A Combined Optical, Thermal and Electrical Performance Study of a V-Trough PV System—Experimental and Analytical Investigations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modeling of V-Trough PV System
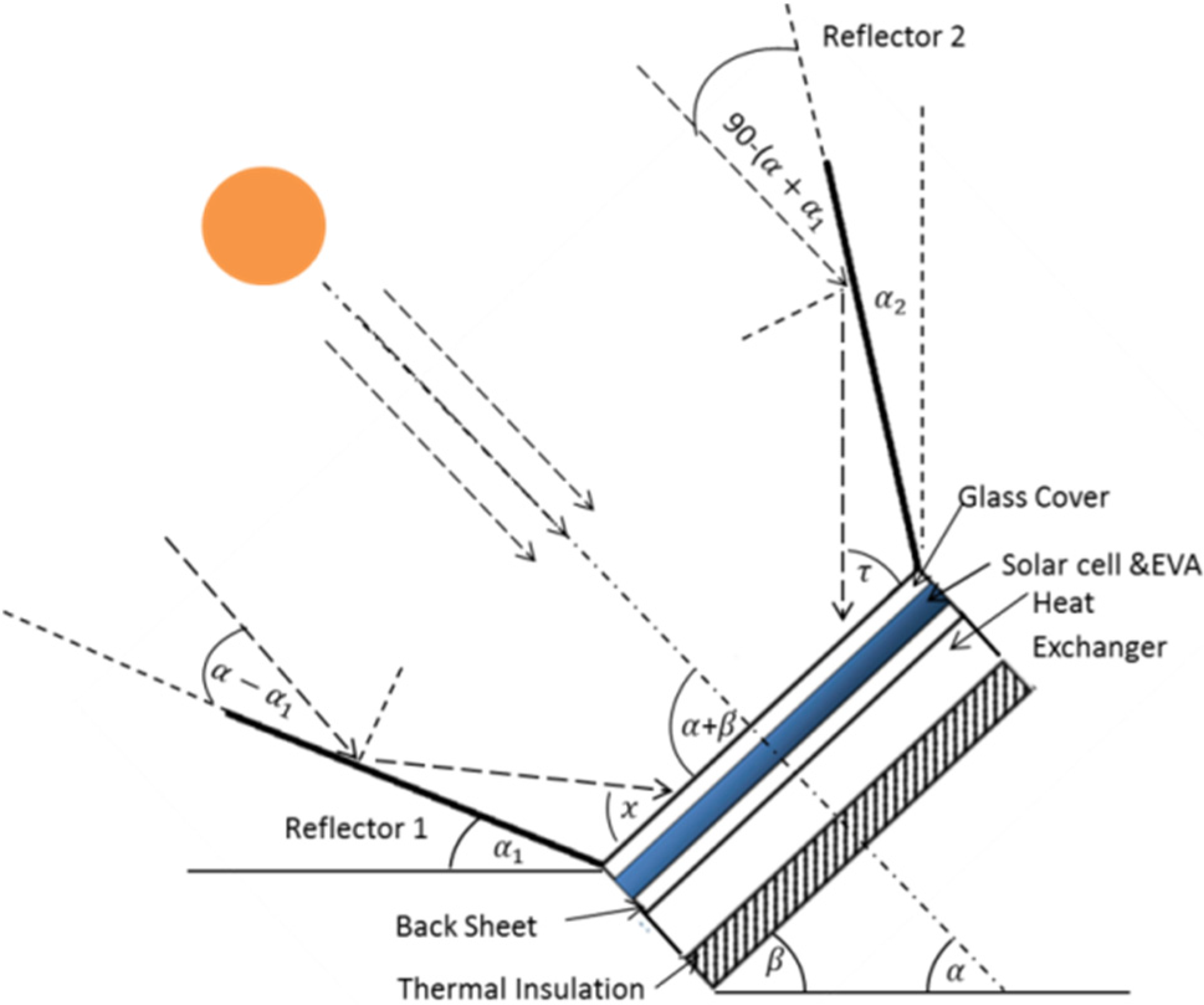
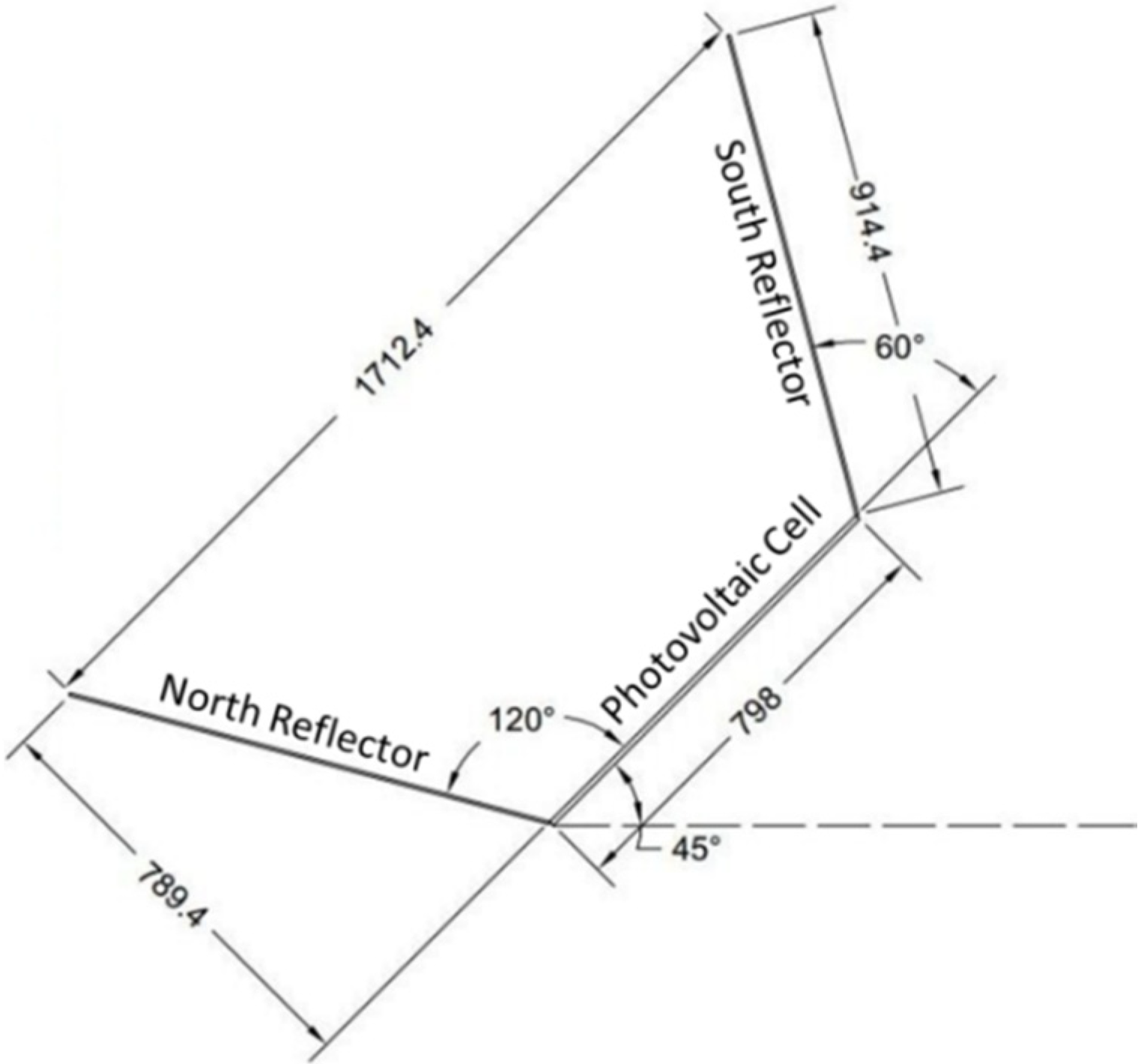
2.1. Optical Modeling of V-Trough PV System
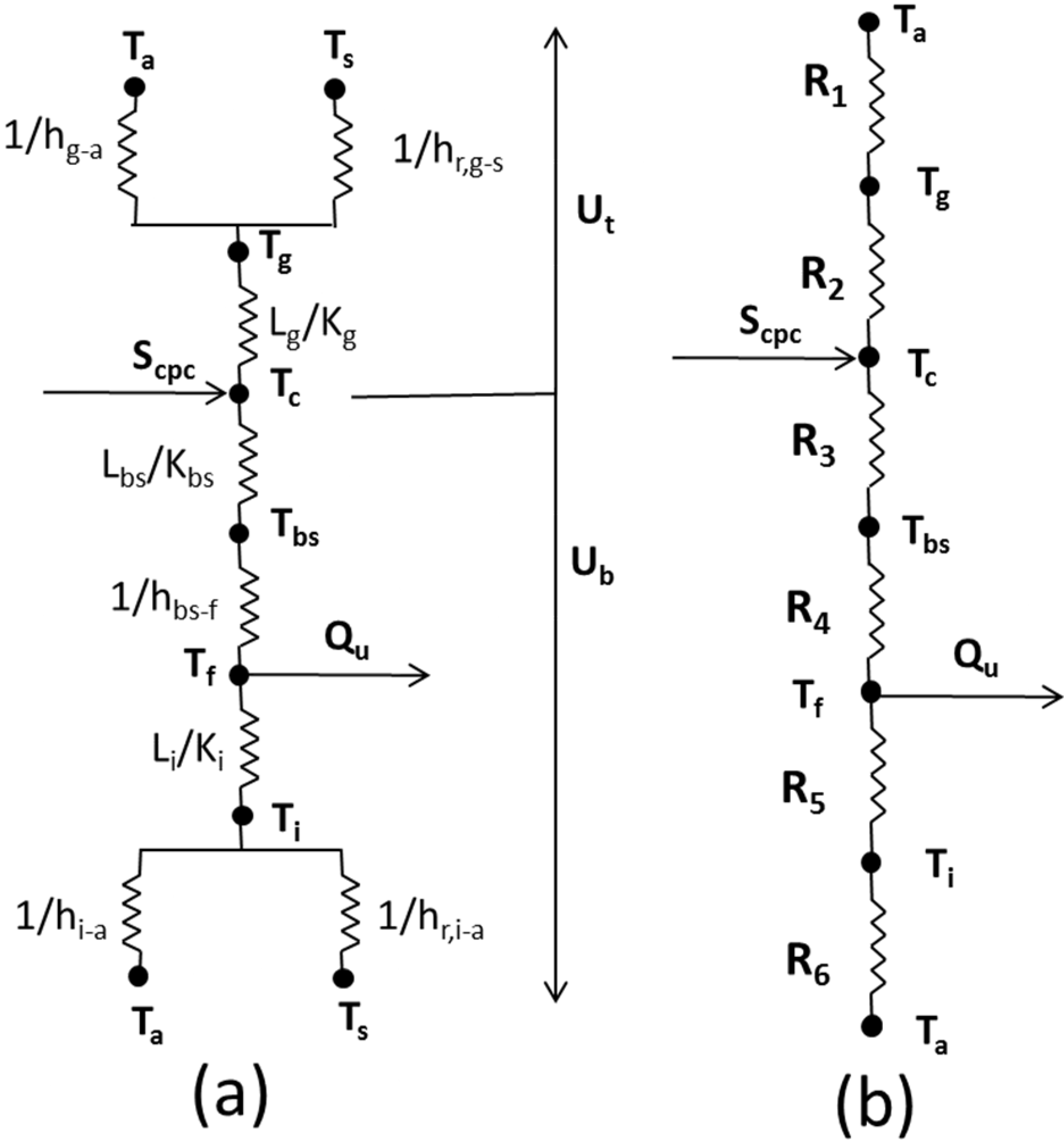
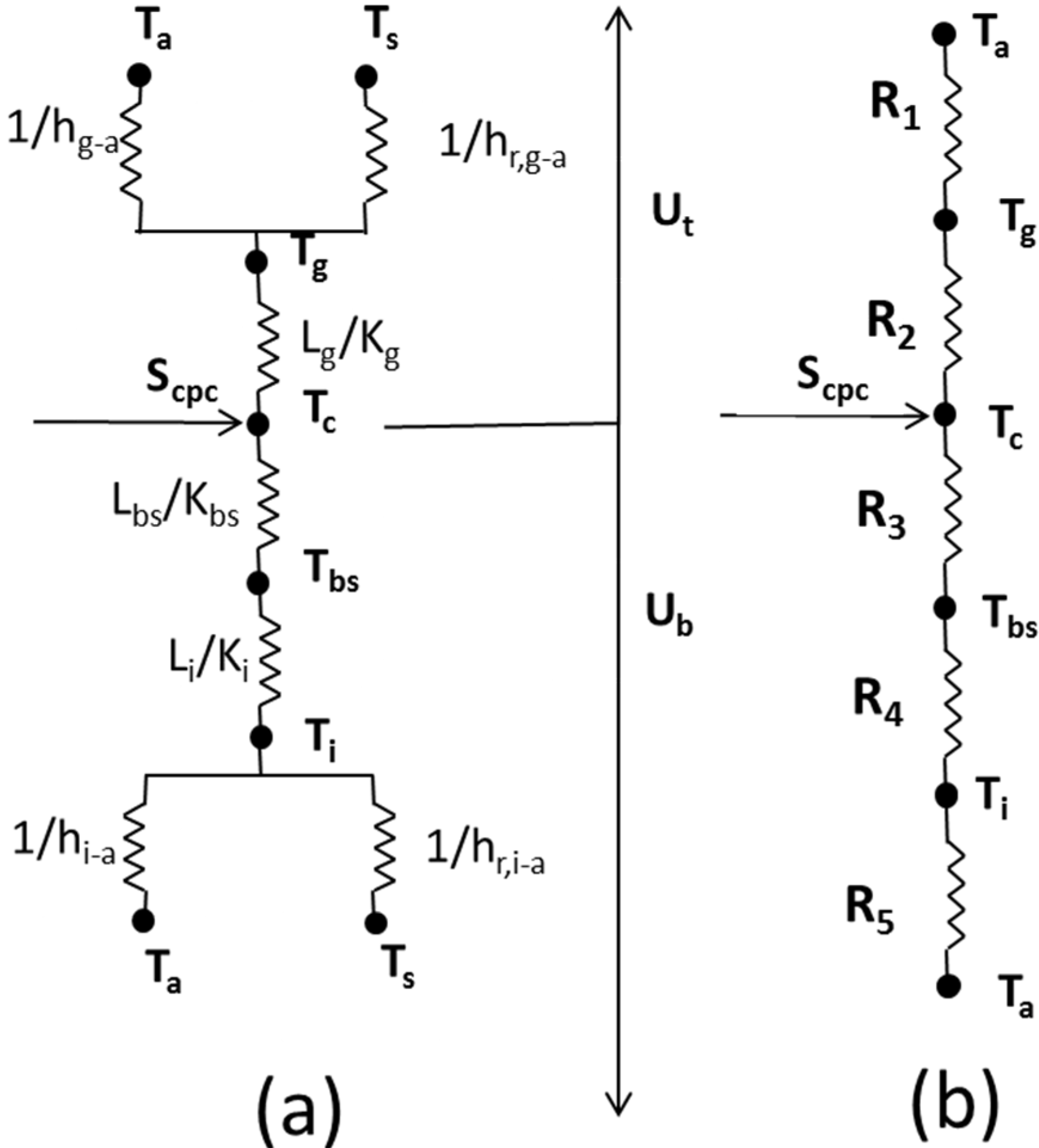
2.2. Thermal Modeling
- One-dimensional energy transfer and steady state of energy transfer is achieved.
- Convection and radiation losses from the front cover and insulation to the ambient were the same.
- The temperature gradient of the glass cover and solar cell was neglected.
- Temperature variation along the thickness and width of the solar cell was considered negligible.
- There was no dust and dirt effect on the collector.
- The water flow in the rectangular channel was uniform and fully developed.
- Contact resistance between the reflectors and the solar cell was neglected.
- (1)
- PV cell:
- (2)
- Cell glass cover:
- (3)
- Back Sheet:
- (4)
- Fluid flowing in the heat exchanger:
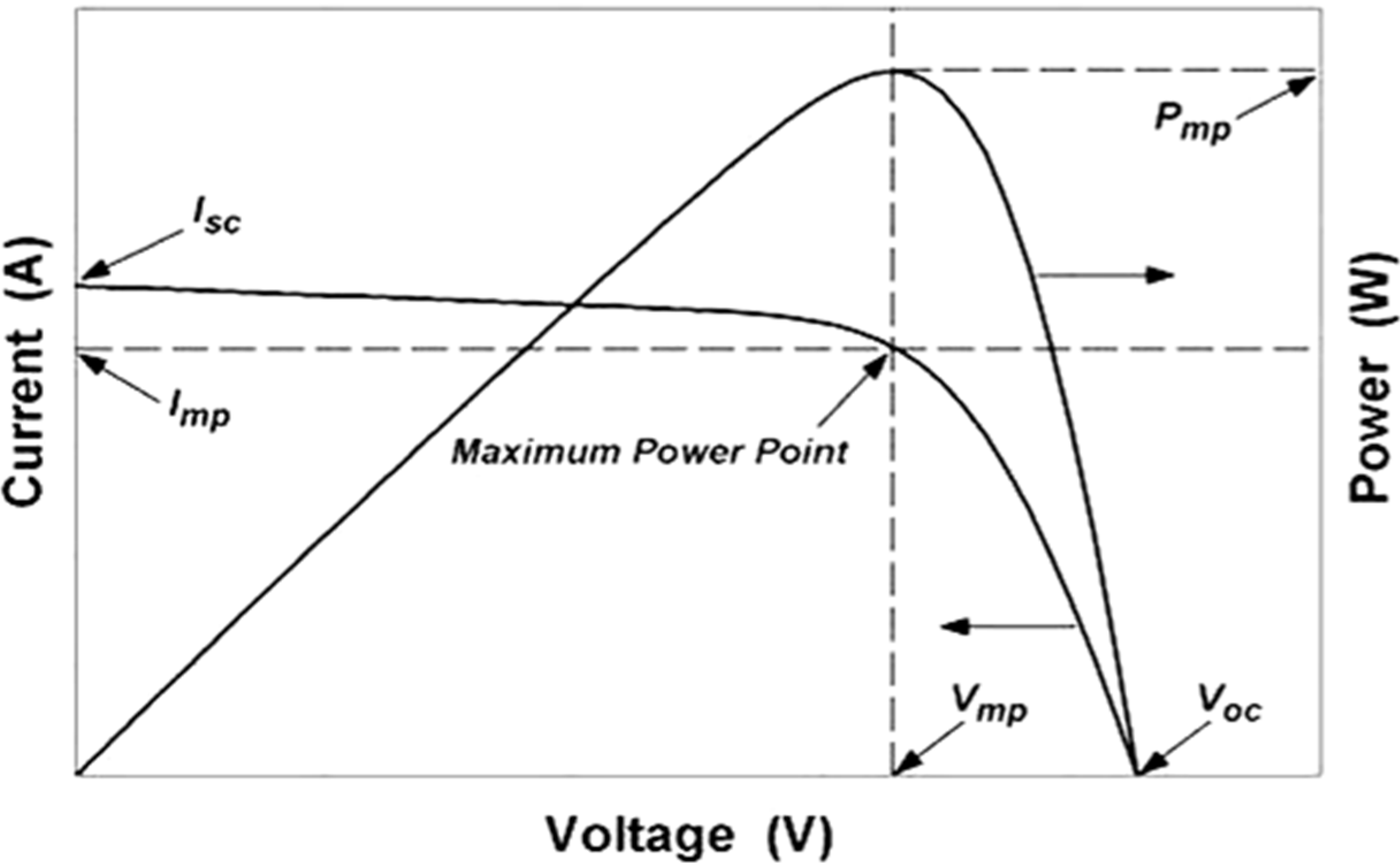
2.3. Electrical Modeling
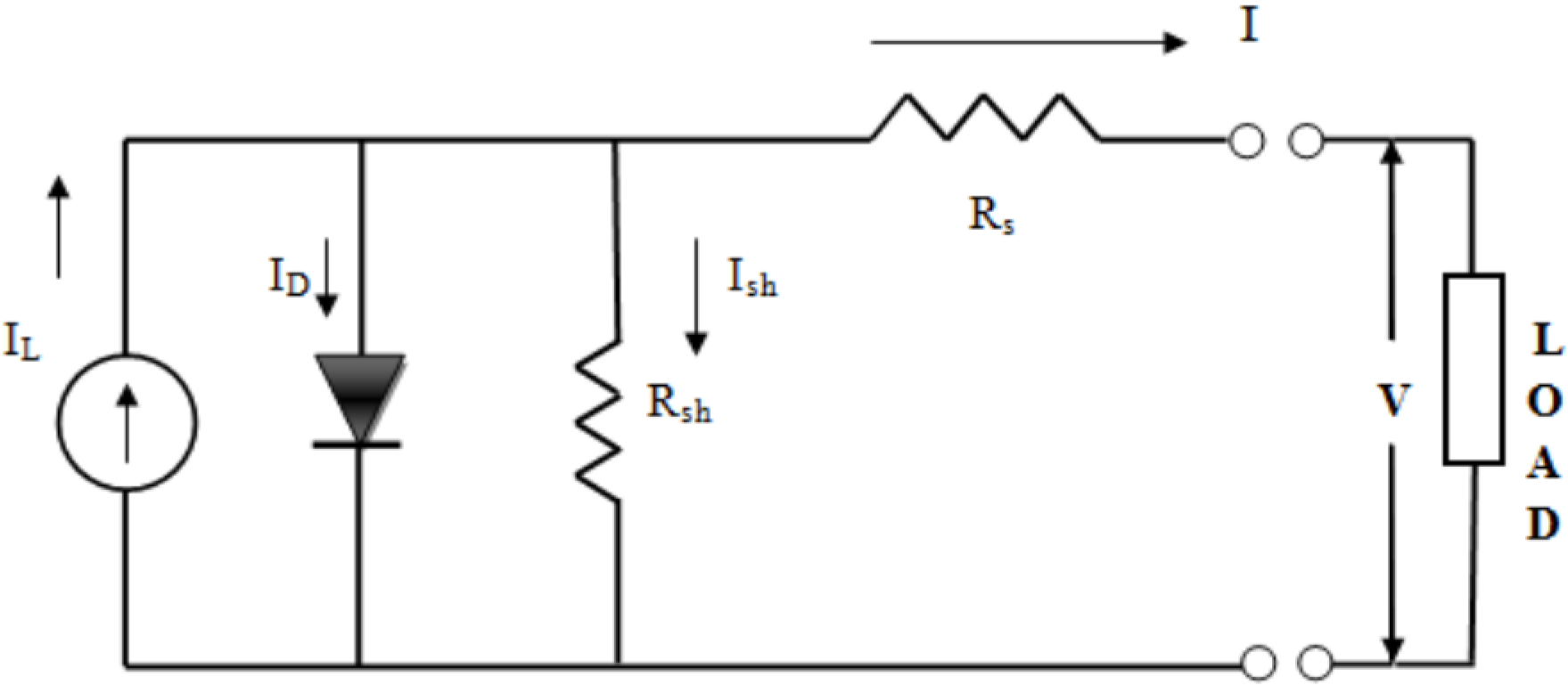
| At short circuit | |
| At open circuit voltage | I = 0, V = Voc,ref |
| At short circuit current | I = Isc,ref , V = 0 |
| At the maximum power point | I = Imp,ref , V = Vmp,ref |
| At the maximum power point |
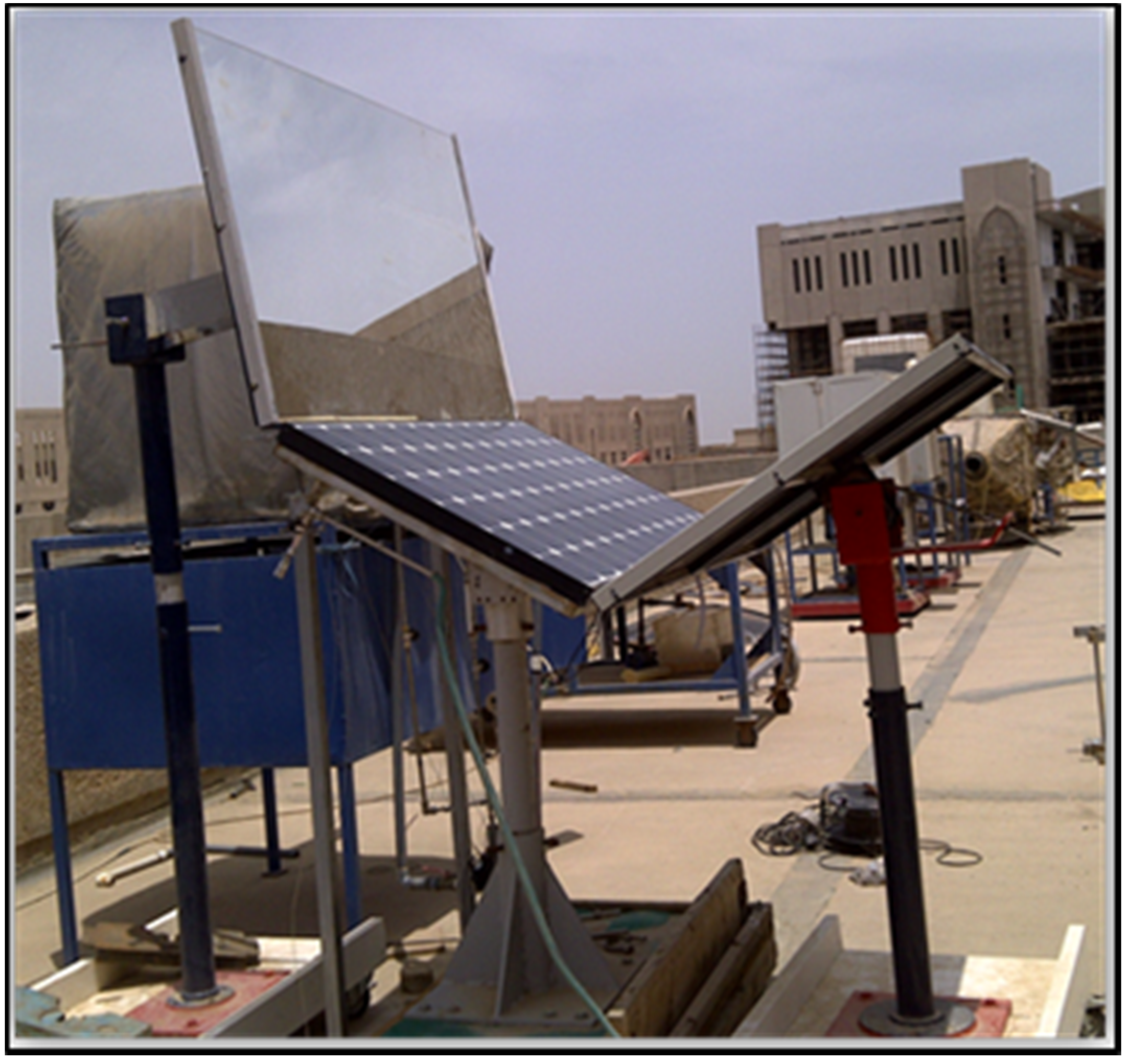
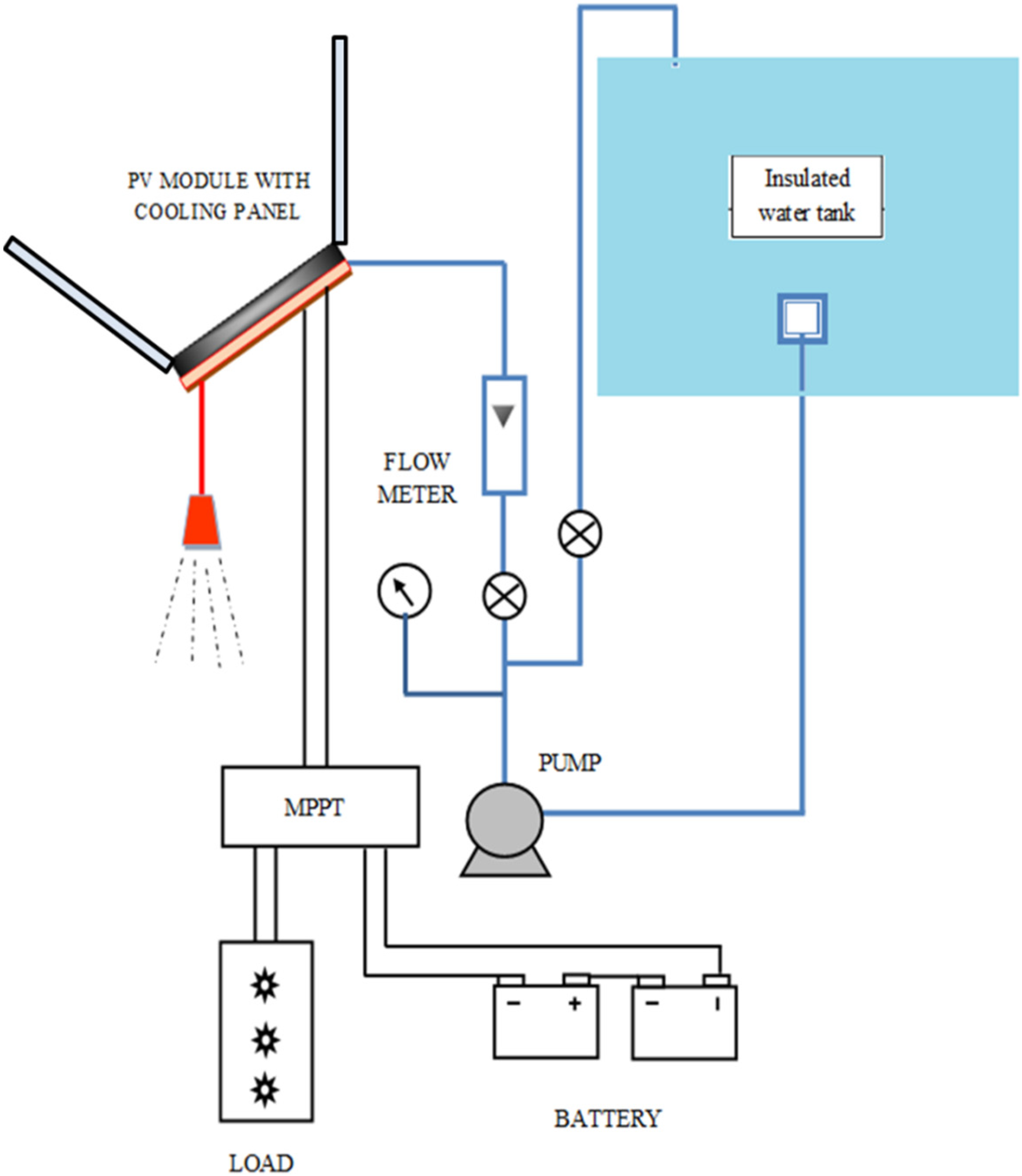
3. Experimental Study

