Abstract
In order to meet the needs of wind speed prediction in wind farms, we consider the influence of random atmospheric disturbances on wind variations. Considering a simplified fluid convection mode, a Lorenz system can be employed as an atmospheric disturbance model. Here Lorenz disturbance is defined as the European norm of the solutions of the Lorenz equation. Grey generating and accumulated generating models are employed to explore the relationship between wind speed and its related disturbance series. We conclude that a linear or quadric polynomial generating model are optimal through the verification of short-term wind speed prediction in the Sotavento wind farm. The new proposed model not only greatly improves the precision of short-term wind speed prediction, but also has great significance for the maintenance and stability of wind power system operation.
1. Introduction
Wind energy is one of the most popular and potential renewable energies worldwide [1,2]. Rapid development of wind energy has contributed greatly to energy supply systems. The Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC) has provided the latest and comprehensive statistics about the development of wind power industries. By the end of 2013, global cumulative and new installed wind power capacities have exceeded 318 GW and 35 GW, respectively. China occupied the largest share of both parts [3]. As a result how to effectively utilize wind resources has received increasing attention [4,5]. Wind power generation in wind farms could make full use of wind energy on a large-scale [6,7], but considering the stochastic volatility nature of wind energy, integration of wind power into power systems becomes a challenge [8,9,10,11]. Necessary measures should be taken to maintain the normal operation of electric systems and decrease losses that could affect people’s daily prodivity and life. Therefore, high precision wind speed and power prediction is urgently needed. Scholars at home and abroad have done lots of studies on wind forecasting and achieved excellent results [5,12,13,14]. In this paper a novel wind disturbance model to improve the performance of conventional back propagation (BP) neural networks is proposed.
Wind formation and variation in the atmosphere are typical nonlinear processes [15]. As Lorenz said in his 2008 lecture at the University of Rome named the Butterfly Effect, the real atmospheric state of motion is actually the observed state plus a small perturbation. This random perturbation is the key consideration that affects wind speed forecasting precision. This problem could not be resolved by linear theory. Lorenz extracted a three-variable system called the Lorenz system from a fluid convection model in 1963 [16,17,18,19]. The Lorenz system is frequently used to study nonlinear science since it was first proposed due to its good performance in accomodating chaos [20,21]. Here it is used as a typical atmospheric disturbance model. Different initial conditions and values of parameters could result in different evolutions of a Lorenz system. Various types of Lorenz disturbances are used to establish wind disturbance models in this article.
2. Nonlinear Lorenz Disturbance and Data Preprocessing Forms
2.1. Different Types of Lorenz Disturbance and Normalization Constants
2.1.1. Different Types of Disturbance in a Lorenz System
The Lorenz system was extracted from the seven-variable fluid convection model of Saltzman [17,18,19,22]. A Lorenz system could exhibit chaotic state in a simplest way in nonlinear systems. It has enriched people’s acknowledgement of the dynamics of nonlinear systems and played a vital role on the development of chaos theory. The fluid convection model simplified by Saltzman can be expressed as follows [17]:
where ψ is a two-dimensional stream function, θ is a temperature difference from that occurring in equilibrium state, g,ς,υ,κ denote the acceleration of gravity, the coefficient of thermal expansion, the kinematic viscosity, and the thermal conductivity, respectively.
The convection Equation (1) describes the following system. The fluid moves between two fixed parallel surfaces, whose temperature difference is kept constant by external heating. The whole procedure was assumed to develop in the vertical plane. If the solution of Equation (1) was unstable, convective motion would develop. This system was similar with what Lorenz studied at that time. Then Equation (1) was further simplified into the following three-variable system called Lorenz system given by:
where x is proportional to fluid intensity, y is proportional to the temperature difference between the ascending current and the descending current, z is proportional to the temperature difference in the vertical direction compared to the equilibrium state, σ, r and b are all positive parameters. We can obtain various Lorenz attractors by taking different values of r. Those attractors in phase space correspond to various forms of disturbance in a real atmospheric system. The values of r can be divided into four intervals as shown in Table 1 [16].

Table 1.
The actual fluid motions in Lorenz system when parameters σ and b are respectively equal to 10 and 8/3.
| Items to be Compared | The Values of r and its Corresponding Fluid Motions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rayleigh Number (r) | 0 < r < 1 | 1 < r < 13.97 | 13.97 < r < 24.74 | r > 24.74 |
| Actual fluid motion | Heat conduction | Regular convection | Transient chaos | Chaos |
2.1.2. Normalization Constant of Lorenz Disturbance
It is convenient to discuss the solutions of Lorenz system in R3. Here we define the European norm of vectors in R3 as the atmospheric disturbance. Let P(x,y,z) be an arbitrary vector in R3. The European norm of P(x,y,z) can be expressed as:
There will be a problem if taking Formula (3) as the form of the Lorenz disturbance. Let the initial condition and parameters σ, b, r be (0,1,0),10,8/3,45, respectively. The Lorenz disturbance defined by Formula (3) is demonstrated in Figure 1a. We can clearly see that the disturbance fluctuates within interval (0,90), which is larger than the range of the actual wind speed changes. Therefore, we need to define a normalization constant to reduce this range to a reasonable small interval like (0,3), which is decided by the deviations occurred in previous wind speed predictions. Let the normalization constant be 50 for the disturbance shown in Figure 1a. The normalized disturbance is shown in Figure 1b. Generally the normalization constant varies according to different size of Lorenz disturbance and wind fluctuations.
