Idle Operation with Low Intake Valve Lift in a Port Fuel Injected Engine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
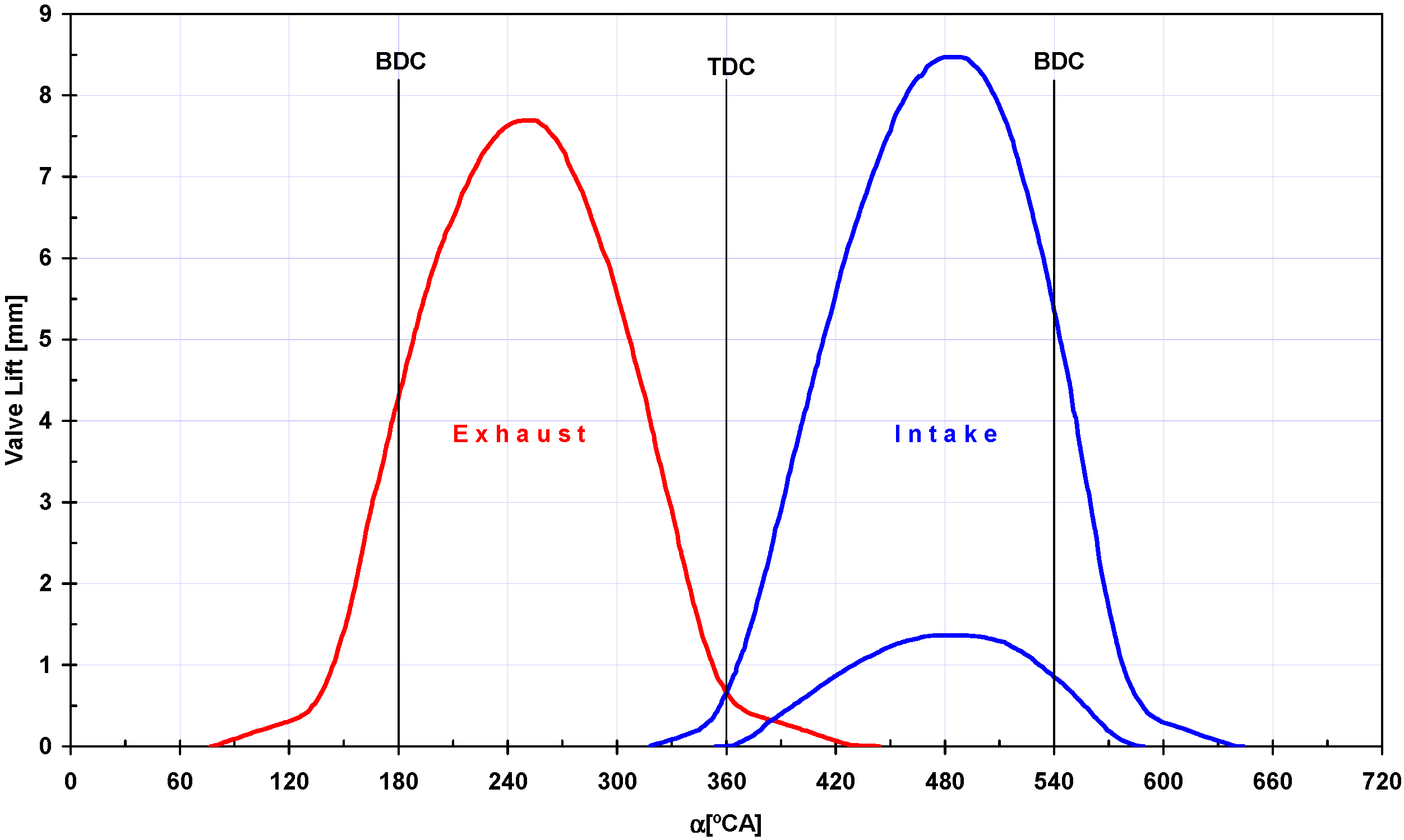
2. Experimental Apparatus and Procedure
2.1. Experimental Setup
| Number of cylinders | 4 | |
| Stroke (mm)/Bore(mm) | 77/76 | |
| Volumetric Compression Ratio | 9.0 | |
| Combustion chamber | Wedge type; 2 valves | |
| Exhaust Valve Law | Maximum Valve Lift, MVL (mm) | 7.5 |
| Exhaust Valve Opening, EVO (°CA BBDC) | 73 | |
| Exhaust Valve Closing, EVC (°CA ATDC) | 42 | |
| Minimum Intake Valve Law | Maximum Valve Lift, MVL (mm) | 1.165 |
| Intake Valve Opening, IVO(°CA ATDC) | 19 | |
| Intake Valve Closing, IVC (°CA ABDC) | 29 | |