| Solar PV module parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Module type | SunPower SPR-230WHT-U |
| Maximum Power (Pmp) | 230 Watt |
| Maximum Power Voltage (Vmp) | 41 V |
| Maximum Power Current (Imp) | 5.61 A |
| Maximum Power point efficiency | 18.5% |
| Open Circuit Voltage (Voc) | 48.7 V |
| Short Circuit Current (Isc) | 5.99 A |
| Area of the module (A) | 1.24 m2 |
| Temperature co-efficient of Short-circuit current | 3.5 mA/K |
| Number of solar cells | 72 (monocrystalline type) |
| SUNSAVER MPPT | SSMPPT-15L |
|---|---|
| Maximum Battery Current | 15 A |
| Maximum Open Circuit Voltage | 75 V |
| Maximum PV Input | 200 Wp (12 V Battery) 400 Wp (24 V Battery) |
| System Voltage | 12/24 V |
| Instrument Used | Accuracy/sensitvity |
|---|---|
| Sunsaver MPPT | Current: 1%; Voltage: 2% |
| Pyranometer | 30.1 µV/(W/m2) |
| Hygro Thermo-Anemometer | 2% ± 0.2 m/s |
| Thermocouple Thermometer | ±1 °C |
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Optical Modeling
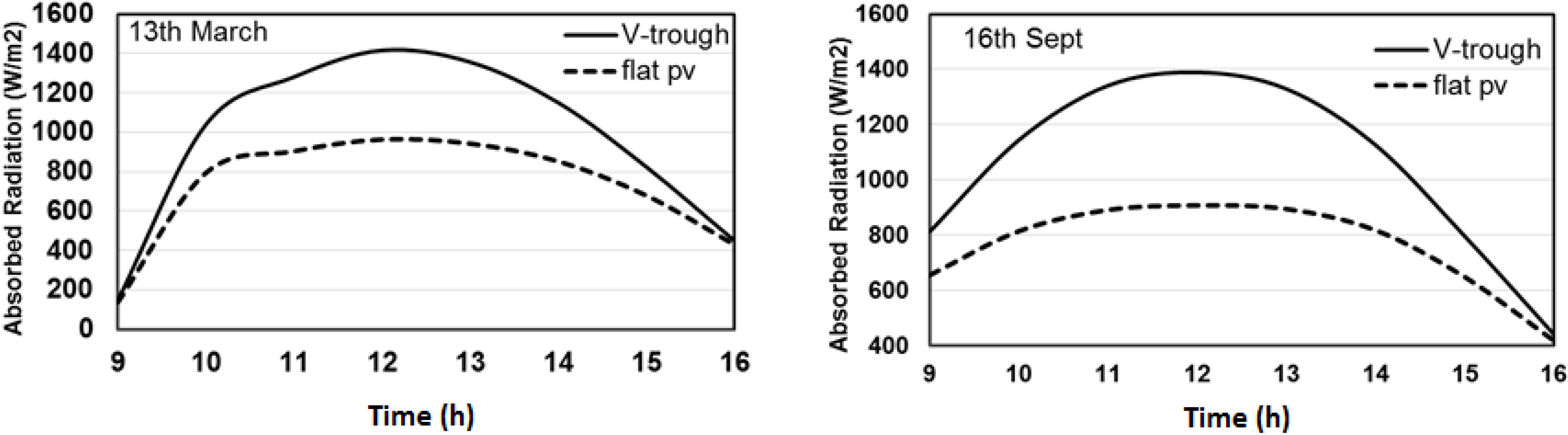
4.2. Thermal Modeling
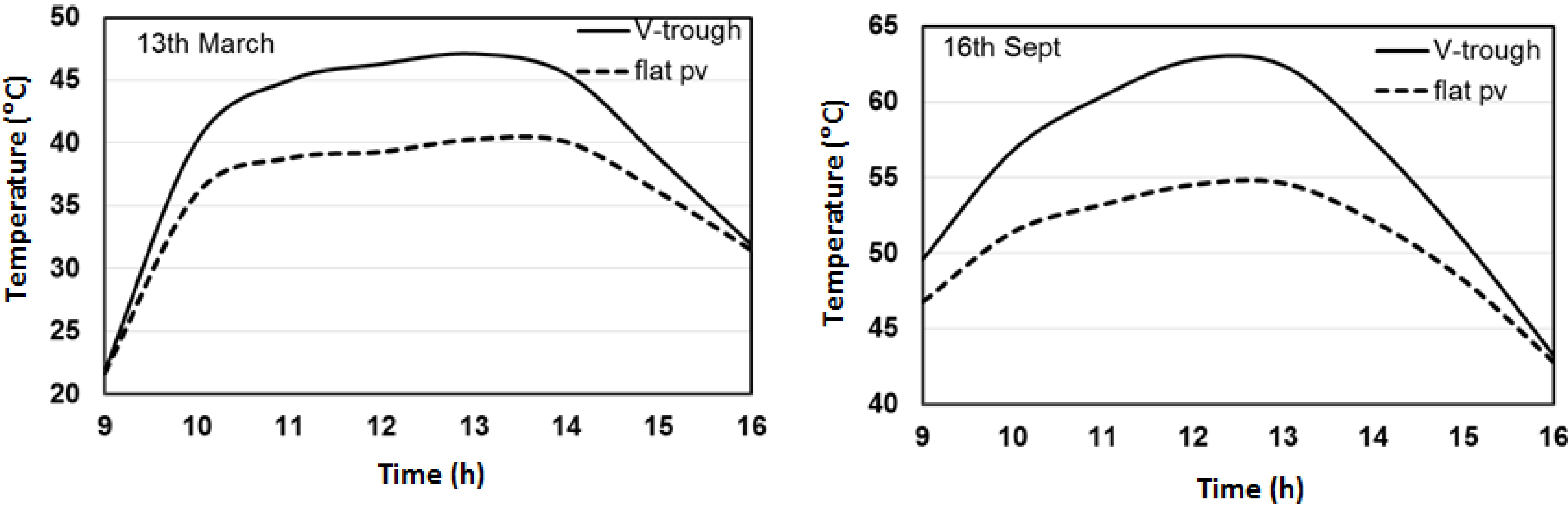
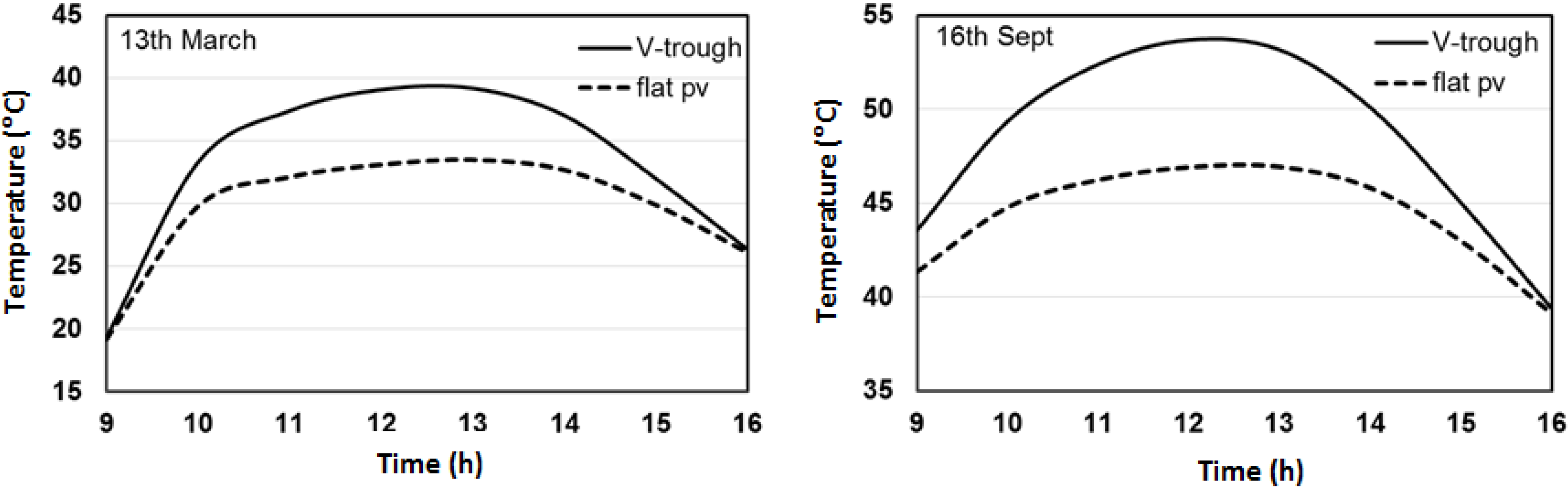
4.3. Electrical Modeling
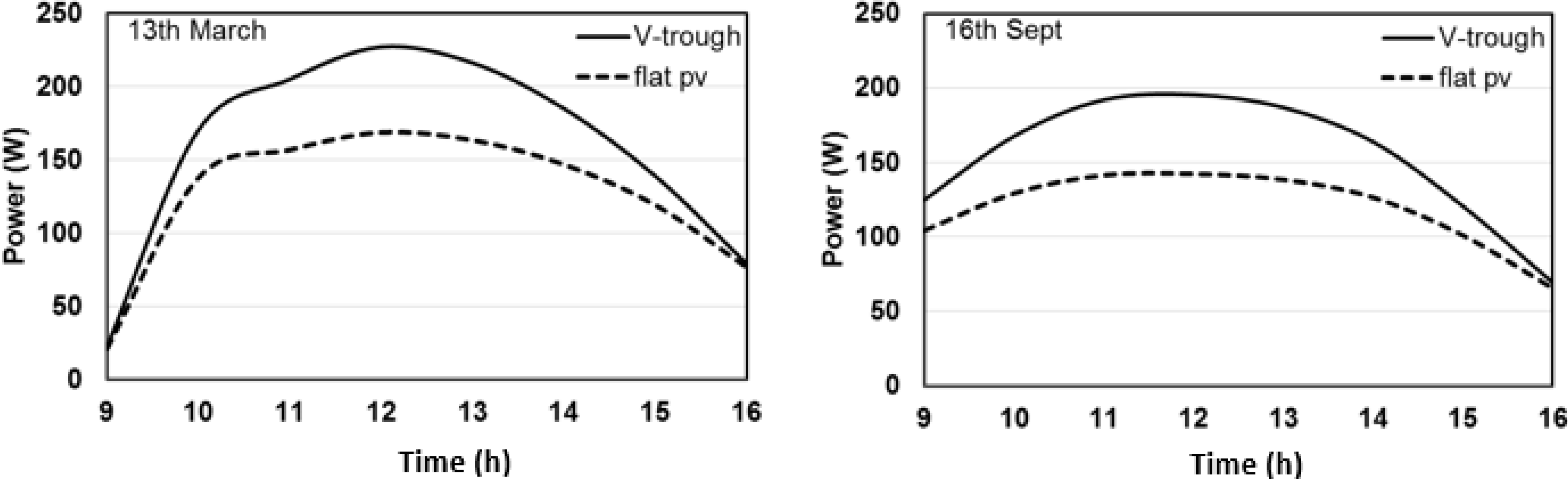
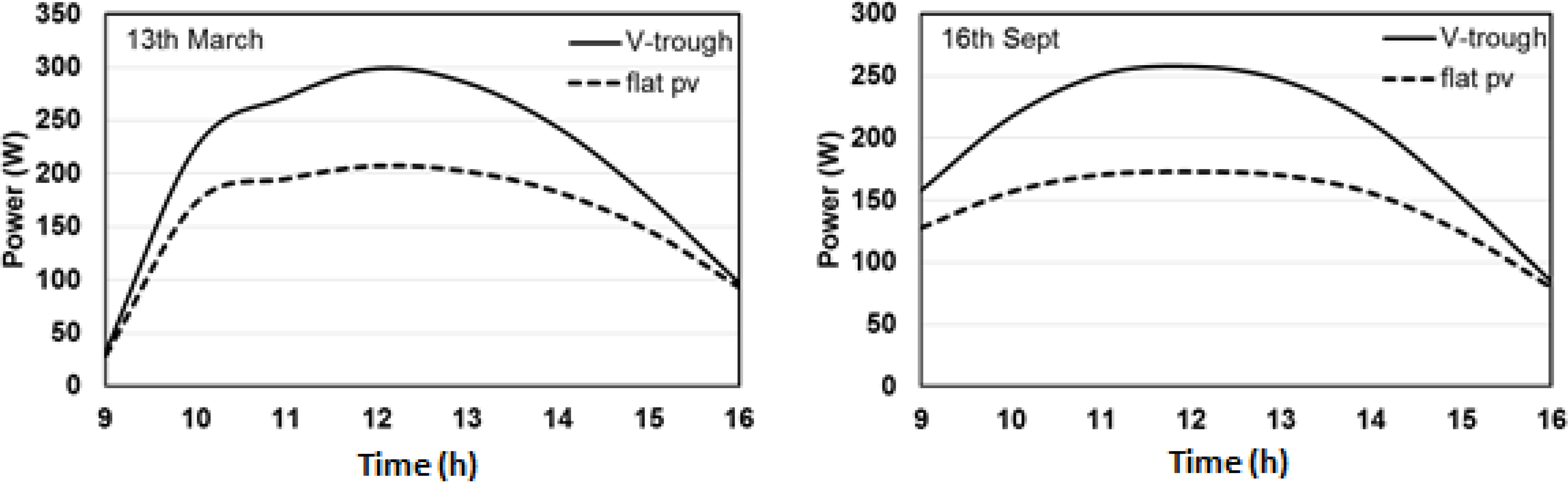
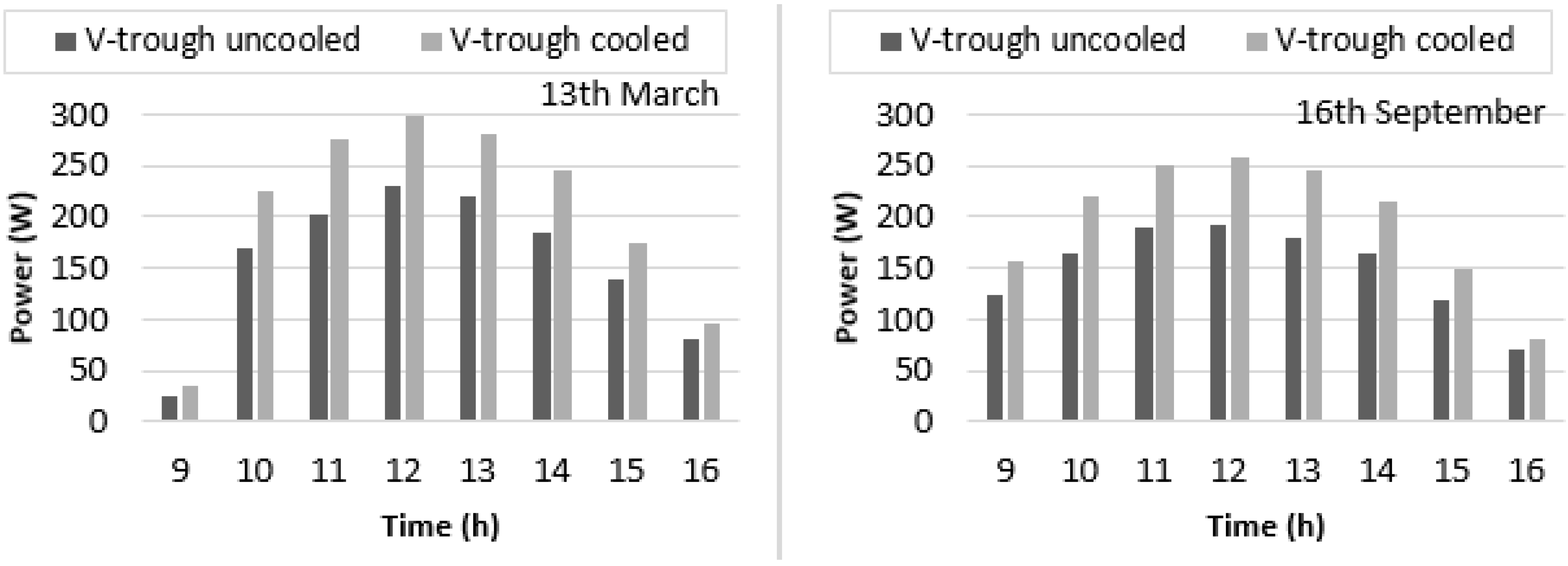
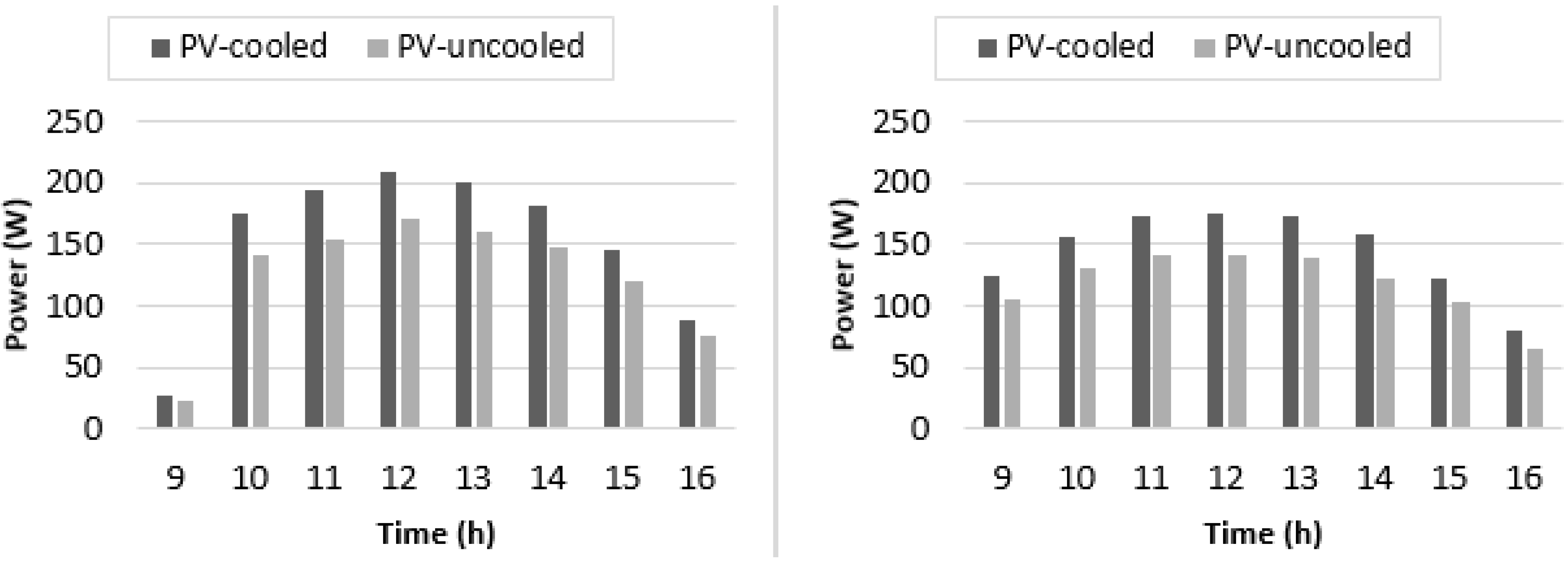
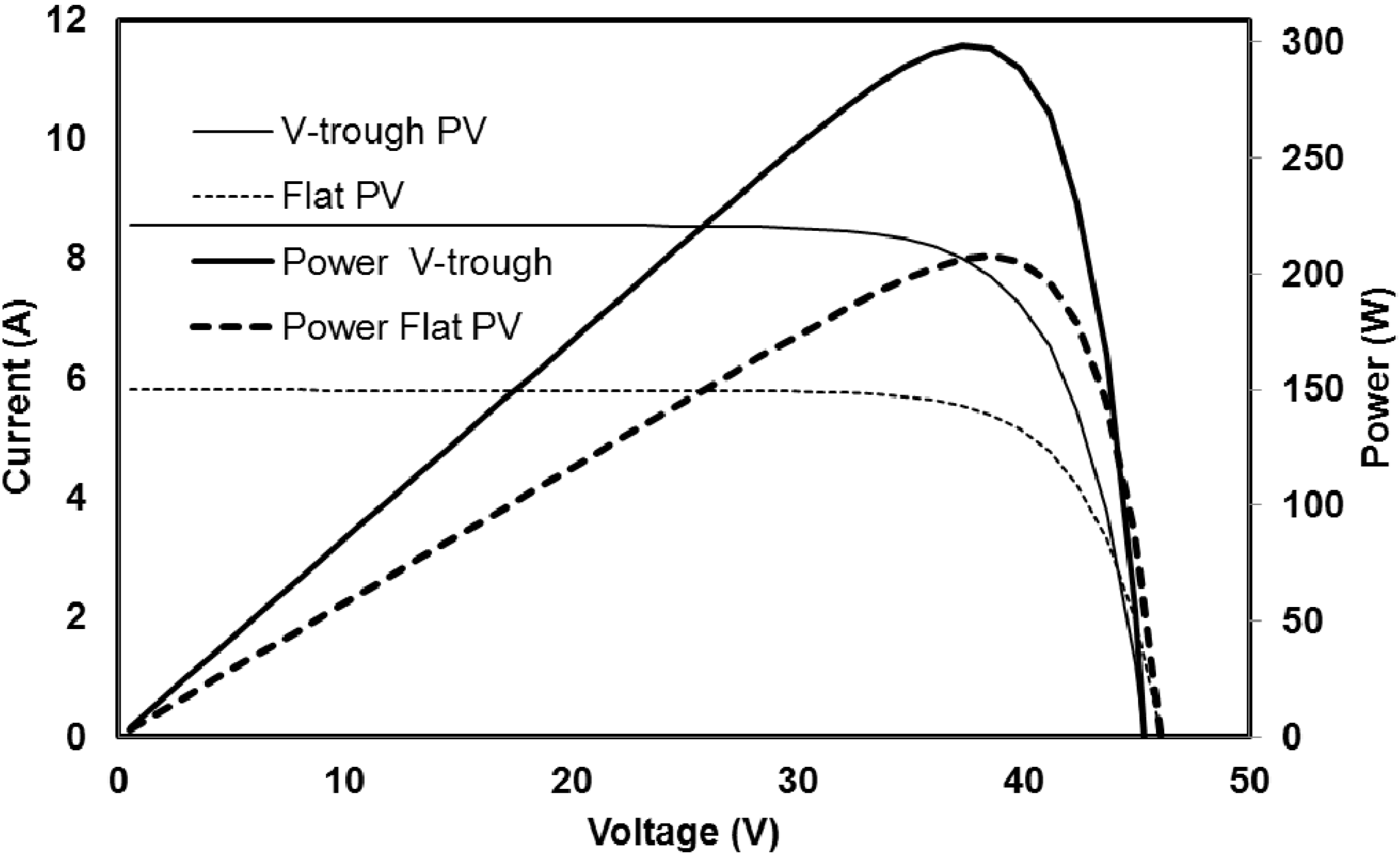
4.4. Experimental Results of V-Trough PV System

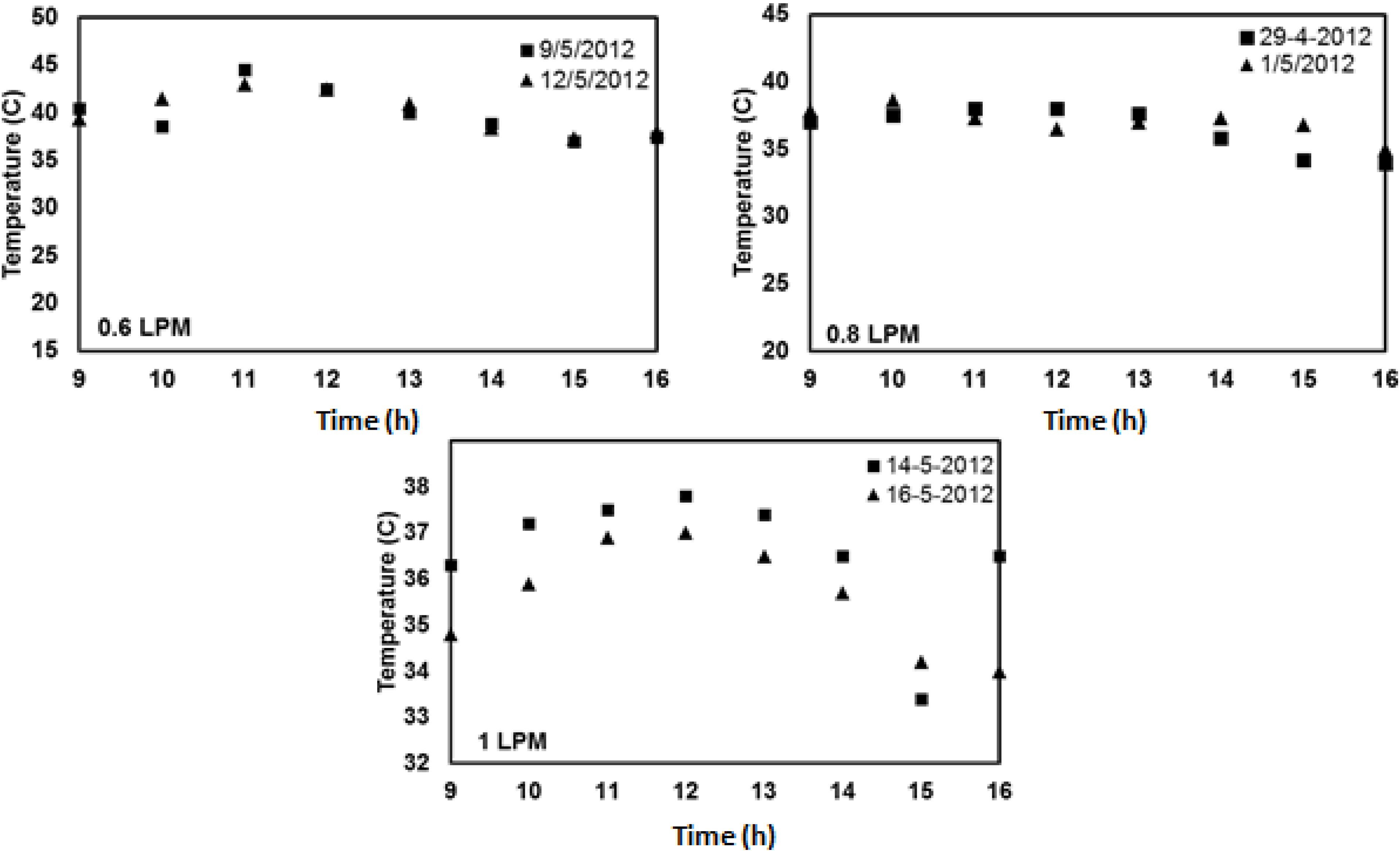
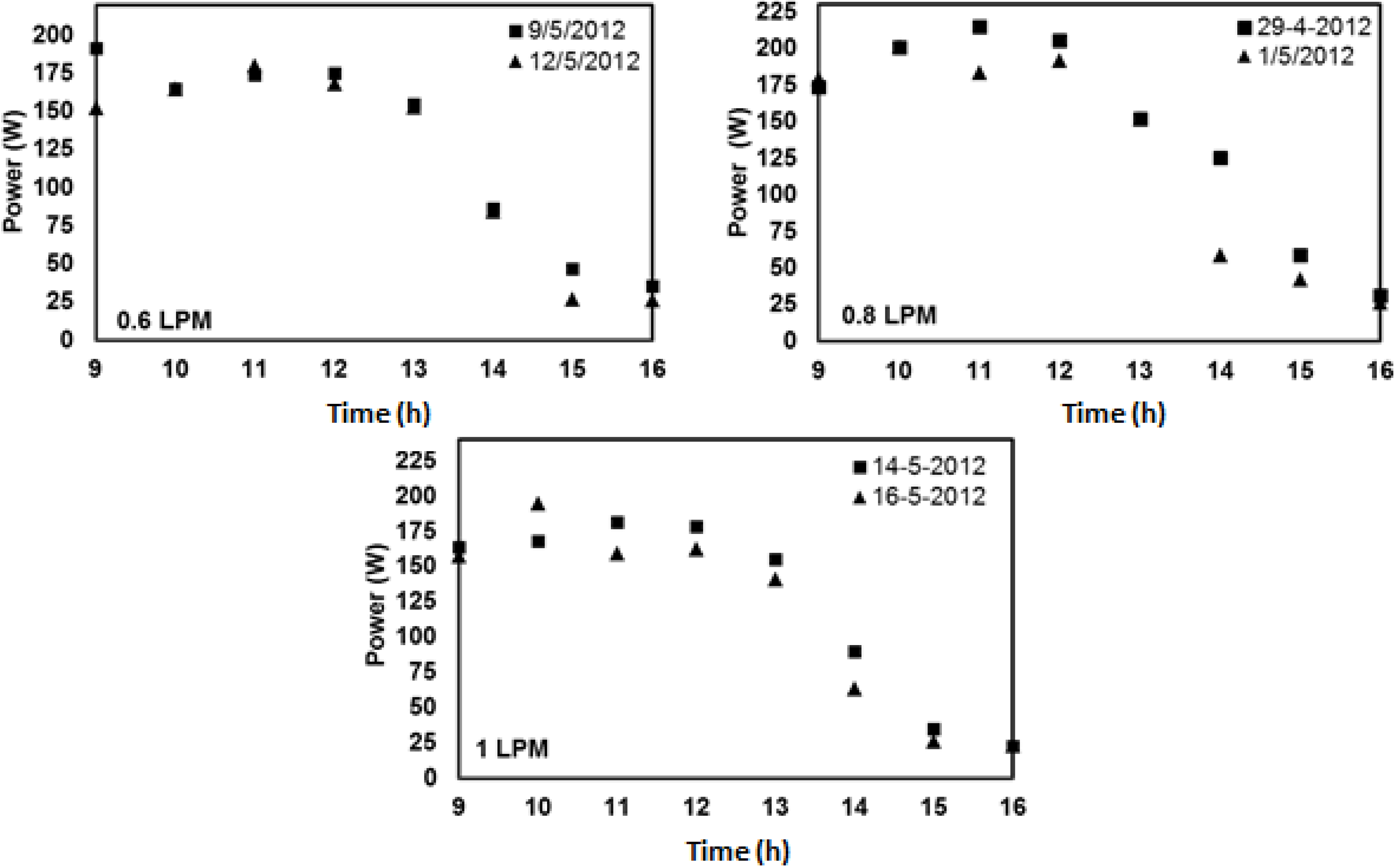
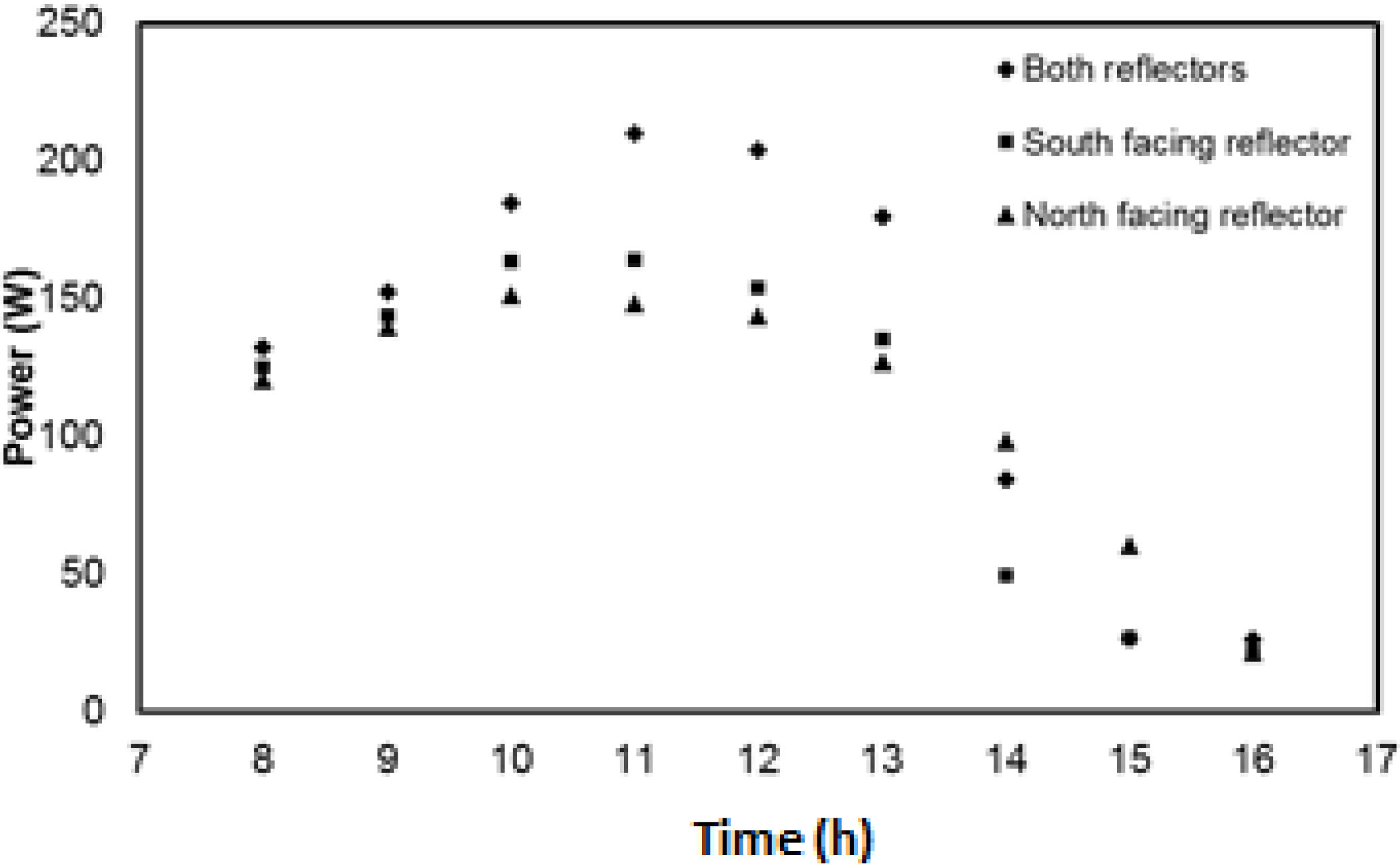
