Potential of Offshore Wind Energy and Extreme Wind Speed Forecasting on the West Coast of Taiwan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Wind Energy Estimation
1.2. Extreme Wind Speed Forecast
2. Research Methods
2.1. Light Detection and Ranging (Lidar)
| Specification item | Range |
|---|---|
| Operating wavelength | 1550 nm |
| Wind speed range | 0–90 m/s |
| Sensing range | 30 to 150 m |
| Number of range gates | 3–6 |
| Range gate depth | ±20 m |
| Wind speed accuracy | ±0.5 m/s |
| Wind direction accuracy | ±1° |
| Relative angular accuracy | ±2° |
| Data output rate | 1 Hz |
2.2. WAsP
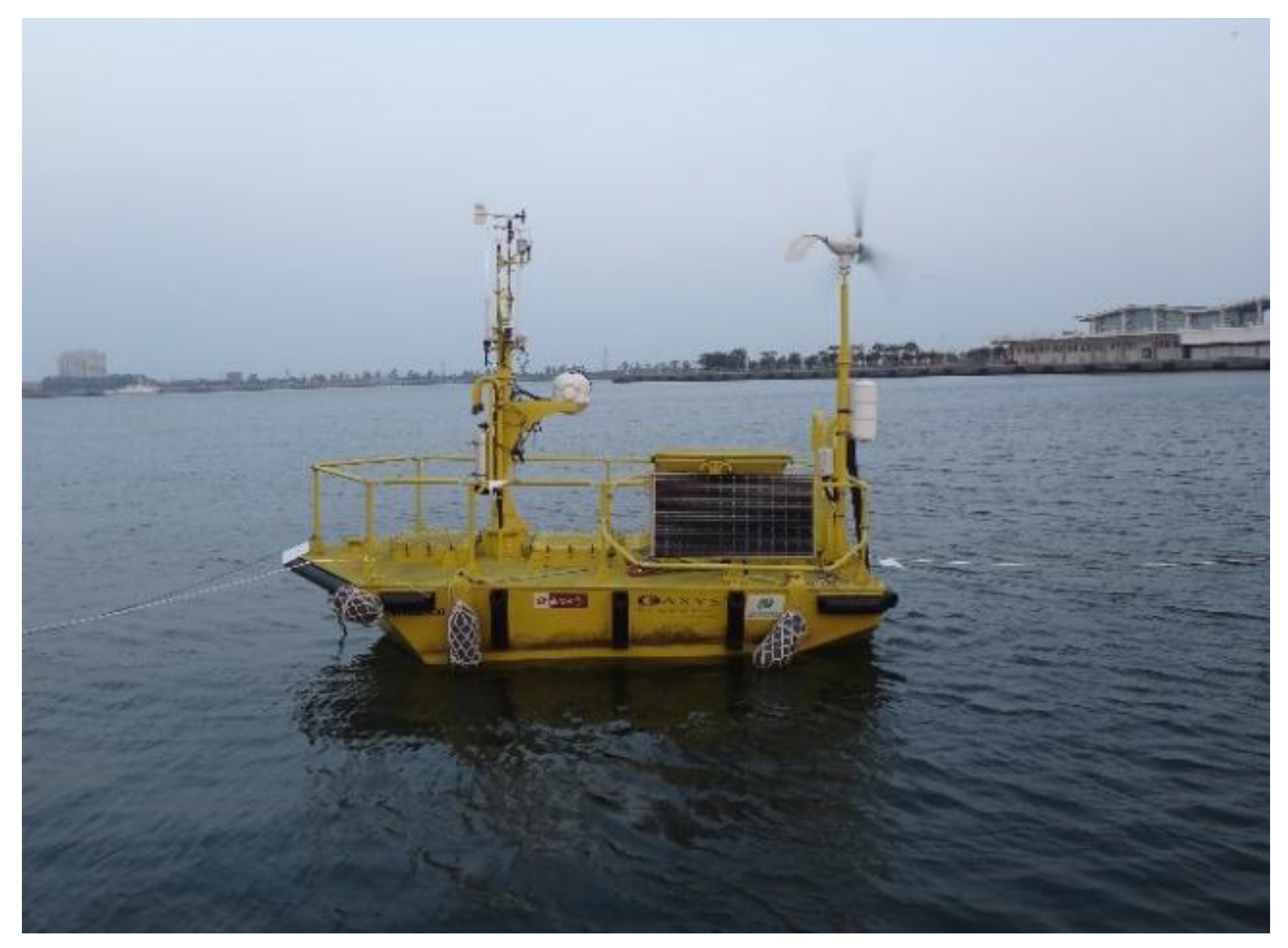

2.3. Empirical Simulation Data versus Lidar Detection Results
2.3.1. Miaoli Region
2.3.2. Tainan Region
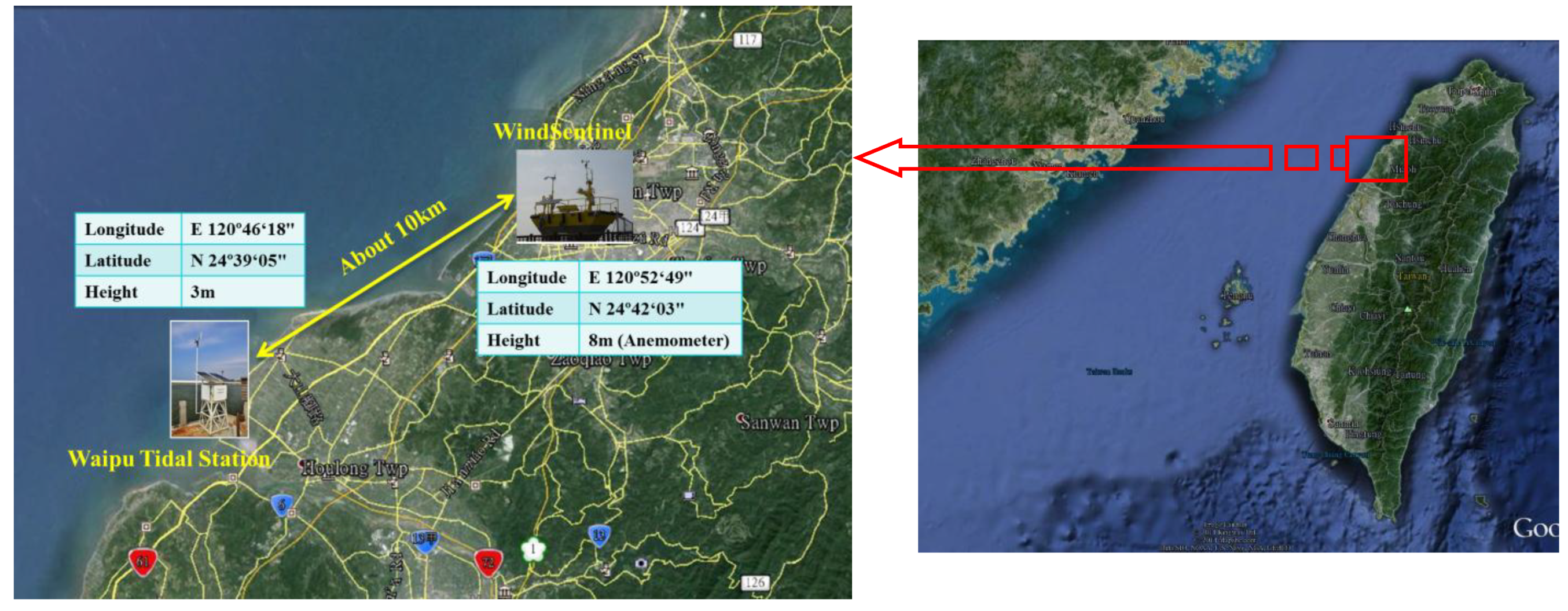
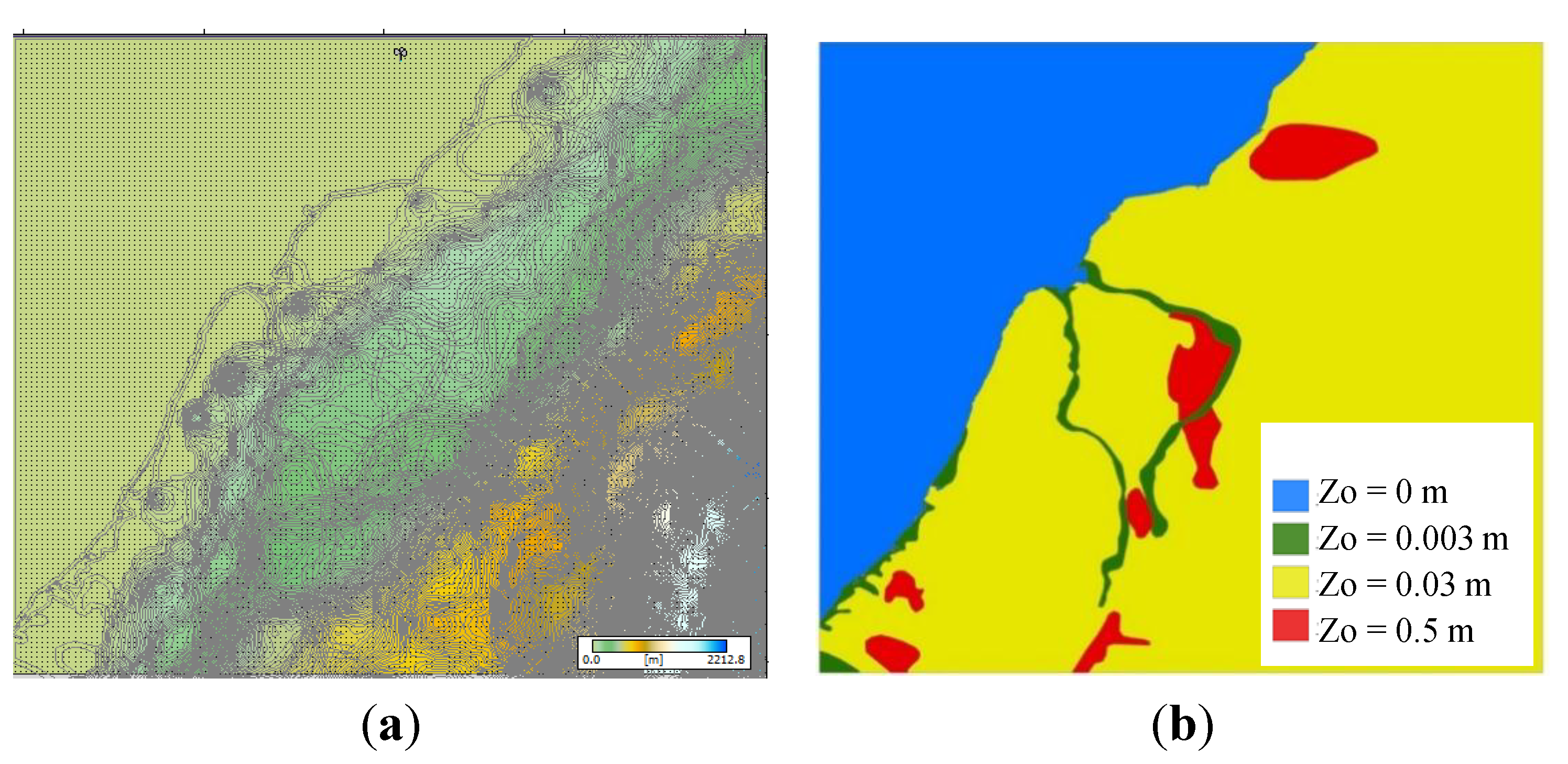
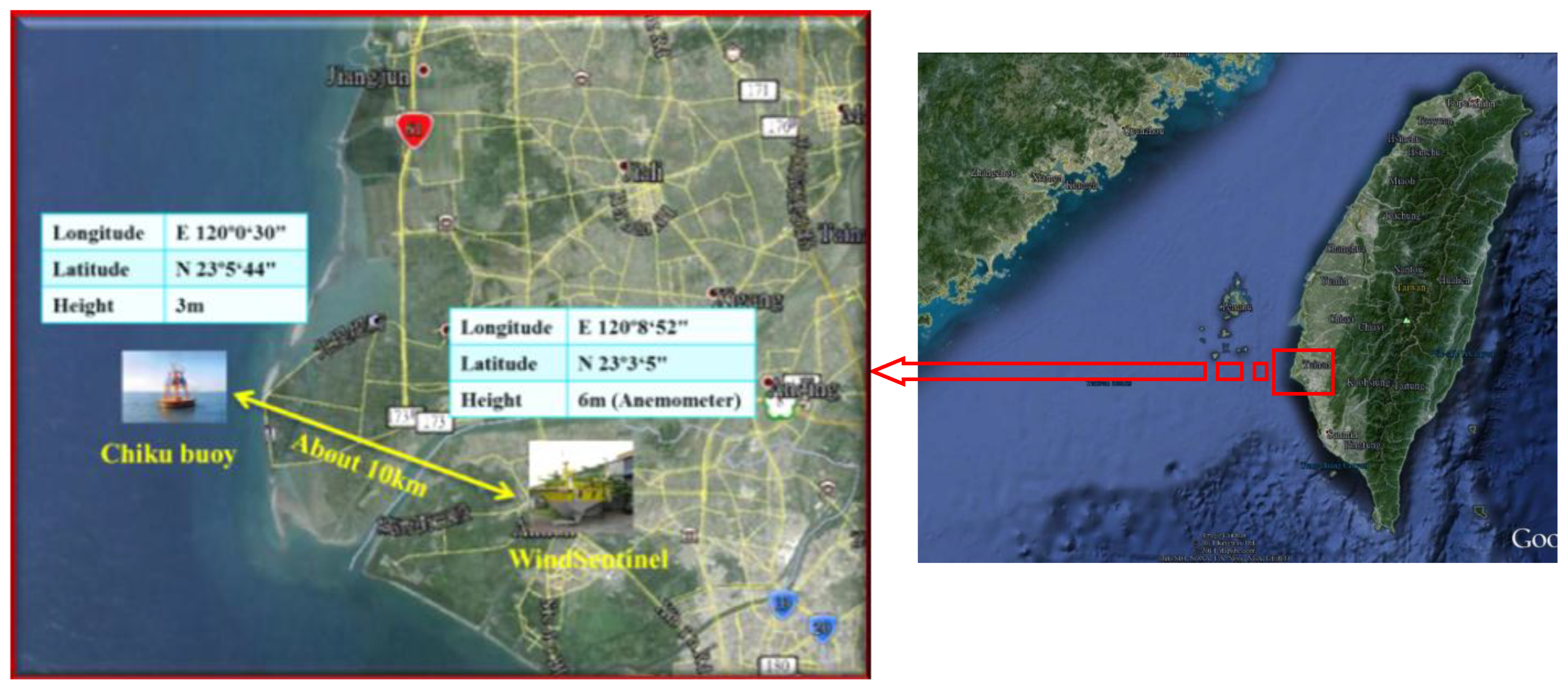
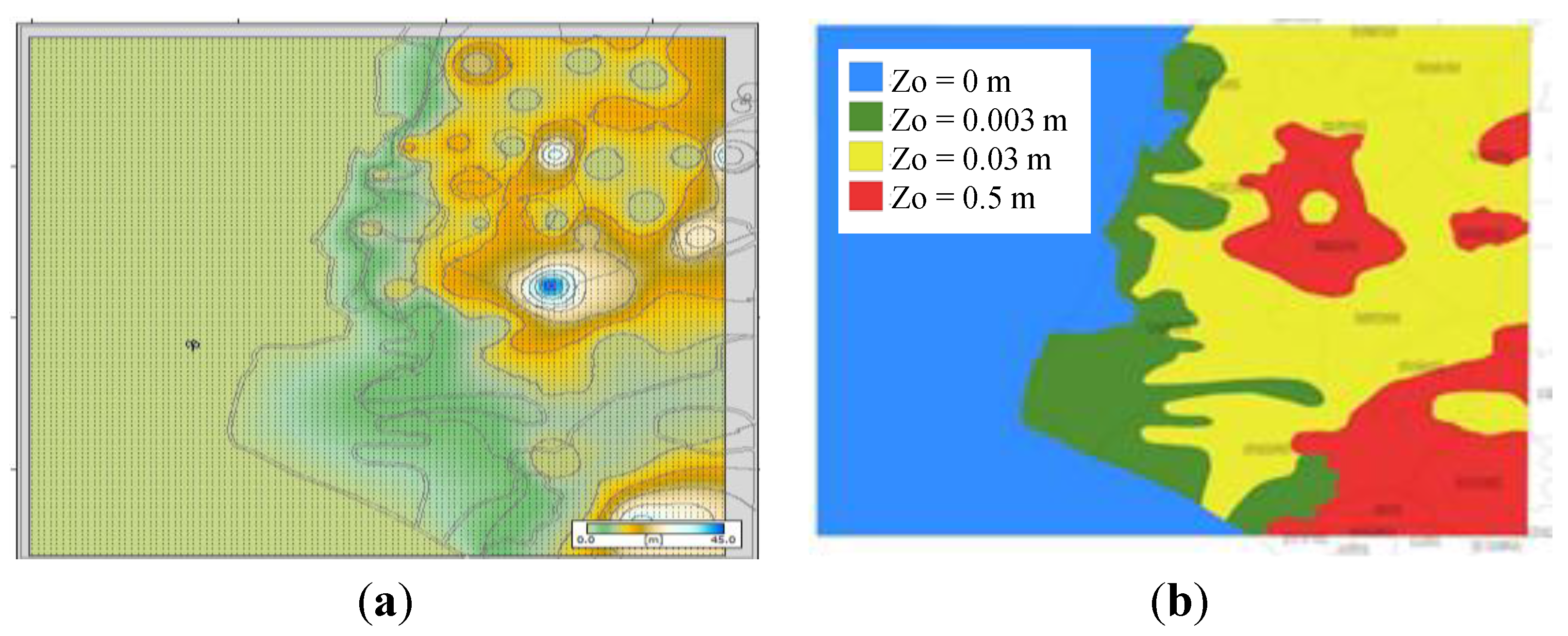
2.4. Analysis of Wind Power Resources on the West Coast of Taiwan