| Maximum Intake Valve Law | Maximum Valve Lift, MVL (mm) | 8.275 |
| Intake Valve Opening, IVO (°CA BTDC) | 15 | |
| Intake Valve Closing, IVC (°CA ABDC) | 73 | |
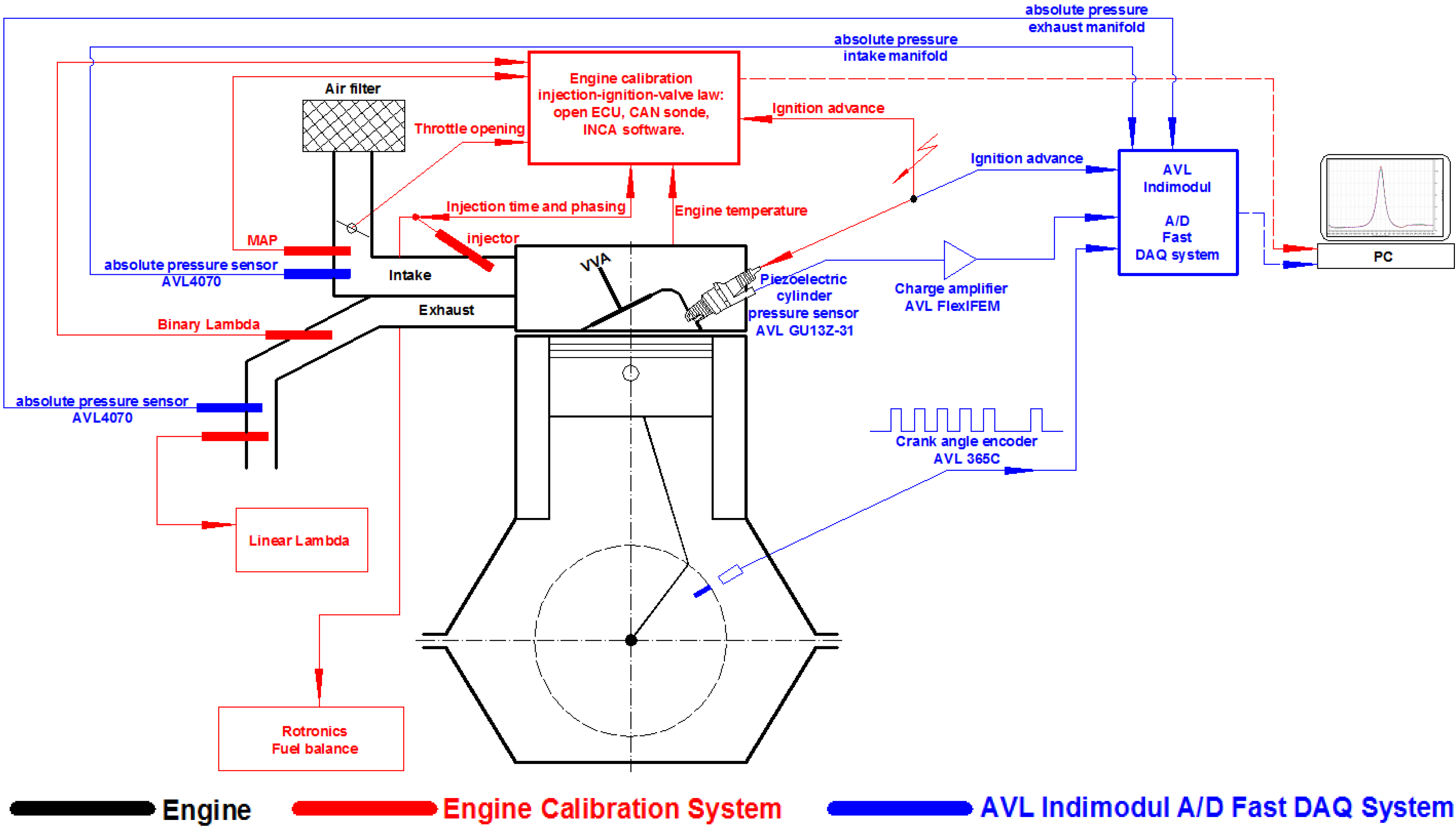
2.2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Ignition Advance
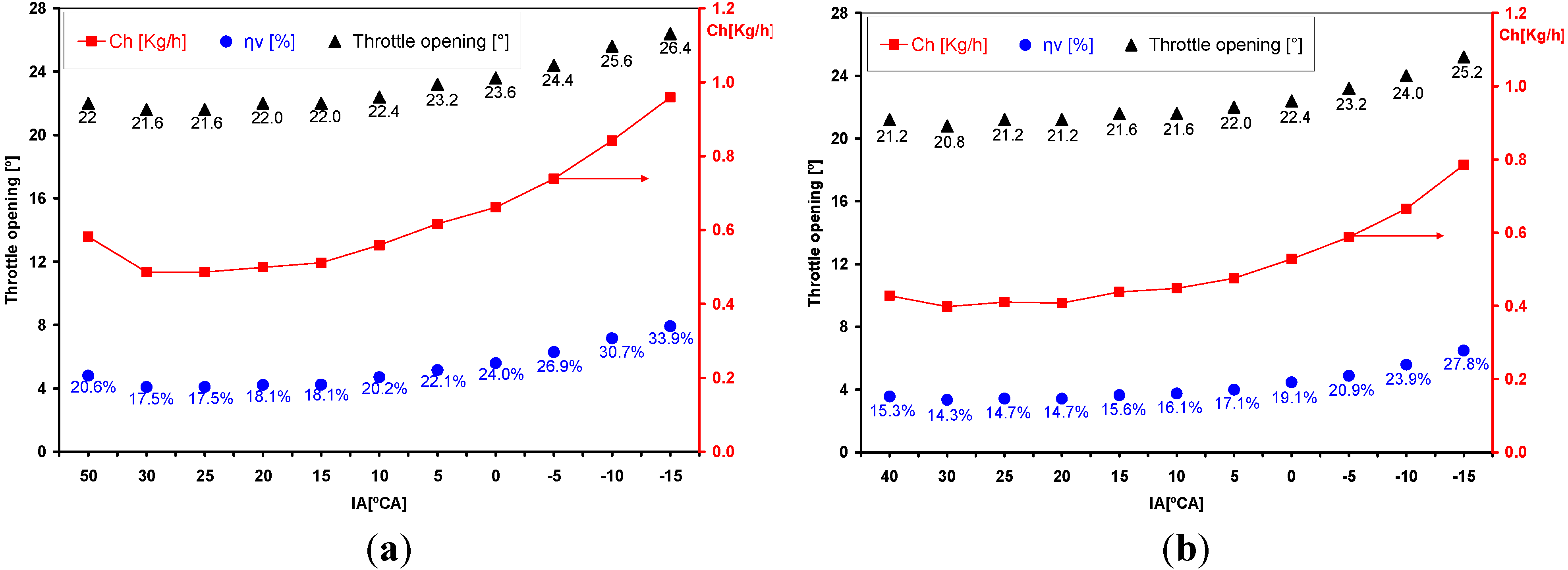
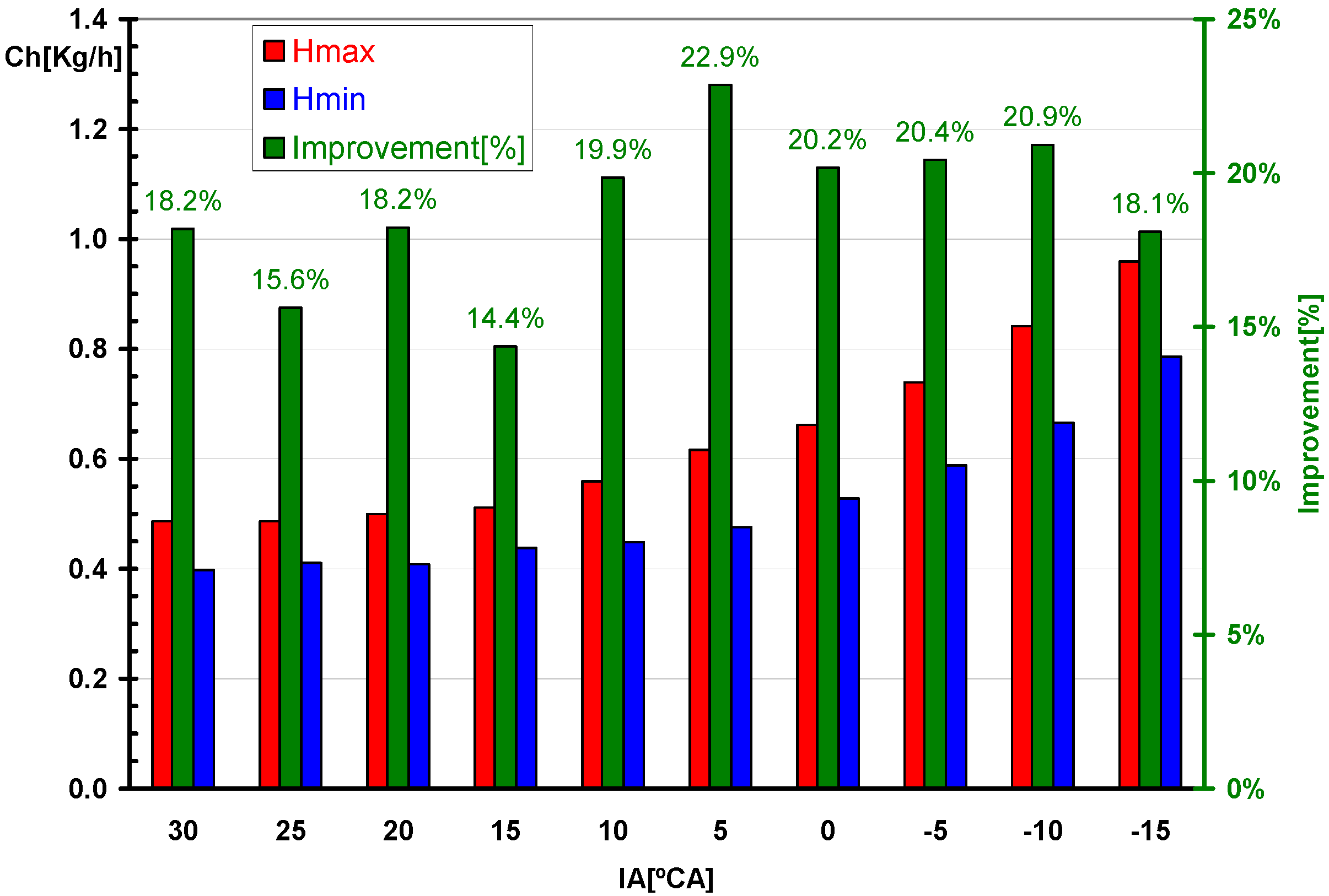

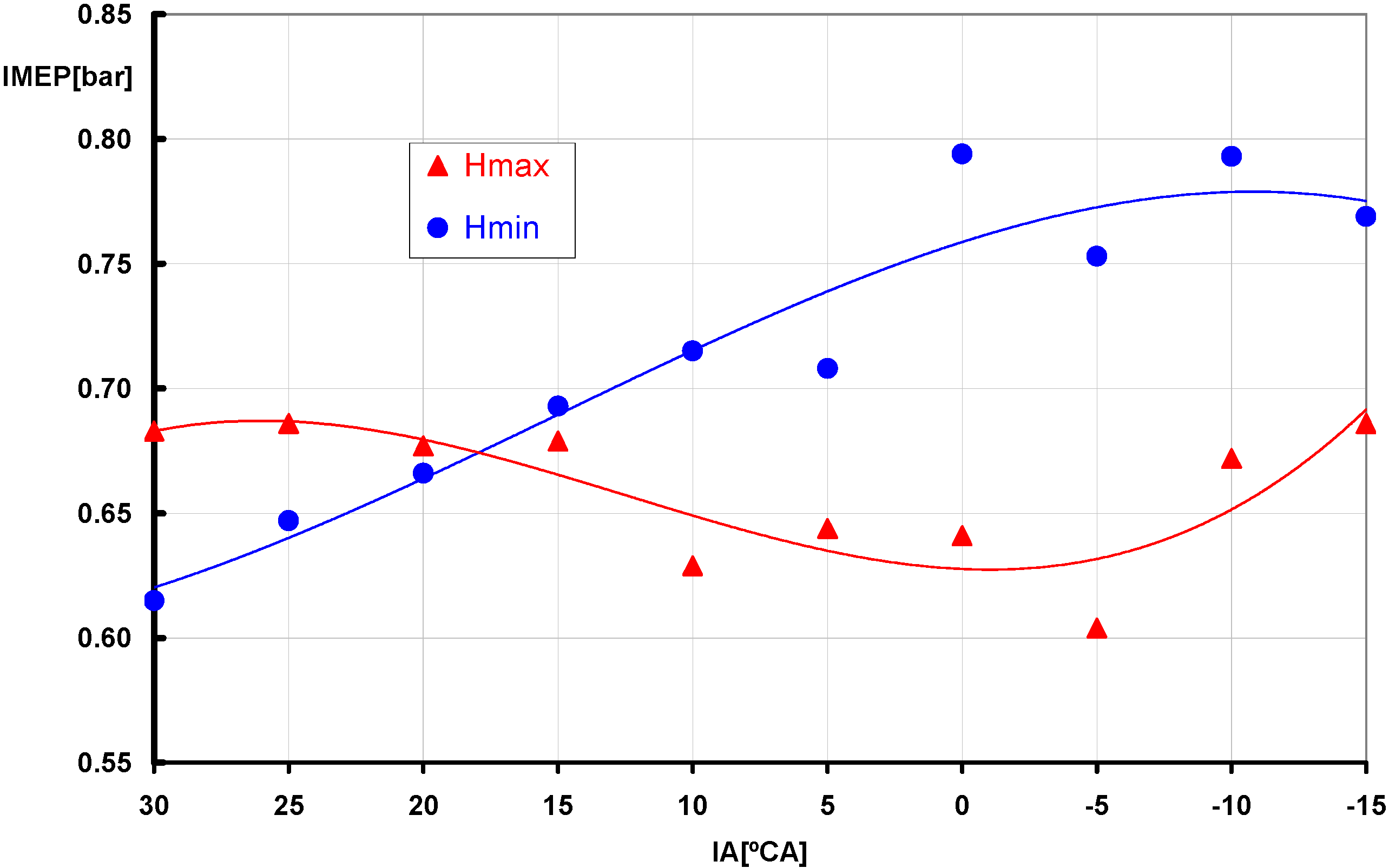
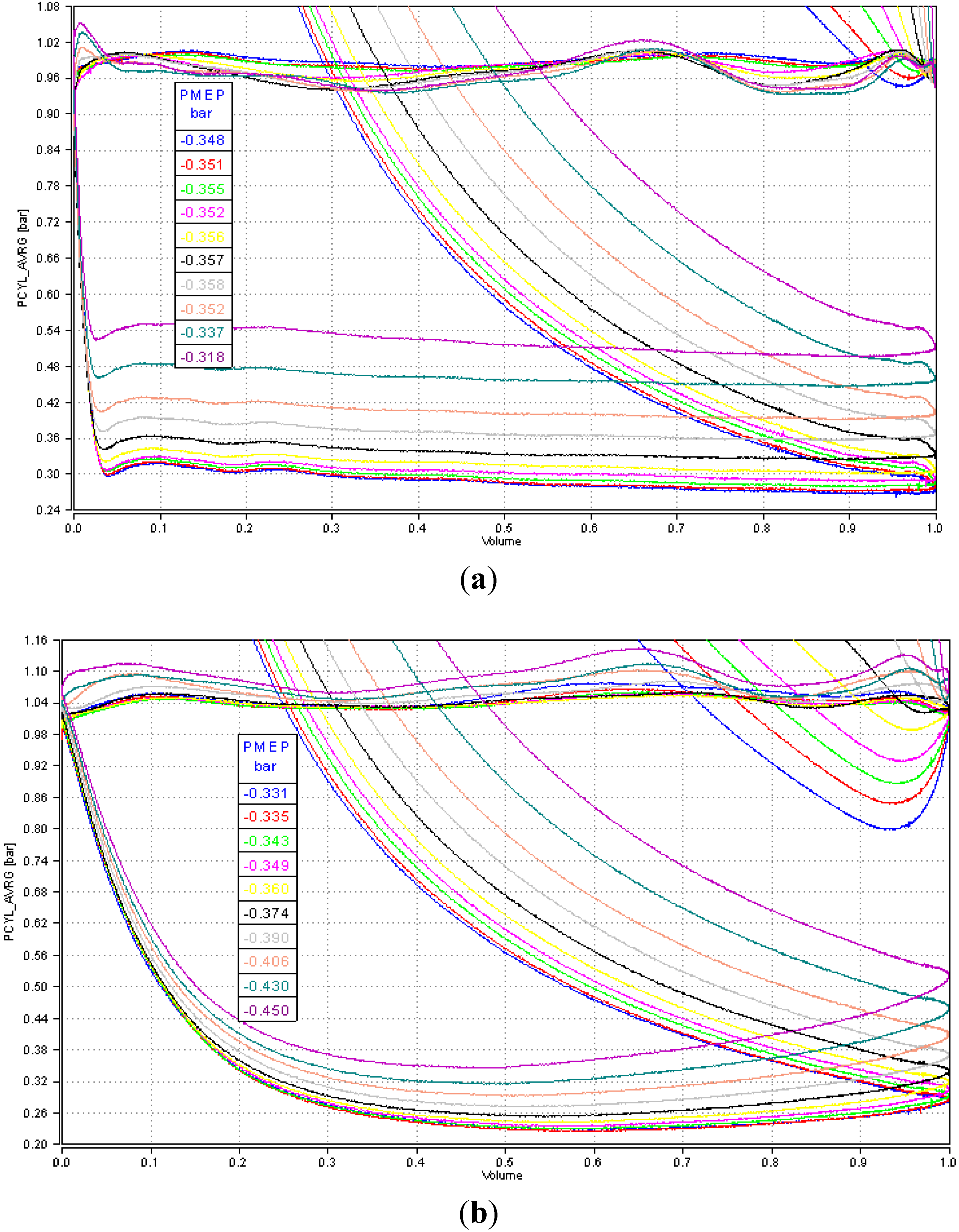
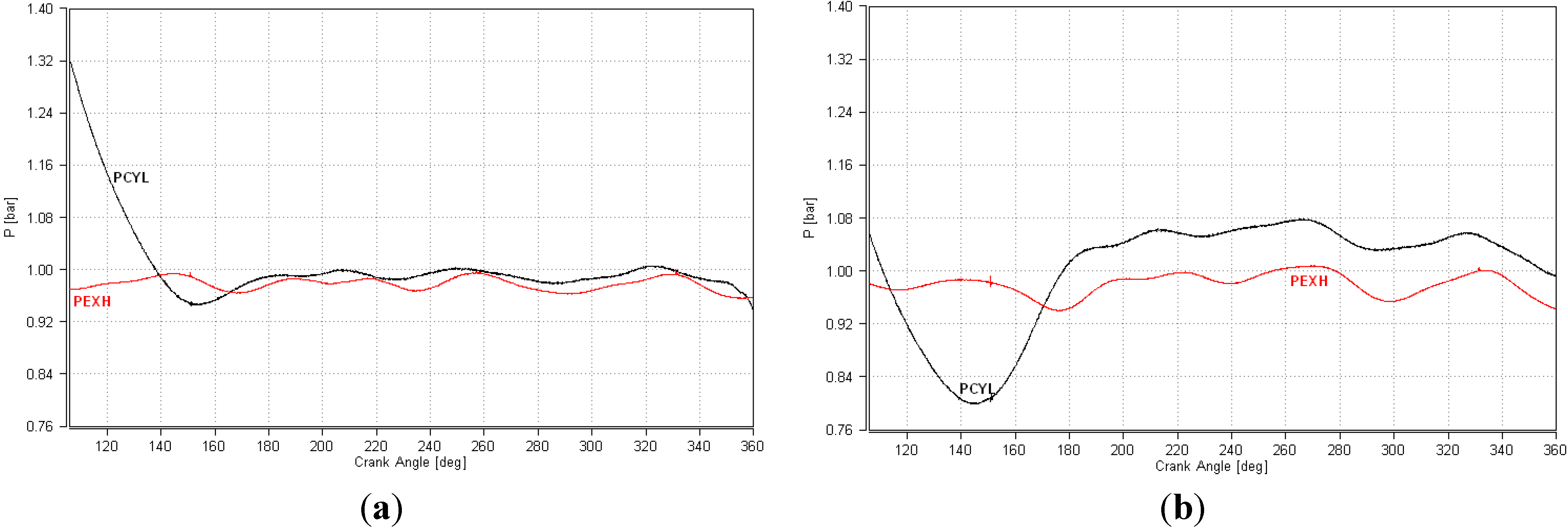
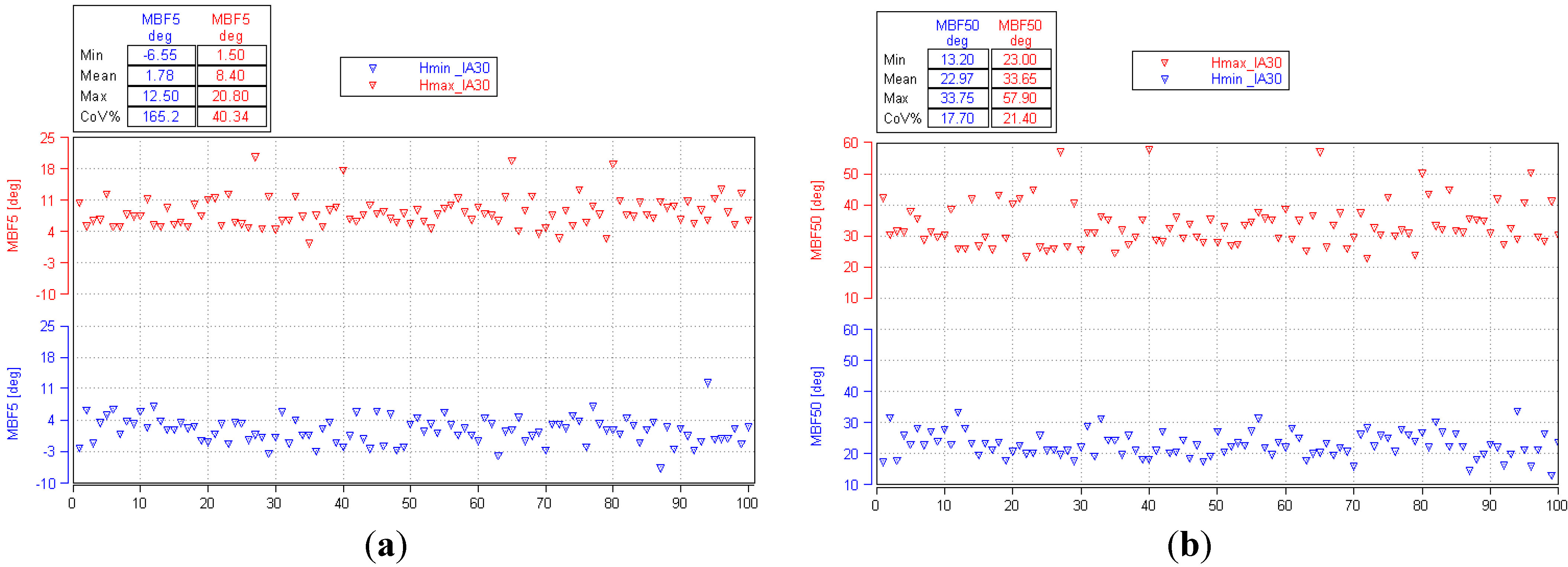
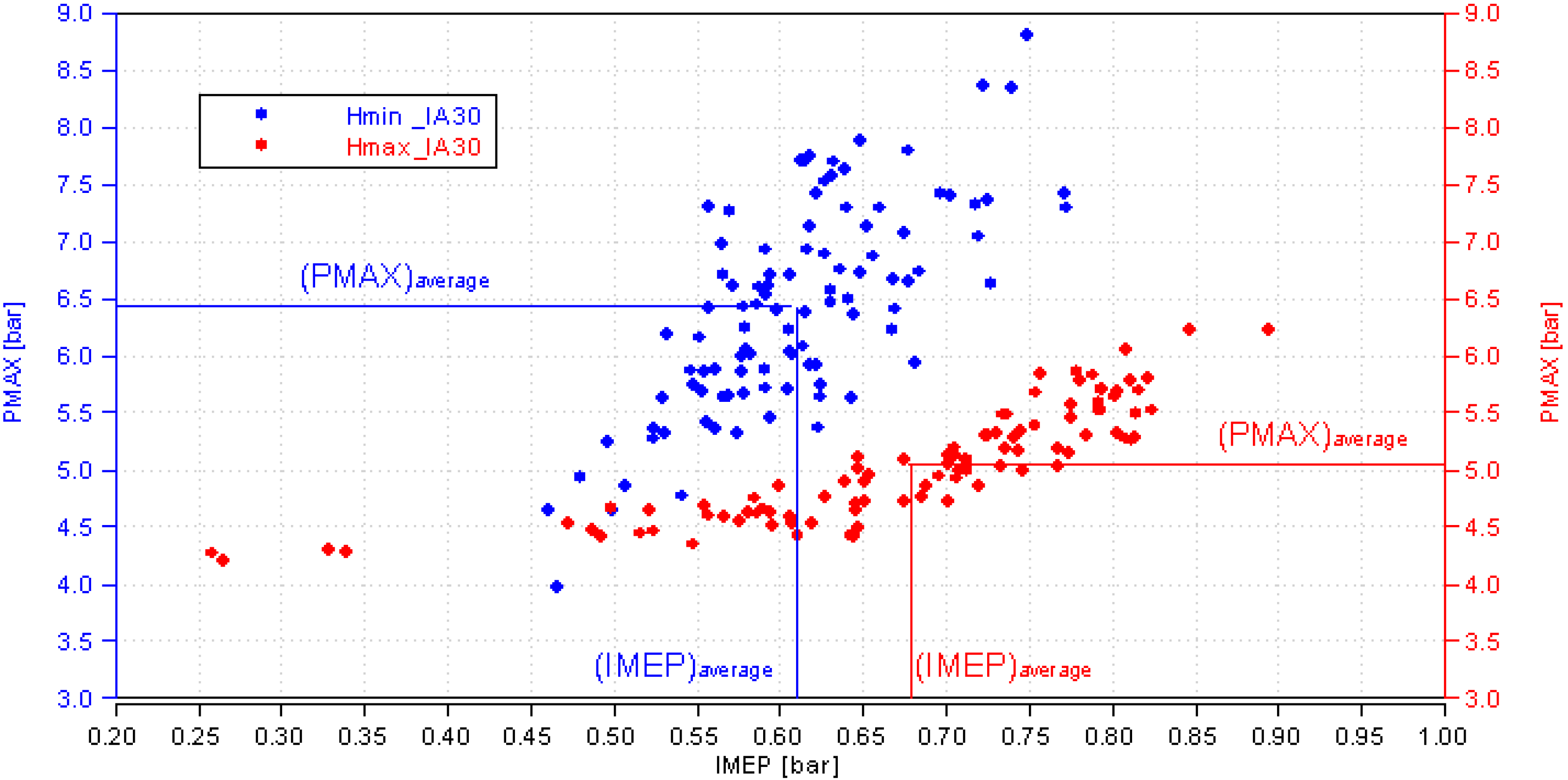
3.2. Comparative Analysis for the Reference Ignition Advance
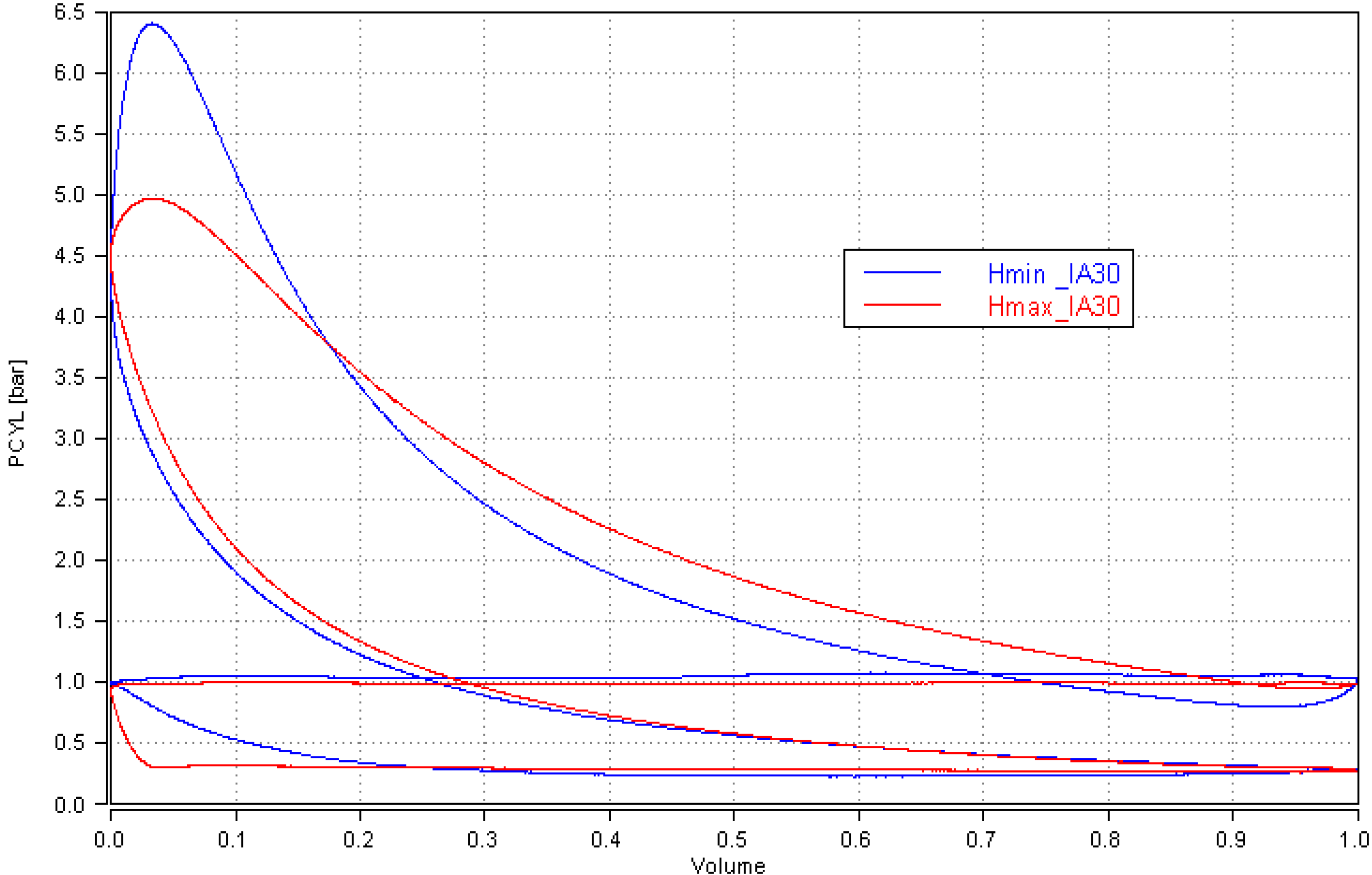
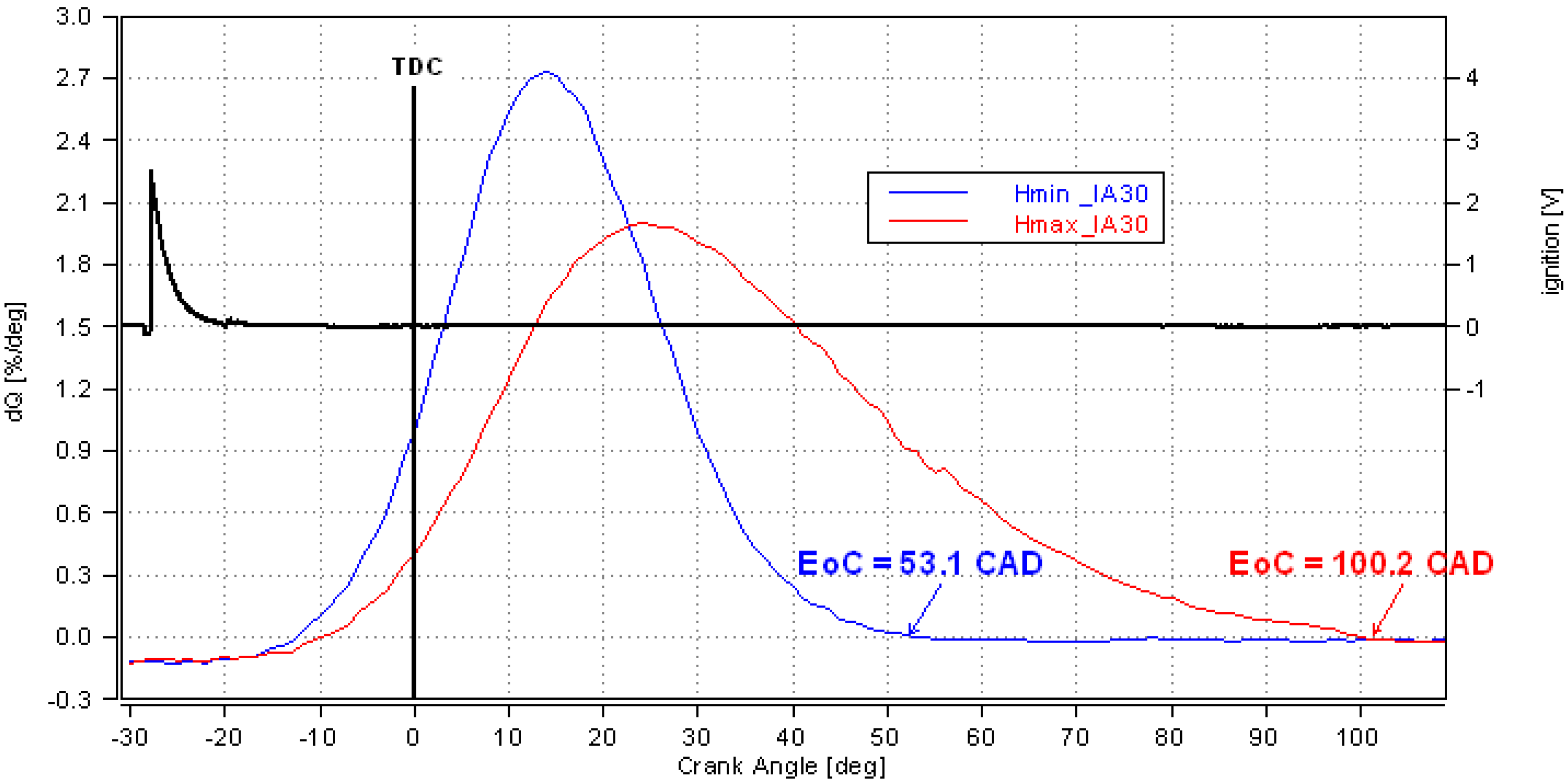
