.; Vringer, K.; Blok, K. The direct and indirect energy requirement of households in the European Union. Energy Policy 2003, 31, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, S.; Dowlatabadi, H. Consumer lifestyle approach to US energy use and the related CO2 emissions. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C.; Lenzen, M.; Schaeffer, R. Energy requirements of households in Brazil. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.C.; Heo, E. The direct and indirect household energy requirements in the Republic of Korea from 1980 to 2000—An input-output analysis. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 2839–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nansai, K.; Inaba, R.; Kagawa, S.; Moriguchi, Y. Identifying common features among household consumption patterns optimized to minimize specific environmental burdens. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 538–548. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Chóliz, J.; Duarte, R.; Mainar, A. Environmental impact of household activity in Spain. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 62, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.M.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Y. Suggestions and solutions to carbon emissions in China. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2006, 2, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.H.; Zou, L.L.; Wei, Y.M. The impact of household consumption on energy use and CO2 emissions in China. Energy 2011, 36, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Masui, T.; Matsuoka, Y.; Fujimori, S. The impacts of China’s household consumption expenditure patterns on energy demand and carbon emissions towards 2050. Energy Policy 2012, 50, 736–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China’s Economic Rise: History, Trends, Challenges, and Implications for the United States. Available online: http://www.crs.gov (accessed on 12 June 2015).
- Zhang, Z.X. China in the transition to a low-carbon economy. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 6638–6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Energy Outlook 2012. Available online: http://www.iea.org (accessed on 25 January 2015).
- Liao, H.; Cao, H.S. How does carbon dioxide emission change with the economic development? Statistical experiences from 132 countries. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, L. Indirect carbon emissions in household consumption: evidence from the urban and rural area in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 78, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golley, J.; Meng, X. Income inequality and carbon dioxide emissions: The case of Chinese urban households. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraseni, T.N. Selecting a CDM investor in China: A critical analysis. Energy Policy 2013, 53, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human Activity and the Environment, Catalogue (16-201-X). Available online: http://www.statcan.gc.ca (accessed on 12 February 2015).
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Campbell, R.J. China and the United States—A Comparison of Green Energy Programs and Policies. Congressional Research Service. Available online: https://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/row/RL33534.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2015).
- Maraseni, T.N.; Gao, X. An analysis of Chinese perceptions on unilateral Clean Development Mechanism (uCDM) projects. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australia’s Energy Sector: Aging, Inefficient and Unprepared. Available online: http://www.climatecouncil.org.au (accessed on 15 June 2015).
- Renewable Energy Network. Available online: http://www.ren21.net/ (accessed on 12 June 2014).
- China’s Power Capacity up 94 m kw in 2013. Available online: http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/business/2014-02/11/content_17276118.htm (accessed on 12 June 2014).
- Hart, M. Primer on Beijing’s Slice-and-Dice Approach to Energy and Climate Reform; Center for American Progress. Available online: https://www.americanprogress.org/issues/security/report/2014/07/07/93278/primer-on-beijings-slice-and-dice-approach-to-energy-and-climate-reform/ (accessed on 12 June 2015).
- Reducing Australia’s Greenhouse Gas Emissions—Targets and Progress Review; Australian Government Climate Change Authority: Canberra, Australia, 2014; p. 401.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 1996.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 1997.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 1998.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 1999.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2000.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2001.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2003.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2004.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2005.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2006.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2008.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2009.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2010.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 1996.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 1997.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 1998.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 1999.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2000.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2001.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2003.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2004.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2005.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2006.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2008.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2009.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2010.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Population & Employment Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- IPCC Guide Lines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): Hayama, Japan, 2006.
- Announcement on 2009 Baseline Emission Factor of China Regional Power Grid; China National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC): Beijing, China, 2009.