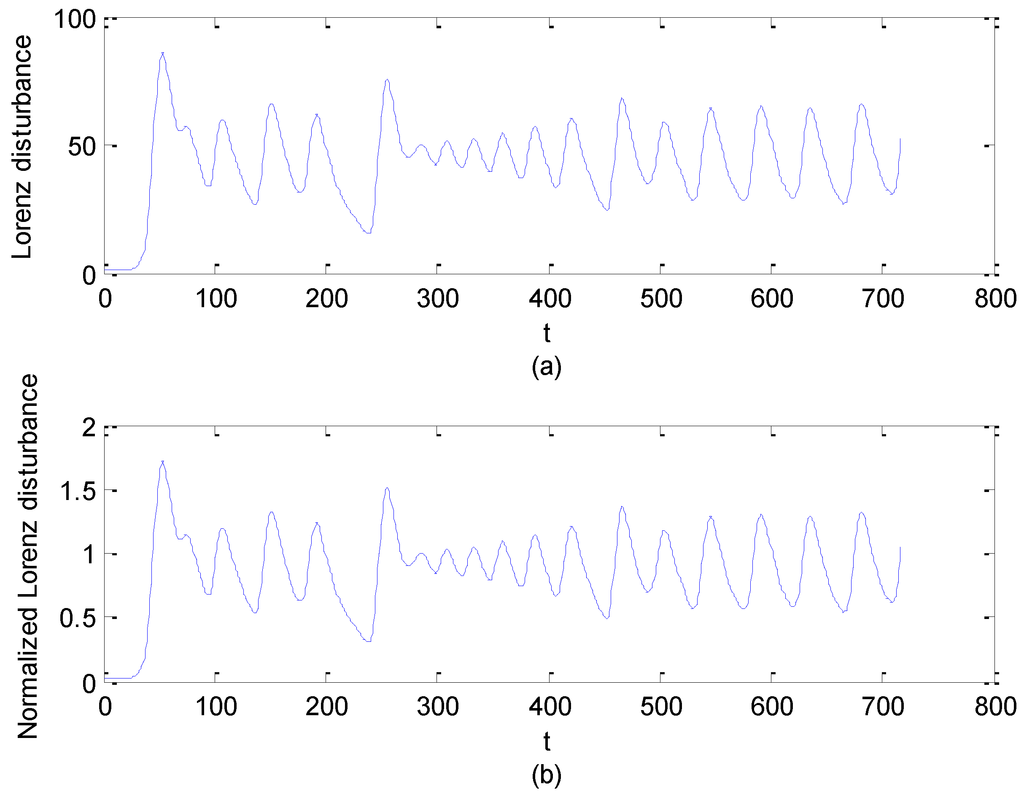
Figure 1.
(a) The initial Lorenz disturbance defined by Formula (3). (b) The normalized Lorenz disturbance.
2.2. Data Preprocessing
It is necessary to preprocess the scattered sample data before building the disturbance model. Figure 2 shows the distribution of wind speed sequence and its corresponding disturbance series in a certain period. For the calculation of the two arrays we can refer to the modeling process in Section 3.3. We can see that the points are distributed extremely irregularly. A further calculation of the correlation coefficient can quantitatively describe the relationship of the two arrays. The calculated result is 0.1713, which is less than 0.3 and proves the irrelevance between the two arrays. The correlation coefficient is expressed by:
where x and y denote the two arrays to be analyzed,
and
denote the average of x and y, respectively.
In this section grey generating is applied to discover the inherent relationship between variables x and y. Grey generating commonly includes Accumulated Generating Operation (AGO), Inverse AGO (IAGO), Mean (MEAN), and Effect Measure (EM), etc. AGO not only does well in establishing a grey model, but also can be used to reduce the randomness of discrete sequences [23,24]. AGO means adding original data in sequence to obtain the generating series [25,26].
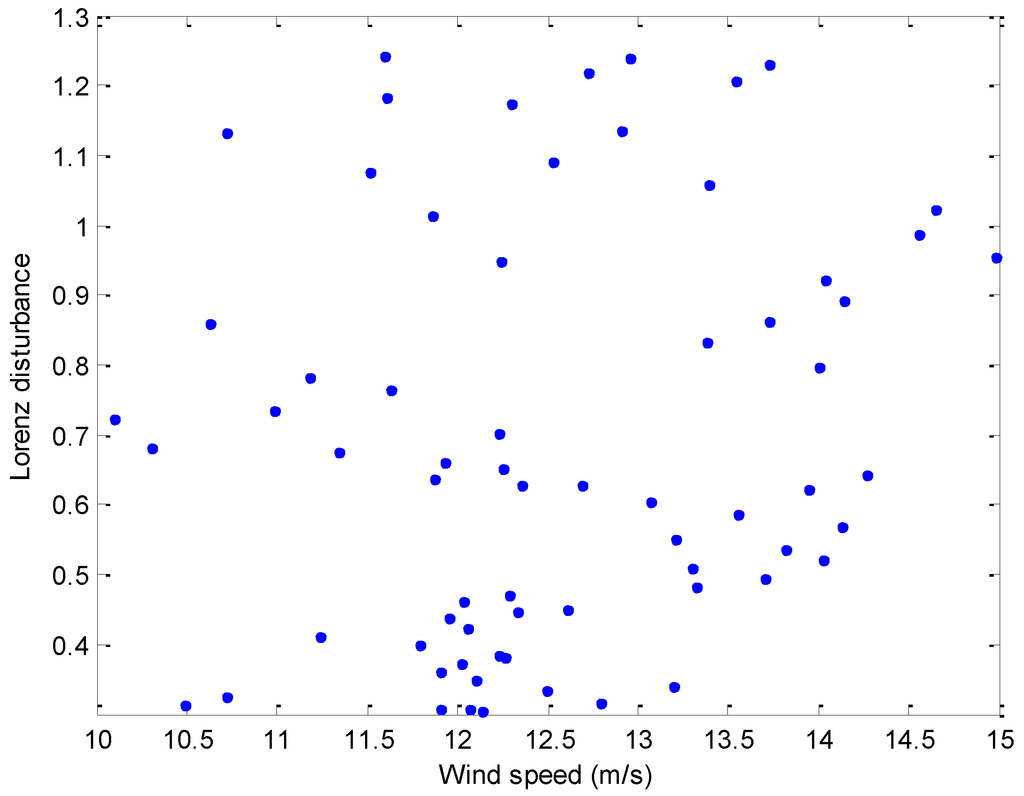
Figure 2.