- Improved mixture homogenization thanks to an increased turbulence, caused by the increased intake flow velocity;
- Reduced residual gas fraction, as a result of a reduced degree of internal exhaust gas recirculation (IEGR).



4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Notations and Abbreviations:
| ABDC | after bottom dead center |
| A/D | analog/digital |
| Aiv | flow area at the intake valve gap (m2) |
| ATDC | after top dead center |
| BBDC | before bottom dead center |
| BTDC | before top dead center |
| °CA | crank angle degrees (CAD) |
| CFD | computational fluid dynamics |
| CGI | charge guided injection |
| CI | compression ignition |
| Ch | hourly fuel consumption, (Kg/h) |
| CoV | coefficient of variance (%) |
| DAQ | data acquisition |
| DPa | “in-cylinder / intake manifold” pressure drop (bar) |
| deg | degrees of crank angle (°CA) |
| dQ | heat release rate (%/deg) or (%/°CA) |
| ECR | effective compression ratio |
| ECU | electronic/engine control unit |
| EGR | exhaust gas recirculation |
| EIVC | early intake valve closing |
| EOC | end of combustion |
| EVC | exhaust valve closing |
| EVO | exhaust valve opening |
| FSI | fuel stratified injection |
| GDI | gasoline direct injection |
| HC | unburned hydrocarbons |
| hiv | intake valve lift height (mm) |
| Hmin | minimum intake valve law |
| Hmax | maximum intake valve law |