4.5. Comparison of Experimental and Numerical Results for V-Trough PV System
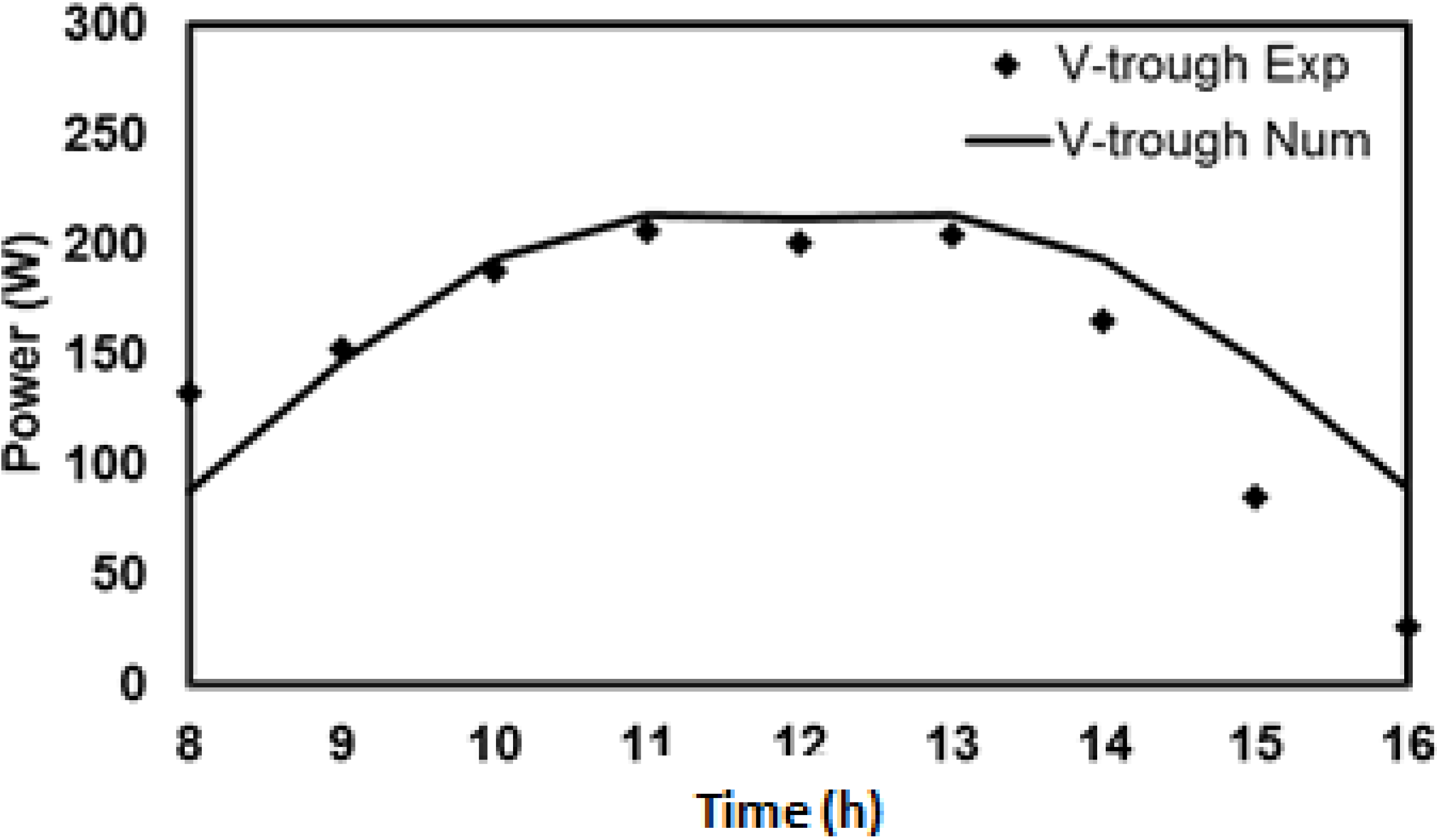
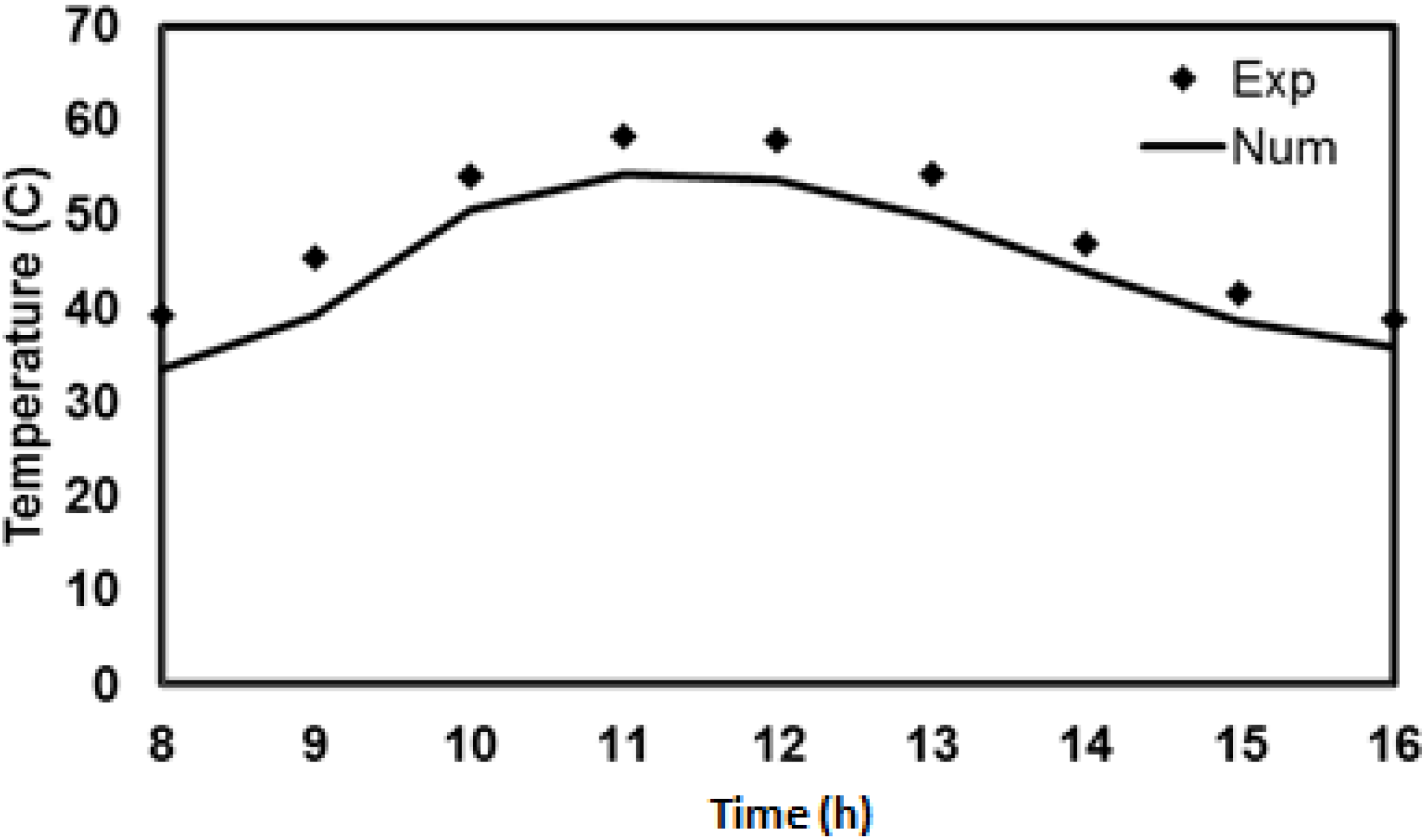
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Nomenclature
| Cp | Specific heat capacity (kJ/kg K) |
| G | Solar radiation intensity (W/m2) |
| hT | Conductive heat transfer coefficient (W/m2K) |
| I | Current (A) |
| IL | Light generated current (A) |
| Io | Extraterrestrial radiation intensity (W/m2) |
| A | Diode reverse current (A) |
| IT | Total incident solar radiation intensity (W/m2) |
| k | Boltzmann’s constant (J/K) |
| Kτα | Incidence angle modifier |
| M | Air mass modifier |
| ṁ | mass flow rate (kg/s) |
| N | number of cell |
| q | electronic charge (C) |
| R | Resistance (Ω) |
| Rb | Geometric factor |
| S | Absorbed radiation intensity (W/m2) |
| T | Temperature (°C or K) |
Mean fluid temperature (°C) | |
| Ut | Heat transfer coefficient (W/m2K) |
| V | Voltage (V) |
Greek Symbols
| α | solar altitude angle |
| β | slope of V-trough PV |
| τα | transmissivity absorptance product |
| ρAl | reflectivity of aluminum |
| α1 | angle of reflector 1 |
| α2 | angle of reflector 2 |
| φ | latitude |
| δ | solar declination angle |
| ω | hour angle |
| μIsc | temperature coefficient of short circuit current (A/K) |
| ρg | ground reflectivity |
| ϵ | Emissivity |
Subscripts
| a | Ambient |
| b | Beam |
| bs | Backsheet |
| bsf | back sheet to fluid |
| c | Cell |
| cbs | cell to backsheet |
| cg | cell to glass |
| d | Diffuse |
| f | Fluid |
| fa | fluid to ambient |
| g | ground reflected |