| Area | Station | Longitude (east) | Latitude (north) | Height (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) Hsinchu | Hsinchu Buoy | 120.8439 | 24.7608 | 2 |
| (b) Miaoli | Waipu Tidal Station | 120.7717 | 24.6514 | 6 |
| (c) Taichung | Lukang Meteorological Station | 120.4222 | 24.0769 | 6 |
| (d) Changhua | Lukang Meteorological Station | 120.4222 | 24.0769 | 6 |
| (e) Yunlin | Mailiao Tidal Station | 120.1607 | 23.7861 | 6 |
| (f) Chiayi | Wai-san-ting-chou Meteorological Station | 120.01 | 23.26 | 10 |
| (g) Tainan | Qigu Buoy | 120.0083 | 23.0956 | 3 |
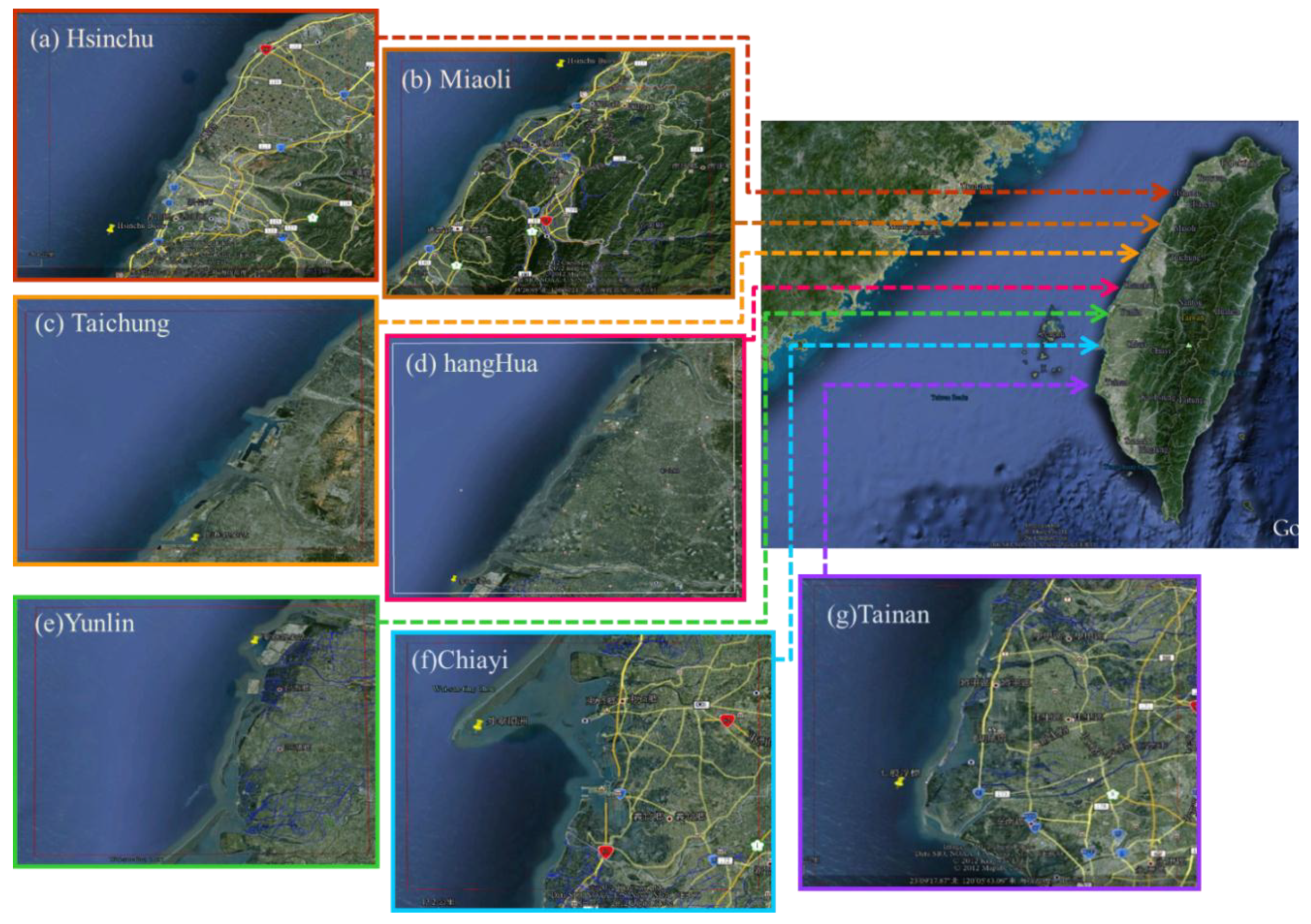

2.5. Extreme Wind Speed Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Lidar Field Data versus WAsP Simulation Results
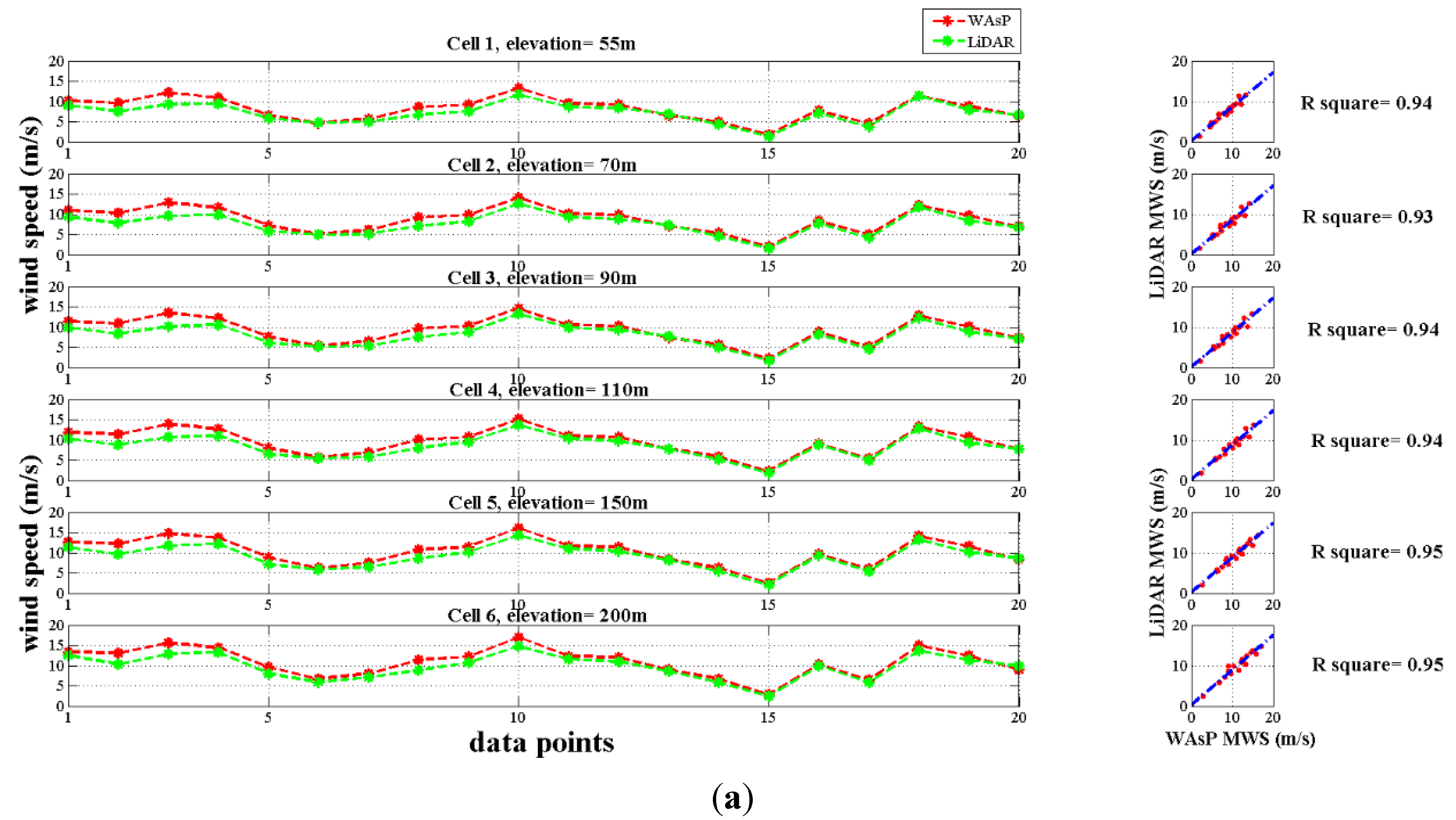
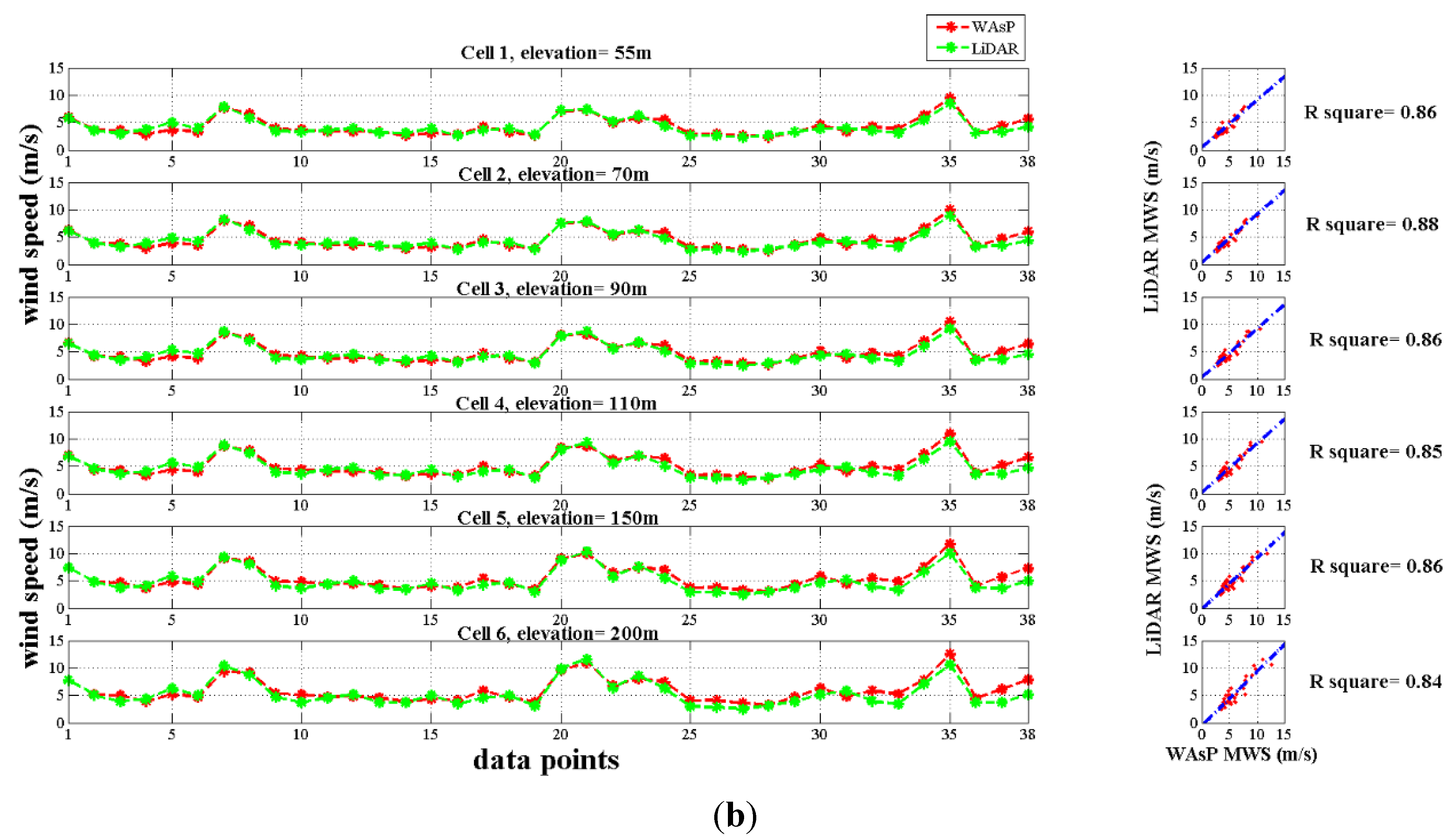
3.2. Wind Speed and Wind Power Density Estimations on the West Coast of Taiwan
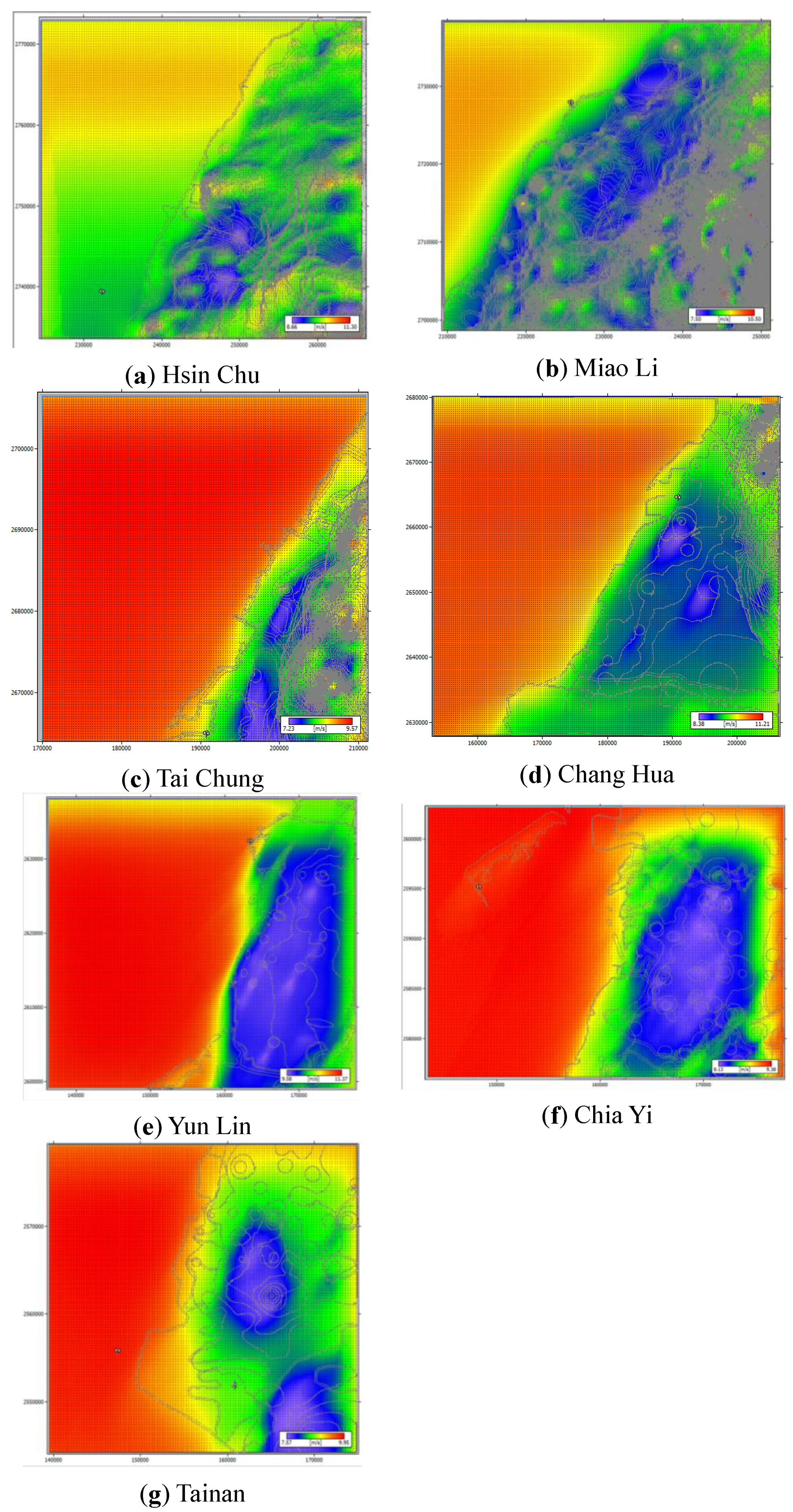
| Area | Wind speed (m/s) | Wind power density (W/m2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55 m | 100 m | 150 m | 200 m | 55 m | 100 m | 150 m | 200 m | |