Wind speed versus the corresponding disturbance series for a period of time.
Definition 1
Let
be raw series:
is AGO series of
, denoted as:
Provided that:
where:
Definition 2
y is IAGO series of
, denoted as:
Provided that:
where:
Based on the ways of data processing like Formulas (5)–(8), the same treatment could be applied to the arrays in Figure 2. Figure 3 shows the generated data of Figure 2. It is clear that the irregular data in Figure 2 are converted into a monotonically increasing sequence in Figure 3. This conversion will realize a high precision curve fitting called accumulated generating model, namely the new proposed wind disturbance model in this research.
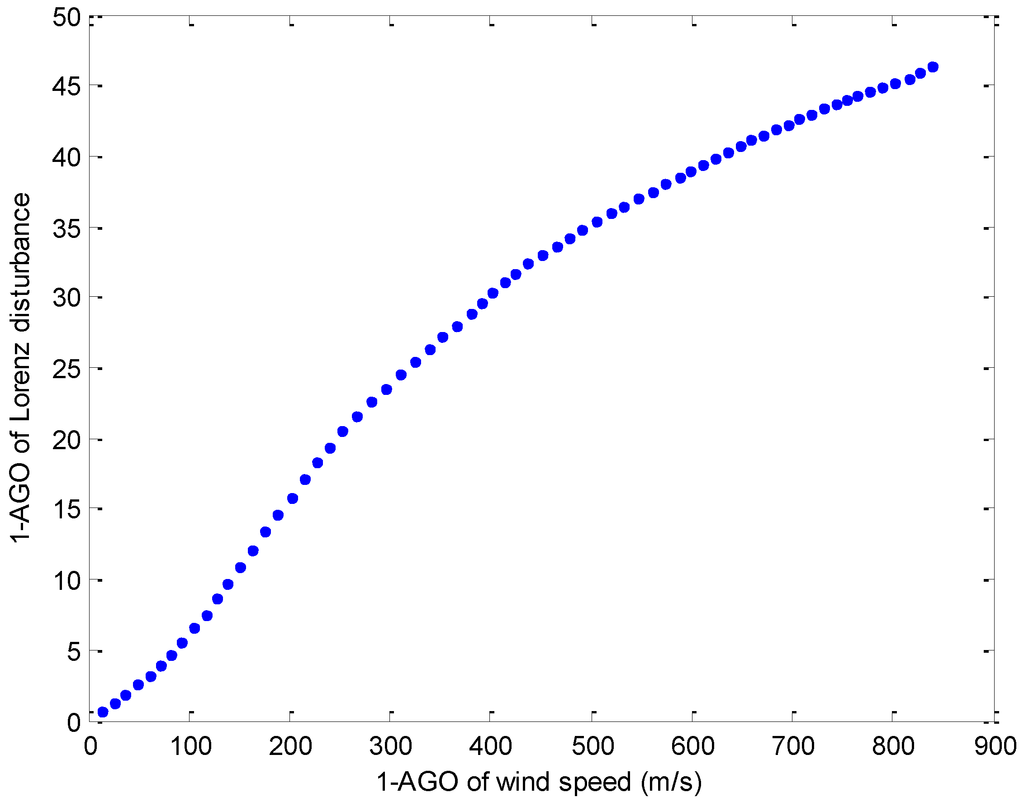
Figure 3.
The points in this figure denote the AGO series of the data shown in Figure 2.
3. Wind Disturbance Model Based on Grey Generation
3.1. Data Description
The modeling data set is derived from the Sotavento wind farm from 1 January to 28 February in 2014. The observations contain 8196 groups of wind speed and wind direction. Figure 4 shows the distribution of wind speed in the above two months. The average, maximum, and minimum wind speed are 10.83 m/s, 38.67 m/s, and 2.6 m/s, respectively. We can see that the range of wind fluctuation is quite large.
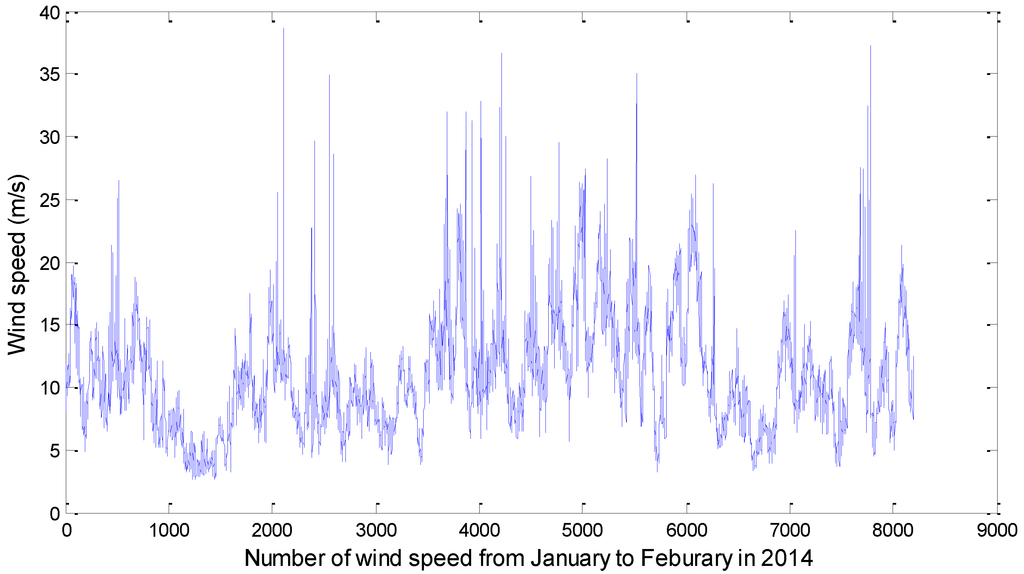
Figure 4.