| HR | heat release |
| IEGR | internal exhaust gas recirculation |
| IMEP | indicated mean effective pressure (bar) |
| IVO | intake valve opening |
| IVC | intake valve closing |
| LIVO | late intake valve opening |
| λ | air excess coefficient |
| MAP | (intake) manifold absolute pressure (bar) |
| MBF | mass burnt fraction |
| MBFx | the angle at which x% of the charge is burned (°CA) |
| MVL | maximum valve lift (mm) |
| NEDC | new European driving cycle |
| P | absolute pressure (bar) |
| PC | personal computer |
| PCYL | in-cylinder absolute pressure (bar) |
| PCYL_avrg | averaged in-cylinder pressure over 100 cycles (bar) |
| PFI | port fuel injected |
| PMEP | pumping mean effective pressure (bar) |
| RON | research octane number |
| SI | spark ignition |
| TDC | top dead center |
| TWC | three way catalyst |
| Vcc | combustion chamber volume |
| VCR | variable compression ratio |
| VIVC | cylinder volume at the intake valve closing moment |
| VVA | variable valve actuation |
| Wiv | flow velocity at the intake valve gap (m/s) |
Acknowledgments
Appendix
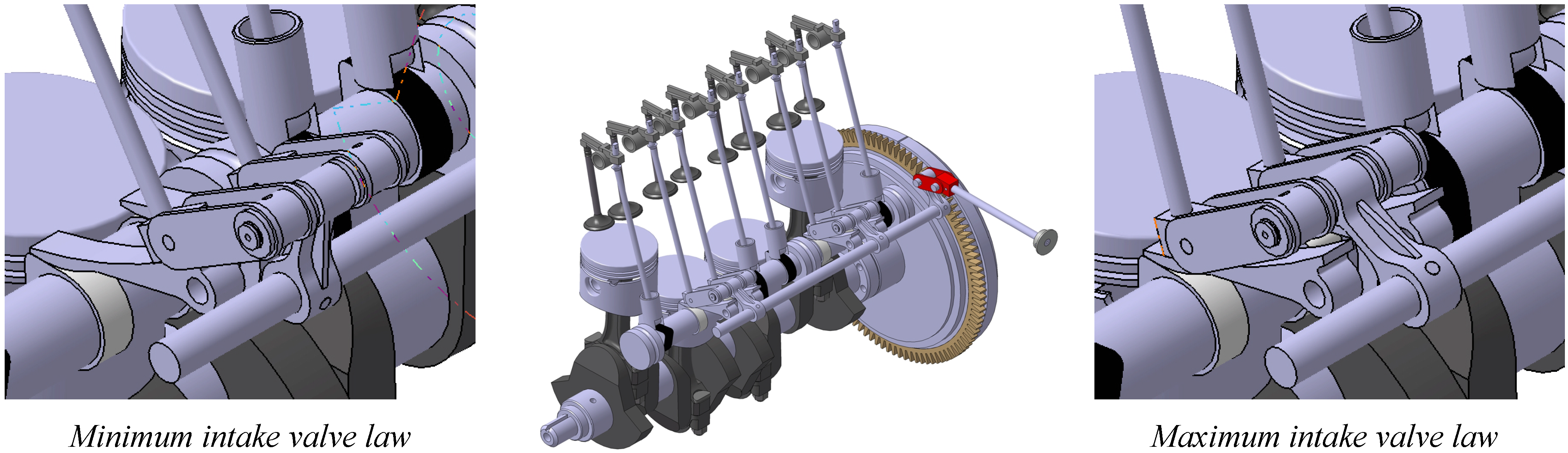
Variable Valve Actuation Prototype Engines

References
- Plotkin, S.E. Examining fuel economy and carbon standards for light vehicles. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 3843–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.M.K.P. Science review of internal combustion engines. Energy Policy 2008, 36, 4657–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, L.; Ferrari, A.; Rinolfi, R.; Vafidis, C. Fuel economy improvement potential of Uniair throttleless technology. J. Ital. Automot. Tech. Assoc. 2003, 56, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard, L. Less CO2 thanks to the BMW 4-cyl. Valvetronic engine. J. Ital. Automot. Tech. Assoc. 2003, 56, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Biziiac, A.; Clenci, A.; Podevin, P. Interests and Concerns of the Variable Valve Actuation. In Proceedings of CNAM-SIA Rational Use of Energy in Internal Combustion Engines and Environment, Paris, France, 20 March 2007.