- Development and Reform Commission (NDRC). China National Greenhouse Gas Inventory; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Weber, C.L. Trade, Consumption, and Climate change: An Input-Output Study of the United States. Ph.D. Thesis, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, C.L.; Matthews, H.S. Quantifying the global and distributional aspects of American household carbon footprint. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 66, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, A.J. Household Carbon Dioxide Emissions in the United States: The Role of Demographic Change. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Nie, R.R.; Wang, S.Z. Study on the evaluation and decomposition of China’s per capita carbon dioxide emissions inequality based on the perspective of intergenerational equity. Stud. Sci. Sci. 2012, 30, 1662–1670. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Peng, X.Z.; Wu, K.Y. Calculation and decomposition of indirect carbon emissions from residential consumption in China based on the input-output model. Energy Policy 2012, 48, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). Input-Output Tables of China; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2008.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Energy Statistics Yearbook 2007; NBSC: Beijing, China, 2008.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Liu, W.L.; Spaargaren, G.; Heerink, N.; Mol, A.P.; Wang, C. Energy consumption practices of rural households in north China: Basic characteristics and potential for low carbon development. Energy Policy 2013, 55, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.F.; Zhang, L.X. Urban CO2 emissions in China: Spatial boundary and performance comparison. Energy Policy 2014, 66, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Wu, Q.; Ren, J.X.; Gao, W.J. Cost-effectiveness analysis of local energy management based on urbanerural cooperation in China. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 64, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkhof, A.C.; Benders, R.M.J.; Moll, H.C. Determinants of variation in household CO2 emissions between and within countries. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glicksman, L.R.; Norford, L.K.; Greden, L.V. Energy conservation in Chinese residential buildings: Progress and opportunities in design and policy. Annu. Rev. Energy Environ. 2001, 26, 83–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X. Private car ownership in China: How important is the effect of income? Available online: http://ura.unisa.edu.au/R/?func=dbin-jump-full&object_id=unisa35333 (accessed on 10 June 2014).
- Wang, Q.H.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Qu, J.S. A review of the research on household carbon emission. Adv. Earth Sci. 2013, 28, 1305–1312. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yao, C.S.; Chen, C.Y.; Li, M. Analysis of rural residential energy consumption and corresponding carbon emissions in China. Energy Policy 2014, 41, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Han, J.; Zhao, H.; Deng, S.H.; Xiao, H.; Peng, H.; Li, Y.W.; Yang, G.; Shen, F.; Zhang, Y.Z. Evaluating the interplays among economic growth and energy consumption and CO2 emission of China during 1990–2007. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rew. 2012, 16, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaeser, E.L.; Matthew, E.K. The Greenness of Cities: Carbon Dioxide Emissions and Urban Development. J. Urban Econ. 2010, 67, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Kammen, D.M. Spatial distribution of U.S. household carbon footprints reveals suburbanization undermines greenhouse gas benefits of urban population density. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.H.; Fend, Z.M. Survey of rural household energy consumption in China. Energy 1996, 21, 703–705. [Google Scholar]
- Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: New York, NY, USA, 2014.
- Jiang, B.; Sun, Z.Q.; Liu, M.Q. China’s energy development strategy under the low-carbon economy. Energy 2010, 35, 4257–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treiman, D.J. The “difference between heaven and earth”: Urban–rural disparities in well-being in China. Res. Soc. Stratif. Mobil. 2012, 30, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbon Pollution Emission Guidelines for Existing Stationary Sources: Electric Utility Generating Units; Environment Protection Agency (EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2014; p. 645.
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, J.; Maraseni, T.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yusaf, T. A Comparison of Household Carbon Emission Patterns of Urban and Rural China over the 17 Year Period (1995–2011). Energies 2015, 8, 10537-10557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en80910537
Qu J, Maraseni T, Liu L, Zhang Z, Yusaf T. A Comparison of Household Carbon Emission Patterns of Urban and Rural China over the 17 Year Period (1995–2011). Energies. 2015; 8(9):10537-10557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en80910537
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Jiansheng, Tek Maraseni, Lina Liu, Zhiqiang Zhang, and Talal Yusaf. 2015. "A Comparison of Household Carbon Emission Patterns of Urban and Rural China over the 17 Year Period (1995–2011)" Energies 8, no. 9: 10537-10557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en80910537
APA StyleQu, J., Maraseni, T., Liu, L., Zhang, Z., & Yusaf, T. (2015). A Comparison of Household Carbon Emission Patterns of Urban and Rural China over the 17 Year Period (1995–2011). Energies, 8(9), 10537-10557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en80910537