The distribution of wind speed recorded from January to February in 2014 in Sotavento wind farm.
3.2. Error Criteria
Selecting a reasonable set of error indicators can objectively evaluate the level of wind speed predictions and the effectiveness of forecasting models. Some common error criteria include absolute error (AE), mean absolute error (MAE), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), root mean-square error (RMSE), standard deviation of error (SDE) [8,15,27,28,29], etc. Compared to MAE, RMSE is more sensitive to large data samples and is robust when dealing with large errors [30]. Here we use MAE and RMSE, given by:
where y(k) and f(k) respectively denote the observed data and predicted value, M is sample size.
3.3. Wind Disturbance model When Rayleigh Number Equals to 45
3.3.1. BP Neural Network
BP neural network is widely used in wind forecasting and does well in dealing with nonlinear problems [31,32,33]. Thus, it is adopted as the basic forecasting model in this study. Based on a gradient descent algorithm, the BP neural network obtains the minimum mean square error between output vectors and the sample values through constantly adjust the weights and biases in networks. This particular network could perfectly learn and store the mapping relations between input and output variables.
The structure of the BP neural network used in this paper is shown in Figure 5. A BP network generally consists of three layers, i.e., input layer, hidden layer, and output layer. The three input vectors of BP network are wind speed (V(t)) and sine-cosine of wind direction ((sin D, cos D)) at time t. The hidden layer has three sigmoid neurons followed by an output layer of one linear neuron. The outputs of hidden layer and output layer are ruled by the following two formulas:
where xi is input vector with i = 1,2,3, yj and y are the output vectors of hidden layer and output layer with j = 1,2,3, fj and f0 are transfer functions of nodes, wij and wj are connection weights, bj and b0 are biases.
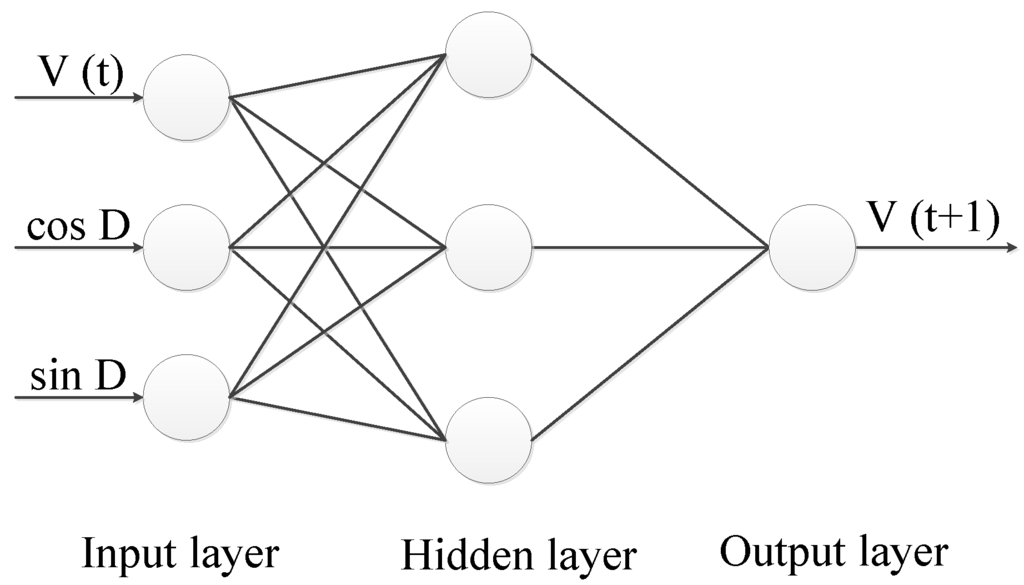
Figure 5.
Three-layer BP neural network.
3.3.2. Modeling Process and Discussion
We attempt to establish a disturbance model that it is able to output a valid disturbance sequence according to a given wind speed series. Then we could use this relevant disturbance sequence to reduce the nonlinear components contained in the wind speed series. Polynomial functions are some of the most widely used and simplest fitting functions. Hence, we use a polynomial generating function to construct the disturbance model, which is based on the principle of least squares. The modeling procedure can be divided into the following four steps:
Step one:
Determine the wind speed and sine-cosine of wind direction as the input variables of BP network. Train the BP network with the training data and predict the subsequent wind speed series. Denote the initial forecasting result and the real wind speed as WI and WR, respectively.
Step two:
In order to seek the minimum deviation between WI and WR, we need to seek a certain disturbance sequence called DL from the normalized disturbance series shown in Figure 1b. DL is said to be the best compensation to WI.
Step three:
According to the data preprocessing method in Section 2.2, we apply AGO to WI and DL, respectively. Then we can obtain two arrays that possess a clear relationship as shown in Figure 3. No more than fifth degree polynomials are applied to analyze the generated data. Table 2 shows the detailed statistics of the disturbance models, including the polynomial expression, accumulated generating model, and the fitting error (RMSE). The polynomial expressions are used to describe the features of related disturbance models. f (x) and x denote 1-AGO of Lorenz disturbance and 1-AGO of wind speed, respectively.

Table 2.