- Clenci, A.; Descombes, G.; Podevin, P.; Hara, V. Some aspects concerning the combination of downsizing with turbocharging, variable compression ratio, and variable intake valve lift. J. Automob. Eng. 2007, 221, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannibal, W.; Flierl, R.; Stiegler, L.; Meyer, R. Overview of current continuously variable valve lift systems for four-stroke spark-ignition engines and the criteria for their design ratings. SAE Trans. 2004, 113, 811–820. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, H.; Parvate-Patil, G.B.; Gordon, B. Review and analysis of variable valve timing strategies—eight ways to approach. J. Automob. Eng. 2004, 218, 1179–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, Y. Comparison of performance of a greener direct-injection stratified-charge (DISC) engine with a spark-ignition engine using a simplified model. Energy 2011, 36, 4136–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Ladommatos, N.; Stansfield, P.A.; Wigley, G.; Garner, C.P.; Pitcher, G.; Turner, J.W.G.; Nuglisch, H.; Helie, J. Un-throttling a direct injection gasoline homogeneous mixture engine with variable valve actuation. Int. J. Engine Res. 2010, 11, 391–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podevin, P.; Clenci, A. Variable Valve Actuation for Internal Combustion Engines; Engineers’ Techniques Publisher: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fontana, G.; Galloni, E. Variable valve timing for fuel economy improvement in a small spark-ignition engine. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuter, P.; Heuser, P.; Reinicke-Murmann, J.; Erz, R.; Ulrich, P.; Böcker, O. Variable valve actuation—Switchable and continuously variable valve lifts. SAE Trans. 2003, 112, 112–123. [Google Scholar]
- Nagaya, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Koike, K. Valve timing and valve lift control mechanism for engines. Mechatronics 2006, 16, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, E.; Bar-Kohany, T. Optimization of variable valve timing for maximizing performance of an unthrottled SI engine—A theoretical study. Energy 2002, 27, 757–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Xie, H.; He, B.Q. Variable-valve-actuation-enabled high-efficiency gasoline engine. J. Automob. Eng. 2010, 224, 1081–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, T.; Jia, M.; Wang, G. Cycle-to-cycle variation analysis of in-cylinder flow in a gasoline engine with variable valve lift. Exp. Fluids 2012, 52, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, J. Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Pietsch, I.; Tschoke, H. Reduced intake valve lift of SI engines to improve mixture formation, fuel consumption and exhaust emissions. Ing. Automob. 2002, 9, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Begg, S.M.; Hindle, M.P.; Cowell, T.; Heikal, M.R. Low intake valve lift in a port fuel-injected engine. Energy 2009, 34, 2042–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koederitz, K.R.; Evers, M.R.; Wilkinson, G.B.; Drallmeier, J.A. Break-up of liquid fuel films from the surfaces of the intake port and valve in port-fuel-injected engines. Int. J. Engine Res. 2002, 3, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y.; Peng, Z.J.; Wang, G.D. In-cylinder air motion characteristics with variable valve lift in a spark ignition engine—Part 1: swirl flow. J. Automob. Eng. 2011, 225, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podevin, P.; Descombes, G.; Clenci, A.; Hara, V.; Boncea, S. Procédé de régulation d’une levée de soupape, dispositifs de soupape à ouverture variable, moteur équipé d’un tel dispositif [in French]. French Patent FR2883927, 6 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Yoon, M.; Sunwoo, M. A study on pegging methods for noisy cylinder pressure signal. Control Eng. Pract. 2008, 16, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Clenci, A.; Bîzîiac, A.; Podevin, P.; Descombes, G.; Deligant, M.; Niculescu, R. Idle Operation with Low Intake Valve Lift in a Port Fuel Injected Engine. Energies 2013, 6, 2874-2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6062874
Clenci A, Bîzîiac A, Podevin P, Descombes G, Deligant M, Niculescu R. Idle Operation with Low Intake Valve Lift in a Port Fuel Injected Engine. Energies. 2013; 6(6):2874-2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6062874
Chicago/Turabian StyleClenci, Adrian, Adrian Bîzîiac, Pierre Podevin, Georges Descombes, Michael Deligant, and Rodica Niculescu. 2013. "Idle Operation with Low Intake Valve Lift in a Port Fuel Injected Engine" Energies 6, no. 6: 2874-2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6062874
APA StyleClenci, A., Bîzîiac, A., Podevin, P., Descombes, G., Deligant, M., & Niculescu, R. (2013). Idle Operation with Low Intake Valve Lift in a Port Fuel Injected Engine. Energies, 6(6), 2874-2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6062874