| (a) Hsin Chu | 10.32 | 11.24 | 12.06 | 12.65 | 1228 | 1563 | 1920 | 2209 |
| (b) Miao Li | 8.97 | 9.54 | 10.00 | 10.34 | 2326 | 2665 | 3046 | 3344 |
| (c) Tai Chung | 8.68 | 9.44 | 10.12 | 10.61 | 949 | 1187 | 1442 | 1647 |
| (d) Chang Hua | 9.91 | 10.69 | 11.37 | 11.85 | 1417 | 1723 | 2032 | 2276 |
| (e) Yun Lin | 10.42 | 11.24 | 11.95 | 12.46 | 1412 | 1745 | 2094 | 2371 |
| (f) Chia Yi | 8.75 | 9.32 | 9.79 | 10.13 | 967 | 1170 | 1365 | 1516 |
| (g) Tainan | 8.95 | 9.84 | 10.66 | 11.23 | 812 | 1079 | 1377 | 1621 |
3.3. Extreme Wind Speed Analysis Results for the West Coast of Taiwan

| OEW (m/s) | (a) Hsinchu | (b) Miaoli | (c) Taichung | (d) Chang Hua | (e) Yunlin | (f) Chiayi | (g) Tainan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Long term 1 | 47.9 (1997.5–2012.8) 3 | 44.2 (1997.5–2012.8) | 47.8 (2000.5–2011.12) | 45.5 (2000.5–2011.12) | 36.4 (2000.1–2011.12) | 39.4 (2000.1–2011.12) | 55.3 (2006.5–2012.6) |