Detailed statistics of grey generating models based on various polynomials.
| Polynomial Expression | Accumulated Generating Model | Fitting Error (RMSE) |
|---|---|---|
| f (x) = p1 · x + p2 p1 = 0.0648, p2 = 2.6455 | 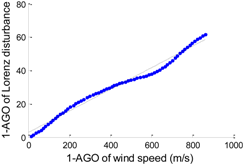 | 2.218 |
| f (x) = p1 · x2 + p2 · x + p3 p1 = −1.0713 × 10−6, p2 = 0.0657 p3 = 2.5099 | 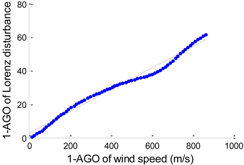 | 2.234 |
| f (x) = p1 · x3 + p2 · x2 + p3 · x + p4 p1 = 1.672 × 10−7, p2 = −0.0002 p3 = 0.1430, p3 = −3.2818 | 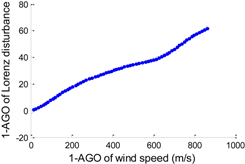 | 0.8353 |
| f (x) = p1 · x4 + p2 · x3 + p3 · x2 + p4 · x + p5 p1 = 9.1690 × 10−11, p2 = 6.0698 × 10−9 p3 = −1.2911 × 10−4, p4 = 0.1248 p5 = −2.4246 | 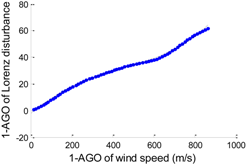 | 0.8027 |
| f (x) = p1 · x5 + p2 · x4 + p3 · x3 + p4 · x2 + p5 · x + p6 p1 = −1.1187 × 10−12, p2 = 2.5436 × 10−9 p3 = −1.9104 × 10−6, p4 = 5.0681 × 10−4 p5 = 0.0429, p6 = 0.2498 | 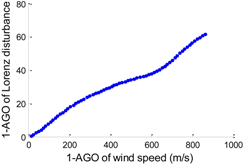 | 0.4496 |
Step four:
In this step we will use the disturbance models to predict wind speed for a period of time in the future. We retrain the BP network and make an initial prediction of the future wind speed, which is similar to Step one. We denote the initial prediction in predicted period as WIP, and then input the
series into the disturbance models established in step three, respectively. The generated outputs are in turn written as
, which needs to be reduced by IAGO. The compensating formula is given by:
where Wi denotes the wind prediction result corresponding to each disturbance model with
. The prediction results are presented in Table 3. The indicator (I), which means initial result, is used to distinguish the result of initial predictions and disturbed predictions.
We can draw the following conclusions through a comprehensive analysis of Table 2 and Table 3. On the one hand, seen from the figures of generating models and the fitting errors in Table 2, the fitting does become much better with a higher degree of polynomial. On the other hand, coefficients of high-order terms of generating functions approximate to zero. Hence, it is not wise to use high order polynomials. Besides, the MAE and RMSE results in Table 3 suggest that the forecasting errors become apparently worse starting from the third degree polynomial model. Therefore, a good fitting cannot promise a good forecasting performance. The universality of disturbance models is seriously reduced due to over-fitting problem. It turns out that linear or quadratic polynomials could work out much better wind predictions compared to other forms of polynomials.

Table 3.
MAE and RMSE results of wind speed prediction in February 2014.
| Degree of Polynomial | Wind Forecasting Error | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE (I) (m/s) | MAE (m/s) | RMSE (I) (m/s) | RMSE (m/s) | |
| 1 | 0.5772 | 0.0729 | 0.5870 | 0.0979 |
| 2 | 0.5935 | 0.0535 | 0.5989 | 0.0789 |
| 3 | 0.6632 | 0.2230 | 0.6720 | 0.2672 |
| 4 | 0.6248 | 0.1897 | 0.6365 | 0.2267 |
| 5 | 0.4377 | 0.1643 | 0.4683 | 0.2268 |
3.4. Wind Disturbance Models When Rayleigh Numbers are Equal to 0.7, 12, and 16, Respectively
A Lorenz system would present various evolutions when taking different Rayleigh numbers. Each evolution corresponds to a concrete fluid motion referred in Table 1. In order to verify the universality of Lorenz fluid motions in founding a disturbance model, we can respectively choose four values of Rayleigh number from each interval in Table 1, such as 0.7, 12, 16, and 45. We have made a detailed analysis when the Rayleigh number is equal to 45. Now we continue to verify the other three cases. According to the conclusions in Section 3.3, a linear or quadratic polynomial generating model is adopted in this section. Similar steps are applied to the modeling processes in this section. The optimal disturbance models are shown in Table 4. Persistence model (PM) is introduced as a reference with indicator (P). Table 5 presents the related wind prediction results. Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 are the wind speed forecast curves corresponding to each disturbance model in Table 5. The red curves, blue curves, and black curves respectively denote the initial wind predictions of BP neural network, the improved predictions of disturbance model, and the actual wind speed series.

Table 4.
The optimal disturbance models when taking different Rayleigh number values.
| Rayleigh Number | Polynomial Expression | Accumulated Generating Model | Error (RMSE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | f (x) = p1 · x2 + p2 · x + p3 p1 = −4.8249 × 10−5, p2 = 0.0919 p3 = 2.3845 | 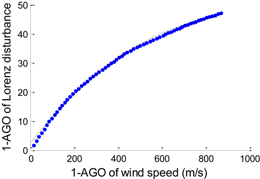 | 0.7586 |
| 12 | f (x) = p1 · x + p2 p1 = 0.0888, p2 = 5.1913 | 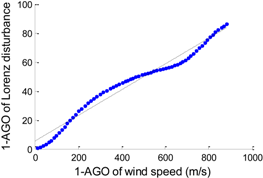 | 4.125 |
| 16 | f (x) = p1 · x2 + p2 · x + p3 p1 = 2.2630 × 10−5, p2 = 0.0542 p3 = 7.8821 | 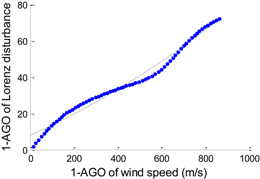 | 2.746 |
| 45 | f (x) = p1 · x2 + p2 · x + p3 p1 = −1.0713 × 10−6, p2 = 0.0657 p3 = 2.5099 | 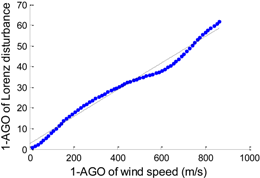 | 2.234 |
Although the improvements are not exactly the same, these results have fully proved that all forms of Lorenz disturbance flow could contribute to the predicted level of a BP neural network. Table 5 presents another important discovery. The models could be easily grouped into two categories by the errors in Table 5. The forecasting accuracy tends to be high when the Rayleigh numbers equal 16 and 45. MAE and RMSE are respectively about 0.056 m/s and 0.078 m/s. The same quantities are about 0.14 m/s and 0.18 m/s when the Rayleigh numbers are equal to 0.7 and 12. Theoretically speaking, when the Rayleigh number is larger than 13.97, a Lorenz system has transient chaotic or chaotic solutions, whose disturbance forms are quite complex. This kind of complexity greatly helps to describe the real wind variations.