| ga | glass to ambient |
| oc | open circuit |
| ref | Reference |
| ref,r1 | reflector 1 |
| ref,r2 | reflector 2 |
| s | Series |
| sc | short circuit |
| sh | Shunt |
| tot | Total |
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Irshid, M.I.; Othman, M.O. V-Troughs with high concentration ratios for photovoltaic concentrator cells. Sol. Cells 1988, 23, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiam, H.F. Bi-yearly adjusted V-trough concentrators. Sol. Energy 1982, 28, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandilli, C. Performance analysis of a novel concentrating photovoltaic combined system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 67, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelman, G.; Kribus, A.; Dayan, A. Solar cooling with concentrating photovoltaic/thermal (CPVT) systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 2481–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, G.L.; Ji, X.; Yin, F.; Xu, L. The performance analysis of the trough concentrating solar photovoltaic/thermal system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 2378–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Tiwari, A. Design, fabrication and performance of a hybrid photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) active solar still. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calise, F.; Dentice d’Accadia, M.; Vanoli, L. Design and dynamic simulation of a novel solar trigeneration system based on hybrid photovoltaic/thermal collectors (PVT). Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 60, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, P.; Huide, F.; Jie, J.; Tin-tai, C.; Tao, Z. Annual analysis of heat pipe PV/T systems for domestic hot water and electricity production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 56, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, M.B.; Chaabene, M.; Chtourou, Z. Artificial neural network based control for PV/T panel to track optimum thermal and electrical power. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 65, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Riffat, S.B.; Su, Y. Theoretical study of the performance of a novel PV/e roof module for heat pump operation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, J.I.; Vallverdu, X.; Lechon, M.A.; Ibanez, M. Design and simulation of a low concentrating photovoltaic/thermal system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2005, 46, 3034–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemisana, D.; Ibáñez, M.; Rosell, J.I. Characterization of a photovoltaic–thermal module for Fresnel linear concentrator. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 3234–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemisana, D.; Ibáñez, M. Linear Fresnel concentrators for building integrated applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1476–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kribus, A.; Kaftori, D.; Mittelman, G.; Hirshfeld, A.; Flitsanov, Y.; Dayan, A. A miniature concentrating photovoltaic and thermal system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 3582–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, N.; Ruiz, J.M. Optical performance analysis of V-trough PV concentrators. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2008, 16, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermenean, I.S.; Diaconescu, D.V. On the geometric modelling of a concentrating PV-mirror system. Bull. Transilv. Univ. Brasov. 2009, 2, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Tina, G.M.; Scandura, P.F. Case study of a grid connected with a battery photovoltaic system: V-trough concentration vs. single-axis tracking. Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 64, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, F.; Brito, M.C.; Corregidor, V.; Wemans, J.; Sorasio, G. Modeling the performance of low concentration photovoltaic systems. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2010, 94, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaltout, M.A.M.; Ghettas, A.; Sabry, M. V-trough concentrator on a photovoltaic full tracking system in a hot desert climate. Renew. Energy 1995, 6, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangani, C.; Solanki, C. Experimental evaluation of V-trough (2 suns) PV concentrator system using commercial PV modules. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2007, 91, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostic, L.T.; Pavlovic, T.M.; Pavlovic, Z.T. Influence of reflectance from flat aluminum concentrators on energy efficiency of PV/Thermal collector. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.Q. Output characteristics study of V-trough PV concentration system. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 71–78, 2077–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, F.; Brito, M.C.; Corregidor, V.; Wemans, J.; Sorasio, G. Ageing of standard PV module when integrated in a V-trough concentration system. MRS Proc. 2011, 1210, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, S.; Banerjee, S.; Vyas, K.; Patel, P.; Ghosh, P.K. Self regulation of photovoltaic module temperature in V-trough using a metal–wax composite phase change matrix. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, C.; Sangani, C.; Gunashekar, D.; Antony, G. Enhanced heat dissipation of V-trough PV modules for better performance. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2008, 92, 1634–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.N.; Künnemeyer, R.; Duke, M.; Carson, J.K. A combined optical, thermal and electrical performance model of a building integrated photovoltaic/thermal concentrator (BIPVTC). In Proceedings of the 18th Electronics New Zealand Conference, ENZCON 2011, Massey University, Palmerton North, New Zealand, 21–22 November 2011; pp. 107–112.
- Vilela, O.C.; Bione, J.; Fraidenraich, N. Simulation of grape culture irrigation with photovoltaic V-trough pumping systems. Renew. Energy 2004, 29, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostić, L.T.; Pavlović, T.M.; Pavlović, Z.T. Optimal design of orientation of PV/T collector with reflectors. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 3023–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffie, J.A.; Beckman, W.A. Solar Engineering of Thermal Processes; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Stutenbaeumer, U.; Mesfin, B. Equivalent model of monocrystalline, polycrystalline and amorphous silicon solar cells. Renew. Energy 1999, 18, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bahaidarah, H.M.; Tanweer, B.; Gandhidasan, P.; Rehman, S. A Combined Optical, Thermal and Electrical Performance Study of a V-Trough PV System—Experimental and Analytical Investigations. Energies 2015, 8, 2803-2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8042803
Bahaidarah HM, Tanweer B, Gandhidasan P, Rehman S. A Combined Optical, Thermal and Electrical Performance Study of a V-Trough PV System—Experimental and Analytical Investigations. Energies. 2015; 8(4):2803-2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8042803
Chicago/Turabian StyleBahaidarah, Haitham M., Bilal Tanweer, Palanichamy Gandhidasan, and Shafiqur Rehman. 2015. "A Combined Optical, Thermal and Electrical Performance Study of a V-Trough PV System—Experimental and Analytical Investigations" Energies 8, no. 4: 2803-2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8042803
APA StyleBahaidarah, H. M., Tanweer, B., Gandhidasan, P., & Rehman, S. (2015). A Combined Optical, Thermal and Electrical Performance Study of a V-Trough PV System—Experimental and Analytical Investigations. Energies, 8(4), 2803-2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8042803