| Long term 2 | 82.8 (1997.5–2012.8) | 73.7 (1997.5–2012.8) | 74.3 (2000.5–2012.8) | 69.9 (2000.5–2012.8) | 57.2 (2005.10–2011.12) | 62.5 (2005.10–2011.12) | 81.4 (2006.5–2012.6) |
| Short term 1 | 43.0 (2009.1–2011.12) | 37.6 (2009.1–2011.12) | 43.0 (2009.1–2011.12) | 41.3 (2009.1–2011.12) | 36.1 (2009.1–2011.12) | 38.2 (2009.1–2011.12) | 36.3 (2006.5–2008.12) |
| Short term 2 | 57.3 (2009.1–2011.12) | 51.5 (2009.1–2011.12) | 62.6 (2009.1–2011.12) | 58.5 (2009.1–2011.12) | 56.2 (2009.1–2011.12) | 59.1 (2009.1–2011.12) | 50.6 (2006.5–2008.12) |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wind Turbines—Part 12-1: Power Performance Measurements of Electricity Producing Wind Turbines, 1st ed.; IEC 61400-12-1; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- Lima, L.A.; Filho, C.R.B. Wind resource evaluation in São João do Cariri (SJC)—Paraiba, Brazil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onat, N.; Ersoz, S. Analysis of wind climate and wind energy potential of regions in Turkey. Energy 2011, 36, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaiologou, P.; Kalabokidis, K.; Haralambopoulos, D.; Feidas, H.; Polatidis, H. Wind characteristics and mapping for power production in the Island of Lesvos, Greece. Comput. Geosci. 2011, 37, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamai, M.; Merzouk, N.K. Wind farm feasibility study and site selection in Adrar, Algeria. Energy Procedia 2011, 6, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz Rodrigo, J.; Borbón Guillén, F.; Gómez Arranz, P.; Courtney, M.S.; Wagner, R.; Dupont, E. Multi-site testing and evaluation of remote sensing instruments for wind energy applications. Renew. Energy 2013, 53, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.R.; Pauscher, L.; Ward, H.C.; Kotthaus, S.; Barlow, J.F.; Gouvea, M.; Lane, S.E.; Grimmond, C.S.B. Wind observations above an urban river using a new Lidar technique, scintillometry and anemometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 442, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutu, S.; Wyrsch, V.; Rossi, L.; Emery, P.; Golay, F.; Carneiro, C. Modelling wind-driven rain on buildings in urbanized area using 3-D GIS and Lidar datasets. Build. Environ. 2013, 59, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standridge, C.R.; Zeitler, D.; Nordman, E.; Boezaart, T.A.; Edmonson, J.; Nieves, Y.; Turnage, T.J.; Phillips, R.; Howe, G.; Meadows, G.; et al. Laser Wind Sensor Performance Validation with an Existing Gage; Grand Valley State University, Offshore Wind Project: Allendale, MI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pichugina, Y.L.; Banta, R.M.; Brewer, W.A.; Sandberg, S.P.; Hardesty, R.M. Doppler Lidar–based wind-profile measurement system for offshore wind-energy and other marine boundary layer applications. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbel, E.J. Statistics of Extremes; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Pandey, M.D. A comparison of methods of extreme wind speed estimation. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2005, 93, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.I. Improvements to the method of independent storms. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1999, 80, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.; Ahn, D.J.; Kim, H.G.; Ha, Y.C. An estimation of the extreme wind speed using the Korea wind map. Renew. Energy 2012, 42, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WAsP/WAsP Engineering. Available online: http://www.wasp.dk/ (accessed on 25 January 2015).
- Jiang, D.; Zhuang, D.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Fu, J. Evaluating the spatio-temporal variation of China’s offshore wind resources based on remotely sensed wind farm data. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.S.; Kwan, W.K. Wind Statistics in Hong Kong in Relation to Wind Power; Hong Kong Observatory: Hong Kong, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, S.H.L.; Fung, J.C.H.; Lau, A.K.H. Mesoscale simulation of year-to-year variation of wind power potential over southern China. Energies 2009, 2, 340–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, P.-C.; Yang, R.-Y.; Lai, C.-M. Potential of Offshore Wind Energy and Extreme Wind Speed Forecasting on the West Coast of Taiwan. Energies 2015, 8, 1685-1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8031685
Chang P-C, Yang R-Y, Lai C-M. Potential of Offshore Wind Energy and Extreme Wind Speed Forecasting on the West Coast of Taiwan. Energies. 2015; 8(3):1685-1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8031685
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Pei-Chi, Ray-Yeng Yang, and Chi-Ming Lai. 2015. "Potential of Offshore Wind Energy and Extreme Wind Speed Forecasting on the West Coast of Taiwan" Energies 8, no. 3: 1685-1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8031685
APA StyleChang, P.-C., Yang, R.-Y., & Lai, C.-M. (2015). Potential of Offshore Wind Energy and Extreme Wind Speed Forecasting on the West Coast of Taiwan. Energies, 8(3), 1685-1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8031685