Table 5.
MAE and RMSE results of wind speed prediction in February 2014.
| Rayleigh Number | Wind Forecasting Error | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE (I) (m/s) | MAE (m/s) | MAE (P) (m/s) | RMSE (I) (m/s) | RMSE (m/s) | RMSE (P) (m/s) | |
| 0.7 | 0.5278 | 0.1447 | 0.4047 | 0.5429 | 0.1720 | 0.5201 |
| 12 | 0.7690 | 0.1397 | 0.7185 | 0.8035 | 0.1903 | 0.9870 |
| 16 | 0.6137 | 0.0581 | 0.4108 | 0.6139 | 0.0769 | 0.5230 |
| 45 | 0.5935 | 0.0535 | 0.4650 | 0.5989 | 0.0789 | 0.6486 |
Besides, the forecasting errors of PM are used to evaluate the existing results. PM is especially suitable for short-term wind prediction [34]. In this paper, PM behaves better than the BP network on short-term wind prediction. Seen from Table 5, except for RMSE (P) when Rayleigh numbers are equal to 12 and 45, all errors of PM are smaller than the corresponding errors of a conventional BP network. Both MAE and RMSE of disturbance models greatly outperform PM and the BP neural network.
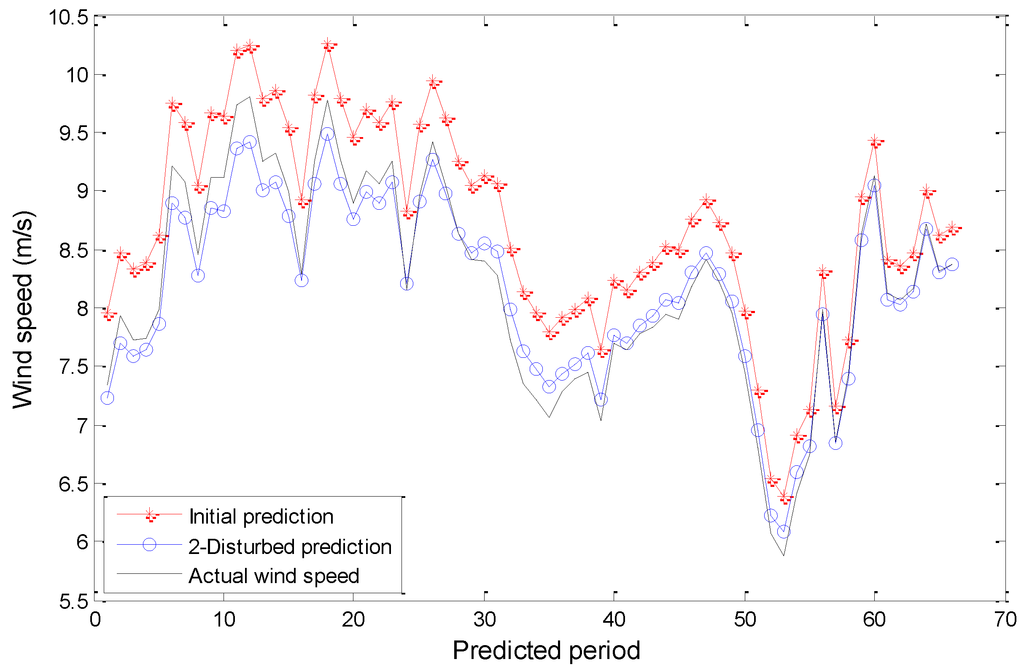
Figure 6.
Wind speed forecasting results of the quadratic polynomial generating model when Rayleigh number equals 0.7.
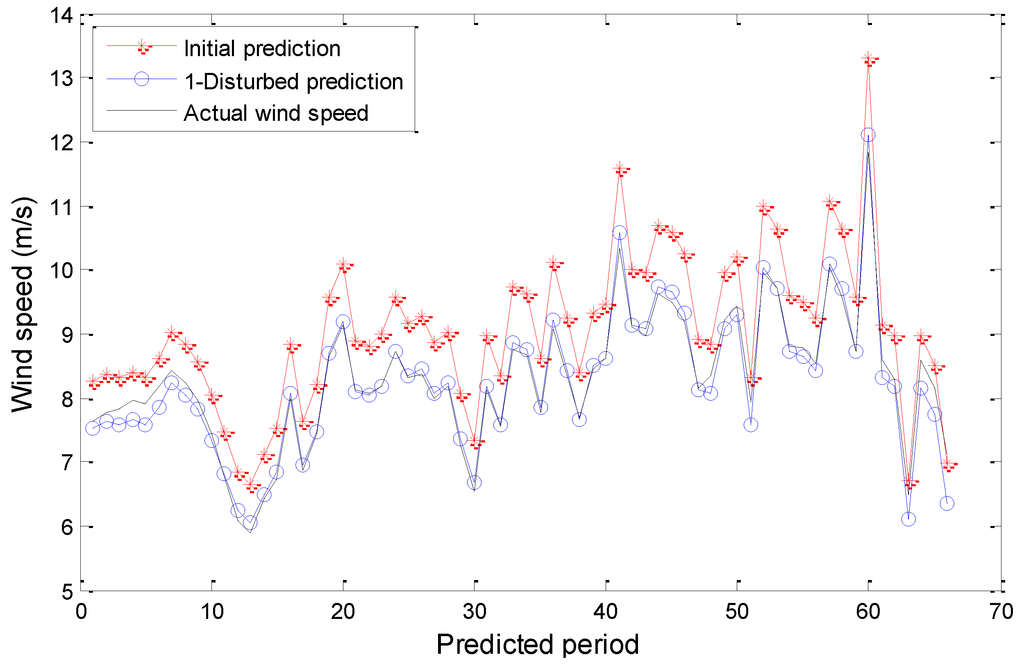
Figure 7.
Wind speed forecasting results of the linear polynomial generating model when Rayleigh number equals 12.
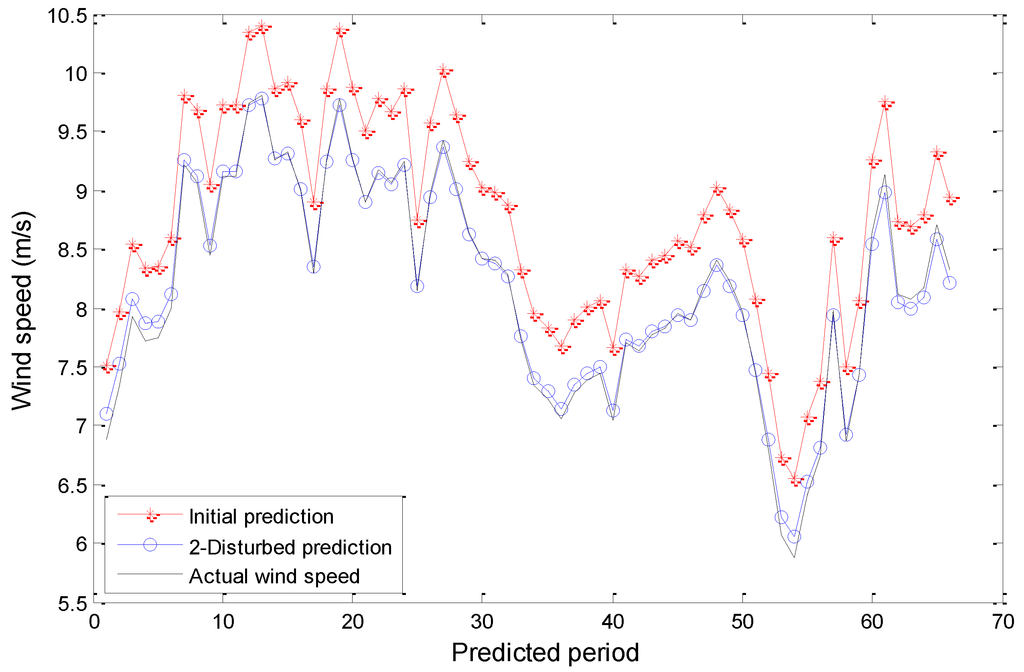
Figure 8.
Wind speed forecasting results of the quadratic polynomial generating model when Rayleigh number equals 16.
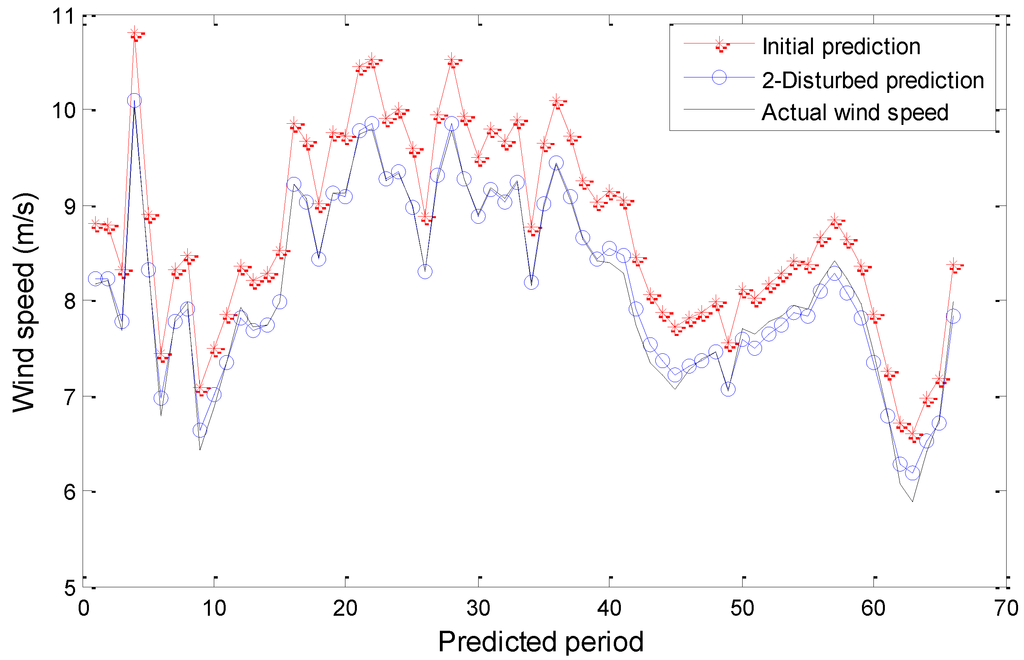
Figure 9.
Wind speed forecasting results of the quadratic polynomial generating model when Rayleigh number equals 45.
4. Conclusions
With the rapid development of the wind power industry, wind speed and power generation forecasting methods have become a focus of research in the fields of power systems and renewable energy. After a deeper study on the atmospheric dynamics system and wind prediction methods, in this paper we introduce the Lorenz system to reduce the negative impact of atmospheric disturbances on wind forecasting. Based on grey generating and an accumulated generating model, we propose a new wind disturbance model to improve the wind forecasting precision of a BP network. PM is also introduced for comparison. The best improvements (r = 45) in this paper are measured by the following two criteria: MAE with 0.0535 m/s and RMSE with 0.0789 m/s. In [32], the new proposed model IS-PSO-BP obtained good wind prediction performance based on different training numbers and data sources, whose MAE is 0.16 m/s and RMSE with 0.4123 m/s. In [34] its authors adopted low-quality measurements as exogenous information to refine the one-hour-ahead wind predictions. The smallest MAE of BP neural network in [34] is 0.18 m/s and RMSE with 0.2236 m/s.
All the above statistics and analysis suggest that we have proposed a valid and feasible wind disturbance model based on a BP neural network. This model fully considers the basic features of nonlinear atmospheric systems. Given an appropriate Lorenz disturbance sequence, it can be used to predict any type of wind speed series without seasonal limitations. Nevertheless there is no unified algorithm or principle at the moment for the selection of Rayleigh numbers. In addition, in view of the advantages and features of grey system theory [26,35,36], the application of the Lorenz system to the grey model is worthy of further exploration.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous referees for their helpful comments and suggestions. This research was supported partly by the National Key Basic Research Project (973 Program) of China (2012CB215200), the NSFC (51277193), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20110036110003) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2014ZD43).
Author Contributions
This paper is a result of the full collaboration of all the authors. However, Jingyun Yang wrote Case Study and Methodology, Kangcheng Wang performed the experiments. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cheng, M.; Zhu, Y. The state of the art of wind energy conversion systems and technologies: A review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 88, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwanto, M.; Gomesh, N.; Mamat, M.R.; Yusoff, Y.M. Assessment of wind power generation potential in Perlis, Malaysia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC). Available online: http://www.gwec.net/global-figures/graphs/ (accessed on 12 June 2014).
- Jung, J.; Broadwater, R.P. Current status and future advances for wind speed and power forecasting. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 31, 762–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Liu, S. Wind speed forecasting method: Grey related weighted combination with revised parameter. Energy Proced. 2011, 5, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, S.S.; Ramasamy, P.; Murthy, K.S.R. Wind power potential assessment of 12 locations in western Himalayan region of India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 530–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, A.; Kristoffer Suld, J.; Kvamsdal, T. A multiscale wind and power forecast system for wind farms. Energy Proced. 2014, 53, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Liu, F.; Yang, X. A hybrid strategy of short term wind power prediction. Renew. Energy 2013, 50, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilbudaka, M.; Sagiroglub, S.; Colakc, I. A new approach to very short term wind speed prediction using k-nearest neighbor classification. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 69, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfetsos, A. A comparison of various forecasting techniques applied to mean hourly wind speed time series. Renew. Energy 2000, 21, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X.; Ju, W. A review on wind power industry and corresponding insurance market in China: Current status and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 1069–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Wang, J.; Lu, H.; Zhao, G. A new hybrid model optimized by an intelligent optimization algorithm for wind speed forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 85, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Dang, Z. Forecasting wind speed using empirical mode decomposition and Elman neural network. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 23, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Shi, H.; Hu, Q.; Li, X.; Dang, J. Fuzzy rough regression with application to wind speed prediction. Inf. Sci. 2014, 282, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheela, K.G.; Deepa, S.N. Neural network based hybrid computing model for wind speed prediction. Neurocomputing 2013, 122, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Z.; Peng, J.H. Nonlinear Dynamics, 1st ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 120–143. [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman, B. Finite amplitude free convection as an initial value problem-I. J. Atmos. Sci. 1962, 19, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963, 20, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. The Essence of Chaos, 1st ed.; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 1997; pp. 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, W.; Feng, J. Multiple limit cycles and centers on center manifolds for Lorenz system. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 238, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algaba, A.; Fernández-Sánchez, F.; Merino, M.; Rodríguez-Luis, A.J. Centers on center manifolds in the Lorenz, Chen and Lü systems. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2014, 19, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayleigh, L. On convective currents in a horizontal layer of fluid, when the higher temperature is on the underside. Philos. Mag. Ser. 1916, 32, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.L. The primary Methods of Grey System Theory, 2nd ed.; Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press: Wuhan, China, 2005; pp. 27–55. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.L. Grey Prediction and Grey Decision Making, 1st ed.; Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press: Wuhan, China, 2002; pp. 45–71. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Qi, L.; Chen, C.; Tang, J.; Jiang, M. Grey system theory based prediction for topic trend on Internet. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2014, 29, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, S.; Hooshmand, R.-A.; Parastegari, M. Short term electric load forecasting by wavelet transform and grey model improved by PSO (particle swarm optimization) algorithm. Energy 2014, 72, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H. Multiscale prediction of wind speed and output power for the wind farm. J. Control Theory Appl. 2012, 10, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Zeng, G. A hybrid forecasting approach applied to wind speed time series. Renew. Energy 2013, 60, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Guo, J.; Zheng, S. Evaluation of hybrid forecasting approaches for wind speed and power generation time series. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 3471–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Li, T. Review of evaluation criteria and main methods of wind power forecasting. Energy Proced. 2011, 12, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sheng, Z.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, S. Lightning potential forecast over Nanjing with denoised sounding-derived indices based on SSA and CS-BP neural network. Atmos. Res. 2014, 137, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; An, N.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Hu, B.; Shang, D. Optimal parameters selection for BP neural network based on particle swarm optimization: A case study of wind speed forecasting. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2014, 56, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Xu, X. A short-term load forecasting model of natural gas based on optimized genetic algorithm and improved BP neural network. Appl. Energy 2014, 134, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomares-Salas, J.C.; Agüera-Pérez, A.; González de la Rosa, J.J.; Moreno-Muñoz, A. A novel neural network method for wind speed forecasting using exogenous measurements from agriculture stations. Measurement 2014, 55, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-Y.; Chen, S.-P. A prediction method using the grey model GMC(1,n) combined with the grey relational analysis: A case study on Internet access population forecast. Appl. Math. Comput. 2005, 169, 198–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzacebi, C.; Es, H.A. Forecasting the annual electricity consumption of Turkey using an optimized grey model. Energy 2014, 70, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).